Intestinal motility is the systematic contraction of the smooth muscles of the organ, which allows food to move through the gastrointestinal tract and ultimately remove undigested debris from the body.
Motor skills are also necessary for effective digestion: due to the contraction of internal muscles, enzymes from the gallbladder and pancreas are delivered to the hollow organs.
The proper functioning of the totality of all systems of the human body is directly related to intestinal health. A person’s immunity, well-being and performance depend on the state of the gastrointestinal tract. Often, malfunctions in the digestive tract become the basis for the development of other diseases.
Impaired intestinal motor function - what is it?
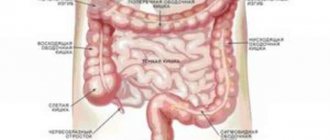
In normal condition, the hollow organ contracts systematically. Muscle fibers line the inner walls in two layers: in the first they are located longitudinally, in the second they are ring-shaped.
The amplitude of the wave-like movement of the muscles varies depending on the region of the intestine: the small intestine contracts at both a slow and fast pace. In addition, several reductions can be made simultaneously in a given department.
The food bolus moves much more slowly through the large intestine. The intensity of the peristaltic impulse increases several times a day at the time of the urge to defecate.
The frequency of contractions is considered normal: for the duodenum - 1-12 per minute, for the rectum - 9-12, for the colon - 3-4 and 6-12, for the rectum - 3.
What happens if intestinal motility increases or, on the contrary, decreases? The process of passage of a bolus of food through the intestinal tube is complicated, as a result of which digestion suffers: beneficial substances from incoming food are absorbed more slowly and not in the proper volume, undigested food stagnates in the body, releasing toxic toxins.
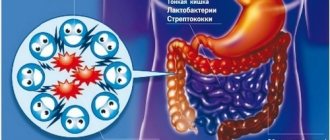
A pathogenic environment provokes the rapid proliferation of parasites, whose activities poison the life of the entire organism.
Impaired motor function leads to the development of a number of diseases that manifest themselves as intestinal disorders in the form of diarrhea or constipation, increased gas formation, abdominal pain, inflammation of the mucous membrane, and ulcerative damage to the walls of internal organs.
Factors contributing to the development of pathology
The main reasons for weakening motor function are:
- poor nutrition, consumption of large amounts of simple carbohydrates, high-calorie foods;
- eating disorders: long intervals between meals, overeating;
- insufficient amount of fluid consumed; dehydration;
- low level of physical activity;
- chronic diseases of the liver, gall bladder, pancreas;
- infection of the body;
- malignant neoplasms in the intestines;
- complications after surgical intervention on the abdominal organs;
- chronic fatigue syndrome, constant stress, depression;
- side effects of medications;
- heredity and characteristics of old age;
- bad habits: smoking, alcohol abuse, drug addiction.
Weak peristalsis, most often a consequence of poor nutrition, leads to constipation. Snacks on the go, junk food (fast food, sweets, flour products, coffee, carbonated drinks) cause digestive disorders.
Constant fermentation and rotting of undigested and unremoved food leads to intoxication: the destructive effect is first on nearby organs - kidneys, liver - then other systems are affected by harmful substances.
A high level of slagging and the formation of fecal stones negatively affect the condition of the mucous membrane. Persistent constipation contributes to the development of hemorrhoids, the formation of polyps in the intestines, which can develop into cancerous tumors.
Another less common variant of peristalsis dysfunction is increased muscle contractions. The following factors can enhance the motor activity of the digestive organs:
- consumption of foods that irritate the mucous membrane: sour, spicy foods;
- oncology;
- dysbacteriosis;
- chronic infectious diseases;
- neuropsychiatric disorders;
- taking certain medications (for example, antibiotics).
In this case, the patient suffers from severe pain and diarrhea: the stool is very liquid and has a foamy consistency. Frequent diarrhea leads to dehydration. Therefore, if motor skills increase, especially in children, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor.
Causes of the condition
Inhibition of peristalsis can be caused by the following factors:
- unbalanced diet, in which most of the food is high-calorie;
- chronic intestinal pathologies;
- neoplasms in the intestines of any nature (benign or malignant); surgical interventions on the abdominal organs; age;
- lack of even minimal physical activity;
- genetic predisposition;
- long-term use of drugs that affect intestinal motility.
Poor diet is the main cause of constipation. Indeed, due to the systematic consumption of flour products and foods rich in starch, fats and sugar, the processes of rotting and fermentation are activated in the intestinal lumen.
Toxins leak into the body through the intestinal walls, affecting neighboring organs. Over time, “fecal stones” form in the intestines. These are such dense structures that their movement through the intestines leads to damage to the intestinal mucosa. Inhibition of peristalsis processes not only causes constipation, but also provokes stagnation of blood in the pelvic organs, which leads to the appearance of hemorrhoids and polyps.
In older people, intestinal motility is disrupted as a result of the progression of chronic pathologies, hormonal imbalances, and muscle atrophy.
Symptoms of impaired intestinal motility
Signs indicating dysfunction of the digestive tract are:
- pain that has varying degrees of severity - from unnoticed discomfort to sharp spasms. Pain sensations decrease after going to the toilet and passing gas. They can also subside at night, and with food intake (with a morning cup of coffee or strong tea) they intensify again. Negative emotions can provoke increased pain;
- Difficulty defecating (constipation). Over time, constipation becomes chronic. It becomes almost impossible to empty the intestines naturally;
- feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen;
- bloating, increased gas formation;
- bad breath;
- loss of appetite due to weight gain;
- pale skin;
- signs of general malaise: lethargy, fatigue, fatigue, headaches, insomnia, irritability;
- dizziness: with anemia developed as a result of lack of nutrients;
- signs of poisoning: allergies, deterioration of skin and hair.
Dysfunction, characterized by an increase in contractile movements of smooth muscles, is accompanied by:
- acute pain in the intestinal area;
- frequent diarrhea with mucus or blood particles;
- flatulence, bloating;
- lack of relief after defecation, false urge to defecate;
- signs of dehydration are observed: dry mouth, weakness, drowsiness, chills, increased heart rate, decreased immunity.
The listed symptoms are warning signs that should not be ignored. To prevent serious consequences, you need to go to a clinic, where specialists, based on the results of tests and studies, will be able to determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective therapy.
The mechanism of accelerated intestinal motility
Malfunctions in the form of an accelerated rate of contractions of the intestinal muscles can occur for various reasons: characteristics of the properties of food products, malfunctions of the central nervous system, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Also, the reason for the acceleration of peristalsis can be the formation of a soapy environment, as a result of the combination of potassium with magnesium salts, the presence of fatty acids and other enzymes.
The rate at which digested food moves is directly dependent on the state of the receptors. The more irritated they are by the factors that are involved in this, the faster and more rhythmic the contraction of the intestinal muscles.
In some cases, a high level of peristalsis is achieved artificially to treat the gastrointestinal tract. For this purpose, a complex approach is used: a special food diet and therapeutic and preventive exercises, which force the peristalsis mechanism to work in the required mode.
What strengthens it?
The main reason for the increased work of peristalsis is the presence of fermentation in the gastrointestinal tract; it is this factor that explains the appearance of bloating, seething, gurgling, rumbling, pain in the stomach, increased flatulence, and diarrhea. An increase in the frequency of contractions of the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract affects the work of peristalsis, accelerating its work. What can provoke speed and intensification of peristalsis:
- The presence of chronic diseases at the acute stage.
- Presence of infection.
- Oncological manifestations in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Dysbacteriosis.
- Genetic innateness.
- Side effects of certain medications.
In some cases, stress or nervous tension can also provoke the intensity of muscle contractions of the gastrointestinal tract, in particular the colon and intestines. The same reaction can be caused by plant foods in combination with other products, as a kind of protective reaction of the body, helping the body cope with the elimination of difficult-to-digest foods and toxic substances.
Symptoms of increased peristalsis
Increased peristalsis of the gastrointestinal tract is expressed in the following symptoms:
- Presence of pain in the gastrointestinal tract. Malfunctions of the intestines can be expressed in varying degrees of pain, which can manifest themselves both in the area where the organ is located and more widely. This symptom is explained by an increase in the intensity of muscle contractions, and this type of symptom can manifest itself as a result of organ diseases, food characteristics, or as a consequence of stressful situations.
- Flatulence, bloating. An increase in the speed of peristalsis can cause bloating and accumulation of gases in the abdomen.
- Fast weight gain. Digestive dysfunction as a result of weight gain is one of the symptoms of increased peristalsis.
- Frequent diarrhea. This type of symptom can manifest itself against the background of various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Bad feeling. Increased peristalsis can negatively affect the general condition in the form of weakness, fever, sweating, and malaise.
Diagnostics
During examination and palpation, bloating and pain when pressing on the abdominal area already manifests itself.
An effective laboratory test would be a coprogram - a stool test for the presence of blood and pathogenic microflora.
Among the instrumental methods the most informative are:
- endoscopy - examination of the intestine with optics;
- colonoscopy - using a special tube with a probe inserted into the anus, the doctor will assess the degree of patency of the organ, the condition of the mucous membrane, and take a sample of material for histological analysis;
- irrigoscopy - x-ray with simultaneous administration of a contrast suspension;
- Pelvic ultrasound and MRI are performed in difficult situations.
Treatment of intestinal motility disorders
To restore the functioning of the digestive organs, an integrated approach is used, which includes changes in diet and physical exercise. In case of chronic constipation and fecal hardening, drug therapy is indicated.
Medicines
First of all, it is necessary to cleanse the digestive tract of stagnant feces. For this purpose, laxative medications are prescribed (Guttalax, Phenolphthalein, Duphalac), presented on the pharmaceutical market in various forms - in the form of tablets, drops, rectal suppositories.
Natural laxatives are rhubarb roots, licorice, buckthorn bark, and senna leaves. Herbal-based drugs include Regulax.
Disease prevention
Any disease is easier to prevent than to treat. Therefore, following these recommendations will make a significant contribution to the health of your intestines:
- adhere to the basics of a balanced diet: the diet should be varied, including plant fiber and protein. Do not allow yourself to overeat, excessive indulgence in sweets, flour products, smoked, salty and fatty foods;
- keep your body in good shape: do morning exercises, walk in the fresh air, ride a bike and ski, swim in open reservoirs or a pool;
- maintain a work and rest schedule: sleep 7-9 hours, avoid psychological stress and negative emotions;
- Visit a gastroenterologist regularly (1-2 times a year) for preventive examinations and timely detection of abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract.
Paying close attention to your body will help you avoid many troubles. Be healthy!
Intestinal peristalsis is the contraction of the muscle wall, due to which chyme moves through the gastrointestinal tract, where the digestion process occurs. When the peristaltic wave decreases or the movement of chyme stops, dynamic intestinal obstruction develops. It leads to severe intoxication of the body and disturbances of all types of metabolism with the development of a life-threatening situation and the need for intensive care and even surgical intervention.
For the normal digestion process, adequate peristalsis is necessary, for this it must have the following characteristics:
- Undulating character. Contractions must occur in sequence with the flow of food.
- Normal temp. Slowing peristalsis leads to stagnant processes (rotting and fermentation) in the intestines, and acceleration leads to insufficient digestion.
- Rhythm. Rhythm disturbances and inconsistencies in the contractions of the muscle fibers of the intestinal tube lead to intestinal colic, accompanied by an acute pain syndrome of a spasmodic nature.
This is controlled by the main regulator of normal activity, which is the autonomic nervous system. Complex processes occur without human consciousness: different parts of the intestine contract at different rates, while acting organically.
In order for the intestines to work like clockwork, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle, which includes proper nutrition, the absence of bad habits and an adequate physical activity. It is also necessary to avoid stressful situations and nervous tension.
If the peristaltic wave slows down, measures must be taken.
Reasons for weakened peristalsis
Before we consider in detail the question of how to strengthen motility, it is necessary to find out the main reasons for the weakening of intestinal motility.
The two most common reasons are:
- poor nutrition;
- sedentary lifestyle.
An unhealthy, unhealthy diet means an unbalanced diet, a predominance of fried, salty, smoked foods, fast food and carbonated drinks. But even if a person does not consume harmful foods, his diet may be incorrect if the balance of proteins, fats and carbohydrates is not maintained, and the menu does not contain fiber, fresh vegetables and fruits. Also, the cause of slow peristalsis is an incorrect diet, for example, when a person fasts most of the day and eats a large portion of food in the evening.
Less commonly, intestinal motility suffers due to various internal factors, that is, diseases. It is noteworthy that the list of causes includes not only somatic diseases and the consequences of surgical operations, but also psychogenic disorders. For example, chronic stress or depression can negatively affect the digestion process. This happens because during worries and experiences, the autonomic nervous system, which controls the functioning of organs, activates its sympathetic department, while the parasympathetic department, during which the process of digesting food occurs, turns out to be inactivated.
Products
To normalize the dynamic functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, it is necessary to adhere to a certain diet. List of allowed and undesirable products:
| Improves peristalsis | Worsening peristalsis |
|
|
Exercise
Physical activity significantly improves peristalsis. Basically, exercises should be aimed at the abdominal muscles. The following disciplines are useful for peristalsis:
- belly dance;
- yoga;
- Pilates;
- swimming.
A simple set of exercises that can significantly improve peristalsis and take only 10-15 minutes of time daily:
- "Scissors". Lying on your back, raise your legs 30˚ above the floor and cross them at a fast pace, imitating the movements of scissor blades for 1-2 minutes.
- "Bike". Lying on your back, raise your legs 90˚, bent at the knee joints, the movements are similar to pedaling a bicycle. Perform for 2-3 minutes, gradually increasing the pace and duration of the exercise.
- Run. A morning jog significantly stimulates all processes in the body.
- Breathing exercises. It can be done even while sitting at your desk in the office. It is necessary to take a deep breath, while the stomach protrudes, and while exhaling deeply, draw in the abdominal muscles as much as possible.
- "Mill". With your legs spread apart and your arms spread out to your sides, alternately bend towards your legs, reaching with the palm of your opposite hand, and make 10-15 movements to each leg.
Any other exercise to strengthen your abdominal muscles is also effective. A sedentary lifestyle does not contribute to the normalization of peristalsis. You must walk at least five kilometers per day.
Drugs
If diet and exercise fail to normalize peristalsis, then drug support is necessary. There are two main groups of drugs most often used:
- Medicines that stimulate muscle tone.
- Laxatives.
Medicines that stimulate muscle tone
Medicines that improve neuromuscular transmission and normalize contractions of the intestinal wall include:
- Prozerin. Used for acute intestinal atony to quickly normalize peristalsis. 0.25 mg is administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly every 4 hours, duration of therapy is 3 days.
- Motilium. It is used for impaired peristalsis due to dyspeptic symptoms, and is approved for use in children. The maximum dosage per day is 80 mg, divided into three doses or taken once at night.
- Aceclidine. It is used for emergency treatment of intestinal atony - 1-2 ml is administered subcutaneously.
Laxatives
Means that facilitate the act of defecation by accelerating peristalsis:
- Bisacodyl. By enhancing secretion, it enhances peristalsis and facilitates the movement of feces.
- Guttalax. Stimulates the large intestine, promoting an increase in electrolytes and water in the lumen.
- Regulax. It acts as an irritant on the intestinal walls, enhancing peristalsis and facilitating the act of defecation. Due to its mild action, it is approved for use in children.
- Senadexin. A herbal preparation that accelerates peristalsis and facilitates bowel movements.
Most people who have crossed the thirty-year threshold are faced with such a problem as dyskinesia, otherwise - poor intestinal motility. This problem brings a lot of inconvenience and therefore people are increasingly wondering how to improve intestinal motility? We will tell you about this in the article.
Foods that reduce intestinal motility
Food products, in turn, are divided into two large groups: the first includes everything that reduces peristalsis, and the second, those that increase it.
So what can reduce peristalsis?
- Any hot drinks such as tea or coffee;
- Red wine;
- Fresh baked goods and any baked goods;
- Chocolate;
- Kissel and dishes with a high content of potato starch;
- Some porridges are such as rice or pearl barley;
- Cream soup or pureed vegetables;
- Meat or egg products with a high butter content;
- Some fruits, for example, quince or pear and dishes made from them, as well as chokeberry and bird cherry.
Foods that increase intestinal motility
- These are any cold compotes, as well as juices from fruits or berries, kvass, wine (white) and mineral water;
- Any fresh fermented milk products containing live lacto- and bifidobacteria;
- Ice cream, especially fruit ice cream;
- Vegetables that contain a lot of fiber (cabbage in any form, beets, carrots, turnips, radishes and radishes);
- Watermelons and melons, tomatoes and cucumbers, onions and legumes perfectly cleanse your intestines;
- This also includes some fruits and berries, including apples, plums and apricots, as well as persimmons. Also included in the list are grapes, strawberries, raspberries, gooseberries, and blueberries;
- Dried fruits such as figs, dried apricots, prunes and raisins help well in this case;
- Oatmeal, buckwheat and barley cereals;
- Almost all vegetable oils;
- Bran and products that contain them;
- Nuts and greens.
Among other things, doctors advise consuming large quantities of fresh vegetables, and they can even be in the form of juices from carrots, beets or cabbage. If you want, you can make a salad seasoned with a little vegetable oil.
Other recommendations include split meals, preferably 5-6 times a day. Portions should be small.
Reduce as much as possible the amount of fried and smoked, pickled and overly salted foods, as well as baked goods and baked goods. Try using something as simple as drinking a glass of water on an empty stomach before breakfast.
There are also a lot of less radical ways to help the intestines, they are especially relevant when you need to correct this condition in a child. They will also be relevant during pregnancy.
You can make a laxative mixture from the following products: take two tablespoons of grain (preferably sprouted wheat) and the same amount of oatmeal, 1 tablespoon of honey and another one of any nuts, half a lemon and 2 apples. Finely chop the apples, mix with all the other ingredients and pour in lemon juice. This mixture can be consumed during any meal.
Try mincing half a kilogram of dried apricots and the same amount of prunes. Then add 2 tablespoons of propolis, 250 milliliters of honey and a pack of senna grass. Take 2 teaspoons before bed.
In addition, you can brew a tablespoon of buckthorn bark in half a liter of boiling water. You need to insist and drink it like tea.
A good remedy is crushed plantain seeds, which you take 1 teaspoon before meals. In the intestines they will swell and help the stool move forward.
One of the simplest and most effective medicines is bran. Just 1-2 tablespoons is enough, which should be washed down with water.
A mild laxative can be fruit decoction, cabbage brine and freshly squeezed juice, tea with dried cherries and apples.
Remember also that while adjusting your diet, you definitely need to diversify your physical activity. Any physical activity will also trigger your intestines.
In addition to physical exercise, you can also do a daily abdominal massage, douse yourself with cold water, or give yourself a contrast shower.
Here are a few exercises that will jump-start any, even the laziest intestines. We lie on our backs and begin to twist our legs, imitating riding a bicycle. We remain in the same position and press our knees tightly to our stomach.
We stand in the so-called knee-elbow position and alternately stretch back the right leg, then the left. Try to raise them as high as possible. You can pump up your abs. The more, the better, but at first 10 - 20 repetitions are quite enough.
At the end of the exercise, do squats. We finish everything by jumping rope or just standing still, alternating legs.
That's all I would like to tell you about improving intestinal motility for today. Use these simple and affordable methods and stay healthy. I look forward to seeing you again on the pages of my blog.
Most people who have crossed the thirty-year threshold are faced with such a problem as dyskinesia, otherwise - poor intestinal motility. This problem brings a lot of inconvenience and therefore people are increasingly wondering how to improve intestinal motility? We will tell you about this in the article.
The concept of peristalsis
The intestine is the largest organ of the gastrointestinal tract, in which the final processing of food products, their neutralization and absorption of useful minerals into the blood occurs. If peristalsis (motility) is impaired, then all these processes are inhibited. This process causes harm to the body and inconvenience to the person.
Symptoms of intoxication and decreased intestinal motility include:
- frequent headaches;
- constant feeling of fatigue;
- heaviness and pain in the abdomen;
- loss of appetite;
- a person gains weight, although he eats the same as usual, or even less;
- the appearance of a rash on the face, possibly on the body;
- sleep problems;
- bloating, flatulence, which worsens after eating;
- changes in stool, there are fewer of them, they take on a denser shape;
- frequent and painful constipation, which can in rare cases be replaced by bouts of diarrhea;
- general malaise and even fever.
Neither an adult nor a child will be happy with such symptoms of intestinal arrest. Therefore, you need to force your intestines to work on their own, or seek help from a doctor.
Moreover, the second option will be much better, because the cause of weak motor skills can be absolutely any disease , or the normal functional state of the body. But to figure out what exactly caused the intestinal stoppage can only be done by conducting an examination and passing tests.
One of the main causes of constipation and diarrhea is the use of various medications.
.
To improve bowel function after taking medications, you need to drink a simple remedy
.
How does intestinal motility work?
intestinal atony intestinal peristalsis intestinal spasm
Intestinal dysfunction is a serious problem. Impaired peristalsis is often a symptom of another disease, but can also occur independently. Luckily, there are several ways to improve your gut muscle tone. But first, let's look at a process called peristalsis.
What is intestinal peristalsis?
Peristalsis is usually called a wave-like contraction of the walls of the intestine (small and large), which leads to the movement of food, chyme or feces in one direction.
Peristalsis is a reflex act that involves intestinal muscle fibers. Their coordinated movement, controlled by the nervous system, creates a contractile wave. The frequency of formation of such waves in different parts of the intestine is different.
Peristalsis also occurs during the interdigestive period.
Peristalsis is a wave-like contraction of the intestinal muscles.
Normal peristalsis
The rate of muscle contraction in the small intestine is different from that in the large intestine. Depending on the situation, food gruel can move at a rate of contraction of the walls of the small intestine from 8 to 10 times per minute.
In the large intestine, where feces are formed, the contraction rate is slower and ranges from 3 to 4 times per minute.
Pathological changes that lead to faster or slower contractions lead to problems with bowel movements (diarrhea or constipation).
What leads to impaired peristalsis
There are many reasons (from minor to serious) that lead to impaired motor skills:
- changes in diet and water imbalance;
- constant stress;
- bad habits;
- side effects of certain medications;
- intestinal infection;
- previous operations on the gastrointestinal tract;
- helminthic infestations;
- pregnancy;
- oncological diseases of the intestine, etc.
As a rule, impaired peristalsis in the form of diarrhea or constipation is just a symptom of a disease. “Irritable bowel syndrome” is an example of a disorder of nervous and humoral regulation. With it, under the influence of negative emotions, the motor and absorption function of the intestine changes, which is accompanied by either constipation or diarrhea.
Prolonged diarrhea is a health condition that causes loss of electrolytes and fluids, disrupts the mineral balance in the body and contributes to dehydration.
Intestinal atony or decreased peristalsis
Atony translated from Latin means lack of tone.
Intestinal atony is associated with loss of muscle tone, resulting in excessive relaxation of the intestines, leading to constipation.
Often the cause of loss of tone is errors in eating food with insufficient fiber content. In addition, psychogenic, endocrine, and toxic causes of atony and constipation are distinguished.
Decreased intestinal muscle tone reduces peristalsis
We are talking about intestinal atony if a person has not had a bowel movement for more than 2 days. Obvious symptoms of constipation include:
- abdominal pain;
- bloating, flatulence;
- general discomfort;
- loss of appetite.
Stool retention does not go away without a trace: fecal stones form and pathogenic microflora multiply. Harmful substances enter the bloodstream, poisoning the body. Against the background of constipation, the intestinal mucosa becomes inflamed, the biocinosis of beneficial microorganisms is disrupted, which predisposes to the development of intestinal cancer.
Colon spasm
The meaning of the word “spasm” translated from Greek means cramp. In fact, this pathological process, accompanied by prolonged compression of the intestinal muscle tissue, is called colic.
Spasm disrupts peristalsis, making it difficult for feces to move through the intestines.
The following can lead to spasms: poisons, parasites, some medications, bacteria, etc. Characteristic symptoms of such a pathology include:
- pain localized near the navel;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- flatulence;
- nausea and sometimes vomiting.
If the cause of the spasm is thrombosis of the mesenteric vessels or intestinal obstruction, then the above symptoms appear very quickly. In this case, the pain is diffuse, the anterior abdominal wall is sharply tense. The condition is considered dangerous if pain disappears against the background of signs of spasm, which indicates possible intestinal necrosis.
How to improve peristalsis
If there are no serious changes in intestinal health, then you can improve intestinal motility with the help of foods containing fiber. It is especially abundant in fresh fruits and vegetables.
The daily diet should include: apples, tomatoes, cabbage, etc. Dried fruits include dried apricots and prunes. You need to drink at least 1.5 liters of water per day.
Fermented milk products will help support microflora.
Other measures to prevent constipation include:
- special gymnastic exercises, walking;
- healthy lifestyle and daily routine;
- the use of traditional medicine that stimulates the intestines.
Deterioration of peristalsis is a serious problem, leading to stagnation of feces and self-poisoning of the body. If you notice this symptom, do not delay visiting a specialist and self-medicate. The above recommendations are only a good addition to medical prescriptions.
Source: https://myzapor.ru/o-zapore/peristaltika-kishechnika/
Causes of weak peristalsis
Many factors influence intestinal function, and now we will try to find out which of them slow down and even completely stop peristalsis, and which can stimulate intestinal motility.
Reasons that slow down peristalsis:
- Unbalanced nutrition , when the diet is dominated by foods with high calorie content, foods of artificial origin (fast foods with a lot of spices and sauces and foods with added chemicals - chips, crackers), lack of regularity of meals, its speed (eating a sandwich on the way to office).
- Treatment with antibiotics or other drugs that reduce the balance of intestinal microflora.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract of all parts, including the stomach, liver, and gall bladder.
- Tumors in the intestine, both small and large.
- Behavior of surgical intervention on the intestine.
- Inactive lifestyle , constant sedentary work, frequent climate change.
- Predisposition to constipation, its chronic course.
- Frequent stress, negative experiences.
- Disturbance in the functioning of nerves, improper innervation of the intestinal walls.
Intestinal motility: symptoms and methods of recovery - Website about
Increased intestinal motility occurs for many reasons. According to statistics, every second inhabitant of our planet has problems with the digestive system.
When exposed to provoking factors, it is the intestines that are the first to lose their functions, which contributes to the development of metabolic disorders and chronic diseases. A person’s normal well-being and ability to work depend on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
The slightest disruptions in the functioning of the digestive system have a negative impact on the general condition of the body and create the preconditions for a weakened immune system.
What is peristalsis?
This term refers to the rhythmic contractions of the muscular walls of the intestine, which promote the movement of food masses from the thin to the thick section. This factor plays an important role in the processes of absorption of nutrients and removal of waste products from the body.
Peristaltic contractions involve smooth muscle fibers that are present in the intestinal walls. One layer is located longitudinally, the other - transversely.
Coordinated contractions contribute to the creation of waves, the frequency of which is different in different parts of the organ. Several types of contractile movements spread throughout the small intestine, which differ in speed.
They can be slow, medium and fast. Often several types of waves appear simultaneously.
Food masses move slowly through the large intestine; peristaltic waves in this section have the lowest speed. 1–2 times a day, rapid contractions occur in the organ, promoting the movement of feces towards the anus.
Peristalsis of the colon is based on a reflex that occurs when food enters the stomach. The normal frequency of contractions of the duodenum is 10 times per minute, small - 9-12 and large - 3-4.
At the moment food moves towards the anus, the frequency indicator increases to 12.
Weak peristalsis slows down the absorption of nutrients and makes it difficult to move feces towards the rectum. Remains of undigested food, feces and toxins linger in the body, gradually poisoning it and creating ideal conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
Impaired intestinal motility is the cause of most pathologies of the digestive system, characterized by constipation and diarrhea, abdominal pain, ulcers and benign neoplasms.
What causes peristalsis to be disrupted?
The causes of poor peristalsis may be:
- unhealthy diet with a predominance of high-calorie foods;
- chronic diseases of the digestive system;
- benign and cancerous intestinal tumors;
- complications after abdominal surgery;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- elderly age;
- genetic predisposition;
- neurological disorders;
- constant stress;
- taking medications that impair intestinal motility.
Improper nutrition becomes the main cause of intestinal motility disorders. Modern people are accustomed to snacking on the go, refusing a full hot lunch. Excess starch, fat and sugar contribute to fermentation processes in the intestines.
Toxins penetrate through the intestinal walls into the abdominal cavity, poisoning the blood and internal organs. By the age of 35, the intestines become so clogged that the fecal stones formed in it injure the mucous membranes. The patient begins to feel that the intestines are not working.
Lack of peristalsis leads to fecal retention, stagnation of blood in the abdominal cavity, hemorrhoids, and the formation of benign and malignant tumors.
For normal intestinal function and the functioning of beneficial bacteria, a slightly acidic environment and a large amount of fiber, which is found in fresh vegetables and fruits, are required.
You need to start restoring intestinal motility with lifestyle changes. Most diseases of the digestive system develop against the background of physical inactivity, sedentary work and prolonged bed rest.
Moderate physical activity is the most effective stimulator of intestinal motility. To do this, you need to allocate at least 10–15 minutes to perform the exercises. Daily walks in the fresh air are especially beneficial.
The reasons for poor bowel function in old age are considered to be: the development of concomitant pathologies, hormonal disorders, muscle weakness and damage to the nerve endings that control the functions of the gastrointestinal tract.
Increased intestinal peristalsis is observed in chronic pathologies of the stomach, gallbladder and pancreas. Malignant neoplasms, stress, infectious diseases and poisoning can contribute to organ dysfunction.
Enhances peristalsis and long-term use of certain medications. However, the majority of digestive problems are caused by poor diet, consumption of fast food and processed foods. Increased peristalsis leads to flatulence, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
This is due to the course of decay processes.
How are peristalsis disorders manifested?
The main symptom of dyskinesia is pain of varying intensity and localization. The severity of discomfort varies from minor discomfort to severe cramps. The pain disappears after defecation or release of gas. Their intensity decreases in the evening and at night.
Unpleasant symptoms return after the morning meal. Enhanced gas formation is facilitated by the fermentation process. Chronic constipation gives way to diarrhea. In the future, the intestine begins to empty only after taking a laxative or giving an enema.
Weakened peristalsis promotes the formation of fatty deposits.
The patient’s well-being worsens: he experiences weakness, sleeps poorly, and becomes irritable. Symptoms of intoxication increase - skin rashes, acne, headaches.
With increased intestinal peristalsis, body temperature often rises and persistent diarrhea appears. Absorption of insufficient nutrients contributes to weight loss.
In such situations, you need to know exactly how to restore intestinal motility.
Treatment options
Restoring the digestive system requires an integrated approach.
The therapeutic course includes taking medications, performing special exercises, and creating a balanced diet.
Decoctions of medicinal plants that can increase intestinal motility are highly effective. The stimulant drug should be prescribed by your doctor; you should not choose it yourself.
You can increase intestinal contractility using a laxative. Currently, there are a large number of drugs that affect certain parts of the digestive system.
Glauber's salt stimulates peristalsis of the entire intestine. This is the most effective and fast-acting drug. Taking it increases osmotic pressure, which slows down fluid absorption.
Defecation occurs 1–2 hours after taking the tablet.
A laxative that increases contractions of the small intestine, facilitating the movement of digested food towards the anus. The effect is observed 5–6 hours after consuming the drug.
Drugs that improve the functioning of the large intestine can be produced on the basis of plant and chemical components. They increase the tone of the organ and accelerate the excretion of feces.
To treat dyskinesia in adults, antidepressants, tranquilizers and antipsychotics can be used. How to strengthen intestinal motility with diet?
All foods are divided into 2 groups: those that strengthen contractions and those that weaken them. The latter include: chocolate, coffee, strong tea, baked goods, jelly, rice porridge, pears, apples, chicken eggs, butter.
Acceleration of intestinal peristalsis occurs when consuming berry fruit drinks, kvass, white wine, mineral water, kefir, fresh vegetables, and dried fruits. You can normalize the functioning of the digestive system with the help of freshly squeezed juices of carrots, beets and cabbage.
These same vegetables can be used to make salads. You need to eat as often as possible, portions should be small. It is necessary to exclude fatty and fried foods, sausages, canned food, and confectionery products from the diet. Drinking a glass of water before meals helps relieve constipation.
You must consume at least 2 liters of fluid per day. The doctor will advise you on how to improve your bowel function using traditional methods.
Alternative medicine
To restore the functions of the digestive system, there is a recipe that increases peristalsis. To prepare you need to take 1 tbsp. l. sprouted wheat grains, 2 tbsp. l. oatmeal, 2 medium apples, 1 small lemon and 1 tbsp. l. honey Apples are grated and mixed with the rest of the ingredients and warm water.
The drug is used in any quantity throughout the week. A mixture of dried fruits has a laxative effect. 0.5 kg of prunes and dried apricots are passed through a meat grinder and mixed with 50 g of propolis, 200 g of senna and 200 ml of fresh honey. The medicine is taken 2 tsp. before going to bed with a glass of cool water.
Buckthorn decoction has a pronounced laxative effect. 1 tbsp. l. raw materials are poured into 0.5 liters of boiling water, infused for 3 hours and consumed instead of tea.
Plantain seeds increase in size after entering the intestines, which promotes the rapid elimination of digestive products. Crushed seeds take 1 tsp before meals. Wheat bran is eaten with warm water.
They are necessary for the formation of a sufficient amount of feces. Fruit and vegetable juices, cabbage pickle, apple and cherry compote have a mild laxative effect.
The course of treatment should be accompanied by an increase in physical activity. You should not lie down immediately after eating; it is recommended to take walks or just walk around the house. Active sports - swimming, running, aerobics - restore the functioning of the digestive system.
Light abdominal massage, hardening, and special exercises are helpful. They are performed in a supine position. The legs are bent at the knees and raised, making circular movements. This increases the strength of the abdominal muscles, restores blood supply to organs, and improves peristalsis.
Improved intestinal tone is the best prevention of diseases of the digestive system.
https://www..com/watch?v=xIOXj0hJhyQ
With increased intestinal motility, it is necessary to cleanse the organ of toxins. Enterosorbents help with this - activated carbon, Smecta, Enterosgel. They bind harmful substances and remove them from the body.
Increased bowel contractions are often a symptom of irritable bowel disease. Treatment involves avoiding fast food products and foods that provoke fermentation. Antispasmodics are used to relieve pain.
If you have frequent bowel movements, you must take an antidiarrheal drug (Loperamide or Imodium).
Source:
Intestinal peristalsis
Impaired intestinal motility is a serious condition in which the entire digestive system malfunctions. The contents of the gastrointestinal tract cannot move normally, and food absorption is impaired. It is important to promptly recognize the first signs that intestinal motility has changed, undergo diagnostics and select treatment.
What is intestinal peristalsis?
A healthy intestine in a normal state contracts all the time, this happens systematically. Thanks to the rhythmic contractions of the intestinal walls, food masses move freely from the small intestine to the large intestine. This promotes the normal absorption of nutrients that enter the body with food and the elimination of waste products naturally.
Normal contraction motility is possible due to the presence of smooth muscle fibers on the intestinal walls. They are located in several layers, some longitudinally, others transversely. Due to systematic contractions, waves of different intensities are created. In different parts of the intestine, the speed of movement of food masses differs.
Normally, the number of contractions per minute is 10 times in the duodenum, 9–12 in the small intestine, and 3–4 in the large intestine.
Intestinal peristalsis functions not only after eating, but also constantly, even at night.
Several times a day, rapid contractions occur that push the contents of the intestines towards the anus.
The first alarming sign of impaired peristalsis is often problems with stool, especially constipation, when motility does not reach the desired speed and waste products do not reach the rectum.
Reasons for violations
The causes of peristalsis disorders, like many other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, can be various factors. Some of them arise due to human fault and are associated with poor diet, lifestyle, and other mistakes. These include:
- bad eating habits, such as eating fatty foods, lack of a meal plan, poor diet;
- smoking, excessive alcohol consumption - tobacco smoke and ethanol negatively affect the condition of all gastrointestinal organs, including the intestines;
- lack of physical activity, sedentary lifestyle;
- frequent stress - intestinal function is regulated by the central nervous system, when a person lives in constant nervous tension, gastrointestinal diseases occur;
- improper or uncontrolled use of antibiotics, hormonal and other potent drugs.
Source: https://crbfirovo.ru/prochee/peristaltika-kishechnika-simptomy-i-sposoby-vosstanovleniya.html
How to improve peristalsis?
Restoring intestinal function and enhancing peristalsis is possible only by using several types of treatment simultaneously, namely:
- Folk remedies. This is the first thing that is better to try than to swallow advertised pills, which can only cause harm if the diagnosis is not established.
- Drugs that stimulate bowel function can also be purchased at the pharmacy, but before doing so, you should consult a doctor so that he can select them for you individually and also prescribe the required dosage.
- An excellent way to enhance peristalsis is gymnastics. It helps increase blood flow to the intestines, as well as the pelvic organs, thereby helping to move feces forward through the intestines. Helps strengthen the walls of the large and small intestines.
- You can increase peristalsis by following a certain diet. Its main rule is that we eat and drink everything that is healthy, and don’t even try anything that is not healthy.
Improving peristalsis will largely depend on how the person himself feels about solving his problem.
In this case, the intestines did not work, do not work, and will not work. But for those who want to normalize the functioning of their intestines, we will tell you in more detail about each point in the treatment of weak peristalsis.
One of the main causes of constipation or diarrhea is poor diet.
.
Therefore, to improve bowel function, you need to drink a simple drink
.
What is peristalsis?
Intestinal peristalsis is understood as wave-like contractions of the intestinal walls, which help push masses of feces towards the anus. This is one of several types of motor activity that occur in the intestines. It is thanks to the correct contractions that normal digestive processes are realized, during which all the necessary microelements are absorbed, and what is not absorbed leaves the body.
In order to maintain the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract for a long time, you need to monitor your diet, introduce physical activity and eliminate bad habits. In addition, it is necessary to promptly treat systemic diseases that affect the performance of the organ. If these conditions are not met, then peristalsis may be increased or, conversely, decreased, which is far from the norm.
Peristalsis begins to occur after the stomach has been filled with food. The norm is considered to be the case when 10-12 contractions occur per minute in the duodenum, 9-12 in the small intestine, 3 contractions in the large intestine, and no more than 3 in the rectum. If the patient experiences disturbances in peristaltic activity, they may constipation or diarrhea occur.
ethnoscience
Before drinking pharmaceutical medicine, try these methods to enhance peristalsis :
Wheat bran
- Take two apples and grate them. Add to them a tablespoon of honey and two tablespoons of oatmeal. Squeeze the lemon juice and add it and a couple of tablespoons of warm water to the mixture. Eat it throughout the day.
- Grind plantain seeds and take a teaspoon of them with meals.
- A couple of tablespoons of wheat bran are washed down with a small amount of water or mixed with it and eaten for breakfast.
- Take ten grams of buckthorn root and pour half a liter of boiling water over it. Let the broth brew and drink it throughout the day instead of tea.
- Take two glasses of dried apricots and prunes and grind them in a meat grinder. Add to them a package of senna and two tablespoons of propolis. Pour in liquid honey, approximately 200 ml. Take this mixture before bed in the amount of a couple of teaspoons.
Medicines
In order to increase intestinal permeability, laxatives are released. These can be tablets, powder, syrup, drops. All laxatives should be divided into three groups:
| Effect of drugs | Description |
| Drugs that affect peristalsis of the entire intestine. | Here you can use sodium sulfate or magnesium. But you should pay attention to the fact that these substances, increasing the osmotic pressure in the intestines, increase peristalsis. The process goes quite quickly, and the medications take effect after two hours, or even earlier. Therefore, you should not take them before your trip. |
| Laxatives acting in the small intestine. | These medications include oils. They envelop feces, facilitating their easy passage through the intestines. At the same time, they also speed up motor skills themselves. The effect of a laxative occurs within two to six hours. |
| Laxatives acting in the large intestine. | These are drugs from a group of irritants. They tone smooth muscles, toning the intestinal walls. You cannot use them yourself, as addiction and intestinal atrophy may occur. Only a doctor should prescribe such laxatives. Such drugs include Regulax, Guttalax, Bisacodyl, Laxigal and others. |
Drugs to stimulate peristalsis
In the treatment of intestinal motility disorders, medications are used that enhance motility and increase muscle tone (prozerin, vasopressin). However, the prescription of such drugs is the prerogative of the doctor.
To activate intestinal contractility, laxatives are often used. They promote its emptying due to increased peristalsis. Today there are many known laxatives that act on individual intestinal sections.
All laxatives are divided into the following groups:
General action laxatives , affecting the functioning of all intestinal sections. Representatives of this group are Glauber's salt and Epsom salt, which are among the strongest and fastest-acting drugs. The principle of their action is to quickly increase the osmotic pressure in the intestinal lumen, which, preventing the absorption of the liquid part of the food bolus, enhances peristalsis. Bowel movement occurs within 1.5 hours after taking the drugs.
Laxatives that affect only the small intestine. An example of such a drug is castor oil. It promotes the passage of intestinal contents and improves intestinal motility. The laxative effect is observed after 2-5 hours, but painful cramps in the abdomen may appear.
Laxatives with action in the large intestine. Herbal preparations (senade, regulax, buckthorn bark) of this group increase the tone of this intestinal section and restore the process of defecation.
Synthetic drugs (guttalax). But you need to remember that addiction to this group of drugs can develop; in addition, allergies to the components of the drugs and intestinal colic of varying intensity may occur.
Gymnastics
To enhance peristalsis, an active lifestyle is very important, as well as gymnastic exercises that enhance intestinal motility, namely:
- the familiar “bicycle” exercise - spin imaginary pedals while lying on your back;
- You need to pump up your abs not only for a smooth tummy, but also for the intestines; 10-20 approaches are enough here;
- lying on your back, alternately raise your straight legs up;
- press your legs bent at the knees to your chest and clasp them with your arms, do this while lying on your back;
- in a knee-elbow position, lift your straight legs up one by one and bend your back;
- deep squats;
- You need to complete the complex by jumping rope or on the spot, a hundred times is enough.