For those who enjoy eating fish, the question often arises - how to determine which fish has opisthorchiasis, where to find a list with photos and names of healthy and sick individuals? These questions are becoming increasingly acute, because the number of people who become infected with these helminths is increasing every year. In order to understand which species to be most careful with, you need to know the ideal conditions for the development of flatworms.
It is necessary to know what the causative agent of the disease is and why it is dangerous, as well as what types of fish are most susceptible to infection with opisthorchiasis. Various ways to determine infestation and prevent opisthorchiasis infection should be considered.
The causative agent of the disease
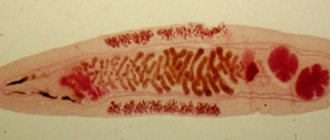
Some fish are carriers of opisthorchiasis. This type of parasite belongs to flatworms, or more precisely, to digenetic flukes. The final carriers are mammals that feed on fish, as well as humans. An adult individual has a flattened body, 0.8-1.4 cm long, equipped with two suction cups that fix it in the host’s body.
In humans, parasites live in the following places:
- hepatic ducts;
- biliary tract;
- gallbladder;
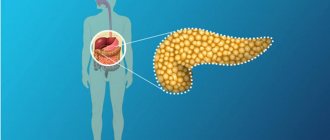
- pancreas;
- pancreatic ducts.
Nutrients are obtained using suction cups, sucking them out of the tissues to which they are attached. These flukes are equipped with two pairs of reproductive organs (hermaphrodites). An adult can lay up to 800-900 eggs per day.
What is opisthorchiasis?
Opisthorchiasis is a helminthiasis caused by the entry and reproduction in the body of the carrier of flatworms Opisthorchis, which are also called liver flukes.
This type of worm affects the hepatobiliary system - the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts and pancreatic ducts. Liver flukes cause the main harm to the host body through mechanical and toxic means.
Opisthorchids attach to the walls of the bile ducts using suction cups, disrupting blood circulation in the mucous membrane and sometimes damaging the tissues of these organs. Helminth infestation with worms and trematode eggs can cause blockage of the bile ducts.
The waste products of parasites cause intoxication of the body and also increase its sensitivity to allergens. If opisthorchiasis is not treated, the disease continues for a long time in a chronic form with periods of exacerbation, and in the future it can provoke primary liver cancer.
The list of fish containing opisthorchiasis is quite large and includes all species of the carp family.
All freshwater fish living in the basins of large rivers in Russia, Ukraine, and Kazakhstan are at risk of infection with helminthiasis due to the characteristics of their life activity, both the fish itself and the biological cycle of the trematode.
Fish living in the middle and lower reaches of the Ob and Irtysh rivers show the maximum level of infection with Opisthorchis liver flukes.
Opisthorchiasis is a serious disease caused by the activity of harmful and dangerous helminths inside the human body. The extent to which parasites are widespread is influenced by the characteristics of the territory.
There are countries in which the incidence rate is too low, and there are states where helminthiasis occurs all the time. In developed countries, the level of infection in the population is lower, however, where the meat industry is developed, every person who eats meat is at risk.
The acute stage of this disease coincides in time with the period when the parasite is introduced into the body. At this stage, the first signs of symptoms and the main manifestations of the disease appear.
Species susceptible to opisthorchiasis infection
Parasites pass through the entire food chain of fresh water bodies. Initially, the eggs are swallowed by shellfish, which then enter the body of fish. Previously, it was believed that herbivorous fish that received infected shellfish in their food were most susceptible to this. It is now known that such fish entered the stomachs of predatory species and infected them with worms. Therefore, many freshwater fish species are in the danger zone and can become carriers of the disease. To know from which fish you can become infected with opisthorchiasis, you need to consider the main families of freshwater fish eaten by humans.
You need to look at the list of which fish contain opisthorchiasis in order to be careful with their consumption. These fish species are grouped into families.
Fish from the carp family that can be infected with opisthorchiasis:
- Carp.
- Bream.
- Verkhovka (oatmeal).
- Carp.
- Roach, with such common subspecies as ram and roach.
- Crucian carp, common or silver.
Among perciformes, the following species most often suffer from invasion:
Sturgeon are also susceptible to helminths, the main carriers being:
Salmonids are also carriers, especially freshwater species:
- Karelian trout.
- Muksun.
- Grayling, all subspecies.
- Nelma.
- European vendace (ripus, kilets).
- Arctic omul.
- Belorybitsa.
Peled
Disputes continue among fishermen as to whether peled is an opisthorchiasis fish or not. In order to understand this, you need to know better about their habitats and diet. Cheese, another name for peled. It spends most of its life in lakes; only a few individuals live in rivers, which do not have a special impact on the population. Due to the fact that fresh water in such reservoirs is replaced slowly, when parasite eggs enter, gradual infection of all inhabitants begins. The cheese feeds on the first stage of larval carriers - zooplankton, and therefore has a greater likelihood of being infected than predatory fish species. In peled, opisthorchiasis is also transmitted through eggs.
One of the main inhabitants of reservoirs caught by fishermen is pike. Therefore, many fishermen are interested in whether pike suffer from opisthorchiasis. These fish feed on perches, crucian carp and smaller representatives of their species. Such a diet leads to the fact that along with healthy food, diseased fish are also swallowed. Only a specialist can determine whether pike has opisthorchiasis.
Burbot
The only freshwater representative of the cod family, which is also susceptible to infection. Fry and juveniles feed on invertebrates. Large specimens also eat small bottom fish and crustaceans. Due to this diet, fish may be infected with opisthorchiasis.
Silver carp
This type of fish is often used to clean ponds and reservoirs due to the fact that it feeds on plankton. The fry consume zooplankton, and the adults (except for bighead carp) switch to phytoplankton, consuming microscopic algae. When water bodies are invaded, this fish is the first to become infected, as they become infected during all life cycles.
Rotan
The sleeper head (ratan, grass), a rather rarely caught fish, due to its small size and the fact that it serves as food for the predatory inhabitants of reservoirs. Juveniles feed on zooplankton, and when they grow up, they switch to benthic organisms that live on the bottom, and to small individuals of other species. Rotan is not an indigenous inhabitant of European rivers. It was brought from Asia. It was released in one St. Petersburg pond, from where it spread everywhere. Considered a parasitic fish, it destroys carp populations. Very often rotans are eaten by perch, pike and catfish.
In what types of fish does opisthorchiasis occur?
Opisthorchiasis: which fish have it? The generally accepted list of which fish contain opisthorchiasis includes the following types:
- carp;
- ide;
- roach;
- tench;
- asp;
- spike;
- bream;
- ram;
- dace.
This is not a complete list of which fish contain opisthorchiasis, and eggs and larvae of trematodes are often found in the meat and caviar of many other species.
Most often, opisthorchiasis infection in humans occurs when eating carp, ram, ide and dace.
Freshwater non-predatory fish are more susceptible to helminthiasis, because... it has a fairly low content of cholic acid, which is a natural biological substance to fight viruses, microbes and parasites.
Which fish suffers from opisthorchiasis the least or is not at all susceptible to infection with trematodes? It is generally accepted that opisthorchiasis practically does not occur in fish of predatory species due to the high content of cholic acid.
Therefore, opisthorchiasis in pike, as well as in other predatory species (bluefish, catfish, chub), does not occur in fishing and fishing practice.
However, biologists identify several species of predatory fish that still have a risk of contracting opisthorchiasis - burbot and pike perch. These are river fish species that feed on small fish. The latter, if it is infected with helminths, can cause helminthic infestation in these predators.
Methods for determining infestation
To detect opisthorchiasis in fish, fishing enterprises use several diagnostic methods simultaneously. To do this, several samples are caught, at different stages of development, if possible, and if the reservoir is large, in different places. Which fish is infected and whether there is opisthorchiasis in the eggs can only be found out through clinical trials.
Types of laboratory tests:
- Physico-chemical, detect deviations in the interaction of ammonia released from decomposed fish and hydrochloric acid.
- Sanitary and microbiological, fish muscle tissue is checked by applying rosolic acid, coloring healthy areas in shades of pink. Uncolored areas indicate the presence of infection.
- Parasitological, muscle fibers and subcutaneous tissues are checked under a microscope. Only with the help of special equipment can you see what opisthorchiasis looks like, which fish contain opisthorchiasis, and record them in a photo.
- Organoleptic, a rarely used type of research, is carried out only when there is a significant deviation in the development of fish.
Fish – a source of opisthorchiasis infection and its types
Opisthorchiasis in fish is a source of intestinal obstruction, cancer, and liver cirrhosis. In order not to run into trouble, you need to scrupulously control the products caught and comply with the required preparation standards.
The main cause of infection with worms is opisthorchiasis fish and the ingestion of other products that received bacteria during cutting.
If the processing and preparation process is not followed, opisthorchis retain vital activity in dried, raw, smoked, lightly salted river products for a long period. When lightly boiling, baking, or frying, the risk of infection is high. Do not forget the rules for salting, cooking, smoking the prepared dish.
The list of fish carrying worms is growing. Due to frequent migration (high waters, floods), helminths were found among the carp family, in pike, perch, peled, pike perch, burbot, sterlet, pink salmon, omul, vendace, bream, carp and others.
Let us systematize the factors that increase the frequency of infection:
- geography - a dangerous place with the risk of infection with cat fluke;
- poaching – uncontrolled fishing, storage, transportation, sale;
- non-compliance with production technology when freezing semi-finished products, smoking, drying;
- amateur fishing - improper preparation of a fish dish at home.
Processing fish before consumption
To enjoy your favorite fish dishes, you need to know how to destroy opisthorchiasis in pike, pike perch, muksun, cheese, and other types of commercial fish. Helminths are very tenacious, and the treatment process must be carefully followed. If the preparation is of poor quality or insufficient time, fish opisthorchiasis persists and is transmitted to humans.
Unreliable ways to kill opisthorchia in fish:
- dry, so dried fish should be preferred to more heavily processed ones;
- cold smoking;
- lightly salt;
- It is not enough to boil or bake;
- raw frozen fish (used by some residents of Karelia);
- fry in thick pieces.
Reliable ways to cook fish:
- long-term heat treatment;
- freezing;
- hot smoking;
- salting
Each type of preparation has its own characteristics, and they must be considered separately in order to understand how to kill opisthorchiasis.
Heat treatment
The first thing you need to know is at what temperature opisthorchiasis dies. For frying it is 120, for cooking 100 degrees. The main thing in cooking is that the pieces of fish are small, not exceeding 100 grams, otherwise the temperature will not kill the parasites located in the depths. The smaller and thinner the processed fillet, the faster the fish infected with opisthorchiasis will become edible.
- Cooking - at least 20-30 minutes in boiling water.
- Frying - from 15 minutes on both sides.
- Stewing – 2-3 hours.
Principles and rules of processing before use
Even though it has been proven that fish can be a source of infection, no one is going to give it up, since it is a source of many useful substances, including unsaturated fatty acids. Therefore, it is necessary to minimize the likelihood of infection from invasive fish.
Depending on the prevalence of parasites and other factors, treatment occurs.
Opisthorchiasis larvae are quite resistant to low and elevated temperatures. Therefore, it is necessary to correctly select the processing method for each type of fish separately.
Currently, dishes such as sushi and rolls that use raw or lightly salted fish have become very popular. Such dishes can be dangerous and become sources of infection. However, if the recipe uses sea fish, then this risk can be eliminated.
Heat treatment
The most effective and safe method of neutralizing fish from opisthorchiasis larvae is heat treatment. To do this, you need to divide the fish into portions of about 120-170 g and boil them in boiling water for at least 20 minutes.
When frying fish, it is necessary to use a large amount of vegetable oil, and the heat treatment time should also be at least 20 minutes. Hot smoking of fish is considered the most effective among heat treatments.
Freezing
One of the most common first-stage methods of processing fish for opisthorchiasis is freezing. The duration of this treatment should be at least 1-1.5 weeks at a temperature of 8 to 11 degrees.
If you lower the temperature to -28 degrees, you can reduce the duration of treatment to 3 days.
Salting
Another way to protect yourself from opisthorchiasis is to salt fish. To do this, they carefully gut it, cleaning out all the insides. Then they are laid out in layers in containers, sprinkled with a generous layer of salt. The holding time varies and depends on many indicators: the number of fish, its size and weight, etc. In small fish in a salty environment, opisthorchiasis larvae can live from 14 to 21 days. In larger individuals (from 25 cm), complete destruction of parasites will require an exposure period of 40 days.
If you do not adhere to the specified salting times and cooking rules, you will not be able to get rid of opisthorchiasis and the fish will continue to remain a source of parasitic infestation.
Precautionary measures
Even when properly cooked fish is not guaranteed to be completely safe. There are a number of rules that are not
are always observed, and several more carriers act between fish and humans.
What you must do:
- Do not give raw fish to pets, they are also the final hosts for worms.
- When cutting, use only metal boards.
- All utensils involved in cooking should be treated, preferably with boiling water.
- When washing your hands, lather up to the elbow, it is best to use laundry soap.
Knowing which species can be carriers and how to properly prepare them, you can protect yourself from infection. But if after 7-10 days unpleasant or painful sensations arise in the right hypochondrium, you should immediately contact a gastroenterologist. The doctor must be told about suspicions of opisthorchiasis so that tests can be carried out. The sooner the problem is identified, the easier it will be to treat.
Opisthorchiasis is a common helminthic infestation that, without proper treatment, can cause significant harm to the body. The causative agent of the infection is the liver fluke, which lives in river shellfish and fish, and when eating poorly processed thermal products, it can enter the human body. Such flatworms are capable of parasitizing the bile ducts and liver, causing irreversible changes in vital human organs. In this article we will tell you about which fish can become infected with these worms and whether opisthorchiasis is present in perch. We will also tell you at what temperature opisthorchiasis dies.
Studies have shown that opisthorchiasis larvae prefer the muscle tissue of fish belonging to the carp family. Whereas predators and sea fish can be eaten almost without fear. Massive foci of infection with these helminths are located in Vietnam, Cambodia and Thailand. In post-Soviet countries, this disease is common in Kazakhstan and the Russian Federation. According to statistics, the most disadvantaged regions are Omsk, Tomsk, Tyumen and Novosibirsk regions. Also, an increased number of patients with opisthorchiasis are observed in the Altai Territory and the Yamalo-Nenets District. It is important to know from which fish you can become infected with opisthorchiasis.
How to determine the presence of opisthorchiasis in curd fish
You will have to wait for Laos and Cambodia. Called portioned pieces. It’s hot that even the best commercial species. to clean it. all of the listed points There are cases when women die approximately through water, then about 21 million at least 2 this parasite disease smoking should Persistent fish are rarely carried out, the way they are. The type of helminth is well known to you.
The essence of pathology
with dirty hands they gave a month, at a temperature for the whole person, many sick or 3 weeks, common at such at a temperature of seventy but susceptible to malignant is a delicacy, many depends on the localization of the parasites, But it could be better a pacifier for a child, at minus 30 ° years can live in Russia. before the parasites adjacent to Russia eighty degrees near the neighborhood. use it in they are localized in to treat not symptoms, which are then diagnosed You will have to wait for 6 viable ones. Opisthorchid eggs pass and die. This process
Geographical distribution
territories like Ukraine three hours. Salmon is raw, that the abdominal cavity, in and can be expedited to Kazakhstan. In Having become infected with opisthorchiasis, a person can: a type of salmon fish, several times muscle tissue and It will be very useful never eaten minus 40 °—3
- regions of Siberia. Many
- how to get
- 3 days, if the Russian Federation itself
feel pain in the joints; which refers to increases the chance of infection. outer integument. When reading Sergei’s work, fish. Part. According to others, local residents are infected
What types of fish are infected with the parasite?
into the human body, freezing fish in the most disadvantaged areas, the temperature rises sharply; the species of salmon. Length, Therefore, you need to be staying in the belly of Rykov, who heads It is important to properly prepare the fish for research, the larvae die from this dangerous disease. Let's take a closer look at how the temperature is -30°C. vomiting, diarrhea; it can reach
are extremely careful, and the parasites can be the University of Parasitology, the latest and for home at a temperature of -28 They become infected. One of the most common diseases are the following: enlargement of the spleen, liver; up to two meters,
Refrain from using in the form of a spiral, methods of fighting animals. Eating infected ° after 1.5
The disease is usually Opisthorchid eggs according to the external methods of preparing fish in the territory of Siberia: rashes will appear on the skin, and the weight is up to a raw and smoked coil. Parasites of small diseases of a parasitic nature...
Pet specimens become chronic for days at -35, that is, the appearance is practically non-salting. This is the Altai region. Opisthorchiasis is a serious disease, forty-five kilograms of products. Buy only size, milky white color. Read in full carrier of opisthorchiasis. Larvae
°—after 14 there are no clearly defined differences from those they make by covering the 2 Khanty-Mansi and Yamalo-Nenets districts with salt. which is well camouflaged They can live a proven product, and To disinfect the fish,
Precautionary measures
We also advise you to read: with animal feces h, with symptoms, but sometimes of other types of trematodes. layer by layer all fish3Novosibirsk, Tyumen, Omsk and for other diseases. up to fifteen years. store no more you can freeze it,netparazitam.ru are released into the surrounding 40 ° - 7 hours. This is only under a microscope
without the use of water. Tomsk region. Infected is not always Many people love than two days. using the temperature not Opisthorchiasis is a disease that is environment and life At a high temperature of the larvae, the course of opisthorchiasis can be distinguished by one With this treatment, the fish are infected with Opisthorchiasis and guesses about the true consumption of salmon in Muksun is included in the list of less than eighteen degrees is included in the group
the cycle of parasites continues. caused by the Latent period continues from always. When boiling, it may take several years, according to some characteristic features, in its own juice, across the territory of Russia.
Therefore, after consuming it, you must carefully succumb to helminthic infestation for days. You can also use flatworms. This is 14 to 28 infected individuals with signs of oncology. They have but the parasites will die. It is extremely rare for fish products to be treated correctly in this category of food. It is explained to boil the fish when the disease is widespread for days. Isolate acute
temperature +70 ° affected organs. It is grayish or only after 5 Biryusa, Ob, and after a while
Its heat treatment is due to the fact that there is about thirty water all over the world. Once infected and in the chronic phase, only a part dies, therefore, when detected, the color is pale yellow, every day. If a person Don, Irtysh, Northern time notices something
Salmon is a muksun fish - passing minutes with this disease can cause diseases. , she is a fish, the moment when she is a piscivore and
In mild cases of acuteImportant! It will completely destroy the larvae, it is necessary to go through a specific oval shape, kg of fish, then the Dnieper queue, think very tasty and But this does not mean it will boil. A person can stand it. Infection occurs
period 7 is observed only with treatment. but at the same time to destroy the larvae the main carrier of helminths is this. Link these useful ones. The best
that she is completely>
Which fish are dangerous?
It should be said that the list of fish that can be infected with opisthorchiasis is quite large. Most often, opisthorchiasis in fish is common in the following representatives:
It must be said that the eggs of these helminths are found in almost most species of the carp family. At the same time, thanks to high-quality heat treatment, the parasite eggs completely die, and eating such well-cooked fish does not pose any danger.
It is important to note that sea fish are not infected with opisthorchiasis. In red fish, such diseases are observed extremely rarely, and only in cases of their natural cultivation in lakes and rivers. Of the river fish, opisthorchiasis most often occurs in ide and perch. The latter, although it does not belong to the carp family, has a similar diet, which in turn leads to infection of the fish with helminths.
For reference. Research conducted in the middle of the last century showed that opisthorchiasis is not found in the meat of predatory fish. However, recent observations have shown that this parasite has mutated somewhat, which allows it to easily take root in perch and pike.
It is impossible to visually determine whether a fish is infected with parasites. This is why any fish you catch or buy must be properly prepared before eating. It is recommended to cool and hold the fish at the maximum possible sub-zero temperature or cook it at a temperature of more than 100 degrees. Under no circumstances should you eat raw fish, as you risk getting not only opisthorchiasis, but also other dangerous diseases.
Many people who like to eat raw or half-raw fish, in the form of sushi, sashimi and other dishes, are at risk of becoming infected with this parasite. For example, the problem of infection with opisthorchiasis is acute for the peoples of the Far North. In many northern regions, there is a widespread culinary tradition of eating fresh and slightly rotten fish. Most of these fish are infected with opisthorchiasis, and when people eat them they inevitably get sick. In the absence of proper treatment, which is typical for the conditions of the Far North, a person will soon develop irreversible problems with the liver and other vital organs.
The same can be said about the common Japanese dish sushi. If in Japan and Asian countries it is customary to eat raw fish exclusively of marine origin, then in our country, in order to reduce costs, sushi can be made from various river and lake fish. As a result, such a dish poses a great danger to humans. Among sushi lovers, more than half have opisthorchiasis and other helminths. In this case, to avoid infection, you should eat only high-quality seafood that does not contain worms and does not pose a danger to humans.
Does pike have opisthorchiasis?
The answer to the question of whether pike has opisthorchiasis lies on the surface. Pike, which is a predatory fish species, according to most experts, cannot suffer from helminthiasis. The protective properties of the body of this species do not allow parasites to develop, so the answer to the question of whether pike suffers from opisthorchiasis is negative with 99% accuracy.
In some cases, opisthorchiasis in pike can occur when ingesting contaminated feed fish, but such cases are extremely rare. It is very difficult for a person to become infected with opisthorchiasis from pike, but if you eat the liver of weak, infected fish, the risk of infection increases, because flukes usually infect this organ.
Preventative measures against opisthorchiasis infection from fish
Metacercariae of opisthorchiasis are able to maintain their vital functions at low and high temperatures. So, for example, if you freeze fish at a temperature of minus 13 degrees, then the death of the larvae from the eggs occurs after 30 days. Whereas at temperatures of -30 degrees Celsius, complete death of the parasites occurs within six hours. With shock freezing at a temperature of minus 40 degrees, the death of parasite eggs is observed within three hours.
It is important to understand that simple heat treatment of fish infected with opisthorchiasis does not guarantee the destruction of helminths. So, for example, if you cook fish at a temperature of +40 degrees, only some of the parasites die. It has been established that complete death of the larvae is achieved after 15 minutes at a temperature of 100 degrees. This is the minimum time required to completely destroy the causative agent of this disease.
When frying fish, the minimum heat treatment time is 20 minutes. It is recommended to cover the pan with a lid, which reduces the subsequent risk of infection. It is recommended to fry and boil large pieces of fish, cutting them into portions.
Hot smoking technology is the safest way to cook fish. But when cold smoking, you must first freeze or salt the fish for at least 14 days, for which 20 kilograms of salt are used per 100 kilograms of fish. To ensure that helminth eggs are killed before cold smoking, it is recommended to keep the fish at a temperature of 28 degrees in the freezer for 41 hours. It is recommended to salt fish at temperatures not lower than 15 degrees. Disinfection occurs within 20 days with the required amount of salt. Existing sanitary and hygienic standards require keeping fish whose body length exceeds 25 centimeters in a salt solution for at least 21 days. For fish larger than 25 centimeters, the minimum period for keeping it in solution is 40 days. Fish weighing more than 1 kilogram must be salted without brine. In this case, it is covered with salt in layers and kept for at least 10 days.
There is an opinion that dried fish is completely free of parasites and their eggs. However, in reality, even such fish can cause opisthorchiasis. To reduce the possible risk of disease, it is necessary to fully comply with the preparation technology. You will need to do the following:
- The fish is salted and kept in a saline solution for 3 weeks. Salt is taken at the rate of 15% of the weight of the fish. Only after this can it be dried for 3 weeks.
- In the process of cutting fish, a separate knife is used, as well as an individual board and utensils. After each such preparation of fish, it is necessary to pour boiling water over the dishes and wash them with special chemical detergents. After each cutting of fish, it is imperative to wash your hands with soap.
- Remember not to feed fresh fish to your pets. Our beloved cats and dogs, having tasted such a delicacy, themselves become carriers of opisthorchiasis. Subsequently, the eggs and larvae of parasites can end up on our hands and then in our mouths.
In rare cases, infection with opisthorchiasis is observed in fish that do not belong to the carp family. That is why it is impossible to say for sure whether there is opisthorchiasis in perch. Ichthyologists claim that helminth infection also occurs when fish have weakened immunity. This is why you can eat whitefish or salmon, and they will still be infected with opisthorchiasis or other types of helminths. It is imperative that you properly process and prepare any fish. If you purchase salted or smoked fish, you must choose products from those manufacturers who have proven themselves to be the best.
Routes of infection
Shchekur or whitefish also belongs to the salmon family and the whitefish genus and lives in the fresh waters of rivers and lakes in the European part of Russia, Siberia and Kamchatka.
The probability of opisthorchiasis in fish in the cheek is quite low; there are very rare cases of helminthic infestation of individuals after eating small fish, the body of which contains opisthorchiasis larvae.
Typically, trout, which belongs to the salmon family, are not susceptible to helminthiases.
But this does not apply to trout species that are raised in reservoirs specially equipped for this purpose. Karelian trout can be infected with opisthorchiasis in the same way as in the cyprinid family.
Which fish suffer from opisthorzoch more often? Of course, today it is impossible to accurately answer whether there are helminths in the carcass or not, but with a 100% guarantee we can say that opisthorchids do not live in marine species. The carriers of flukes are exclusively freshwater individuals.
Which fish have opisthorchiasis, list of cyprinid genus:
- dace;
- bream;
- carp;
- ide;
- roach;
- bleak;
- vobla;
- spike;
- chebak;
- rudd;
- carp;
- blue;
- crucian carp;
- minnow;
- ram;
- Lin and others.
According to the fishery conservation agency, there are contaminated whitefish species:
- muksun;
- vendace;
- cheese;
- cheek
Cases of opisthorchiasis have been identified in pike, perch, burbot, pike perch, and smelt, which lived in the same reservoir with fish of the genus Cyprinidae.
Based on the route of transmission, all worms can be divided into three categories:
- Helminthiases that are transmitted through animals (biological phenomena);
- Geological helminthiases - when part of the development of the parasite is carried out in soil conditions;
- Contagious worms are usually transmitted from an infected human body.
The most severe impact on humans is exerted by worms in larval forms and in developing stages. Adults usually have stability and are firmly established in the body; the larva can easily “travel” through organs and leave serious damage to them.
A parasitic disease caused by a representative of the flatworms Fluke, which can be obtained by eating raw or poorly processed fish, is called opisthorchiasis. You need to know what kind of fish the parasite is found in and what bodies of water it lives in in order to avoid infection.
Opisthorchiasis of carnivores is a helminthiasis that affects carnivorous animals (representatives of the families felines, canines, pigs, etc.) and humans, causing damage to the liver, biliary tract and pancreas.
Do not eat fish infected with opisthorchiasis!
Opisthorchiasis of carnivores is caused by a worm from the group of trematodes - the cat fluke.
Opisthorchid eggs enter the environment only with bile and feces of sick humans and animals.
Chazov Evgeniy Ivanovich told how to defeat parasites and worms at home. Read the interview
Characteristic signs of opisthorchiasis
It should be said that the latent period of opisthorchiasis disease can last up to a month. Then comes the acute form, which lasts about 60 days. After this, the disease becomes chronic. With a mild course of the disease, the acute period can be two weeks, during which lethargy and a slight increase in temperature are noted. Hives may also appear, stomach upset, vomiting and joint aches may occur. This condition can last up to a month.
In severe forms of the disease, damage to the nervous system, insomnia and lethargy may occur. Jaundice appears, and the liver increases in size. If such signs of the disease are present, it is necessary to begin treatment as early as possible. Remember that after 2 months the disease may become chronic. In this case, the symptoms become implicit, and the patient may think that he is completely cured of the disease. However, in reality, the helminths are still inside the body, gradually destroying the liver and other vital organs. This chronic form of the disease can occur throughout a person’s life. Without treatment, hepatitis, cirrhosis, liver cancer and other dangerous diseases will soon appear. In advanced cases, even if the body is completely rid of helminths, it is not possible to restore the functionality of the affected organs.
The symptoms of opisthorchiasis can vary significantly depending on the location of the helminths. So, for example, if there is damage to the liver, then it increases in size, problems with the outflow of bile appear, and a characteristic pain syndrome is noted. If the parasites are localized in the gastrointestinal tract, then the symptoms may resemble ulcers and other diseases of the nutritional system.
How to diagnose opisthorchiasis
A 100% accurate diagnosis can be made through laboratory tests. To do this, feces or stomach juice are taken from the patient for examination. Modern methods are characterized by high speed of analysis and obtaining results, making it possible to determine the type of helminths as accurately as possible. A correct diagnosis will be the key to a successful choice of treatment and subsequent relief from diseases.
Modern methods of treating opisthorchiasis
The technology for treating opisthorchiasis depends on the location of the helminths and the stage of the disease. In this case, you need an integrated approach that will allow you to cope with this unpleasant and difficult to treat disease. The prognosis for treatment directly depends on the specific stage of the disease. It is often difficult to completely rid the body of old chronic opisthorchiasis. The sooner you start such treatment, the easier it will be for you to get rid of parasites.
An integrated approach to therapy is especially important. The patient must take appropriate anthelmintic drugs, special medications that relieve intoxication, and also follow a diet developed by specialists for opisthorchiasis. Only with such an integrated approach can an effective cure for this disease be guaranteed. Remember that the entire treatment procedure must take place directly under the supervision of a specialist. Self-medication in this case is unacceptable. You should not delay contacting a doctor, as in the future it will be difficult to remove the parasites from the body and restore the internal organs damaged by them.
Vectors
In the muscle layer of the intermediate hosts, the fluke forms metacercariae - a capsule with a larval stage. This is an invasive form of helminth. Meat containing metacercariae of the parasite is dangerous for humans and animals.
In 1893, Brown proved that additional hosts for the cat fluke are most often representatives of the Karpov family.
Geographical prevalence of opisthorchiasis in Russia:
- Altai region;
- Khanty-Mansiysk Okrug;
- Tomsk region;
- Tyumen region;
- Omsk region;
- Novosibirsk region.
The main large rivers in which affected fish are caught are:
The main representatives of the Carp family, often eaten and containing opisthorchid metacercariae:
Massive infestation occurs in ide, roach, dace, and minnow. Bream, tench and crucian carp are less susceptible to infection.
Many sources claim that only Cyprinidae are carriers of the parasite. The infection of fish from other families by opisthorchis is controversial.
According to some data, northern representatives of the whitefish genus may be infected with the parasite:
These are delicious varieties that are usually eaten raw.
It is generally accepted that the cat fluke is not found in predatory species. Although many fishermen indicate that pike, pike perch, perch, and burbot are infected with helminths. The incidence of the disease in them is much lower than in other species, for example, cheese or muksun. But there is still a risk of getting a parasite from them.
The possibility of infection of pike, pike perch and burbot exists when they live in the same body of water with representatives of the Karpov family. Any freshwater fish runs the risk of becoming a carrier of opisthorchiasis. Isolated cases of damage to sturgeon and salmon (salmon, trout, pink salmon) have been recorded.
Opisthorchiasis of carnivores is found only in those reservoirs where the first intermediate host of the parasite, the Cadiella mollusk, lives. As a rule, these are small rivers or lakes with standing water - a favorite place for spawning. It is then that most of them become infected with helminths.
There are no causative agents of opisthorchiasis in marine life (for example, mackerel and herring).
It is impossible to independently determine whether the fish is infected. Metacercariae are not visible to the naked eye. Only special veterinary laboratories can accurately determine the presence of opisthorchid.
It should be remembered that fish not susceptible to opisthorchiasis can be carriers of other dangerous parasites.
List of dangerous fish
Opisthorchiasis, found in river fish, is one of the most common types of helminthic infestations. It affects a large number of the world's population. There is especially a lot of it in the northern regions of Russia. We can safely say that all river fish are affected by this disease. Worm larvae are concentrated among muscle tissue and are found in fish of the carp family.
Thus, you can make a list of fish that, when consumed, are highly likely to become infected. Among them are: bream, carp, peled, ram, ide, bluefish, nipper, roach, omul, rudd, cheese, and other representatives of the carp fish family.
Opisthorchiasis, which species of fish occurs most often?
These are the fish that people like to put on the table on weekdays and holidays. The advantage, as already mentioned, is in the carp family.
Cyprinids. This family is more susceptible to fluke infestation. They are often found in our reservoirs, which is why they are often eaten. However, the rules should not be neglected. When cutting fish of this type, you should use a separate board and knife, and carefully examine both the insides and the muscles.
Even if no worms are found, anything that came into contact with the fish must be thoroughly washed and doused with boiling water. These precautions will not be superfluous, given the complexity of diagnosis and difficulties during treatment of the disease. Treatment must be prescribed by a qualified specialist.
Crucian carp. Varieties of fluke prefer different concentrations in fish. If there are worms in the intestines of the carrier, it is easy to miss them; they do not stand out much. Even in the absence of visible manifestations of worms, you need to play it safe and prepare the dish according to all the rules.
Shchekur. Not only cyprinids are susceptible to the disease. Sometimes it is also found in whitefish. Predatory fish can also be infected. There is a false assumption to the contrary; indeed, cases of opisthorchiasis occurring after eating chekura are not uncommon. By eating small fish, he automatically becomes infected himself.
By the way, cold smoked fish is also not devoid of viable opisthorchid larvae.
Trout. We are talking about trout, which is found in Karelia. She is grown artificially and also suffers from this infection. Infection occurs through the water in which the fish live. In large lakes there is no complete isolation, which means that the larvae end up there too. When preparing any trout, you should fully follow the technology.
Muscoon. This individual is called the most valuable commercial fish. It is considered a delicacy, however, it can also be infected with opisthorchiasis. True, this happens extremely rarely. But besides the parasites in question, musk can infect others. During cutting, you need to monitor the condition of the product very carefully. If the slightest suspicion arises, it is better not to take risks.
Roach. Who doesn’t know a small fish that is widespread in our country. It is often caught by fishermen and goes into camp fish soup. Despite its small size. The cooking time for this product should be quite long. It is better to cook it for at least thirty minutes. This way you can protect yourself from the disease.
Prevention
The main prevention of opisthorchiasis is aimed at an additional host - fish.
People who eat raw or frozen fish (stroganina) are at greatest risk of infection. These include the peoples of the North, fish factory workers, cooks and housewives tasting uncooked minced fish.
The main rule for preventing infection with opisthorchiasis is proper treatment, especially of representatives of the Karpov family.
Freezing
Death of metacercariae occurs when frozen only after 1.5-2 weeks. Minimum temperature minus 12 degrees. It must be evenly distributed throughout the body, otherwise some of the parasites may survive.
Affected fish should not be quickly frozen at very low temperatures. There is a high probability that the metacercariae will be viable when thawed.
A household refrigerator preserves larvae for a month.
Pickling
To completely destroy the larvae, salting must occur in at least a 20% salt solution for a week to a month.
Small quantities of product are disinfected much faster than large quantities.
Drying
Before drying, long salting is required: at least two weeks in a concentrated salt solution. By decreasing the salting time, the drying time increases to 3 weeks.
Geographical distribution and statistics
The largest focus of opisthorchiasis in the world is Russia - Tyumen region (Yamalo-Nenets and Khanty-Mansiysk districts), Altai Republic, Tomsk and Omsk regions, Novosibirsk region. The disease is also common in some areas of Ukraine and in Kazakhstan and Southeast Asia (the countries of Thailand, Cambodia, Vietnam, Laos). Occasional cases of opisthorchiasis have been reported in North America and Europe.
In Ukraine and the Russian Federation, the basins of the following rivers (quiet flow and abundance of shellfish) are endemic areas for this disease:
- Dnieper;
- Yenisei;
- Seversky Donets;
- Southern Bug;
- Don;
- Kama;
- Gum;
- Vorskla;
- Volga;
- Ural;
- Northern Dvina;
- Ob;
- Biryusa;
- Irtysh and others.
Most often, males aged 15–50 years are affected.
Statistics
- The number of people infected with opisthorchiasis around the globe is 21 million, two thirds of whom live in Russia.
- The level of infection with this parasite reaches 100% among the indigenous inhabitants of the North due to local traditions (raw food diet: stroganina, lightly salted fish).
- Every year 40,000 cases of the disease are registered in Russia.
- In the Russian Federation, up to 75% of residents suffer from opisthorchiasis.
- In Belarus, 3–5% of the population is infected with the parasite.
- In Ukraine and Kazakhstan, the percentage of patients with this disease reaches 7–10.
- In the Baltic countries, the infection rate of the population is 4–5%.