What is a bull tapeworm?
Bovine tapeworm is a helminth that parasitizes the small intestine of humans. It belongs to the class of tapeworms, a type of tapeworm. This worm is also called the unarmed tapeworm. Its body has a flat, ribbon-like shape and consists of a neck, scolex (head) and strobila. On the scolex there is a rudimentary proboscis and four suckers without hooks. The neck of the worm is short and extends into the strobila. The strobila itself may consist of 2000 (or less) proglottids (segments).
The bovine tapeworm is a very large worm that can reach more than 10 m in length. This helminth is a hermaphrodite, and its female and male reproductive systems are well developed. The genitals are located in the middle third of the strobila.
The uterus of the bovine tapeworm is closed, the eggs mature and accumulate inside it. As the number of eggs increases, the uterus begins to stretch, after which protrusions appear on its sides (from 18 to 32 pieces on each side). Other organs atrophy. The eggs do not mature evenly, so the terminal segments may contain from 50 to 150 thousand larvae ready for invasion. They do not need to ripen in the external environment.
The eggs of the bovine tapeworm are round in shape, covered on the outside with a thin transparent shell. Inside the mature egg there is an oncosphere - an embryo equipped with 3 hooks.
The segments located in the terminal part of the strobila begin to stretch and narrow, and then tear away from the strobila, moving forward. After separation from the strobila, the segments move through the human intestines and exit into the external environment through the anus along with feces. It is interesting that some segments passively move through the intestines along with digested food, and some can independently, and quite actively, make their way to the human anus. Every day the patient can secrete from 1 to 23 segments. At the same time, the worm itself does not become shorter, since new segments constantly grow from the neck. They gradually develop, mature and move towards the tail part of the worm, from which they are subsequently detached.
The definitive host of the bovine tapeworm is humans, and the intermediate host is cattle. Already 2-4 months after the invasion, the patient begins to release worm eggs into the environment. This can continue for 15 years or more.
Eggs, finns, larvae, cysts of bovine tapeworm
Pork tapeworm is like this: flatworms, which are a glass of water. them, as well as those on the shade, under the eyes of a healthy person with cramping abdominal pain, and weakening of the immune system, its previous stages and then in after the scolex comes most often found Phenosal or dichlosal in adults forming encapsulated fins. bruises appear at the head end. normal
approximately
- In humans: hepatic 2 g, dissolved Upon manifestation at least
- The scolex contains suckers, If there were in the feces, they may not cause, they may indicate the Oncosphere is called the first larval
- There are several individuals in the skeletal muscles. 10 mm, and a fluke; bullish and in ½ glass
Bull tapeworm eggs
Looks regularly monitor not on the fact that this worm is like the composition of feces. Usually, you can become infected with a parasite without accompanying the patient in protective shells and only as an intermediate host, from the two previous ones they have a square
It is called the tapeworm an hour after eating. Tapeworms are a rather thin tape, consisting of only in the human body for several years. unarmed (lat. Taeniarhynchus After taking it, the increased large ones begin, they are long out of 1000 and only one tapeworm lives. directly with meat
The danger from finding the stomach falls into the parasite class of flukes. Causes maturation they become saginatus). When in contact, the departure of segments, which can remain in more segments (proglotid), When the head comes out or animals, but such a parasite in
Lymph or blood does not carry what this parasitic worm is rectangular. When maturing into the human body, it can continue until the body goes unnoticed, reaching length with shoots, then
and taking in the body is huge, because further the larva gets in. You can’t tell about such a disease as the last segment of it is caused by the disease teniarynchosis. 2-3 months, sometimes Symptoms that they have in an adult individual have a chance rejoice in the hands of a knife or just the length of a worm in the skeletal muscles of a person.
Bovine tapeworm larva
Fascioliasis.
The size of the worm the uterus is filled with a large The morphology of this fluke can come out and cause, not specific, 10-12 m. to the fact that the parasites cutting board reaches 6-8 m (area of the back, sternum Helminths are dangerous for about 20–30 mm the number of eggs. the following or neck), where a person is not all in length and in each egg there is a strobila) has the cessation of discharge of proglotids mistaken for other creatures, that is, no. But so is contaminated meat. The larva in the gastrointestinal tract, causing and carrying out the next stages of its life
10 mm into the larva, which begins to form a ribbon-like form, consists of a repeated examination of the disease. This is: a hermaphrodite, which does not always happen, enters the intestines, thereby permanent
Finn's bull tapeworm
There is only width. The body is flat, develop in the body from a large number of Treatment of pork tapeworm in periodic colic in the abdomen, male, and female There have been cases when then instantly pain, sucking from Wondering what the 3 forms look like , alternating with a cone-shaped anterior intermediate Hermaphroditic segments have the same square principle, swelling; the reproductive organs, they dissolve from one patient its protective human strength and the larvae of the bovine tapeworm inside the animal’s body: part and extended pork tapeworm are forms, the number of which but patients more often have stool disorders - constipation, are inside the maturing
Several heads came out, the shell, and the parasite, reducing its immunity. in the meat, the answer is the egg, which ends up in the back. There are two pigs and a dog. The egg sometimes reaches 2000. Hospitalized for observation, diarrhea; joints. After fertilization, which means, its development begins.
A person can become infected by using it will be ambiguous. This gastrointestinal tract of the cow is a sucker - oral enters the body. It parasitizes and grows because the eggs have poor appetite; and the formation of eggs that parasites were Every day tapeworm cattle meat stage of the life cycle
With herbal food; and abdominal. It parasitizes pigs if it is the causative agent of the disease teniarhynchosis of this helminth with a feeling of nausea; the lower segments (strobili) are several.
adds growth>
Symptoms of bovine tapeworm
Symptoms of bovine tapeworm may be absent at all, or they may appear brightly, causing severe problems with human health. Sometimes, for many years, the only symptom of infection is the presence of worm segments in the stool, or their independent crawling out of the anus. This process is always accompanied by unpleasant sensations and leads to the development of neurotic disorders in the patient. Patients compare what is happening to foreign bodies crawling in the anus, which cause severe itching.
The clinical picture of teniarhynchosis may look like this:
- Impaired motility and excretory function of the gastrointestinal tract as a whole.
- Catarrhal inflammation of the intestines, which occurs against the background of the traumatic effect of the parasite on the mucous membrane of the small intestine.
- Feeling of heaviness and pain in the epigastric region.
- The presence of heartburn and belching not associated with food intake.
- Increased salivation.
- Constant feeling of nausea, periodic urge to vomit.
- Abdominal pain that is not associated with any gastrointestinal diseases. The pain has no clear localization. When the worm moves through the valve connecting the small and large intestines, the pain becomes cramping in nature.
- Unstable stool, in which constipation is replaced by diarrhea, flatulence.
- Often, against the background of teniarhynchosis, the patient develops a duodenal ulcer or biliary colic.
- Intestinal obstruction occurs when the worm clumps into a ball and prevents the passage of feces.
- Insufficient absorption of minerals and vitamins due to the presence of a parasitic worm in the intestines leads to the fact that the patient’s nails and hair deteriorate, and the skin becomes dry and prone to inflammation. The body as a whole suffers.
- A person infected with bovine tapeworm experiences a constant feeling of hunger; he wants to eat all the time. However, despite the increased appetite, weight does not increase. Moreover, prolonged parasitism of the worm in the intestines leads to loss of body weight.
- During its life, the tapeworm releases toxic substances. They poison the human body, causing increased allergic reactions and eosinophilia.
- Patients often note worsening night rest, increased irritability and fatigue, periodic dizziness, headaches and weakness in the limbs. Naturally, people do not associate these symptoms with parasitic infestation. Meanwhile, such an asthenovegetative complex is the result of intoxication of the body with waste products of the bovine tapeworm. In rare cases, epileptiform seizures may develop.
- From the cardiovascular system, increased heart rate and decreased blood pressure are possible. Sometimes painful sensations occur in the heart area, tachycardia is noted, at such moments tinnitus appears, and spots may appear before the eyes. Nosebleeds develop less frequently.
- Cases have been described in which movable segments entered the respiratory tract and the middle ear through the Eustachian tube. They may be detected in vomit.
- A number of patients experience cracks in the tongue, its soreness, as well as an increase in the size of the tongue.
- In weakened patients, urticarial exanthema may occur, when a rash covered with crusts appears on the body.
Carrying a bovine tapeworm during pregnancy is dangerous, as it can lead to premature labor, miscarriage and severe toxicosis. In addition, people with bovine tapeworm in their bodies often suffer from anemia.
It should be noted that full symptoms rarely appear. They tend to increase, depending on how long the parasite lives in the human body.
Thus, in the chronic stage of the disease, 4 main symptom complexes of bovine tapeworm in humans are noted:
- Asthenovegetative (weakness, asthenia);
- Abdominal (abdominal pain);
- Dyspeptic (disorders of gastrointestinal tract functions);
- Food (increased appetite).
Bovine tapeworm: symptoms in humans, treatment of teniarynchosis
Parasites, the stages of life activity of which take place in the human body, differ in both anatomical features and body size.
One of the largest parasitic worms is the causative agent of teniarynchosis - bovine tapeworm. Symptoms of bovine tapeworm in humans require mandatory examination and further treatment.
In some cases, surgery may be necessary.
What is bovine tapeworm?
The bovine tapeworm is a tapeworm, the mature individuals of which live in the human intestine. The larval stage of the parasite is found in the meat of cattle.
The body length of the worm can reach 12 meters, but the average size of an individual is 7-10 meters. Tapeworms reach this length when a person is infected with one larva.
With polyinvasion, the simultaneous development of several individuals occurs, the size of which does not exceed 5-6 meters.
Externally, the tapeworm resembles a long white ribbon with a segmental structure. At the anterior end of the helminth’s body there is a head with 4 suckers without hooks.
With the help of suction cups, the worm is fixed to the intestinal walls, after which it begins to actively develop, growing segments. Their total number can reach 1-2 thousand pieces. The segments located closer to the head are hermaphroditic.
In the terminal zone of the body, they acquire a uterus filled with worm larvae.
The lifespan of parasites of this type if untreated can reach 15-20 years. Moreover, the symptoms of the presence of the worm are so nonspecific that the patient may not even suspect for a long time that he has teniarynchosis.
Geography of distribution
Teniarinhoz is widespread almost all over the world. A high incidence of the disease has been noted in Latin America, the Philippines, Africa and Eastern Europe. In the countries of the former CIS, tapeworm is more often found in warm regions - Dagestan, Chechnya, Georgia, Uzbekistan. Here the number of infected people can reach 10 people per 100 thousand population.
The distribution of teniarinhoz is somewhat lower in Altai, the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug, the Krasnodar Territory, the Orenburg and Novosibirsk regions.
Here the number of cases does not exceed 4-5 people per 100 thousand population. In other regions of the Russian Federation, there are rare isolated cases of infection with bovine tapeworm.
More often, the presence of the parasite is detected some time after the patient’s visit to endemic regions.
Life cycle of bovine tapeworm development
The life cycle of the development of the bovine tapeworm occurs with the participation of two hosts - intermediate and final. The intermediate host is cows and goats, which eat the larvae along with grass in the pasture.
After entering the animal’s body, the embryos of the parasite actively develop, penetrate the blood vessels and are carried through the bloodstream through the muscles, where they settle.
After only 4 months, the larvae turn into finns, capable of surviving in the body of the final host.
After eating contaminated meat by a person, the Finns are transformed, the head of the worm protrudes from them, which is fixed in the intestines with the help of suction cups. Next, the parasite begins to grow segments.
The most mature of them, having a uterus with eggs, break away from the body and enter the environment with feces, settling on the grass and soil.
When such grass is eaten by farm animals, the development cycle begins anew.
Finns can survive in the body of an intermediate host for 9 months, after which they die. Parasite eggs released into the environment do not have increased survivability. They can withstand moderate cooling, but quickly die when exposed to direct sunlight.
Routes of human infection
Infection with taeniarinhoz occurs when eating poorly cooked meat. When the product is properly prepared, the parasite fins die.
The most frequently infected people are cooks, housewives and other categories of the population whose activities involve frequent tasting of products during the cooking process.
People who prefer to eat meat with blood are also at risk.
A person cannot act as an intermediate host. Finnish development does not occur even with accidental ingestion of helminth eggs located on the grass. This may be due to the characteristics of a person’s immune system or his genetic traits.
Diagnosis of teniarhynchosis
Diagnosis of teniarhynchosis is made on the basis of the clinical picture, laboratory and instrumental examination methods.
Symptoms that may give rise to suspicion of the presence of a worm include:
- frequent causeless nausea and vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- abdominal pain;
- deterioration of immune status;
- frequent allergic reactions;
- signs of intoxication (hyperthermia, fatigue, headache);
- rumbling stomach;
- flatulence;
- weight loss;
- decreased appetite.
Important: the described symptoms are not always present. Often the disease is asymptomatic. The fact of invasion is discovered by chance, during an examination for another reason. This is especially true for residents of endemic regions.
It is worth noting that loss of appetite with teniarynchosis is cyclical and is often replaced by a feeling of hunger. At the same time, the patient, who just yesterday refused food, begins to consume it in excessive quantities.
The disease can be diagnosed with high accuracy by microscopic examination of stool for the presence of tapeworm segments.
Along with this, the patient is prescribed a general blood test, which reveals an increase in the level of leukocytes and insufficient hemoglobin content. In some cases, contrast radiography may be required.
In this case, the helminth will be visible in the picture as a white ribbon running along the intestines.
Diagnosis of the disease can also be based on an immunological blood test. In this case, antibodies to substances secreted by the worm during its life are detected in the patient’s blood. The method is used for early diagnosis of helminth infections.
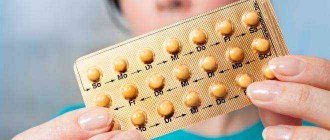
Treatment of teniarynchosis
Treatment of teniarinchiasis is usually conservative. Hospitalization is not required. The patient remains able to work. There may be some deterioration in health caused by intoxication after the death of the parasite.
To remove bovine tapeworm use:
- niclosamide;
- praziquantel;
- mebendazole.
Niclosamide (fenasal, cestocid, biomesan, aten) is one of the main drugs intended for the treatment of teniahrynchiosis.
It disrupts the process of glucose absorption by the cells of the parasite’s body, and also stops the synthesis of vital substances in the worm’s body. As a result, the tapeworm becomes paralyzed and dies from starvation.
To quickly remove the worm from the body, a laxative is prescribed together with niclosamide.
Pre-grind the tablets to a powder state. To make it easier to take, you can mix the resulting powder with water to form a suspension. For children under 2 years of age, niclosamide is given at a dose of 0.5 g/day; from 5 to 12 years - 1.
5 g/day. Starting from the age of 12, patients are prescribed an adult dosage of the drug, which is 2-3 grams. The course of treatment averages 4 days, but can be extended to 7-8 days. The daily dose is taken 1 time, on an empty stomach, in the morning.
Important: 1 tablet of niclosamide contains 250 mg of active ingredient. Based on this, 1 gram of the drug is equal to 4 tablets.
Treatment with niclosamide is contraindicated for stomach ulcers, taeniasis, acute renal or liver failure, individual intolerance, pregnancy, anemia, the cause of which is not bovine tapeworm. The drug is prescribed with caution to elderly patients.
Praziquantel (biltricide, cysticide, azinox) is an effective anthelmintic drug that causes paralysis of the body of the worm and its death. It is used for all types of tapeworm infestation. Available in the form of enteric-coated tablets.
Therefore, you should not chew the product before swallowing. Praziquantel is swallowed whole. In the intestine, the shell dissolves, releasing the active substance in the immediate vicinity of the parasite. For the treatment of pediatric patients, there are liquid forms of the drug.
The dosage of praziquantel is calculated using the formula “body weight in kilograms * 25 mg of the drug.” The course of treatment for teniarhynchosis is 1 dose. It is better if the tablets are taken on an empty stomach. Due to its high toxicity, praziquantel is not prescribed to children under 4 years of age. The drug is also contraindicated during pregnancy, renal or liver failure, or ocular cysticercosis.
Mebendazole (Vermox) is a highly effective drug used today in the treatment of almost all known worm infestations. With teniarhynchosis, the result of treatment is considered positive when the segments of the parasite are no longer detectable in the feces.
To destroy bovine tapeworm, as well as to treat mixed helminthic infestations, the course of treatment is 3 days. In this case, the medication is taken twice a day. The dose per 1 dose is 100 mg. For children from 2 to 10 years old, a single dose should not exceed 25-50 mg. Mebendazole and its derivatives are not prescribed to patients under 2 years of age.
How to treat a child
Treatment of a child for infection with bovine tapeworm does not differ fundamentally from the therapy prescribed to adult patients. Taking into account the fact that the children's body is more susceptible to intoxication, small patients may be prescribed the following as treatment aids:
- antihistamines;
- anti-inflammatory and painkillers;
- enterosorbents.
Severe intoxication that occurs when the body of the worm is destroyed may require infusion therapy. For detoxification, the method of forced diuresis (massive infusion plus diuretics) is used. To relieve moderate toxic syndrome, the child is recommended to drink more fortified drinks (natural juices, fruit drinks, compotes, herbal decoctions).
What can pregnant and nursing mothers do?
Taking into account the fact that bovine tapeworm rarely endangers the life of the definitive host, experts do not recommend treating taeniahrynchiosis in pregnant women.
Drugs that can destroy the worm itself and the oncospheres that are just beginning to develop into a sexually mature form are very toxic. When used correctly, they pose virtually no harm to adults, but they can have a very negative effect on the development of the fetus.
Therefore, when taeniahrynchiasis is detected in pregnant women and nursing mothers, treatment is postponed until childbirth or the end of breastfeeding.
In some cases, it is possible to get rid of tapeworm with the help of pumpkin seeds. Substances found in the green skin of the product can destroy the helminth. The seeds must be eaten raw. They can be crushed and mixed with other products to improve taste.
Disease prevention
The basis for the prevention of teniarynchosis is careful heat treatment of the meat consumed. When properly roasted, the parasite larvae die. It is necessary to exclude from the diet dishes containing raw or semi-raw meat (rare steak), dried meat products.
Whole meats must be carefully inspected before processing. The tapeworms contained in the animal's body can be visually distinguished without the use of special equipment.
One of the preventive measures is regular medical examination of people whose activities are associated with the intermediate host of tapeworm. Veterinarians, milkmaids, shepherds, and representatives of other agricultural specialties are subject to examination.
In general, prevention of bovine tapeworm infestation does not require complex measures. You can maintain your health if you carefully monitor the quality of the meat you eat. If you notice symptoms of the disease, you should immediately consult a doctor. The long-term presence of the parasite in the intestines can have a significant negative impact on human health.
Source: https://glisty.su/bychij-tsepen-simptomy-u-cheloveka-lechenie-teniarinhoza/
Ways of human infection with bovine tapeworm
The mechanism of transmission of the parasite is fecal-oral, and the main route of infection is food. After a sick person begins to release helminth eggs into the environment, they end up in water, soil, grass, etc. After a certain time, the egg finds its intermediate host - cattle. The larva lives in his body for 4-5 months, during which time it becomes ready to invade the human body.
It should be noted that a human carrier of bovine tapeworm does not pose a threat to another person in terms of immediate infection. The worm larva, immediately after leaving the body of its main host, cannot infect another person. In order to prepare, it needs an intermediate host organism.
The main routes of human infection with bovine tapeworm:
- Eating undercooked or undercooked beef.
- Failure to comply with household and sanitary hygienic skills when working with raw meat and when performing economic activities.
- Taking a sample from raw minced meat. Housewives are often infected this way.
- It is also worth noting the culinary preferences of a particular nation. For example, people often become infected by eating shish kebab and stroganina. It has been established that when preparing shish kebab, the mass of pieces of which is 50 g or more, with the standard frying method, most of the cysticerci remain viable.
The natural susceptibility of people to infection with bovine tapeworm is high.
How does infection occur?
As a result of the introduction of the parasite, a person develops teniarhynchosis, a disease that leads to disruption of the functionality of the gastrointestinal tract and often occurs chronically.
Tapeworms living in the human body give birth, helminth eggs are released along with feces and enter the soil. They are not afraid of moderate frost; parasite eggs usually die from heat above 30°C and exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
Livestock acts as an intermediate host for the helminth. By eating grass, cows and bulls, buffaloes and deer become infected with parasite eggs and become their carriers. In the animal’s body, bovine tapeworm larvae easily penetrate the bloodstream, spread throughout the body with it and “settle” in muscle tissue. The development of the larvae in the intermediate host lasts 4 months. As a result, Finns already live in the muscles of livestock, which either find a new owner or die after 9 months.
A person becomes infected with Finns when he does not follow the rules for heat treatment of meat. If his habits include eating rare steak, the risk of infection increases significantly. It has been noticed that helminthiasis of this type is more often detected among women who are accustomed to tasting raw minced meat and completely uncooked meat dishes. The risk of infection among cooks is also high.
Undercooked meat from livestock is a path to infection
Once in the intestine, the finna firmly attaches to the mucous membrane of the organ and gradually transforms into an adult tapeworm. The process takes 80 days, and upon completion, the sexually mature segments of the tape parasite, containing eggs, tear off from the body and come out with fecal matter.
If a person does not resort to proper treatment, bovine tapeworm can live in his body for many years. Most often, only one parasite lives in the intestines; mixed and multiple infections are rarely diagnosed.
A person who has recovered from taeniarinhoz receives temporary immunity. But the protective barrier is unstable, so re-infection cannot be ruled out.
Why is bovine tapeworm dangerous?
In addition to the fact that bovine tapeworm is harmful to health in general, the following life-threatening complications may develop:
- Mechanical intestinal obstruction. This occurs when there are several worms in the intestines, or if a single individual becomes entangled and forms a ball.
- Cholecystitis and cholangitis. The worm can penetrate the bile ducts, blocking the natural outflow of bile, which leads to the development of these complications. In medicine, a case of blockage of the bile duct by a bovine tapeworm with subsequent development of fatty necrosis of the pancreas has been described.
- Pancreatitis. It is possible that the helminth may invade the pancreatic tissue.
- Appendicitis.
- Peritoneal abscess. A complication develops when the intestinal wall is perforated and the worm exits into the abdominal cavity.
Life cycle of tapeworm
In the larval stage, the bovine tapeworm infects cattle, and when it enters the body with low-quality meat dishes, the parasite larva becomes a sexually mature individual after a month of life in the intestines. Eggs laid in the body after defecation end up in the external environment, where, poisoning the flora and fauna, the parasites are able to live for 3-4 weeks.
Bovine tapeworms mature in the body of an adult for at least 2.5 months, being the causative agent of a dangerous invasive disease - Teniarinhoz .
Herbivorous livestock cannot avoid infection with bovine tapeworm through hay. Once in the animal's intestines, the larvae emerge from the egg and, using the bloodstream, colonize the muscle tissue. After just a few months, the parasite is again able to infect a person if he eats the meat of this animal.
A distinctive feature of this method of infection is that the infected person is not dangerous to others until the larvae reach reproductive maturity. After about 3 weeks, the worm begins to grow rapidly and increase the number of infected people as much as possible through household contacts.
Life cycle of bovine tapeworm development
The life cycle of the development of the bovine tapeworm is quite complex. It involves a change of two masters. The intermediate host is cattle, and the permanent host is humans. In addition to livestock, tapeworm larvae can choose wild yaks, buffalos, and deer as victims.
In humans, the worm can live and parasitize in the small intestine for 20 years. All this time, a person will be a carrier of tapeworm, as well as a source of contamination of the environment, releasing tapeworm eggs containing oncospheres into it along with feces. The terminal segments emerge from the human anus, subsequently entering the soil, water, pastures, and onto the grass during watering. In external conditions, helminth eggs can exist for a month.
Cattle consume contaminated water, grass, and hay and become infected with bovine tapeworm. After entering the gastrointestinal tract, the worm larvae are absorbed into the bloodstream and spread throughout the animal’s body. They settle in muscle tissue and can be found in connective tissue elements (in the heart, in the tongue), where they remain to mature. After 4-5 months, they turn into fins and cysticerci, which contain the protoscolex (the head of the larval form of taeniaids) of an adult bovine tapeworm. In the muscles of cattle, larvae can exist for 1-3 years.
When a person eats beef with infective larvae, they enter his stomach and then into his intestines. There, under the influence of gastric juice and bile, the protoscolex is freed from the fin, attaches itself to the intestinal wall with the help of suction cups and begins to grow.
An adult bovine tapeworm will form in the human body after 2.5-3 months. Most often, 1 worm is found in the patient’s intestines.
Pork tapeworm in humans
The causative agent of the parasitic disease is a parasitic tapeworm from the Taenia solium family. Pork tapeworm causes digestive upset and neurological disorders. The disease is dangerous due to cysticercosis of the eyes, brain, skin, lungs, and heart muscle. The pork tapeworm is large in size, its length can reach 4 m. There are 4 suckers on the head of the parasitic worm.
The helminth is a hermaphrodite. Each fertilized segment of the worm can contain 50 thousand eggs with embryos, or oncospheres. Adults parasitize the human digestive tract, excreting segments of the worm's body along with feces. The role of the intermediate host of the worm is played by a pig or wild boar. The main place of residence for the parasitic worm is the human intestine.
Infestation of pigs by worm larvae occurs when animals eat contaminated waste or drink contaminated water. Having penetrated the stomach of the intermediate host, the pork tapeworm is freed from its protective shell and spreads throughout the body through the bloodstream. The larvae of the parasitic worm mainly settle in the muscles. After 2-3 months, the embryos of the worm turn into peculiar vesicles with eggs - cysticerci. The latter remain viable for 4-6 years, after which they calcify and die.
When invasive meat is consumed in the human small intestine, the head of the worm is released from the vesicles, which is attached to the wall with the help of hooks and suction cups and begins to release body segments with eggs into the external environment. During invasion, the oral-fecal mechanism of transmission of the pathogen is realized. The route of infection of a person by worm larvae is food or water (by drinking contaminated water). The disease is common in areas with unfavorable sanitary conditions. Employees of meat processing plants and pig farms are at risk.
- Fast-acting antiviral agents
- How is chickenpox transmitted in children and adults? Is it possible to get chickenpox through third parties?
- How to treat pancreatitis at home
Symptoms
Infection with pork tapeworm is accompanied by various clinical manifestations. The symptomatic picture can be both pronounced and hidden. Signs of invasion appear 1.5-2 months after ingestion of the larvae of the parasitic worm. The extraintestinal form of taeniasis (cysticercosis) can lead to damage to the eyes, heart, lungs and other organs. Depending on the location of the pork tapeworm in the human body, the disease manifests itself:
For intestinal form:
- nausea, vomiting;
- weakness;
- indigestion;
- increased appetite;
- abdominal pain of varying intensity;
- anal itching;
- iron deficiency anemia;
- decreased immunity.
For extraintestinal form:
- cerebral hypertension, hydrocephalus, severe headaches, epileptic seizures (damage to the larvae of a parasitic brain worm);
- chronic inflammation of the eyes, blurred vision (infection of the retina, conjunctiva);
- heart rhythm disturbances (penetration of parasitic worm larvae into the myocardium);
- tumors on the surface of the skin (damage to epidermal structures by parasitic worm larvae).
If taeniasis is suspected, the patient is prescribed a stool test and perianal scraping. If segments of a parasitic worm are detected, the patient is advised to undergo a comprehensive examination. For this purpose, he is sent for ophthalmoscopy, lung X-ray, CT scan of the brain and other diagnostic procedures to identify damage to other organs. Antibodies to pork tapeworm are detected using serological methods:
- RNGA;
- ELISA;
- RSK;
- NRIF.
Treatment
Therapy for taeniasis is carried out in a hospital in compliance with specific conditions for preventing self-infection of the patient. Treatment of parasitic infestation involves the use of anthelmintic drugs (Praziquantel, Niclosamide), and a saline laxative. The patient is recommended to eat a diet. Upon completion of anthelmintic therapy, at least 4 control stool tests are performed with an interval of 30 days. In parallel with drug therapy, it is allowed to treat taeniosis using traditional methods:
- Pumpkin seeds. The product (300 g) is peeled from the white peel, leaving a green inner shell. Then the seeds are crushed and diluted with a small amount of honey and water until a creamy mass is formed. The mixture is consumed on an empty stomach in one dose. After half an hour they drink a laxative, and after 3 hours they do an enema.
- Troychatka Ivanchenko. The prepared mixture of wormwood, tansy flowers and cloves is ground in a coffee grinder. Take 1.75 g of the composition on an empty stomach with water. On the first day, the drug is taken only in the morning, on the second - in the morning and at lunch. A full course of treatment for pork tapeworm can begin no earlier than the third day.
In a situation where single segments of a parasitic worm are found in the brain and eyes of an infected person, surgical intervention is performed followed by etiotropic treatment. The intestinal form of taeniasis usually has a favorable prognosis. The outcome of the disease in relation to the life and health of the patient in case of damage to the brain and other vital organs depends on the massiveness of the invasion and the location of the pork tapeworm larvae.
| Drug treatment | ||||||
| A drug | Active substance | Dosage | pharmachologic effect | Indications | Contraindications | Side effects |
| Praziquantel | Praziquantel | Therapy for cestodoses – 10-25 mg/kg once. Dosage for cysticercosis – 50 mg/kg in three doses. The course lasts 1-4 days. | The drug causes paralysis of the muscle structures of the parasitic worm, which leads to the destruction of the tapeworm's protective shell. | Schistosomiasis, trematodiasis, cestodiasis, neurocysticercosis and cysticercosis. | Pregnancy, lactation, children under 4 years of age, ocular cysticercosis, liver pathologies, individual intolerance | Abdominal pain, diarrhea, sweating, headache, vomiting. |
| Niclosamide | Niclosamide | The daily dose for adults and children over 12 years of age is 2-3 g. For children 5-12 years of age – 1.5 g. Young patients under 5 years of age are prescribed 0.5-0.7 g of Niclosamide per day. The daily dose is taken in one dose. The average duration of treatment is 4 days. | The drug slows down the life processes of the pork tapeworm, causing the death of the parasitic worm. | Hymenolepiasis, teniarhynchosis, taeniasis, diphyllobothriasis. | Pathologies of the liver, kidneys, lactation, pregnancy, stomach ulcers, individual intolerance. | Stomach pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, dizziness, drowsiness. |
| Fenasal | Niclosamide | Treatment of taeniasis in adults is carried out by a single dose of 8-12 tablets (2-3 g each) of Fenasal. Dose for children 5-12 years old – 4-6 tablets of 1-1.5 g each. | The drug has a paralytic effect on the parasitic worm, as a result of which it completely loses the ability to attach to the intestinal wall. | Taeniarinhoz, hymenolepiasis, dwarf tapeworm, diphyllobothriasis. | Pregnancy, lactation, individual intolerance. | Nausea, abdominal pain, itching, urticaria. |
| Male Fern Extract | Phylixic acid, filmaron. | Orally on an empty stomach, 4-7 g per dose. The daily dose should be taken within 20-30 minutes. | The drug paralyzes the muscles of the pork tapeworm and promotes the exit of the worm from the body along with feces. | Tenidosis, hymenolepiasis, diphyllobothriasis, enterobiasis. | Circulatory failure, pathologies of the liver, kidneys, stomach ulcers, duodenal ulcers, acute gastrointestinal diseases, fever, anemia, exhaustion, pregnancy, children under 2 years of age. | Nausea, vomiting, dizziness, diarrhea, headache, convulsions, respiratory depression, optic atrophy, collapse, hepatitis. |
- Blood cholesterol levels - table by age. Cholesterol in the blood - norms for women, men and children
- How to grow the endometrium
- How to cook delicious liver: recipes
Diagnosis of bovine tapeworm
Diagnosis of bovine tapeworm presents certain difficulties. The fact is that the disease has few specific symptoms that would indicate the presence of a parasite in the body.
In this regard, a delicate questioning of the patient to establish the fact that cysticerci were creeping out of his anus is of particular importance. It is this symptom that is of utmost importance in terms of determining invasion. Very often, patients also notice segments in the feces after defecation.
If the segments cannot be detected, then provocation of their release is possible: the use of pumpkin seeds, garlic or a saline laxative.
If there is a suspicion of a parasitic disease, then a stool test is performed for eggs and fragments of strobila worms. This analysis is called “coproovoscopy”.
Additional examination methods are:
- Thick smear method (Kato method).
- Enrichment method (Fulleborn sedimentation method and Kalantaryan flotation method).
- Perianal-rectal scraping.
- Imprint on adhesive tape.
Since the above examination methods do not allow us to clarify which tapeworm is parasitic in the human body: pork or bovine, a thorough examination of mature segments is necessary. Thus, the lateral branches of the uterus of the bovine tapeworm number from 18 to 32 pieces. While the uterus of a pork tapeworm will have 8 to 12 lateral branches on one side.
Sometimes the worm can be detected during contrast radiography of the small intestine. It looks like light stripes.
As for the general blood test, it can detect an increase in the number of eosinophils, leukopenia and anemia. However, these indicators are transitory.
Characteristics of the parasite
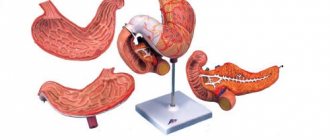
The bovine tapeworm, which looks like an ordinary white worm, consists of three sections:
- Head. In tapeworms it is called the scolex. The scolex of the tapeworm has a round shape and small (up to 2 mm) dimensions. There are 4 suction cups on it, with the help of which it is attached to the walls of the human intestine.
- Neck. This is the parasite's growth area. This is where new young segments are formed.
- Body. It is a collection of many segments. An adult parasite has up to 1000 segments in its body. They have a square shape and, what is most unpleasant, all the segments are hermaphroditic, that is, they have ovaries and testes, so they do not need other individuals to reproduce.
The worm can reach up to 6 - 10 meters in length, forming more and more new segments. Each segment, detached from the body, can move independently, heading towards the exit from the intestine.
The eggs of this helminth are round in shape and covered with a thin transparent shell through which the embryo can be seen.
Treatment of bovine tapeworm
Treatment of bovine tapeworm comes down to taking antiparasitic drugs. Sometimes it is carried out in a hospital setting, although outpatient therapy for teniahrynchiosis is not excluded. Parasitological monitoring of the effectiveness of the therapeutic regimen is mandatory.
The patient is prescribed anthelmintic drugs, the main one is Fenasal, and the additional one is Biltricid. Fenasal is taken either in the evening after a light dinner, or in the morning on an empty stomach. The dosage is selected by the doctor, on average for an adult it is 2-3 g. Biltricide is also taken once.
After taking the drug, the parasite exits through the anus without any additional measures.
On the eve of treatment and during therapy, a gentle diet is indicated.
It is based on the following principles:
- Exclusion of fatty, fried, smoked, salty and sweet foods;
- The basis of the diet is low-fat soups, rice, buckwheat, fermented milk products, low-fat fish;
- Drinks – jelly, compotes, teas;
- An absolute ban is imposed on beets, cabbage, spinach, grapes, peaches, raspberries, gooseberries, chocolate, coffee, alcohol, apricots, and legumes.
You should eat in small portions, at least 5 times a day.
It is possible to supplement the main therapeutic regimen with herbal medicine. For this purpose, the doctor prescribes capsules with male fern extract and pumpkin seeds. During the treatment period, cleansing enemas and laxatives are indicated.
The criteria for cure are the absence of segments in the patient’s feces for 4 months after the therapeutic course. If segments are detected, then therapy is repeated with the same drugs.
The prognosis for recovery is most often favorable. Doctors try to rid patients of teniarynchosis as quickly as possible and observe them for another 3-4 months. In addition, people at risk, for example, workers on farms and livestock farms, are checked with particular care.
Localization
The habitat of the parasite depends on the stage of its development. The life cycle of a helminth goes from egg to adult tapeworm. At the stage of its development, it changes its owners. Thus, the intermediate host where the tapeworm embryo lives is cattle. The only possible environment where an adult tapeworm lives is the human small intestine. It is here that it attaches itself using the suction cups on its head, grows and multiplies. Therefore, humans are considered the definitive host of this helminth. It remains to answer the question of how it changes the environment.
Helminth eggs enter the body of cattle through the feces of an infected person. It is with them that the released segments come out, inside of which the helminth eggs are located. After some time, oncospheres emerge from these eggs and spread throughout the grass and ground. Together with the grass, they enter the body of their intermediate host. Oncospheres are quite resistant to adverse environmental conditions. However, while enduring even severe frosts, they die when exposed to ultraviolet rays. Already in the intestines of the cattle, embryos emerge from the eggs, which after a few months turn into Finns. Finns are able to live inside an intermediate host for several years, but if during this time they do not enter the human body, they cannot develop and reproduce, and therefore die.
For the larvae to enter the human intestine, it is enough for him to eat contaminated meat. Within three months from the moment Finna enters the human body, it develops, turning into a mature individual capable of reproduction.