Cicatricial ulcerative deformity of the duodenal bulb is a disease that is left behind by an ulcer of the duodenal bulb and an ulcer of the gastric bulb. This disease is quite common these days, and this is facilitated by many factors in modern life: lack of exercise, bad habits, poor nutrition, fasting, eating fast food.
When cicatricial deformation of the duodenal bulb is formed, it becomes covered with scars that interfere with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Let's figure out what this disease is, what its causes are and how to avoid encountering it.
Formation of scar deformation
As already mentioned, the duodenal ulcer appears first. When a duodenal bulb ulcer begins to heal, there are no symptoms, and a scar gradually forms in its place. This is a kind of scar, like after deep wounds, if the injury is neglected and infection is allowed to cause inflammation.
The same process occurs with ulcers. If you do not pay attention to it, do not treat it and do not follow a diet for ulcers, then there is a risk of complications that will forever deprive the organ of the ability to function normally, like a healthy person.
Relapses can be deadly: in the most severe cases, the bulb can become deformed, reach large sizes and close the intestinal passage. As a result, digested food cannot pass into the intestines. Stagnating, it provokes the process of decay and intoxication of the body. In this case, urgent surgical intervention is simply necessary to cut out the inflammation and connect the sections of the intestine properly.
That is why bulb ulcer must be cured immediately. With the right approach, not a trace will remain at the site of the ulcer; in extreme cases, a small linear scar that does not create discomfort and does not pose a threat to health.
To avoid provoking a relapse,
you need to ensure complete rest to the intestinal tract, follow a diet and avoid stress. Of course, taking medications is also a mandatory measure.
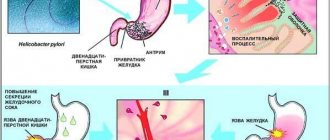
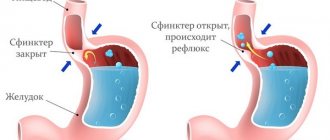
When acute ulcerative deformation of the duodenal bulb becomes large and blocks the passage, the pylorus of the stomach, where hydrochloric acid is located, also begins to perform its job worse. This leads to stomach acid entering the intestines, and bile and pancreatic fluid migrate from the intestines to the stomach, and this is a pathology. All this contributes to diarrhea, constipation, pain in the upper abdomen, belching, nausea, and sometimes vomiting.
Next, we will consider the symptoms and treatment of cicatricial deformation of the duodenum.
- Pain in the upper abdomen. Sometimes the sensations are very sharp.
- Pain radiating to the back or heart area. Usually appears when hunger sets in, or at night, when no food enters the body.
- Feeling of hunger after eating, belching, nausea.
- Increased gas formation (flatulence).
- Intestinal discomfort.
- Blood in stool or vomit. This sign is the most dangerous, since it indicates that internal bleeding has begun, and as is known, it can lead to the death of the patient.
Symptoms of duodenal bulb ulcer
Symptoms:
- The most common and sure symptom of a bulb ulcer is pain in the upper abdomen. Pain sensations can be sharp and burning, aching and piercing.
- The pain can radiate to the back or to the heart area. Such pain usually appears at the time of exacerbation of the ulcer and makes itself felt at night or in moments of hunger, but after eating the pain disappears.
- Sometimes the feeling of hunger haunts the patient even after eating, as a result of which the person suffers from belching, nausea, and vomiting.
- Flatulence and bloating may indicate the presence of a peptic ulcer and show that some organs are deformed.
- If a person suffers from abdominal pain at night, this is a signal of increased acidity in the body, since around two o’clock in the morning the stomach produces the largest amount of it. The disease may occur without any symptoms, which often occurs in older people.
- However, if a bulb ulcer is left unattended, blood may appear during vomiting or during bowel movements. This symptom indicates the onset of internal bleeding, which can be fatal.
Diagnosis of bulb ulcer and scar deformity
The most effective method
diagnostics is invasive. With its help, you can certainly detect the slightest deformed bulbous area and scar, as well as an acute ulcer of the duodenal bulb. It is necessary to do a penetrating examination already at the first degree of duodenal ulcer. At the stage when the duodenal bulb begins to deform.
Very often, such a medical mistake is made as neglecting invasive diagnostics. Many limit themselves to an external examination of the patient, which leads to incorrect conclusions. Therefore, the patient should insist on a penetrating examination, even if the doctor says that this is not necessary and there is nothing to worry about.
Penetrating diagnostics is a set of measures carried out using fibrogastroduodenoscopy. Briefly it is called FGDS.
The above method is the main one. However, there are other ways to make a diagnosis with more detailed research:
- Blood analysis.
- Blood chemistry.
- Gregersen test (stool is studied). Helps detect the presence of blood.
- General stool analysis.
How to reduce the risk of cicatricial deformation of the bulb and ulcers to a minimum? These two diseases are related to each other. Deformation of a chronic ulcer of the duodenal bulb appears against the background of an intestinal defect.
Therefore, to avoid scar formation, ulcers must be avoided.
Causes of pathology
Inflammatory cicatricial deformation of the intestine is formed at the site of a protracted duodenal ulcer.
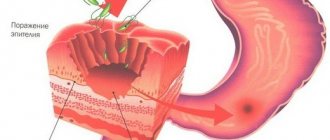
Erosive lesions that turn into ulcerations develop due to the pathological effects of increased amounts of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice and pepsin, as in the formation of ulcers in the stomach.
If there is no treatment for the stomach and intestines, then peptic ulcer disease affects the lower layers of the epithelium and can lead to perforation of the intestinal wall with subsequent bleeding.
Reasons leading to the appearance of erosions and ulcers of the mucous membrane and, as a consequence, to cicatricial deformation of the duodenum:
- inflammatory processes on the mucous membrane (gastritis);
- long-term use of corticosteroids and NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs);
- drinking alcoholic beverages in large quantities;
- repeated stress and nervous tension;
- increased secretion of gastrin, leading to an increase in the level of acid in gastric juice;
- the presence of Helicobacter Pylori bacteria on the mucous membrane;
- untimely treatment (ignoring the first symptoms of the disease).
These factors lead to the gradual development of inflammation of the gastric and duodenal mucosa.
Peptic ulcers and scars on the intestinal mucosa appear if treatment has not been prescribed. This process can take place in different parts of the duodenum, but is more often localized in the bulb.
Like all granulations, scar formation of the intestine tightens the tissues surrounding it, thereby changing the shape of the section.
1 - relief niche; 2 - relief-niche and cicatricial deformation of the duodenal bulb in the form of a trefoil; 3 - niche extending beyond the contour of the bulb; 4 - niche with an inflammatory shaft around
If scars are contained in large quantities in one place, then this accumulation leads to deformation of the duodenal bulb.
READ Symptoms and treatment of chronic duodenitis
This pathological condition usually does not manifest itself with any symptoms, and after a few years the mucous membrane straightens again, the changes go away on their own.
Any serious problems are talked about only if the peptic ulcer is recurrent in nature, forming new scar tissue.
In this situation, cicatricial-ulcerative deformation of the duodenum is constantly present, gradually narrowing this intestinal section.
This leads to the fact that the food bolus cannot move through the gastrointestinal tract. Complete obstruction of the bulbous sector of the duodenum by scar tissue develops.
Extensive changes in this part of the intestine can only be treated with surgery.
Ulcer of the duodenal bulb: treatment
There are many ways to prevent duodenal ulcers and treatment options. In the simplest cases of this disease, the following treatment regimen is used:
- Drug therapy is prescribed.
- A diet for ulcers is being developed.
- Preventive measures are being taken.
If the patient has a more complex stage of development of an ulcer of the intestinal bulb (for example, kissing ulcers), then complex treatment is resorted to. It usually consists of several methods combined together according to the individual condition of the patient.
The following methods are found:
- Pharmaceutical treatment (painkillers, antimicrobials, improve peristalsis, to restore mucous membranes).
- Dietary food for ulcer patients (you can’t eat fatty, fried, salty, spicy, smoked foods, drink alcohol and coffee).
- Physiotherapeutic method. It does not bring any noticeable benefit on its own. Used to increase the effect of medications.
- Medicines for diarrhea, constipation, malaise and other symptoms of ulcers and scarring.
- Surgery.
- Preventive measures (it is recommended to introduce a large amount of vegetables and fruits into the diet, as well as take medications for inflammation of the gastrointestinal mucosa).
Proper nutrition and diet in the presence of scar deformity
If an ulcer of the 12pk bulb or cicatricial deformation of the dpk bulb is detected, the first thing you need to do is adjust your diet and create a healthy menu. The latter must be done so that you don’t have to think about dishes for lunch or dinner and don’t resort to some tasty but unhealthy food.
Healthy eating can also be tasty, contrary to popular belief. So, it is forbidden to use the following for ulcers and deformities of the duodenal bulb:
- Alcohol.
- Fatty, fried.
- Smoked meats, pickles.
- Meat, fish.
- Canned food.
- Rich broths.
- Rye bread.
Mild irritants to the gastrointestinal tract are mineral waters, milk and dairy products, boiled lean meat, pureed vegetables, cereal soups, boiled vegetables, berries and fruits. All these foods can be eaten, but not very often.
Liquid foods, as well as cereal porridges in boiled or slimy form, irritate the intestines and stomach the least.
Under no circumstances should you eat
food is very hot if there is a disease of the intestinal bulb. Cold food should also not be eaten, since it goes directly into the intestine without undergoing alkaline treatment, which means that hydrochloric acid enters the intestine. It follows that you need to exclude ice cream, cold drinks, ice, chilled milkshakes and the like from your diet.
If you have ulcers, the body needs a lot of protein to heal the wounds. Protein is a building material, and it also neutralizes excess gastric secretion.
The diet of an ulcer patient should contain proteins in the following quantities: 65% - animal, 35% - plant. It is recommended to eat rabbit meat, as it is digested better than chicken and especially beef, and contains a large amount of protein.
The salt content in dishes should also be kept to a minimum, as it provokes the release of acid in the stomach, and therefore aggravates the disease.
Cicatricial deformation of the duodenal bulb is formed in the initial section of the intestine. The disease develops after an ulcer in the place where the wounds were. The disease is characterized by the formation of scars, which can change shape and disrupt the functioning of the bulb.
Most often, an ulcer forms on the bulb, which is located on the border of the upper and lower gastrointestinal tract. Scars form during the healing process of wounds. The principle is very similar to the healing of a wound on the human body when a scar is formed. If duodenal ulcers are poorly treated, the patient may develop scars. Soon, deformation of the duodenal bulb can lead to the formation of a lumen, and food can leave the stomach. In this case, surgical intervention cannot be avoided.
Possible complications
Cicatricial deformation of the duodenal bulb often causes complications, especially in the presence of predisposing circumstances. The most common problems:
- Relapse of the ulcerative process. Observed on average in a quarter of patients, even when they undergo full-fledged treatment 3-6 months after therapy,
- Blockage of the duodenum. It is formed in the case of advanced forms of scar deformities, with the development of an extreme pathological process. Leads to systemic spillage of bile/hydrochloric acid throughout the gastrointestinal tract, requiring hospitalization,
- Bleeding. Caused by a violation of the integrity of the mucous membranes and epithelial structures in the localization of scars. Requires first aid and qualified treatment in a hospital with hospitalization of the patient.
- Secondary manifestations. Dyspeptic disorders that do not disappear for weeks and months, induction of the development of irritable bowel syndrome, and so on.
Symptoms
The fact that scarring of the ulcer has begun is indicated by a small number of symptoms. The disease is an asymptomatic illness. It can develop over many years and not show any significant signs.
It is almost impossible to find out that the duodenal bulb has begun to deform. During research and identification of repeated attacks of peptic ulcer, in which new scars are formed, a narrowing of the lumen between the intestines and the stomach becomes noticeable.
However, the disease has some significant symptoms that are a bit similar to those of an ulcer:
- nausea before meals, in the morning and on an empty stomach;
- colic;
- flatulence;
- heartburn;
- constant feeling of hunger;
- there may be bleeding.
Why is this condition dangerous?
If the ulcer is cured well, then at the site of localization there is a linear defect, insignificant in parameters, which does not affect the functions performed by the organ. With large, poorly treated, numerous ulcers and their recurrences, deformation can develop from a slight tightening of the walls to a state of obstruction.
After several months, in most cases, the duodenal bulb returns to its original state, but in the presence of a complicated form of the disease and the patient refuses to follow a diet or take medications, this does not happen.
This condition is dangerous due to a malfunction of the digestive system. Along with the bulb, the functionality of the pylorus of the stomach deteriorates. As a result, a significant amount of acid from the organ enters the intestines, and bile and pancreatic juice, on the contrary, in a different direction - into the stomach. Neither one nor the other process should occur in the body. The result is a malfunction of digestion, the presence of diarrhea, constipation, pain and discomfort in the upper abdomen, and bitter belching.
A serious consequence is a decrease in the lumen as a result of the presence of a scar with the development of intestinal obstruction. This pathology is divided into compensated and decompensated courses. In the case of the first, a narrowing of a pronounced nature appears, but the remaining hole is considered quite sufficient to at least somehow (if there are certain problems) perform the necessary functions.
With decompensated obstruction, there is no possibility of food gruel entering the intestines in normal and sufficient quantities. In view of this, stagnation of food is appropriate, and the process of fermentation is inevitable. These undesirable changes occur in combination with pain in the upper abdomen, a feeling of fullness in the stomach, the smell of rot in the mouth, frequent vomiting of undigested food, and unpleasant belching. There is only one treatment procedure in this situation – surgery.
Diagnostics
To identify the disease, the doctor prescribes the same examination methods to the patient as for a stomach ulcer. Instrumental methods can help identify affected areas:
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- X-ray of the stomach and duodenum;
- Ultrasound of the stomach.
Additionally, ultrasound of the digestive organs and gallbladder, endoscopic and X-ray examination of the intestines can be performed.
The doctor also resorts to laboratory diagnostic methods. To do this, the patient needs to undergo the following tests:
- blood;
- feces;
- study of hydrochloric acid levels.
Diagnosis of the disease.
To confirm the diagnosis, in addition to routine blood and urine tests, additional research methods are prescribed:
- Gastroscopy - allows you to assess the presence of a causative disease (ulcer, polyp, tumor), determine the degree of pyloric stenosis, dilatation of the stomach and its atonic, stretched walls, - X-ray of the stomach with contrast barium suspension is carried out immediately after filling the stomach and after a few hours. A violation of the evacuation function of the stomach is considered to be a delay of contrast in it for more than 8 hours. A delay of 24 hours or more is a sign of decompensated pyloric stenosis. — MRI or CT scan of the abdominal cavity allows you to better assess the location of the tumor, the extent of damage to adjacent organs, as well as determine the thickness of the walls of the stomach and the thickness of the pylorus.
Treatment
A peptic ulcer must be treated, especially if it has begun to heal. The disease can affect all organs, the symptoms will become stronger and malignant tumors may form. Doctors prohibit treating duodenal ulcers with any folk remedies. Therapy can only be prescribed by a doctor, which should consist of medications and diet.
Drug therapy is aimed at protecting the duodenal bulb from hydrochloric acid.
During treatment, the patient needs to adhere to the correct diet. The diet excludes the consumption of spicy, fried and fatty foods, ham, smoked meats, yeast products, and canned food. Doctors advise patients to eat:
- White bread;
- vegetables;
- soups without cabbage;
- cooked meat and fish;
- slimy porridge.
In order for the duodenal ulcer to heal, it is also recommended to consume dairy products - natural cream, cottage cheese, cheese. You can cook an omelet. In case of pathology, you can eat sweet fruits without rough peels.
Duodenal bulb deformity
The duodenal bulb is deformed as a result of the ulcerative process.
This deformation appears directly at the beginning of the section where food enters from the stomach. The contents of the duodenum in healthy people are alkaline. If a person develops an ulcer, the intestinal mucosa becomes inflamed and the environment becomes acidic. The produced acid riddles the organ with ulcers, after which scars remain on the mucous membrane. They are the ones who deform the bulb, tightening the mucous membrane.
Over time, the duodenal bulb will return to its normal shape, but if exacerbations occur frequently, they will lead to the appearance of more and more scars, which can tighten the passage into the intestines so much that food cannot continue its journey through the gastrointestinal tract, and correct The situation will only be possible through the intervention of a surgeon.
It is possible to stop changes in the structure of the duodenal bulb in similar ways as an ulcerative condition, but to do this you need to know what exact causes led to the disease. Many doctors believe that an incorrect rhythm of life, irregular food intake and junk food can affect the duodenal bulb to a greater extent than the stomach itself. Chronic duodenitis develops, in which the elevated level of gastric acidity remains stable.
The disease is not an ulcer in itself, but a poor diet, constant overexertion and frequent alcohol consumption can quickly lead to an ulcer. It’s enough just to protect yourself from such terrible diseases.
To do this, you need to normalize your daily routine, take care of your proper and timely nutrition, avoid bad habits and allow yourself walks in the fresh air more often. It should be remembered that chronic duodenitis makes itself felt in cold and wet weather, which usually occurs in spring and autumn, so a visit to the doctor and examination will not be superfluous. In addition to the medications recommended by your doctor, it is useful to drink mineral water and devote time to physical exercise.
As healthy foods, the doctor may recommend the patient white bread, vegetable soups without cabbage, boiled meat or fish, cereals, and puddings. It is recommended to take milk, cream, and cottage cheese if the duodenal bulb is deformed. Cheese, omelet and various sweet fruits without peel are allowed to be eaten with duodenitis: oranges, tangerines, tea with lemon. Of course, it is prohibited to consume alcoholic beverages, canned food, fatty ham, smoked and baked goods.
Obviously, nervous overstrain leads to the appearance of an ulcer of the duodenal bulb, so you should take care of the health of your nervous system and try to maintain your own comfortable state. Teas made from various herbs help a lot with this. For example, a mixture of plantain, marsh cudweed, valerian and motherwort, poured with one and a half glasses of boiled water and left for about twelve hours, will not only calm the nerves, but also have a beneficial effect on the condition of the mucous membrane of the duodenum.
Forecast
If the treatment of a peptic ulcer is successful and correct, then the bulb will not be deformed, and a small scar may form on the organ. Large ulcers can cause tightening of the intestinal walls, which leads to obstruction.
With proper therapy, the healed section of the intestine can return to its original position for several months or a year. If the patient is faced with a severe form of duodenal ulcer, then quick and complete restoration of the organ is impossible.
Prevention
In order not to encounter cicatricial deformation of the intestinal bulb, a person needs to follow preventive measures that are associated with ulcers and peptic ulcers. If it was not possible to avoid these diseases, then the patient needs:
- listen to the doctor's recommendations;
- undergo timely and correct treatment;
- do not break your diet;
- take medication.
In this case, all ulcers will be able to heal safely, and the peptic ulcer will not progress.
A dangerous complication of peptic ulcer disease is cicatricial deformation of the duodenal bulb. Occurs in patients with a history of a long course of the disease with occasional exacerbations. Let's consider the pathogenesis of the disease, clinical picture, main complaints, diagnostic methods and choice of treatment tactics.
Treatment and prevention
Severe scar damage in the intestine can be eliminated surgically, and relapse can only be prevented with supportive care and regular examinations.
One of the most common types of treatment is to take a drug that neutralizes the acidic environment, thereby preventing it from irritating the intestinal walls. They take medications that stop the production of gastric juice.
Severe deformation of the duodenum can only be treated with surgery. In milder cases, this disease is treated with proper and balanced nutrition, taking the necessary medications, and do not forget about a healthy lifestyle. The main requirement for a therapeutic diet is a temporary refusal of salty, fried, smoked, and too sweet foods. It is recommended to exclude carbonated and alcoholic drinks and quit smoking during treatment. All these foods and bad habits increase gastric secretion, which irritates damaged intestinal walls.
To avoid cicatricial deformation of the duodenum, it is necessary to prevent the development of peptic ulcers. If gastritis or an ulcer is detected, you must immediately consult a doctor and follow his instructions. But the best way out is careful health care, proper nutrition and as little alcohol consumption as possible. After all, the earlier a disease is detected, the easier it is to cure it.
Causes
The duodenal bulb is topographically located near the pyloric section of the stomach. Therefore, if the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract organs is disrupted (in this case we are talking about the final section of the stomach and the initial section of the intestine), acidic contents may be thrown into the duodenum, where pH is alkaline. The aggressive effect of gastric juice irritates the intestinal wall, causing a violation of its integrity.
In addition to local factors, bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse) and stressful situations also play a significant role in the pathogenesis of the disease. Detection of Helicobacter pylori in the body increases the risk of peptic ulcer disease.
Education mechanism
More often, scars appear at the junction of the upper and lower gastrointestinal tract. This part is called the bulb. Like any other scar, the scar tightens the area around it. Deformation occurs when many such scars are concentrated in one place. The development of peptic ulcers can be caused by many factors. This includes constant nervous tension, smoking, alcohol abuse, non-compliance with diet, and refusal to take special medications.
There are two main mechanisms due to which duodenal ulcer develops:
- increased acidity and its negative effect on the mucous membrane;
- Helicobacter, which release harmful substances that destroy the intestinal walls.
Pathogenesis
Erosion affects the surface layers, regeneration processes take place without scarring. An ulcer eats away at the wall of the organ down to the muscle tissue (with perforation, the muscle layer also becomes completely thin), so during the recovery stage it is not possible to avoid the development of a connective tissue scar.
The more often a person experiences exacerbations of peptic ulcer disease, the more severe the morphological and functional changes are experienced by the initial section of the intestine, represented by the duodenum.
In the development of scar deformity, experts distinguish the following stages: compensation, subcompensation, decompensation. Let's see what the difference is.
- The compensatory and subcompensatory stages are characterized by the presence of a lumen in the area of the duodenal bulb of at least 0.5 cm.
- The process is said to be decompensated when the degree of narrowing is significant (lumen diameter
Diagnosis of scars in the duodenum
The regular appearance of ulcers in one place leads to the appearance of a large number of scars in this place. Due to the large number of scars, the duodenum is at risk of cicatricial deformation. The intestinal walls are constantly narrowing, which can lead to complete obstruction of the bulbous part of the duodenum. If you experience symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, drowsiness or weakness, you should consult a physician.
This is followed by a visit to a gastroenterologist, who will prescribe the necessary examination. The most effective method for diagnosing cicatricial deformity is gastroscopy. This method will help to examine the deformed part of the intestine and determine its current condition.
Clinic
Patients with deformation of the duodenal bulb are people with a long history of the disease. Clinically, each of the 3 stages described above is characterized by certain symptoms. Let's take a closer look at them.
Compensation phase. The movement of the food bolus through the gastrointestinal tract is slightly disturbed. Retention of gastric contents occurs for 6-8 hours.
Patients complain of:
- feeling of heaviness in the epigastric area after eating;
- nausea;
- periodic vomiting;
- belching (there is a feeling of acid in the mouth).
With a pronounced concomitant inflammatory process, periodic pain is also observed. There is deep, enhanced peristalsis.
The subcompensation phase is characterized by signs of motor-evacuation failure, the food bolus lingers in the stomach for up to 24 hours, peristalsis is weakened. The following symptoms are expressed:
In the decompensation phase, signs of intoxication increase. Due to the lack of lumen in the area of scar deformation, symptoms of complete intestinal obstruction develop.
- Weakness, obvious deterioration in general condition.
- Progressive loss of body weight.
- The presence of symptoms of dehydration: dry skin, sallow color, pointed facial features.
- Feeling of increased dryness in the mouth.
- Diuresis decreases.
- Tachycardia increases.
Increased disturbances in water-electrolyte metabolism lead to severe hypochloremia and hypocalcemia. And this in turn causes the appearance of signs of convulsive syndrome.
Diagnostics
X-ray is indicated to detect an area of stenosis due to cicatricial deformation, clarify its nature, and the stage of compensation of the pathological process.
- The study is carried out after emptying the stomach using the polypositional technique.
- A double contrast method using a barium contrast mixture and air is also used.
- The narrowing of the lumen of the duodenum due to peptic ulcer is characterized by smooth contours and a smooth mucous membrane. In the case of a tumor process, there is a constant rigidity of the stenosis area, the contours are uneven, corroded, and a filling defect is observed.
- In the stage of decompensation, a significant expansion of the stomach containing a large amount of mucus, liquid, and food debris is determined by X-ray. Since the walls are hypotonic, the contrast mass immediately sinks to the bottom, forming a bowl with a horizontal level.
Laboratory research. Massive dehydration leads to loss of electrolytes, salts, protein, water, and chlorides.
- Hypoproteinemia.
- Hypokalemia.
- Azotemia.
- Alkalosis.
- Water and electrolyte imbalance: hypochloremia, hypocalcemia.
- Blood thickening.
- Polyhypovitaminosis.
- Decreased kidney function.
Treatment
Treatment of patients with cicatricial deformation of the duodenum is surgical. Significant importance is also given to preoperative preparation, which includes measures aimed at normalizing motor skills and restoring metabolic disorders.
First of all, regular gastric lavage is indicated. Taking into account the level of hypochloremia, hypokalemia, azotemia, metabolic alkalosis, hypoproteinemia, intravenous infusions of polyionic solutions and protein hydrolysates are performed:
- To correct the water-electrolyte composition, an isotonic solution is administered.
- To restore carbohydrate metabolism, 10-20% glucose is used.
- Normalization of protein balance is achieved by using plasma, proteins, and albumins.
- Cardiac glycosides are prescribed to stabilize the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
- Vitamins B, C, K are indicated for hypovitaminosis.
Peptic ulcer disease is dangerous due to the development of severe consequences. The morphological changes in the structure of organs that arise in this case are irreversible and lead to increased functional disorders. A healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, absence of bad habits, minimizing stressful situations - all this significantly reduces the likelihood of signs of the disease and its complications.
Treatment of pyloric stenosis.
Treatment for pyloric stenosis is surgical only. If there is an underlying disease in an adult, surgical removal of part of the stomach (resection) in the area surrounding the ulcer or tumor is indicated. For polyps, polypectomy is indicated. In parallel with gastric resection, pyloroplasty is performed - a longitudinal dissection of the pylorus from the outside with suturing of the incision in the transverse direction to expand its lumen. In the case of an inoperable tumor, a gastrojejunostomy is indicated - an anastomosis between the stomach and intestines to ensure the passage of food.
In children, it is sufficient to perform pyloroplasty while maintaining the anatomical integrity of the stomach.
The operations are performed under general anesthesia with laparotomic access - with dissection of the anterior abdominal wall. Two to three days before the scheduled intervention, preoperative preparation is carried out - gastric lavage, intravenous infusion of electrolytes and protein solutions in order to correct dehydration and disorders of salt metabolism in the body.
Postoperative treatment boils down to following a strict diet, prescribing antibiotics, taking anti-ulcer drugs, and in the case of stomach or intestinal cancer, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are indicated.