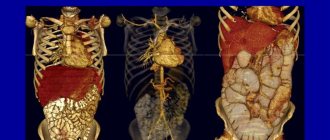
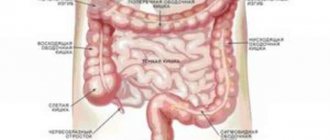
By imagining the structure and location of a person’s internal organs, you can independently determine the source of pain and which specialist you should contact for help first. Each organ of the human body occupies a specific place and has its own unique structure.
In this regard, you should know the location of a person’s internal organs in order to independently diagnose the location of pain and contact the right doctor immediately.
The structure, location and function performed are closely interconnected; the images in the article and the video after will help to facilitate the memorization process. Conventionally, the human body is usually divided into three cavities, inside of which all the organs of the human body are located:
- The chest cavity is from the neck to the end of the sternum.
- The abdominal cavity is from the end of the sternum to the hip joint.
- The pelvic cavity (small and large pelvis) is within the boundaries of the hip joints.
The chest cavity is separated from the abdominal cavity by a special muscle - the diaphragm, designed to expand the lungs. Human internal organs: the layout and structural features begin to be studied, as a rule, from top to bottom - from the neck to the pelvic organs. Therefore, the first organ is the thyroid gland, located in the neck, usually under the Adam's apple.
However, the location of its localization in an adult is not constant. It may increase in size or become smaller; in some cases, prolapse of this organ of the endocrine system is observed.
Location of organs in the chest cavity
The location of the photo below shows the internal organs of a person more clearly. The heart, lungs, bronchi and the mysterious thymus gland, also called the thymus, are located here.
Heart
An important element of the cardiovascular system, the heart, is responsible for ensuring the movement of blood in the vessels. Its location is the chest, above the diaphragmatic muscle. To the right and left of it are the lungs.
In this case, the heart is not located with symmetrical precision in the center of our body, but slightly at an angle. Two-thirds of the cardiomuscle is located to the left of the midline, and one-third is located to the right. The shape of the heart is an individual characteristic and depends on age, gender, body constitution, health status, etc.
Lungs
The location of the human internal organs in the picture, which schematically reflects the structure of the chest cavity, is continued by the most important elements of the respiratory system - the lungs. Their volume is slightly less than that of the cavity, and their sizes themselves depend on the phase of the respiratory cycle: during inhalation they expand, and during exhalation they contract. The shape of the lungs resembles a truncated cone. The base of this cone rests on the dome-shaped diaphragm muscle, and the apex is directed towards the subclavian region.
Bronchi
Anyone who is familiar with the structure of the bronchial tree - the continuation of the trachea outside the windpipe - can show the location of the human internal organs in the chest cavity. Each of the branches of this tree is in a strict hierarchy and has its own name and structural features. Directly from the trachea there are two main bronchi, each of which goes to the corresponding lung. The thin, long and less vertical left main bronchus can be easily distinguished from the right one in the figure.
In the lungs of the human internal organs, the location depends on their location: on the surface of the lung or inside it. Therefore, the bronchial branches of the first and second order are called extrapulmonary, and all the rest will be intrapulmonary. Each order has its own name: the first is lobar, the second is segmental, the third is subsegmental, etc. The branching ends with bronchioles, which gradually pass into the alveoli of the lungs.
Thymus
For a long time, what exactly the thymus gland is intended for remained a mystery to scientists. If you look at the location of the internal organs of a person in the video, you will notice that it is located at the very top of the sternum.
To date, its role has also been studied. It is now known that the thymus gland is the most important element of the immune system. And the name is identified with its appearance: the shape of the gland resembles a two-pronged fork.
Human anatomical structure
The functional elements of the human body are cells. Their accumulation forms the tissue from which all parts of the body are composed. The latter are combined in the body into systems:
- Digestive. It is considered the most difficult. The organs of the digestive system are responsible for the process of digesting food.
- Cardiovascular. The function of the circulatory system is to supply blood to all parts of the human body. This includes lymphatic vessels.
- Endocrine. Its function is to regulate nervous and biological processes in the body.
- Genitourinary. It differs in men and women and provides reproductive and excretory functions.
- Intercession. Protects the insides from external influences.
- Respiratory. Saturates blood with oxygen and converts it into carbon dioxide.
- Musculoskeletal. Responsible for moving a person and maintaining the body in a certain position.
- Nervous. Includes the spinal cord and brain, which regulate all body functions.
- How to open a Metacom intercom without a key
- How to name a male puppy
- Low-calorie meals for weight loss with calories indicated
Location of organs in the abdominal cavity
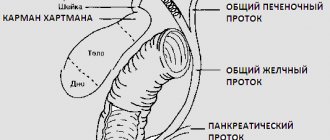
The abdominal cavity is the location of almost all elements of the gastrointestinal tract, digestive glands and organs of the excretory system. The incoming “food bolus” begins to be digested in the stomach, then it enters the intestines, from where the ducts of the pancreas and gall bladder open, collecting liver secretions.
You can learn more about diseases that affect the gastrointestinal system of the human body, such as stomach and duodenal ulcers, as well as details of the diagnosis and treatment of dyspepsia
The absorption process is completed in the large intestine, and filtration continues in the kidneys and spleen. The adrenal glands are also present here, controlling many processes in our body. The drawing will help you better understand the location of the internal organs of a person.
Stomach
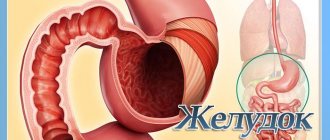
The abdominal cavity is separated from the chest cavity by the diaphragm, so immediately below it, to the left of the midline, is the stomach - a sac-like outgrowth of the digestive canal. Its main function is the primary reservoir for food and the first stage of breaking down incoming complex nutrients into simpler elements.
The fullness of the stomach determines its size. Food from the esophagus enters the stomach, where, with the participation of gastric juice, biological oxidation processes begin.
Pancreas
The location of human internal organs in the peritoneum is subject to their role in metabolic processes. Therefore, immediately under the stomach, closer to the spine, is the permanent location of the pancreas. This is one of the largest secretory organs of the human body, performing a dual function.
The pancreatic juice it produces is saturated with digestive enzymes and is a waste product of the exocrine gland. At the same time, the pancreas secretes a whole complex of hormones that regulate the metabolism of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, as befits endocrine glands.
Liver
When describing the internal organs of a person, the arrangement of which is limited to the abdominal region, one cannot help but dwell on the liver - one of the vital elements of our body. The liver is located on the right side of the stomach under the dome of the diaphragm and is an organ of cleansing.
It consists of two unequal lobes: the small left and large right, occupying the upper right position under the diaphragm. She is in charge of a whole range of physiological programs, the slightest failure in the implementation of which is detrimental to the body:
- neutralization of drugs and other unsafe substances into substances that are less toxic in composition;
- removal of excess hormones, vitamins and other substances;
- control of saturation and blood glucose levels;
- regulation of fat metabolism, cholesterol and lipid production;
- participation in the hematopoietic processes of the embryo, etc.
Gallbladder
The main function of this organ is the accumulation of bile (a greenish viscous liquid) synthesized by the liver and its removal into the duodenum using the bile and cystic ducts. It is located in the lower part of the liver, on the border of its lobes. The shape of the gallbladder resembles a longitudinal sac with very thin walls.
In this peculiar pouch, bile produced by the liver is collected, which is then released in portions into the duodenum to regulate the process of digestion of fats received from food. The location of the photo will only help to identify some internal organs, for example, the gallbladder located in the lower third of the liver can be seen in the pictures at the end of the article.
Spleen
Looking at the location of the human internal organs in the pictures in the area of the peritoneum, at the top left you can see the spleen in shape resembling a flattened hemisphere. In shape it is represented by a hemisphere, which is flattened. In both children and adults, this organ performs hematopoietic and immune functions through the formation of lymphocytes.
The spleen also filters the flow of platelets and red blood cells if their structure is damaged. If we continue the conversation about filtration, we can note that the spleen also prevents the passage of protozoa, foreign particles and bacteria. It is also worth noting that this organ takes an active part in the exchange of food products.
Functions of the spleen
The spleen is actively involved in both the hematopoietic and immune processes of our body, namely:
- formation of lymphocytes and filtration of microorganisms;
- participation in metabolic reactions and filtration of damaged blood cells;
- accumulation of platelets and the platelet organ and hematopoietic organ at the initial stage of embryonic development.
Intestines
It is quite simple to imagine the location of the human internal organs below the stomach, since all this space is occupied by the compactly packed intestines. Starting immediately from the stomach, a long tangled tube is the small intestine, which on the right transforms into the large intestine. The latter describes a kind of circle, the end point of which is the anus.
Smooth functioning of the intestines is the key to the health of the human body. Two-thirds of all cells that provide immunity are localized in this area of the human internal organs: the location of such a large number of immunocytes is the best proof of the importance of this organ. A glass of warm water drunk on an empty stomach triggers peristalsis, and the entire body is cleansed of accumulated toxins.
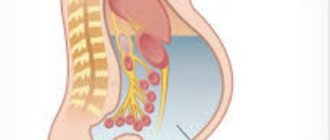
Kidneys
One of the few organs represented by a pair. One of the few organs represented by a pair. The kidneys are paired bean-shaped elements of the urinary system. They are located to the right and left of the spinal column in the lumbar region. Their size does not exceed 10-12 cm, with the right kidney slightly smaller than the left. By studying the location of the internal organs of a person in the video, one can understand the main function of the kidneys, which is to maintain stability in the internal environment and in urine formation. This is the main organ of the genitourinary system.
The localization of the kidneys in the body is the lumbar region, behind the intestines, and, accordingly, the parietal abdominal layer. Without pathology, this organ weighs from 110 to 190 grams. The main functions of the kidneys are secretion and filtration of urine, regulation of chemical homeostasis.
The kidneys are divided into cortex and medulla. On its side there is the renal pelvis, in which there is an opening for the renal vein, artery, and also for the ureter. On top, this organ is covered with a fibrous membrane.
Adrenal glands
Localized at the apex of the kidney cortex from the outside. These are paired, like the kidneys, endocrine glands. Like the kidneys, they consist of a cortex (outer) and medulla (inner). The activity of the adrenal glands is regulated by the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems.
They, in turn, regulate metabolism and also help the body adapt to changes in the external environment. The latter function is due to the fact that the adrenal glands synthesize norepinephrine, adrenaline, corticosteroid hormones and androgens, which are the main hormones of the reproductive system of the human body.
On the upper parts of the kidneys there are paired endocrine glands - the adrenal glands, consisting of the medulla and cortex. Their main function is to regulate metabolic processes, especially during stressful situations and the adaptation period.
Musculoskeletal system
This system is a set of structures that provide support to parts of the body and help a person move in space. The entire apparatus is divided into two parts:
- Osteoarticular. From a mechanical point of view, it is a system of levers that, as a result of muscle contraction, transmit forces. This part is considered passive.
- Muscular. The active part of the musculoskeletal system is muscles, ligaments, tendons, cartilaginous structures, and synovial bursae.
Anatomy of bones and joints
The skeleton consists of bones and joints. Its functions are the perception of loads, the protection of soft tissues, and the implementation of movements. Bone marrow cells produce new blood cells. Joints are the points of contact between bones, between bones and cartilage. The most common type is synovial. Bones develop as a child grows, providing support for the entire body. They make up the skeleton. It contains 206 individual bones, made up of bone tissue and bone cells. All of them are located in the axial (80 pieces) and appendicular (126 pieces) skeleton.
- Massage of the collar area - how to do it at home. Neck massage technique, video
- Mulberry compote for the winter
- How to call a phone via the Internet for free from a mobile phone and computer
The weight of bones in an adult is about 17-18% of body weight. According to the description of the structures of the skeletal system, its main elements are:
- Scull. Consists of 22 connected bones, excluding only the lower jaw. Functions of the skeleton in this part: protecting the brain from damage, supporting the nose, eyes, mouth.
- Spine. Formed by 26 vertebrae. The main functions of the spine: protective, shock-absorbing, motor, supporting.
- Rib cage. Includes the sternum, 12 pairs of ribs. They protect the chest cavity.
- Limbs. This includes the shoulders, hands, forearms, hip bones, feet and legs. Provide basic motor activity.
The structure of the muscular skeleton
The human anatomy also studies the muscle apparatus. There is even a special section - myology. The main function of muscles is to provide a person with the ability to move. About 700 muscles are attached to the bones of the skeletal system. They make up about 50% of a person’s body weight. The main types of muscles are as follows:
- Visceral. They are located inside organs and ensure the movement of substances.
- Heart. Located only in the heart, it is necessary for pumping blood throughout the human body.
- Skeletal. This type of muscle tissue is controlled by a person consciously.
How are the pelvic organs located?
Between the hip joints, the location of the human internal organs in the figure fits into the following sequence: if the body is female, then the ovaries and uterus are localized here, if the body is male, the testicles and prostate gland are located here. This is the location of the bladder.
Ovaries
These are the glands of the reproductive system, represented by a pair and performing an endocrine function. They synthesize female sex hormones (steroids, estrogen, and partially androgens), and also the maturation and excretion of cells of the reproductive system.
Localized on both sides of the uterine walls. As already mentioned, a pair of female reproductive glands, the ovaries, not only produce hormones (estrogen, steroids and weak androgens), but also serve as a site for the development and maturation of eggs.
Uterus
The uterus is a hollow organ made of smooth muscle, the purpose of which is to bear the fetus during pregnancy. The pelvis is a relatively small cavity, so the location of the human internal organs in this area is described relative to each other. So, the uterus is located in front of the rectum directly behind the bladder.
The rounded lower part ends with the cervix. The size of this organ depends on the presence/absence of pregnancy and the stage of embryonic development. During gestation, the uterus enlarges along with the fertilized egg, and after childbirth it returns to its normal size, not exceeding 10 cm.
Bladder
In the lower third of the pelvis there is a hollow smooth muscle element of the excretory organ system - the bladder. Its functionality is associated with the reservation of urine secreted by the kidneys and its subsequent removal during urination. In the male body, the prostate gland is located below it, and in the female body, the vagina is located behind it.
By imagining the location of the internal organs in your body, you can quickly identify the suffering organ and have a constructive conversation with the doctor. And this, in turn, will lead to a more accurate diagnosis and the appointment of timely and effective treatment, which will have a positive effect on the speed of recovery.
Preparation for diagnosis
To ensure accurate diagnostic results without distortion, the human abdominal cavity must be properly prepared for the procedure. To do this, you need to strictly follow a special food and medication diet. It is also very important to tell the doctor who will perform the ultrasound examination what medications you are taking and what diseases you have already been diagnosed with. All this will allow you to create the most complete and accurate clinical picture and help make the correct diagnosis. Diet before examination:
- For two to three days before diagnosis, it is prohibited to eat flour, sweets, fermented milk products and milk, carbonated drinks, fatty meats and fish, alcohol, caffeine, raw vegetables and fruits, juices, legumes, sauerkraut and other foods. , which are on the list of causing increased gas formation;
- It is allowed to eat meat and fish, which are low-fat varieties, steamed, baked apples, pearl barley, buckwheat and oatmeal in water, and low-fat hard cheese. At this point, it is not recommended to overeat, but it is better to divide the daily food intake strictly into several small portions;
- You need to drink at least one and a half liters of fluid per day. Plain still water or tea without sugar is best;
- The last meal should be strictly no earlier than six hours before the diagnosis, since the study should be carried out on an empty stomach and nothing inside the stomach should interfere;
- For people with diabetes, it is permissible to eat a light breakfast before the procedure. In this case, it would be best to have tea with a little sugar and part of a portion of porridge;
- Pregnant women are allowed to eat late, but for best results it is recommended that it be no later than three hours before diagnosis;
- If an ultrasound is being performed on an infant, it is also acceptable to do the last feeding three hours before the procedure to ensure the stomach and intestines are empty.
Medicines:
- To ensure that the examination of the intestines and stomach is as accurate as possible, it is allowed to take medications before the procedure to reduce bloating;
- It is also permissible to take, in the absence of contraindications, any of the enterosorbents, which promote the binding of harmful substances inside the stomach and intestines;
- If you take medications on an ongoing basis, for example, for the cardiovascular system, you should consult your doctor about its effect and notify your sonologist;
- If you have noticed problems with your stomach or colon, it is recommended that you take a laxative to cleanse your colon twelve hours before the test;
- It is highly not recommended to take aspirin and no-shpa before the examination.
It should be strictly taken into account that before using medications, a preliminary consultation with a doctor is necessary, who will help you choose the right drug and prescribe the right dosage. It is highly not recommended to choose medications on your own. Also, immediately before the diagnosis itself, it is necessary to warn the doctor who will do the ultrasound about what medications you took.
A couple of hours before the examination of the kidneys and urinary system, it is advisable to drink a liter or one and a half of water so that the bladder is full. This is necessary so that parts of the body, and in particular the bladder itself, are easier to examine, since the fluid that is in it straightens it and makes it more visible in the image.
It should not be forgotten that for the most complete picture reflecting your condition, you need to inform the doctor who performs the diagnosis about what examination procedures you underwent shortly before. This applies to colonoscopy, gastrography, FGDS, and irrigoscopy, which use contrast during the procedure.
Caring for the body is the key to health
Despite the extensive knowledge of humanity and its own anatomy, the human body still remains the most important object of study and experimentation. We have not yet solved all of its mysteries; there are a great many of them ahead.
At the same time, the instinct of self-preservation, protection of the entire body and internal organs is inherent in all living beings from the very beginning. However, people often forget to treat their body with due respect. Not only leading an unhealthy lifestyle and having bad habits, but also engaging in heavy physical labor or other situations that require the body to work to the limit can cause disruptions in the functioning of internal organs and lead to diseases. Therefore, do not forget about caring for your body.
Carrying out an ultrasound
The ultrasound procedure is a painless examination method, since it is performed by ultrasound, which is not perceived by our body. During the examination, the patient lies on his back, and the sonologist uses a special sensor to examine the internal organs. In order for the human abdominal cavity to be located in the most convenient position for examining a particular part of the body, the doctor may ask the patient to take a deep breath and hold his breath or, conversely, change the position slightly and turn slightly onto the right or left side.
After diagnosis, the doctor deciphers all the results obtained by the ultrasound machine and issues a research protocol with a conclusion, on the basis of which it will be possible to make a diagnosis and prescribe the necessary course of treatment. Also, based on the data obtained, the doctor can strictly refer the patient for additional examinations if there are deviations from normal values, as well as if neoplasms, cysts or fluid accumulations have been detected around the gallbladder, stomach, glands and in another area of this part of the body.