Inflammation of the duodenum. Causes
For example, duodenitis is an inflammatory lesion of the mucous membrane of the duodenum (its mucous membrane). In response to an “acute” stimulus it will be acute; in response to long-term - chronic. What threatens the integrity of the mucous membrane:
- mechanical impact (foreign bodies);
- toxic substances (including hydrochloric acid of gastric origin);
- bacteria (for example, Helicobacter pylori);
- spicy food;
- strong alcohol.
Inflammation of the duodenum can be a response to a violation of trophism - blood supply and innervation of tissues. But this can no longer be attributed to local causes; these are consequences of disturbances at the level of the whole organism.
The duodenum does not remain indifferent to the troubles of neighboring organs - the stomach, intestines (small and large), liver, gall bladder, pancreas. The inflammation that initially began in these organs, if not stopped in time, will sooner or later affect it too. This is why chronic duodenitis is almost never isolated.
Instructions
Symptoms of duodenal disease may be similar to those of stomach and colon disease. therefore, a complete examination of the gastrointestinal tract is prescribed. Most often, inflammatory processes of the duodenum manifest themselves in the form of pain 1.5-2 hours after eating, as well as hunger pain, digestive insufficiency, which manifests itself in the form of constipation or diarrhea. These symptoms can be attributed to all diseases associated with damage or inflammation of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
You will be prescribed a blood test for the presence of antibodies to determine parasitic infections, a general and biochemical blood test and an analysis for tumor markers, and stool for worm eggs.
The doctor always prescribes an ultrasound, but this method does not always make it possible to make an accurate diagnosis, especially in obese patients, but it helps to determine the location of all organs and the presence of foreign inclusions.
If you have been prescribed irrigoscopy, then a radiopaque substance will be administered using an enema and diagnostics will be carried out using X-rays, which allows you to determine the patency of the duodenum.
During colonoscopy, a hardware examination of the duodenum is performed for clearance. This allows you to make an accurate diagnosis of damage to the mucous membrane and determine the extent of the damage.
During a barium fluoroscopy, you will be given 500 mg of a solution that resembles dissolved chalk to drink. If there are significant lesions of the mucous membrane, then an x-ray will show the presence of niches.
Fibrogastroscopy allows you to determine the size of the lesions and allows you to obtain material for a biopsy. If the ulcers are deep and bleeding, then this method allows you to carry out medical manipulations and stop the bleeding.
Clinical manifestations of inflammatory diseases of the colon and small intestine are diverse. In the initial stage, the course of the disease is practically asymptomatic and is manifested by intestinal discomfort, delayed or frequent bowel movements, bloating, general malaise and unpleasant sensations. To make an accurate diagnosis in a timely manner, it is necessary to undergo a medical examination.
Inflammatory diseases of the large and small intestine always affect its inner lining. If you experience the listed symptoms, consult a proctologist or gastroenterologist. The examination must be carried out across the entire gastrointestinal tract, since a disease of one part of the intestine leads to disruption of the entire gastrointestinal tract.
Any doctor begins an examination by listening to the patient’s subjective complaints and examining by palpation. In this case, the abdomen is palpated from all sides. A hardware examination is prescribed after collecting an anamnesis of the disease and after careful preparation of the patient.
You will be prescribed a stool test, scraping, and a blood test for tumor markers and antibodies, the presence of which may indicate the presence of parasites in the body. Among the hardware methods used are radiography, ultrasound, irrigoscopy with the introduction of a radiopaque substance using an enema, and colonoscopy - this is an examination of the intestinal lumen.
Before any type of hardware examination, you will be prescribed a diet for 10 days, daily enemas, and laxative pills.
Eliminate from your diet all indigestible foods, meat, cheese, and legumes. Completely avoid bread, alcohol, carbonated drinks, and sweets. Eat pureed porridge with water or pureed vegetables. Do an enema daily using an Esmarch mug.
Do an enema the day before the examination. Do not eat food 24 hours before the examination, and do not drink water 6 hours before.
Based on the examination, you will be given an accurate diagnosis and prescribed outpatient, inpatient or surgical treatment. Inflammatory bowel diseases include: colitis, enteritis, proctitis, typhlitis, appendicitis, sigmoiditis. In severe cases of the disease, liquid pus or serous exudate may be released from the rectum.
Related News
Duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum). Symptoms
The duodenum serves as a kind of “crosshair” of the gastrointestinal tract. It receives both what requires further digestion (food from the stomach) and what is necessary for this (bile, pancreatic enzymes, its own secretions). Such anatomical and functional proximity of the duodenum and neighboring organs does not allow us to identify unique signs of its damage (with the exception of the picture obtained using invasive methods, for example, duodenoscopy). In addition, isolated duodenitis is a rare phenomenon. Much more often, its symptoms are intertwined with those characteristic of gastritis, gastric and intestinal ulcers, colitis, enteritis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, etc.
Depending on the level of the gastrointestinal tract involved in the inflammatory process, these may be:
- heartburn, belching;
- nausea, vomiting;
- loss of appetite;
- constipation, diarrhea;
- weight loss;
- pain in the epigastric region of varying nature and intensity;
- low-grade fever;
- asthenic syndrome, etc.
Folk remedies
View gallery
Despite the fact that most doctors now know how to treat inflammation of the duodenum using traditional methods, patients still trust centuries-old herbal complexes. The most commonly used medications are the following, which are easy to prepare:
1. Pour boiling water over 1 tsp. flaxseed, after which everything is left for 20 minutes. The prepared drink is consumed in small sips on an empty stomach. The medicine is taken for a month without interruption. 2. Chamomile, lemon balm, licorice and marshmallow root, buckthorn bark, lavender, and shepherd's purse are mixed in equal parts. Next 1 tsp. The prepared mixture is poured with a glass of boiling water and sent to a water bath. Strain and drink everything 30 minutes before eating. 3. Crush 0.5 kg of sea buckthorn and pour in 0.5 liters of sunflower oil. This composition is infused for a week in a closed container. Next, the mass is ground and taken, if inflammation of the duodenal bulb is observed, 1 tbsp. l. every day for a month. 4. An aqueous solution of St. John's wort is prepared and in moments of exacerbation, several sips are taken every day. 5. The juice is squeezed out of the leaves and stems of the large plantain, after which a little honey is added. The resulting mixture is drunk 1 tsp. before eating. 6. Rhubarb sprigs are soaked in clean and warm water, then they are applied as a compress in moments of inflammation on the stomach area.
Duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum). Treatment
Duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum). Treatment in adults
In the acute phase, rest - fasting for one to two days - can save the situation. This will avoid additional damage, reduce intoxication and provide material and energy resources for tissue restoration. What should not be forgotten is the drinking regime. Water is vital for the body, and doubly necessary for those actively recovering. Water is a purifier, a solvent, and a source of energy. But the water should not be very hot or cold!
Rest concerns not only eating, but also general motor and emotional activity. This principle of energy saving will help the body concentrate fully and effectively on the main task.
Food . At the end of the fast, at first it should be gentle. And in consistency, and in temperature, and in composition, so as not to provoke too much juice secretion, which can slow down tissue regeneration.
Medicines can also help the body get more confidently on the path to recovery: painkillers, antacids, enzymes, vitamins, etc.
In rare complicated cases (with erosive-ulcerative duodenitis), emergency surgical measures may be required.
In the remission phase, on the contrary, physical activity is important . It helps the gastrointestinal tract better absorb food and maintain the natural rhythm of cell repair. But it is also important not to forget about the nuances of nutrition.
Duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum). Treatment in children
In treating children, as well as adults, it is important to remember that symptomatic therapy (painkillers, anti-inflammatory, enzyme replacement) deals with consequences. And our task is to prevent their reappearance (or even better, their initial appearance). The gastrointestinal tract is a mirror of the lifestyle as a whole, both from a physical and psycho-emotional point of view. Scientific discoveries clearly indicate a close physiological connection between the organs of the digestive system and the brain. Therefore, not only poor nutrition (and this concept has both general principles and individual characteristics), but also “wrong” emotional reactions (stress) disable the food absorption system, which affects the functioning of the body as a whole.
The younger the child, the more his condition is influenced by the habits and reactions of his parents (especially his mother). Therefore, the main role in the formation of healthy habits is played not so much by the instructions of adults, but by the living example of their own behavior.
Inflammation of the duodenum (duodenitis) occurs among all age categories, regardless of gender, and the symptoms and treatment of this disease depend on the factors that influenced the occurrence of the pathology. The development of the inflammatory process in this part of the intestine can be caused by both poor nutrition and other diseases: gastritis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis.
Most often, duodenitis occurs in men aged 50 to 60 years. In women, the disease may appear due to hormonal imbalance.
Diagnosis of ulcers
This is the newest way to examine the body’s digestive system to identify various pathological processes. This diagnostic tool is a miniature capsule with a video camera. After being swallowed and entering the intestines, it naturally passes through all parts of the gastrointestinal tract and records its path on camera up to 35 frames per second. The information is recorded and stored with subsequent decoding, giving a complete picture of the condition of the intestines.
The information content is high and accounts for more than 90% of the diagnosis of various diseases. The procedure has a number of positive qualities:
- painlessness - the capsule is miniature in size, so it is easy to swallow;
- safety - it is sterile and disposable, so infection with any infection is excluded;
- comfort - during diagnosis, the patient is not limited in movement, so there is no discomfort.
The disadvantage of this diagnostic procedure is its high cost.
It is a universal way to diagnose various pathologies of internal organs. In intestinal diagnostics, ultrasound is used in the form of two methods:
- The transabdominal technique through the outer abdominal wall is a classic method that gives a general picture of the condition of the organs.
- Endorectal ultrasound is more informative and is performed by inserting the main sensor through the anus.
Before the examination, the intestinal cavity is filled with a sterile contrast agent, which makes it possible to more accurately determine the condition of the organ. Often both of these methods complement each other in terms of diagnosing the presence of pathology.
Virtual MSCT
Virtual colonoscopy or colonography - a method of multislice computed tomography of the intestine is an analogue of computed tomography. Diagnosis is carried out by rotating the tomograph around the patient, when examining and fixing a certain section of the intestine with its surrounding tissues in a section.
Magnetic resonance imaging is the safest and most effective diagnostic procedure aimed at identifying the nature and localization of the pathological process not only in the intestine, but also in surrounding tissues. The diagnostic principle is based on contrasting the walls of the organ.
Before the procedure, the patient consumes up to one and a half liters of sorbitol or mannitol solution and is injected intravenously with a contrast agent that accumulates in the walls of the colon. The measures taken promote distension of the intestine, which leads to obtaining high-quality images that make it possible to clearly determine the presence of a pathological process.
The procedure is performed in a prone position and lasts about an hour.
The method is based on the ability of pathological formations in the intestines to accumulate a radioactive chemical administered intravenously. Most often, this element accumulates in tissues with increased metabolism, that is, in malignant formations. The radiation that is emitted by this pathological process is recorded by a special device.
When diagnosing duodenal ulcers, various methods are used. The main method is fibrogastroduodenoscopy, as well as various examinations (stool, blood), and palpation. Recently, much more effort in treating ulcers has been focused on eradicating the Helicobacter bacteria. As a result, antibiotics and drugs that reduce stomach acidity are increasingly used.
In severe cases, when the ulcer perforates or bleeding begins, surgical intervention is resorted to. For timely diagnosis and treatment of duodenal ulcers, you need to undergo regular follow-up from time to time. To prevent the disease, it is desirable to reduce the frequency of stressful situations and follow a diet.
Causes
Inflammation of the duodenum (duodenitis) is a disease caused by the inflammatory process of the internal mucous membrane of the intestine. The duodenum (duodenum) is an important component of the digestive process. It is responsible for the functioning of the digestive organs and metabolism in the body. The duodenum's own glands produce enzymes and hormones that break down proteins and enhance the secretory function of the pancreas.
Enlargement or irritation of this organ can lead to disruption of the entire digestive process. The inflammatory process of the duodenum most often occurs due to irritation of the receptors caused by the production of high concentration gastric juice that comes from the stomach.
Another cause of inflammation can be poor passage of undigested food in the duodenum, which accumulates in the upper part of the organ. This leads to irritation of the mucous membrane, and then to infection and inflammation.
Also, the occurrence of the inflammatory process can be provoked by:
- poor nutrition and bad habits. Sour, smoked, spicy, fried foods, as well as excessive consumption of coffee or alcohol have a strong influence on the development of duodenitis;
- medicines and pills. Taking some anti-inflammatory drugs leads to damage to the duodenum and contributes to the occurrence of an inflammatory focus;
- infections (especially bacterial). The bacterium Helicobacter pylori is the main cause of stomach ulcers and gastritis. Gastric juice with high acidity is a comfortable environment for the proliferation of this microorganism. If not treated in a timely manner, these bacteria can provoke a pre-ulcerative condition, and then a duodenal ulcer;
- chronic diseases. These include: gastritis, stomach ulcers, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, gallstones;
- severe stress. Nervous disorders are the main cause of poor functioning of the valve between the stomach and duodenum;
- injuries, bruises, tears and cracks in the mucous membrane;
- food poisoning;
- foreign bodies in the organ.
Complications and consequences
Erosion and ulcerative lesions of the duodenal bulb are extremely serious conditions that cannot be ignored. Against this background, the following may occur:
- bleeding;
- perforations;
- penetration;
- stenosis;
- periododenitis.
If an ulcer of the duodenal bulb penetrates deep into the layers of the organ, a through lesion of the organ occurs and spreads to nearby organs (pancreas), the bottom of the ulcer in this case becomes the wall of the organ. The patient complains of circular, annular pain that cannot be relieved by taking antacids.
Perforation (perforation) leads to a breakthrough in the intestinal wall and the release of its contents into the abdominal cavity, which causes peritonitis, a life-threatening condition. It is characterized by severe, unbearable pain and requires surgical treatment.
With stenosis, there is a decrease in the diameter of the bulb of the initial section of the intestine. This causes difficulty in moving the bolus of food from the stomach to the small intestine. The patient complains of:
- loss of strength and weakness;
- general weight loss;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach;
- burping rotten egg;
- frequent vomiting with pieces of food.
Symptoms and manifestations of the disease
Very often, the symptoms of inflammation of the duodenum are moderate, and the patient is not even aware of the disease. Each symptom manifests itself depending on the cause of the pathology. The first signal of the onset of duodenitis is a feeling of pain in the upper, central area of the abdomen.
You should also pay attention to several characteristic signs of the inflammatory process in this part of the intestine:
- Digestion is disrupted and appetite disappears;
- there is heaviness and a feeling of fullness in the stomach after eating;
- there is constant diarrhea, belching, heartburn and gas formation;
- there is a periodic feeling of burning and nausea, vomiting;
- there is aching pain in the chest area, which intensifies at night;
- blood comes out along with feces or vomit;
- anemia, indicating internal bleeding;
- hyperemia (mucous membrane is hyperemic);
- there is a feeling of weakness.
The symptoms of different types of duodenitis differ from each other and manifest themselves in different ways. In case of duodenal obstruction, bursting and twisting pain is felt on the right under the ribs and in the upper, central area of the abdomen. Painful sensations are accompanied by flatulence and rumbling. A bitter taste appears in the mouth, vomiting mixed with bile.
Duodenitis in combination with an ulcer, in addition to other characteristic symptoms, is characterized by severe pain that occurs in the morning on an empty stomach. These “hunger pains” help determine the presence of a duodenal ulcer. The location of foci of inflammation in the lower intestine causes pain, which is transmitted from the stomach to the small and large intestines. The same unpleasant sensations are observed as with colitis and enteritis, namely diarrhea, flatulence, and increased peristalsis.
A prolonged form of inflammation of the duodenum can lead to atrophy of the mucous membrane of the organ. The secretion of digestive enzymes is disrupted and the absorption of nutrients in the intestine is impaired. These disorders can cause consequences such as gastric lymphostasis, lymphofollicular dysplasia, mucosal lymphangiectasia, anemia and micronutrient deficiency in the body, as well as have a negative impact on the functioning of the cardiovascular, muscular and nervous systems.
Symptoms
As the disease develops, the patient does not even suspect where the duodenum is located and how it hurts.
And only over time the following signs are observed:
- appetite disorder appears;
- there are disruptions in digestion;
- there is discomfort in the stomach;
- the patient complains of belching, bloating;
- Vomiting or nausea may occur. This symptom occurs more often in women;
- pain and spasms are felt;
- possible pain at night;
- there are severe hunger pains;
- the symptom of semolina in the intestine is pronounced;
- during a diagnostic examination, the bulb is irritated;
- the intestinal mucosa is hyperemic;
- blood may be excreted in the stool;
- anemia is observed;
- the patient often experiences a feeling of weakness;
- a person has diarrhea due to duodenitis;
- There is a feeling of liquid splashing in the stomach.
If duodenal disease is not detected, an ulcerative process begins, mucosal hyperemia is observed, and pathological changes occur in the gastrointestinal tract.
Another article on this topic: What is abdominal ascites? Causes of fluid in the abdomen.
Duodenitis in children
In childhood, the causes of duodenitis include: ingestion of foreign objects, infections, helminth infection, dry food, food allergies. Stress and depression have a very strong influence on the development of the disease in children and adolescents.
An acute form of inflammation of the duodenum may be accompanied by fever, high temperature, headache, weakness, decreased appetite, bloating, vomiting, diarrhea and increased salivation. Pain appears in the upper abdomen, heart rate increases and blood pressure decreases.
With an exacerbation of the chronic form of duodenitis, pain in the upper abdomen is observed, appearing on an empty stomach or a couple of hours after eating. Over time, attacks of pain intensify and spread to the right hypochondrium and the navel area. Pain can also occur at night and be accompanied by a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, bitter belching, and heartburn.
Inflammation of the duodenum in children causes headaches and drowsiness, reduces academic performance and can lead to delayed physical development. Therefore, if suspicious symptoms are detected in a child, it is necessary to consult a specialist.
Diagnosis of duodenitis
How can one suspect the presence of inflammation in the duodenal bulb? There are no specific symptoms characteristic of inflammation of this particular area of the gastrointestinal tract. Sometimes I am bothered by pain that occurs some time after eating, nausea, heaviness in the stomach after eating. However, similar symptoms may occur in cases of impaired motility of the biliary tract (dyskinesia), peptic ulcer disease, exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis and a number of other diseases.
Gastroscopy (“light bulb” for the stomach) is the only way to examine the condition of the mucous membrane of the duodenum down to the smallest detail. If during the examination the endoscopist sees redness of the mucous membrane (hyperemia) in the area of the bulb, then, most likely, a diagnosis of “bulbitis” will be made. This “redness” looks about the same as a red throat when you have a cold.
If inflammation is present not only in the bulb, but throughout the entire length of the duodenum, then the endoscopic report will write: “duodenitis” (inflammation of the duodenal mucosa). The intensity of inflammation can vary, so bulbitis and duodenitis differ in severity (ranging from asymptomatic manifestations to severe diseases that are accompanied by severe symptoms).
Diagnostics
To diagnose this disease, you need to contact a gastroenterologist. Already at the first examination, based on complaints, anamnesis and palpation of the abdomen, the doctor will be able to establish a preliminary diagnosis.
The following diagnostic procedures help differentiate the signs of inflammation of the duodenum:
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound). Detects the pathology of the organ, its changes and the presence of formations. Helps determine the fluid content in the intestinal lumen and detect an enterogenous cyst;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD or gastroscopy). What it is? This is a method for studying the gastrointestinal tract. A probe with a camera is inserted through the oral cavity, with which you can detect the presence of inflammation and pathological changes in the stomach and duodenum, as well as symptoms of the so-called “semolina” (lymphoangiectasia) - a pinpoint rash in the intestine;
- X-ray of the digestive organs. X-rays using a contrast agent help identify defects in the digestive system;
- biopsy - examination of the mucous membrane for the presence of a tumor process. Helps identify adenoma, brunneroma, polyp and other neoplasms of the duodenum;
- coprogram - stool analysis. Helps check the speed and quality of food digestion;
- blood test for biochemistry. Determines the level of total protein, cholesterol, bilirubin and other indicators characterizing the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- examination of gastric juice. The composition and concentration of acid in gastric juice is studied;
- Helicobacter pylori analysis is carried out in case of suspected infection;
- stool analysis for blood impurities. Helps identify internal bleeding in one of the sections of the gastrointestinal tract.
What does a properly composed daily menu look like?
The menu for inflammation of the stomach and duodenum is considered quite strict.
Breakfast includes tea with milk, a soft-boiled egg, cottage cheese with prunes. For second breakfast, you can drink fruit jelly or carrot puree. For lunch, a steamed lean fish or meat cutlet, vegetable broth soup, compote. For an afternoon snack, a piece of natural marshmallow with milk. Dinner in the form of curd pudding with berries and jelly. A few hours before bedtime, a cup of warmed milk. It is also necessary to adhere to a drinking regime of 30 ml of water per kilogram of body weight.
Frying must be eliminated completely - steaming, boiling, baking and stewing. There are many recommendations with different variations so that a person does not feel deprived and hungry during the period of therapeutic nutrition.
Treatment
After studying the examination results, the gastroenterologist draws up an individual treatment plan. The duration of therapy is prescribed based on the characteristics of the patient’s body. When treating duodenitis, a combination of medications, physiotherapeutic and sanatorium methods is used.
In acute form or exacerbation of chronic duodenitis, symptomatic therapy is prescribed using the following drugs:
- Papaverine, Duspatalin, No-shpa are antispasmodics that help relieve pain;
- Almagel, Omeprazole - antacids, neutralize hydrochloric acid and reduce the acid content in gastric juice;
- Vis-Nol, De-Nol are medicinal preparations that have an adsorbing and enveloping effect. Restore intestinal microflora and protect the mucous layer of the stomach and duodenum;
- Flemoxin Solutab is an effective antibiotic to combat Helicobacter pylori;
- Domperidone, Maalox are drugs that stimulate motility and enhance peristalsis of the gastrointestinal tract.
In the chronic form of duodenitis, the doctor prescribes long-term treatment, which uses the following medications:
- Atropine, Peritol, Gastrocepin are anticholinergics. Relieves spasms and pain;
- Phosphalugel, Smecta, Enterosgel - antacids and enterosorbents. Protect mucosal tissues from irritation and damage;
- Methyluracil, Duogastron, aloe extract, vitamin B are drugs with regenerating and anti-inflammatory effects. Promote tissue healing and actively fight the progression of inflammation;
- Reglan, Cerucal - dopamine blockers. Help with nausea and vomiting in case of impaired motor function of the gastrointestinal tract. Used for duodenal dyskinesia;
- Sandostatin is a synthetic hormonal drug. Used in the treatment of lymphangiectasia.
- Motherwort and valerian are sedative drugs. Calm the nervous system, fight neurasthenia that accompanies duodenitis.
In case of phlegmonous form of duodenitis, surgical intervention is used, after which the patient must undergo a course of antibiotic therapy. Physiotherapy is prescribed as an auxiliary method in complex treatment in the absence of exacerbations.
Physiotherapeutic procedures include:
- thermal procedures (heating pads, paraffin baths, diathermy);
- ultrasound therapy;
- magnetotherapy – therapy using a magnetic field;
- Diadynamic therapy (DDT) is a method of treatment with electric current;
- balneotherapy – treatment with mineral, fresh or sea water;
- electrosleep therapy - the effect of weak current discharges on the brain. Eliminates functional disorders of the central nervous system and normalizes blood supply to the brain.
For preventive purposes, sanatorium-resort treatment is prescribed. This therapy is used to prevent relapses during the period of remission of the disease. Sanatorium-resort treatment is not recommended for exacerbation of chronic duodenitis.
ethnoscience
Before treating duodenal inflammation at home, you should consult your doctor. Folk remedies can be used as an adjuvant to the main treatment.
To reduce the concentration of gastric juice, protect and regenerate the mucous membrane, the following recipes are used:
- sea buckthorn oil . It is an excellent wound healing agent. You should consume 1 teaspoon of sea buckthorn oil once a day with meals.
- potato decoction or juice . To treat duodenitis, you can use not only juice, but also potato decoction. Potatoes should be cooked without seasoning. If you experience pain in the abdomen, drink half a glass of warm liquid.
- chamomile . This antiseptic plant perfectly fights Helicobacter. Brew chamomile tea and drink it chilled several times a day.
- aloe _ Has a wound healing effect. Half a kilo of aloe leaves must be washed and passed through a juicer. Add red wine and honey to the juice in a 1:1 ratio, 500 ml each. everyone. The resulting mixture is poured into a glass container and infused for two weeks. After this, it is filtered and bottled. Drink 1 teaspoon of tincture 3-4 times a day. Duration of therapy: 3 months.
- propolis . Add 500 ml to 20 grams of propolis. alcohol Place in a dark place and leave to infuse for 3 weeks. Dilute 15 drops of tincture in a glass of warm milk and drink 3 times a day. Alcohol tincture of propolis is contraindicated for children.
Video on the topic:
Drug treatment
Painkillers - Medicines can help relieve pain. The most recommended are:
- Papaverine;
- No-shpa;
- Drotaverine.
Antacids - Designed to restore acidity:
- Omeprazole;
- Almagel.
Enveloping tablets - They are prescribed to protect the mucous membrane of the duodenum and stomach. Effective are:
- De-Nol;
- Vis-Nol.
Antibiotics - If Helicobacter is present, the following is prescribed:
- Flemoxin solutab.
Motility stimulants - Medicines help increase intestinal motility:
- Maalox;
- Domperidone.
Anticholinergics - Allow you to reduce or completely eliminate unpleasant sensations. These include:
- Gastrocepin;
- Atropine.
Another article on this topic: How to check the intestines? Comparison of methods
Antacids and enterosorbents - Have protective properties, protecting the duodenal mucosa from damage. These are drugs such as:
- Enterosgel;
- Phosphalugel.
Anti-inflammatory - Have a healing effect and have an anti-inflammatory effect:
- Methyluracil;
- Duogastron.
Dopamine blockers - Reduce vomiting and improve motor skills:
- Raglan;
- Cerucal.
Sedatives - Medicines that have a sedative effect:
- Valerian;
- Sedavit;
- Tozepam;
- Phenozepam.
Prevention and diet
Prevention of inflammation of the duodenum consists of proper and regular nutrition. You should exclude spicy, salty and fried foods, alcoholic beverages from your diet, stop smoking, constantly monitor your health and undergo a medical examination once a year.
Prevention for diagnosed duodenitis is aimed at preventing relapses and the transition of the disease to an ulcer. The patient must register with a gastroenterologist and undergo routine examinations. For inflammation of the duodenum, the doctor prescribes medications and a strict diet.
You need to eat fractionally 5 - 7 times a day at the same time. This diet helps reduce the production of gastric juice, which irritates the duodenum. You should chew your food thoroughly. Food should be steamed or grated.
The incidence of duodenal diseases is high - more than 10% of all inhabitants of the planet suffer from ulcerative lesions alone.
Important digestive processes occur in this section: alkalization of the acidic food bolus coming from the stomach, the entry of bile and pancreatic enzymes into it, and the humoral regulation of the acidity of gastric juice. Anatomists distinguish 7 types of shape and position of this section. The complexity and accuracy of the ongoing processes determines the quality of digestion, and the likelihood of various failures is high.
Therapy
View gallery
Initially, the patient is required to adhere to a strict diet. How to remove inflammation of the duodenum? Treatment is carried out with medications taking into account the underlying cause of the disease.
1. Analgesics and enveloping agents are used for pain relief. 2. If an infection is detected, a course of antibacterial therapy will be required. 3. To reduce the acidity of gastric juice, specialized medications are needed. 4. To overcome enzyme deficiency, additional nutritional correction is needed. 5. General strengthening medications, antispasmodics and vitamins will be prescribed.
Sometimes therapy requires the use of immunocorrectors and sedatives. Physiotherapeutic methods have an excellent effect, namely magnetic therapy, electrophoresis and ozokerite, as they effectively remove inflammation of the duodenum. Symptoms and treatment of this disease may vary, so the patient is recommended to go through certain stages:
- stationary;
- outpatient;
- health resort
Then you can know for sure that all possibilities have been used to combat the disease.
Symptoms of diseases
Characteristic signs that are of concern during an acute disease or exacerbation of a chronic process:
- night pain in the epigastric region (slightly below the stomach);
- hunger pains - occur after a long break in eating, relieved even by a piece of bread;
- pain that occurs 2-3 hours after eating - from irritation of the intestines with food coming from the stomach;
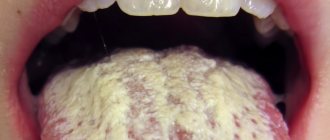
- permanent white coating on the tongue;
- decreased appetite, partly due to fear of pain;
- frequent nausea;
- constant heartburn;
- frequent constipation;
- admixture of blood in vomit and feces - with ulcerative lesions.
In the case of the chronic form of the disease, persistent digestive disorders are added, leading to loss of body weight, pale and dry skin, weakness, constant fatigue, changes in blood count, and decreased performance.
Diseases of the duodenum affect people of working age, but rarely cause disability. The main provoking factor is considered to be hereditary predisposition, since almost everyone has errors in nutrition, but diseases do not.
Instrumental studies
View gallery
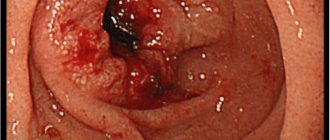
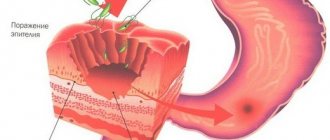
The most reliable method for diagnosing duodenitis is endoscopy. If there is superficial inflammation of the duodenum, then the monitor will show an unevenly swollen mucous membrane. Thus, it is possible to detect sharp hyperemia in the form of single spots. These zones protrude slightly above the rest of the surface.
With severe duodenitis, the mucous membrane takes on a diffusely edematous appearance. The patchy areas of hyperemia are much larger, often connecting into fields up to 2 cm in diameter. Small punctate hemorrhages are also present in such areas. The mucous membrane becomes easily wounded; a light yellow opalescent liquid and a large amount of mucus can be found in the lumen.
If there is pronounced inflammation of the duodenum, then the endoscopic picture will be even more vivid. With this disease, the phenomenon of semolina is noted. Ultrasound can lead to local pain under the sensor when pressing in the antrum, which helps differentiate unpleasant syndromes caused by the disease.
Diseases of the duodenum
Duodenitis
This is a simple inflammation that can develop on its own (primary) and complicate the course of other diseases of the digestive canal (secondary). Duodenitis is often secondary to diseases of the gallbladder and pancreas. In this case, a constant spasm of the sphincter of Oddi develops, which regulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juice. At the same time, the intestinal walls thicken, and in advanced stages it can lead to mucosal atrophy.
- constant dull pain, “whining” in the epigastric region;
- emetic syndrome or nausea interspersed with vomiting;
- heaviness in the stomach after eating;
- weakness due to decreased appetite.
Diagnostics
A gastroenterologist deals with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the duodenum . In rural areas, primary (rather approximate) diagnosis can be carried out by a general practitioner or family doctor, but with a mandatory, at least one-time, consultation with a gastroenterologist.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy
FGDS or gastroscopy is the most informative method in which the internal surface is examined using an endoscope inserted through the mouth. The fibrogastroscope is equipped with a video camera that allows you to take pictures, a biopsy instrument and a probe through which you can inject medicine directly into the lesion. The device also allows you to apply hemostatic clips.
The procedure is unpleasant, but harmless, and in many cases allows one to avoid surgery.
Biopsy
Excision of a tiny piece of living tissue for further histological examination. The cellular composition, tissue fluid, and pathological formations are examined. Allows you to reliably distinguish between acute inflammation and chronic inflammation, a benign tumor from a malignant one, and a developmental anomaly from a scar.
Analysis for Helicobacter
Helicobacter is considered the main etiological factor of peptic ulcers and gastric cancer. This is the only bacterium that can live in the hydrochloric acid produced by the stomach. The test is an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay or ELISA for antibodies to Helicobacter; venous blood sampling is required.
Some laboratories examine stool or exhaled breath.
General blood analysis
The severity of inflammation, the presence of anemia and other general clinical indicators reflecting the general level of health are determined.
Occult blood test
The stool is examined, in which altered red blood cells can be detected. Allows you to detect hidden bleeding from the digestive canal. The pharmacy has express tests for detecting occult blood in the stool on your own.
Sonography of the duodenum reveals thickening of the intestinal walls or an ulcerative defect found in the form of a crater. The boundaries of inflammation and the place of transition into healthy tissue, as well as tumors, if any, are clearly visible.
MRI and CT
Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography detect lipomas (tumors from adipose tissue) and leiomyomas (from muscle tissue). These tumors are benign. Duodenal cancer or adenocarcinoma is a rare case, but they are also visible in these studies.
Pregnancy
View gallery
During this period, treatment of duodenitis should be differentiated, comprehensive and strictly individual, and also be based on certain principles: drug therapy is carried out only at the time of exacerbation and if there is a lack of effect from following the diet, diet and antacids.
If inflammation of the stomach and duodenum is detected, then non-absorbable drugs are used during therapy. When selecting medications, you should exclude those that contain sodium (to avoid the development of metabolic alkalosis, as well as fluid retention in both the fetus and the mother) and give priority to drugs that have a high neutralizing ability and a well-balanced composition of laxatives and fixatives. These include "Maalox", which is prescribed 1 serving of powder every few hours after meals (3-5 times a day). Phosphalugel, Almagel, Koalin and aluminum hydroxide are also used.
Astringent and enveloping preparations are often used (herbal origin is recommended - decoctions of St. John's wort, chamomile and yarrow flowers).
First of all, the following components are selected:
- anti-inflammatory (oak, plantain);
- antispasmodic (licorice, dill, mint, chamomile);
- antiseptic (St. John's wort, calendula);
- laxatives (rhubarb, zhoster, buckthorn).
Antisecretory drugs may include some non-selective M-anticholinergics. “Atropine” reduces the tone of the smooth muscles of the esophagus, inhibits the secretory function of the stomach, but at the same time promotes dilatation of the cervix, as a result of which there is a possibility of miscarriage in the first trimester, and also activates fetal tachycardia. Therefore, if a pregnant woman has chronic inflammation of the duodenum, it is preferable to use Metacin or Platifillin, which have a less aggressive effect on the body of the fetus and mother. In addition, these drugs have a relaxing effect on the uterus, which allows it to be used by women who have been diagnosed with a threat of miscarriage. In case of secondary duodenitis, therapy for the underlying disease is recommended.
Treatment
Depends on the type of disease, severity, presence of complications, concomitant diseases and age of the patient.
Surgery
Immediate surgery is required in case of ulcer rupture and bleeding that cannot be stopped by other means. The scope of surgical intervention includes excision of the ulcer followed by suturing the wound, maintaining intestinal patency.
Surgery is also necessary for cicatricial stenosis (narrowing), if food cannot pass on its own. The site of stenosis is excised, and the intestine is sutured end to end.
Drug treatment
Prescribed individually using the following groups of drugs:
Diet food
An integral part of treatment, without which recovery is impossible. Therapeutic nutrition consists of pureed boiled dishes containing a lot of mucus - rice water, jelly, steamed meat. The diet creates conditions for the healing of erosions and ulcers and the cessation of inflammation.
Which method will be most suitable
When examining the intestines to determine the pathological process, primarily oncology, it is impossible to give an unambiguous answer about the advantage of one or another non-invasive diagnostic method. In each specific case, an individual approach is carried out, taking into account:
- general condition of the patient;
- presence of complaints;
- time of illness;
- certain contraindications.
The decision to order an examination and the choice of method is made by the doctor. But colonoscopy today is the most informative method of examination, especially in the early stages of the development of the disease. It allows you to visually recognize a pathological focus in the intestine, the size of which does not exceed 1 mm, and take the material for a biopsy.
The final diagnosis made after the conclusion of the histological examination makes it possible to determine further tactics in the treatment of the identified intestinal pathology.
The decision to order an examination and the choice of method is made by the doctor. But colonoscopy today is the most informative method of examination, especially in the early stages of the development of the disease. It allows you to visually recognize a pathological focus in the intestine, the size of which does not exceed 1 mm, and take the material for a biopsy.
Diagnosis of inflammatory diseases of the duodenum makes it possible to begin timely treatment and prevent major damage to the mucous membrane, which invariably turns into an ulcer. Diagnostic methods include general surveys, reviews for the presence of parasitic infections, ultrasound, irrigoscopy, colonoscopy, fluoroscopy with a barium suspension solution, fiberoscopy.
You will need
- – referral from a gastroenterologist for examination.
Instructions
1. Signs of disease of the duodenum may be similar to manifestations of disease of the stomach and colon; therefore, a full examination of the gastrointestinal tract is prescribed. Most often, inflammatory processes of the duodenum manifest themselves in the form of pain 1.5-2 hours after eating, as well as hunger pain, insufficiency of digestion, which manifests itself in the form of constipation or diarrhea. These signs can be attributed to each disease associated with damage or inflammation of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
2. You will be prescribed a blood test for the presence of antibodies to determine parasitic infections, a general and biochemical blood test and a review of tumor markers, stool for worm eggs.
3. The doctor will certainly prescribe an ultrasound, but this method does not always make it possible to make an accurate diagnosis, only in obese patients, but it helps to determine the location of all organs and the presence of foreign inclusions.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w8RxI47fXwU
4. If you have been prescribed irrigoscopy, then with the support of an enema, a radiopaque substance will be administered and diagnostics will be carried out using X-rays, which allows you to determine the patency of the duodenum.
5. During colonoscopy, a hardware examination of the duodenum is performed for clearance. This allows you to make an accurate diagnosis of damage to the mucous membrane and determine the extent of the damage.
6. During fluoroscopy with barium support, you will be given 500 mg of a solution to drink, which resembles dissolved chalk. If there are significant lesions of the mucous membrane, then an x-ray will show the presence of niches.
7. Fibrogastroscopy allows you to determine the size of the lesions and allows you to obtain material for a biopsy. If the ulcers are large and bleeding, then this method allows you to carry out medical procedures and stop the bleeding.
Clinical manifestations of inflammatory diseases of the colon and small intestine are varied. In the initial stage, the course of the disease is virtually asymptomatic and is manifested by intestinal discomfort, delayed or frequent bowel movements, bloating, general malaise and unpleasant sensations. In order to make an accurate diagnosis in a timely manner, you need to undergo a medical examination.
You will need
- - referral for examination.
Instructions
1. Inflammatory diseases of the colon and small intestine invariably surprise its inner lining. If you feel the listed signs, consult a proctologist and gastroenterologist. An examination should be carried out on each gastrointestinal tract, because a disease of one part of the intestine leads to disruption of the functioning of each gastrointestinal tract.
2. Every doctor begins an examination by listening to the patient’s subjective claims and examining with the support of palpation. In this case, the abdomen is palpated from all sides. A hardware examination is prescribed after collecting an anamnesis of the disease and after thoroughly preparing the patient.
3. You will be prescribed a stool examination, scraping, and blood examination for tumor markers and antibodies, the presence of which may indicate the presence of parasites in the body. Of the hardware methods, radiography, ultrasound, irrigoscopy with the introduction of an enema of a radiopaque substance are used, and colonoscopy is an examination of the intestinal lumen.
4. Before any type of hardware examination, you will be prescribed a diet for 10 days, daily enemas, and laxative pills.
5. Eliminate from your diet all indigestible foods, meat, cheese, legumes. Completely avoid bread, alcohol, carbonated drinks, and sweets. Eat pureed porridge with water or pureed vegetables. Do an enema every day with the support of an Esmarch mug.
6. On the day before the examination, do an enema. Do not eat food 24 hours before the examination, and do not drink water 6 hours before.
7. Based on the examination, you will be given an accurate diagnosis and prescribed outpatient, immobile or surgical treatment. Inflammatory bowel diseases include: colitis, enteritis, proctitis, typhlitis, appendicitis, sigmoiditis. In severe cases of the disease, liquid pus or serous exudate may be released from the rectum.
Video on the topic
A duodenal ulcer is an ulcer that occurs due to the action of acid and pepsin on the mucous membrane of the duodenum. Peptic ulcer disease is characterized by a relapsing course, when periods of exacerbations and periods of remission alternate. The ulcer heals with the formation of a scar.
- Duodenitis is the most common ailment of the duodenum of acute or chronic type, manifested in the form of inflammation of the mucous membrane.
- Ulcer – develops as a result of chronic duodenitis. Chronic damage to the duodenum, in which ulcers form in the mucous layer.
- A cancerous tumor is a malignant neoplasm localized in different layers of the duodenal wall.
Duodenitis
More than 90% of patients develop chronic duodenitis. It can develop due to many factors, including:
- consumption of low-quality products;
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
- ingress of foreign bodies and toxic substances;
- other chronic intestinal diseases.
This disease manifests itself in the form of pain in the epigastrium of moderate intensity, weakness, belching, heartburn, nausea, turning into vomiting. Symptoms are often accompanied by fever.
A variation of this inflammatory phenomenon is bulbitis, in which the pathological process occurs only in the duodenal bulb. This form of duodenitis does not occur just like that - it is a consequence of other pathologies of the intestines or stomach. The cause of bulbitis can be:
- gastritis;
- stomach or duodenal ulcer.
If the disease is at an acute stage, the person feels pain and nausea and suffers from repeated vomiting. Acute bulbitis develops against the background of long-term use of a large group of drugs, or poisoning. In the chronic form, there is also an aching pain syndrome, sometimes it can be accompanied by nausea.
Patients also experience chronic duodenal obstruction, which occurs against the background of tumor processes, developmental anomalies and other disorders in the duodenum. It is expressed in a violation of motor and evacuation functions in this part of the intestine and is characterized by the following symptoms:
- heartburn;
- decreased appetite;
- feeling of heaviness and discomfort in the epigastric region;
- constipation;
- gurgling and bubbling.
The manifestation of this disease is influenced by the causes that caused duodenal obstruction, the stage of progression and how long ago the disease arose.
Peptic ulcer
The main cause of this dangerous disease is the reflux of acid from the gastric contents and its destructive effect on the mucous membrane of this part of the intestine. But this pathological process develops only when the surface layers of the intestine fail to cope with their protective functions. The ulcer is localized in the initial part of the duodenum and in the bulb, that is, in that zone of the intestine that is located at a minimum distance from the stomach.
Many gastroenterologists unanimously speak about the negative impact of frequent use of anti-inflammatory drugs, which lower the protective barrier of the mucous layer of the duodenum. These drugs are aspirin and dosage forms based on it, ibuprofen, diclofenac, etc. Therefore, if possible, you should limit the use of drugs in this group as much as possible.
Poorly treated or neglected duodenitis, alcohol abuse and consumption of foods harmful to the body can also cause the development of duodenal ulcers.
The Helicobacter bacterium also tends to infect not only the stomach, but also the mucous membrane of the duodenum. It is a fairly common cause of ulcerative pathology, opening the way for acid into the mucous layers of the intestine. In 19 out of 20 cases of the development of ulcers of this organ, it is the Helicobacter bacterium that is to blame.
Since this disease is very common in gastroenterological practice, you should know what kind of symptomatic picture it manifests. This is a paroxysmal pain syndrome in the upper abdomen slightly below the sternum. Pain in the epigastrium when feeling hungry or, conversely, immediately after eating. After eating, symptoms worsen such as:
- bloating;
- nausea;
- urge to go to the toilet.
The main dangerous complications of this disease of the duodenum are bleeding or perforation, which require emergency surgical assistance. Bleeding is fraught with dangerous loss of blood and filling of the abdominal cavity with it. Perforation is when food with all the enzymes and acids enters the abdominal cavity through an ulcerative hole formed in the intestine.
Prevention
It can be primary and secondary. Primary – measures aimed at not getting sick, secondary – preventing exacerbations in those who are already sick.
If there is a hereditary predisposition, you need to pay special attention to nutrition. Food needs to be fresh, boiled, baked or steamed. No fast food or other food of suspicious quality, snacks or other foods full of flavor enhancers and preservatives. If possible, it is advisable to avoid stress.
Secondary prevention is timely and high-quality treatment of seasonal exacerbations, preferably in a hospital. It is advisable to use a temporary disability certificate to give the body the opportunity to cope with an exacerbation. During calm times, sanatorium treatment, especially alkaline mineral waters, is useful.