Reasons for the appearance of suspended matter
Suspension in the gallbladder is a pathology.
In a healthy person, such a symptom cannot be observed, and its appearance may be associated with various factors. All reasons for the appearance of sediment in the lumen of the gallbladder can be divided into several groups:
- diseases of the liver and biliary tract: therapy aimed at destroying gallstones, pancreatic diseases, blockage of the bile ducts, long-term use of certain groups of medications, fatty liver and others;
- features of diet and lifestyle: consumption of large amounts of fatty, fried foods, sweets, alcohol, as well as sudden weight loss or weight gain;
- genetic factors: abnormalities in the structure of the gallbladder and bile ducts, which impede the outflow of bile;
- auxiliary factors: female gender, pregnancy, old age, limited physical activity.
The activity of the gallbladder is directly related to the condition of the stomach, intestines, liver and other organs. Normally, bile does not stay long in its cavity and does not accumulate there in large quantities. It is produced by liver cells and enters the gallbladder only to wait until food reaches the stomach.
As soon as the digestion process starts, it is excreted further into the intestines. It can accumulate if you eat irregularly or abuse harmful foods, for the processing of which the body spends more resources, including bile. Its quantity may increase and its composition may change if its outflow is obstructed due to narrowing of the lumen of the bile ducts or their blockage with foreign objects.
Characteristic
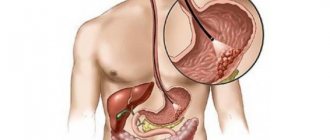
If the natural functioning of the biliary tract deteriorates, then a person experiences bile stagnation. As a result, it begins to crystallize into grains of small diameter. From this, a suspension is formed in the gallbladder. It is also called sludge syndrome. This condition is considered a harbinger of gallstone disease. Particles of suspension in the gallbladder gradually form conglomerates, which are stones that are dangerous to health.
The disease can develop in both women and men. That is why every person should be prepared for the occurrence of a disease. Do not think that the pathology is harmless to health. Firstly, it often indicates additional problems with internal organs. Secondly, it can lead to various complications.
Prognosis and prevention
With early detection, in 90% of cases, the suspension is completely removed from the gallbladder without causing negative consequences. But occasionally the disease progresses and causes complications:
To prevent the formation of suspension in the gallbladder, it is important to eat right, lead a healthy lifestyle, and promptly treat diseases of the digestive system. Persons with a family history, or those suffering from chronic diseases of the gallbladder and liver, should undergo sonography of the abdominal organs at least once a year, consult with a gastroenterologist and, if necessary, with a therapist.
Source: kiwka.ru
Symptoms
Symptoms when a suspension appears in the gallbladder depend on the cause of its occurrence. In most cases, the fact of the presence of sediment does not cause any inconvenience to the patient and is discovered by chance on an ultrasound. It is a small formation that cannot injure the walls of the gallbladder and cause acute pain. Also, the suspension will not clog the lumen of the bile ducts and will not disrupt the flow of bile.
Common symptoms that may indicate sediment in the gallbladder include:
- painful sensations in the right hypochondrium that last from several minutes to several hours;
- the pain can be short-term cramping or constant aching;
- heaviness in the right side;
- nausea and vomiting;
- bowel disorders;
- loss of appetite.
Signs are expressed in cholecystitis, which can also be accompanied by the formation of suspension. In this case, the pain is severe, and an acute attack is accompanied by biliary colic. In most cases, the appearance of sediment is associated with poor diet and poor lifestyle, and not with more serious pathologies, so there is no clinical picture.
During the examination, the patient must change his body position so that the doctor can observe how the sediment moves.
The presence of sediment in the gallbladder can be recognized in a timely manner by characteristic signs. You should know them so that you can consult a doctor in time. It often happens that during a routine ultrasound, suspensions are found that interfere with the full functioning of the biliary tract. It is worth noting that the disease can be a latent form and a type with clinical symptoms.
If a person has no signs of pathology, then without examination one may not even know that it exists. When symptoms are still present, in this case people themselves turn to the doctor with complaints about their well-being.
Signs of pathology:
- A feeling of heaviness and pain in the right side, which increases significantly after eating heavy food.
- Loss of appetite. A person may even completely refuse food, especially fatty and spicy foods.
- Bitter taste in the mouth. It can occur in the morning and also after eating.
- Nausea, as well as vomiting, in which bile impurities are observed. This is not a mandatory symptom, but it is still quite common.
- Stool disorders. Constipation and diarrhea may occur.
It is worth noting that symptoms can increase as the contents of the gallbladder thicken. As thick bile moves through the duct, a person begins to experience colic, during which short-term cramping pain in the right hypochondrium may be observed. If there is a lot of suspension, then a person may experience constant aching pain. If the bile becomes too thick, then blockage of the duct may occur, as well as obstructive jaundice.
How can a suspension be classified?
Medical opinions are divided on what constitutes sediment in the gallbladder. Some doctors argue that this symptom is the initial stage of gallstone disease and requires urgent medical treatment. In their opinion, small grains can eventually turn into large stones that clog the bile ducts and irritate the walls of the gallbladder.
The chemical composition of the suspension can be of different origins:
- consist of cholesterol, a component of bile;
- represent calcium salts;
- be bile pigments.
Ultrasound can determine the degree of echogenicity of a suspension, that is, its ability to reflect or absorb ultrasound rays. The color that the sediment will have on the screen depends on this. The echo suspension may be different shades of gray, while the gallstones will be white.
Echogenic suspension
An echo-positive suspension is clearly visible already in the first stages of the disease. Normally, liquid and homogeneous bile changes its consistency, and flakes in the gallbladder are visible on the screen. This symptom indicates that the sediment is not yet dense enough and can be freely destroyed and excreted into the intestines. The flocculent suspension has a dark gray tint.
Over time, the flakes become denser, and so-called sludge appears in the cavity of the gallbladder. This term refers to dense clots that are visualized as a hyperechoic sediment. They have a lighter shade, and the consistency of the bile becomes less uniform.
Biliary sludge
Biliary sludge in the gallbladder is a general name for suspension of various origins. Sediment grains alter normal bile, which is why inclusions of various sizes and shades, from dark to light gray, can be seen on ultrasound. The lighter the sediment, the denser the suspension crystals.
Echogenic suspension can also be classified according to the size of its particles:
- fine suspension ─ is a collection of small (up to 4-5 mm) hyperechoic elements that do not produce an acoustic shadow;
- sludge ─ these are clots of jelly-like consistency that move freely in liquid bile;
- sludged bile is a syndrome in which it contains both sludge and a finely dispersed suspension.
Sludge syndrome is a term that often refers to the presence of any suspension in the cavity of the gallbladder. The formation of biliary sludge may be the first stage of cholelithiasis, or cholelithiasis. Even if the syndrome does not cause pain or discomfort in the patient, it is recommended to treat it to prevent the appearance of large, dangerous stones.
Sludge syndrome was previously considered a disease of adults, but among patients there are also children from the first year of life
Types of suspension in the gallbladder
According to the etiology, chemical composition and ultrasound data, the sling is classified into types:
- Echo-heterogeneous bile with clots - single high-density nodes are recorded in the area of the posterior wall of the organ. This is an echogenic suspension detected by ultrasound;
- Hyperechoic formations do not provide an acoustic shadow and are detected only during an ultrasound examination, and only when the patient’s body position changes. These include fine suspension consisting of protein, cholesterol, calcium salts;
- Putty-like bile - characterized by the presence of putty-like clots moving in the space of the organ.
Diagnostic methods
The main reasons for the development of the disease:
- primary hypercholesterolemia of genetic origin;
- secondary disorder of cholesterol metabolism, which occurs as a result of an unhealthy lifestyle and poor diet;
- pregnancy, which contributes to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure and, as a result, the development of bile stagnation;
- taking contraceptives that affect the composition of bile.
The progression of cholelithiasis is promoted by diabetes mellitus and the development of liver cirrhosis. Changes in the composition of bile are a manifestation of cholesterol metabolism disorders, and therefore are often accompanied by obesity and (or) systemic atherosclerosis.
At the initial stage of development of the disease, when the first clots form in the gallbladder, the patient often does not experience discomfort. As the pathological condition progresses, symptoms such as:
- pain in the right hypochondrium (the manifestation of pain can be different, its nature is paroxysmal or constant, which becomes more intense after eating);
- loss of appetite;
- nausea and vomiting (sometimes mixed with bile);
- heartburn;
- stool disorders (constipation, diarrhea or their alternation).
The diagnosis is made based on several factors. First of all, the gastroenterologist collects anamnesis: asks when the first symptoms appeared, what their nature is and where the pain is localized. Be sure to take into account the patient’s gastrointestinal pathologies and the facts of taking medications or regularly drinking alcohol.
After this, the doctor conducts an examination and prescribes urine and blood tests. Laboratory tests can determine the content of liver enzymes, bilirubin, cholesterol and total protein in the blood. Traditional research methods include:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs, which allows you to detect flakes and determine their quantity, as well as assess the condition of the walls of the gallbladder;
- magnetic resonance imaging, which makes it possible to identify various changes in the gallbladder and liver tissues;
- duodenal intubation, which involves obtaining bile and studying its composition.
Depending on the condition of the biliary tract, treatment can be carried out according to one of three schemes:
- For patients with minimal disorders, a corrective diet similar to table No. 5 is indicated, and drug therapy involves eliminating the causes that led to the development of the pathology.
- The second (main) group of patients is prescribed conservative treatment, which involves taking medications that eliminate bile stagnation, protect liver tissue and relieve pain. The patient is also prescribed a diet that excludes fatty, fried and spicy foods, flour products, eggs, mayonnaise and sauces.
- If such treatment is ineffective, surgery is prescribed.
If echogenic impurities in the bile are not eliminated in a timely manner, the patient may develop biliary colic, pancreatitis, cholangitis or cholecystitis, and cholesterol pseudopolyps in the gallbladder. The condition of the gallbladder affects the entire body - read the article about why we need a gallbladder for details.
Secondary prevention involves normalizing body weight and eliminating diseases that contribute to the development of gallbladder pathology.
Suspension in the gallbladder can form gallstones over time. How to prevent this, as well as what to do if an attack of cholelithiasis does occur, read in a separate article.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uIwh7bCip9w
You can contact the hepatologist in the comments. Don't hesitate to ask!
This article was last updated: 07/18/2019
Didn't find what you were looking for?
If there is a suspension in the gallbladder of a person, you should consult a doctor in order to get diagnosed. Based on its results, it will be possible to clearly understand what exactly you have to deal with. First, you will need to tell the doctor about your complaints, after which he will be able to draw an approximate conclusion about the state of the person.
Diagnostic methods:
- Magnetic resonance imaging. With its help, you can see pathological changes in the area of the gallbladder, as well as the liver. This study is considered safe for the body, while it is informative. If an illness occurs, it is definitely recommended to undergo an MRI.
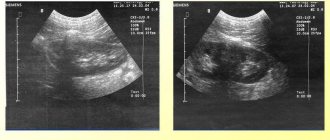
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity. With its help, you can see suspension and sediment in the gallbladder area. It is noteworthy that ultrasound has a small number of contraindications. That is why it is prescribed to many patients.
- Laboratory analysis of urine and blood. It will be possible to analyze how much liver enzymes are contained, as well as how much cholesterol, bilirubin and total protein are in the body. With the help of analysis, it will be possible to clearly understand what exactly we are dealing with.
- Duodenal sounding. Thanks to him, you will need to take a bile sample in order to conduct the study.
Using these procedures, it will be possible to draw conclusions about the state of human health. You will definitely need to find out an accurate diagnosis, as well as understand what treatment regimen will help improve your well-being. You should not wait until the disease begins to actively progress. The sooner therapy is started, the easier it will be to get rid of the pathology.
Diagnostics
Ultrasound is considered a reliable method for detecting suspended matter in the gallbladder. Thanks to ultrasound diagnostics, the presence of suspension can be recognized at the initial stage. In a healthy person, there should be no suspensions or sediment in the cavity of the gallbladder; the structure of the organ when visualized is homogeneous.
Suspension in the cavity of the gallbladder at different stages of pathology is determined differently:
- echo suspension is visualized in the form of flakes with a heterogeneous structure; the presence of echogenic suspension indicates the initial stage of bile stagnation;
- hyperechoic suspension is visualized as denser contents with less homogeneity, which is due to the gluing of sediment particles and the formation of bile clots;
- biliary sludge is a directly formed sediment represented by bile pigments, lipid particles, and salts.
To clarify the diagnosis, anamnesis is collected on complaints and lifestyle. It is important to find out what gastrointestinal diseases the patient has suffered, whether there is long-term use of medications, or the presence of bad habits. A physical examination is performed to determine abdominal tenderness and assess the size of the liver and pancreas.
Of the clinical tests, the most informative is a blood biochemistry test. Among the instrumental methods, in addition to ultrasound, duodenal intubation is used, followed by microscopic examination of the composition of bile. Occasionally, if there is doubt about the diagnosis, CT and MRI are performed to identify changes in the structure of the organs of the biliary system.
Baby's suspension
If previously the formation of suspensions in the cavity of the gallbladder was considered exclusively a disease of adults, now among the patients there are children from the first year of life. Such cases are quite rare, but a child is also likely to develop sludge syndrome. There may be several reasons for this phenomenon:
- improper, unbalanced feeding of the child, weight loss;
- pathologies in the production of liver enzymes, due to which some drugs cannot be utilized in full;
- organ and tissue transplantation operations;
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the gallbladder and biliary tract, which prevent the normal outflow of bile;
- mother taking medications during breastfeeding;
- in adolescence - stress that leads to prolonged involuntary contraction of smooth muscles and the sphincter of the gallbladder.
Diagnosis of the disease in children is carried out in the same way as in adult patients. Parents should closely monitor the child’s well-being and consult a doctor if any alarming symptoms appear. It should be understood that this disease is registered from the first year of life, when the only clinical signs are loss of appetite, anxiety and weight loss.
Therapy
Treatment of suspension in the gallbladder is selected individually for each patient, taking into account the preservation of organ functions, age, general condition and type of sediment. Depending on the amount of suspension in the bile cavity and the size of the particles, treatment tactics are divided into several options:
- sludge syndrome, which does not require conservative therapy, requires nutritional correction in the form of table No. 5 to remove suspended matter;
- sludge syndrome requiring non-surgical treatment;
- surgical intervention.
In the presence of echogenic, hyperechoic and finely dispersed suspension, the following drugs are prescribed:
- choleretic and antispasmodics to dilute bile, eliminate stagnation and normalize motility - Hepatocholan, Gepabene;
- products containing ursodeoxycholic acid for crushing and painlessly removing suspension from the bladder - Ursosan;
- herbal medicines to restore normal functioning of the biliary tract - Hepatosan, Phosphogliv.
Additionally, a course of enzymes (Creon, Panzinorm) is prescribed to help relieve the symptoms of dyspepsia and improve digestion. The duration of drug therapy is at least 2 months. During this period, it is possible to stop the process of suspension formation, optimize the composition of bile and remove the sediment naturally.
Treatment Options
Only a doctor can definitely tell you exactly how to treat sediment in the gallbladder. Drug therapy will definitely be required, because with its help it will be possible to quickly normalize well-being. The most important thing is to prevent blockage of the ducts, as well as the occurrence of other complications.
Medicines can only be selected by a medical specialist. He can also, if necessary, change the list of medications that are required for a person. At the same time, you should not select treatment options on your own if you do not want to face negative consequences later. Even if a person believes that with the help of specific pills he will improve his condition, then in fact he can only worsen his health.
All medications must be taken in strict dosages. It is important not to exceed the prescribed course of treatment. In another situation, the patient may face negative consequences, in particular, additional deterioration of the liver and gallbladder.
If a person feels that their health will suddenly become worse, then they should stop taking the medication. It is imperative to call a doctor to understand what exactly is happening with your health.
It is worth noting that choleretic drugs such as Ursosan, Allochol and Ursofalk are often used. Naturally, only one remedy is selected from them. Antispasmodics are often used, for example, Papaverine and No-shpa. In this case, treatment will be prescribed only after an examination has been carried out for blockage of the bile ducts.
Additionally, a person will need to follow a diet to improve their well-being. And the permitted foods are lean meat, fresh fruits and vegetables, cereals and high-quality pasta. In this case, you will need to give up animal fats, fatty meats, fried and spicy foods, as well as pickles and canned food. A person will definitely need to drink more fluids to normalize their health. At a minimum, you will need to drink 2 liters of water per day.
Additionally, the doctor may prescribe traditional methods of treatment if he believes that they will help in a particular situation. In this case, it will be possible to significantly improve your health without harming the body. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate, because it often leads to negative changes in the condition of the liver and gallbladder. Only properly selected therapy will allow you to get rid of the pathology and prevent the occurrence of complications due to lack of treatment.
Causes
Suspensions in the gallbladder can occur for various reasons. It will be useful for a person to know the provoking factors so that they can be avoided. In this case, it will be possible to maintain good health.
Provoking factors:
- Poor nutrition. If a person consumes a large amount of animal fats, salty, spicy and fried foods, then he may develop problems with the liver and ducts. Fast food is also unhealthy, overeating and irregular eating are harmful to health. Because of this, the body’s cholesterol metabolism is significantly disrupted, which in turn contributes to the occurrence of pathologies.
- Physical inactivity. Some people are forced to lead a sedentary lifestyle. It can be caused by sedentary work or a reluctance to go for walks. As a result, the whole body suffers from physical inactivity, which leads to dangerous diseases.
- Pregnancy. During this period, intra-abdominal pressure increases in expectant mothers. As a result, this causes stagnation of bile.
- Alcohol abuse. Drug therapy also worsens the condition of the liver, because not every medicine is harmless to the body. Situations in which a person voluntarily increases the dosage of the drug or the duration of the course of treatment often lead to suspension in the gallbladder. In this case, you can provoke intoxication of the body.
- Bad heredity. If close relatives have had problems with the gallbladder, then you are likely to encounter sludge syndrome.
- Taking hormonal contraceptives. Many of them lead to a deterioration in the composition of bile.
It is worth noting that quite a portion of the suspension in the gallbladder may appear against the background of other pathologies of the digestive system. It is worth knowing about them, because it is also important to start treating them in a timely manner. Many of them can lead to health and life-threatening conditions, so the disease should not be neglected.
What pathologies may be:
- Various diseases of the digestive system. If a person has problems with the gastrointestinal tract, then he may develop gallstone disease.
- Obesity. Being overweight generally worsens your health. That is why it is important to get rid of unnecessary pounds to prevent the occurrence of diseases.
- Atherosclerosis. It occurs against the background of the formation of cholesterol plaques. They, in turn, can arise due to old age, poor nutrition and various vascular problems. Atherosclerosis is a dangerous pathology because it leads to blockage of blood vessels. Under no circumstances should the disease be ignored, because it is important to normalize the condition of the cardiovascular system.
- Cirrhosis and fibrosis of the liver. Both conditions are dangerous to human health and life. However, they can lead to various complications, such as suspension in the gallbladder.
- Diabetes. If a person has been diagnosed with this, then he should carefully monitor his health. Only in this case will it be possible to avoid dangerous consequences for the body.
- Bending of the bladder, as well as narrowing of the ducts. These are anatomical features of the body, which often lead to various problems.
- Inflammatory process in the pancreas and gall bladder. It requires timely treatment in order to avoid dangerous health consequences.
Quite often, several reasons can negatively affect health. That is why it is not always possible to immediately say what in a particular situation led to the development of the disease. It is also worth considering that the risk group includes people who have undergone stone crushing surgery or have undergone therapy using agents for dissolving choleliths.
Therapeutic measures
Drug treatment should be selected by a doctor. In different cases, it is necessary to take drugs from different groups, which depends on the reason for the appearance of the suspension. So, choleretic drugs will be useful only if there is no mechanical blockage of the biliary tract. If bile is not excreted due to decreased tone of the smooth muscles of the gallbladder, taking antispasmodics will only worsen the problem.
In any case, the patient will have to follow a diet. It is common to all diseases of the liver and gallbladder and is aimed at reducing the load on these organs:
- You need to eat at least 4-5 times a day, in small portions.
- The basis of the diet is cereals, lean meat, fruits and vegetables. Animal products should be boiled or steamed. Citrus fruits are especially useful among fruits.
- Fatty, fried foods, smoked foods, sauces and alcohol will have to be completely excluded. To process them, a large amount of bile is needed.
- You need to drink at least 2 liters of pure still water per day. Other liquids consumed during the day in the form of soups, tea or juices are not included in this amount.
According to indications, the doctor prescribes medications of different groups. For pain and increased muscle tone of the gallbladder, antispasmodics are needed. If its tone is reduced, choleretic agents should be taken. In some cases, the patient's condition can be normalized solely by diet and physical activity. This scheme should be chosen if the suspension in the gallbladder does not cause discomfort.
After consulting with your doctor, you can supplement your diet with folk remedies and decoctions. You should choose those herbs that relieve inflammation and provoke the outflow of bile. Among the well-known and safe recipes, you can try decoctions of chamomile, corn silk or wormwood, as well as sea buckthorn tea or berry juice.
Not all folk recipes are equally useful, but your doctor may recommend drinking medicinal decoctions, teas or infusions
Treatment methods
Treatment of bile suspension is combined with mandatory adherence to a dietary diet. The patient is recommended to eat food in small quantities, 5-6 times a day. Fatty and fried foods, smoked meats, pickles, spices, spicy foods and seasonings should be excluded from the diet.
It is also recommended to minimize your salt and sugar intake. For patients with a slight accumulation of bile suspension, diet No. 5 is excellent.
A pathological formation in the gallbladder is treated as prescribed by a doctor. First of all, it is planned to eliminate the causes that led to the stagnation of bile in the organ. Conservative treatment is based on the use of drugs that destroy the stagnation of the bile mass.
The patient is also prescribed medications that protect liver tissue and relieve pain. The effectiveness of treatment depends on compliance with the recommendations of the gastroenterologist. If a course of medication does not bring positive results, the patient is scheduled for surgery.
Treatment of suspension is carried out surgically and is carried out in different options:
- extracorporeal lithotripsy;
- cholecystectomy;
- cholecystectomy using endosurgery.
After the pathology and its etiology have been established, the doctor decides how to treat the disease and what means will help remove the fine suspension. Doctors often use complex therapy, which consists of using several techniques:
- diet No. 5;
- medicines;
- phytotherapy;
- surgery – for complications.
Drug treatment is prescribed to:
- restore the functionality of the gallbladder, small intestine and sphincter of Oddi;
- improve the physicochemical properties of bile;
- normalize digestion;
- restore the gastrointestinal microflora.
Along with medications, the patient needs to adjust his diet. If characteristic symptoms are detected, doctors advise fasting for several days and drinking only water. This can relieve the liver and cleanse the body a little. After this, you can gradually return to your usual diet, but some restrictions should be adhered to:
- eat fresh and healthy vegetables, fruits, berries;
- exclude from the diet sour foods, spinach, sorrel, cranberries, lemon, yeast products and sweets with cream, marinades, sauces, smoked meats, processed meat products;
- meat and fish should be of lean varieties;
- eat cereals and low-fat dairy products.
To maintain the tone of your whole body, you need to exercise regularly. Even moderate abdominal exercises will help get rid of sludge and improve the functioning of the digestive system.
It is very important to begin treatment of the disease immediately after the discovery of sludge syndrome, since without proper therapy this disorder will develop into cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, cholangitis.
Traditional medicine suggests treating the disease with decoctions of medicinal herbs and herbs. This treatment has a gentle effect and a complex positive effect on the entire body.
In addition to taking medications, it is necessary to understand why sludge syndrome developed and radically change your lifestyle. You need to give up bad habits, exercise and follow a strict diet. Only in this case can the development of cholelithiasis be prevented and the functioning of the biliary system normalized.