Every mother is concerned about the well-being of her child. The state of health can be judged by many factors, one of which is stool. The regularity of bowel cleansing and the quality of stool certainly depend on nutrition, general development, and physical activity. But other things can also affect the digestion process, such as certain diseases. Today you will learn what to do if a child (2.5 years old) has loose stools. The action taken depends on what is causing the condition.
Loose stools in a 2 year old child
Stools that are repeated more than three times a day can be called diarrhea. This condition is familiar to every person. The causes of diarrhea can be very different:
- infectious and inflammatory processes in the intestines;
- taking certain foods that cause fermentation and thin stool;
- use of medications;
- psychological reasons and so on.
Diarrhea is usually caused by one of two factors:
- most often, diarrhea is caused by increased intestinal motility, as a result of which the food you take is quickly evacuated;
- less often, stool becomes more frequent due to the entry of large amounts of water into the large intestine.
Loose stools in a 2-year-old child often have additional symptoms. Using them, you can determine the cause of the ailment, and then correct it. Remember that diarrhea can be quite dangerous for a baby. Therefore, first of all, it is necessary to show the little patient to the doctor. It is permissible to give any medications only as prescribed by a doctor. Let us consider in more detail what can cause loose stools in a 2-year-old child.
Causes of loose stools with belching
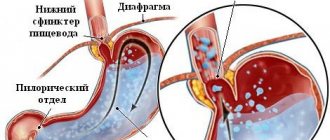
The course of putrefactive processes in the intestines leads to the active proliferation of pathogenic microflora. And if we feel the release of hydrogen sulfide as a bloated belly full of gases. Diarrhea is a consequence of toxic poisoning by waste products of pathogenic bacteria.
If the appearance of diarrhea and belching is accompanied by an increase in temperature, the patient experiences profuse vomiting and stomach pain, most likely we are talking about an intestinal infection. Most often, these symptoms are triggered by infection with staphylococcus, salmonella or cholera.
Infectious diseases: rotavirus or intestinal flu
Viral loose stools in a 2-year-old child begin suddenly. It is often accompanied by vomiting (single or frequent). The temperature may remain within normal values or rise, but usually the thermometer level does not exceed 39 degrees. Rotavirus infection, also called intestinal flu, is highly contagious. Therefore, outbreaks of the disease occur in small epidemics. Usually, within a few weeks, everyone who surrounded the infected child becomes ill. In adults, the symptoms of pathology can be blurred and almost unnoticeable. With viral diarrhea, a large amount of salts are lost along with water. Protein is practically not lost. Diarrhea lasts from 3 days to a week, after which recovery occurs.
Viral diarrhea can occur with diseases such as swine and bird flu. These infections are already more dangerous for the child. Additional symptoms include abdominal pain, migraine, photophobia and skin irritation.
Uninvited guests
It happens that the mother, while taking out the potty, notices helminths (worms) in the feces. Most often these are pinworms. They live in the lower sections of the small and large intestines. Infection (invasion) occurs when eggs or larvae of parasites enter the body. Most often they fall from dirty hands into the baby's mouth. Young children are especially susceptible to worms, since the protective functions of the gastrointestinal tract are not yet perfect. A baby can become infected at home, on a walk, in kindergarten through contact with outdoor shoes, the floor in the hallway, toys, common areas, picking up dirty objects, fiddling in the sandbox, touching animals.
Symptoms of helminthic infestation:
- salivation;
- nausea;
- decreased or increased appetite (the child constantly wants to eat);
- cramping pain around the navel or without a specific localization, which appears regardless of food intake;
- bowel disorders (diarrhea, constipation);
- itching around the anus;
- increased fatigue;
- frequent headaches or dizziness;
- paleness and blueness under the eyes;
- child chokes on food.
Poisoning
If a child is 2 years old and has loose stools without fever some time after eating, this may be a sign of poisoning. Pay attention to what the baby ate shortly before his health deteriorated. In case of poisoning, you can often find pieces of undigested food in the stool. Vomiting may or may not be present. The child in this situation complains of abdominal pain. You can hear fermentation and gurgling. A distinctive feature is the fetid odor of feces.
In case of poisoning, severe intoxication occurs. The child's condition may become severe due to dehydration. If you see that your baby is getting worse, call an ambulance immediately. Often, the use of incompatible products results in mild poisoning.
Causes
Foul-smelling diarrhea can occur for the following reasons:
- unbalanced diet, poor nutrition, resulting in vitamin deficiency, overeating;
- helminthic infestation;
- inflammatory intestinal pathologies (dysbacteriosis, colitis);
- intestinal infection, food poisoning;
- hormonal changes;
- introducing new foods to the baby;
- rotavirus infection;
- ARVI;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- enzyme deficiency (pancreatitis);
- psycho-emotional state;
- putrefactive dyspepsia;
- allergy;
- some medications, in particular after treatment with antibiotics.
Often, defecation with a pungent odor occurs due to severe stress or moving and climate change. This condition does not require treatment - diarrhea will disappear spontaneously in a few days.
Salmonellosis
A child can get an acute intestinal infection from insufficiently processed foods (meat, fish), raw, untreated water. In children, salmonellosis develops acutely and quickly.
The initial symptoms of infection are:
- malaise, fatigue;
- headaches, dizziness;
- vomiting and temperature up to 38-39 °C.
Signs of gastrointestinal disorders:
- a feeling of pain near the navel, in the stomach (the symptom intensifies when pressing on the stomach);
- flatulence;
- strong coating on the tongue, dry mouth;
- vomiting with pieces of food, bile;
- putrid, foamy diarrhea.
Complex therapy is carried out using antibiotics, enzymes and enterosorbents. Treatment aimed at preventing dehydration will also be needed.
Dysentery
An infectious disease that affects the digestive system and colon . Caused by the bacterium Shigella, when decomposed it produces toxins that poison the small organism.
Dysentery progresses rapidly and at the first stage is characterized by signs of intoxication. Gastrointestinal distress is expressed by mild abdominal pain, which subsequently spreads and turns into cramping, acute pain.
There are 3 forms of dysentery:
- Mild - a short-term fever, minor abdominal pain is possible, feces may be accompanied by a putrid odor. Bowel movements are observed up to 10 times a day.
- Average - the child suffers from cramping pain, bowel cleansing in the form of watery stool occurs 10-20 times a day, and blood and mucus are also noted. Babies with this form constantly cry and are irritable. The skin is pale, the tongue has a strong white coating, and the mouth is dry.
- Severe – considered the most dangerous, develops instantly, has complex intoxication of the body, and heart damage.
The temperature is very high, exceeding 40 °C, children suffer from intense headaches, malaise, dizziness, and chills.
The main dangerous symptom of the disease is a constant urge to go to the toilet. The act of defecation is frequent, the stool is watery with the smell of a rotten egg, and even rot.
Dysentery leads to rapid dehydration of the body. In this regard, if diarrhea with an unpleasant odor appears and to prevent the development of this disease, you should immediately consult a specialist.
Enterovirus
The incubation period of infection is 7-10 days, then signs of enterovirus appear:
- temperature changes from 37-39 °C;
- apathy, malaise;
- loss of appetite;
- diarrhea with a rotten egg smell;
- expansion of the submandibular and cervical lymph nodes.
Enterovirus infection should be treated immediately, since the state of health can be aggravated by the inflammatory process of the spinal cord, brain, and cause heart problems.
Therapeutic measures include the consumption of antipyretics, probiotics, replenishing the body with fluid, providing the child with healthy nutrition, and rest.
Taking antibiotics
If the child is 2 years old, loose stools with mucus may result from drug treatment. This condition is often provoked by antibacterial drugs. Remember if you gave these to your baby the day before. It often happens that a child has a disease, for example, bronchitis or tonsillitis. The doctor prescribes an antibiotic, after which diarrhea begins within a few days. This is a completely normal reaction. The fact is that drugs with a wide spectrum of action destroy not only pathogenic flora, they kill beneficial microorganisms. Because of this, digestive failure occurs, accompanied by fermentation, bloating and loose stools.
It is highly likely that the doctor will not cancel your antibiotic therapy, but it is still worth informing the doctor about such a reaction to treatment.
Green chair
If the stool of a newborn baby seems to be the usual yellow-green or green color, but has become very foamy and a sour, foul odor appears. This often indicates a lack of breast milk from the posterior chamber. According to its properties, it is fattier, higher in calories and contains enzymes that help digest lactose (milk sugar). If a similar situation occurs, it can be easily corrected:
- It is impossible to change the breast at the first difficulty in sucking; this way the child does not receive milk from the posterior chamber.
- To stimulate milk production in the posterior chamber, the baby should be breastfed on demand, not on a schedule.
- You should not give your baby water or juices in the first half of the year, as this reduces the baby’s desire to breastfeed.
- It is necessary to ensure the correct position of the newborn baby during sucking. If the baby is uncomfortable, he will often abandon the breast.
- For good lactation it is necessary to feed in a calm environment and on a full stomach.
Has your child developed loose green stools with a lot of mucus? You need to worry if the child’s behavior changes - if the child has become restless, capricious and irritable. If the child’s behavior has not changed, the appearance of mucus may be normal.
Individual characteristics
Yellow loose stools in a 2-year-old child may appear due to psycho-emotional stress. Young children are very susceptible to stressful situations. They can react this way to severe fright, excitement, or prolonged fear. In this case, the increased urge to defecate is not accompanied by additional symptoms; attacks occur periodically.
Digestive disorders in children are often due to lactase deficiency. If this diagnosis is made to a child, then it is necessary to refrain from consuming dairy products, which cause bloating and diarrhea. It is also possible to correct this condition with the help of medications containing the missing enzyme.
Alimentary diarrhea in children appears due to prolonged malnutrition, an imbalance in the level of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, and insufficient functioning of the liver, stomach or pancreas. In this case, green liquid stool is observed in a child (2 years old).
Features of stool during breastfeeding
In a baby who feeds only on mother's milk, the stool is yellow, yellow-green or dark mustard in color with various shades and granular impurities. The feces have the consistency of thick sour cream or mushy, possibly foamy and liquid, with a slightly sour odor. The frequency of stools up to 1.5 months of age is 5–12 times a day; the older the baby, the less frequent the stools. If the child is developing correctly, by the age of three months the frequency of stool should be 4-6 times a day, in some babies 1 time.
The color of stool can also be affected by the content of hormones in mother's milk, the physiological imbalance of the infant's intestines, and the immaturity of the enzymatic system. Also, rapid oxidation of feces in the open air can lead to discoloration. The color of feces in a newborn baby during natural feeding changes very often, and depends to a large extent on the mother’s nutrition and on the child’s absorption of nutritional ingredients.
Liquid green stools may occur in a baby if a nursing mother changes her diet suddenly. You need to introduce new dishes into your diet very carefully. Nutrition should be complete and multifaceted; attention should be paid not only to the choice of products, but also to their preparation. For example: fatty, fried, spicy foods can easily cause changes in a child’s stool. Care should be taken when using medications that can cause changes in the color and odor of stool, cause loose stools, and lead to allergic reactions.
To maintain normal digestion in the baby, the mother should apply the following nutritional rules:
- Use different types of meat, fish and poultry - lean and preferably boiled.
- In addition to meat, protein should come from dairy products in the form of cottage cheese and cheese. You should avoid consuming large amounts of whole cow's milk because... it often leads to allergies in the first year of life; it is better to replace it with kefir or yogurt.
- Food should contain a large amount of dietary fiber, coming from vegetables and fruits. It is not recommended to eat orange and red fruits, as well as exotic foods.
- To avoid the appearance of foamy stool in your baby, you should limit foods that lead to fermentation in the intestines. These include: confectionery, grapes, sweet drinks and all products with a huge sugar content. Also highly concentrated broths, smoked products and pickles.
- Be extremely careful when adding foods with a high risk of allergy to your diet. These include citrus fruits, tomatoes, chicken protein, strawberries, chocolate, and peanuts.
The goal of treatment is to normalize electrolyte balance
Whatever causes indigestion, the main task is to replenish the lack of fluid. For this, the child is advised to drink plenty of fluids. If there is no vomiting, and diarrhea is of non-infectious origin, then you can get by with clean water. If salts and other important elements are lost, it is necessary to use special solutions: “Regidron”, “Glucosan”, “Citroglucosan” and others.
Give your baby a small sip every 2-5 minutes. Do not overdo it so as not to provoke vomiting. It is preferable to use solutions at the same temperature as the baby’s body. In this case, the substances will be absorbed most quickly.
Prevention measures
- Limit your child's access to the toilet, put outdoor shoes in the closet.
- Make sure that on the street the baby does not pick up or drag objects into his mouth, and do not allow contact with animals.
- Try to wean your baby from the habit of licking his fingers.
- Strictly ensure that, when coming home from the street, all family members thoroughly wash their hands with soap.
- Once a week, carry out wet cleaning with disinfectants, wash toys with soap or wash them.
- Do not give your baby unwashed vegetables and fruits, meat and fish that have not undergone heat treatment, and do not drink raw water.
- If you have dogs or cats in your home, get tested for worm eggs at least twice a year.
- If someone in the family is found to have worms, it is necessary to treat all members of the household in order to avoid the formation of a persistent focus of the disease.
Adjust your diet
For indigestion of various types, it is recommended to exclude all dairy products. This environment is the most favorable for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. Giving your child milk and kefir for diarrhea will only worsen his well-being.
Put the little patient on a specific diet. Give your baby rice water, jelly-like soups, light porridge with water. Completely eliminate raw fruits and vegetables, carbonated drinks and sweets. As soon as the child gets better, gradually introduce boiled lean meat and eggs. For each of the listed diseases, an individual diet is prescribed. Be sure to discuss it with your doctor.
A 2-year-old child with loose stools: how to treat?
Many parents ask this question, because they want to help their little patient. Drugs such as Imodium and Loperamide are excellent at stopping diarrhea, but they should not be given to children under 6 years of age. Remember this important rule. You can help your baby with the following medications:
- enterosorbents “Smecta”, “Enterosgel”, “Polysorrb” will remove toxins, allergens, poisons and toxic substances from the child’s body (can be given without a doctor);
- calcium gluconate will have an anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effect (it can be used independently in the absence of contraindications);
- antispasmodics “Drotaverine”, “No-Shpa”, “Papaverine” will relieve abdominal pain (only after diagnosis);
- carminatives “Espumizan”, “Bobotik” will reduce gas formation and relieve discomfort (can be used without prescription);
- antipyretics "Ibuprofen", "Panadol" will eliminate fever and malaise (only at high temperatures or after diagnosis).
Sometimes doctors prescribe additional enzymes that normalize digestion (Lactazar, Creon), and also prescribe probiotics (Linex, Maxilak), which will restore the natural intestinal microflora.
Summarize
If your baby starts having diarrhea, and then the temperature rises or additional symptoms of illness appear, then don’t guess with coffee grounds. See your doctor as soon as possible. Prolonged diarrhea accompanied by vomiting can lead to dehydration. This condition occurs especially often in children. It is dangerous because the kidneys and cardiovascular system suffer, acetone appears in the urine, and severe intoxication occurs. With timely diagnosis and proper treatment, the body recovers within two weeks. Discuss with your pediatrician the possible causes of baby loose stools, and be on the lookout.
Often, mothers at pediatrician appointments hear the question - how do we poop? A person who is far from being a toddler will raise his shoulders in bewilderment. Well, who cares how the child solves his toilet problems. But experienced mothers know that the color, consistency, nature of feces and, in general, the process of defecation are an important criterion for assessing the overall health and development of the baby.
And if feces of a suspicious color, smell or consistency are found in a diaper or potty, then the right mother will draw certain conclusions and visit the pediatrician with the toddler.
Belching: why it happens and what it means - Rotten eggs
March 08, 2009
Rotten egg burps are caused by hydrogen sulfide (H2S), a gas that is formed from sulfur-containing proteins found in some foods after sulfur bacteria break down those proteins in the stomach or small intestine.
You can get rid of rotten egg burps, or at least significantly reduce the smell, if you avoid the following foods:
Vegetables: asparagus, broccoli, cabbage, garlic Garlic for health: almost a panacea, mustard, onions, pak choy, parsley, sweet potatoes, beets, tomatoes, watercress
Helycobacter pylori, a bacterium that causes chronic gastritis, stomach or duodenal ulcers, bloating, heartburn and belching. Diagnosed using special tests; Antibiotics are prescribed for treatment.
Intestinal giardia, a single-celled parasite, usually transmitted through food or water, causes diarrhea, bloating and regurgitation of rotten eggs.
Intestinal bacteria that are part of the normal intestinal flora, but when they multiply in too large numbers cause rotten egg burps, bloating, flatulence or diarrhea. This condition is called bacterial overgrowth syndrome (SIBO). It can develop with lactose or fructose intolerance. Fructose - the benefits and harms of a natural product. In some diseases, such as celiac disease and Crohn's disease, food is not completely digested and is therefore broken down by sulfur bacteria, which produce hydrogen sulfide.
Limit your intake of sulfur-containing foods as much as possible. This will reduce the burp smell in just a day or two. However, you will still need to find the cause of the burping.
If you suspect that you have celiac disease, in addition to limiting the amount of sulfur-containing foods in your diet, try a gluten-free diet (exclude wheat, barley
Source
Hello! The child is 3 months old, over the last month he has gained 500 grams (in the first 2 months - 3200). He is breastfed (eats every 2.5-3.5 hours, 7-10 minutes each), does not look hungry. Intestinal colic has been bothering him since birth (diagnosis from a pediatrician). What worries me: since two months they seem to have intensified or not at all ((The regurgitation has become more frequent, and maybe an hour, an hour and a half or even two hours after eating. He regurgitates cottage cheese with a characteristic vomitous smell, twice a day violently (about 3 tablespoons spoons) and little by little throughout the day (not visible, only heard swallowing). About two weeks ago, stools became rare (once every three to four days), liquid like water, bright orange in color (once it was mushy, swamp-colored) with the smell of rotten eggs, very smelly farts. No fever. Attacks of pain twice a day every day, the rest of the time the child is active, smiling, playing. What is it? And is treatment necessary? The pediatrician insists on testing for dysbacteriosis, but we can’t collect feces ((
Comments on this post
Intestinal colic can be reduced and helped by the child: 1. DO NOT overfeed, children do not feel the measure and when they are full, as a result they overeat, hence your frequent regurgitation, as soon as there is less milk in the chest (after a couple of months, the flow on demand will normalize) you you will understand this. 2. Ventilate the room as soon as the baby has fallen asleep or taken him out of the room (windows wide open) + humidity. 3. Place it on your tummy more often. 4. After eating, wait until the air comes out and lie down in a horizontal position. 5. Walk in the fresh air for at least 2 hours. And be healthy!
It’s normal for a breastfed baby to poop once every 3-4 days, don’t worry and don’t stress yourself out, milk is absorbed well, be happy. As for the color of the poop, we had different colors and consistencies, but the smell is something to see the doctors...
newborn doesn't sleep for 5 hours straight what to do The first problem new parents face is that their newborn doesn't sleep as much as they would like. It’s not that the baby doesn’t close his eyes at all, he sleeps a little, but wakes up too often
3. I try before every feeding. I noticed if
Source
Normal color of stool at different ages in children
Normal baby's stool in the first days of life is blackish-green in color.
Normal adult feces are brown or yellow-brown in color. But digestion in children differs significantly from the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract of adults.
In the first days of life, infants have black or black-green stool. This is meconium coming out. After 3–4 days, the color of the baby’s feces changes.
If the baby is breastfed, then his stool will be yellow in color and have a soft, even liquid consistency. If the child receives an adapted formula, then the parents will find pale yellow excrement in the diaper.
Currently, infant formulas are additionally fortified with iron to prevent anemia, so the stool takes on a greenish tint. The normal number of bowel movements in a child under one year of age is from 1 to 3 bowel movements per day.
After 6 months, the baby begins to receive additional nutrition and his feces begin to approach the usual brown color.
Diarrhea with a sour smell
For people in the postoperative period, diarrhea with a sour smell is very familiar. It occurs after treatment with antibiotics. In order to stop it, it is advisable to take lactobacteria to restore the “killed” flora.
Sometimes, diarrhea with a sour smell can occur as a result of increased inflammation in the small intestine. Often, the cause of this phenomenon is enteritis. Along with the smell, a person’s stool is profuse, light in color, repeated up to 6-8 times a day.
A simple intestinal infection can cause diarrhea with a sour smell.
When should you not worry?
If a mother eats spinach, the baby's stool color may change.
Yellow liquid stool may be normal in toddlers in their first year of life. When not to sound the alarm:
- the episode of loose stool is isolated;
- the baby is active, walks and is interested in toys;
- there are no signs of fever or intestinal colic;
- the tummy is not bloated or seething;
- feces are not foul-smelling or foamy.
In this case, parents should calm down and enjoy life with their little one. Yellow feces can be caused by excess juices in the diet and the period of dentition. At this time, teeth are being cut, and this puts a strain on the digestive system as well.
But in this case, diarrhea begins at the moment of tooth eruption and lasts no more than a day. As soon as the tooth breaks through the gum, tummy troubles go away on their own.
The yellow liquid nuisance in the diaper is caused by improper introduction of complementary foods. Eliminate new foods and introduce complementary foods under the guidance of your pediatrician.
The smell of feces in infants as one of the indicators of a child’s health
The parameters of a baby's stool are one of the most important indicators of the correct functioning of his body. Changes in the color, smell and consistency of stool are a response to changes in the baby’s diet and condition. What should a healthy newborn's stool smell like? And for what reasons do deviations from the norm occur?
Breastfeeding norms
In the first 2-3 days after birth, the baby's feces are called firstborn or meconium. It consists of ingested amniotic fluid, epithelial cells and other substances. Meconium, characterized by a tarry consistency and black-green color, has no aroma.
Until the 10th day of life, the mucous membranes of the newborn are actively colonized by bacterial flora, and his intestines adapt to mother's milk. During this period, transitional stool is greenish in color and has a mushy, liquid consistency. It smells sour.
Subsequently, a stable individual defecation schedule is established. The baby's feces become mature. Its main characteristics are:
The appearance of the stool of a breastfed baby depends on the mother's menu. Slight deviations from the given standards are possible. They should not frighten parents if the baby is gaining weight and does not show signs of anxiety.
Norms for formula feeding and complementary feeding
In a bottle-fed newborn, formed feces appear immediately after the passage of meconium. It has a thick, uniform consistency, a dark yellow or brown color and a typical odor, but not too pungent or putrid. A newborn's bowel movements occur 1-3 times a day.
Regardless of the type of feeding, after the introduction of complementary foods, the baby’s stool begins to gradually approach “adult” parameters. On this
Source
For about a month now, the baby’s poop has been smelling like acetone. There is no smell from the mouth, there is no smell from the urine, the urine was tested - everything is normal, there is no acetone. The behavior is normal. He doesn't complain about anything. But sometimes she suffers from constipation. We went to the pediatrician, announced our menu, our diet did not change, only from the new year we allowed her to drink adult juices. He told them to remove them and observe. There was an improvement, but it was short-lived, as they again smell strongly of acetone, but we don’t give them juices.
Has anyone encountered this, what to do? With what it can be connected? What medications should I take? (We weren’t prescribed anything except Creon) Who else can we turn to, maybe it’s worth doing an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. (My husband has a problem with his pancreas - perhaps it’s hereditary).
Kaprogram - undigested fiber in a significant amount, needles of fatty acids in a significant amount, muscle fiber. in small quantities
This happens to us, there are problems with the gastrointestinal tract, but not with acetone. Don’t give these juices, they’re just disgusting. I personally still don’t give it, he doesn’t even know what it is. The juice I give is fresh, but it’s basically kampot made from dried and frozen fruits.
In Kyiv, the City Gastroenterological Center operates on the basis of Children's Clinical Hospital No. 9. His address: st. Kopylovsky, 1/7. Tel. 468-33-06
They held out for a week, I thought maybe my teeth were affecting me that way, but I still decided to call the doctor for a consultation; I couldn’t go for an examination.
Then snot and coughing appeared, the child was tormented by pain in the tummy, and reacted strangely and the pain in the foot, when he pressed on the foot, he writhed violently.
The doctor told me to take nifuroxazide and smecta. We’ve been drinking for three days now, the frequent poops have gone away, but the smell is terrible…..(roses have nothing to do with it) the smell is like carrion….
And now I’m reading different reviews about this drug, and many do not write very well about nifuroxazide. What to do? Donate calla lilies? I'm at a loss. is it possible with
Source
Baby of the first year of life. Yellow feces as a sign of pathology
The color of a child's stool depends on complementary foods.
If a baby begins to have diarrhea of any color, this causes concern and even panic among parents.
At this age, the yellow tint of stool and its liquid consistency is not considered a pathology.
If the baby is breastfed, then the mother should first review her diet and eliminate medications, if any. A banal overload of food can also cause a negative reaction in a baby.
A similar disorder can occur if the baby sucks only part of the mother's milk. This happens when a woman, having listened to the advice of her grandmothers, expresses foremilk before feeding.
Previously, there was a myth that this milk burns out and therefore it should be expressed and only then given to the baby. In this case, the baby receives only fatty hind milk, but does not receive fore milk - less fatty, but rich in proteins. The result is yellow diarrhea.
The unexpected color of stool causes dysbiosis - a violation of the ratio of beneficial and opportunistic bacteria. In addition, this pathology may exhibit the following symptoms:
- regurgitation of milk;
- belching;
- pain and rumbling in the stomach;
- increased gas formation;
- the baby is worried, crying, pulling his legs towards his tummy;
- development slows down, the baby does not gain weight.
If dysbiosis is suspected, it is recommended to take a stool test and, based on its results, the doctor will prescribe antibacterial therapy to suppress pathogens and drugs to normalize the microflora. An infant is not immune from intestinal infections, especially when the active period of crawling and exploring the world begins. The alarm should be sounded in the following cases:
- liquid stool does not stop during the day;
- against the background of suspicious stool, the temperature increased;
- refusal of food;
- vomiting appears, especially if the urge to vomit cannot be stopped;
- irrepressible crying, screaming without tears or apparent reasons;
- the baby's eyes or fontanel are sunken;
- In the stool there is mucus, pieces of undigested food after the introduction of complementary foods, and blood clots.
This requires immediate medical attention to determine the cause of diarrhea. If diarrhea occurs during treatment for other diseases, you should also contact your pediatrician to change the treatment method.
Important! Diarrhea in a baby in the first year of life is fraught with dehydration and poses a threat to life. Therefore, during treatment, drugs are prescribed to rehydrate the body. They are administered intravenously or orally depending on the child’s condition.
Yellow feces are caused by abnormalities in the development of areas of the gastrointestinal tract and inflammatory processes in the intestines. In this case, in addition to diarrhea, additional symptoms will be observed.
Foul diarrhea in a 1 year old child
A child has diarrhea with an odor. Smelly diarrhea in a child
If you notice a symptom such as smelly diarrhea in a child, you should immediately call a doctor.
Diarrhea in a child with an odor may indicate quite serious infections. It's no secret that children are quite a grateful audience in terms of massages or taking various medications to support the immune system. A child’s body reacts in exactly the same way to taking medications aimed at treatment; for example, all side effects from taking, say, antibiotics will follow immediately. For example, a common consequence of taking a particular medication may be vomiting or even diarrhea, depending on what medicine was prescribed by the doctor.
Most often, pediatricians also try to prescribe various supportive medications if taking strong antibiotics cannot be avoided. However, there are often situations when side effects still make themselves felt, and you should report them to your doctor immediately. For example, a common symptom indicating that the chosen medicine is not suitable for him is smelly diarrhea in a child.
Under no circumstances should you try to stop such a symptom on your own with other medications; it is better to abruptly stop taking all medications and call a doctor. Only a doctor can prescribe medications that will cause resistance.
However, if you plan to continue taking this drug in the future, then this can also be done under the supervision of a doctor; most often, the dose of the irritant is simply reduced. However, diarrhea in a baby can also be caused by the infection itself introduced into the body, and in this case we are not talking about poisoning, but rather the so-called rotavirus, which is introduced into the body by airborne droplets. In this case, treatment is also carried out directly under the supervision of a doctor, and antibiotics will most likely be prescribed.
Often, diarrhea in a child with a smell can be caused by poor quality food, as a result of which the baby’s body is poisoned.
The best method of treatment in this case would be fasting for a certain time, and the method of treatment most often depends on what other symptoms were present in addition to diarrhea.
Sometimes doctors perform gastric lavage, which is necessary in case of severe poisoning, and also prescribe a strict diet. There is no point in resisting if the doctor decides to hospitalize the child because he has diarrhea with a characteristic odor; it is quite possible that the baby’s life is not in danger, but the pediatrician decided to play it safe and monitor him in a hospital setting.
Diarrhea with odor
Diarrhea itself causes a lot of trouble. In addition to pain in the abdomen, a constant urge to defecate, painful bowel movements and a painful sensation in the gastrointestinal tract, diarrhea with an odor may appear. And if during normal digestion the smell is not the most pleasant, then the admixture of sour, rotten and other odors makes you think about diseases of the digestive tract. If such manifestations become frequent, then it is worth visiting a gastroenterologist to find out the real reasons for its manifestation.
Child has diarrhea with odor
Any health disorder in children gives their parents many reasons to worry. If a child has diarrhea with a smell, then you should immediately visit a pediatrician or call an ambulance.
Almost always, for young children, diarrhea with a smell is typical during a rotavirus infection. In this case, abundant and frequent stools are yellow in color with a characteristic sour odor. The baby may suffer from severe abdominal pain, fever, and constant thirst. In addition, the so-called “stomach flu” may be accompanied by redness of the eyes and severe tearing. The child needs to normalize the drinking regime, and only the pediatrician can tell you what to do next.
In some cases, a child’s diarrhea with odor may occur after eating low-quality foods or unripe fruits. Often in such cases, the stool has a slightly greenish tint with admixtures of food pieces and a corresponding smell.
Diarrhea with a sour smell
For people in the postoperative period, diarrhea with a sour smell is very familiar. It occurs after treatment with antibiotics. In order to stop it, it is advisable to take lactobacteria to restore the “killed” flora.
Sometimes, diarrhea with a sour smell can occur as a result of increased inflammation in the small intestine. Often, enteritis is the cause of this phenomenon. Along with the smell, a person’s stool is profuse, light in color, repeated up to 6-8 times a day.
A simple intestinal infection can cause diarrhea with a sour smell.
Diarrhea with rotten egg smell
If a person has diarrhea with the smell of rotten eggs, then most likely the problem lies in the large intestine. Colitis often provokes similar manifestations. In this case, stool may be accompanied not only by a putrid odor, but also by foam and mucus. In this case, inflammation in the colon has been going on for a long time and has worsened under the influence of external factors. Frequent bowel movements can occur up to 15 times a day. It is preceded by severe pain in the abdominal area.
If you have diarrhea with the smell of rotten eggs and there are small blood clots in it, then the cause may be dysentery. Contacting a specialist and passing all tests is mandatory.
Diarrhea with a strong odor
If a person has diarrhea with a strong odor, there can be many reasons for this. For children, such pungent odors are characteristic of rotavirus infections. In adults, strong-smelling bowel movements may be caused by:
- intestinal poisoning
- exacerbation of chronic diseases
- inflammation of the large or small intestine
- food allergies to foods eaten
- stomach virus.
- Viral stomatitis in a child treatment
- Speech therapy examination of children with stuttering
In each of these cases, diarrhea with a strong odor has specific symptoms, frequency, color and many other associated factors.
Diarrhea with putrid odor
When you are bothered by diarrhea with a putrid odor, the reason may lie in inflammatory processes actively occurring in the large intestine. Often the cause of the putrid odor of diarrhea can be fermentation processes. They can be caused by eating foods rich in fiber. In this case, the patient does not experience severe pain in the intestinal area, the flatulence is not strong, but particularly foul.
Enterocolitis often provokes diarrhea with a putrid odor.
Often, the diarrhea itself, and with it the putrid smell, go away when food rich in protein and fiber is excluded from the diet. The chair is restored quite quickly.
Diarrhea with fishy odor
Often, diarrhea with the smell of fish is a symptom of very serious diseases. So, with discharge similar to rice grains with a clear smell of rotten fish, cholera can be detected.
Quite often, diarrhea with a fishy odor indicates salmonellosis. Treatment of these diseases should be carried out under strict medical supervision. Otherwise, very unfavorable consequences may occur.
In most cases, diarrhea with odor is a clear indication of an exacerbation of chronic diseases or intestinal infections. It is advisable to carry out the correct treatment prescribed by a specialist to effectively combat this symptom.
Diarrhea in children.
Infants have a hard time with diarrhea, regardless of the cause of its occurrence. This can be overfeeding, when the mother breastfeeds too often, or during feeding, when the cow's milk is not quite fresh or too fatty, etc. Diarrhea from the above reasons can sometimes reach up to 20 times a day, the feces have a yellowish appearance with white lumps of undigested milk , and sometimes with greenery, blood and mucus. The smell also changes. Typically, digestive disorders in children are mild and recover quickly if treatment is started on time.
Indigestion should be considered a serious illness, indicated by the following symptoms: watery stools or blood in the stool. vomit. temperature above 38C° the child looks exhausted or has gray circles under the eyes. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor. It often happens that it is difficult to get to a doctor. Therefore, advice on how to provide emergency assistance when diarrhea occurs may be useful.
A child who is exclusively breastfed. It is recommended to continue breastfeeding. However, the less milk he sucks, the better. You can deprive the child of all food for 12 - 24 hours. giving only teaspoonfuls of sugar-sweetened water. You can give him protein water: mix 1 raw protein well in 3 glasses of water, add a little sugar and a few drops of cognac, shake the mixture well before drinking and feed it with a spoon, but not often.
For a bottle-fed baby, milk should be diluted halfway with water before consulting a doctor. It’s even better to dilute skim milk rather than whole milk. Give your baby as little milk as possible just to satisfy his hunger. Feed this way until the stool returns to normal. If mild diarrhea does not go away after 2-3 days, try to show the child to a doctor. If the child’s diet includes, in addition to milk, solid food, it should be excluded from the diet completely until the diarrhea passes.
After a stomach upset, start giving solid food little by little: on the first day only 1/3 of the usual portion, on the second - 2/3, and on the third - a full portion. At this time, new foods should not be introduced into the child’s diet.
When greenery appears in the baby's stool. you need to infuse the chalk in clean water (until it becomes transparent), and give this infusion, clear as water, 3 times a day, half a teaspoon with mother’s milk or cow’s milk if the baby is being fed artificially.
If there is mucus in the stool. blood or both, this may be an indication of dysentery. Consultation with a doctor is necessary. But if you still cannot see a doctor, give your child a drink prepared according to the following recipe: 250 ml of water. sugar - 1 tablespoon (without top), salt 3/4 teaspoon. Give from 30 to 120 ml. of this mixture, depending on how much the child wants and can drink. Keep him on this mixture for one or even three days until the stool takes on a normal appearance, then gradually return to the previous diet.
The sequence of changes in a child’s diet after a severe digestive disorder.
If the child recovers quickly, the duration of each stage can last 1 day. If recovery is slow, the duration of each stage is 2 days.
1. First stage. skim milk, diluted halfway with water. If feeding is carried out with formula milk, the milk formula should be diluted with twice as much water as usual. Pour only 2/3 of the mixture into the bottle, and leave the rest in case the baby needs to be fed more often.
2. Second stage. diluted skim milk with sugar in the usual amount. Or a mixture of half regular milk, adding water to the norm and 1 tablespoon of sugar.
3. Third stage. undiluted skim milk with 2 tablespoons of sugar. Or half the usual amount of milk, added water to the usual amount, with 2 tablespoons of sugar.
4. Stage four (normal stool): regular milk.
5. Fifth stage. gradually adding solid foods if the child was already eating them before illness.
If the stool becomes more liquid again, go back 2 stages.
If diarrhea intensifies, start all treatment from the first stage, that is, with a mixture of milk, and be sure to find an opportunity to consult a doctor.
As a rule, young children should never be given anything cold; everything should be warm, like fresh milk. From cold food they develop not only intestinal but also other diseases.
To treat diarrhea, you can use the following remedies:
• Rice broth.
Pour one teaspoon of rice into 6 - 7 cups of water and boil over low heat. Strain the broth through cheesecloth or a sieve, cool and give warm to a sick child 1/3 cup every 2 hours.
• Lingonberry: berries, leaves.
The juice of the berries is taken for putrefactive diarrhea, the berries are taken for diarrhea. One tablespoon of leaves per 1 cup of boiling water. Boil for 5 minutes. leave, wrapped, for 1 hour, strain. Take the infusion one tablespoon 5-6 times a day for diarrhea.
• Pomegranate, peel.
One teaspoon of dry peel to 1 glass of water. Boil for 10 - 15 minutes, leave, covered, for 2 hours, strain. Take 1 tablespoon 3 times a day before meals. For young children, take 1 teaspoon. Follow the dosage exactly.
• A decoction of dried pears has a fixing property.
• Gray blackberry, leaves.
Four teaspoons of leaves per 2 cups of boiling water. Infuse, wrapped, for 2 hours, strain. Take 1/2 cup 4 times a day for 30 minutes. before meals.
• Blackberry fruits are gray.
Dried blackberries, crushed into powder and mixed with sugar (to taste), are a cure for diarrhea. Children are given 1/2 teaspoon 3 times a day. Powdered fruits are best consumed freshly crushed.
• Infusion of walnut leaves or fruits.
Take 20 g of chopped young leaves or unripe fruits in 200 ml of boiling water and leave for 20 minutes. Take 1 tablespoon 3 times a day. Used in folk medicine internally for catarrh of the stomach and intestines, for diarrhea, rickets and exudative diathesis.
• Decoction of poppy flowers.
A decoction of poppy flowers in milk is taken for measles (to stop the rash from developing) and whooping cough, as well as for dysentery and diarrhea in children.
• Powder from tubers of Lyubka bifolia.
Used orally, as well as as an enema for diarrhea of any origin, including dysentery and cystitis.
• Powder from male orchis tubers.
This powder, known as salep, is considered very useful for diarrhea, dysentery, cystitis and food poisoning, when enveloping mucus is required to treat inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. You can prepare salep at home as follows. The dug up orchis tubers are cleaned of small roots and outer skin, the tubers are strung on a thread and immersed in boiling water for several minutes to destroy the unpleasant odor and remove bitterness, and also to prevent the tubers from germinating. After removing the tubers from boiling water, they are dried in air (in the shade) or in a warm room. Dried tubers should have a yellowish color and some glassiness or transparency.
Before use, the tubers are ground into powder, first diluted in cold boiled water (in 10 parts), and then 90 parts of boiling water (or hot milk) are added and shaken until a thick liquid is obtained, like liquid sour cream.
• Salep decoction.
a) Take 3 - 10 g of powder per 180 ml of boiling water. Take 1 - 2 tablespoons 3 - 4 times a day.
b) For diarrhea, for greater effect, take enemas from salep infusion: 2 teaspoons per 2 cups of boiling water (the powder is pre-moistened with cold water) and add (if available) 1/4 teaspoon of crushed flaxseed. Treatment with salep for children suffering from intestinal catarrh is very effective.
• Oak bark .
Used as enemas for dysentery and dyspepsia in children (on
3 parts bark decoction 1 part starch).
• Children suffering from dysentery are recommended to be given 30 - 60 g of honey per day along with medications. In this case, dysentery bacilli disappear from the stool faster than with treatment with medications alone.
For the treatment of gastrointestinal problems, read the articles “Diarrhea”, “Dysentery”, changing the dose in relation to the age of the child.
According to popular belief, all diarrhea goes away if a child is fed donkey milk.
Sometimes persistent, but not bloody, diarrhea goes away if you give a small enema of very strong tea and leave it until the child can hold it.
Sympathetic remedy: if bloody diarrhea appears, apply a daffodil bulb to the baby’s tummy.
To prevent intestinal diseases, you should never wean your baby in the summer.
Healing remedies
Categories
Diarrhea is frequent and loose bowel movements caused by intestinal dysfunction.
The causes of diarrhea are too intense peristalsis of the intestines, when their liquid contents move faster than usual and do not have time to be absorbed. This can occur as a result of overeating or food poisoning, fermentation of food in the intestines caused by incomplete digestion of carbohydrates, as well as nervous excitement, and the use of laxatives. Infectious diarrhea is caused by bacteria and viruses that enter the body with food and water.
Manifestations of diarrhea: rumbling in the stomach, bloating, “loose stools” with foamy stools, light in color with fermentative diarrhea and darker with a sharp foul odor in case of putrefactive diarrhea.
Folk remedies for treating diarrhea: Decoctions of: lingonberry leaves (6 g per 200 ml, boil for 30 minutes, drink 100 ml 2 times a day) cherry stalks (10 g per 200 ml, boil for 30 minutes, drink per day) oak bark ( 20 g per 200 ml, boil for 30 minutes, drink 2 tablespoons 3-4 times a day) lungwort herb (2 tablespoons per 400 ml, boil for 15 minutes, drink 100 ml 20 minutes before meals) tansy flowers (10 g per 200 ml, boil for 15 minutes, drink 1 tablespoon 20 minutes before meals) burnet, alder (fruit), cinquefoil erect (2 tablespoons per 0.5 l, boil for 30 minutes, drink 5-6 times a day 30 minutes before meals, take 2 months). Infusions: plantain leaves (1 tablespoon per 200 ml, leave for 15 minutes, drink 1 tablespoon 3–4 times a day) sunflower flowers (20 g per 200 ml, leave for 30 minutes, drink 3 tablespoons for 15–20 minutes before meals) celandine herb (3 g per 200 ml, leave for 30 minutes, drink 1 tablespoon 20 minutes before meals) dry watermelon rinds (1 tablespoon per 200 ml, leave for 1-2 hours, drink 100 ml 3 times a day) of bergenia rhizomes (50 g per 1 liter, boil for 10 minutes, leave for 1 hour, drink 100 ml before meals). Pour a tablespoon of dried chamomile flowers into 1 cup of boiling water, leave in a thermos for 4 hours, strain. Take 2 tablespoons 4 times a day after meals. Use for gastrointestinal disorders. Pour 2 teaspoons of dill seeds into 400 ml of boiling water, leave for 30 minutes, strain. Take 1/2 cup 3 times a day half an hour before meals. The infusion is recommended for gastrointestinal disorders, liver diseases and decreased lactation. Dry blueberries have an astringent, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect for non-infectious indigestion, colitis and enteritis. Make blueberry infusion, tea or jelly from them. For infusion, take 4 teaspoons of fruits, pour 1 glass of cold water over them and leave for 8 hours. Consume the infusion in small sips throughout the day. Brew the fruits with boiling water and drink as tea. Cook the jelly as usual. Pour a teaspoon of potato starch into 1/2 cup of cold boiled water, stir well and drink in one serving. This remedy is quite effective in treating indigestion. Take 100 g of dry green tea, pour 2 liters of water. Leave for 30 minutes and boil for 1 hour, stirring occasionally. Pour the remaining tea leaves back into 1 liter of water and boil for 10 minutes, then strain. Mix both decoctions, pour into clean bottles and sterilize. This medicine can be stored for 3 months at room temperature, and in the refrigerator for 6 months. Take the decoction 1-2 tablespoons 3-4 times a day 20-30 minutes before meals. This remedy is also used to treat patients with dysentery. Boil 3 tablespoons of oatmeal in 400 ml of water, leave for 1 hour, drink 100 ml 1-2 times a day. For bloody diarrhea, the following are recommended: a decoction of the rhizomes of cinquefoil erecta, burnet (25 g each), shepherd's purse herbs (50 g), an infusion of the rhizomes of snakeweed, burnet (50 g each), a decoction of comfrey (10 g, pour 200 ml of milk, leave for 1 hour , drink 2 tablespoons 4-5 times a day). Cut young, unripe walnuts with green peel into slices, fill 3/4 of the bottle and add vodka. Leave for 3-4 days. Take 1/2 teaspoon no more than 2 times a day for diarrhea. It is not recommended to give to children. Pour a tablespoon of a mixture of calamus rhizome (1 part), common oak bark (1 part) into a thermos overnight with a glass of boiling water, strain in the morning. Take 1/4 cup 3-4 times a day before meals. Add a teaspoon of unbroken rice to 7 cups of cold water. Simmer over low heat until the rice is completely cooked. Give the resulting decoction without rice to a child with diarrhea, warm, 1/3 cup every 2 hours. Mix the rhizome and roots of Potentilla erectus and the bark of common oak equally. Pour a tablespoon of the crushed mixture into a thermos overnight with 200 ml of boiling water, strain in the morning. Take a tablespoon 5-6 times a day before meals for chronic diarrhea. Pour 10 g of crushed dried willow bark into a glass of boiling water and simmer covered over low heat for 20 minutes. Let cool, strain and take a tablespoon 3-4 times a day. 300 g of walnuts are chopped and the partitions that separate the parts of the grain are removed. Fill them with 250 ml of alcohol and leave for 3 days. Take 6-10 drops for diarrhea, diluting with warm boiled water. Combine the ingredients in the following proportions: cinquefoil rhizome - 2 parts, knotweed root - 2 parts, shepherd's purse herb - 3 parts, peppermint leaf - 1 part, chamomile flowers - 1 part. Pour a tablespoon of the mixture into a glass of boiling water, leave for 30 minutes, strain. Take 1/2-1/3 cup 3-4 times a day before meals. An infusion of oak leaves with vodka helps. Drink 1 tablespoon on an empty stomach. Bird cherry fruits have long been used as an astringent for non-infectious diarrhea. A tablespoon of fruit is poured into a glass of boiling water and boiled for 20 minutes, then filtered. Adults take 1/4 cup 2-3 times a day. For chronic diarrhea, take an infusion from the following collection: plantain leaves - 2 parts, knotweed herb, cinquefoil herb - 1 part each. Brew two tablespoons of the mixture with 2 cups of boiling water, leave for 30–40 minutes, strain. Drink 1/2 glass 4 times a day 30 minutes before meals. For prolonged diarrhea, drink hot tea on an empty stomach from a mixture of St. John's wort and common yarrow herbs, taken equally. Brew a tablespoon of the mixture with 1 cup of boiling water and drink as tea. Pour a tablespoon of crushed sea buckthorn leaves and branches with cold water, bring to a boil, boil for 5 minutes over low heat, leave for 30 minutes, strain. Drink at one time, repeat if necessary. An infusion of angelica officinalis root suppresses fermentation processes in the intestines, enhances the secretion of gastric juice, as well as bile secretion. Pour three tablespoons of raw material into 1 cup of boiling water, leave in a boiling water bath for 10 minutes, cool for 10 minutes and strain, bring the volume to the original volume by adding boiled water. Brew a tablespoon of crushed pomegranate peels with 1 cup of boiling water, leave until the water turns color. Drink in 1 serving. Prepare the ingredients in the indicated quantities: Japanese sophora (flowers) - 4 parts, honeysuckle (leaves) - 1 part. Brew a teaspoon of the mixture with 1 cup of boiling water. Take the infusion hot 3 times a day after meals. Pour a tablespoon of horse sorrel roots into 300 ml of water, boil for 15 minutes, leave for 4 hours. Drink 1 tablespoon 3–4 times a day before meals. Prepare the ingredients in the indicated quantities: blackberry leaves - 2 parts, calendula inflorescences - 1 part. Brew a tablespoon of the mixture with 1 cup of boiling water, leave, strain. Take 3 tablespoons per day. Brew a tablespoon of barley grains with 200 ml of boiling water, leave for 5 hours, cook for 10 minutes, strain. Drink 1 tablespoon of the decoction 4-5 times a day. Pour 2 teaspoons of peppermint leaves into 200 ml of boiling water, leave, strain. Drink the infusion throughout the day in several doses. Mix the ingredients in the indicated proportions: rowan fruits - 4 parts, marshmallow root - 2 parts, St. John's wort herb - 3 parts. Pour 500 ml of boiling water over a tablespoon of the mixture, leave for 1 hour, strain. Drink 1/2 glass 4 times a day.
Diet. It is recommended to fast for 1-2 days, depending on the severity of symptoms, to allow the gastrointestinal tract to rest. During this time, drink only hot water to compensate for fluid loss. Then gradually introduce foods into the diet.
If you have fermentative diarrhea, you should limit foods rich in carbohydrates and eat mainly protein (cottage cheese, eggs, meat and fish). For putrefactive diarrhea, on the contrary, protein foods (especially animal proteins) are not recommended and foods rich in carbohydrates (sugar, dry cookies, crackers, potatoes, jelly, porridge) are prescribed. This diet is short-term, since the diet is not balanced. As your condition improves, your food should be varied. Raw foods can be eaten after complete recovery.
It should be remembered that hot strong tea, strong coffee without milk, cocoa, decoctions and compotes of dried pears, as well as red wine have an astringent effect. One of the most effective home remedies for diarrhea is whey. It helps restore healthy intestinal microflora. Drink 3-4 times a day with a pinch of salt.
Sources: www.webkarapuz.ru, ponos-x.com, narodmediciny.ru, www.smdoctors.ru
Next articles:
Yellow diarrhea in older children
In the first months, infants have loose stools - this is the norm!
Unpleasant symptoms in children over one year old and adolescents can be caused by a number of reasons:
- Poor quality and stale food, consumption of prohibited foods.
- This is a kind of food intoxication. In mild cases, it causes only disruption of bowel movements; in severe cases, it causes serious food poisoning with pain, diarrhea, and in severe cases, disruption of the functioning of other organs.
- Infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Violation of the production of necessary digestive enzymes.
- Enzymepathies can be acquired or hereditary; intolerance to certain foods and drinks is a separate category.
- The specific symptomatology of this disease in children is a reaction to certain foods. Often in childhood, doctors are faced with hereditary enzymopathies - galactosemia, phenylketonuria, celiac disease. In addition to yellow diarrhea, the child will have other signs corresponding to a particular pathology.
- Chronic inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract - gastritis, colitis, enterocolitis. Diarrhea is one of the symptoms of the pathology. Additional signs will help make a correct diagnosis - pain in the epigastric region in different locations, the nature of the pain, intestinal bloating, the appearance of stool and the frequency of bowel movements.
- Stressful situations, nervous tension.
- Imbalance of beneficial and opportunistic intestinal microflora.
- Acute leukemia is a malignant blood disease. With this pathology, bleeding occurs from various parts of the gastrointestinal tract, ulcerative-necrotic processes in the intestines.
If yellow diarrhea appears, you should carefully monitor the child's condition. If, in addition to defecation disorders, additional symptoms appear, you should definitely contact a medical facility.
Thematic video material will tell you what diarrhea in a child means:
Diarrhea with rotten egg smell
If a person has diarrhea with the smell of rotten eggs, then most likely the problem lies in the large intestine. Colitis often provokes similar manifestations. In this case, stool may be accompanied not only by a putrid odor, but also by foam and mucus. In this case, inflammation in the colon has been going on for a long time and has worsened under the influence of external factors. Frequent bowel movements can occur up to 15 times a day. It is preceded by severe pain in the abdominal area.
If you have diarrhea with the smell of rotten eggs and there are small blood clots in it, then the cause may be dysentery. Contacting a specialist and passing all tests is mandatory.
Diarrhea with a strong odor
If a person has diarrhea with a strong odor, there can be many reasons for this. For children, such pungent odors are characteristic of rotavirus infections. In adults, strong-smelling bowel movements may be caused by:
- intestinal poisoning;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- inflammation of the large or small intestine;
- food allergies to foods eaten;
In each of these cases, diarrhea with a strong odor has specific impurities, frequency, color and many other associated factors.
Diarrhea with putrid odor
When you are bothered by diarrhea with a putrid, fetid odor, the reason may lie in inflammatory processes actively occurring in the large intestine. Often the cause of the putrid odor of diarrhea can be fermentation processes. They can be caused by eating foods rich in fiber. In this case, the patient does not experience severe pain in the intestinal area, the flatulence is not strong, but particularly foul.
Enterocolitis often provokes diarrhea with a putrid odor.
Often, the diarrhea itself, and with it the putrid smell, go away when food rich in protein and fiber is excluded from the diet. The chair is restored quite quickly.
Diarrhea with fishy odor
Often, diarrhea with the smell of fish is a symptom of very serious diseases. So, with discharge similar to rice grains with a clear smell of rotten fish, cholera can be detected.
Quite often, diarrhea with a fishy odor indicates salmonellosis. Treatment of these diseases should be carried out under strict medical supervision. Otherwise, very unfavorable consequences may occur.
In most cases, diarrhea with odor is a clear indication of an exacerbation of chronic diseases or intestinal infections. It is advisable to carry out the correct treatment prescribed by a specialist to effectively combat this symptom.
Ophthalmology department
Orthopedic traumatologist at the Avers veterinary clinic
Yellow diarrhea after antibiotics
Antibiotic drugs destroy pathogenic microflora in the intestines. But at the same time, beneficial symbionts that ensure the normal function of the gastrointestinal tract also suffer. Although gentle forms of antibiotics are currently being produced, some of which do not upset the balance of flora in the gastrointestinal tract and can be used for a long time.
In children, the balance between beneficial and pathogenic microorganisms is easier to disturb than in adults. And no one has canceled the side effects of medications. If diarrhea begins after taking antibiotics, you should monitor the child’s condition and consult a pediatrician.
If the violation of defecation was a one-time occurrence, then you should not stop taking the medicine.
Child has bad breath
Not only adults, but also children face the phenomenon of bad breath (halitosis). Sometimes it is caused by a simple failure to comply with the rules of oral hygiene, but there are also quite serious diseases that are accompanied by this symptom.
Why does my child's breath smell?
The mechanism for the appearance of bad breath in a child in many diseases is complex; parents do not need to know it, but they should be attentive to their child in order not to miss the beginning of a problem in his body.
The accumulation of food debris between the teeth, as well as in the smallest folds of the tongue, leads to their decomposition (rotting) and the release of hydrogen sulfide under the influence of microbes, which can lead to the appearance of a “rotten egg” smell from the mouth. The situation is aggravated by the presence of carious teeth.
Dry mouth is common in children, and there can be many reasons for its occurrence. Among them, difficulty in nasal breathing due to adenoids and a runny nose
, stress, anxiety, dehydration during an intestinal infection, heat or physical activity. Also, the amount of saliva (in the direction of its reduction) is affected by diabetes mellitus, damage to the salivary glands, and the use of medications (anti-allergic or anti-cold). If there is insufficient salivary secretion, a large number of bacteria accumulate in the oral cavity, whereas normally saliva washes the tongue, teeth and in itself is destructive for microbes.
Candidiasis (fungal infection) of the oral cavity is characterized by a sweetish odor from the mouth; it can appear after taking antibiotics, chemotherapy and radiation therapy, as well as against a background of reduced immunity.
If a child brushes his teeth and tongue every day, he does not have a white coating on the mucous membrane, and the smell does not go away, other organs and systems should be examined. The disease may also be the reason why
Source
What should parents do before consulting a doctor?
Smecta is a remedy for diarrhea for children.
First of all, do not panic and observe the child’s behavior. For older children, find out what he ate, drank, simply tasted, and with whom he communicated.
For babies under one year of age, carefully monitor the eating process, since when they have health problems, they first refuse food.
If, despite diarrhea, the baby actively takes the breast or drinks formula from a bottle, then most likely the yellow liquid nuisance will go away on its own.
It is advisable to give enterosorbents to children over one year of age in doses according to their age. These are enterosgel, smecta, activated carbon. Even if the enterosorbent does not stay in the stomach for long, it will collect some of the toxic substances and remove them from the body. If vomiting occurs, start drinking liquid - boiled water, weak tea, ready-made solutions for hydration.
If the temperature rises, epigastric pain appears, or the general condition worsens, the child should be urgently taken to a medical facility. Diarrhea can be a sign of a number of pathologies.
Therefore, if the issue with loose stool cannot be resolved on your own and other symptoms are added, then the child needs to be comprehensively examined. Don’t play with traditional medicine recipes and listen to the advice of strangers. You are wasting time and risking the health and life of your baby.
Perhaps the most common situation that any adult has to deal with is diarrhea in a child. The functioning of a child’s body is not entirely smooth, so some parents take such situations calmly. It should be remembered that sometimes serious infectious diseases can cause gastrointestinal disorders and cause severe dehydration of a fragile body.
Diarrhea is stool containing a large amount of water, which is characterized by frequent and sharp urges with spasms that are difficult to control. The bowel movements increase greatly: the more often the child is drawn to the toilet, the thinner the consistency.
Mom and Dad should be concerned if the stool becomes profuse and has a greenish tint. It happens up to eight times a day or even more often. This poses a danger: a significant volume of water leaves the body and the substances necessary for its development are displaced; in addition, changes in the blood are noted.
The nature of the bowel movement will indicate the cause of what is happening:
- foam indicates the development of infection;
- green color is a sign of the development of staphylococcus;
- with salmonellosis, the normal color of stool changes to swamp;
- a sign of hepatitis is discolored stool;
- The infectious disease dysentery is associated with the crimson color of stool.
Situations requiring treatment
- The frequency of stool has increased, the stool has become watery and has an unpleasant odor. Sour-smelling stool often indicates lactose deficiency. The smell is putrid, pungent and appears with a viral or bacterial infection of the intestines and the intestinal form of cystic fibrosis. Severe diarrhea more than 12 times a day indicates damage to the small intestine, most often due to a viral infection.
- Body temperature rose.
- The stool is green, foamy, with a lot of mucus, often mixed with blood. At the same time, the child is restless, refuses to eat, and does not sleep. This situation often develops with bacterial damage to the large intestine and with allergic reactions to food or medications.
- In addition to diarrhea, vomiting and regurgitation appeared, the child did not gain or lost weight. Weight change in children in the first year of life is an important indicator of health.
Breast milk is the most suitable food for newborns. It contains many useful substances and microelements necessary for the full development of the child. Typically, breastfed babies get sick less often and more easily than babies who are formula fed. But even if a child in the first months of his existence feeds only on breast milk, various problems cannot be avoided that accompany the adaptation of the child’s body to the outside world. Many parents are faced with the problem of constipation in their infants. The most important thing in this situation is not to treat the baby yourself, on the advice of a relative or friend, as this can only cause harm. Only a pediatrician can determine whether this problem is normal or pathological, and, if necessary, prescribe the correct treatment.
You need to understand that the functioning of a baby’s body differs from the functioning of an adult’s body, therefore, identifying the fact of constipation in a child should not be carried out according to the criteria for identifying it in an adult.
Causes of diarrhea
The child’s digestive system malfunctions if the body is attacked by various viruses and infections, allergens. A similar thing happens when a baby is teething, irrationally introduced complementary foods or feeding food that is not accepted by the body. The main cause of diarrhea is inflammation of the intestinal mucosa.
Infectious diarrhea
It is called the “disease of dirty hands”, because children constantly put everything they see in their mouths, and as they get older, they systematically violate the rules of hygiene. Unwashed apples, pears, plums, etc., close contact with pets, and untreated water contribute to the entry of pathogenic microbes into the child’s body. That is why, when it occurs, it is necessary to immediately eliminate the threat of infection, which is often caused by common pathogens. It is not diarrhea that causes infection, but the opposite! It happens that the child is not in pain.
Dyspepsia
Watery stools are sometimes associated with eating disorders: excessive consumption of foods rich in carbohydrates and fats, unlimited amounts of fruit, or ordinary overeating. Vomiting, nausea, and diarrhea can result from regular overeating at a party or at home.
Coordinate replacement of the established list of products is an additional cause of diarrhea that occurs in young children, which occurs during moving. A change of country or city inevitably leads to a new composition of dishes, in which previously unused products appear.
Dyspepsia in children is associated with overfeeding, when parents or another adult try to feed the child food from the “adult table”, a sudden cessation of the baby’s natural nutrition, an unadapted formula, or untimely complementary feeding. All of the above causes diarrhea, vomiting, and stabbing sensations.
Dysbacteriosis
Dysbacteriosis is a failure of the intestinal microflora. It is considered the most common cause of the disease. Diarrhea becomes chronic or is interrupted by difficult bowel movements. The process causes bursting sensations and active formation of gases in the intestines. If the disease is advanced, the stool takes on a rotten smell, becomes greenish, and the consistency includes undigested particles.
Food intolerance
A baby's aversion to milk is due to a lack of lactose. If the required substance is not produced in the required volume, each feeding ends with diarrhea containing foam and a sour smell. In infants, the reaction may be temporary, but as they grow older, lactose is produced well.
Sometimes a child's body does not accept gluten. An allergy to it is called celiac disease. The cause of the disease lies in the predisposition to an undesirable reaction to grains.
Other diseases
The alternation of profuse disorders and persistent constipation is a sign of a genetic disease - cystic fibrosis. This is the case when the glands of the digestive and respiratory systems suffer.
Particular attention should be paid to the presence of blood in the baby's stool. Similar symptoms serve as signals: colitis, Crohn's disease, intestinal yersiniosis. The listed diseases must be treated immediately.
Parents should keep in mind that if a child develops diarrhea, they will definitely have to visit a doctor, since the disease poses a danger to the child and to others.
Causes
There are not many reasons why a child has diarrhea with the smell of rotten eggs.
As a rule, bowel dysfunction is associated with viral or bacterial infections and diseases of the large intestine.
Enterovirus
Enterovirus is the general name for a group of pathologies caused by exposure to the Coxsackie virus, echo and polyviruses.
The incubation period of enterovirus infection is 7-10 days, after which the child suddenly develops symptoms of the disease, which include:
- alternation of febrile and subfebrile temperature;
- decreased or lack of appetite;
- lethargy and apathy;
- enlargement of the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes.
If a sign of an enterovirus infection appears, it is necessary to begin urgent treatment, since the condition is often complicated by inflammation in the heart, brain and spinal cord.
Be sure to watch the video about this condition
Salmonellosis
Acute intestinal infection caused by the influence of agents of the Salmonella genus on the body.
A child can become infected with salmonellosis through untreated water and thermally untreated food: dairy products, chicken eggs, fish and meat.
The disease in younger patients develops rapidly and acutely.
The first signs of infection are general intoxication, which manifests itself:
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- headaches;
- febrile temperature.
Symptoms of damage to the digestive system include:
- pain in the stomach, in the area around the navel;
- abdominal pain on palpation;
- single (in mild forms) or repeated (in severe forms) vomiting with undigested food particles or bile;
- foamy diarrhea, often mixed with green mucus and a rotten odor;
- dry tongue;
- white persistent coating on the tongue;
- flatulence.
Treatment of salmonellosis should be comprehensive and include the use of antibacterial, enterosorbent and enzyme drugs.
Putrid dyspepsia
A condition characterized by impaired digestion of proteins and their decomposition in the large intestine.
Putrefactive dyspepsia is a consequence of fast eating, in which the child does not chew food well. Pathology also develops as a result of:
- plentiful protein nutrition;
- decreased secretion functions of the pancreas and stomach;
- intestinal hypersecretion.
Rotavirus infection
The most common cause of diarrhea in children.
The main routes of infection with rotavirus are fecal-oral (through contaminated food, raw water) and airborne droplets.
Rotavirus in children is acute and is accompanied by fever, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, which often has the smell of rotten eggs.
The disease is also characterized by sore throat, weakness, and lethargy.
Dysentery
An infectious disease that affects the digestive tract, especially the large intestine.
The disease is caused by bacteria of the genus Shigella, which, when destroyed, release toxic substances that poison the child’s body.
Dysentery develops quickly and at the initial stage is characterized by signs of general intoxication. Damage to the gastrointestinal tract is manifested by dull pain in the abdomen, which subsequently “spreads” throughout the entire abdominal area and becomes sharp, cramping. The pain is localized in the lower abdomen, most often in the lower right corner, and intensifies before defecation.
The mild form is characterized by short-term fever, moderate abdominal pain, stool that has the consistency of mush and a putrid odor. A child has bowel movements up to 10 times a day.
In the moderate form, the baby suffers from cramping pain in the abdomen and a false urge to have a bowel movement. Defecation is carried out from 10 to 20 times a day, the feces are liquid, consisting of mucus and blood.
Children with a moderate form of dysentery are irritable and tearful. The skin is pale, the tongue is dry and covered with a thick white coating.
The most dangerous form of dysentery is severe, which develops rapidly and is characterized by severe intoxication and dysfunction of the cardiovascular system.
One of the main signs of the disease is a frequent urge to empty the bladder and bowels. The baby defecates constantly, the stool is liquid, watery, and has the smell of rotten eggs or rot.
Important: dysentery leads to rapid dehydration of the body, so if you suspect the development of the disease, immediate medical attention is necessary.
What are the dangers of diarrhea?
Frequent loose stools deprive the body of the necessary fluid content and nutritional components, which leads to serious disorders. For a baby this amount is 100 ml each time, for older children - up to the volume of a glass of water. All of the above leads to dehydration. In addition, salts are lost. An imbalance leads to disturbances in electrolyte metabolism and can cause the heart to stop beating. Frequent diarrhea causes a small amount of nutrients: the child loses weight, grows slowly, is inactive and indifferent.
When this condition occurs, the skin and mucous membranes dry out, crack, and dark circles appear around the eyes. The child becomes restless, has no appetite, and is constantly half asleep. A clear sign of danger is that the urine is dark and is rarely excreted in small volumes.
Help with diarrhea
The first step is to invite a pediatrician. Initial signal for contact: stool more often than 8 times a day, does not go away for a long time; watery, profuse bowel movements; the presence of blood impurities in the stool; temperature above 38 degrees; complaints of abdominal pain; changes in skin color (yellow); presence of diarrhea in other family members.
It is necessary to talk with the doctor about the child’s diet in recent days, whether he went anywhere during his summer vacation, or whether this has happened before.
Before the doctor arrives, follow the rules:
- The baby should not be fed; after a bowel movement, wash it and treat it with baby cream to avoid irritation.
- Stop dehydration.
- The baby should be fed frequently with mother's milk, and the teenager should be given tea with sugar or water with salt. In such situations, special solutions, such as Regidron, help. You can prepare your own saline solution: dilute half a teaspoon of salt and four tablespoons of glucose in half a liter of water. This mixture is given in small portions at intervals of ten minutes. At the age of up to one year, the child’s diet contains up to 700 ml of liquid, after one year to two years - 900 ml, up to five years - 1400 ml.
- Monitor your baby's well-being: temperature, blood in the stool.
If you feel worse, call an ambulance immediately! Remember that you cannot take medications without a doctor’s recommendation. Treatment is prescribed exclusively by a doctor.
Activated carbon, Smecta and antipyretics (if necessary) are acceptable.
What to give a child with loose stools?
To treat diarrhea in a teenager, use alternative medicine and a therapeutic diet. Here are a few recipes:
- Pour a glass of water into a tablespoon of fennel, oak bark, and sage. Boil the mixture and cook for 15 minutes. Drain the solution by straining through a sieve or cheesecloth. Drink 120 ml before main meals.
- Mix dried blueberries and bird cherry in a ratio of 2:3. Then pour 1 tablespoon of fruit with a glass of water and boil for 20 minutes. The liquid must be refrigerated and taken three times a day.
Diet is the key. This is a prerequisite for getting rid of diarrhea. You should not force feed your baby. The main thing is to provide his body with the necessary amount of fluid. Breastfed babies will not need to change anything: breastfeed and do not introduce routine supplements. Mom needs to avoid allergenic and bloating-causing foods. It is better to feed those who are bottle-fed with lactose-free and hypoallergenic formulas.
For other categories of children, the recommendations are as follows:
- do not use smoked, salted, fried foods; give up dairy products, peaches, bananas, grapes, cabbage, beans and peas, mushrooms, baked goods, carbonated water;
- It is mandatory to include puree soups, water porridges, and jelly in the diet;
- milk-free puree with sunflower oil;
- boiled, stewed or steamed vegetables, dried fruit compote;
- blueberries, lingonberries;
- drinks prepared on the basis of sour milk;
- steamed meat and fish cutlets.
Medications
The following medications are used to treat diarrhea:
- Enterosgel, Polysorb, Polyphepan, which bind and retain various toxins.
- Abomin, Somilase, Pancreatin, which free the stomach from accumulated food and the intestines from feces.
- Espumisan, Bebinos - for bloating and gas formation.
- Drugs that relieve spasms - Drotaverine, No-shpa.
- Intestinal flora is restored by probiotics and prebiotics.
- Loperamide and Imodium are antidiarrheals that have age restrictions. It is not advisable to take them until a diagnosis is made by the attending physician.
- For infectious diseases, antibacterial and antiviral drugs are prescribed.
- If infected with worms, use anthelmintic drugs.
- Lactrase is prescribed to infants with enzyme deficiency.
Traditional methods for black diarrhea
If a child's black stool is associated with eating food that stains, no measures need to be taken. If blood in the stool is suspected, medical attention is required. If it is not possible to see a doctor, traditional methods to stop bleeding are temporarily suitable:
- It’s easy to prepare a solution from 1 tbsp. chamomile poured with a glass of boiling water. After 20 minutes of infusion in a water bath, the solution is filtered and the patient is given 1 tsp to drink. three times a day.
- Pour a glass of boiling water over crushed oak bark. Insist 1 tbsp. l. in a water bath for 20 minutes, then remove from heat and leave for 45 minutes. The finished decoction is applied orally, 1 tsp. 4–5 times a day.
Important! Medicinal plants are used to assist in basic therapy. When you try to cure diarrhea only with herbs, the infection takes a chronic form.