What is pancreatitis like?
The disease occurs in acute or chronic form.
The chronic form, as a rule, is observed in men who did not treat the disease at an early stage of its development, triggering inflammation that turned into a chronic stage. The disease is prone to frequent relapses and exacerbations. In the acute form more often, in the chronic form - less often. If there are separate areas of inflammation (dots), pancreatitis is considered edematous. When inflammation spreads over larger areas - medium or large-focal.
Prevention
Acute pancreatitis
It is worth remembering that chronic diseases are easier to prevent than to live with them. Basic measures will help prevent the development of pancreatitis, the main one of which is a healthy lifestyle.
Quitting alcohol and proper nutrition in themselves practically eliminate the entire risk, of course, if there are no other factors leading to damage to the pancreas. Timely treatment of other gastrointestinal diseases and vaccinations against infections that can trigger an autoimmune process are also important.
Why does pancreatitis occur?
Gallstones as one of the causes of pancreatitis
The main reason for the development of the disease in men is the consumption of alcohol, which negatively affects the pancreas, also the liver, stomach, and brain.
The occurrence and development of the disease is possible when:
- gallstone disease, which also often develops as a result of alcohol abuse;
- genetic predisposition;
- complications after surgery;
- abdominal injuries;
- allergies in the patient;
- the presence of viral, infectious, fungal diseases;
- use of certain medications.
Causes of pancreatitis
- Alcohol consumption is the most significant of all risk factors. Usually in this case the disease makes itself felt between 30 and 40 years,
- Gallstone disease is in second place. Blockage of the bile duct with a stone or viscous sludge blocks the release of pancreatic secretions, which entails the process of autolysis. In the same way, helminthiasis can lead to pancreatitis,
- Autoimmune diseases,
- Injuries of the pancreas and abdominal organs, congenital defects of the pancreatic ducts, adhesions and other complications of abdominal surgery,
- Hereditary predisposition and endocrine diseases, unhealthy diet,
- Taking hormonal medications such as estrogens and some antibiotics.
In approximately 10-15 percent of cases, the cause remains unclear.
It is important to note that acute pancreatitis occurs more often in men than in women. More than half of the cases are caused by alcohol abuse, and among males there are much more chronic alcoholics.
In addition, women on average are more careful about their diet and avoid fried and fatty foods, which can also have a detrimental effect on the pancreas.
The main cause of the disease is alcohol abuse. Its excessive doses negatively affect the normal functioning of many internal organs, including the pancreas. But there are many more reasons due to which pancreatitis can develop:
- cholelithiasis;
- previous infectious and other diseases;
- complications due to surgery;
- taking medications with side effects that affect the gastrointestinal tract;
- heredity;
- severe allergies.
That is, against the background of other diseases, pancreatitis begins to develop as a complication. Therefore, all diseases must be treated in a timely manner.
To detect pancreatitis, the doctor conducts a detailed survey of the patient. At this stage, the possibility of a congenital disease is excluded. After which the patient must undergo the following studies:
- General analysis of urine and blood. Required to detect inflammatory processes in the body.
- Ultrasound of the peritoneum. Determines whether there are stones in the gall bladder and the general condition of the internal organs.
- CT scan. Helps identify affected areas of the pancreas.
Based on the results of the measures taken, the specialist doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes a specific treatment.
Why is pancreatitis dangerous? This disease can lead to unpleasant consequences. If you do not fight it, the following diseases can develop:
- infectious formations in the pancreas;
- purulent inflammation of the bile ducts;
- stomach ulcer;
- diabetes;
- tumor in the pancreas;
- fistulas and cysts;
- neuropsychiatric disorders.
Ignoring the symptoms of the disease is fraught with new dangerous diseases. Therefore, it is very important to identify and begin to treat pancreatitis in time.
The main reason for the development of pancreatitis in men is constant poisoning of the body with alcohol.
Among the reasons that cause pancreatitis in men are overeating and frequent consumption of fatty foods.
The development of pancreatitis in many cases is facilitated by gallbladder disease and cholelithiasis. Inflammation of the pancreas can provoke diseases of the duodenum.
The use of certain medications, such as furosemide, can also cause pancreatitis in men.
Past infectious diseases (mumps, mumps, viral hepatitis) often cause pancreatitis in men.
Pancreatitis often occurs after surgery on the stomach or duodenum.
Among the causes of pancreatitis in men, metabolic and hormonal disorders, cardiovascular diseases and hereditary factors should be noted.
Often the cause of pancreatitis is simply impossible to determine.
The pancreas is an elastic organ, soft to the touch, with small pink lobules and weighing about 80 g. With pancreatitis in men, it turns into a rough rope mixed with stones.
Untreated pancreatitis leads to a chronic form of the disease. To restore the pancreas, patients are prescribed Allohol, a choleretic drug that normalizes bile production and the performance of the gastrointestinal tract. There is a medicine containing an extract of the contents of the pancreas - “Pancreatin”.
Acute pancreatitis
A severe form of acute pancreatitis is hemorrhagic pancreatitis - death of pancreatic tissue. Its main symptom is severe pain. The patient's condition rapidly deteriorates, blood pressure drops, tachycardia appears, and death is possible. Pancreatic disease is characterized by repeated vomiting, which leads to dehydration, so you need to drink water in small portions often. As a result of the action of enzymes, blue-violet spots may appear on the skin of the abdomen.
Symptoms of the disease in the remission stage are absent or mild. As a rule, an aching, dull pain occurs after eating heavy fatty foods, and occasional vomiting is possible. Chronic pancreatitis is often accompanied by weight loss in the patient; this is due to pancreatic dysfunction, poor digestion of food and poor absorption.
The development of pathological processes in the pancreas may remain unnoticed for several months or even years. Since the organ gradually loses its functions, the disease will certainly make itself felt. Some factors can provoke inflammation and cause an attack:
- alcohol consumption;
- cholelithiasis;
- overweight;
- viral hepatitis;
- poisoning;
- heredity.
Find out what are the symptoms of pancreatitis in women.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
Chronic pancreatitis develops gradually, along with deterioration of the pancreas. Patients exhibit the following early signs:
- bloating;
- discomfort, feeling of heaviness after eating in the upper abdomen, sometimes tingling;
- constipation
If previously any food and alcohol were well tolerated, then gradually unpleasant sensations arise after eating - at first slightly expressed and often left without due attention. Subsequently, pain appears above the navel, in the area of one or both hypochondriums. Then the pain spreads around and becomes girdling.
Severe diarrhea occurs within 15-20 minutes after starting a meal. The stool is light, liquid, foamy, and plentiful. The patient feels a sharp rumbling in the stomach. After bowel movement, the condition improves somewhat, the pain subsides, but does not disappear.
Subsequently, normal pancreatic tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue, which is unable to secrete enzymes and hormones. This stage of the disease is characterized by:
- gradual reduction of abdominal pain;
- chronic diarrhea several times a day with whitish drops of fat that are poorly washed off with water from the surface of the toilet;
- weight loss;
- dry tongue, increased tissue bleeding (for example, when brushing teeth, cuts), decreased vision in the dark, bone pain;
- development of secondary diabetes mellitus.
Rice. 2 - Possible symptoms of pancreatitis.
If such symptoms are present, medical supervision and research are necessary to exclude malignant processes in the body.
With alcoholic pancreatitis, the symptoms are similar to the symptoms of a chronic disease; there is a gradual increase in symptoms:
- signs of diabetes;
- weight loss;
- frequent diarrhea, which contributes to the removal of most vitamins and microelements, and leads to metabolic disorders, the functioning of all organs and systems;
- yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes (jaundice), the appearance of a skin rash;
- dyspeptic symptoms.
Untreated pancreatitis leads to a chronic form of the disease. To restore the pancreas, patients are prescribed Allohol, a choleretic drug that normalizes bile production and the performance of the gastrointestinal tract. There is a medicine containing an extract of the contents of the pancreas - “Pancreatin”.
Acute pancreatitis
A severe form of acute pancreatitis is hemorrhagic pancreatitis - death of pancreatic tissue. Its main symptom is severe pain. The patient's condition rapidly deteriorates, blood pressure drops, tachycardia appears, and death is possible. Pancreatic disease is characterized by repeated vomiting, which leads to dehydration, so you need to drink water in small portions often. As a result of the action of enzymes, blue-violet spots may appear on the skin of the abdomen.
Symptoms of the disease in the remission stage are absent or mild. As a rule, an aching, dull pain occurs after eating heavy fatty foods, and occasional vomiting is possible. Chronic pancreatitis is often accompanied by weight loss in the patient; this is due to pancreatic dysfunction, poor digestion of food and poor absorption.
Symptoms of pancreatic inflammation | Symptoms of pancreatitis
Attention! The information presented in the article is for informational purposes only. The materials in the article do not encourage self-treatment. Only a qualified doctor can make a diagnosis and give treatment recommendations based on the individual characteristics of a particular patient.
Signs of inflammation of the gland in acute form are more distinct. In the chronic form of the disease they are insignificant and blurred. It is men who suffer mainly from the chronic form of the disease as a result of frequent alcohol consumption. In women, in most cases, an acute form of the disease is detected.
Increased gas formation with pancreatitis
Maybe:
- temperature rise to high levels, often febrile;
- increased flatulence;
- nausea, vomiting;
- rashes on the body;
- dizziness, tremor;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- lack of appetite, poor digestibility of food taken, resulting in weight loss and weakness in the body;
- the appearance of yellowness on the skin.
Tests for pancreatitis
Of course, the signs of inflammation are similar to some other diseases and an accurate diagnosis cannot be made on their basis. In addition, pancreatitis can be congenital, and this requires at least a family history.
When you contact a doctor, the following will be prescribed:
- general blood test, also for biochemistry;
- urine test to determine amylase levels;
- undergoing endoscopy of the gallbladder and ducts to assess the condition of internal organs;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity to detect stones in the ducts and gall bladder;
- computed tomography to determine the degree of damage to the pancreas, the presence of stones in the ducts;
- cholangiopancreatography to obtain cross-sectional images of the pancreas.
Pancreas: symptoms of a disease of inflammatory etiology
Non-infectious inflammatory processes in the tissues of the pancreas are the most common cause of dysfunction and pathologies of this organ. Most inflammatory processes are expressed by the clinical picture of pancreatitis, accompanied by swelling, decay and death of glandular tissue.
Long-term inflammatory processes lead to the replacement of glandular connective tissue, disturbances in the anatomical structure and functions of the pancreas. The primary inflammatory process of a non-infectious nature can be complicated by the layering of bacterial infections, the formation of cysts, inflammation of the peritoneum, internal bleeding and other complications of the disease. Depending on the symptoms and clinical picture, acute and chronic types of pancreatitis are distinguished.
Acute pancreatitis
The most common cause of acute pancreatitis is a complication of cholelithiasis due to poor diet, excess fatty foods, and alcohol. The average age of onset of the first episode of acute pancreatitis is 40-50 years.
Among the varieties of the disease are:
- acute interstitial (edematous) form of pancreatitis;
- acute hemorrhagic form;
- acute purulent form of pancreatitis;
- acute pancreatic necrosis with total or partial tissue death.
When symptoms of pancreatitis appear against the background of cholecystitis, cholecystopancreatitis is diagnosed. Acute pancreatitis can manifest itself in a variety of ways and not have a clear, homogeneous clinical picture, which makes diagnosis difficult.
Diseases and dysfunctions affecting the pancreas are not limited to inflammatory processes. Although most pathologies are characterized by pain, dyspepsia and blood count characteristics, symptoms vary depending on the type of disease, its form, stage and extent of the pathology.
Laboratory studies are not very informative. Ultrasound, biopsy Exceeding the reference norms of glucose and glycated hemoglobin in the blood
| Disease/symptom | Chronic pancreatitis | Cancer | Cystic changes in glandular tissue | Diabetes mellitus type I |
| Painful sensations | During periods of exacerbation | Depending on the location and volume of the tumor | Depending on the size and location, they may be absent | None |
| Dyspepsia | During periods of exacerbation and if the diet is violated: constipation, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting | Unstable fatty stools, nausea, at a later stage - profuse diarrhea, vomiting | Depending on the location of the cyst: frequent stools, bloating (cyst on the head of the gland), constipation, nausea, discolored feces (body, tail of the gland) | Feeling of nausea, vomiting with ketoacidosis. Increased hunger during hypoglycemia |
| Features of the clinical picture | Exacerbations due to violation of dietary rules | Jaundice, pale skin, weight loss to the point of exhaustion | Expressed in late stages and bacterial suppuration by pain and the possibility of palpation of cysts | Increased thirst, frequent urination, itchy skin, dry mucous membranes. Ketoacidosis, hypoglycemia |
| Laboratory indicators and diagnostic methods | In exacerbations similar to acute pancreatitis | The blood picture shows anemia, leukocytosis, increased ESR. Ultrasound, biopsy |
Ulcerative changes in the glandular tissue of this organ are classified depending on the stage: erosive, exacerbation and chronic, with possible complications upon penetration into the tissues and organs of the peritoneum. The symptoms of the ulcer are similar to the clinical picture of pancreatitis with the additions of heartburn and salivation.
Therapy is carried out under the strict supervision of specialists. During treatment, it is necessary to remember that without following a diet, limiting fatty, fried, smoked foods, certain types of foods (mushrooms, tomatoes, honey) and alcoholic beverages, the disease will worsen and progress.
The pancreas in humans is the largest exocrine and intrasecretory digestive organ. The intrasecretory function of the organ is the implementation of digestive enzymes - pancreatic juice.
By producing biologically active organic compounds, the pancreas provides the body with the regulation of fat, protein and carbohydrate metabolism. Another important functional purpose of this organ is the active production of insulin, which helps reduce the level of glucose concentration in the blood.
Hormonal disruption due to inflammation of the pancreas can lead to impaired insulin secretion, which will lead to the development of diabetes mellitus.
The structure of the pancreas
The anatomical structure is an elongated lobular formation of a grayish-pinkish color, located in the abdominal cavity of the upper section on the posterior wall of the abdomen behind the stomach with the organ in close contact with the duodenum.
In an adult, the length of the pancreas reaches 14-25 cm, with a mass of about 70-80 g. The macroscopic structure is the head, body and tail. The head of the pancreas is adjacent to the duodenum through the minor duodenal papilla.
It is through the head of the digestive system that the portal vein passes, collecting blood into the liver from all unpaired organs of the abdominal cavity - the stomach, spleen and intestines.
The body of the pancreas has a triangular configuration - anterior, posterior and inferior. The tail of the pancreas is cone-shaped or pear-shaped and extends to the spleen. The gland is supplied with blood through the pancreaticoduodenal arteries, which branch from the superior mesenteric and hepatic arteries.
It is typical that in newborns the pancreas measures from 3 to 5 cm in length, with an organ weight of 2.5-3 g. The formation of a gland characteristic of adults occurs by the age of 5-7 years.
Inflammation of the pancreatic parenchyma, possibly for several reasons. Alcoholism is considered the most likely - this is 70% of cases of acute and chronic pancreatitis and cholelithiasis, accounting for 20% due to blockage of the bile ducts with stones. The remaining 10% of cases of inflammation occur due to the development of so-called triggering cause-and-effect factors:
- bacterial or viral infection;
- the result of food poisoning;
- trauma affecting the pancreas;
- malfunction of the pancreaticoduodenal artery;
- fungal infection.
In addition, there are frequent cases of inflammation of the pancreas after direct unsuccessful surgical intervention in the abdominal cavity or through endoscopic manipulation.
Also, an inflammatory reaction can occur as a result of hormonal imbalance, leading to impaired insulin production.
Inflammation of the pancreas can also be associated with acute or chronic clinical pathology.
Exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis
Pancreatitis
The most common type of disease of the digestive system is acute and chronic pancreatitis. The disease is characterized by an enzyme deficiency in the production of pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
Enzymes are activated in the body of the gland and begin to destroy it, that is, self-digestion of nutrients occurs. The toxins released during this process are released into the bloodstream, which can lead to damage to other vital anatomical organs - kidneys, liver, heart, lungs and brain.
You can slow down the inflammatory symptoms of acute pancreatitis by applying cold to the painful area. However, treatment of inflammation of the pancreas in acute pancreatitis requires hospitalization. Chronic pancreatitis is an advanced condition of the acute form.
The gradation between the recurrent acute form and chronic pancreatitis is very arbitrary.
Diagnosis and treatment for inflammation of the pancreas
Inflammatory pain symptoms can be caused by stones in the pancreas, which form during chronic pancreatitis. The accumulation of enzymes and toxins forms a certain phosphorus-calcium sediment, which, when thickened, becomes calcified and ensures the deposition of stones. Pancreatic stones can only be identified using instrumental diagnostics:
- computed and/or magnetic resonance imaging;
- cholangiopancreatography;
- endoscopic and ultrasound examination.
To date, there is no effective therapeutic and/or drug removal of stones from the pancreas. Only surgical intervention in specialized clinics can save a person from this problem.
Pancreatectomy
Chronic disruption of the glandular epithelium and pancreatic ducts contributes to the formation of various tumors, including malignant ones. The tumor in 50% of cases affects the head of the pancreas; the development of pancreatic cancer in the body and tail accounts for 10% and 5%, respectively. Metastasis of pancreatic cancer has four stages:
- Damage to the pancreaticoduodenal lymph nodes of the gland.
- Involvement of retropyloric and hepatoduodenal nodes in the cancer process.
- Spread of cancer to the superior mesenteric and celiac zone.
- Damage to the retroperitoneal lymph nodes.
Metastasis affects distant anatomical organs of vital activity - these are the kidneys, lungs, liver, bones and joints of the skeletal frame. Only radiation and surgical diagnosis of pancreatic cancer will reliably determine the painful manifestation of the oncological disease.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YFJhfBMOIjc
Inflammation of the pancreas cannot be ignored. As a rule, the symptoms of exacerbation have a pronounced complex of clinical manifestations:
- Girdle pain in the upper parts of the abdominal cavity, radiating to the scapula.
- Nausea and gag reflex are another clear sign of inflammation of the pancreas.
- Irregular heart rhythms developing into tachycardia.
- Excessive sweating, fever and an increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels are also a sign of an inflammatory reaction.
Girdle pain in the pancreas - The whites of a person’s eyes and skin acquire a yellowish tint, and so-called obstructive jaundice develops.
- Other dyspeptic and abdominal disorders.
Patients also complain of dizziness and general weakness of the body, lack of appetite, weight loss, and surges in blood pressure.
The severity of pain can be regulated by a certain position of the body. Lying on your side with your legs bent, the symptoms of inflammation of the pancreas subside sharply, and the person feels some relief.
Causes of pancreatic disease
The most common cause of pancreatitis in men is regular consumption of large amounts of alcohol. In addition, the causes of pancreatitis may be:
- disturbances in the outflow of bile in inflammatory diseases of the biliary tract and cholelithiasis;
- the predominance of fatty foods in the diet, as well as its combination with alcohol;
- deepening of the duodenal ulcer and its spread to the adjacent pancreas;
- gastritis and duodenal ulcer with high acidity;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - disorders of sphincter tone, developmental anomalies, gastritis, duodenitis, diverticula;
- viral hepatitis, especially B, mumps, infectious mononucleosis, Coxsackie and ECHO viruses, parasites;
- endocrine disorders - overproduction of hormones by the parathyroid glands, which leads to calcium deposition in the pancreas tissues;
- large doses of hormonal drugs, chemotherapy in the treatment of oncology, overdose of diuretics and other drugs - tetracycline, sulfonamides;
- methyl alcohol poisoning;
- closed and penetrating abdominal injuries;
- vascular diseases.
If the bile that gets into the pancreatic ducts is infected with bacteria, the situation gets worse. Bile components cause necrosis of pancreatic tissue and activate its own enzyme systems. As a result, the process of self-digestion begins.
Rice. 3 - Possible causes of pancreatitis.
Hereditary (familial) forms of pancreatitis are associated with genetic disorders of the metabolism of certain amino acids and their accumulation in pancreatic tissue (aminoaciduria).
The development of pancreatitis in men is promoted by smoking, which causes prolonged spasm of the pancreatic vessels. This leads to a deterioration in metabolism in the organ and contributes to the chronicity of the disease.
Acute pancreatitis can appear as a result of a number of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures:
- after endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) to diagnose bile outflow obstructions (stones, tumors, adhesions), in which contrast may enter the pancreatic duct;
- after operations on the stomach and bile ducts and bile leakage;
- after kidney transplantation during treatment with azathioprine and corticosteroids.
Therefore, it is very important to identify the factors that resulted in the development of the disease. Only in this case can the progression and relapse of the disease be prevented.
The development of pathological processes in the pancreas may remain unnoticed for several months or even years. Since the organ gradually loses its functions, the disease will certainly make itself felt. Some factors can provoke inflammation and cause an attack:
- alcohol consumption;
- cholelithiasis;
- overweight;
- viral hepatitis;
- poisoning;
- heredity.
Find out what are the symptoms of pancreatitis in women.
The cause of malfunction of the pancreas is endocrine and excretory insufficiency.
Factors leading to the formation of pathology may be:
- surgical intervention on the gastrointestinal tract;
- genetic predisposition;
- diseases of the biliary system;
- hormonal imbalance;
- pathologies of the duodenum;
- abdominal injuries;
- uncontrolled use of certain medications;
- vascular pathologies.
The disease can occur due to the influence of several factors.
Inflammatory processes can also develop under the influence of external and internal (exogenous and endogenous) factors.
External reasons
External causes of pancreatitis include:
- the presence in the menu of a large amount of fatty, spicy, salty foods, in addition, excessively hot or cold dishes;
- alcohol abuse. The presence of chronic pancreatitis is observed in almost all men diagnosed with alcoholism;
- smoking. The danger of this addiction lies in the deterioration of blood circulation in the pancreatic tissues, as well as in the increase in the secretion of pancreatic juice, which causes destruction of the gland.
- frequent stress;
- long-term treatment with certain types of medications (diuretics, hormonals, certain types of antibiotics);
- pancreatic injuries, well-being after surgery.
Internal reasons
Internal causes of pathology include:
- gastrointestinal pathologies. These include cholelithiasis, in which, due to blockage of the pancreatic ducts, the transportation of pancreatic juice to the duodenum is disrupted and congestion occurs. Risk factors include diseases such as: cholecystitis, gastritis, hepatitis, duodenitis;
- obesity;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland or other organs of the endocrine system;
- gastrointestinal infections (fungal, helminthic, viral, bacterial invasions);
- hereditary predisposition, congenital pathologies of the structure of the pancreas and other digestive organs;
- allergic reactions (inflammation of the pancreas).
Where is the pancreas located in humans?
The most important human organ is the pancreas. It performs two important functions - exocrine and endocrine.
The first function is considered external, it is responsible for the secretion of pancreatic juice, the second is internal: it produces hormones and regulates metabolic processes.
To understand how the gland hurts, it is recommended to find out where it is located and what other functions it performs:
- Location. The gland is located in the abdominal cavity, so it can be determined independently. It is located at the back of the stomach, leaning against it and the duodenum. Its level borders on the location of the upper lumbar vertebrae - the first and second. If you look at it in projection, it is located 5-10 centimeters above the navel.
- Structure. The gland has 3 components - head, body, tail. The head is located in the recess of the duodenum, which goes around it. The upper part of the body of the gland rests against the posterior wall of the stomach. The tail of the organ reaches the spleen and has the shape of a cone.
- Dimensions. Many people are surprised by the question why the pancreas hurts if it is enlarged. In normal condition, the organ has dimensions: the width of the head is up to 5 centimeters, its thickness is from 1.5 to 3 centimeters. The width of the body of the gland in an adult is from 1.75 to 2.5 centimeters. The length of the tail is 3.5 centimeters.
If an ultrasound shows that the gland is enlarged, this is associated with various gastrointestinal pathologies.
What are the signs of pancreatitis in men?
Damage to the gland leads to nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and these are the main symptoms besides pain due to pancreatitis. But it is too early to confirm the diagnosis of this disease; only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis based on a series of tests that the patient must undergo. Often, in addition to vomiting, the temperature rises during illness and inflammation progresses.
Nausea and vomiting
The disease can be recognized by vomiting; it has a number of features:
- painful, indomitable, repeated constantly, does not bring relief;
- the masses may contain remnants of undigested food, then bile is released;
- discharge of blood impurities in severe damage to the pancreas.
At the acute, early stage of the disease, constipation and diarrhea appear, alternating with each other. The feces are light gray in color, have an unpleasant odor and contain particles of undigested food. The development of flatulence is inevitable.
The disease is dangerous for men, leading to complications and disastrous consequences; it must be treated.
Peeling skin
Pancreatitis affects the general well-being of the patient, changes the skin and its color:
- hypovitaminosis appears;
- the skin dries and peels, becomes less elastic, turns pale, and signs of cyanosis appear;
- hair becomes brittle and thin;
- the corners of the lips are affected by jams;
- The skin tone of patients with pancreatitis becomes earthy-gray.
As the disease progresses, the mouth becomes constantly dry, the tongue and palate are inflamed, there is constant belching with a putrid odor, and hiccups. The weight decreases sharply, the stomach swells, and upon examination the doctor will find bluish spots with a marble tint on the navel and lower back.
Among the adult population, problems with the pancreas often arise due to systematic alcohol consumption, but the symptoms of acute pancreatitis are the same in men and women. In childhood, organ dysfunction is less common. With a mild degree of the disease, the symptoms are weakly expressed, and the acute form is painful and difficult. There is a high probability of complications, such as hemorrhagic pancreatitis or pancreatosis (total damage to the pancreas due to self-destruction).
The main clinical sign of the onset of the disease is severe abdominal pain. It must be borne in mind that pain can radiate to the heart area, which resembles a myocardial infarction. The sick person:
- continuous vomiting occurs;
- blood pressure drops;
- general weakness appears;
- the skin turns pale.
General symptoms of pancreatic disease are similar to other abdominal diseases:
- inflammation of the gallbladder;
- hepatic colic;
- acute intestinal obstruction;
- food poisoning.
Different forms of pancreatitis may have a similar clinical picture. Symptoms may vary in severity and duration. Among the symptoms of all types of the disease are the following:
- pain syndrome;
- change in skin color, rash;
- symptoms of dyspepsia;
- intoxication.
Acute pancreatitis is diagnosed more often in men than in women. The most common symptom of an attack of pancreatitis is pain that is girdling in nature, localized in the epigastric region and radiating to the back.
Some relief occurs when the patient takes a certain position: leaning down forward.
Another sign of pancreatitis is diarrhea, which may contain remnants of undigested food. The process of defecation may be accompanied by bloating, belching, vomiting, and loss of appetite (this leads to weight loss). The process of absorption of nutrients is disrupted.
The weight loss process can be explained by the presence of severe pain that can accompany eating, which subsequently leads to a fear of food. This contributes to loss of appetite and severe exhaustion (cachexia).
In acute pancreatitis, patients experience attacks of pain of such intensity that it is impossible to eliminate them with conventional antispasmodics and mild painkillers.
In addition, signs of the acute form are:
- severe weakness;
- dizziness.
Diagnosis is also possible based on the type of vomiting:
- it is indomitable, debilitating, regularly repeated, does not bring relief;
- there are undigested food residues in the vomit;
- there is an admixture of blood in the vomit in severe forms of the pathology.
The disease contributes to the deterioration of the patient’s general well-being, has a bad effect on skin color and its condition, hair becomes brittle, hypovitaminosis may occur, and pockets appear in the corners of the lips.
In severe forms of the pathology, dry mouth, hiccups, putrid belching, inflammation of the tongue and palate may be observed. The patient suddenly loses weight, bloating and cyanotic spots appear on the abdomen and lower back.
The exacerbation phase proceeds as acute pancreatitis, but the symptoms are often not so pronounced. The remission stage may be asymptomatic.
Symptoms that suggest pancreatitis:
- abdominal pain. The localization depends on the location of the gland lesion: pain in the right hypochondrium - the tissues of the head of the pancreas suffer, with pathology of the tail of the gland - in the left hypochondrium, with inflammation of the body, pain appears in the epigastric region. The pain is of a girdling nature, radiating to the lower back; pain can also be felt inside the chest or lower abdomen.
- stool disorder. Diarrhea or mushy, sticky, shiny stools often occur.
- nausea, vomiting after eating.
- fever, general intoxication symptoms in acute pancreatitis of moderate and severe severity of the pathology.
Diabetes mellitus – as a sign of pancreatic pathologies
This is a disease that cannot be completely cured. In this case, the endocrine system is affected.
Since the pancreas is responsible for the production of insulin, any changes and malfunctions can cause the appearance of diabetes mellitus, which means the symptoms of pancreatic disease in men will be expanded.
When glucose levels are high, the destruction of all body systems begins. This also affects metabolism. The onset of diabetes mellitus is often influenced by the development of pancreatitis.
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes in men and women:
- Sudden loss of vision.
- Frequent urge to urinate.
- Headache.
- Losing weight.
- Dry mouth and constant thirst.
- Lethargy, malaise, weakness, decreased performance.
- Constant feeling of hunger.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Pain in the chest and lower extremities.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
Diagnosis of pancreatitis is carried out by a therapist or gastroenterologist. To confirm the diagnosis, a number of laboratory and instrumental examinations are carried out:
- General and biochemical blood test. It allows you to identify inflammatory changes, increased enzyme activity and glucose levels, which indicate destruction of glandular tissue;
- urine test for diastase;
- ultrasound, computed tomography, magnetic resonance, and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
Instrumental studies make it possible to identify structural changes: organ enlargement, formation of fistulas, cysts, calcifications, involvement of the peritoneum in the process.
To confirm chronic pancreatitis, it is necessary to examine functional changes in the enzymatic activity of the pancreas. The most modern are the breath test for diagnosing Lipase activity, as well as determining the activity of pancreatic Elastase 1 in feces. Also, a stool examination (coprogram) allows you to identify the amount of undigested food, fat, and the amount of fiber, which determines the severity of chronic pancreatitis.
If a specific infectious or other process is suspected that has led to the development of pancreatitis, additional specialized studies are carried out: infections are identified, diseases of the digestive system are diagnosed, and oncological processes are excluded.
How to recognize the disease and symptoms?
If acute pancreatitis is suspected and there is severe pain, it is important not to overuse analgesics: a similar picture is sometimes observed with other diseases of the abdominal organs, and painkillers can distort symptoms that are important in diagnosis.
Despite the fact that the signs characteristic of inflammation of the pancreas are quite specific, it is impossible to determine the nature and severity of the disease only from them.
The patient will first need cholangiopancreatography and ultrasound of the pancreas, which will allow them to determine the degree of its damage, the presence and size of necrotic foci and cystic cavities, as well as endoscopic ultrasound of the liver and bile ducts.
A general and biochemical blood test, an analysis of amylase in the urine, and a coprogram are necessary in order to get an idea of the severity of the condition of the body as a whole.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, doctors can begin treatment.
For pancreatitis of any form, you should not self-medicate by taking painkillers. They relieve pain, but do not eliminate its causes. Even specialists in some cases cannot always make the correct diagnosis. Even with a CT scanner and the results of all ultrasound and laboratory tests, this may not be achieved.
First of all, a doctor treating a disease such as pancreatitis will write a referral for biochemical tests of blood and urine, which detect increased levels of glucose, amylase and trypsin.
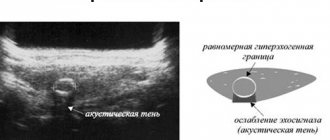
To make a correct diagnosis, basic research is necessary. These are computed tomography and ultrasound. During an ultrasound examination of the pancreas, the diagnostician first of all pays attention to its size. If the pancreas is enlarged and has a heterogeneous structure due to multiple inclusions - calcifications, then we can talk about the presence of chronic pancreatitis in the patient.
An X-ray of the pancreas is performed, which can reveal pancreatitis.
Gastroscopy to check for enlargement of the stomach and duodenum can help diagnose pancreatitis.
In addition, various tests and studies of stool can reveal the presence of pancreatitis in men.
Treatment of pancreatitis
In severe cases of pathology, hospitalization in the intensive care unit is required.
The acute form of the pathology is treated surgically. Surgery is necessary for advanced or severe forms of the disease; a laparoscopic method is used, in which drainage can be installed.
During the rehabilitation period, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs are taken to eliminate pathological processes in the body. If necessary, the patient is prescribed intravenous dehydration.
The success of treatment of acute pancreatitis in men is associated with the duration of taking enzyme preparations. In addition, the doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- hormonal;
- sedatives;
- enveloping;
- calcium preparations.
Chronic pancreatitis is characterized by phases of remission and exacerbations. To prolong the period of remission, you need to follow a diet and diet, and avoid bad habits.
To maintain immunity and accelerate recovery, therapy should include microelements, vitamins and the following choleretic and enzyme agents:
- "Digestal";
- "Creon";
- "Pancitrate";
- "Festal".
To improve intestinal functionality, prokinetics are prescribed (Metoclopramide, Cisapride, Domperidone).
Treatment of pancreatitis depends on the form and severity of the disease. In chronic pancreatitis, much attention is paid to the patient's diet, but medications are not excluded. Acute pancreatitis must be treated in a hospital and both drug and surgical treatment and diet are used.
It is necessary to begin treatment of acute pancreatitis by excluding any food intake (complete fasting) for a period of up to 3 days.
Drug treatment is prescribed:
- to reduce pain - antispasmodic and analgesic drugs (No-shpa, Papaverine, Analgin);
- to reduce enzyme activity and digestion in general - antisecretants (Sandostatin, Omeprazole, Famotidine);
- to maintain metabolism - intravenous infusions of saline and protein solutions;
- to prevent the development of infectious complications - broad-spectrum antibiotics (cephalosporins, penicillins);
- to reduce bloating, courses of sorbents and defoamers are recommended: activated carbon, Atoxil, Espumisan;
In chronic pancreatitis, antispasmodics Duspatalin and Meteospasmil are prescribed for pain. Enzyme preparations containing pancreatin, lipase, and amylase are required to replace impaired pancreatic function. Outside of exacerbation, alkaline mineral or weakly mineralized waters such as Borjomi and Essentuki have a positive effect.
Surgical intervention is necessary for the development of acute complications:
- abscesses;
- large areas of necrosis;
- significant cysts;
- if there are stones in the gallstones or pancreatic duct;
- with a large amount of inflammatory fluid in the organ itself and surrounding tissues.
Treatment of chronic pancreatitis is aimed not only at easing pain and preventing complications, but also at preventing a decrease in the level of enzymes and hormones in the pancreas.
Without strict adherence to the diet, treatment of chronic pancreatitis is ineffective. Basic principles of dietary nutrition:
- frequent doses in small portions (no more than 300 g);
- a small amount of fat, preferably vegetable;
- abstinence from sweets if carbohydrate metabolism is impaired.
Completely excluded:
- fatty meat and fish broths;
- carbonated drinks;
- alcohol;
- Rye bread;
- coffee and strong tea (see “Personal experience of giving up coffee and tea”);
- hard cheeses;
- sour juices (grape, apple, grapefruit);
- spices (pepper, mustard);
- cocoa;
- chocolate.
The basis of nutrition should be dairy products, eggs, lean meat and fish, boiled or stewed vegetables and fruits.
Observation of the attending physician is mandatory, who determines the dosage and time of taking the drugs.
Treatment at home and what medications you can take
Before starting treatment at home, it is important to determine for sure whether the gland hurts or whether the pain is coming from another organ.
The symptoms listed above will help you draw conclusions. In addition, during the treatment period it is necessary to follow a diet and know what you can eat during an exacerbation.
Several folk recipes, as well as pills that need to be taken, will help cope with the situation:
- Starvation diet. During an attack of pain, it is recommended to completely abstain from food. You are allowed to drink clean, non-carbonated drinking water. You can start eating 2 days after the attack: you can eat pureed soups and slimy porridges.
- Pain relief. To relieve pain during an attack, doctors recommend taking painkillers - Ibuprofen, Analgin. If there are no changes, the narcotic analgesic Tramadol is prescribed.
- Alternative medicine. Potato juice is something that can be used to treat pain in any case. Raw potatoes are washed and grated, the juice is squeezed out and consumed immediately.
During pregnancy, many women are interested in the question of what to do during attacks of pain? In this situation, it is allowed to take enzyme-based products, as well as use gentle nutrition.
Useful video
Share this post
- Related Posts
- How to determine ovarian inflammation in women and how to treat it at home
- How to increase testosterone in a man’s body using natural and folk remedies
- What are the health benefits of instant chicory?
- How to treat fibroadenoma of the mammary glands, causes and symptoms, removal surgery
- How to use royal jelly internally and in cosmetology, what are its beneficial properties and contraindications
- What is a person’s normal blood pressure by year, and what are the causes of deviations?
What complications can pancreatitis lead to?
Complications of pancreatitis are dangerous and can lead to death. Early complications of acute and recurrent chronic pancreatitis:
- shock - the patient’s blood pressure drops sharply and vital organs fail;
- acute renal and liver failure (cessation of liver function, as well as urine filtration, which leads to poisoning of the body with toxic metabolic products);
- ulcerations of the digestive tract mucosa, gastrointestinal bleeding due to intoxication;
- thrombosis of blood vessels of internal organs, which leads to necrosis of their areas;
- psychosis due to intoxication. Patients who have consumed alcohol experience hallucinations and motor agitation.
Late complications, as a rule, are associated with infection and develop no earlier than 2 weeks of illness. The most common:
- purulent processes - abscesses, phlegmon, melting of fatty tissue surrounding the pancreas, peritonitis;
- sepsis;
- cysts;
- fistulas;
- damage to the lungs and surrounding pleural layers.
When the head of the pancreas increases in size, obstructive jaundice occurs.
Complications from the disease can be very dangerous; the symptoms will intensify. If the pancreas is affected by toxins after drinking alcohol, then purulent formations begin to appear on the surface of the gland, and internal bleeding is possible.
Chronic pancreatitis is the cause of the development of heart failure, cyst formation, the liver begins to suffer, the skin becomes jaundiced, diabetes mellitus develops, and duodenal obstruction develops.
Internal reasons
General characteristics of pancreatitis
If inflammation of the pancreas occurs, then most likely, after diagnostic measures, a diagnosis of pancreatitis will be made. There are only 2 forms of the disease. These are acute and chronic.
Initially, a person may encounter precisely the first form of pathology. And only if the treatment was not carried out properly, the pathology develops into a second one.
In acute pancreatitis, severe inflammation of the organ, its enlargement, and swelling are observed. Gradually, with pancreatitis, replacement with connective tissue is noted. Thus, cell decay and necrosis occurs.
This is a good environment for pathogenic bacteria that cause infectious pathologies to enter and multiply.
With this course, the performance of the pancreas sharply decreases. The organ stops producing both digestive enzymes and insulin. Subsequently, diabetes mellitus develops.
Complications include the formation of ulcers, erosions and bleeding in the abdominal cavity.
Classification of acute pancreatitis:
- Hemorrhagic.
- Hydropic.
- Purulent.
- Cholecystopankretitis.
- Pancreatic necrosis.
Very often, pancreatitis takes on another form – chronic. In this case, the patient faces a period of exacerbation and the onset of remission.
The inflammatory process in chronic pancreatitis causes disruption of endocrine and exocrine functions.
Pathological changes affect pancreatic cells. Blood supply and metabolic processes are disrupted in them.
During the examination, specialists note that replacement with connective tissue occurs.
This completely rebuilds the organ. As a result, the pancreas is not able to work at the same pace.
More about pancreatitis in men
In men, the causes of pancreatic inflammation are quite varied. They are associated with gallstones, abnormalities in the structure of the organ, and tumors. Symptoms of pancreatitis occur more often in men than in women. There is also a predisposition to pancreatitis in older and obese people. The symptoms of pancreatitis that occur depend on the cause of the disease, the stage of the process, and the degree of damage to the organ.
In addition to men’s adherence to an unhealthy lifestyle (diet, smoking, drinking alcohol), the presence of more physical activity in men’s lives is important, which negatively affects the condition of the pancreas.
Men mistakenly consider the signs of acute pancreatitis to be food poisoning or chronic fatigue.
Although, according to statistics, this pathology is more common in the male population, gender does not have any significance for the appearance and development of pancreatitis.
A good marker for diagnosis is pancreatic amylase, which serves as a digestive enzyme and helps absorb carbohydrates and digest food.
To determine the amount of amylase, a blood test is performed, for which you need to prepare: the day before donating blood, you must stop eating fatty, fried foods and alcohol. The test is taken on an empty stomach, food should be taken 6-8 hours before, and smoking is also prohibited.
The norm of amylase in the blood of men is 0 - 53 units/l. For adults (men and women) over 18 years of age, this norm is the same; for children and adolescents, the values are different.
Ultrasound of the organ, x-ray, general blood and urine tests can also help in making a diagnosis.
The pancreas is harmed by alcohol, fatty, fried, spicy foods. First of all, you need a diet, eating chicken, lean veal, and fish. The digestibility of fresh milk is poor, since the stomach usually suffers along with the pancreas. It is better to take low-fat fermented milk products. You can eat vegetables, fruits, and non-sour apples. It is better to bake them, use sweet varieties.
Treatment of pancreatitis in men
You should not eat raw egg yolks. The main thing is to give up bad habits when you are sick: smoking, alcohol, drinking coffee. If you give up unhealthy foods, follow a diet, and eat right, the discomfort and symptoms of pancreatic disease will become much less.
Complex carbohydrates are beneficial. The introduction of rice, buckwheat, millet, pasta, and rye bread into the diet is mandatory. It is important to minimize the load on the pancreas and protect it from the irritating effects of harmful products. It is better to take food chopped and boiled. You should give up fried, spicy, carbonated foods forever.
Milk thistle will help cleanse the liver and pancreas of toxins. Soy regulates blood sugar levels. Taking turmeric will relieve inflammation, symptoms, pain and nausea. It can be added as a seasoning to dishes. It will prevent rotting and necrosis of areas in the pancreas, and constant intake of a decoction of gentian root will relieve the unpleasant symptoms of this disease.
Why can’t you delay treatment?
In a hospital setting, especially in acute cases of the disease, the necessary medications and nutrients are administered to the patient intravenously. At the same time, the doctor prescribes a strict diet. In the hospital, this is not difficult - they give you exactly the dishes that are allowed on the diet.
In severe cases, when conservative treatment does not produce results, they resort to surgical intervention, an operation is performed to remove an organ that is inflamed to such an extent that its tissue can no longer be regenerated.
Treatment with medications:
- Spasms and severe pain are relieved with injections of Papaverine, No-shpa, Spasmol.
- Reduce the secretion of gastric juice with Gastrozol, Duoran, Ranitidine, Altramet, Kvamatel.
- Digestion is restored by taking Allohol, Holonerton, Creon, Mezim, Enzistal.
- Relieve bloating and remove toxins by taking sorbents and defoamers.
In adult men, treatment of pancreatitis based on symptoms is supplemented with folk remedies. The difficulty in treating men is that they are less responsible in following doctors’ orders, and as soon as they are relieved of severe pain, they can stop taking medications, and there is no need to talk about taking folk remedies at home.
Treatment of chronic pancreatitis is possible at home, but after consulting a specialist and strictly according to his instructions. First of all, a patient with pancreatic disease is recommended to follow a strict diet: it is necessary to avoid eating salted, fried, smoked foods, as well as processed foods.
It is recommended to drink purified water as much as possible - drinking plenty of water can reduce the inflammatory processes occurring in the pancreas. It is allowed to take weak tea, it is better if it is green. The patient should avoid drinking coffee, energy drinks, and all alcoholic beverages.
For treatment at home, the specialist prescribes enzyme preparations to the patient: “Mezim”, “Pancreatin”. To relieve painful spasms, it is prescribed: “No-shpu” or “Ibuprofen”. Additionally, herbal preparations specifically designed for restoring the pancreas can be prescribed, which can be purchased at pharmacies.
Diet for exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis
Treatment of acute pancreatitis should be carried out strictly in a surgical hospital. The patient should always be under the strict supervision of specialists so that the latter can intervene in a timely manner if urgent surgery is necessary. Treatment, as with the chronic form of the disease, begins with following a strict diet and taking the above medications.
But when foci of infection develop in the pancreas, the patient is necessarily prescribed a course of antibiotics, the purpose of which is to stop the infectious foci. The patient is also prescribed antioxidants and antacids, which are necessary to reduce and control the level of acidity in soft tissues. Pancreatic secretion is controlled by prescribing Atropine to the patient.
Development of inflammation of the pancreas
If pancreatitis has acquired an advanced form and the patient’s pancreas has undergone necrosis, surgical intervention is necessary to get rid of the dead part of the pancreas and prevent further spread of foci of necrosis.
Pancreatitis is a serious disease, often leading to serious consequences:
- pancreatic necrosis;
- purulent damage to the pancreas (formation of abscesses) and other abdominal organs that are located next to the pancreas;
- peritonitis, sepsis, infectious-toxic shock;
- internal bleeding to hemorrhagic shock;
- diabetes mellitus with associated complications;
- severe cachexia;
- gland cancer.
Pancreatitis in men is diagnosed quite often, usually due to alcoholism and poor nutrition. In combination with other risk factors, acute inflammation of the pancreas develops. This condition, due to delays in seeking medical help and lack of proper treatment, develops into chronic pancreatitis; in severe cases, the patient may die due to fatal complications that develop.
To avoid this, the main thing when making a diagnosis is to seek medical help in a timely manner and strictly follow all the recommendations of a specialist in the treatment and prevention of the disease (take prescribed medications, switch to a therapeutic diet, give up bad habits, normalize your daily routine, use herbal traditional medicine for no contraindications).
Bibliography
- Maksimov, V. A. Clinical symptoms of acute and chronic pancreatitis. Directory of General Practitioners. 2010 No. 3 pp. 26–28.
- Bozhenkov, Yu. G. Practical pancreatology. Guide for doctors M. Medical book, N. Novgorod Publishing house NGMA, 2003.
- Merzlikin N.V., Pancreatitis. – M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2014.
- Khazanov A.I., Vasiliev A.P., Spesivtsev V.N. et al. Clinical problems of chronic pancreatitis. Chronic pancreatitis: Mater, scientific. conferences. M.: GVKG im. N. N. Burdenko, 2000, pp. 3–14.
Source
Forecast
The prognosis of pancreatitis depends on the cause, timeliness and adequacy of treatment measures, as well as the presence of complications. Death can occur only with large volumes of necrotic damage to pancreatic tissue. With mild acute pancreatitis, complete recovery is possible.
Chronic diseases of the liver and bile ducts, stomach and intestines, non-compliance with doctor's recommendations and diet increase the likelihood of acute pancreatitis becoming chronic.
Two thirds of patients suffering from alcoholic pancreatitis live more than 10 years if they stop drinking alcohol. Otherwise, death occurs much earlier.
- Is your beard not growing? Or is it not as thick and chic as you would like? All is not lost.
- Cosmetics and accessories for proper care of your beard and mustache. Log in now!
Reactive form of the disease
With reactive pancreatitis, men lose their appetite and experience burning pain in the stomach and pancreas of varying intensity. However, it can weaken when bending and squatting. Nausea is accompanied by vomiting with a large amount of bile, heartburn and dizziness are possible.
The gland can hurt both in the area of the right hypochondrium and in the left hypochondrium, depending on the location of the inflammation. The area where the pain syndrome is most severe can be determined by palpation.
The role of breathing exercises in pancreatitis
Breathing exercises for pancreatitis
Massaging the internal organs is very useful, so performing breathing exercises can significantly help reduce attacks of pancreatitis and achieve stable remission. After attacks of illness, you need to perform exercises several times a day, gradually increasing the number to 9 procedures per day.
- Inhale and hold your breath for a count of 3 seconds. Exhale deeply, tighten your stomach. Hold your breath while inhaling for 2-3 seconds, then quickly draw in your stomach, exhale, relax your abdominal muscles.
- Pull your stomach in, while exhaling, hold the position for 3 seconds, relax your abdominal muscles. Inhale, inflate your stomach. Exhale, draw in your stomach.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YFJhfBMOIjc
The manifestation of symptoms in pancreatitis is influenced by the form, type, and severity of the disease. The signs and symptoms of pancreatic disease are quite varied, and it is difficult to make a diagnosis on your own. If similar symptoms appear, men should not hesitate to visit a doctor. As a result, pancreatic disease leads to complications, relapses, and is quite dangerous. If you suspect it, it is better to immediately consult a doctor, undergo an examination and prescribed treatment.
Symptoms and signs
The main sign of the occurrence of acute pathological processes is a sharp deterioration in health. In this case, the following signs of pancreatitis in men are possible:
- severe pain in the abdomen and right hypochondrium;
- nausea and vomiting that does not bring relief;
- temperature increase;
- bloating, persistent flatulence;
- stool disorder;
- the appearance of yellowness on the skin and sclera;
- drop or increase in blood pressure.
The set of signs and symptoms may vary depending on the causes of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient. At the same time, the appearance of pain, especially after a meal, indicates the need for urgent hospitalization and diagnostics.
Symptoms of incurable chronic pancreatitis in men are somewhat different and occur during an exacerbation of the disease. So, the pain can be dull and paroxysmal. Most often they occur immediately after drinking alcohol or junk food.
Signs of pancreatic disease in alcoholism in men are similar to symptoms in other situations. However, in this case, with prolonged development of the disease, changes in the skin are possible. With alcoholism, the pores on the face expand and the surface of the skin turns red.
If the consequences of a bad habit affect the liver, yellowing of the tissues and whites of the eyes often occurs. Persistent severe nausea and rapid weight loss are also characteristic. Vitamin deficiency, hair loss and brittleness, and brittle nail plates may occur.
Pain occurs in most cases when the problem worsens. But often men suffering from alcohol addiction do not attach importance to negative changes, which entails multiple complications.
Types of pancreatitis:
- Chronic – characterized by inflammation of the pancreas, which disrupts its exocrine and endocrine functions. The inflammatory process leads to disruption of the blood supply to organ cells and metabolic processes in them. This is the reason for the gradual replacement of gland cells with connective tissue, restructuring of the organ occurs and it loses its functional activity. The chronic form of pancreatitis is characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission.
- Acute – characterized by severe inflammation of the pancreas, a significant increase in the organ’s size, the occurrence of severe swelling, disintegration and necrosis of gland cells. As a result, there is a risk of infection entering the abdominal cavity through foci of organ decay. The pancreas completely stops producing hormones and enzymes that play a vital role in digestion.
Types of acute pancreatitis
| View | Characteristic |
| Edema (interscitial) | It is characterized by swelling of the gland lobules, as well as the interstitial space. There are no destructive changes |
| Hemorrhagic | It is characterized by rapidly advancing destructive processes of the parenchyma of the gland, as well as its blood vessels, with its own enzymes. As a result, necrosis, toxemia, peritonitis and hemorrhage occur |
| Purulent | It is characterized by the occurrence of micro- and macroabscesses in the pancreatic parenchyma. As a result, pseudocysts may appear - cavities filled with necrotic tissue, as well as purulent contents. |
| Pancreatic necrosis | It is characterized by partial or complete death of the pancreas, due to the digestion of the organ by enzymes that are secreted in it. Often causes the development of renal, respiratory and vascular failure, which in 30% of cases leads to death |
| Cholecystopancreatitis | Characterized by simultaneous inflammation of the pancreas and gallbladder. May be accompanied by inflammation of the liver, in which necrotic as well as dystrophic changes occur in the organ |
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Sanatoriums in Russia for the treatment of diabetes mellitus: services and wellness
The chronic form of pancreatitis is characterized by mild symptoms. There is pain on the left, under the ribs. The pain can spread to the right hypochondrium, abdominal cavity, and radiate to the heart or lower back. There may be discomfort in the stomach, as well as a slight enlargement of the liver.
As the above disease develops and becomes acute, the signs become more pronounced. Attacks of pain occur more often, dispersion disorders appear, characterized by stool disturbances (it becomes liquid, mushy, or, on the contrary, constipation occurs). Mucus may be present in the stool.
Also symptoms of acute pancreatitis in men are:
- excessively frequent urge to go to the toilet;
- diarrhea;
- nausea and vomiting;
- bloating;
- fever;
- rapid weight loss;
- feeling of weakness in the body;
- dehydration;
- rapid pulse and heartbeat;
- severe pain surrounding the abdomen and lower back.
Acute pancreatitis is characterized by inflammation and necrosis. In chronic cases, there are disturbances in the blood supply and nutrition of cells, which are subsequently replaced by connective tissues. As a result, a restructuring of the internal organ occurs, functions lose their activity, and the release of enzymes and hormones necessary for digestive and metabolic processes in the male body stops.
Chronic pancreatitis can either worsen or be in remission. Signs of acute pancreatitis The cause of the disease is heavy intake of alcoholic beverages and excessive amounts of spicy and fatty foods. Symptoms of pancreatic disease in men depend on the volume of affected pancreatic tissue, the condition of the body as a whole, and the various causes that led to the onset of the disease.
The stool is mushy, with pieces of food, foamy, with a sour and pungent odor. The pain intensifies during meals, especially fatty, fried and spicy foods. After lunch, severe vomiting occurs. Then the situation worsens: the pain increases, vomiting becomes more frequent, the temperature rises, the man’s skin and mucous membranes acquire a slight yellowish tint. Carbohydrate metabolism is disrupted.
If such symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Acute pancreatitis is treated in the hospital under constant supervision, since surgery may be required at any time.
If previously food and alcoholic drinks were easily tolerated, then over time an unpleasant sensation arises after eating, at first slightly expressed and left unattended. Pain gradually appears above the navel and in the hypochondrium area, which will spread around and become encircling.
Signs of chronic pancreatitis in men also include severe bowel movements (diarrhea) 20-25 minutes after eating. The stool is copious, liquid, light-colored and foamy, accompanied by rumbling in the abdomen.
After emptying, the condition normalizes a little, the pain temporarily subsides, but does not completely disappear. Subsequently, normal pancreatic tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue, which is not able to secrete the enzymes and hormones necessary for the body.
Gradual decrease in pain in the abdominal area,
The presence of these signs requires medical supervision and a thorough examination to exclude the appearance of malignant processes in the man’s body.
If bile infected with bacteria penetrates the pancreas, the situation can worsen dramatically. Bile components can cause necrosis of pancreatic tissue and activate its enzyme system. As a result, a self-digestion reaction occurs.
Acute pancreatitis
- alcohol consumption;
- cholelithiasis;
- overweight;
- viral hepatitis;
- poisoning;
- heredity.
- shock - the patient’s blood pressure drops sharply and vital organs fail;
- acute renal and liver failure (cessation of liver function, as well as urine filtration, which leads to poisoning of the body with toxic metabolic products);
- ulcerations of the digestive tract mucosa, gastrointestinal bleeding due to intoxication;
- thrombosis of blood vessels of internal organs, which leads to necrosis of their areas;
- psychosis due to intoxication. Patients who have consumed alcohol experience hallucinations and motor agitation.
Medicines for pain in the pancreas
A rather unpleasant symptom is pain in the pancreas. How to relieve pain? The choice of drug largely depends on the degree of development of the pathology. So, sometimes, such traditional drugs as “No-Shpa” are enough, and sometimes you have to resort to narcotic substances (for example, “Morphine”). Of course, symptomatic treatment is not enough. By eliminating unpleasant sensations, you do not eliminate the cause.
It is necessary to ensure complete rest for the organ if there is pain in the pancreas. How to relieve pain? For this purpose, experts prescribe pancreatic enzymes. It could be “Panzirin” or “Creon”. At the same time, it is worth taking proton pump inhibitors (for example, Pantoprazole or Omeprazole). All these drugs protect enzymes from destruction, and therefore the pancreas works in moderation.
If acute pancreatitis is diagnosed, antimicrobial therapy is necessary. It is produced through the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics. This could be Kefzol, Klaforan or Ampicillin. Naturally, in parallel, you should take antihistamines, as well as means to maintain normal intestinal microflora.
Treatment
If pancreatitis is manifested by mild pain, its treatment only includes the use of restorative drugs (vitamins, herbal medicines) and following a proper diet. The patient should not engage in intense physical activity.
If the disease is severe, and its symptoms become stronger every day, patients need to take drugs that cleanse the blood of toxins, relieve pain and relieve spasms.
Doctors often prescribe enemas. If such complex treatment does not give the expected results, it is necessary to cleanse the blood of poisons and stimulate urination. Nutrition is usually carried out through the veins by introducing nutrients into the blood. Sometimes surgery is required.