What is frequent belching of odorless air, the reasons for this? This is an involuntary release of odorless gases into the mouth that does not depend on a person. A healthy person, during a normal swallowing movement, swallows a small portion of air (about 2-3 ml), which subsequently comes out back through the mouth in small portions and is not felt at all.
In a normal state, an adult’s stomach can contain up to one and a half liters of air , which forms internal pressure there. Normally, air can exit through the mouth, through the intestines, and be absorbed through the intestinal walls. As air pressure increases, the body itself regulates it by releasing excess air.
Pathological belching of air occurs as a result of a regular excess of air in the stomach , which gets there during swallowing. This unpleasant phenomenon can be caused by pneumatosis or airbrushing. If burping is not associated with food and bothers you at any time, then we may be talking about neurotic aerophagia - a pathology characterized by nervous swallowing of air regardless of food.
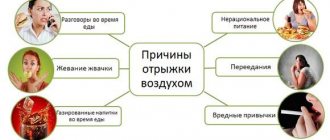
Causes
There can be many reasons for normal physiological belching:
- problems with nasal breathing;
- fast food or habit of snacking on the go;
- dental problems;
- binge eating;
- conversations at the table;
- physical activity after meals;
- addiction to chewing gum;
- addiction to regular and alcoholic carbonated drinks;
- taking soda to reduce heartburn;
- during pregnancy, the uterus begins to lift the diaphragm, which can cause this condition;
- aerophagia;
- neurosis.
Belching after a heavy meal, when the stomach is full of food after a meal, is not a painful sign. In this case, the sphincter at the entrance to the stomach does not close completely, pushing gases back. If it appears regularly, you should contact a specialist for diagnosis. However, odorless belching occurs more often in the absence of nutritional culture.
Pathological belching is caused by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, thyroid gland, etc. Usually it has a pronounced taste and smell: sour, bitter, acetone or smells of hydrogen sulfide. In all these cases, you should immediately consult a therapist.
Another article on this topic: Esophageal ulcer: what is it and how to treat?
Types of belching
Belching is one of the physiological acts of the digestive organs. In pathological conditions it can acquire peculiarities. There is a burp:
- silent or noisy;
- empty or with part of food;
- tasteless or with a bitter, sour, putrid aftertaste.
Based on the sensations a person experiences when belching, one can judge possible digestive disorders and causes. Pathological belching is a symptom of diseases:
- gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- gastritis;
- inflammation of the esophagus;
- diaphragmatic hernia;
- bending of the stomach;
- weak peristalsis;
- gastric stenosis;
- ulcers of the stomach and duodenum
- disorders of the liver and gallbladder;
- abnormalities in the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- abdominal abscess.
Belching that has a sour taste indicates an increased level of acid in the stomach. The level of acidity increases with excessive secretion of gastric juice, fermentation processes caused by insufficient production of hydrochloric acid.
Belching with bitterness indicates that gall bladder secretions have entered the stomach due to liver dysfunction. If a person previously did not suffer from liver problems and did not know what belching is, then with liver pathologies, a bitter taste in the mouth after belching will remain more and more often.
Strong belching of hydrogen sulfide with a rotten smell, called egg belching, indicates stagnation and decomposition of food. It saturates the stomach with gases - hydrocarbons, hydrogen sulfide and ammonia. A rotten smell may indicate:
- stomach cancer;
- ulcer;
- pyloric stenosis.
The smell of acetone indicates problems with the kidneys or that the person is following a protein diet.
Belching air after eating
If the gastrointestinal tract is functioning normally, belching of air occurs extremely rarely. This happens due to snacking on the run or talking (reading, working on a laptop, texting on a smartphone) while eating, and as a result, due to poor chewing of food and swallowing it in large pieces.
Due to accidentally swallowed air, a large air bubble forms in the stomach, pressing on its walls. Due to increased pressure, the cardiac sphincter opens: air flows into the esophagus and further into the mouth.
Odorless burping after eating in adults
When eating or drinking, it happens that a portion of air enters the digestive system. This does not pose a health hazard, however, in case of frequent cases of aerophagia, you need to completely reconsider your gastronomic habits and make adjustments to them.
Belching of odorless air after eating is disturbing as a result of:
- habits of eating in a hurry, on the go;
- chewing gum addiction;
- poor chewing of food;
- talking while eating;
- stressful situations (neurotic aerophagia).
In a healthy adult, belching after eating also occurs as a result of ordinary overeating. A stomach filled to the limit is not able to completely close the sphincter, and the gas easily finds its way out.
Belching often occurs when making sudden active movements with a full stomach, during which it is compressed or slightly displaced. Belching air without pathologies occurs with frequent consumption of carbonated drinks. To relieve pressure, the sphincter opens and the accumulated gases are able to freely exit through the mouth - this is natural belching. It’s easy to cure – just give up your favorite soda.
If belching after eating bothers you from time to time, does not have an unpleasant odor, and does not bother you with bloating, stomach pain, or a lump in the throat, then you can be sure that everything is in order with your health, and there is no need for examination or further treatment not required.
Frequent belching with stomach discomfort
If belching is accompanied by such unpleasant and painful symptoms as pain in the stomach, chest, heartburn, bloating, then we are talking about a disruption in the proper functioning of the digestive system due to enzyme deficiency.
It is common to eat a large amount of food at one time, which provokes increased gas formation. Accumulating in the stomach, gases put pressure on the organ, causing a lot of discomfort. Belching air slightly alleviates the condition, but if the digestion process was taking place at this time, then along with the gases, food particles will end up in the esophagus, which will lead to heartburn. Other symptoms will also intensify: pain in the stomach and esophagus, in the area behind the sternum, burning sensation, belching of sour air.
Pain under the shoulder blade when burping
If pain occurs in the right hypochondrium during belching, then most often this occurs with biliary dyskinesia. With this disease, the outflow of bile is disrupted, as a result of which it accumulates, thereby provoking pain in the side, under the rib, and less often in the chest area.
In addition to these unpleasant symptoms, new ones are added: increased body temperature, frequent belching of air, general weakness, lethargy.
Belching and feeling of a lump in the throat
Belching in combination with a feeling of a lump in the throat is a manifestation of the following diseases:
1. reflux gastroesophageal disease - characterized by inflammation of the esophageal mucosa, inadequate functioning of the sphincter, increased acidity of gastric juice, which leads to heartburn, nausea, belching of air, a sour aftertaste in the mouth, lump in the throat;
2. esophagitis - an inflammatory lesion on the mucous membrane of the esophagus, which is characterized by paroxysmal pain in the sternum or shoulder blades, discomfort when swallowing food, belching;
3. neurosis – the body’s reaction to a severe stressful situation in the form of increased emotionality and irritability, which is why a lot of air is swallowed while eating or talking. The feeling of a lump in the throat in this case is a sign of problems not with the esophagus, but with the nerves.
Why does burping occur on an empty stomach?
The causes of belching do not always lie in health problems. Sometimes the release of air, especially on an empty stomach, is a sign of a nervous disorder and acts as a psychosomatic symptom.
Belching air on an empty stomach often indicates inflammatory processes in the stomach, accompanied by nausea and periodic spasmodic pain.
Belching during pregnancy
Unlike toxicosis, which worries most expectant mothers in the first trimester of pregnancy, belching makes itself felt until childbirth. The reasons for belching air in this case are exclusively physiological in nature and are caused by changes in the female body:
- hormonal changes;
- exacerbation of chronic gastrointestinal diseases (if any);
- pressure of the uterus on the diaphragm, as a result of which the intestines and stomach are compressed and displaced;
- inactive lifestyle coupled with overeating.
Pregnancy is not a diagnosis, and you need to lead the healthiest lifestyle possible: move more, walk, avoid lying for long periods of time, eat right.
Belching during pregnancy is unpleasant, but drug treatment is not required in this case. You can get rid of it with the help of a balanced diet, giving preference to not too sour dairy products, boiled and baked vegetables, fresh fruits, and nuts.
Causes of belching in a child
Belching in infancy is quite natural and does not require any treatment. The digestive system is still imperfect, and belching in infants is regular, causing a feeling of great discomfort. To prevent painful colic, immediately after finishing feeding, the baby should be held upright for some time.
Belching is acceptable during the first year of life, but if it continues to bother older children, this indicates:
- poor nutrition that is not appropriate for the child’s age;
- the habit of eating while playing or watching TV;
- development of chronic rhinitis and tonsillitis, enlargement of adenoids.
In children of preschool or primary school age, frequent belching is considered a sign of hepatitis, gastritis, duodenitis, requiring immediate treatment.
Constant belching of air
Most often, constant belching of air occurs as a result of overeating, eating too often, poor chewing, etc. However, neurotic aerophagia can also cause this.
The symptoms of the pathology are as follows:
- belching with a loud sound;
- burping can occur at any time: after eating and regardless of food intake;
- accompanied by a feeling of fullness and heaviness in the stomach;
- sometimes flatulence may occur;
- in patients with cardiac ischemia, painful sensations in the cardiac region and angina attacks are observed;
- Sometimes there may be difficulty breathing.
With aerophagia, bloating of the upper abdomen is noticeable. The x-ray shows an air bubble in the stomach, which causes the diaphragm to rise. There is also an accumulation of gases in the intestines.
Treatment
Each specific cause of belching after eating requires an individual approach, so treatment begins with a visit to a gastroenterologist and conducting instrumental and laboratory tests. In most situations, it is necessary to prescribe a diet that helps reduce the load on the diseased organ (kidneys, liver, stomach, esophagus, intestines), while other treatment methods depend on the cause of the problem:
- With atrophic gastritis, you cannot do without antibiotics that act on the pathogen (bacterium Helicobacter pylori).
- For diseases of the liver and gall bladder, antispasmodics, fatty acid inhibitors, and enzymes (Mezim, Pancreatin) are required.
- In the presence of tumors in the gastrointestinal tract or hiatal hernia, surgical intervention is mandatory.
- Treatment of neurotic aerophagia involves the use of sedatives (calming) drugs and antidepressants.
Article on the topic: Study of oral automatism reflexes in neurology
Often, the treatment regimen includes drugs that help normalize the acidity of the stomach (especially with GERD), control its motility and reduce gas formation . Such medicines include:
- Rennie is an antacid, recommended for dyspepsia during pregnancy, heartburn, stomach pain and other symptoms of high acidity. To treat these conditions, 1-2 tablets are taken after meals up to 5 times a day. Contraindications are renal failure, hypophosphatemia, hypercalcemia, nephrocalcinosis, children (up to 12 years).
- Omez is an antacid, prescribed for ulcers, gastritis with high acidity, pancreatitis, GERD. The drug is prohibited for pregnant women and children under 12 years of age. Take 1 capsule once a day, half an hour before meals, with water.
- Gastal is an antacid prescribed for the complex treatment of hiatal hernia, peptic ulcer, reflux esophagitis, heartburn and other dyspeptic symptoms. The drug is prohibited for renal failure, hypophosphatemia, and Alzheimer's disease. Children are allowed from 6 years of age. For treatment, the tablet is dissolved under the tongue, the daily dose is 8 pieces, divided by 4-6 times. Take one hour after meals.
- Motilak is an antiemetic drug prescribed for the symptomatic treatment of a complex of dyspeptic symptoms and nausea of any etiology. Prohibited for children under 5 years of age, with prolactinoma, gastrointestinal bleeding. Classic treatment regimen: 1 tablet 3 times a day, regardless of meals. If necessary, add a tablet before bedtime.
- Simethicone – reduces foaming in the stomach and intestines. Used to treat flatulence, aerophagia, gastrocardial syndrome. The drug is prohibited for intestinal obstruction. Take after meals, dose of suspension – 25-50 drops, capsules – 1-2 pcs. The medicine is used once a day.
Non-drug therapy
For situations where non-pathological factors are the cause of belching, treatment does not involve the use of pharmaceutical drugs. You can cope with the situation using simpler methods, but you need to follow them for several weeks:
- quitting smoking, alcohol, carbonated drinks;
- transition to fractional meals with small portions;
- eliminating the habit of eating on the run or talking while eating;
- chew food thoroughly (slowly and carefully);
- avoidance of foods that increase gas formation (onions, garlic, confectionery, legumes, raw fruits);
- reducing intra-abdominal pressure by avoiding smoked, fatty foods, and meats with a lot of spices;
- getting rid of tight belts;
- giving up the habit of lying down after eating;
- setting the interval between food and physical activity (1.5-2 hours).
Folk remedies
The simplest method of home treatment for belching that does not occur against the background of severe pathologies or chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is the regular consumption of mint tea with honey (1 teaspoon of leaves per glass of boiling water). The remedy is undesirable for hypermotor dyskinesia of the biliary tract, since mint has choleretic properties. A few more recipes:
- Chew dry dill or anise seeds (1 tsp) slowly before each main meal. This can be done for 2-3 weeks.
- Combine fennel, mint (seeds) and flax fruits in equal proportions, add linden flowers. Pour 1 tsp. collect a glass of boiling water, leave for half an hour, wrapped in a towel. Drink 100 ml warm half an hour before meals. Treatment lasts 10-14 days.
- Pour 1 tbsp. l. calamus root with boiling water (300 ml), let stand for an hour. Filter. Take 50 ml 15 minutes before meals. The course of treatment lasts 3 weeks.
Aerophagia in children
This is a fairly common pathology for newborns and infants. The baby's developing nervous system cannot cope with the regulation of the digestive process. Pathology can also develop if the mother has little milk in the breast or the baby sucks on an empty nipple.
The main signs of aerophagia:
- nervousness and crying during feeding;
- bloating;
- refusal to eat, leading to weight loss.
After a burp, the child usually calms down. The diagnosis is confirmed by radiography.
In older children, belching may occur due to chatting while eating or if the child is chewing a sandwich and running at the same time. Sometimes this phenomenon occurs in children after inhalation. It is also common for children to experience belching due to ENT problems:
- adenoids;
- runny nose;
- tonsillitis;
- inflammation of the sinuses.
With such problems, the baby may swallow excess air while eating. As a rule, these problems go away after recovery.
Another article on this topic: Diseases of the small intestine: symptoms and signs of the disease
Belching of air accompanied by pain
If belching air is accompanied by pain in the stomach, we can say with confidence that gastrointestinal disease begins to develop in the body. Typically, these symptoms develop as a result of:
- smoking after a meal: most smokers are accustomed to finishing their meal with a cigarette, but when smoking the smoker swallows the smoke;
- eating fruit for dessert. Traditionally, it is customary to finish a meal with fruit, but gastroenterologists advise eating fruit after a meal a couple of hours later. Otherwise, fruit organic acids interact with mineral elements from other foods eaten, having an undesirable effect on the digestive process;
- traditional tea drinking after meals: the tea leaf contains enzymes that weigh down proteins and prevent digestion;
- a bath after dinner is not at all beneficial for digestion, since the blood drains from the stomach, which weakens the digestive process;
- the habit of unfastening your belt while eating has a negative effect on the intestines;
- drinking a cold drink after a meal (traditional cola after a burger or finishing a meal with a milkshake) interferes with the fermentation process and the absorption of lipids;
- Sleeping after a heavy meal can also lead to gastroenterocolitis, since the digestion process is disrupted during sleep.
Diseases characterized by belching air along with pain:
- peptic ulcer;
- chronic cholecystitis;
- inflammation of the pancreas;
- gurgle;
- malignant tumors with numerous symptoms.
If belching occurs with painful sensations in the stomach, you should contact a gastroenterologist to identify the causes.
Prevention
If a burp has already appeared, you need to do something to make it disappear. But if there is no belching yet, you can try to prevent its occurrence. To do this, it is necessary to follow a number of preventive measures:
- To protect yourself from belching that occurs after eating, you should eat less foods that slow down the production of enzymes (fatty meat, smoked fish, sauces, sour and spicy foods, fast food, concentrated dressings).
- Arrange fasting days for yourself, eat light foods, become physically active in order to improve intestinal motility and cope with excess gas formation. The stomach must independently produce enzymes and regulate the digestive process, but enzymes in tablets will not help, because they cannot be taken for a long time.
- Belching, which occurs rarely, is not a cause for concern, provided that it is not accompanied by other symptoms. You can get rid of such belching or prevent its occurrence by simply normalizing your diet, giving preference to dietary products and giving up those that have a bad effect on the gastrointestinal tract.
- Eat slowly, try to swallow as little air as possible with food and not overeat.
- You should not sit at the table in a nervous state, but first get rid of it with a walk or some kind of physical activity and only then eat.
Lump in throat and belching
The feeling of a lump in the throat, accompanied by belching, is characteristic of a wide range of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, thyroid gland, as well as neurological disorders. The patient should be examined not only by a gastroenterologist, but also by an endocrinologist and a neurologist. This symptomatology is typical for:
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- VSD;
- laryngeal tumors.
How to get rid of air burps
Belching air is not only a digestive failure, but also a social and aesthetic problem. Few people enjoy sitting in a large company and constantly burping noisily.
All other recommendations relate to the process of eating:
- while eating, there is no need to talk;
- food should be eaten slowly, thoroughly chewing small portions with the mouth closed;
- It is better to exclude from the menu foods that linger in the stomach for a long time, contain carbon dioxide, onions, and dairy products;
- It is better to eat 5-6 times in small portions;
- do not rush to eat in a state of psycho-emotional overexcitation;
- do not get carried away with chewing gum: chew gum for no more than 15 minutes;
- do not eat too cold or hot food, do not drink hot drinks, avoid oxygenated drinks;
- avoid physical activity after eating, do not sleep after eating - prefer quiet rest;
- It is better not to swallow saliva, but to spit it out.
Another article on this topic: What are the symptoms of exacerbation of gastritis? Diagnosis and treatment
If belching is a rare occurrence, drug therapy is not required. For constant belching after eating, treatment consists of taking Gastal, Almagel, Rennie. These drugs normalize acidity and enzyme levels, and also have an enveloping and moderate anesthetic effect. Psychotherapy is used to treat neurotic aerophagia.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are a good complement to traditional methods of treatment. They are especially effective in combating belching, which sometimes appears and has no connection with serious pathological conditions. Mineral water is considered one of the best remedies, but it needs to be treated carefully, only on the recommendation of a specialist. Other most proven folk remedies are:
- Goat's milk will not only relieve belching, but will also have a beneficial effect on the entire body as a whole. You just have to drink it for 2-3 months three times a day at a time, 0.5 liters at a time.
- Flaxseed infusion , prepared from seeds (1 tbsp.), poured with 1 tbsp. boiling water and infused for 30 minutes. Drink ¼ glass four times a day before meals for 2-3 weeks.
- Calamus root . Grind the dry root of the plant in a coffee grinder. Pour the raw material (0.5 tsp) into pre-prepared warm water, stir and drink.
- Tea with mint . Pour boiling water (1 tbsp) over dried mint (1 tsp), leave for 5 minutes. Strain, add honey (2 tsp) to the tea, dissolve it and drink.
- Linden-chamomile infusion . Take a teaspoon of dry linden and chamomile, pour a glass of hot water, wrap and leave for half an hour to infuse. Then strain and, if desired, add honey (1 tsp) to the infusion.
- Cranberry and aloe juice with honey . To prepare the medicinal mixture, take cranberry and aloe juice in equal proportions (0.5 cups each). Stir, add honey (1 tbsp.) and boiled warm water (1 tbsp.). Take the mixture 1 tbsp. l. three times a day for a week. Then interrupt the treatment for a couple of weeks and you can start a second course. You can use this folk remedy alternating with breaks for six months.
- Herbal collection of dill seeds, St. John's wort, yarrow inflorescences and peppermint leaves . Take 1 tbsp. l. All the listed components, mix well, pour 400 ml of boiling water. Place in a water bath, boil, and cool naturally. Strain, take 2 tbsp three times a day. l.
Currently reading: Frequent belching