What antibiotics does a doctor prescribe for the treatment of paraproctitis?
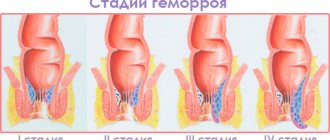
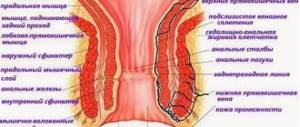
Inflamed pararectal tissue in an acute or chronic condition is called paraproctitis.
It is often encountered in the practice of proctological diseases. Mostly males are affected. With paraproctitis in adults, the routes of infection include the anal glands, lesions on the mucous membrane of the rectum, and from neighboring organs in which the inflammatory process occurs.
Peculiarities
Paraproctitis can act as a complication in nonspecific ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. The disease spreads from the rectum. Purulent formations form. The fluid spreads along the paths of the blood vessels. Flows into the space between the muscles. Tissue destruction occurs.
There is a risk of infection of neighboring organs. If the purulent formation communicates with the intestine or an outlet appears on the skin, damage to the cellular space of the pelvis will decrease. If there is no communication, the risk of fistula formation increases. A breakthrough of the abscess into the abdominal cavity or intestinal lumen is possible. Purulent paraproctitis is dangerous due to complications.
With the spread of treatment with antibacterial drugs, they are used in small quantities to relieve paraproctitis. The therapeutic effect of using these drugs in their pure form is small. Antibiotics for paraproctitis are practically not used on their own.
The way to get rid of the disease is surgical. The acute form requires emergency surgery. In case of chronic – planned. The presumed cause of the development of a chronic form of paraproctitis is the transition of the existing surgical infection into the active phase.
Therapy of paraproctitis using antibiotics is indicated:
- In the postoperative period, an increase in body temperature is recorded. The doctor assesses the condition of the wound. It is recommended to conduct a study of the contents, as well as perform bacteriological culture. After studying the results obtained, the doctor comes to the conclusion about prescribing a drug from the spectrum of antibiotics.
- After surgery, increased inflammation processes were recorded in the tissues close to the wound, as well as in the perirectal tissue and in the rectal area. The purpose of taking antibiotics is to speed up the healing process. Suppuration at the suture is noted.
- Upon completion of plastic surgery for rectal fistulas. The operations are represented by excision of the fistula with reduction of a rectal flap and excision followed by suturing of the sphincter.
To treat the categories of paraproctitis described above, systemic antibiotics are used in most cases. The doctor takes into account the patient’s age and weight, the severity of the disease and the type of pathogen. In some cases, combining the drug with other medications is indicated.
Features of therapy
The structure of the treatment of a patent intestine leads to the disease. The doctor recommends medications that have a systemic effect. The main form of treatment consists of intramuscular or intravenous injections. The dosage is calculated by the doctor individually. The basis is the current condition of the patient.
The antibiotic Amoxiclav is often included in prescriptions. The peculiarity of the drug is its antibacterial properties. Metronidazole in combination with Amoxicillin prevents the formation of blood clots. Generations of antibiotics used in therapy may be different.
Depending on the severity of the patient's condition, drugs from the cephalosporin group may be prescribed.
After analyzing the results obtained, the doctor can make adjustments to the prescribed treatment of paraproctitis with antibiotics. The group of drugs for which the body has not yet developed agents is used. The duration of taking systemic antibiotics is up to seven days.
Depending on the course of the disease, it is possible to administer an antibiotic deep into the fistula canal.
Prescribed after laboratory examination of a purulent mass:
- To stop the inflammatory process caused by anaerobic flora, Metronidazole is used. Has no effect in aerobic lesions. It is effective against protozoan microorganisms. It is taken orally or intravenously. It is highly effective when combined with Amoxicillin.
- Drugs from the aminoglycoside group are applicable for aerobic sources of infection. The main route of administration is intramuscular. The first generation of drugs is represented by Streptomycin, Neomycin and Kanamycin. The second generation of drugs consists of Gentamicin, Tobramycin, Netilmicin. Third generation - Amikacin. This group increases effectiveness when combined with penicillins. The main disadvantage is the negative effect on the ears and kidneys. They have a reversible effect when the drug is discontinued.
- In some cases, the use of synthetic penicillins is permitted. The drugs have a wide spectrum of action. Can be used orally, intravenously, intramuscularly.
Local treatment
Systemic antibiotics reach the site of pain through blood vessels. Presented mainly in tablets. Local treatment medications have been developed. Represented by ointments, creams, powders. The effect applies only to the place of application.
Used to treat paraproctitis in the period after surgery. Reduce the duration of the recovery process. Fight bacterial complications. The advantage of local treatments is low absorption into the blood. Ointment for paraproctitis has an effect.
Reduced side effects.
Often applicable in use:
- Levomekol. It contains an antibiotic and a regenerating drug. Has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and healing effect. Applicable for the treatment of scars and tissue regeneration.
- Levosil. Combination drug. Available in ointment form. Reduces inflammation in the rectum. Effectively relieves pain.
- Proctosedyl. It is shaped like candles. Proven to be effective against most common bacteria. Relieves itching. Hormonal agent. Suppositories for paraproctitis are highly effective.
- Olestesin. Antifungal and antimicrobial drug. It is in the form of suppositories. Relieves pain. Restores damaged areas of the mucous membrane. Promotes healing.
The medications discussed above are suitable for use for preventive purposes. The result has been proven for secondary infection. Reduces scarring time.
A diet prescribed by a doctor helps relieve constipation and hemorrhoids. Symptoms of paraproctitis will gradually decrease in intensity.
Self-administration of antimicrobial drugs without consultation with a doctor is unacceptable. To accurately determine the right antibiotic, it is necessary to know the sensitivity of bacteria to the drug. It is impossible to determine this without laboratory tests.
A feeling of severe itching and constant pain in the anus or rectum is a direct reason to contact a specialist.
The use of folk remedies can lead to negative consequences. The condition will deteriorate sharply. All traditional medicine must be agreed with a doctor and be an additional means of treatment.
The information on our website is provided by qualified doctors and is for informational purposes only. Don't self-medicate! Be sure to consult a specialist!
Rumyantsev V. G. Experience 34 years.
Gastroenterologist, professor, doctor of medical sciences. Prescribes diagnostics and carries out treatment. Expert of the group for the study of inflammatory diseases. Author of more than 300 scientific papers.
To the doctor We recommend: What is melanosis of the colon and why is it dangerous?
Source: https://gastrot.ru/kishechnik/antibiotiki-pri-paraproktite
What it is?
Paraproctitis is an acute or chronic inflammation of the perirectal tissue. This is one of the most common proctological diseases (20-40% of all rectal diseases). Paraproctitis is in 4th place in frequency after hemorrhoids, anal fissures and colitis.
Men get sick more often than women. This ratio ranges from 1.5:1 to 4.7:1. Paraproctitis is a disease of adults: descriptions of rectal fistulas in children are rare.
Treatment of paraproctitis without surgery and conservative therapy: suppositories, antibiotics
Treatment of paraproctitis depends on the form of the disease, the degree of neglect of the inflammatory process, and concomitant pathology. Proctologists say that it is impossible to cure the disease with medications alone. Delaying a surgical solution to the problem causes worsening results and repeated relapses.
The conservative method is indispensable during the period of preparation for surgery and during recovery.
The pathogenesis of an abscess begins with tissue infiltration. If you start treatment at an early stage, you can avoid surgical intervention, so you need to contact a proctologist at the first symptoms, when pain appears during bowel movements, false urges, and unstable temperature.
Basic methods of treating paraproctitis
Proctological surgeons believe that it is impossible to do without surgery for paraproctitis. Conditions for the development of inflammation in the perirectal tissue favor suppuration and spread to neighboring tissues and organs.
“Replenishment” of the infection comes from the rectum with feces, clogged glands of the anal sphincter, and in case of chronic inflammation from the genitourinary organs (in men - from the prostate, in women - from the vagina and ovaries, bladder).
In acute paraproctitis, due to the rapid development of pathology, a tendency to develop into sepsis, and melting of the intestine with peritonitis, the main method of treatment is emergency surgery. Only through drainage of the abscess cavity and cleansing can recovery be achieved.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qeE3dgF2Fx4
The chronic course of the disease allows the formation of an abscess in the perirectal area. It lies closer to the surface or deep in the sacral region. Self-opening briefly alleviates the patient’s condition, but does not remove the existing paths for the spread of pus.
A one-stage excision method or stage-by-stage elimination of first the cavity, then the fistula are used. Recovery is slow. It is necessary to achieve complete closure of communication with the intestines and cessation of the inflammatory process.
After surgery, patients need complex use of antibacterial drugs orally, intramuscularly, locally in suppositories and ointments.
The modern method of laser coagulation of the fistula outlet can be used in cases of complete cleansing of the cavity. It is impossible to verify this without opening the channel. The method is suitable for patients with a weakened immune system (especially with diabetes), in old age when surgery is not possible. Acute symptoms go away, but the risk of relapse remains high.
Drug therapy is indicated to prepare children and adults for surgery. It helps to activate local immunity, strengthen the abscess capsule, and reduce the severity of the infection.
Important! Conservative medications should only be used in consultation with a doctor. When the fistula opening is closed without first cleaning the cavity and destroying the source of inflammation, the disease recurs in the near future.
Conditions when surgery can be avoided
The sequential development of the inflammation process in the perirectal tissue can be stopped with subcutaneous localization at the infiltration stage. The abscess has not yet formed and has not formed a fistulous tract with an opening in the intestine.
The condition is optimal for treating paraproctitis without surgery. When a cavity is formed containing pus and passages into neighboring tissues and organs, the deadline is missed.
By contact, feces will break into the genitourinary organs, which will cause pyelonephritis, cystitis, and in women - colpitis.
When the infection spreads, there are no conditions for treating rectal fistula without surgery. It is necessary to eliminate the main abscess and stop communication with the rectum.
Methods of conservative treatment of paraproctitis
To achieve resorption of the infiltrate, you need a full antibacterial effect while observing a laxative diet and semi-bed rest.
The complex of conservative treatment includes:
- diet;
- antibiotics to combat pathogenic pathogens;
- drugs with antimicrobial properties acting at the level of the large intestine;
- rectal suppositories and ointments with anti-inflammatory and analgesic components;
- physiotherapy;
- antiseptics for treating postoperative wounds;
- medicinal herbs in decoctions for sitz baths, washing, applications, microenemas;
- folk herbal remedies in ointments.
The use of baths with various herbal decoctions is part of complex therapy. Their use should be agreed with a doctor.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are selected depending on the aggressiveness of the process. Shown:
- ultraviolet irradiation of the anus, subcutaneous area;
- UHF;
- microwave.
Treatment is carried out in a specialized office as prescribed by a doctor. Duration - up to 10 minutes, number per course - from 5 to 20. Prescribed during the rehabilitation period after surgery.
Important! For superficial paraproctitis, home treatment is allowed. Physical activity should be reduced; sitting is not recommended. It is better to lie on your stomach; in this position, sphincter tension is relieved. You cannot heat the area of inflammation; massaging is strictly prohibited.
Suppositories prescribed for paraproctitis
The components of the suppositories quickly enter through the anus into the surrounding tissue. Effective in the connection of paraproctitis with rectal fissures. For mild paraproctitis without fever, inexpensive rectal suppositories and more complex combination drugs are prescribed, which are correspondingly more expensive:
- Ichthyols - contain sulfur from peat deposits, relieve pain, dry out the formation of mucus in the anal canal.
- Calendula DN - a concentrated plant extract helps treat inflammation that begins on the mucous membrane, eliminates sphincter spasms.
- Methyluracil - has healing properties, promotes the development of granulations on cracks and erosions, restores the intestinal wall, causes healing of the fistula opening.
- Hema-Pro - a combination of natural anti-inflammatory components (propolis, chestnut, sea buckthorn oil, aloe, ginkgo biloba, yarrow) helps get rid of inflammation in the pelvic organs and tissues.
- Salofalk - the main component of mesalazine produces a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect by enhancing phagocytosis and inhibiting the production of substances that stimulate inflammation. It is used in suppositories and microenemas; suspension and foam are produced for this purpose.
Salofalk is a strong anti-inflammatory agent, the action of which is activated in the intestines. Use during pregnancy is not recommended.
For more intensive postoperative treatment, drugs are used that include antibiotics, corticosteroids, and painkillers:
- Relief Ultra - based on shark oil, contains benzocaine, zinc sulfate, hydrocortisone.
- Proctosan - has an anti-inflammatory effect due to bufexamac (prostaglandin blocker), anesthetizes and covers small cracks in the intestine (lidocaine, bismuth salts).
- Ultraproct - a combination of fluocortolone and cinchocaine allows you to cope with inflammation and intense pain.
Before using candles, careful toileting of the anus is necessary. After deeply pressing the suppository, you need to lie down for 30 minutes to ensure absorption.
List of antibiotics for the treatment of paraproctitis
Antibiotics are prescribed in tablets, intramuscularly, intravenously or in suppositories. Medicines are injected into the solution to wash the ulcers. Reserve drugs, which are characterized by the development of less resistance of microorganisms, are most suitable for urgent treatment. For paraproctitis, the following groups are used:
- semisynthetic penicillins - Oxacillin, Ticarcillin, Azlocillin, Amoxicillin;
- cephalosporins - Bayotax, Betasporin, Bidroxil, Bastum, Biotraxon, Biotum;
- macrolides - Erythromycin, Clarithromycin, Roxithromycin, Oleandomycin, Josamycin, Azithromycin.
Doctors add Metronidazole to antibiotics, a drug that is active against anaerobic bacteria, and sulfonamide Sulfadimethoxine, which is absorbed in the large intestine.
Important! You cannot interrupt the course of antibiotic treatment prescribed by your doctor. If the temperature does not decrease for a long time, the proctologist can replace the drug.
Ointments
Ointment products are convenient for use in the form of local skin applications over the site of inflammation. The napkin is fixed with adhesive tape. Tampons are prepared for deep impact. Modern drugs are equipped with applicators that allow a dose of ointment to be administered directly into the rectal canal. For superficial paraproctitis, the following are effective:
- Levomekol - contains chloramphenicol, penetrates the site of inflammation, copes with anaerobic purulent infection;
- Vishnevsky ointment - a combination of birch tar, xeroform and castor oil has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect;
- Proctosedyl - contains hydrocortisone and benzocaine, anesthetizes and suppresses the inflammatory response;
- Levosin - is represented by a combination of methyluracil with chloramphenicol, sulfadimethoxine, trimecaine. A strong anti-inflammatory and analgesic.
Levosin is an antimicrobial agent used for paraproctitis to relieve the inflammatory reaction and eliminate the causative agent of infection that causes fever.
Diet Basics
The purpose of the diet for paraproctitis is to limit intestinal irritation, prevent constipation, ensure the absorption of essential food components, and support the immune system. For this it is recommended:
- organize five meals a day in compliance with the schedule;
- drink 1.5 liters of water per day or more;
- give up alcoholic and carbonated drinks, spicy and fried meat dishes, canned food, coarse vegetables (turnips, radishes, cabbage), mushrooms, sauces;
- do not eat foods that cause increased fermentation with intestinal distension (legumes, milk, grapes, sweets).
The following must be present in the diet:
- boiled or steamed meat products;
- semi-liquid mucous porridges without milk;
- low-fat soups;
- butter and vegetable oil;
- vegetable casseroles;
- cottage cheese, soft cheese, fermented milk drinks;
- fruits stewed, baked, in compote.
Important! It is impossible to cure with diet alone, but it is quite possible to relieve pain and the course of the disease.
Folk remedies
People's councils can provide assistance if used wisely. They cannot be opposed to taking medications. The known bactericidal properties of herbal decoctions are used in baths, hygiene procedures, and microenemas. Suitable for them:
- chamomile;
- sage;
- yarrow;
- calendula;
- series;
- aloe;
- oregano;
- Oak bark.
Oak bark is a natural antibiotic, has a negative effect on pathogenic organisms, and relieves inflammation. It can be used internally or as a component of sitz baths.
It is convenient to prepare decoctions in advance in a thermos. The next day, add to water for washing or bathing. The remaining pulp is applied to the site of inflammation in the form of a compress for 15 minutes. A warm solution of 100 ml is injected into the anus to combat intestinal spasms, fissures, and the threat of paraproctitis.
Proctologists do not recommend inserting suppositories made from raw potatoes into the anus. For this, in the pharmacy there are enough good natural preparations with propolis and sea buckthorn oil.
What happens if paraproctitis is not treated at all: can the disease go away on its own?
Paraproctitis does not cure on its own.
If the patient refuses medical care, then, at best, he will develop very unpleasant fistula tracts connecting the intestines with the skin of the perineum and neighboring organs.
The excretion of feces causes an unpleasant odor and additional infection of the genitourinary organs. A person suffers from problems and pain when urinating, kidney disease. In women, the appendages, uterus, and vagina become inflamed.
Important! It makes no sense to treat all complications without eliminating the cause. With each exacerbation the patient loses his protective capabilities. The immune system is spent constantly fighting infection. A person is completely unprotected from any microorganisms. Constantly suffers from respiratory diseases with severe complications.
In the worst outcome, a limited superficial abscess turns into a widespread pelvic phlegmon, causing melting of the rectum with peritonitis, sepsis. The condition is life threatening.
Therapeutic measures should be carried out in agreement with the proctologist. The specialist will determine the possibility and duration of non-surgical treatment and prescribe the best medications. Delaying consultation and self-medication cause irreparable harm to health and dramatically worsen life prognosis.
- Goshchitsky JI. G., Mozel Y. JL, Mikhlin B.A. Purulent diseases of the perineum and rectum. St. Petersburg Problems of proctology. M. 1994, pp. 15-19.
- Ryzhikh A.N., Barkan M.B. Paraproctitis. State publishing house of medical literature. 1951
- Protsenko V.M., Koplatadze A.M., Bolkvadze E.E., Shmakov V.A., Egorkin M.A., Kozhin D.G. Current issues of etiopathogenesis and treatment of anaerobic paraproctitis. Current problems of coloproctology. IV All-Russian conference with international participation. Irkutsk 1999 pp. 84-85.
- Bolkvadze E.E. Features of diagnosis and surgical treatment of anaerobic paraproctitis. Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Coloproctology. 2009 No. 3. Page. 63-69.
Source: https://MojGemorroj.ru/konservativnoe-lechenie-paraproktita.html
List of antibiotics effective in treating inflammation in paraproctitis?
Antibiotics for paraproctitis are prescribed by specialists and have a wide range of effects on the body, including the disease. Drug therapy can be used in case of complications or concomitant diseases. While taking antibiotics, it is necessary to monitor the patient's condition and the body's reactions.
Description of the disease
Antibiotics for paraproctitis without surgery are used in the initial stages of development as prescribed by the doctor. The dosage and treatment regimen depend on the severity of the disease. Paraproctitis is purulent formations that occur in the tissue joints that surround the rectum. The disease occurs in the form of inflammatory foci that change the location.
Inflammation occurs accompanied by a feeling of heaviness and discomfort. There is a burning sensation, a pain syndrome that occurs not only when going to the toilet, but also in a calm state. These are the main symptoms.
If not treated promptly, purulent masses accumulate, their quantity can reach an impressive volume. Due to further accumulation, the purulent formation may burst when all the contents enter the intestines, rectum.
How and where does paraproctitis develop?
Reasons for the development of the disease
Treatment of paraproctitis with special antibiotics is mandatory therapy in case of an advanced stage. Having burst, the purulent masses spread throughout the mucous membranes of the rectum, which can provoke infectious foci that complicate the disease.
The spread of pathological subcutaneous lesions depends on several factors.
- The main pathogens in both adults and infants are staphylococcus, streptococcus, and E. coli; infections spread quickly and cause serious harm to vital processes.
- In the process of complications, stool stagnates in the anal canal, which contributes to the penetration of infection into the perirectal area.
- Chronic or acute infection can lead to the pathogen entering the intestines, which provokes the development of the disease and complicates the functioning of the digestive system.
- The presence of injuries, both surgical and physical.
- baths based on medicinal herbs, medicinal ingredients,
- antibiotic-based suppositories,
- Ichthyol and Vishnevsky ointment are actively used,
- therapeutic enemas based on herbs.
The reasons may be individual irritants that affect the ability of the digestive system to function in adults and children.
Any therapeutic prescriptions must be observed in strict accordance with medical recommendations
What antibiotics or medications should be taken for paraproctitis is determined by specialists based on the diagnostic results.
Removal of the pathology occurs through surgery, but in some cases antibiotic drugs may be prescribed. The effectiveness of such therapy is determined by the stage of the disease and its characteristics.
In the case when a purulent neoplasm forms near the skin, there is a risk of developing a fistula.
If you do not seek help in a timely manner, the disease can take on a chronic form, which is dangerous due to complications. Surgery, according to experts, is the most effective method of therapy, but it is worth considering a number of contraindications to surgery that the patient may experience.
If surgical treatment is not possible, effective methods are prescribed that have been successfully used in practice for many years:
In the chronic stage of the disease, these methods are not effective and therefore are not recommended for use. Baths, suppositories and enemas for paraproctitis in adults can remove inflammatory foci, which has a beneficial effect on the course of the disease and the prevention of exacerbations.
In order for a period of remission to occur, it is necessary to get rid of purulent accumulations, after which the treatment will be more productive. The course of any therapy is prescribed depending on the stage that has occurred and can take a long period.
Effective ointments based on antibiotic substances for paraproctitis
Correctly prescribed antibiotics will prevent the development of the disease, after which a period of remission begins.
Only after determining the causative agent of the pathology, drug therapy is prescribed, which will be aimed directly at the cause. Treatment is carried out after a full diagnostic examination based on the results obtained.
The following antibiotics are used:
- cephalosporin,
- macrolide,
- semisynthetic penicillin.
These are the main components found in medications. The dosage and type of antibiotic is determined by the doctor. Self-prescription of antibiotics is unacceptable, as is changing the treatment regimen prescribed by the doctor.
Medicines are also prescribed during the postoperative period, when side effects such as chills and high fever occur. If signs of complications develop, you should undergo additional tests to determine their cause, and then undergo a course of antibiotic therapy.
For anaerobic microflora, Metronidazole is prescribed - this is an antiprotozoal drug that does not affect the microflora. The drug is considered more effective when used in combination with amoxicillin. You need to take the drug after consultation with a specialist.
Antibiotic ointments:
- Levosin - the drug has a combined effect, anti-inflammatory and calming effect,
- Fuzimet - restores tissue, it contains the antibiotic fuzidin,
- Levomekol – has an antibacterial effect, allows you to heal and restore damaged tissue.
Suppositories are often used in the treatment of paraproctitis, but they must be selected individually according to indications
Groups of antibiotics may have the same main component, but different names.
Paraproctitis is a serious disease that requires competent therapeutic treatment and diagnosis. Laboratory tests are performed based on the doctor’s recommendations after an initial examination by a proctologist. Antibiotic therapy is considered effective, but in the early stages of the disease or in the postoperative period. All appointments are made based on the results of the study and the overall clinical picture.
You can learn about how the disease manifests itself, effective methods of treating it and recommendations regarding the prevention of pathology from the video:
Loading…
Source: https://MedBoli.ru/gemorroj/preparaty/perechen-antibiotikov-effektivnyh-v-lechenii-vospalenij-pri-paraproktite
What antibiotics are used to treat paraproctitis?
Paraproctitis is a very serious disease. It is rarely possible to cure it using medications alone. It is possible to get rid of this disease once and for all only through surgery. Therefore, antibiotics for paraproctitis are not used as the main therapy. Such drugs are prescribed only in some cases.
When are antibiotics used?
There are several situations in which antibacterial therapy may be required:
- Inability to perform surgery. For example, when a patient, in addition to paraproctitis, has other serious chronic diseases in the acute stage. In such a situation, the operation is postponed for some period and conservative therapy is prescribed, which may include antibiotics.
- The patient does not have the opportunity to see a doctor. For example, if a person is far from a hospital, he can use topical antibiotics to slow down the process.
- In the postoperative period. For daily dressings, local antibacterial agents in the form of ointments are always used.
- The presence of severe inflammatory processes after surgery. Antibacterial drugs can be used if severe inflammation in the rectum, perirectal tissue or wound area persists for some time.
- High temperature in the postoperative period. On the first day after surgery, a rise in body temperature is considered normal. However, if it stays above 38 for a long time, action must be taken. In such situations, the condition of the wound is assessed and its contents are examined. After this, if necessary, suitable antibacterial agents are prescribed. If antibiotics are used earlier, this will not make it possible to accurately determine what is happening to the patient.
- During complex operations for excision of a fistula. These include excision with suturing of the sphincter or reduction of a flap of intestine.
For paraproctitis, systemic antibiotics can be used, these are tablets or injection solutions, or local ones - suppositories, ointments. Each type of these drugs is necessary to solve different problems.
Systemic antibiotics
Systemic antibacterial agents reach the site of infection through the blood. Such antibiotics for paraproctitis are usually used only after surgical interventions, in the presence of severe inflammation, fever, etc. The need to use a particular drug is determined after bacteriological culture, through which the flora that caused the infection is established.
- For anaerobic flora, Metronidazole can be prescribed orally or intravenously. It is often combined with Amoxicillin. Other agents active against this flora are cephalosporins and penicillins.
- For aerobic flora, aminoglycosides are usually used intramuscularly. These are Gentamicin, Netilmicin, Tobramycin, Kanamycin, Amikacin.
Broad antibacterial agents, for example, Amoxicillin, Ampicillin, can also be used. Carfecillin is suitable for oral administration, intravenous or intramuscular - Azlocillin, Ticarcillin, Carbenicillin.
Paraproctitis: treatment and prevention of the disease.
What is an anal fistula and what it looks like can be found here.
How to most effectively treat Crohn's disease?
Local antibiotics
Such drugs are treated only at the site of their application. Local antibiotics are used both after and before surgery. Such remedies prevent bacterial complications and speed up healing. For paraproctitis, ointments or suppositories can be used.
The former are usually prescribed for treating postoperative wounds during dressings. The latter are more often used when it is impossible to perform an operation, in preparation for surgery, or in the absence of the opportunity to seek medical help.
Antibacterial suppositories:
- Proctosedyl. In these suppositories, framycetin is the main active ingredient. It is active against streptococci, Klebsiella, staphylococci, pseudomonas, enterobacteria and other microorganisms. In addition, the product contains painkillers and hormonal components.
- Olestesin. The antibacterial effect of the drug is provided by sodium sulfonamide etazol, and this substance also has an antifungal effect. In addition, the drug contains anesthesin, which has an analgesic effect, and sea buckthorn oil, which has anti-inflammatory, healing and hemostatic properties.
Antibacterial ointments:
- Levosin. This is a combination drug that contains chloramphenicol, methyluracil, sulfadimethoxine and trimecaine. The drug has antibacterial, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Fuzimet. The ointment uses fusidine and methyluracil as an antibiotic, which is also included in its composition and has a regenerating effect.
- Levomekol. Chloramphenicol provides the ointment with an antibacterial effect, while methyluracil promotes rapid healing and tissue restoration.
After surgery for chronic or acute paraproctitis, dressings with such ointments must be carried out daily for at least 3 weeks.
First, the wound is treated with any antiseptic solution, for example, hydrogen peroxide or chlorhexidine. After which it is dried and a thin layer of ointment is applied to the wound surface.
Next, the wound is closed with gauze folded in several layers.
When using antibiotics for paraproctitis, it is worth remembering that using only these drugs it is impossible to completely cure the disease. Of course, such drugs can somewhat reduce the inflammatory process, but they cannot directly affect the contents of the abscess. Moreover, using antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription can only worsen the situation.
What antibiotics are used to treat paraproctitis Link to main publication
We recommend reading
Source: https://gemor.guru/paraproktit/antibiotiki-pri-paraproktite.html
Diagnostics
For diagnosis, as a rule, it is sufficient to collect complaints, anamnesis of the disease and an external examination. In rare cases, especially with a deep location of the abscess, there may be difficulties in differentiating the diagnosis. Then instrumental research methods may be required, for example, computed tomography or ultrasound with a rectal sensor.
In the presence of fistulas, fistulography is performed - staining of the fistula tract to determine its depth, length and direction of the tract.
Laboratory research methods determine the presence of inflammation.