General rules
The most common reasons for bowel resection are:
- Thrombosis of mesenteric vessels.
- Intestinal obstruction . The operation is performed in the least traumatic way - only the altered intestine is resected, volvulus and intussusception are eliminated.
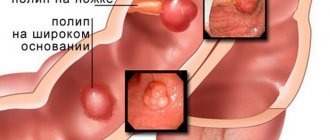
- Malignant or benign tumors.
- Abdominal injuries.
- Crohn's disease . Resection of a significant portion of the small intestine is performed in the presence of massive bleeding or small intestinal fistulas . However, resection is not a cure for this disease and the relapse rate without drug treatment is quite high.
- Nonspecific ulcerative colitis . They resort to subtotal resection of the colon with the formation of ileosigmostoma (after 10-12 months, reconstructive operations are performed). colectomy is also performed .
The extent of resection determines the severity of the patient’s condition and disturbances in nutritional status. Can be carried out:
- Partial resection - the length of the removed area is up to 100 cm.
- Extensive - more than 100 cm is removed.
- Short intestine - the preserved part of the small intestine is less than 100 cm. “Short small intestine syndrome” develops.
After resection, the ability of the digestive canal to perform functions is impaired to varying degrees. With extensive resections of the small intestine, absorption is impaired. The small intestine takes an active part in digestion: food gruel is exposed to bile, intestinal juice, and pancreatic enzymes, under the influence of which food is broken down into individual components. This is where nutrients are absorbed.
After major operations, various types of metabolism are disrupted, including the exchange of bile acids , which take part in the digestion of fats. During operations on the colon, the microbiota and immune changes occur.
Extensive resection of the jejunum (part of the small intestine) is accompanied by malabsorption with the development of malabsorption syndrome . Diarrhea is typical , and sometimes bloating occurs.
During resection of the jejunum, hypersecretion of hydrochloric acid , and an increased load with it aggravates diarrhea. Patients experience weight loss, adipose tissue decreases, and protein loss occurs. In the early stages, appropriate nutrition and medication can eliminate diarrhea.
Complete resection of the ileum (part of the small intestine) causes serious problems. It normally absorbs 80% of the bile acids produced by the liver, and the rest in the colon is deconjugated by the intestinal flora. Deconjugated products are partially absorbed in the colon, and some are converted into secondary bile acids, which, when absorbed, enter the liver for repeated cycles (5-10 cycles per day). This ensures savings in bile acids, the daily synthesis of which the liver is not able to provide.
The cause of diarrhea in patients with removal of this part of the intestine is loss of bile acids, as well as unabsorbed fatty acids. The severity of diarrhea depends on the length of the remaining intestine (stump). With its length from 50 to 200 cm, it adapts to new anatomical conditions, but the adaptation time is different and depends on the volume of the removed part and the reserves of the remaining part. of iron deficiency anemia may appear . Deficiencies of proteins, potassium and magnesium also develop. Requirements for the protein component and energy should be increased by 1.5 times.
With subtotal resection of the small intestine (jejunum and ileum are removed), the condition of patients is more severe. There are no functional intestinal reserves. Due to malabsorption of nutrients, patients lose significant weight and their fat mass sharply decreases, they are bothered by severe weakness, and have a deficiency of potassium, calcium, magnesium, zinc, chlorides, trace elements and vitamins .
Severe anemia is noted due to impaired absorption of iron, folic acid and vitamin B12 and impaired protein absorption. Patients develop protein-energy malnutrition, a deficiency of omega-3 fatty acids , and show signs of cachexia . Patients need correction of metabolic disorders in a hospital setting, since weight loss can be 5% per year. In the absence of infusion-nutritional correction, the prognosis is unfavorable.
With small-colic resections, osmotic diarrhea . Colon bacteria ferment lactose and produce lactic acid, which worsens diarrhea. Translocation of the intestinal microflora occurs and its activity changes, which leads to a deficiency of microelements, vitamins, magnesium, and a decrease in the immune response. The body's need for protein is within normal normal limits, but the energy supply should be increased by 1.5 times.
Considering these disorders, the diet after intestinal surgery should be as gentle as possible on the mucous membrane of the digestive tract with a gradual expansion of the load. After the operation, the patient receives parenteral nutrition in the form of intravenous solutions for a week. From the fifth day, oral administration of adapted mixtures is possible. By the end of the second week, the patient can be transferred to Diet No. 0A , which includes liquid and jelly-like dishes:
- low-fat meat broth;
- berry jelly;
- rice water with cream;
- compote;
- rosehip decoction;
- fruit (diluted) juices.
After three days, you can introduce a soft-boiled egg. Meals are organized 7-8 times a day. After three days, it is possible to switch to Table No. 1A (surgical), including:
- liquid pureed porridge (rice, oatmeal, buckwheat) in meat broth, water with milk;
- slimy soups;
- low-fat meat broth with the addition of semolina;
- scrambled eggs;
- protein steam omelette;
- soufflé/puree from low-fat meat or fish;
- jellies, mousses;
- cream (no more than 100 g).
The next stage of nutrition is Table No. 1B (surgical). It serves to transition to physiologically nutritious nutrition and contains:
- puree soups;
- steam dishes from pureed boiled meat/chicken/fish;
- pureed fresh cottage cheese with the addition of cream or milk;
- fermented milk drinks;
- pureed milk porridge;
- baked apples;
- vegetable and fruit purees;
- white crackers;
- tea with milk.
Further nutrition and the possibility of expanding the diet are agreed with the doctor and depend on the scope of the operation. The patient may be recommended a table of therapeutic Diet No. 1, which is physiologically complete with a limitation of gastric secretion pathogens and irritants, or taking into account functional disorders (diarrhea, malabsorption) - Diet No. 4B (mashed), which the patient must follow for up to two months. This diet provides moderate intestinal sparing and includes:
- fractional meals;
- boiled and steam methods of its preparation;
- pureed and puréed vegetables, grains and meats;
- stimulants of gastric secretion (radish, radish, celery, turnip, sorrel, mushrooms), solid and roughage foods are not allowed;
- products that cause fermentation are excluded (grapes, sweet fruits, legumes, brown bread, sweets, bananas, baked goods, whole milk, cabbage, cucumbers, carbonated drinks).
More details about the features of Table No. 4B , indicated for patients with diarrhea, will be discussed below.
For patients with a resected colon, microbiocenosis disorders are more typical. The patient is bothered by bloating and discomfort in the intestines, but the digestion and absorption of food is not impaired. The functional reserve of the remaining intestine is sufficient to ensure vital activity or may be reduced during the first 6 months after surgery.
This is a common type of intervention performed for colon cancer , polyposis , ulcerative colitis complicated by bleeding, diverticulosis , Crohn's disease and intestinal obstruction . With left-sided hemicolectomy (removal of the left part of the large intestine), more pronounced dysbiosis is observed than with right-sided hemicolectomy. Among the consequences of colon resections, one can note a deficiency of magnesium, vitamin K and B vitamins.
Benefits of diet
Carefully selected dietary therapy for people in the postoperative period promotes recovery and reduces the risk of complications.
The diet after intestinal surgery provides all useful substances, vitamins, and has a number of main features, which include:
- Sparing parts of the gastrointestinal tract, including the operated surface.
- Normalization of metabolism.
- Restoring immunity.
- Assisting in the healing of postoperative wounds.
- Prevention of pain symptoms.
Recovery of the body depends on the supply of nutrients. You will need to consume low-fat foods, steamed, in the oven or cooked in the usual way. Since the cooking will take place at home, the person who will be preparing dietary dishes will need a steamer, blender or food processor.
What can you eat after intestinal surgery and what are the main requirements? The food should resemble puree and not be rough. The menu should include vegetable broths, light cereals, low-fat fermented milk products, and taken hourly.
IMPORTANT! Don't be afraid of this diet. After all, it does not irritate the intestines, but stimulates it to work, ensuring the absorption of nutrients. In the form of pate or puree, boiled and steamed food is always tasty if prepared from fresh ingredients.
Authorized Products
The diet after surgery allows the use of:
- Puree porridges that are boiled in water or weak broth. You can take any cereals, except for coarse and difficult-to-digest ones: millet, pearl barley, corn. If the patient tolerates milk well, then it can be added to porridge in small quantities. Patients tolerate steam puddings made from various cereals well, especially pureed rice and semolina. If tolerated well, boiled thin vermicelli can be added to the diet.
- Soups with weak (secondary) meat/fish broth and vegetable broth. The first courses include vegetables that are devoid of coarse fiber - these are potatoes, carrots, cauliflower or zucchini. They are boiled well and, if possible, kneaded or ground. Cereals in soups are also kneaded, and buckwheat and rice are recommended to be pureed. Meatballs, tender meat or fish dumplings, egg flakes or a milk-egg mixture, and rolled boiled minced meat are added to soups. All these protein supplements increase the nutritional value and calorie content of dishes, which is very important for patients. When cooking, add dill, parsley and bay leaves to soups.
- Lean meat and fish. Their choice is quite large: beef, pike perch, bream, veal, chicken, rabbit, pollock, blue whiting, pollock, cod, hake. Meat/fish dishes are steamed in the form of soufflés, cutlets, meatballs, meatballs, quenelles, and a little later you can eat them in pieces.
- Lightly dried wheat bread, dry low-fat cookies and biscuits. With good tolerance (no diarrhea or bloating), you can eat up to 200 g of bread and low-fat baked goods per day.
- Vegetables without high fiber content (they were indicated above). Vegetables for side dishes are boiled, stewed, then pureed or finely chopped. The use of steamed vegetable cutlets with semolina is not excluded. During the season, you can add chopped ripe tomatoes without skin.
- Acidophilus, kefir and other fermented milk drinks, which can be consumed during the day as additional meals. Milk and cream are introduced into the diet as additives in tea, coffee drink, cottage cheese or porridge. Every day you need to eat freshly prepared cottage cheese and mild cheese, which is best grated. Butter is used with bread and in dishes.
- Soft-boiled eggs (up to 1-2 per day) - omelettes, egg white omelettes. Egg whites are used to make desserts (meringues, meringues).
- Sauces prepared with meat and fish broth, milk and the addition of sour cream.
- Ripe peeled fruits and raw sweet berries, baked apples and pears. However, melons, watermelons, plums, peaches and apricots are excluded due to the possibility of increased diarrhea. You can make jelly, compotes, jellies from the berries - you can add vanillin and cinnamon to all desserts. You can eat fruit marmalade and homemade marshmallows (without dyes), marshmallows, homemade jam and jam. Sweet desserts are introduced very carefully, as they can cause loose stools.
- Diluted natural juices (apple, cherry, orange, tangerine, strawberry).
- You can drink tea, chicory drink with milk, rosehip decoction, cocoa in water.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
Fruits | ||||
| quince | 0,6 | 0,5 | 9,8 | 40 |
| pomegranate | 0,9 | 0,0 | 13,9 | 52 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| dogwood | 1,0 | 0,0 | 10,5 | 44 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| blueberry | 1,1 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 44 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| dried pears | 2,3 | 0,6 | 62,6 | 249 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Bakery products | ||||
| white bread crackers | 11,2 | 1,4 | 72,2 | 331 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jam | 0,3 | 0,1 | 56,0 | 238 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| fruit and berry marmalade | 0,4 | 0,0 | 76,6 | 293 |
| meringues | 2,6 | 20,8 | 60,5 | 440 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
| Maria cookies | 8,7 | 8,8 | 70,9 | 400 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| dried bird cherry | 8,4 | 0,0 | 16,8 | 101 |
Dairy | ||||
| skim milk | 2,0 | 0,1 | 4,8 | 31 |
| sour cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,2 | 206 |
| acidophilus | 2,8 | 3,2 | 3,8 | 57 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cheese | 24,1 | 29,5 | 0,3 | 363 |
Meat products | ||||
| boiled beef | 25,8 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 254 |
| boiled veal | 30,7 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 131 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken | 25,2 | 7,4 | 0,0 | 170 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| Red caviar | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| Orange juice | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| Cherry juice | 0,7 | 0,0 | 10,2 | 47 |
| Strawberry juice | 0,6 | 0,4 | 7,0 | 31 |
| tangerine juice | 0,8 | 0,3 | 8,1 | 36 |
| Apple juice | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 42 |
* data is per 100 g of product
Features of the postoperative period
After surgery, proteins, fats and carbohydrates are not absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract for some time. In this regard, on the first day the patient is supported with parenteral medication and is prohibited from eating. Then little by little they begin to accustom the body to eat, but in small portions.
The timing of the transition to special nutrition after intestinal surgery depends on the individual characteristics of the body, the type of operation, food tolerance, and the functional activity of the gastrointestinal tract. First there is a diet with pureed food, then without pureed food. This stage continues for several weeks or months.
During the postoperative period, the sensitivity of the gastrointestinal tract to whole milk, strong broths and fresh fruits increases, so they are prohibited so as not to irritate the intestines.
IMPORTANT! If a person is used to drinking milk and it is difficult for him to give up this habit, it is allowed to replace the product with soy milk. Soy milk proteins contain highly plastic protein that is beneficial for the body.
Diet sequence
After the operation, the patient is shown dry fasting. If you are really thirsty, you can wet your lips with water. Nutrients for life are given through an IV.
Starting from days 2 to 5, the menu after intestinal surgery begins to include: decoctions of rice, rose hips, jelly, low-fat broth, berry jellies. Meals are taken in small portions up to 8 times a day. Liquids are allowed in small portions.
On days 6-14, the doctor prescribes a surgical diet, which consists of pureed soups, cereals and various purees, taken 6 times a day. The portion is 400 g - this is no longer possible, since it is necessary to eliminate additional stress on the digestive tract. This regime should be followed for up to 2 weeks.
Then you can add boiled fish and chicken. Add crackers, biscuits, soufflé, steam cutlets, omelet, low-fat dairy products, baked apples.
The conclusion of the diet after intestinal surgery is the introduction of uncut food into the diet. Chopped meat, apples and bananas are allowed here. Gradually introduce juices diluted with water without gas, low-fat cottage cheese, kefir. Allow some small vermicelli with a small amount of butter. Meals are divided into 5-6 meals.
The diet after intestinal surgery after a month gradually allows you to return to your usual eating regimen, but you still cannot eat fried, spicy, smoked, marinades, sauces, alcohol, or concentrated juices.
IMPORTANT! Food restrictions can last for several years. It is advisable to follow them so that additional gastrointestinal diseases do not arise and the disease for which the operation was performed does not worsen.
Fully or partially limited products
- Products that enhance putrefactive and fermentation processes: legumes, rye bread, coarse vegetables, baked goods made from wholemeal flour, whole milk, fresh yeast bread, baked goods, kvass, white cabbage. Also excluded from the diet are soups made from legumes, cabbage soup, borscht, rassolnik (due to the presence of pickles and pearl barley), cold first courses (okroshka, beetroot soup) and cold drinks that stimulate intestinal motility.
- Strong and fatty broths.
- Beets, radishes, celery, onions, radishes, garlic, mushrooms, rutabaga, turnips, cucumbers, sorrel, spinach.
- Milk in its natural form, sharp and overly salty cheeses.
- Fatty meats/fish/poultry, canned meat and fish, lard, smoked meats.
- Any fats (including vegetable fats), except butter.
- Millet, pearl barley, corn, barley cereals.
- Grapes, apricots, plums, dried fruits.
- Hot sauces, mustard, mayonnaise, horseradish, all types of pepper.
- It is not allowed to consume ice cream, chocolate, cakes, pastries, carbonated drinks, kvass, fruit drinks and juices from plums, grapes and apricots.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| parsnip | 1,4 | 0,5 | 9,2 | 47 |
| parsley (root) | 1,5 | 0,6 | 10,1 | 49 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| turnip | 1,5 | 0,1 | 6,2 | 30 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| melon | 0,6 | 0,3 | 7,4 | 33 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| dried fruits | 2,3 | 0,6 | 68,2 | 286 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| Wheat groats | 11,5 | 1,3 | 62,0 | 316 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
Bakery products | ||||
| vysivkovy bread | 9,0 | 2,2 | 36,0 | 217 |
| Old Russian grain bread | 9,6 | 2,7 | 47,1 | 252 |
| Rye bread | 6,6 | 1,2 | 34,2 | 165 |
Confectionery | ||||
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| cookie | 7,5 | 11,8 | 74,9 | 417 |
| Kurabye cookies | 6,7 | 25,8 | 64,6 | 516 |
| butter cookies | 10,4 | 5,2 | 76,8 | 458 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| seasonings | 7,0 | 1,9 | 26,0 | 149 |
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
Sausages | ||||
| dry-cured sausage | 24,1 | 38,3 | 1,0 | 455 |
Bird | ||||
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| dried fish | 17,5 | 4,6 | 0,0 | 139 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| vegetable oil | 0,0 | 99,0 | 0,0 | 899 |
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| bread kvass | 0,2 | 0,0 | 5,2 | 27 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| grape juice | 0,3 | 0,0 | 14,0 | 54 |
| plum juice | 0,8 | 0,0 | 9,6 | 39 |
* data is per 100 g of product
What should patients pay attention to after surgery?
- You should drink only water for the first 12 hours after surgery.
- You should start eating with pureed, semi-liquid dishes, light pureed soups, water porridges, low-fat natural yoghurts, natural juices.
- You should very carefully introduce new foods into your diet - no more than two items per day.
- In the first two days after surgery, you need to eat small portions at least five times a day. Serving sizes should be no more than 200 grams. The doctor must indicate how much liquid is allowed to be consumed. Preference should be given to juices, water, herbal infusions, and rosehip decoction. It is not recommended to increase the daily volume of fluid consumed so as not to cause tissue edema.
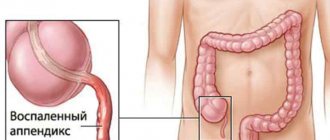
- When the risk of developing various postoperative complications has already passed, a gradual transition to an appropriate therapeutic diet (treatment table) can be made. For example, the diet after appendicitis or during a gastric ulcer is table 1.
- The rehabilitation period requires a gentle approach, so the diet after surgery should not include heavy foods: nuts (in large quantities), mushrooms, seeds (they tend to clog the stomach, which significantly complicates the digestion process), lard, fatty meat, seafood, fish. Vegetables prohibited: cabbage, corn and those vegetables that cause increased gas formation. After operations on the intestines and stomach, sour fruits and berries, as well as citrus fruits, are contraindicated.
- As the basis of the diet after surgery, you can use various soups (light chicken, cereal, vegetable, dairy), porridge with milk (or, if there are contraindications, with water). You can also eat bread in limited quantities, biscuits, all fermented milk products, a little butter, berries, fruits and vegetables. Different diseases, however, require different culinary processing of products. Therefore, you should consult with your doctor about the best form to consume fruits and vegetables (boil, bake, chop, or you can eat them raw).
- For any diet after surgery, it is contraindicated to consume coffee, alcohol, cocoa, chocolate in large quantities (chocolate consumption is allowed no more than 50 g per week), canned food, smoked and fried foods, salty delicacies, as well as any confectionery products that contain artificial additives.
The postoperative diet also depends on many factors. The most important thing is whether the operation was performed under anesthesia?
Nutrition after general anesthesia prohibits fluid intake for two hours. Then you can drink in small sips, and only after 5-6 hours after the operation it is recommended to drink heavily. This is due to the fact that general anesthesia inhibits the swallowing reflex and everything returns to normal gradually. That is, the patient needs some time for the paralysis of the pharynx to pass, otherwise he will simply choke.
Further, everything depends on the organ and system on which the operation was performed. The strictest is after operations on the gastrointestinal tract, usually No. 0 according to Pevzner. Its principle is liquid food with a minimum set of proteins, fats and carbohydrates to provide a gentle regime for the recovering system.
Unfortunately, doctors do not always give complete nutritional recommendations to patients after surgery, while it is simply necessary to comply with certain restrictions.
There is no need to think that the diet after surgery should be meager; rather, it should be taken under control and prohibited foods should be excluded from it. The body should eat well and gain strength after the ordeal. Food should be rich in vitamins, proteins, minerals and carbohydrates.
Be sure to organize at least 4-5 meals, with snacks if necessary. The amount of food consumed should not be large. After any operation, the stomach decreases in size, so you should not immediately load it. To avoid feeling hungry, it is better to increase the frequency of meals.
It is important to limit salt intake, excess of which can lead to increased blood pressure in the patient. After surgery, sugary carbonated drinks are prohibited.
Each individual case requires a more thorough approach, because everything depends on the organ on which the operation was performed.
On the first day after surgery, you can only drink a little. The first meal after surgery on appendicitis, stomach or intestines is possible only after 24-36 hours. You can start consuming light soup or broth. Borscht, fish and pea soups, okroshka, solyanka and other first courses should be avoided.
You should consider porridge or mashed potatoes as second courses. Among the cereals, rice, oatmeal, and buckwheat should be distinguished. During the first week after surgery, you should not eat meat. Sometimes doctors allow a small amount of rabbit meat, which is dietary. Pastries, pies, and fast food items are prohibited. Particular attention should be paid to the temperature of the food, which should not be hot or cold.
Low-fat yoghurts, kefir and milk porridges can be considered as products from the dairy series. You should start taking fresh berries and fruits with small portions to see how the body reacts to them.
Diet after surgery helps to lose weight and develop a proper diet. If the operation is not too complex, then the subsequent diet should include foods rich in protein and low in calories.
At this stage of recovery, it is important what and how much patients eat. The process of absorbing food should be leisurely - about 20 minutes. It is also undesirable to drink during meals, so as not to provoke an enlargement of the stomach.
If the operation was performed, for example, on an arm or leg, then no special restrictions are implied.
If operations were performed on one of the abdominal organs, then for the first few days food intake will be carried out through intravenous injections. You can start eating normal food on the second or even third day.
After gastric surgery, you can start eating as usual only after 14 days. If the cause of the operation is appendicitis, then one week is enough.
While eating, you should listen to your body so as not to miss the moment of satiety. If you overeat, there is a high probability of vomiting.
- At the first stage after surgery, eat only liquid food. In addition to 150 ml of light soups, you can add drinks to your diet. You should only drink 100 ml of liquid: low-fat kefir, apple juice, orange juice.
- At the second stage after surgery, you can start eating soft foods (porridge, purees).
For breakfast, you can afford 150 ml of low-fat yogurt. A small slice of bread with pate or soft cheese. For lunch, you can diversify your dishes with 150 grams of puree. Moreover, the puree can be prepared from banana, pear, melon, or boiled zucchini, potatoes or squash.
After surgery, the intestines are less able to absorb nutrients. For this reason, food should not only be easy on the gastric tract, but also rich in proteins.
Nutrition menu after intestinal surgery (Diet regimen)
A gradual expansion of the diet with new products allows you to diversify your diet after surgery. This is achieved by alternating meat and fish dishes, cottage cheese, cereals and vegetables. All dishes can be prepared with sauces, which diversify the taste. You can make egg dishes, fruit drinks and baked fruit for dessert every day.
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Useful and prohibited foods
General recommendations regarding the nutrition of patients for all types of surgical interventions are the same.
The postoperative diet after intestinal surgery during the first two months includes a ban on the following food categories:
- all types of alcoholic drinks;
- fresh vegetables;
- smoked and spicy dishes;
- grape juice;
- pickled vegetables;
- fish and fatty meats;
- berries and fruits;
- carbonated drinks;
- corn, legumes;
- wheat bran;
- spices, seasonings;
- coffee and tea (except fruit or black - it is needed for diarrhea);
- sweets, ice cream and baked goods.
Since the postoperative period in some patients occurs with stool disturbances, the following products are recommended for constipation:
- pureed soups;
- vegetable purees;
- fermented milk drinks;
- decoctions and compotes of dried fruits;
- whole grain or bran bread;
- plum or apple jelly;
- finely ground buckwheat or oatmeal;
- boiled beet puree.
For diarrhea, doctors recommend:
- strong tea;
- crackers or dried bread;
- decoction of rose hips, rice or raisins;
- boiled lean chicken;
- cottage cheese 0% fat;
- rice porrige;
- blueberry or cranberry jelly;
- carrot puree.
Postoperative intestinal nutrition after 2 months should include:
- white meat chicken or turkey;
- flax seeds (can be ground in a coffee grinder);
- light porridge with added butter;
- soy products;
- mineral water without gas;
- diluted vegetable and fruit juices (apple, peach, birch, tomato, carrot);
- fruits and vegetables;
- honey (minerals and vitamins);
- sufficient amount of liquid.
As mentioned above, foods that are dense and hard are considered prohibited. Nutrition should be gentle. Great preference is given to pates, which, with the addition of a small amount of chicken or turkey meat, help the body cope with the effects of anesthesia. Sour milk products help restore intestinal microflora faster.
IMPORTANT! Upon discharge, doctors give their patients an annotation: Dietary dishes after intestinal surgery (table No. 4), which shows in detail the menu with a list of restrictions that must be observed for a full recovery.
Reviews and results
In some cases, recovery of bowel function after surgery may take several months. This nutrition helps to more quickly adapt to changed anatomical conditions. Moderate sparing, preparing dishes by boiling, eating in small portions and excluding foods that provoke deterioration are necessary points for restoring the function of the organ.
Only patience and careful implementation of all nutritional recommendations will ultimately help restore health. This is reported in patient reviews. A balanced diet allows you to follow the diet for a long time.
- “... I have been suffering from nonspecific ulcerative colitis for 15 years. Frequent exacerbations and unsuccessful treatment for many years, the appearance of non-healing fistulas led to me being offered surgery. As a result, a meter of the small intestine and part of the large intestine were removed. Nutrition began with a pureed and gentle diet, but it accompanies therapy and does not lead to a cure. Only after four months did she begin to selectively and very carefully expand her diet. Now I already know what I can eat and what remains forbidden forever. The diet is healthy and I tolerate it well. We can say that I adhere to it constantly with minor deviations. There is no diarrhea, and I am not losing weight. I allow myself sweets, soft sweet fruits”;
- “... Crohn's disease often worsened (pain, diarrhea, blood in the stool) and treatment was ineffective. In addition, a narrowing of the intestines appeared. After 10 years of suffering and hospitalizations 2 times a year, the doctor suggested removing the altered section of the intestine and said that with subsequent proper treatment, exacerbations may not occur at all. The operation was performed laparoscopically, but a section of the intestine had to be removed because balloon expansion failed to achieve results. Now the only way out is constant proper nutrition and treatment. The diet helps me: pain and diarrhea are reduced, activity is restored, and appetite improves. Cooking in a double boiler does not take much time (I cook vegetables, meat and porridge in a bag all at once). I have forever excluded smoked, fried, spicy and unhealthy foods”;
- “... For my son, due to Crohn’s disease, a section of 15 cm of the ileum and 15 cm of the cecum was removed using the laparoscopic method. There was stenosis of the ileum - this was manifested by severe pain after any food, severe weakness and shortness of breath. At that time, he could eat thin porridge for baby food and drank Modulen. The operation was successful, removal of 30 cm had almost no effect on intestinal function, and the son recovered relatively quickly. Of course, for a period of 3-4 months I had to strictly follow a diet and learn to eat again. It was also important not to give up treatment. Humira and Azathioprine were prescribed. Today, my son has recovered, plays sports, and life has improved. I teach the whole family to eat healthy.”
Differences in the diet of patients
Dietary nutrition after intestinal surgery varies among patients with different diagnoses. For example, people who have had adhesions removed are initially advised to consume a sufficient amount of liquid in the form of unsweetened compotes and herbal decoctions. This helps replenish the loss of nutrients. Cereals, lean meats and milk products are also prescribed. All cooked foods must be pureed. This is necessary for two months after surgery.
For people who have had cancerous tumors removed, doctors recommend a diet that emphasizes protein intake. Boiled meat and fish are introduced into food within two weeks after the intervention. Bananas, containing potassium and carbohydrates, replenish strength in such patients, and the astringent properties of the product help heal internal scars.
Patients who have undergone surgery for intestinal obstruction receive only parenteral nutrition for 3 days. Then gradually they begin to be given broths and decoctions.
For patients, the diet after intestinal surgery in the form of a menu, when they are allowed to eat little by little, looks something like this:
- 8.00 - rice porridge with 2 boiled quail eggs;
- 11.00 - 0% curd mass;
- 14.00 - vegetable soup with croutons, meat soufflé;
- 17.00 - apple jelly, biscuits or banana jelly;
- 20.00 - boiled fish, mashed potatoes and carrots or omelet and yogurt;
- 22.00 - chamomile tea.
Gentle nutrition during the postoperative period is the key to health for many years. A person needs to listen to the sensations of his body and pay attention to products that he likes and suits. If, during a gradual transition from liquid, pureed and pureed food to normal nutrition, some stage lasts longer than expected, this is not considered a deviation - this is a hint from the body, general well-being.
IMPORTANT! The doctor will always monitor the recovery periods of the diet, paying attention to calorie content, susceptibility to allergies and food tolerance.
What is recommended for nutrition?
When drawing up a dietary regimen during the postoperative period, it is important to select products that do not have a mechanical or chemical effect on the intestines and are easily digestible, and dishes made from them do not have a thermal effect.
The list of products desirable for consumption is as follows:
- coarse grain;
- vegetables;
- sweet type fruits;
- blueberry;
- cottage cheese and low-fat cheeses;
- crackers;
- porridges based on rice, wheat and oats;
- flax seeds;
- potato;
- juices from freshly squeezed vegetables;
- water with slight mineralization and always without gas;
- black and fruit tea;
- fermented milk products.
The list of desirable products for consumption includes low-fat cottage cheese.
20-25 days after the operation, you can switch from a strict diet to eating according to diet No. 4, and one of the most important requirements in it is the elimination of fermentation and putrefaction in the intestines. At the 3rd stage of dietary nutrition, you can prepare the following dishes from permitted products:
- Bread products are only dried, you can use crackers.
- Porridges are prepared in water or lean broth from pureed cereals.
- Minced meat from lean meats or fish. Poultry meat is best.
- Unrich meat and fish soups, and the meat must be thoroughly chopped.
- Eggs are eaten soft-boiled or as a steam omelet.
- Butter is significantly limited.
- Sweet berries and fruits, pureed or baked, jelly, mousse, jelly.
- Vegetable decoctions can be consumed safely.
- Recommended drinks: rosehip decoction, diluted juices, tea, coffee with a doctor’s permission.
After 20-25 days, it is recommended to drink rosehip decoction.
Proper nutrition for various diseases
The menu should be selected taking into account the individual needs of the body. Products that are acceptable for some types of diseases may not be suitable for other affected areas. Therefore, you should always adhere to the opinion of a specialist and not make arbitrary decisions. However, it will be useful to understand the general principles of choosing a diet.
If adhesions are removed
The diet after resection performed to remove adhesions has its own characteristics. At the very beginning of the recovery period, the body will need more fluid - still water, herbal infusions, dietary broths, tea. A little later, light soup, thin porridge or puree are allowed to be included in the meal. If you feel good, the next step is to introduce dairy products into your diet, and even later protein dishes are allowed. It is necessary to ensure that the food consumed does not burden the digestive organs, but is small and soft. During this period, alcohol, salty and spicy foods are contraindicated. After undergoing surgery, there is a danger of recurrence of adhesions, so you need to take responsibility for your health by choosing a diet to restore the intestines.
If the reason for the operation was a tumor
For rehabilitation after removal of a tumor in the intestine, a balanced diet will have a beneficial effect on the body. At such a moment, it is very important to support the digestive organs. Consulting with your doctor will help you choose an effective way to eat a healthy diet. Vegetable broth, puree soup, simple soups, and cereals are allowed to be included in regular consumption. Fruits will be beneficial to the intestines, but not all fruits, except for sour and bloating-causing crops.
To maintain immunity, saturate with vitamins and fiber, a banana is suitable - it will give you a quick feeling of fullness and is easily digested in the intestines. You can eat vegetable oils - they will “lubricate” the damaged areas and relieve inflammation. You will have to give up heavy, fatty foods. Meat products can be gradually introduced into the diet after several weeks of rehabilitation. You can only eat processed meat in small portions. All food should be chewed thoroughly so that it is easier to digest. The easier food is processed, the better for the well-being of patients. You need to eat small meals - often and little by little, so as not to overload the gastrointestinal tract. You will have to follow the regime for about a month.
Intestinal obstruction
This disease is very dangerous and the process of postoperative intestinal restoration is characterized by a strict regime. In the first days, eating and drinking is prohibited. Nutrients and vitamins are administered to patients by injection through the blood or using a probe. A little later, liquid nutrition is allowed - water, broths, herbal infusions. After a while, you can use mashed and pureed recipes, the so-called zero nutrition - these are light porridges and steamed vegetables, jelly, cereal infusions (wheat, rice, oatmeal). Food should not be too hot or cold. If your body reacts normally to all foods, you can return to your normal diet after a month.
If you have had rectal surgery
During the first 24 hours of recovery, the patient is advised to fast. Then it is possible to consume light puree dishes, vegetable broths or steamed food. Diet products should not irritate the mucous membranes and contribute to flatulence. The food temperature should be room temperature and gentle on the stomach. Foods that are difficult for the intestines and other digestive organs are contraindicated and the diet should be followed for as long as possible. Fat, alcoholic beverages, and smoked foods should be left out of the diet forever. Proper nutrition and diet will support damaged parts of the gastrointestinal tract and prevent other abnormalities.
Principles of diet planning
The diet after intestinal surgery is compiled taking into account the reasons that led to surgery, the current condition of the patient and the presence of complications. For example, if the operation involved removing the appendix, already on the 3rd day you can eat mashed potatoes and boiled pureed chicken. Removal of a tumor of the sigmoid colon involves switching to decoctions and pureed dishes from about the 4th day. But nutrition after resection of the small intestine in some cases allows even semi-liquid meals only after 2 weeks. Food for intestinal adhesions should be pureed for about 2 weeks.
Nutrition should help normalize stool: it should not be liquid or turn into diarrhea (this leads to exhaustion of the body), or be too hard (increases the risk of a hernia).
In case of oncology of the sigmoid colon and a number of other diseases, the operation often ends with the imposition of an intestinal stoma - a surgically created opening on the anterior surface of the abdominal wall (the so-called colostomy). In this case, diet therapy should ensure normal stool. It is recommended to keep records to track the body's reaction to certain foods. Digestive problems (diarrhea, constipation, vomiting, etc.) require diet correction. In case of constipation, plums or prunes, as well as beets, are recommended. For diarrhea - grain porridge. When the stoma is closed, a new diet cycle is necessary.
You need to eat at the same time - this makes it easier to digest food. To eliminate pain at night and improve sleep, dinner should be very light. Breakfast should be the heaviest meal. The number of daily servings depends on the time elapsed after surgery.
In many cases, it is recommended to drink a glass of water on an empty stomach. For constipation, it should be cool. If you need to cleanse the body or thin the blood, use warm water.
Fried food is not allowed. Boiled, stewed or baked dishes without crust are recommended.
Diet for the week
Intestinal cancer is very difficult to treat. After intestinal surgery, the patient should not neglect the diet and doctor’s advice regarding nutrition and lifestyle.
Below is a sample menu for a person undergoing bowel surgery for seven days.
- The first day: In the morning you need to drink a glass of clean water, after half an hour you need to have a snack of oatmeal in water with the addition of a small amount of walnuts and wash it down with jelly. After three hours, be sure to make a snack - applesauce. For lunch, the patient should eat vegetable soup with dumplings, pureed buckwheat porridge and tea. The afternoon snack should consist of dried fruits and mint tea. For dinner, it is preferable to eat a salad of chopped vegetables (tomato, cucumber) and drink a glass of jelly.
- Second day: Drink a glass of fruit juice in the morning. For breakfast, semolina porridge, biscuits and tea are suitable. Snack will consist of yogurt and banana. For lunch you can eat oatmeal soup with vegetables. The patient's afternoon snack includes a glass of jelly and a handful of crackers. For dinner you are allowed to eat rice porridge, steamed chicken cutlets and herbal tea.
- Day three: in the morning on an empty stomach, drink a glass of water, 30 minutes later, eat a bowl of oatmeal porridge with nuts, drink jelly with cookies. After a couple of hours you can eat raspberry jelly and orange. For lunch, buckwheat soup with fish dumplings and herbal tea are suitable. A snack after a couple of hours includes mashed potatoes, cookies and jelly. The patient can have oatmeal with fruit for dinner.
- Day four: Before breakfast, drink a glass of diluted juice and then eat meatballs, rice porridge, and tea. After three hours, you should eat a handful of nuts and applesauce. For lunch, a steamed omelette, minced meat, jelly with crackers are perfect. The afternoon snack will consist of kefir and biscuits. For dinner, the patient is supposed to eat a vegetable salad from permitted products and drink blueberry jelly.
- Day five: barley porridge, compote for breakfast for the patient. Afterwards, you can eat a baked apple for a snack. For lunch there will be fish stew and buckwheat porridge, herbal tea. An afternoon snack for the patient is a banana and half a glass of berries. Dinner – stewed liver, jelly and baked pear.
- Day six: in the morning, patients drink a glass of compote. An hour later, the patient eats oatmeal with water and half a glass of raspberries. The snack consists of jelly with crackers. For lunch they offer pureed vegetable soup with the addition of day-old bread or croutons and tea. For an afternoon snack, a soft-boiled egg, and for dinner, baked zucchini, barley porridge and compote.
- Day seven: For breakfast they eat buckwheat porridge, and a snack consists of blueberry jam with cookies. For lunch you can eat soup with mashed potatoes and vegetables, chopped lean meat. The patient's afternoon snack includes mashed potatoes and fish dumplings. For dinner - vegetable salad, chicken soufflé and compote.
Problems with the intestines can be completely eliminated only over time, but for now you should not load the body with unhealthy and heavy food, otherwise the well-being of an oncology patient may worsen sharply.
One of the main causes of constipation or diarrhea is poor diet.
.
Therefore, to improve bowel function, you need to drink a simple drink
.