Causes of diarrhea
Experts divide the causes of diarrhea into infectious and non-infectious. Diarrhea is also divided into chronic - it can bother the patient for a long time, causing damage to health, and acute - the urge to go to the toilet can bother you more than 5 times a day, while diarrhea is accompanied by pain and discomfort in the abdomen.
Infectious type
If you suspect an infection that has caused loose stools, medical attention is required. Infectious diarrhea is manifested by weakness, nausea, vomiting, stools may become green with mucus, have an unpleasant odor, and sometimes there may be an increase in body temperature.
- parasitic diseases: cyclospora, dysentery bacillus, lamblia;
- pathogenic bacteria: E. coli, salmonella;
- diseases of viral etiology: intestinal flu, enterovirus, rotavirus.
Non-infectious type
The non-infectious type of diarrhea is less dangerous than the infectious type, but also requires treatment, since prolonged loose stools can cause poor circulation and dehydration. Non-infectious diarrhea can be caused by the following factors:
- frequent use of laxatives;
- antibacterial therapy;
- frequent consumption of milk;
- thyroid diseases;
- decreased level of immunoglobulin;
- pancreatic diseases;
- insufficient production of digestive enzymes;
- the presence of tumors and cysts that cause circulatory problems;
- ulcerative colitis;
- eating disorder;
- eating poor quality food;
- intolerance of the body to certain nutrients.
Chronic diarrhea is most often not infectious; it occurs almost every day for several weeks or months. The main cause of its occurrence is poor nutrition or inflammatory diseases of the digestive system.
Each disease or factor may differ in the nature of the stool: diarrhea may be accompanied by other symptoms, have a foamy or liquid consistency, a different color (white, black, green, yellow), the presence of mucus or blood in the stool, and a foul odor.
It is not always possible to prevent the development of chronic diarrhea. However, it is possible to prevent infectious diarrhea. Follow the rules so that improper bowel function does not periodically create inconvenience:
- drink water only from clean (verified sources), use a filter;
- clean the meat thoroughly before cooking;
- fry and bake the meat well;
- wash your hands after preparing food and handling raw food;
- thoroughly wipe kitchen surfaces;
- Always wash fruits and vegetables before eating;
- do not eat in untested places where sanitary standards are not observed;
- wash your hands as often as possible, and especially after visiting the toilet, changing a diaper, or having contact with a sick person.
Chronic diarrhea and its types
Chronic diarrhea is a dangerous pathology that causes dehydration of the body. Intestinal dysfunction develops for various reasons, causing it to be divided into several types. According to the duration of the course, they are distinguished:
- acute diarrhea lasting up to 14 days;
- frequent diarrhea that has become chronic, lasting 4 weeks or more.
Loose stools are accompanied by unpleasant sensations, pain, discomfort near the rectum, and fecal incontinence.
Constant diarrhea in an adult also has its own classification, and it happens:
- secretory;
- fatty;
- osmotic;
- inflammatory.
Frequent loose stools in an adult develop under the influence of psycho-emotional factors (for example, chronic stress, depression, neuroses), gastrointestinal diseases, and intoxications. Frequent diarrhea that occurs in adults also occurs due to prolonged use of potent antibiotics.
Secretory diarrhea
The development of secretory diarrhea in adults is caused by exposure to potent drugs, fatty and bile acids, and toxic substances. Chronic loose stools are caused by stimulant laxatives (eg Aloe or Bisacodyl). Daily diarrhea and abdominal pain occur due to regular alcohol consumption. The reason why chronic diarrhea occurs in an adult may be poor absorption of bile acids.
A condition when a person’s stomach is seething and liquid stool appears, occurs due to the accumulation of bacteria in the intestines, inflammation in the ileum, its complete or partial removal. It rarely happens that frequent diarrhea occurs due to cancer:
- gastrinomas;
- carcinoid tumors;
- oncological diseases of the thyroid gland.
If diarrhea appears against the background of cancerous pathologies, it is usually accompanied by additional symptoms. However, a patient with persistent diarrhea should not immediately suspect the presence of cancer. It is better to visit a specialist and undergo the necessary tests that will confirm or refute your fears.
Osmotic diarrhea
Frequent osmotic diarrhea occurs due to an increased amount of osmolar components located in the lumen of the rectum. A peculiarity of this type of diarrhea is that liquid stool appears even with complete fasting.
Causes of frequent osmotic-type diarrhea:
- products containing mannitol or sorbitol components;
- taking medications with Lactulose, Magnesium sulfate, Oristat or constant use of Neomycin or Cholestyramine;
- short bowel syndrome;
- fistulas in the intestines;
- lack of lactase in the body (this condition can be either congenital or acquired due to inflammation in the intestines).
Inflammatory diarrhea develops against the background of intestinal inflammation resulting from:
- Crohn's disease;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- immunodeficiency;
- increased sensitivity;
- malignant tumors;
- use of cytostatic drugs;
- parasitism of protozoan microorganisms in the intestines.
Constantly loose stools in an adult can be a consequence of increased activity of the pancreas, irritable bowel syndrome, or taking prokinetic drugs (Citapride, Metoclopramide). All these problems accelerate the contraction of the intestinal walls, and as a result, a disorder of its functions occurs.
Fatty diarrhea
Fatty diarrhea is one of the most common disorders that develops as a result of a malfunction in the digestive system and malabsorption of food. Such conditions are often provoked by diseases of the pancreas. The diseased organ is unable to fully perform its excretory functions or, conversely, produces pancreatic juice in large quantities.
Intestinal dysbiosis
Dysbacteriosis is one of the most common causes of bowel dysfunction. As chyme moves forward, feces are formed in the intestines. At the same time, the processing and absorption of useful substances occurs, as well as the absorption of water and electrolytes. Digestion of food, as well as the absorption of nutrients, occurs thanks to microflora, which, during normal functioning, contains lactobacteria, bifidobacteria, E. coli and other beneficial microbes.
Dysbacteriosis can develop as a result of taking antibiotics, insufficient intake of vitamins from fruits and vegetables, reduced immunity, chronic gastrointestinal diseases, and radiation. With this disease, grade 3 or 4 diarrhea is observed, which leads to exhaustion of the patient, weight loss and the development of chronic enterocolitis. The main reasons for the development of diarrhea due to dysbacteriosis are:
- deterioration of fluid absorption;
- increased intestinal motility;
- accumulation of large amounts of bile acid.
Diarrhea when taking pharmaceutical drugs
This digestive disorder is considered drug-induced diarrhea. Most often it is provoked by antibiotics.
In addition to them, diarrhea can be caused by uncontrolled use of other medications: laxatives, antihypertensive drugs, antacids.
If diarrhea occurs while taking medications, consult a doctor. Antibiotics are not stopped; probiotics are additionally prescribed.
If intestinal upset occurs while taking any other medicine, then after consultation with a doctor, reduce the dosage or replace the drug with an analogue.
This may be a side effect of some components of the drug.
Symptoms of the disease
When pathogenic microorganisms develop in a person's intestines, diarrhea often occurs - the body's reaction to their waste products. In this case, you may feel unwell, nausea, vomiting and fever.
With infectious diseases, the stool becomes watery; in a short period of time, a person can lose up to several liters of fluid, which negatively affects the health of the body.
Depending on what kind of infection is present, the stool can change its appearance, for example, with cholera it has a liquid state, and with dysentery it is scanty and slimy.
If treatment is not prescribed in time, the disease may develop into a more serious condition. In addition to dehydration, which negatively affects the body, there is a toxic effect of microbes, the severity of which depends on the type of pathogen. This condition should not be treated independently; you need qualified assistance from a doctor who will prescribe the necessary medications.
Frequent loose stools are not the only symptom that occurs with chronic diarrhea. This pathology is one of the main signs of gastrointestinal disorder. Expanded symptoms will allow you to determine exactly why diarrhea appeared and how to treat the disorder.
- Diarrhea and severe vomiting are the result of poisoning or acute infection with intoxication. In an adult, vomiting and diarrhea occur once and disappear after gastric lavage and use of absorbent drugs. If the cause of diarrhea is an intestinal infection, then the symptoms do not disappear so quickly, but, on the contrary, increase. Additional signs appear in the form of pain in the abdomen, a feeling of squeezing and gas. The feces become gray and have a clayey consistency.
- Diarrhea, accompanied by a gag reflex or slight vomiting and a temperature of 37 °C during the first hours of symptoms, is a sign of acute appendicitis. Abdominal pain occurs periodically, gradually intensifying. During the day the temperature rises to 38 °C. In such a situation, you need to urgently call an ambulance.
- Against the background of pancreatitis, diarrhea occurs due to indigestion. The necessary enzymes are produced in insufficient quantities, so the lump of food becomes stale, fermented, gases are released and slight poisoning of the body occurs. Feces are light brown, whitish or yellowish in color.
- Intestinal parasites provoke frequent diarrhea, alternating with constipation. Feces are loose, mushy. A slight intoxication develops, nausea appears (sometimes with vomiting), headaches, high weakness, and anemia develops.
- Diarrhea also occurs due to Salmonella parasitism. This pathology is accompanied by an increase in temperature to 38–39 °C, the stool becomes greenish-brown in color, and a lot of mucus appears in it, sometimes mixed with blood.
- Liquid black stool indicates that bleeding has occurred in the intestines. This symptom signals an ulcer or Crohn's disease.
If the stomach constantly hurts and severe diarrhea begins in an adult, this may indicate the development of pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract.
It is worth noting that frequent bowel movements are not the only sign of diarrhea:
- Poisoning. Vomiting is observed, which stops after gastric lavage.
- Intestinal infection (acute), in which the body becomes intoxicated. Stomach upset continues for several days. Pains, squeezing, cramps, and gases appear in the abdomen. Feces become gray in color and have a clayey consistency.
- Acute appendicitis. In addition to diarrhea, the patient's temperature rises, severe pain develops, and vomiting occurs.
- Worm infestations. In patients, the process of defecation is disrupted, nausea, a gag reflex, headaches appear, anemia develops, general weakness, and the temperature rises. Liquid stool becomes dark or greenish-brown in color and may contain blood and mucus.
- Bleeding in ulcerative pathologies. The stool becomes black, severe pain appears, gas formation, dry mouth, thirst, etc. increase.
Treatment
Treatment for diarrhea depends on the cause. In this case, both neutral, preventive agents and weak antibiotics against the growth of pathological microorganisms can help. In case of acute infection, a special strong drug is selected under the supervision of a doctor.
List of modern anti-diarrhea drugs:
Regidron
(and gastrolit) are general purpose drugs. Used for all types of diarrheal conditions. Restores the water-salt balance of the body. Frequent bowel movements in an adult lead to the rapid elimination of electrolytes such as sodium, calcium and potassium. The preparations contain these microelements for replenishment, as well as glucose.
The approximate price is 19 rubles for 1 sachet.
It is not advisable to restore fluid during attacks of vomiting.
Smecta
It can help both adults and children. The drug is obtained from natural ingredients (shell rock). It has the property of a safe absorbent, absorbs and removes toxins, excess enzymes, bile acids. Protects the intestinal walls from further damage, erosion, restores microflora.
The approximate price is 151 rubles for 10 sachets, the cost of 1 is within 25 rubles.
Enterosgel
Absorbent, safe for children, pregnant women and adults. Available in the form of a paste in tubes. Composition of the substance: colloidal silicon dioxide, few contraindications. It works the same way as Smecta.
Approximate price from 230 – 300 rubles.
Enterol
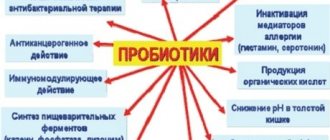
Probiotic based on the direct effect of Saccharomycetes boulardii on pathological bacteria and intestinal infections, spectrum of action: salmonella, shigella, yersinia, yeast-like fungi Candida, amoebas, lamblia. Does not destroy beneficial microorganisms, destroys bacterial toxins. Accelerates and stimulates the synthesis of polyamides in the intestine, acts as an immunomodulatory drug. Useful for any diarrhea.
Approximate price – 270-500 rubles.
Hilak Forte
The prebiotic, available in the form of an acidic liquid with a dropper in a bottle, contains ready-made beneficial microorganisms for populating the intestinal microflora. Used for dysbiosis, dyspepsia, constipation.
Approximate price – 240-490 rubles.
Bactisubtil
A bacterial preparation that contains spores of Bacillus subtilis bacteria, which create an acidic environment in the intestines, thereby killing pathogens. They secrete beneficial enzymes.
Approximate price: 800 rubles.
Enterofuril
An antiseptic that acts against gram-negative bacteria, it has the greatest effect on staphylococci and streptococci.
Approximate price – 329 rubles.
Treatment with folk remedies
What to do and how can you help the body calm the symptoms of diarrhea and normalize stool? For non-infectious gastrointestinal disorders, you can use folk remedies:
- To create an acidic environment in the intestines, you can use an aqueous solution of apple cider vinegar or lemon juice. For 1 glass of water – 1 tablespoon of apple cider vinegar or lemon juice.
- Pomegranate peels have a weak antimicrobial and astringent effect. Make a decoction when frequent loose stools are observed. Take 2 tablespoons of crushed fresh pomegranate peel, pour a glass of water and boil on the stove for 20-30 minutes.
- Rice water - soothes the intestines, normalizes stool. You need to take a handful of unwashed rice and add plenty of water. The cooked rice water is filtered and taken every 3-4 hours.
- Chicken stomach, against diarrhea, use dry powder made from the inner lining of the chicken stomach.
- To cure diarrhea at home, use potato starch. A teaspoon of starch is diluted with a glass of water, shaken and drunk.
- A decoction of oak bark is taken as an antidiarrheal agent: a teaspoon of bark in a glass of water, boiled for 10 minutes.
- Dried bird cherry berries also have astringent properties; you can prepare a compote decoction: 1 tablespoon of dried berries per glass of water, simmer for a while over low heat. Blueberries are also recommended - dried or fresh berries.
Pancreatitis
With pancreatic disease, one of the clinical manifestations is diarrhea. The pancreas is actively involved in the process of digesting food and when its functioning is disrupted, namely, when diagnosing chronic pancreatitis, stool disturbance is always observed. This disease is characterized by a decrease in the production of enzymes involved in food digestion.
Diarrhea with pancreatitis occurs due to the fact that fragments of digested food enter the large intestine. A high amount of nutrients activates bacteria, resulting in a putrefactive and fermentative process, leading to bloating and stool disturbances.
Stool with pancreatitis often has a liquid consistency, usually mushy with inclusions of undigested food. In addition to diarrhea, inflammation of the pancreas also manifests itself in other symptoms: pain in the lower back or left side, nausea and lack of appetite.
Causes of pathology
Chronic diarrhea in adults develops due to impaired microflora of the intestinal mucosa (in medicine this is called dysbiosis). Pathology manifests itself as a result of long-term use of antibiotic drugs and drugs with bactericidal properties.
Diarrhea can be nutritional, and develops due to erratic, improper food intake. The pathological condition occurs as a result of a sudden change in diet (for example, when switching to complex animal proteins or foods of plant origin). Such adverse consequences result from drinking carbonated drinks or alcohol along with meals.
When poisoning occurs, sharp pain, vomiting, hallucinations (up to loss of consciousness), and sometimes fever appear in the abdomen. Severe poisoning is accompanied by diarrhea with severe symptoms. There are several reasons that cause intestinal upset.
- Entry into the body of bacterial or infectious pathogens (salmonella, cholera, dysentery bacillus).
- Dysbacteriosis caused by taking potent medications.
- Crohn's disease.
- Poisoning of the body with chemicals or poor-quality food with the addition of infection.
- Chronic pancreatitis.
- Nonspecific ulcerative colitis.
- Parasites in the liver or intestines (enterobiasis, lamblia).
- Impaired production of pancreatic enzymes (excess or deficiency).
If diarrhea continues for a long time, you should pay attention to the color and consistency of the stool. Using them, you can find out the true cause of the disease.
Prevention
To prevent diarrhea, it is recommended to monitor the state of the intestinal microflora. During a course of antibiotics, you need to take products that support healthy microflora.
Preventive intake of metabiotics, for example, the drug Actoflor-S, supports local and general immunity, improves the condition of the intestinal mucosa and promotes the growth of its own beneficial bacteria.
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis
Also, one of the causes of bowel dysfunction is diseases of the large intestine, in particular ulcerative colitis. Most often, this disease affects people from 20 to 40 years old, and it is characterized by the following symptoms:
- diarrhea;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- the presence of mucus or blood in the stool;
- bloating.
95% of patients with ulcerative colitis complain of the appearance of loose stools, which prevents them from living fully and enjoying life, since the frequency of bowel movements can occur about 4 times a day in the chronic form, and more than 5 times in the acute form. Often, diarrhea can be replaced by constipation.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of the suspected pathology is carried out by a doctor after a preliminary conversation with the patient. The specialist finds out the nature of the disorder (acute or chronic), then takes stool for analysis and checks whether the problem remains if the person completely refuses food. A set of diagnostic procedures allows you to find out the exact cause of persistent diarrhea.
If the disorder is chronic, you must quickly undergo the required blood tests:
- general;
- identifying the concentration of vitamin B12 (diarrhea when taking vitamins);
- Ca concentration level;
- folic acid level;
- checking the correctness and completeness of the functioning of the thyroid gland and liver;
- Fe concentration;
- study of biomaterial for celiac disease.
The causes of chronic diarrhea necessitate additional tests that will help confirm the diagnosis and prescribe adequate, effective treatment. Taking into account the patient’s complaints, the doctor prescribes special examinations:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
- Colonoscopy, during which a biopsy of the intestinal mucosa is taken for further histopathological examination.
- X-ray of the abdominal cavity.
The patient will be required to undergo a set of laboratory and instrumental tests:
- Analyzes of stool, urine and blood.
- Examination by a proctologist.
- Ultrasound.
- Gastroscopy.
- Sigmoidoscopy.
- Colonoscopy, etc.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the causes of the tray begins with an analysis of complaints and symptoms. During the examination, the doctor asks a number of questions in order to understand which organ disease could cause bowel dysfunction.
For an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to carry out the following studies:
- Coprogram.
- Analysis of stool for dysbacteriosis.
- Examination of feces for occult blood.
- Stool culture with determination of bacterial sensitivity to antibiotics.
- General blood analysis.
- General urine analysis.
- Blood chemistry.
- Immunogram.
- Analysis of thyroid hormones.
- Lactose test.
In addition to laboratory tests, in case of chronic diarrhea in an adult, an examination of the entire gastrointestinal tract is performed. The doctor prescribes sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy if he suspects a pathology of the colon. To exclude diseases of the upper digestive tract or biliary tract, an X-ray examination of the stomach and small intestine is performed. The function of these organs is assessed using gastroduodenoscopy, during which the doctor examines the organs from the inside and then takes gastric or small intestinal juice for laboratory testing.
Additionally, the doctor may prescribe an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, as well as Dopplerography of the abdominal vessels.
What you need to know during treatment
If frequent diarrhea occurs, you should consult a doctor, he will prescribe tests and diagnostics, which will help identify the cause of bowel dysfunction. First of all, treatment is aimed at eliminating the unpleasant symptom with the help of antidiarrheal drugs, while simultaneously treating the underlying disease.
Since diarrhea severely dehydrates the body, the doctor additionally prescribes rehydrating drugs (Normasol, Gamtrolit, Regidron, etc.), which restore the water-salt balance in the body. Also, during treatment, it is important to drink enough liquid and monitor your diet (exclude: spicy foods, fresh fruits and vegetables, alcohol).
We recommend that you read
- Diarrhea in a child, causes and treatment of diarrhea
- Treatment of diarrhea at home in adults, quickly and effectively
- Fast acting diarrhea tablets for adults
- Treatment of IBS - irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea
- Diarrhea due to pancreatitis
- Folk remedies for diarrhea in adults
Treatment of chronic diarrhea is based on changes in the diet plan and the use of irrigation. The use of probiotics and drugs that help maintain intestinal motility is also recommended. Antibacterial medications also have a good effect. If medications are the cause of diarrhea in adults, then it is better to stop using them.
Treatment of chronic diarrhea is not an easy procedure. Sometimes it is provoked by nonspecific inflammatory processes in the intestines caused by ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease. In this case, the doctor prescribes symptomatic therapy, which helps reduce the severity of negative symptoms. It is mandatory to take medications that compensate for the lack of microelements.
If diarrhea continues for a long time, its treatment is carried out with medication or using traditional recipes. Remember that persistent diarrhea can be cured only after receiving medical advice. The specialist conducts diagnostics, finds out the causes of chronic diarrhea, and then develops a suitable treatment regimen.
The recovery course for persistent and persistent diarrhea is based on the use of a complex of medications.
- Medicinal compounds that reduce the level of mucus secretion in the intestines. They are recommended to be taken in the first days after the onset of abdominal pain and loose stools (to prevent the pathology from becoming chronic). Anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Sulfasalosin) effectively fight Crohn's disease.
- Sorbents (Smecta, De-Nol) are the basis of the therapeutic course for those patients who often have diarrhea. They reduce the formation of gases in the intestines, reduce bloating, and remove harmful bacteria and viruses.
- Medicines to reduce intestinal motility will help stop diarrhea (Imodium, Loperamide, Octreotide), but they are not prescribed if diarrhea is caused by an infection.
- Fermented drugs are prescribed when chronic diarrhea develops as a result of gastrointestinal diseases, and its treatment is based on the use of Mezim, Festal or Creon.
Additionally, many doctors recommend taking activated charcoal (1 tablet per 10 kg of weight) for abdominal pain and diarrhea.
If the symptoms do not worsen and there is no pain in the abdominal area, try to eliminate the diarrhea. Take antidiarrheal medications, but this is a short-term solution. If medications do not help for a long time, do not abuse them, but consult a doctor.
Pay attention to the diet: perhaps diarrhea is the body’s reaction to a specific product. To find out which food triggers your frequent cravings, keep a food diary. After a few weeks, the food causing the illness will become clear. You will need to exclude the dish from your diet.
Recommended:
- avoid caffeinated, sweet and alcoholic drinks;
- consume foods low in fiber;
- drink more water;
- don't overeat.
Include probiotic-containing foods in your diet (yogurt, kefir, cottage cheese, dark chocolate, sourdough bread, etc.). “Good” bacteria restore the functioning of the intestinal tract.
We treat the cause
Simple measures do not help - consult a doctor and find out the underlying ailment. In this case, diarrhea is a symptom; it is necessary to eliminate the root cause. You will have to spend a lot of time and effort, but this is how you select the right therapy and prevent life-threatening consequences.
- A triple stool test is needed to determine the presence of parasites, as well as leukocytes, signaling the presence of inflammatory processes.
- Blood tests determine albumin content, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, liver function tests, analysis of thyroid-stimulating hormone levels, and iron content.
- A biopsy examines the presence of pathological conditions.
- X-ray studies make it possible to diagnose dilation of intestinal loops - tumors, polyps, ulcers and other pathologies.
After conducting the necessary research and establishing a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment for a specific disease. Complex therapy, a regular diet and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are prescribed.
Treating complications
Acute diarrhea is harmless in most cases. With chronic diarrhea, there is a risk of dehydration due to large loss of fluid. Warning signs:
- dark urine;
- constant thirst;
- intense sweating;
- fatigue;
- nausea;
- temperature increase;
- insufficient skin elasticity.
Dehydration can become life-threatening - the patient suffers from dizziness, possible fainting and confusion, kidney failure, shock and death. Remember to consume fluids, including water, broths, and unsweetened decaffeinated tea.
You can buy medications at the pharmacy. They will maintain or restore the balance of salts in the body. If you can’t visit a pharmacy, a saline solution is suitable - it will help effectively cope with diarrhea; it can be prepared at home. To do this, dilute 1 tablespoon of sugar, 1 teaspoon each of salt and soda in warm boiled water. Drink carefully after cooling.
Complications
For diarrhea that lasts several days and is accompanied by fever, antidiarrheal drugs should not be used. In case of infectious inflammation, diarrhea is a protective reaction of the body. Medicinal strengthening of stool without a doctor’s prescription can result in the retention of toxins in the body.
If you have watery stools, it is very important to prevent the loss of water and salts in your stool. Therefore, to prevent dehydration, you need to drink plenty of fluids.
Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is one of the most severe diseases associated with an inflammatory process in the digestive tract, which affects all layers of the intestine: submucosal, muscular and mucosal. The inflammatory process can occur in the lower and upper segment of the digestive tube, but most often it is the small intestine that is affected.
Crohn's disease has 3 degrees of severity:
- In mild cases of the disease, the incidence of diarrhea is no more than 4 times, streaks of blood in the stool are absent or weakly expressed.
- Moderate severity is manifested in more frequent bowel movements, up to 6 times. The presence of blood in stool can be detected with the naked eye.
- Severe disease is characterized by the occurrence of diarrhea more than 10 times a day, in which case complications such as bleeding, abscesses and fistulas may occur.
Folk piggy bank recipes against diarrhea
Traditional medicines can help cure abdominal pain and chronic diarrhea in men and women. In the first days of deterioration, they help normalize intestinal function. We bring to the attention of readers several popular recipes from the people's piggy bank.
- Herbal decoctions prepared from chamomile, bird cherry, oak bark. They can be taken throughout the day, and the raw materials for them are sold at the pharmacy.
- Herbal mixture of immortelle (4 tbsp), sage (2 tbsp), St. John's wort (2 tbsp), rhubarb root (1 tbsp). All ingredients are mixed, the resulting composition is taken in the amount of 2 tbsp. l. and steam with a glass of boiling water. Then the product is infused in a water bath for 10 minutes, and then another half hour in a dark place. When the infusion is prepared, filter it and take 1/3 cup three times a day until bowel movements normalize.
- Collection of herbs from calendula, chamomile, blueberry and plantain leaves, calamus rhizomes, activated carbon tablets and caraway seeds. Each of these components is taken 1 tbsp. l., pour 1 glass of boiling water and leave in a water bath for 15–20 minutes. Then the infusion is cooled, decanted, and the missing volume of liquid is topped up with boiling water. Take anti-diarrhea medication 1/3 cup three times a day.
- A good remedy for constant loose stools are dill seeds. They are ground to a powdery state, then take ½ tsp. the resulting product and pour 1 glass of milk. The mixture of components is boiled for 3 minutes, then cooled and drunk 4 times a day.
- For intestinal disorders, a collection prepared from agrimony, Chernobyl, chicory, plantain, mint, oregano, yellow bedstraw, city gravilat, geranium, chamomile, and burnet helps. This fee is taken in the amount of 2 tbsp. l., pour 0.5 liters of boiling water, wrap warmly and leave for 1 hour. The infusion should be drunk warm, 0.5 cups, half an hour before meals. It is consumed 4 times a day, the last time being before bed. The composition is also suitable for the treatment of diarrhea in children. Babies under 1 year old should be given 1 tbsp. l. 4 times a day, for children 1–2 years old, take 2 tbsp. l., 3–6 years old – ¼ cup each, and 7–12 years old – 1/3 cup each.
- A mixture of dogwood juice, blackberries and grapes has good effectiveness in combating indigestion. The active components of the berries help get rid of dysentery microbes in the intestines. Half a glass of juice daily will help improve intestinal microflora and normalize the bowel movement process. If intoxication develops during use of the drug, it is better to stop treatment with it.
How to eat properly?
Treatment of any form of diarrhea includes mandatory diet. Eating the necessary food and avoiding unhealthy foods is half the success of therapy. The menu of an adult patient should include the following products:
- Low-fat fish and meat broths.
- Bread crumbs (made from wheat flour, optionally with added bran).
- Cool rice broth.
- Rice and oatmeal porridge, cooked in water.
- Steam omelet from several eggs.
- Meat - low-fat varieties (it can be steamed or baked in the oven).
- Steamed fish (pollock, sea bass and some others).
- Bananas and baked apples are suitable as food.
The patient needs to drink plenty of fluids. You need to use herbal decoctions, weak teas, unsweetened dried fruit compotes, jelly, and fruit drinks. If you suffer from constant diarrhea, then it is better to avoid adding seasonings and spices to your dishes.
The list of prohibited foods for diarrhea is quite wide. This includes everything fried, fatty, pickled, salted, smoked, as well as preserved food. All confectionery products are not recommended for loose stools. The most strict diet, including complete abstinence from food, should be followed on the first day of the development of the disease. Only accurate identification of the causes and comprehensive treatment will allow you to get rid of constant loose stools.
Psychosomatic causes of diarrhea
The human body is a complex mechanism that reacts to any negative factors, including poor mental health. Therefore, very often diarrhea appears when a person experiences severe nervous shock. Diarrhea and frequent worries can provoke serious illnesses, and most of them are psychosomatic in nature.
For some people, when fear arises, not only their movements, but their entire body becomes stiff. Many patients, when experiencing fear, in addition to the urge to go to the toilet, are bothered by abdominal pain and other unpleasant sensations. After the fear goes away, the stool may remain liquid throughout the day. If diarrhea occurs frequently due to anxiety, experts recommend taking sedatives.
Constant diarrhea in an adult can be caused by various external and internal factors:
- enterobiasis (the cause of the development of pathology is the pinworm, which parasitizes the large and small intestines);
- penetration of Giardia into the intestines (infection occurs due to eating unwashed fruits and vegetables);
- dysentery (the frequency of bowel movements can reach 10 times a day), in which mucus and blood are detected in the stool;
- salmonellosis (stool takes on a consistency that can be compared to swamp mud);
- lack of enzymes in the pancreas (stool becomes gray in color and has an oily, shiny surface).
The main causes of regular diarrhea
Factors influencing the occurrence of diarrhea:
Spasmodic pain in the abdomen, deterioration in health, and frequent bowel movements are common symptoms of an intestinal infection. During the examination, this group of diseases is first excluded.- A pathological condition in which there are no obvious lesions of internal organs is irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). This disease develops as a result of stress and prolonged emotional tension.
- Long-term use of the medicine provokes indigestion. You should tell your doctor about this at your appointment. Perhaps diarrhea is a reaction to some component of the drug.
- Intolerance to lactose, gluten, and animal protein causes chronic diarrhea. A person may not even be aware of an allergy. In this case, it is necessary to monitor which foods make you feel worse after consuming them.
- Helminthiasis leads to bowel dysfunction.
- Inflammation, erosion, tumors in the digestive organs are manifested by diarrhea.
- Dysbacteriosis after taking antibacterial agents.
- Poor nutrition, overeating, non-compliance with diet for diseases of the stomach and intestines.
- Chronic pancreatitis is a severe pathology of the pancreas, which is accompanied by regular diarrhea.
Additional reasons include the following: lack of personal hygiene, dental disease, insufficient chewing of food, decreased immunity.
Diet food
When the causes are determined and treatment is prescribed, it is worth taking another important step on the path to recovery, namely, reviewing your diet. You should drink plenty of water to prevent dehydration. Doctors recommend giving up physical activity and following a diet. In addition to water, you can drink tea, compotes, and fruit drinks. To make things easier on your stomach, you should take your food with a small amount of liquid.
Natural pectins must be present in food. They are found in large quantities in yogurt, banana pulp and applesauce. Foods that contain a lot of potassium (milk and dairy products, boiled potatoes, fresh fruits) help normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Remember to salt your food and use enough salt. This component will help retain water in the body. The diet should contain protein foods. Eat boiled eggs, boiled chicken, fried turkey meat.
It is better to exclude raw vegetables from the menu, because fresh plant fibers can cause a deterioration in the condition. Before use, they are blanched or doused with boiling water. Firm vegetables (zucchini, asparagus, celery) are immersed in boiling water for several minutes.
You should know what aggravates the condition of chronic diarrhea. Prohibited products include caffeine, which is found in large quantities in carbonated drinks, cocoa and coffee. They should be completely removed from the diet. It is also recommended to avoid heavy and fatty foods (for example, those cooked with a lot of fat or oil).