Causes
Foamy diarrhea is a nonspecific syndrome that can be either a sign of minor disturbances in the functioning of the intestines or the first manifestation of serious diseases.
Foamy diarrhea can occur when:
- Lactase deficiency
- Antibiotic-associated syndrome
- Pseudomembranous colitis
- Celiac disease
- Salmonellosis
- Food allergies
If diarrhea with foam occurs against the background of a change in the color of the stool, a foul odor appears and the temperature rises, you should urgently consult a doctor, as such symptoms may be a sign of a serious intestinal infection.
Next, we will consider the common causes of foamy stools in adults in more detail.
Lactose intolerance
Intolerance to the main component of dairy products, lactose, is quite common. Due to the lack of an enzyme that breaks down the substance, milk enters the intestines almost unchanged and becomes a nutrient medium for the growth of microflora. The enzyme may not be completely absent, so many people have no idea about the causes of periodic digestive disorders. Moreover, a number of people with intolerance can even eat cottage cheese and hard cheese.
The main symptoms appear about half an hour after consuming dairy products. Occurs:
- Foamy stool
- Flatulence
- Feeling nauseous
- Cramps and rumbling in the intestines
- Possible vomiting
Most often, lactose intolerance manifests itself in childhood, but can also occur in adults, after rotavirus infection, long-term use of antibiotics, as well as with other chronic intestinal diseases (celiac disease, Crohn's disease).
Celiac disease
Celiac disease, or celiac disease as it is also called, is characterized by atrophy of the villous tissue of the small intestine due to an inflammatory reaction to gluten (a substance found in many grains). Symptoms often begin in childhood, then subside and return again after age 30.
The main manifestations of celiac disease are:
Profuse foamy diarrhea with undigested food- Discharge with fatty impurities
- Weight loss
- Bloating
- Abdominal pain
- In childhood, there is a delay in growth and weight
Due to insufficient absorption of essential substances from food, other diseases may appear, such as anemia, defects in tooth enamel, and joint pain. Therefore, if you notice that foamy diarrhea has begun to occur quite often, especially after eating cereals, flour products and pasta, you need to consult a doctor to select the necessary treatment. Symptoms of celiac disease can be completely eliminated after dietary adjustments and drug therapy.
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD)
Long-term use of antibiotics inhibits the growth of lacto- and bifidobacteria, which normally populate the intestines and help digest food.
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea is a clinical diagnosis, in contrast to dysbiosis, which, as a rule, does not occur in practice (implies the complete destruction of microflora, which is possible only in people with immunodeficiency).
Despite the frequent substitution of terms, antibiotic-associated diarrhea can actually be quite dangerous when it develops into a severe form - pseudomembranous colitis (chronic inflammation with a violation of the integrity of the intestinal walls). People over 65 years of age and patients staying in hospital for a long time are most susceptible to this disease.
Most often, diarrhea with foam in an adult occurs after taking the following antibiotics:
- Clindamycin
- Cephalosporins
- Aminopenicillins
- Quinolones
- Macrolides
With antibiotic-associated diarrhea, symptoms can range from mild and manifest as infrequent (up to 3-5 times a day) foamy stools and abdominal discomfort, or become severe with frequent diarrhea and vomiting.
When an imbalance of microflora occurs in the human body, susceptibility to infectious diseases, especially viral ones, increases.
Drug treatment for foamy diarrhea
The treatment for foamy diarrhea in an adult will depend on the cause of its occurrence. The most important thing is not to try to diagnose yourself, and not to use self-medication methods to relieve symptoms. Any medical procedure must be coordinated with a medical specialist.
- If the appearance of yellow foamy diarrhea occurred one-time and is mainly associated with a malnutrition, then the best solution would be to take an adsorbent (Filtrum-Sti, White Coal, Activated Carbon). Sorbents will absorb harmful substances that cause intestinal irritation, pain and diarrhea and remove them from the body naturally. Since these drugs also absorb a lot of water from the body, while taking them you should drink filtered or boiled water often and in large quantities.
- When diarrhea caused by allergies occurs, medical specialists prescribe not only adsorbents, but also antihistamines to reduce the number of allergy symptoms and alleviate the patient’s condition.
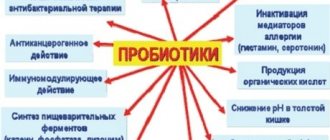
- Disturbances in the intestinal microflora and diarrhea that arise as a result of them are stopped by taking medications that contain beneficial bacteria and microorganisms or create a positive environment for the development of surviving intestinal bacteria. Such drugs are taken over long courses and under the supervision of a doctor, since they are prescribed only after thorough laboratory diagnostics.
- When infectious diseases are detected, the doctor makes a decision: to prescribe antibiotic treatment to the patient at home or, in especially dangerous and complex cases, to send him to a hospital for treatment.
- If diarrhea was caused by parasitic diseases, strictly specific medications are prescribed, the action of which is aimed at one or another type of parasite (Dekaris, Nemozol). In case of parasitic diseases, not only the sick person, but also his family members need to undergo radiation treatment. It is necessary to treat for parasites and pets.
Nutrition for diarrhea
In addition to taking medications, the patient must follow a special diet to successfully get rid of unpleasant symptoms. There are certain nutritional standards for diarrhea. There are cases when, to recover, it was enough to simply exclude some harmful foods from the diet.
- If diarrhea occurs, you must avoid harmful, intestinal irritating foods, processed foods, home-canned food, fermented milk products, and fruits that cause dyspepsia. The patient should eat unsalted rice boiled in water. For baked goods, only rye bread is acceptable, and for fruits, bananas.
- A prerequisite is strict adherence to fluid balance in the body. Diarrhea causes severe dehydration, so the fundamental factor in the diet for diarrhea is drinking plenty of fluids. Drinking non-carbonated alkaline mineral water will be beneficial. The use of herbal teas is acceptable in cases where there is no allergy.
- First of all, it is necessary to restore intestinal functions lost during illness and soothe painful sensations if the stomach hurts. Therefore, those foods that cause irritation should be excluded from the diet.
If you follow these simple rules, your stool will soon return to normal and the problem will be resolved. Returning to normal foods and a normal diet should be slow and careful. You need to introduce different foods one at a time, carefully monitoring the condition of the body.
Folk remedies
In cases where diarrhea was not provoked by a dangerous disease in the body, you can use simple folk methods to strengthen stool at home. Infusions and decoctions of medicinal plants (St. John's wort, yarrow, rose hips, chamomile) and various fruits containing stool-strengthening substances (bird cherry, blueberries) have long been used. Various nuts (walnuts, hazelnuts) are good for getting rid of diarrhea.
It must be remembered that diarrhea with foam in prolonged cases can lead to dehydration, weakness and exhaustion of a person. If you do not pay attention to the symptoms of foamy diarrhea and a sore stomach in time, the consequence may be intestinal inflammation. Therefore, you need to take the disease responsibly and consult a doctor in time.
Diagnostics
If the illness lasts more than 2 days, is accompanied by vomiting, increased diarrhea and a strong increase in temperature, you need to visit a specialist to find out the causes of the illness.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, carry out:
- Bacteriological analysis of secretions
- Coprogram
- Colonoscopy or irrigoscopy
- Breath tests to detect antibodies
- Sigmoidoscopy
- X-ray with barium contrast
- Ultrasound or CT scan of the abdominal cavity
- Exercise tests (to identify food intolerances)
A general blood and urine test is also prescribed to identify inflammatory processes in the body.
What symptoms accompany diarrhea with foam?
In adults and children, diarrhea with foam is accompanied by a number of additional symptoms. They are not so characteristic as to establish a diagnosis, but they clearly indicate the origin of the disease:
- An increase in temperature in an adult or child is a characteristic sign of infection. Foamy diarrhea does not always cause fever, but if left untreated, it certainly leads to a worsening of the condition: vomiting, nausea, stool changes color, and acquires a foul odor. If such signs occur, you should consult a doctor immediately.
- Dysbacteriosis rarely causes fever, but provokes weakness, drowsiness, and lack of appetite. If the disease is ignored, signs of intoxication appear.
- In a newborn, the disorder is most often accompanied by white foam. This means that the diarrhea is caused by a secondary lactase deficiency or a difference between the so-called foremilk and hindmilk. This happens when a woman changes breasts while breastfeeding.
- In adults, diarrhea with white foam is a sign of inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. Diarrhea is accompanied by stomach pain and rumbling in the abdomen.
- Another nonspecific sign is skin rashes. Occurs both with an allergic reaction and with sensitive skin.
[adsp-pro-6]
Important! You should call a doctor immediately when you need emergency help. The appearance of bloody impurities in green stool, pain during defecation, and increased temperature are a clear sign of an acute disorder.
Treatment
The main therapy is prescribed according to the identified disease and the severity of its manifestations. However, if the symptoms do not bother you too much, and there are no additional signs of deterioration in your health, you can try to eliminate the diarrhea on your own.
If the frequency of bowel movements exceeds 4 times a day, you need to dilute 1 packet of Regidron per liter of water and drink throughout the day. This will help cope with the loss of water and mineral salts.
For an astringent effect and removal of toxins, use Smecta, Enterosgel, Polysorb or Atoxil. These drugs also have an antimicrobial effect and promote wound healing. Thanks to their enveloping properties, they protect the intestines and relieve inflammation.
For one-time use, you can take drugs that normalize peristalsis. Loperamide hydrochloride (Imodium) is a good choice, as it slows down motility and restores food digestion.
After diarrhea stops, you need to take a course of probiotics, which will help restore beneficial bacteria. You can use Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Hilak-Forte. These preparations contain live lacto- and bifidobacteria, which repopulate the intestines and restore its natural immune barrier.
Causes of diarrhea
Loose, foamy stools can be caused by viral or bacterial pathogens, which lead to the following diseases:
- Rotavirus infection, or intestinal flu, is a dangerous infectious disease that is accompanied by nausea with vomiting, diarrhea with green stool, and severe dehydration.
- Dysbacteriosis occurs when the number of harmful bacteria prevails over beneficial ones. This imbalance can be caused by taking antibiotics, and its symptom will be yellowish foamy diarrhea.
- Parasitic infestation – that is, the appearance of unpleasant “guests” in the body. Antihelminthic drugs will help get rid of foamy stools.
- Inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract of various etiologies, including ulcers, enterocolitis, Crohn's disease and others, the symptom of which is loose stools with the presence of white foam.
- Lactase deficiency in a child, when the body cannot digest milk sugar due to a lack of lactase in the body. In adults, it can be caused by pathologies of the pancreas.
- Allergic reactions - when drugs or products that cause allergies irritate the intestines.
All these and some other reasons, for example, poor nutrition, insufficient chewing of food and overeating, taking foods that cause flatulence and fermentation in the intestines, excessive alcohol consumption, even stress can lead to foamy diarrhea in an adult - a phenomenon that is not only unpleasant, but also requiring sometimes urgent medical intervention.
This is especially important if the cause of intestinal disorder is serious pathology - frequent loose stools lead to dehydration of the body, and lack of fluid and intoxication can cause cardiac dysfunction, a sharp deterioration in well-being, even death.
Folk remedies
Some folk methods, when used correctly, help relieve symptoms and somewhat reduce the manifestations of the disease.
Here are some recipes to help stop diarrhea:
1. A small amount of rice, approximately 50-100 grams, is boiled until a decoction of a viscous consistency is formed. Then add one teaspoon of starch to the resulting mixture (which is previously diluted in cold, preferably boiled water). The resulting decoction is consumed in one dose.
2. Chopped rosehip root is poured with a small amount of water and boiled over low heat for 10 minutes. Then, the liquid is allowed to brew for about an hour. Drink 3-4 times a day.
3. Pour 100 grams of burnet into boiling water and cook for 10-15 minutes. By analogy with rose hips, the decoction should be left for about an hour, strained, and taken 5-6 times a day in the amount of 1 tablespoon per glass of warm water.
You should refrain from using these drugs after diarrhea has stopped, since the large number of astringent components in their composition can lead to undesirable effects such as constipation, nausea and discomfort in the intestines.
Treatment of loose, foamy stools
To diagnose bowel disorders, consult a gastroenterologist. The doctor will begin to diagnose, based on the laboratory data obtained, and prescribe therapy. Treatment occurs in a complex of medications and a therapeutic diet.
Use of drugs
In some situations, self-medication becomes dangerous to health. If the patient is suspected of having an intestinal infection, then therapy must be carried out in a hospital setting. First of all, the patient is prescribed drugs that eliminate foamy feces. For this, Imodium or Loperamide is used.
Antibiotics are not prescribed for foamy stools. Many causes of unpleasant symptoms cannot be treated with such medications. During loose stools, the patient needs to restore the intestinal microflora. Therefore, probiotics are prescribed:
- Linux;
- Bifidubakterin Forte;
- Hilak Forte.
Lactose intolerance
Diarrhea with foam in infants usually occurs as a result of a conflict between the front and rear breast milk. Most often, a small child sucks out the foremilk because it is easiest to obtain, while the hindmilk remains in the breast. In this case, the baby has difficulty digesting large amounts of lactose, which leads to lactose deficiency. It appears as follows:
- deterioration of the child’s well-being;
- loose, foamy stools with an unpleasant sour odor;
- nausea, vomiting;
- increase in body temperature.
Lactose deficiency can be congenital and is associated with the inability of the pancreas to produce lactose. It is detected by the results of a stool analysis.
It happens that a child feels normal, but at the same time he often experiences bloating, colic and foamy diarrhea. The baby can be active, eat with appetite and gain weight well. If lactose deficiency occurs, it is necessary to reconsider the child’s diet. When he is bottle-fed, it is best to use fermented milk or low-lactose formulas.
Diet features
In order for foamy diarrhea to go away as quickly as possible, treatment should be combined with diet. If you exclude certain foods from your diet, you can do without medications. At the first manifestations of the disease, it is recommended to avoid heavy and fatty foods, exotic fruits and dairy products.
A diet based on rice boiled in water without salt and fat is considered very effective. Rye bread is also a healthy product. The only fruit allowed is bananas. It is important to maintain water balance. You should drink a lot and it is best to brew teas from linden, raspberry, chamomile, and non-carbonated mineral alkaline water is also useful.
The diet is aimed at restoring intestinal function, so it is necessary to exclude foods that irritate it. If you follow these recommendations, your stool will normalize after a while. To avoid relapse of the disease, you should give up spicy and unusual foods, and return to your usual diet gradually.
- Causes of diarrhea with foam in adults
- Causes of daily diarrhea in an adult
- Undigested food in feces: causes in adults and children
- What helps an adult with diarrhea?
How to deal with diarrhea
If only one foamy stool appears in an adult and there are no other alarming symptoms, then you can try to improve your health on your own. Here are some recommendations:
- For the period of acute diarrhea, fasting (no more than one day) or a limited diet excluding foods that increase intestinal motility and secretion are recommended. From the next day, you should give preference to food that strengthens, making stool denser - dried white bread, rice, boiled potatoes.
- Diarrhea leads to an imbalance of water balance, so you need to drink plenty of liquid - still water.
- For mild foamy diarrhea, you can try to do without pills and drink a chamomile decoction, a decoction of oak bark or walnuts. You can make rice, bird cherry or blueberry decoctions.
If you are unable to get rid of loose foamy stools on your own, additional symptoms appear and the condition of an adult worsens, you need to start drug treatment:
- Antidiarrheal medications are taken for one or two days (until improvement occurs). They quickly tone the intestinal walls and promote thickening of stool. Most often, doctors prescribe Dermatol, Phthalazol, Atropine sulfate (for diarrhea with increased colonic motility), Becarbon, Imodium, Baktisuptil, Activated carbon, Enterosgel, Loperamide, Smecta.
- Liquid stool for food allergies in both children and adults is treated comprehensively; in addition to adsorbents, the doctor prescribes antihistamines. It is imperative to identify the allergen and prevent the patient from further consuming it.
- If diarrhea is caused by dysbiosis, then treatment includes taking probiotics containing beneficial microorganisms. This will help not only get rid of foamy stools, but also restore intestinal microflora.
- If the diagnosis reveals that foamy stool is a sign of an infectious disease, then a course of antibiotics is prescribed. Treatment can take place at home, but more often it is necessary to keep the patient in the infectious diseases department of the hospital (to prevent the spread of infection).
- If loose stool is a sign of parasites, treatment includes anthelmintics to get rid of the parasitic worms. All members of the patient's family will need to undergo prophylaxis against worms.
All of the above measures help relieve the symptom and do not cancel a trip to the doctor. As soon as the diarrhea passes and your health improves, you need to go to the clinic and get tested to find out the cause of the foamy diarrhea.
Treatment options
If an adult or child has diarrhea with foam: what to do in this case? It is best to see a doctor to avoid dehydration. In the case of using medicinal antibacterial drugs, their use should be agreed with a specialist, especially if it concerns a child.
Thus, the treatment of foamy stools is carried out with the following drugs:
- etiotropic therapy with drugs that relieve inflammation in the intestines - cephalosporins or antibiotics;
- antidiarrheals that suppress intestinal motility: “Imodium”, “Loperamide” (prohibited for children under 12 years of age);
- adsorbents that remove toxins in 5-7 days (“Enterosgel”, “Smecta”, “Atoksil”);
- probiotics containing live bacteria that restore intestinal microflora (Bifiform, Linex, etc.);
- enzymes that help restore digestion (Pancreatin, Festal, Panzinorm).
If the illness was caused by an allergic reaction, in this case the irritant must be excluded from the diet. To normalize digestion, you should take antihistamines.