Diarrhea
is the body's protective reaction to harmful or toxic substances.
Causes of diarrhea
can be:
- binge eating,
- eating spoiled food
- contaminated water,
- allergies to certain foods and medications,
- dysentery,
- salmonella,
- gastritis.
Diarrhea and vomiting
accompanied by loss of fluid, which is very dangerous, because may develop. High temperatures can increase the risk of dehydration. Bloody or black stools indicate internal bleeding from the intestines or stomach. In this case, emergency medical attention is required.
Folk remedies for diarrhea
There are a large number of folk recipes for diarrhea. Here are some of them.
- Boil a handful of onion peels for 10 minutes in one liter of water, strain. Drink half a liter a day in small sips for chronic, severe diarrhea.
- Pour four tablespoons of blueberry leaves into one liter of boiling water and leave for half an hour. Drink half a glass of the decoction before meals for two days.
- Dry the pomegranate peels, remove the pulp, and chop. Pour one dessert spoon of crusts with one glass of boiling water. Bring to a boil, simmer for five minutes. Take half a glass twenty minutes before meals. This decoction even helps with dysentery.
- Boil four carrots in their skins, peel, mash, adding a little boiled water. You will get a thick puree. Take two to three tablespoons four times a day until the illness passes.
- For diarrhea with blood, take one branch of young fresh wormwood, wash it and chew it, swallow the juice, spit out the grass. The recipe is very effective.
- A tincture of walnut partitions helps. Pour half a liter of vodka into a third of a glass of partitions and leave in the sun for two weeks. Drink a glass of tincture twice a day.
- A good remedy is ginger tea. Pour one teaspoon of ground ginger into a glass of boiling water, leave for twenty minutes, drink a tablespoon every 30 minutes.
It is necessary to select according to symptoms. It is very difficult to find a drug that will immediately relieve intoxication. Before use, it is necessary to take into account any pathological changes that have occurred. It is recommended to take medications immediately after the first symptoms appear. Delay can lead to severe complications that lead to dehydration.
Severe poisoning and diarrhea can lead to kidney failure
, destruction of the gastric mucosa, changes in the liver and pancreas. But timely treatment can relieve all symptoms that have arisen and restore liver function. After eliminating the poisoning, a diet should be prescribed. Proper nutrition will bring the entire body back to normal and eliminate dehydration. The pressure and temperature will be normalized. Experts also recommend doing gastric lavage. Properly prescribed medications will eliminate intoxication in a few hours or days.
Procedure
In most cases, the correct procedure can not only alleviate the health condition of the sick person, but also help to quickly cure him. At the first symptoms of poisoning, you must first seek help from special services.
.
Sometimes, due to the busy schedule of employees, an ambulance may arrive several hours after the call. The temperature must be brought down and a special diet prescribed. Therefore, before the doctors arrive, it is necessary to take urgent measures
:
- Urgently restore water and electrolyte balance. The most optimal and common remedy is a glucose-saline solution. This medicine can be purchased at every pharmacy. The bottle is carefully opened and the product is given to the patient in small portions.
- If you can’t go to the pharmacy, you can prepare the medicine yourself. To create a home remedy, you need to use dried medicinal herbs. Herbal tea made from chamomile and rose hips is perfect. Even regular, strongly brewed black long tea can stop diarrhea. Sometimes a compote of raisins and dried fruits is used internally.
- Food must be excluded. Before the ambulance arrives, feeding the patient is strictly prohibited. An adult can get by with decoctions of medicinal herbs. With the help of healing decoctions, vomiting and fever can be eliminated.
- Before being examined by a specialist, the patient should not take medication that can relieve the symptoms of the disease. Otherwise, finding the cause and making a diagnosis will be very difficult. In the most extreme critical case, the consumption of sorbents is allowed. Treatment is carried out by removing toxins from the human body.
- After poisoning, a special diet should be prescribed. Consumption of sour and salty foods is not allowed. Consumption of spicy, fried foods is not recommended. The diet should include more fresh fruits and vegetables rich in vitamins.
- When should you see a doctor?
- The most dangerous symptom of poisoning is double vision. This symptom may be a consequence of botulism. Without surgical intervention by specialists, the patient may die. In this case, it is necessary to urgently prescribe treatment. Every moment is a threat to the patient's life. Vomiting and fever must be eliminated.
- A doctor must be called if a child is sick.
- The doctor is called for patients over 65 years of age. Elderly people need special attention, diet and treatment. If, after poisoning, there is severe vomiting or fever, then calling a specialist cannot be delayed for long.
- A specialist is called for people with heart disease. A doctor is also needed for patients suffering from diabetes, cancer and HIV infections.
- A gastroenterologist is called in case of prolonged intoxication lasting more than two days. In this case, diarrhea in case of poisoning must be eliminated as quickly as possible. Delay can cause complications of diseases. After treatment, a diet must be prescribed.
- Vomiting or diarrhea lasting more than three days is also a dangerous consequence.
- A dangerous symptom is blood in the stool or vomit.
- Another dangerous symptom that requires calling a doctor is a fever above 38°.
- A specialist should be called in case of dehydration. Patients may have sunken eyes, a dry mouth, and very little or no urine.
Which doctor should I contact?
The patient can see a therapist
, which should make the correct diagnosis. After visiting a specialist, the patient can visit another doctor. The choice of specialist is determined depending on the diagnosis.
- A resuscitator is visited in extremely difficult situations. Treatment is carried out using special devices. This specialist treats intoxication and revives people after clinical death.
- An infectious disease specialist studies pathogens that are the result of poisoning. Prescribes medications.
- A toxicologist can treat those patients whose poisoning with diarrhea occurred after exposure to chemicals.
- People turn to a narcologist after poisoning with alcohol, tobacco or narcotic products. The specialist must prescribe the correct treatment.
- The gastroenterologist prescribes treatment that restores the gastrointestinal tract. Eliminates developing diseases after poisoning.
Treatment of the causes and consequences of vomiting and diarrhea
When vomiting and diarrhea without fever, the main thing is to eliminate the cause. It is important to avoid dehydration. Simple drinking water does not contain sugar or minerals, and the body loses them during diarrhea; it is important to restore this loss. You should drink a lot of liquids containing these substances: broths, mineral water. It is advisable to do this every half hour.
You can take medications to treat the cause of vomiting and diarrhea:
The main thing to remember is that you must wash your hands before eating and preparing food. Products should be stored correctly. It is not recommended to eat in dubious establishments or drink untreated tap water.
- baked apples;
- bananas;
- yogurt, kefir;
- boiled carrots;
- broccoli.
During the recovery period, it is necessary to replace lost substances. Food should be high in calories, but not irritate the stomach. Be sure to be fresh, not too hot or cold. Eat in small portions 5-7 times a day. During the first days, prefer liquid dishes: soups or pureed purees. Do not fry foods, but boil, simmer, or steam. Make puree from vegetables, take cottage cheese, low-fat soups. Grind the meat. Do not add sugar to porridge.
In case of poisoning, certain groups of drugs are used:
- Antimicrobial, having a wide spectrum of action, killing almost all or all pathogens of diarrhea. Treatment is aimed at the root causes of the disease. They act in the intestines without having a systemic effect. They are not absorbed into the intestine itself and do not penetrate into the blood.
- Adsorbents are able to eliminate gases and toxins, reducing severe symptoms. Taking it leads to an improvement in the condition for a while, but does not lead to a complete cure.
- Synbiotics, prebiotics, stimulate the production of normal microflora. These are live lactobacilli located in the intestines, normalizing the activity of its own microflora. Medicines are important, since with diarrhea it is difficult to recover on its own.
- Painkillers are used for severe discomfort.
Drug Review
Sorbents
. These products are able to remove toxins and waste. They cleanse the intestinal walls and restore the digestive tract. They easily cleanse the blood and show the best results among other medications after poisoning.
| Name | Description | Application | Contraindications | Price, rub |
| Smecta | Snow-white powder | Recommended for vomiting, nausea, severe intoxication. Dissolves in boiled water. | The product is not recommended for hypersensitive people. Not applicable at temperatures. | From 152 |
| Enterosgel | Product in the form of a homogeneous suspension | Used for acute or chronic intoxication. | Not recommended for intestinal atony. | From 378 |
| Neointestopan | It is a biconvex tablet | Used for vomiting and diarrhea. | Not recommended for children, people suffering from fever or intestinal obstruction. | From 50 |
| Kaopectate | Is a suspension | The product is used for diarrhea, vomiting, and dehydration. | Not recommended for children. | From 100 |
| Activated carbon | They are dark-colored tablets. | Used for dyspepsia and intoxication. | Not recommended for people with ulcerative lesions. | From 20 |
Preparations for restoring water-salt balance
normalize the gastrointestinal tract. Easily eliminate germs, sticks, and infections. Restore water and electrolyte balance after poisoning.
| Name | Description | Application | Contraindications | Price |
| Regidron | It is an odorless powder | Restores the acidic environment during diarrhea and after poisoning. | Not recommended for people with impaired renal function. | From 396 |
| Gastrolit | Available in powder form | Can be used by children after acute intoxication and diarrhea. | Not recommended for hypersensitive people and patients with renal failure. | From 100 |
| Humana electrolyte | Powder for making suspension | Easily normalizes electrolyte metabolism. | Not recommended for hypersensitive people. | From 300 |
Antispasmodics
taken after poisoning for pain syndromes. They relieve pain with ease.
| Name | Description | Application | Contraindications | Price |
| No-shpa | They are tablets with an amber tint. | Used after poisoning | Not recommended for renal and liver failure. | From 63 |
| Papaverine | Available in the form of suppositories and solutions | Used for acute pain after poisoning with diarrhea. | Not recommended for glaucoma. | From 37 |
| Lactofiltrum | Available in the form of dark tablets | May stimulate the growth of beneficial microorganisms. | Prohibited for people with intestinal obstruction. | From 265 |
| Hilak forte | Available in the form of drops | Easily normalizes the bacterial composition. | Prohibited for hypersensitive patients. | From 262 |
Preparations for restoring microflora
must be taken immediately after poisoning. They normalize the activity of the body, intestines, and stomach walls.
Diarrhea remedies
eliminate intestinal infection. Typhoid and dysbacteriosis are prevented from developing. Eliminate dysentery and other intestinal infections.
Sorbents against poisoning
The list of popular medications acting on the principle of mucosal envelopment and adsorption consists of the following items:
- Enterosgel. Doctors recommend using a homogeneous suspension both in case of acute poisoning and to alleviate the symptoms of chronic pathology. Contraindications include intestinal atony.
- Smecta. Helps get rid of signs of acute infection if the cause of the disease is viral flora. The duration of treatment is up to 7 days.
- Activated carbon. Cheap tablets with a characteristic black color quickly improve the condition if symptoms of dyspepsia are present. The only condition for refusing therapy is the identification of ulcerative lesions of the mucous membranes of the digestive system.
- Enterodesis. The tolerability of the drug allows it to be included in the treatment regimen for poisoning even for a small child. If you follow the recommendations, diarrhea disappears in a matter of hours, even if the disease is of an acute infectious nature.
- Kaopectate. Depending on the age group, tablets or a suspension with active ingredients in the form of aluminum silicate hydrate and a similar magnesium compound are selected.
- Filtrum. A natural herbal medicine based on hydrolyzed lignin powder blocks toxic substances of various natures.
Video: Enterosgel - indications for use
The sorbent anti-poisoning agent binds viruses, toxins, bacteria, water in the intestinal lumen and at the same time forms a protective layer on the walls of the digestive organ that prevents unwanted absorption of harmful substances.
Features of treatment
Treating intoxication during pregnancy is very difficult. The main symptoms are nausea, vomiting, acute pain, and fever. Poisoning and diarrhea can cause dehydration
. The question arises: what should expectant mothers do if taking medications is not recommended? Fortunately, today a special medicine has been developed that is not absorbed into the blood. Such tablets, suspensions, syrups, powders act only in the intestines. They do not contain harmful chemical components. Pregnant and nursing mothers can also relieve intoxication using saline solutions. After eliminating all symptoms of poisoning, a special diet is prescribed. Meals should be packaged. Products must contain large amounts of vitamins and microelements.
Particular attention should be paid to young children. A child's body is vulnerable. Dehydration develops quite quickly. Therefore, if a child is poisoned, it is necessary to prescribe treatment as quickly as possible. Children are prescribed sorbents. Older children can undergo gastric lavage. After symptoms are relieved, it is necessary to prescribe a special diet. The diet should include plenty of fruits and vegetables. In this case, fast food, sweet, spicy and salty foods should be excluded.
Many mothers do not know what to do if poisoning and diarrhea occur in their newborn child. In infants, the only source of food is breast milk. Meals should be planned for the whole day. Therefore, it is prohibited to continue breastfeeding your baby. But at the same time, constant monitoring of his health is necessary.
The video contains useful information about choosing medications
When to call an ambulance
- Severe symptoms of poisoning. If blood appears in your stool within 24 hours.
- You belong to a risk group.
- If botulism is suspected, life-threatening food poisoning occurs (occurs when botulinum toxin gets into food). It is most often found in home canning, especially green beans and tomatoes.
Symptoms other than vomiting and diarrhea:
- blurred vision;
- muscle weakness, even paralysis;
- difficulty urinating;
- difficulty breathing and dry mouth;
- migraine.
Drug interactions
Treatment of poisoning should include drugs from one or at most two diverse groups
. For example, the use of saline solutions and the simultaneous use of sorbents are allowed. But it is worth considering that any type of drug interaction changes the combination and the final pharmacological effect. Ultimately, both an enhanced effect of both drugs may be observed, and vice versa – the manifestation of side effects.
Poisoning with diarrhea can severely dehydrate the body. Therefore, immediately after intoxication it is necessary to consult a specialist. The doctor must prescribe the correct treatment and prescribe the appropriate pills. Gastric lavage is also allowed. You need to pay attention to your diet.
A properly selected diet will eliminate dehydration and normalize the functioning of the body.
Note!
The presence of symptoms such as:
- smell from the mouth
- stomach ache
- heartburn
- diarrhea
- constipation
- nausea, vomiting
- belching
- increased gas formation (flatulence)
If you have at least 2 of these symptoms, then this indicates developing gastritis or a stomach ulcer.
These diseases are dangerous due to the development of serious complications (penetration, gastric bleeding, etc.), many of which can be FATAL. Treatment needs to start now. Read the article about how a woman got rid of these symptoms by defeating their root cause.
When diarrhea (diarrhea) appears, discomfort and a lot of unpleasant sensations in the stomach are guaranteed to everyone. Pain, frequent urges, sometimes with nausea and vomiting - you wouldn’t wish this on anyone. The desire to stop the process as quickly as possible is natural, so many people urgently begin self-treatment, choosing the first medicine for diarrhea they come across in the medicine cabinet. But few people, in their desire to help themselves, think about the fact that it is important to eliminate not the symptom, but the root cause.
Treatment
If the causes of diarrhea with vomiting are much more serious, then the patient is prescribed drug therapy in accordance with the cause of the pathology.
- First, sorbent preparations such as activated carbon, Sorbex, Enterosgel or Smecta are prescribed. If vomiting does not stop and prevents you from taking the drug orally, you can do an enema with a sorbent.
- Self-administration of drugs whose action is aimed at suppressing peristalsis, for example, Loperamide or Imodium, is unacceptable. Diarrhea and vomiting are natural organic reactions aimed at cleansing toxic substances. If these reactions are stopped, toxins will enter the bloodstream, leading to dangerous consequences.
- If diarrhea and vomiting are indomitable, it is recommended to prevent dehydration. To do this, you need to take solutions like Regidron or simply drink more water.
- If the ailment is of bacterial origin, antibiotic therapy or antimicrobial drugs such as Enterofuril or Nifuroxazide are prescribed. They are prescribed only by a doctor; self-medication can be dangerous.
- If there is a deficiency of enzyme substances or overeating, patients are recommended to take pancreatin, for example, Festal or Mezim.
- If vomiting is too frequent and does not go away for too long, then in addition to drinking plenty of fluids, medications like Metoclopramide or Diazepam can help calm the stomach.
When you have a fever, it is not recommended to take antipyretics, because hyperthermia in this case is a protective reaction.
Drinking plenty of fluids is necessary. You can use medications if the readings exceed 38 degrees. If the temperature continues to rise, then you need to call an ambulance.
Vomiting reactions with diarrhea are caused by various reasons. Whether to call a doctor or not depends on the specific situation.
If the patient has a high fever, then an ambulance must be called, as in the case of mushroom poisoning. Timely assistance sometimes saves the patient’s life, so be prudent.
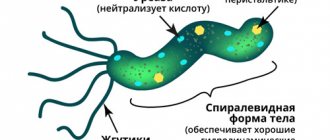
What causes diarrhea?
At its core, diarrhea is a defensive reaction consisting in the body’s attempts to quickly remove harmful or contaminated contents from the intestines. Sometimes the causes of diarrhea are obvious, but often loose stools are caused by diseases that only a specialist can determine. Let's name the main factors:
- stressful state (upcoming exams, decisive interview, etc.);
- unusual food products (happens among tourists traveling to different countries, especially exotic ones);
- intestinal irritation (after prolonged or frequent consumption of spicy and sour foods);
- inability to digest lactose (diarrhea, gas, vomiting, cramps due to undigested milk sugar);
- side effects after treatment with certain medications, including antibiotics;
- poisoning from stale or dirty food, including vomiting;
- unbearable abdominal pain;
- inflammation, neoplasms, and colon ulcers.
To stop diarrhea, you need to immediately consult a doctor to prescribe the correct treatment. This is especially important in the following cases:
- there is reason to believe that the cause is poisoning;
- changes in stool color (from black to greenish) and consistency (from watery to foamy or cheesy);
- diarrhea lasts more than a day;
- frequent profuse vomiting;
- stools are copious and frequent (5 or more times per day);
- blood admixtures are observed.
Once the cause has been established, the question of medications arises: what medications should I choose to ensure that the treatment is successful? This is especially acute in cases where loose stools and vomiting occur in a child or during pregnancy.
When choosing an antidiarrheal drug, you need to firmly know the direction of action of the drug, because different medications are designed to eliminate certain causes of diarrhea. Sometimes, by choosing the wrong medicine, you can achieve only a visible improvement, temporarily suppressing the main problem.
All possible causes of vomiting in an adult?
- drinking large amounts of alcohol, toxins;
- neoplasms, meningitis, intracranial hemorrhage;
- anorexia, bulimia;
- gastrointestinal tract diseases: food poisoning, allergic reactions, intestinal obstruction, peptic ulcer and duodenal ulcer, inflammation, peritonitis;
- cholecystitis;
- cirrhosis;
- pancreatic diseases;
- endocrine problems (adrenal crisis, diabetic ketoacidosis);
- uremia, pyelonephritis;
- prolonged fasting, postoperative nausea, radiotherapy.
Vomiting without fever and diarrhea can occur during an attack, accompanied by rapid heartbeat, pale skin, general weakness, and dizziness. There are also complaints of tremors in the legs and headache. Single vomiting and diarrhea without fever in an adult is a common cause of motion sickness or a reaction to poisoning (possibly from alcoholic beverages). It does not last more than two days due to explainable causes, which are infections, toxins or diseases of the digestive system.
In women, it can be observed during pregnancy, being a sign of toxicosis, especially in the first months. There is another reason - a hormonal imbalance that has formed as the body adapts to pregnancy.
Single vomiting in men is a sign of appendicitis and acute pancreatitis. On an empty stomach, it contains bile mucus mixed with bile, a yellow liquid. With appendicitis, this is a reaction to pain.
Vomiting helps rid the body of substances that irritate the stomach and intestines. A common cause of this symptom is gastroenteritis, a gastrointestinal infection caused by viruses and bacteria. It is often accompanied by diarrhea, but sometimes only vomiting. The body is able to cope with this problem within a few days.
There are more serious reasons for nausea and vomiting - kidney stones or intestinal obstruction. In this case, you need to consult a doctor. A common problem with symptoms is rotavirus or poisoning. The infection disables bowel function (absorption of water from food). Therefore, watery diarrhea occurs. Dehydration is a common complication of gastroenteritis.
Some types of this disease are contagious. The infection spreads through dirty hands or food. With such an illness, it is not recommended to visit crowded places for two days after stool normalization. Gastroenteritis usually goes away without treatment within two days. But, there are cases when hospitalization is required.
- salmonellosis, an intestinal infection characterized by damage to the gastrointestinal tract;
- dysentery, accompanied by diarrhea, intoxication resulting from a pathogen (shigellosis);
Similar symptoms are also caused by various types of fungi that enter the body through poor-quality food, unboiled water, and poor hygiene.
High temperature, intoxication of the body, malaise, nausea, vomiting are symptoms of intestinal flu, rotavirus. It begins as a respiratory syndrome, then symptoms of enteritis or gastroenteritis are expressed. Gastrointestinal upset is also accompanied by an increase in temperature to 38 - 39 degrees. In addition, weakness, breathing and heart failure appear. Dehydration is a dangerous symptom that can be fatal in some cases.
Probiotics
Linex
Available in capsules. A good antidiarrheal agent that tidies up the intestinal microflora, including after antibiotics. The course of treatment is usually 10 days or more. Indicated from infancy, but a child under 2 years of age needs to open the capsule and give the contents diluted with water. Do not use if you are sensitive or with hot food.
A pleasant sour liquid, diluted with water when taken. Actively tidies up the intestinal microflora, acts against poisoning and some intestinal diseases. The drug is approved for use in children from infancy and during pregnancy. Do not take with dairy foods.
Normobakt
Preparation with bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. Helps not only directly with diarrhea, but also with loss of appetite and vomiting. Approved for use by children under one year of age (after 6 months).
Enterosorbent drugs
Smecta
Contains natural materials (chalk, shell rock). The drug “binds” toxins and bacteria and removes them from the body, helps against diarrhea of any origin (poisoning, diarrhea after stress, etc.), except for irritable bowel syndrome. Suitable for everyone, including children from 0 years old.
A good auxiliary product that cleanses the intestines (including in cases of poisoning) and kills pathogenic bacteria. Dosage for treatment: 1 tablet per 10 kg of weight. Safe from the age of 1 year, can be taken during pregnancy.
Attapulgite
Tablets that normalize microflora, thicken stools, reduce inflammation, urge, and relieve spasms. Can be given to a child after the third year of life; during pregnancy and breastfeeding, take with caution.
Antimicrobials and antibiotics
Phthalazole
For effective treatment of hemorrhoids, our readers advise. This natural remedy quickly relieves pain and itching, promotes the healing of anal fissures and hemorrhoids. The drug contains only natural ingredients with maximum effectiveness. The product has no contraindications, the effectiveness and safety of the drug has been proven by clinical studies at the Research Institute of Proctology.
It is used against infectious intestinal diseases (salmonellosis, dysentery), as well as food poisoning. The effect is noticeable after 2 days: suppression of the infection occurs over time. At the age of 0 to 3 years, give 1/2 tablet, and from 3 to 6 years - a whole tablet.
Tablets in a jelly-like coating. The drug relieves pain, fights against harmful bacteria, relieves inflammation, and has an astringent effect. Suitable for children under one year of age, with caution during pregnancy.
Levomycetin
Antibiotic drug, a strong remedy. It fights bacteria, calms vomiting, helps with poisoning, but it is powerless against fungal and viral diseases. Improvement occurs after 3-4 hours.
Levomycetin is contraindicated during pregnancy and under the age of 3 years.
Tetracycline
A strong drug that can quickly stop the growth of pathogenic bacteria in the intestines, but along the way it also kills beneficial ones, which can provoke dysbacteriosis while taking an antibiotic. Contraindicated during pregnancy, breastfeeding and children under 8 years of age.
It acts against intestinal infections and the consequences of poisoning, without harming the natural microflora. The medication is prescribed to adults and children after 1 month. Allergy in the form of a rash is possible.
Polysorb
Removes toxins and bacteria from the body. The drug is intended for the treatment of dysbiosis, intestinal infections, and the consequences of poisoning. For children from 0 years of age, during pregnancy, feeding is completely safe.
Folk remedies
Dried blueberries
A good anti-diarrhea remedy that has an antiseptic and astringent effect. Can stop inflammatory processes in the intestines. Drink half a glass a day. No contraindications.
Potato starch
A very effective remedy: strengthens the stool, slows down peristalsis. It is enough to give 1 teaspoon to small children, 1 dessert spoon to teenagers, and 1 tablespoon to adults twice a day. Can be dissolved in water.
Congee
A popular remedy that can stop even severe diarrhea. Cook the rice without salt until the water becomes viscous and sticky, strain, and drink lukewarm. This remedy has no contraindications; it can be used for diarrhea in both adults and children.
Important: diarrhea almost always carries the threat of dehydration, so during such a period, in addition to drug treatment, you need to drink a lot of fluids.
Diarrhea itself is not a disease, but a symptom of disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, including pathological ones. Therefore, in order to avoid serious complications, you should not experiment with medications on your own, but get the help of a doctor who will find out the causes of diarrhea and decide what treatment to prescribe.
First aid for vomiting and diarrhea
Once in the gastrointestinal tract, microbes synthesize toxins that cause unpleasant symptoms. Poisoning can be infectious or non-infectious. Diseases that cause diarrhea and vomiting are also different. Therefore, first aid will be provided differently. But the main thing that needs to be done is to free the body from toxic substances.
When the first symptoms appear, it is necessary to rinse the stomach with a weak solution of potassium permanganate and baking soda. Drink it and induce vomiting. Repeat the process until the vomit is free of impurities and clean.
Tip 1. Taking sorbents that help remove toxins is activated carbon, which reduces the absorption of heavy metals and other harmful substances. 1 tablet per 10 kg of human weight. Crush it and mix with water. There are white and black coal. The first drug not only removes toxins, but also preserves an important set of microelements in the body. The dosage is half as much, that is, 1 tablet per 20 kg of weight. For an adult, 2–3 tablets are enough, but it all depends on the degree of poisoning.
Tip 2. Rice water, wormwood, flax seeds and garlic will help stop diarrhea. But they are used as additional, not primary means. If diarrhea is caused by an infection, then you need to take a glass of strongly brewed tea, add 4 teaspoons of sugar, ½ cup of grape juice (sour). Even with severe diarrhea, relief will come within 2 hours.
Tip 3. Burnet root is a good remedy for the disorder. Boil it for half an hour, then strain. Pour a tablespoon of broth into a glass of water. Drink 5 times a day. This decoction is bactericidal and is useful for inflammation of the colon and diarrhea.
Tip 4. Knotweed (knotweed) per half liter of boiled water, boil for 10 minutes. Cool, strain. Drink 4 times a day, ½ glass.
Tip 5. Blackberries help well with poisoning accompanied by diarrhea. 2 tbsp. l crushed leaves per glass of water. Boil for 5 minutes, strain. Drink 1 glass 3 times a day.
- Smecta is an antidiarrheal agent, a natural aluminosilicate. It is excreted from the body in an unchanged form and does not enter into metabolism. Used for acute diarrhea, also infectious. Use 6 sachets per day. Taken between meals and other medications.
- Enteros-gel is a special molecular sponge that repels water, absorbing toxins. These are substances produced by bacteria that cause diarrhea. Available in tubes, like a paste. To take it, you should adhere to the general rules of sorbents: 1 tablespoon 3 times a day. Mix in water at room temperature. Duration of treatment is 4 days.
- Polysorb. Used to treat intestinal diseases with diarrhea and food infections. Removes toxins of various origins from the body. They cleanse the body of microbial endotoxins, products formed during the breakdown of protein in the gastrointestinal tract. Helps remove toxins, amines and other substances from the blood. They leave the body through the intestines.
- Polyphepan. The drug has high absorption activity. Removes pathogenic bacteria, heavy metals, salts, medications, alcohol. Absorb metabolic products, cholesterol, metabolites. The medicine is not absorbed, has no toxins, and is completely eliminated from the body within 24 hours.
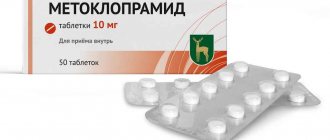
- Cerucal. Blocks serotonin receptors, reduces the sensitivity of nerve cells responsible for impulses from the pylorus to the duodenum to the vomiting center. Normalizes motility of the gastrointestinal tract. The action of metoclopramide increases the tone of the walls of the intestines and stomach, improves peristalsis of the small intestine.
- Domperidone. Used during indigestion, hypotension with the development of refluxesophagitis. Relieves the symptoms of dyspepsia associated with poor gastric emptying and vomiting, regardless of the cause. Soothes hiccups, eliminates nausea, normalizes gastrointestinal activity.
- Motilium. The medicine is useful for vomiting and nausea. Especially if they are caused by infectious and functional origins, dietary disorders, or medications.
- Metoclopramide. Antiemetic, motility stimulant. Accelerates gastric emptying and the passage of food through the small intestine. Affects the central brain stem. Taken to relieve nausea caused by chemotherapy and acute migraine.
- Lopedium reduces motility and smooth muscle tone of the stomach and intestines. Makes the passage of intestinal contents longer. Retains feces, reduces the urge to defecate. The action lasts 4-6 hours.
- Enterobene has a depressing effect on intestinal motility, increases the time of water absorption, and slows down the passage of feces. Fecal incontinence stops. Does not have a morphine-like effect on the nervous system.
- Loperamide (Imodium) is the best antidiarrheal drug. The medicine is intended to eliminate diarrhea without signs of colitis. Take 2 tablets if you have stable, watery stools. Then 1 after an episode of diarrhea. It reduces tone and reduces intestinal motility. Sold in capsule or tablet form.
- Acipol acts as a preventive and therapeutic agent. Used for dysbacteriosis, acute intestinal diseases, chronic colitis. Increases the overall resistance of the body. This medicine is used to restore microflora, strengthen the immune system, and eliminate symptoms of dysbacteriosis. Contains quick-response bacteria that become active as soon as they enter the intestines.
- Bifidumbacterin is used for bloating, diarrhea, nausea, and flatulence. Acts as an antibacterial agent and helps restore the intestinal microbiota.
- Linex is an effective probiotic. Available in capsules, it is approved for use even by small children. Contains biphodobacteria of two types LA-5 and BB-12. They promote normal intestinal function and suppress pathogenic bacteria. Reduce acidity and support immunity. Prescribed for constipation, diarrhea, infectious and viral diseases, dermatitis. Supports intestinal flora.