Description
Gastroenteritis is an infectious disease of the gastrointestinal tract. People call it “stomach flu”. It is the main cause of high mortality in third world countries. Most common among children of the younger age group. Statistics show that in our country every year more than 1 thousand patients go to hospitals with gastroenteritis. Often the consequences of such appeals are very sad. Thanks to clinical studies, it has been established that gastroenteritis is caused by viral, parasitic and bacterial endopathogens. Accompanied by loss of appetite, severe diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, and less commonly, fever. In developed countries, outbreaks of infectious diseases are rare. Patients who come to the clinic on time easily undergo treatment and recover. There are no consequences after gastroenteritis.
Types of gastroenteritis
The type of disease depends on the cause of the disease and the pathogen. The infection can be caused by viruses, bacteria or parasites. The following types of enterovirus are distinguished:
- infectious (causative agents are various types of viruses); rotavirus (most common in young children);
- coronavirus (transmitted by airborne droplets);
- parvovirus (the person in this case is a carrier of the disease).
Other non-infectious gastroenteritis:
- enteritis;
- colitis.
Acute and chronic gastroenteritis
The most common cause of acute gastroenteritis is the consumption of low-quality food. As a result, intoxication and the first signs of the disease appear: nausea, vomiting, fainting. Since the symptoms are similar to other stomach diseases, the diagnosis is not specified until the underlying cause is determined. The doctor prescribes treatment for general diseases.
Chronic gastroenteritis is a type of non-infectious disease. A complex disease requires special and long-term treatment, including lifestyle changes. A special diet is prescribed. The severity determines the duration of treatment.
Gastroenteritis in children
Children under three years of age are most susceptible to this disease. The infection occurs in a more severe and acute form than in adults. An important measure in the prevention of the disease is the timely identification of the carrier of the infection in kindergarten, preschool institutions and school.
Often gastroenteritis in children occurs due to a sudden change in diet or the introduction of new foods in the diet. In infants, an outbreak of the disease can occur due to improper nutrition of the nursing mother. Newborn babies on artificial feeding are especially at risk of disease, since they are deprived of breast milk, which contains the necessary elements that protect the intestines from infection. In case of acute gastroenteritis in breastfed children, it is necessary to continue feeding. Rotavirus gastroenteritis is also a common occurrence among children. This is due to insufficient personal hygiene. It is important that parents pay great attention to the hygiene of the child and regularly treat the baby’s toys, dishes and hygiene products.
Gastroenteritis in adults
After contracting the infection, the incubation period reaches up to 5 days, the first sign is loose stools. There are three degrees of severity of the disease:
- mild degree;
- average degree;
- severe degree.
Each degree is characterized by the frequency of occurrence of the symptom. Accordingly, the level of development of the inflammatory process is determined. In severe forms of the disease, the frequency of stools can reach up to 13-15 times a day. This leads to dehydration of the body. Like children, pregnant women are also at high risk of developing gastroenteritis. If you notice symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. Timely treatment at the hospital will help cope with the infection without serious consequences.
Atrophic gastroenteritis
Middle-aged people are susceptible to the disease. The cause of acute atrophic gastroenteritis is malnutrition, excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, and a long course of taking medications. The process of mucus formation is disrupted and atrophy of the mucous membrane occurs. The functioning of the digestive system becomes abnormal, the patient loses weight and complains of feeling unwell, pain in the abdomen, and dizziness are noted. The first symptoms appear within a few hours after poisoning.
Possible complications
Gastroenteritis is a severe disease that entails undesirable consequences. An advanced acute form of an infectious disease leads to a chronic stage. The following fatal complications have been observed:
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- damage to vital organs;
- dehydration of the body;
- sepsis;
- asymptomatic carriage;
- toxic shock;
- disruption of immunological mechanisms;
- death.
A dangerous pathology is asymptomatic carriage of the infection. Without showing any symptoms of the disease, a person remains a carrier and carrier of the infection. This leads to infection of other people.
Which doctor should I contact for an intestinal infection?
If the first symptoms of the disease occur, you should contact your local physician. If the symptoms become more pronounced, you can call a doctor at home (general practitioner or pediatrician for the child). Treatment will take place on an outpatient basis. If the patient's condition worsens, you should immediately call an ambulance and take the patient to an infectious diseases hospital. It is not always possible to determine an accurate diagnosis based on clinical symptoms. Therefore, the patient needs to tell the doctor exactly what foods he consumed, what public places he visited, and whether he traveled to places with a bad epidemiological situation. Self-medication is strictly prohibited.
Causes
What is gastroenteritis? This is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the stomach and small intestine. Many reasons are involved in the development of pathology. The main causative agents of gastroenteritis are infectious and non-infectious agents that negatively affect the mucous membrane of the stomach and small intestine:
- bacteria;
- viruses;
- helminths;
- protozoa;
- poisonous mushrooms;
- allergies to certain foods;
- chemical components that enter the body with food.
All these pathogens cause an inflammatory process. Then the body is poisoned with the products of their vital activity, the absorption of nutrients is impaired, and pain appears. The incubation period lasts 2-3 days, in some cases – 5 days.
Gastroenteritis in children is often caused by poor nutrition. For example, if a child simultaneously consumes dairy products and fresh (raw) vegetables or fruits.
But the culprit of the disease can also be the incompatibility of certain products or their intolerance by the body. You can reduce the risk of developing pathology by reviewing your child’s diet. Provoking factors also include:
- roughage foods rich in fiber;
- cold carbonated drinks;
- various seasonings;
- hypothermia of the body;
- hypovitaminosis;
- dysbiosis.
Taking certain medications can also cause childhood gastroenteritis. Usually, the disease is caused by medications that the child took without prescribing a specialist and taking into account their effect on the digestive system.
In this case, they talk about an allergic or toxic form of pathology. In addition, the following everyday causes play an important role in the occurrence of the disease:
- failure to comply with the rules for preparing foodstuffs and dishes made from them;
- contaminated household items, for example, poorly washed dishes, pacifiers;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules – unwashed or poorly washed hands;
- as a result of improper introduction of new food into the diet (for children under one year);
- in kindergarten, you can become infected with the disease through toys and other common things;
- contacts with infected people.
Thus, there are many reasons for the development of the disease. Therefore, only the treating pediatrician can tell you what gastroenteritis is in children and how it is transmitted. The duration of the pathology depends on the causes of its occurrence and how timely the child received adequate therapy.
Symptoms
Photo: greendiet.com
Gastroenteritis is a disease with pronounced symptoms. At the initial stage of gastroenteritis, the main symptoms are: nausea, vomiting, indigestion, abdominal pain. If the disease is not treated, then over time these symptoms will be accompanied by loss of strength, lethargy, cold sweat, and body temperature rises. Also, problems such as intoxication and even vascular collapse may appear. Very rarely, symptoms characteristic of an inflammatory process in the small intestine may appear. During the examination, the doctor may identify problems in the epigastric area.
Gastroenteritis quite often develops in the same way as most bacterial diseases, and the symptoms are similar: the frequency of stool in patients increases to 20-30 times a day, bowel movements are watery, and there may be an admixture of blood or mucus in the stool.
Forms of gastroenteritis
When this disease occurs, doctors distinguish three degrees of severity:
- Mild forms of the disease are characterized by vomiting and diarrhea, but bowel movements are infrequent. What is characteristic is that the temperature practically does not change and dehydration does not occur.
- With moderate severity, an increase in body temperature is characteristic (but not higher than 38.5 degrees). The patient also experiences vomiting and increased bowel movements. The skin is dry and very thirsty.
- Acute gastroenteritis symptoms of the disease are increased body temperature (up to 40), in addition to vomiting, loose and frequent stools, loss of consciousness and severe convulsions may be observed. Severe dehydration, in which the patient refuses to drink, the skin becomes dry and flabby.
Symptoms of gastroenteritis in adults
The incubation period of the disease lasts from several hours to 4 days - it all depends on the individual characteristics of the body and immunity. Typically, the incubation period for gastroenteritis lasts three to five days.
The severity of symptoms will vary depending on the causative agent of the disease, the severity of the disease and the individual characteristics of the body. Some people may experience the disease much more easily, while others may suffer more severe symptoms.
At the initial stage, adults experience symptoms such as:
- Severe nausea
- Vomit
- Bloating
- Increased flatulence (formation of gases)
- Stomach ache
- Diarrhea
- The appearance of mucus and blood in the stool
- Increased stool frequency
- Emptying color change
- Increased body temperature, possibly up to 40º C
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Decreased appetite
- Drowsiness
- Chills
If this disease is severe, then dehydration caused by frequent bowel movements may be added to the previous symptoms. At the same time, the skin on the body becomes flabby and sluggish, the lips and oral cavity are dry. Also, the skin easily folds and slowly straightens back.
If, when such symptoms occur, the patient does not seek help from a doctor, then his condition worsens significantly (even to the point of loss of consciousness). Seizures may occur and blood pressure decreases. In an extremely severe course of this disease, the patient may experience delirium.
Symptoms of gastroenteritis in children
Depending on the causes of gastroenteritis, this disease is divided into: acute and chronic. Symptoms of chronic gastroenteritis can occur due to a malnutrition, allergies, or the presence of infections, especially parasitic ones. The first signs of gastroenteritis are the occurrence of severe cramping pain near the navel, which spreads over the entire surface of the abdomen. This is especially true during meals. Such pain can spontaneously arise or disappear. The first sign of the disease in children is also an increase in temperature.
The child has bloating and strong gas. If you press on the abdomen, rumbling may occur in the area of the cecum. If a child with acute gastroenteritis experiences vomiting of blood, loose stools with impurities of blood and mucus, a strong increase in temperature that does not subside throughout the day, then it is necessary to seek help from a doctor as soon as possible, otherwise this may cause the condition to worsen.
If the temperature rises during gastroenteritis, this is one of the most dangerous and serious symptoms. Gastroenteritis can occur without diarrhea, but with severe pain in the abdominal area.
Viral gastroenteritis: symptoms
The first signs of this disease appear immediately or at most a couple of days after the infection enters the body. Symptoms of viral gastroenteritis are:
- The appearance of a severe runny nose
- Cough
- Pain and sore throat
- Severe increase in body temperature
- Strong headache
- Vomit
- Diarrhea
- Dehydration
The most dangerous is dehydration, which is observed due to vomiting and frequent bowel movements. This can lead to the body being significantly weakened, strength being lost, and the patient experiencing lethargy and drowsiness.
Bacterial gastroenteritis: symptoms
The main symptoms of this type of disease are:
- Increased body temperature
- Chills
- Muscle pain and aches
- Strong headache
- Frequent spontaneous abdominal pain
- Severe vomiting
- Diarrhea
Allergic gastroenteritis: symptoms
Another type of this disease is food allergy. Quite often this disease can be observed in children. Typical symptoms are:
- Severe epigastric pain
- Vomit
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Dysphagia
Only a doctor can distinguish allergic gastroenteritis from ordinary gastroenteritis. Therefore, in order to avoid serious consequences for the body, at the first symptoms you should immediately seek help from a qualified specialist.
Symptoms and signs of acute gastroenteritis in children
Uncomplicated gastroenteritis: vomiting, diarrhea, possible fever.
Rash - mainly due to rotavirus infection.
Symptoms from the respiratory system (otitis, bronchitis, pneumonia) - with rotavirus infection.
Additional symptoms (septic fever, vascular shock, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly) indicate generalization of the disease (for example, sepsis, typhus).
Symptoms of dehydration up to hypovolemic shock (toxicosis):
- decreased skin turgor, delayed straightening of skin folds, decreased tone of the eyeballs;
- sunken fontanel, dry mucous membranes;
- clouding of consciousness, rare blinking.
Clinical assessment of the volume of fluid lost.
In hypertensive dehydration (hyperpyrexic, hypernatremic toxicosis), the volume of fluid lost is often clinically underestimated. Ask your parents about your last weigh-in.
Complications:
- convulsions with pronounced shifts in electrolyte balance (for example, hypernatremia, hyponatremia);
- temporary intolerance to cow's milk and lactose;
- joint pain, swelling of the joints, redness of the skin over the joints (an associated symptom with shigellosis, salmonellosis and yersiniosis).
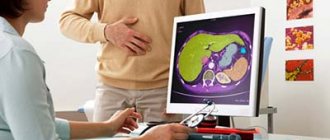
Diagnostics
Photo: beautymedicaltouch-usa.com
Most often in practice, infectious gastroenteritis occurs, the symptoms and diagnosis of which depend on the type of pathogen. However, the reason may also be the damaging effects of drugs and chemicals that are aggressive to the mucosa. Gastroenteritis is not an independent nosological entity and usually represents a symptom complex of manifestations of other diseases.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of gastroenteritis consists of examining the patient, collecting an anamnesis of his disease, differential diagnosis with similar pathologies, and the use of laboratory and instrumental research methods.
As a rule, diagnosis of gastroenteritis can be made based on examination and complaints of the patient. Signs of gastroenteritis can vary in severity. It all depends on the nature of the disease, its etiology, severity, age of the patient, and concomitant pathologies.
The disease manifests itself suddenly.
Patient's complaints
The main complaints are as follows:
- lack of appetite;
- weight loss;
- nausea, vomiting;
- rumbling in the abdomen;
- pain of varying intensity of a spastic nature;
- diarrhea of various types;
- muscle pain;
- general severe weakness;
- feeling of bloating;
- temperature increase.
Diarrhea may be absent, but this does not exclude the presence of rumbling in the abdominal cavity, which is one of the specific features of this disease, which facilitates the diagnosis of gastroenteritis.
Vomiting and diarrhea can be so significant that they sometimes provoke dehydration with corresponding manifestations: decreased blood pressure, increased heart rate, and renal failure.
Increased temperature: it can vary from low-grade to high, depending on the pathogen.
Features of the disease depending on the pathogen
With viral etiology, the main manifestation of gastroenteritis is loose to watery stools. Rarely there are mucus or blood impurities.
Rotavirus causes significant intoxication. The temperature is often low-grade, but can sometimes rise to high levels. Vomiting is typical. The acute period lasts about a week.
Caliciviruses are characterized by an acute onset of the disease with severe vomiting and spasmodic pain of significant intensity. Vomiting is more pronounced in children, and diarrhea in adults. Often all this is accompanied by headache and muscle pain. This period does not last long - 1-2 days.
Under the influence of adenoviruses, the disease lasts a long time - 2-3 weeks. Vomiting is not expressed. Begins 1-2 days after diarrhea. In half of the cases, an increase in temperature is observed, but rarely to high levels.
Bacterial gastroenteritis is accompanied by severe intoxication symptoms: high fever, severe general weakness. Severe diarrhea, accompanied by bleeding. Some bacteria synthesize large amounts of enterotoxin, which causes profuse, watery stools.
Parasites do not cause acute symptoms. As a rule, gastroenteritis caused by them develops with mild diarrhea. Blood in the stool is rare. Only for amoebic dysentery. Characterized by severe general malaise and weakness.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is carried out by analogy with acute diseases of the abdominal organs (appendicitis, ulcerative colitis, cholecystitis).
Gastroenteritis is supported by watery diarrhea, consumption of potentially contaminated food, and the presence of the disease in others.
Stool examination
The attending physician determines what tests should be taken if gastroenteritis is suspected. A rectal examination is performed. Feces with gastroenteritis are indicative. If blood and watery diarrhea persist for more than a couple of days, a test is carried out for occult blood, for the content of parasites and their eggs in the feces, and a bacterial culture is carried out.
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent method can be used to determine the presence of lamblia and some viruses. However, such studies are carried out only in the event of a disease outbreak.
All patients who have bloody diarrhea must be tested for the presence of E. coli.
If bloody diarrhea occurs in adult patients, sigmoidoscopy is performed. In this case, a biopsy is taken and culture of the contents is taken to test the blood for gastroenteritis.
General tests for acute gastroenteritis
General blood tests for this pathology are not very specific. A general blood test for gastroenteritis can reveal inflammatory manifestations and an increase in the level of eosinophils. In severe cases, the number of electrolytes may change, which requires their correction.
Diagnosis, as well as treatment, should only be carried out by a specialist. Self-diagnosis can lead to erroneous diagnoses and, consequently, complications.
Diagnosis of acute gastroenteritis in children
- Full blood count, platelets, CRP level.
- Liver parameters (ACT, ALT activity, γ-glutamate transferase, bilirubin level), blood glucose concentration.
- Content of electrolytes, creatinine, blood gas composition.
- Feces for viruses and pathogenic bacteria.
- In case of special suspicion: warm feces for eggs of worms and pathogenic protozoa to the parasitology laboratory.
- Serology: Yersinia, Salmonella, Amoeba.
- Hemoculture.
- Urine volume, urine tests.
Treatment
Photo: marimedia.ru
Treatment of gastroenteritis in adults and children in most cases occurs at home. When the first symptoms appear, you need to immediately take some measures that are aimed at improving the patient’s condition.
Treatment of all forms of gastroenteritis includes the following aspects:
- normalization of water-salt balance in the body;
- the first hours after the onset of the disease - complete refusal of food, after which you need to adhere to a certain diet;
- taking medications that are aimed at stopping vomiting and diarrhea;
- use of antibiotics.
Treatment of gastroenteritis in adults can be done with folk remedies, which are aimed at restoring the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines. Also, these medications are acceptable for oral use to replenish fluid loss in the body. To improve the patient’s condition, the use of physiotherapy is quite effective:
- paraffin applications;
- warm compresses;
- inductothermy.
After relief of the main symptoms, you need to begin restorative therapy, which is aimed at normalizing the functioning of the digestive system.
Viral gastroenteritis - treatment
If you have symptoms that may indicate the development of the disease, you should contact the on-duty therapist. During the examination, the doctor will determine the treatment tactics. If the patient’s condition does not improve after 1-2 days, a decision is made to place him in a hospital.
The main aspect of the treatment of viral gastroenteritis is the elimination of dehydration. In this case, the use of saline solutions is indicated. Both pharmaceutical drugs and homemade products have a positive effect.
Complex treatment of the disease includes taking the following medications:
- antiviral;
- enzymatic;
- astringents;
- eubiotics.
As a preventive measure against viral gastroenteritis, vaccines are used against certain types of viruses that cause the development of the disease.
Treatment of infectious gastroenteritis
In the presence of the infectious nature of this disease, the use of dehydration therapy is indicated, which is aimed at restoring the water-salt balance. In acute gastroenteritis caused by various bacteria, antibiotics are prescribed. It is strictly forbidden to take them on your own, since if you choose the wrong treatment regimen, this can cause increased dysbiosis.
In the treatment of infectious gastroenteritis, agents are also used that are aimed at eliminating the main symptoms of the disease - fever, diarrhea, vomiting. Enzyme preparations are often prescribed to improve digestion. Also shown are agents that have an enveloping effect on the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines.
Acute gastroenteritis - treatment
Treatment of the acute form of the disease occurs in a hospital. At the same time, it is important to monitor the patient’s condition and take measures aimed at improving it. In this case, treatment is carried out by a gastroenterologist.
Rehydration of the body in acute gastroenteritis is most often carried out intravenously in several stages. First, the entire volume of the missing fluid is restored, after which special solutions are gradually introduced as diarrhea and vomiting develop.
Also, therapy for acute gastroenteritis includes the following aspects:
- gastric lavage at the first stage of treatment;
- taking symptomatic medications that will help eliminate high fever, diarrhea, vomiting, pain and cramps in the stomach;
- sorbent preparations;
- dietary nutrition;
- medications to restore intestinal microflora;
- enzyme preparations.
Treatment of gastroenteritis in children
Treatment of any form of the disease in children is no different from treatment in adults. If you have alarming symptoms, you should contact your pediatrician, who, after an examination, will determine whether the baby needs to be hospitalized. If the child's condition is satisfactory and improves after taking rehydration medications, treatment is carried out at home.
If your baby gets sick, there is no need to stop his usual diet. Breast milk or formula will not harm him. When treating older children on the first day, it is best not to feed him at all. You need to give your child plenty to drink to replenish the loss of fluid in the body.
Diet for gastroenteritis in children
The diet for gastroenteritis includes the following nutritional rules:
- For the first hours after the onset of vomiting and diarrhea, you can only drink water, unsweetened compotes, and herbal decoctions.
- After the child’s condition improves, introduce mashed baked apples, bananas, and potatoes into the diet.
- Starting from the third day, you can eat vegetable soups, porridges and lean boiled chicken.
- Only from the fourth day introduce boiled eggs, lean meat and fish, and biscuits into your diet.
- The next day, you can gradually return to your normal diet.
- Eliminate dairy products from your diet for at least a week.
What can you eat if you have gastroenteritis?
Proper nutrition for gastroenteritis is one of the main aspects in the successful treatment of the disease. During the acute onset of symptoms and for at least two weeks afterward, the following foods should not be consumed:
- raw vegetables and fruits;
- fat meat;
- rich broth;
- milk;
- all sweets, fresh pastries, sugar;
- alcohol.
All food should be light, thermally processed. Do not eat anything spicy or hot, so as not to cause even greater inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Portions should be small, and each new product should be tried in small quantities.
Prevention of gastroenteritis
To prevent the development of the disease, first of all, you should always wash your hands thoroughly before eating and after visiting the toilet. All perishable foods should be stored in the refrigerator. Also, do not forget to wash fresh vegetables and fruits.
If someone in your home is sick, try to isolate them from the rest of the family. Provide the patient with separate dishes and a towel.
Also, always eat only in trusted catering establishments, where you can be sure of the quality of the food and compliance with sanitary standards in the kitchen.
Prevention
To avoid illness (or relapse), it is recommended to follow a number of preventive rules:
- Wash your hands thoroughly before eating.
- Avoid contact with infected people.
- Use only boiled or bottled water for drinking.
- Wash fruits and vegetables well before eating.
Gastroenteritis causes discomfort to babies, causing them to experience pain in the abdomen and a number of other unpleasant symptoms. Therefore, the disease requires timely treatment (not always using antibiotics) and proper rehabilitation of the child, including proper nutrition and drinking enough clean water. In most cases, the disease goes away within a few days, but acute gastroenteritis can drag on for a long time, turning into a chronic stage.
Medicines
Photo: techno.spb.ru
Effective medications for treating gastroenteritis
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the stomach and small intestine should be treated under the supervision of a physician. The specialist prescribes effective medications and calculates the dosage of the medication. The forms of drug administration vary depending on the degree of development of the disease. For the treatment of gastroenteritis, tablets, suspensions, solutions for intravenous infusions and intramuscular injections are prescribed. Medicines used:
- Rehydrants. Helps avoid dehydration.
- Multienzyme drugs. Improves the functioning of the liver and digestive system.
- Astringents and enveloping agents. Strengthens the intestinal walls, promotes the restoration of the mucous membrane.
- Enterosorbents. They bind and remove toxic metabolic products from the gastrointestinal tract.
- Eubiotics. Populate the small and large intestines with beneficial microflora.
- Antibiotics. It can be used to treat gastroenteritis when associated with a bacterial infection.
To eliminate the symptoms of the disease, medications must be taken in combination. It is important to take vitamins to activate the body's immune forces. Acute gastroenteritis must be treated in a hospital under the supervision of a gastroenterologist.
Rehydrants
Gastroenteritis often causes dehydration. This condition is characterized by dry mouth, dry lips, and general weakness. Therefore, it is important to replenish fluid loss in the body. To make it easier to calculate how much liquid to drink, you can follow the formula: pour in as much as it comes out. Of course, sometimes the volume is difficult to calculate, you just need to drink a couple of sips after each visit to the toilet and vomiting. To replenish the water-salt balance during gastroenteritis, the following drugs are used:
- Oralit.
- Regidron.
- Normohydron.
The main composition of these drugs used to treat gastroenteritis includes: sodium chloride, sodium citrate, potassium chloride, dextrose. The drugs help maintain the acid-base balance of the intestines and remove heavy salts and citrates. Rehydrating solutions with potassium chloride are contraindicated if there is an excess of potassium in the body.
Multienzyme preparations
The medications contain pancreatic enzymes that facilitate the digestion of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. These drugs compensate for the lack of secretory function of the pancreas and help improve the digestion process. Your doctor may prescribe pills that are effective for gastroenteritis:
- Pancreatin.
- Festal.
- Abamin.
Some enzyme preparations are contraindicated for use in children under two years of age and for intestinal obstruction in adult patients.
Astringents and enveloping agents
For gastroenteritis, to restore the mucous membrane of the large and small intestines, the doctor may prescribe tablets with astringent and anti-inflammatory properties. These medications increase mucus production and increase the stability of the lining of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Bismuth nitrate.
- De-nol.
- Tenalbin.
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, astringent medications should be used with caution.
Enterosorbents
Often, for gastroenteritis, Smecta or similar enterosorbents are prescribed. The composition of the drug includes double silicate of magnesium and aluminum. Smecta stabilizes the mucous barrier of the gastrointestinal tract, reduces the negative effects of toxins, and removes only toxins, viruses, and pathogenic bacteria from the body. Doctors also prescribe:
- Hydroxyquinoline derivatives.
- Polysorb.
- Neosmectin.
Enterosorbents are contraindicated for chronic constipation and individual intolerance to the components of the drug.
Eubiotics
To normalize intestinal function, it is necessary to take eubiotics. Active bifidobacteria help improve gastrointestinal function, stimulate metabolic processes, and help get rid of toxic substances. Treatment of gastroenteritis with drugs containing eubiotics should be long-term.
- Bifidumbacterin.
- Colibacterin.
- Linux.
There are no contraindications for taking eubiotics in adults; the use of drugs should be limited in children with lactase deficiency.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are rarely prescribed for gastroenteritis. This is done if it is definitely established that the infection is caused by a bacterium. Only a doctor, based on tests, can select an effective antibacterial drug to treat the disease. In the first stages, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used, which are poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The use of antibacterial medication for the treatment of gastroenteritis is necessary to reduce the manifestations of the disease and prevent complications.
- Cefotaxime.
- Amoxiclav.
Antibiotics for gastroenteritis are taken for a short period of time, the dosage and type of medication is determined by the gastroenterologist.
Why does enteroviral gastroenteritis occur?
The disease has a fecal-oral transmission mechanism: through water, food and household objects. The waterway is considered particularly dangerous as it causes mass infections. In patients, the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, pharynx, and small intestine are affected.
Rotavirus gastroenteritis develops as follows: rotavirus enters the gastrointestinal tract through the mouth, into the cells of the duodenal mucosa, where it actively multiplies. As a result, mucosal cells die and villi are torn off, through which nutrients are absorbed into the blood. Rotavirus is the main causative agent of diarrhea with dehydration. It accounts for the largest number of hospitalizations of children due to intestinal infections.
Infection can occur:
- In the absence of personal hygiene rules. A sick person did not wash his hands after using the toilet and touched some object. A healthy person took the object in his hands, then brought the infection into the oral cavity with his hands - this is a contact and household route of infection.
- When drinking contaminated water. The cause may be not only water taken from open sources, but also bottled water spilled in violation of sanitary standards. This is the so-called waterway, one of the most dangerous, which can lead to mass infections.
- When consuming contaminated food, most often dairy. This route of infection is called nutritional.