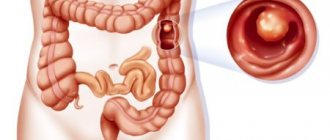
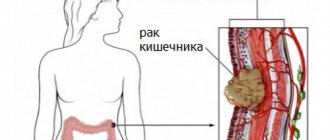
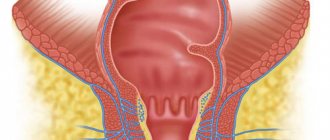
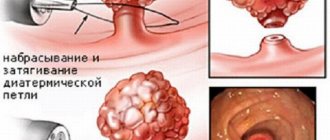
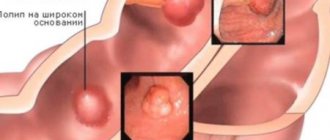
Colon cancer is a malignant transformation of the epithelium that can affect any segment of the intestine.
The disease occurs with all the signs of cellular atypia, such as rapid infiltrative growth, metastasis to nearby tissues (as a rule, intestinal cancer gives rise to metastases in the tissue of the liver, uterus, ovaries, prostate), and there is also a high probability of relapse after treatment. This disease most often affects people over forty years of age, but it also occurs in young people and children. This type of cancer occurs equally often in both men and women.
Symptoms of colon cancer in the initial stages are quite mild, which makes early diagnosis difficult. Treatment for intestinal cancer is usually radical, that is, it involves excision of malignant tissue. After bowel cancer surgery, the chances of five-year survival depend on the stage at which treatment was started.
Obviously, if bowel cancer is detected at an early stage, it is much easier to treat.
Causes
Medicine, even with its modern development, cannot give a definite answer to the question of the cause of the development of intestinal cancer. But the factors that increase the risk of developing the disease in question are well defined and studied. These include:
- Age after 50 years - precisely people from this age group are most often susceptible to the degeneration of healthy polyp cells on the intestinal mucosa into malignant ones.
- Previously diagnosed certain intestinal diseases - for example, Crohn's syndrome or ulcerative colitis.
- Improper lifestyle – frequent alcohol consumption, various stages of obesity, lack of physical activity (physical inactivity), poor diet (consumption of too fatty foods).
The hereditary factor plays a major role in the development of intestinal cancer - people in whose family there have been cases of intestinal cancer being diagnosed are at increased risk.
Please note: some doctors and scientists believe that even ordinary intestinal diseases (of an inflammatory nature) in relatives can be a reason to include patients at increased risk for developing intestinal cancer.
Doctors recommend that people at high risk contact specialists for examination, regular preventive examinations and advice on dietary nutrition.
Causes
The main role in the pathogenesis of the disease is played by disruption of the nasolacrimal duct.
In the congenital variant of the pathology, this is associated with anomalies in the development of the nasolacrimal duct (true atresia), the presence of a gelatinous plug or epithelial membrane in it. Most often, dacryocystitis develops in diseases such as acute respiratory viral infections, sinusitis or rhinitis, skull fractures, nasopharyngeal polyps, eye injuries when the lacrimal openings are damaged. In these cases, soft tissue swelling often occurs, which leads to stenosis of the nasolacrimal duct.
Due to the disruption of the outflow of tear fluid, its ability to suppress bacterial growth is reduced. Moreover, substances contained in the secretion of the lacrimal glands can become the basis for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.
As secretion accumulates in the lacrimal sac, its walls stretch and microscopic damage to the epithelium occurs along its entire length. As a result, microflora can easily penetrate the wall of the lacrimal sac and cause inflammation.
Certain groups of people have an increased risk of developing dacryocystitis. This includes people with diabetes, immunodeficiency, and regularly exposed to various harmful factors at work.
For children with congenital dacryocystitis, the main cause is anatomical deviations in the structure of the lacrimal system of the eye: too narrow or tortuous channels, blockage with a film, mucus plug, the presence of adhesions. Incorrect development of the palate, eyelids, face.
In adults, other causes of dacryocystitis predominate:
- Inflammatory, infectious processes of the eyeball: conjunctivitis, blepharitis, stye, keratitis. Inflammation provokes the formation of adhesions in the lacrimal gland or nasolacrimal ducts.
- Staying in dusty, contaminated areas without personal eye protection.
- Bruises, abrasions, injuries, cuts, foreign body of the eye.
- Dry keratoconjunctivitis.
- Physical, chemical, thermal effects.
- The occurrence of dacryocystitis as a complication after surgical interventions.
- Oncology of the nose, skull bones, eyes, polyps, growths.
- Taking certain medications.
- Formation of stones in the lacrimal sac.
- Foci of inflammation in the nose and sinuses: rhinitis, sinusitis.
- Allergic history, decreased immunological properties of the body, stress, hypothermia, chronic fatigue.
- Metabolic disorders, diabetes mellitus.
- Severe systemic diseases of the body: tuberculosis, HIV, syphilis.
- Narrowing of the canals can occur due to the patient's age, as well as the natural aging process.
Our tear fluid is secreted from the tear glands located above each eye. Tears flow down the surface of the eye, moisturizing and protecting it. The tear fluid then seeps into the thin openings in the corners of the eyelids.
Blockage of the lacrimal canal at any point in this complex system leads to disruption of the outflow of tear fluid. When this happens, the patient's eyes become watery and the risk of infection and inflammation increases.
• Congenital obstruction. In some children, the drainage system may be underdeveloped. Often the tear duct becomes blocked with a thin mucus plug. This defect may disappear on its own in the first months of life, but may require a special procedure - bougienage (probing).
• Abnormal development of the skull and face. The presence of abnormalities such as those found in Down syndrome increases the risk of tear duct obstruction.
• Age-related changes. Older people may experience age-related changes associated with narrowing of the openings of the tear ducts.
• Infections and inflammation of the eyes. Chronic inflammation of the eyes, nose and tear ducts leads to obstruction.
• Facial injuries. When a facial injury occurs, the bones near the tear ducts can be damaged, which disrupts normal drainage.
• Tumors of the nose, lacrimal sac, bones, when significantly enlarged, sometimes block the lacrimal canals.
• Cysts and stones. Sometimes cysts and stones form within this complex drainage system, causing drainage problems.
• External medications. In rare cases, the use of eye drops (for example, to treat glaucoma) can cause blockage of the tear ducts.
• Internal medications. Obstruction is one of the possible side effects of the drug docetaxel (Taxoret), used to treat breast or lung cancer.
Risk factors
• Age and gender. Older women are more likely to suffer from this disease as a result of age-related changes.
• Chronic inflammation of the eyes. If your eyes are constantly irritated and inflamed (conjunctivitis), there is an increased risk.
• Previous surgical operations. Surgeries on the eye, eyelid, or nasal sinuses can cause scarring in the drainage system of the eye.
• Glaucoma. Glaucoma medications sometimes cause tear duct obstruction.
• Previous cancer treatment. If a person has had facial radiation or taken certain anticancer drugs, the risk increases.
There are many causes of dacryocystitis in children and adults. But in some cases, doctors cannot determine what caused this disease. The cause of inflammation may be:
- Congenital anomaly of the duct development - narrow or too tortuous tear ducts.
- Injuries of various types.
- Damage to the nasal cavity caused by syphilis.
- Sinusitis.
- Blepharitis and keratitis.
- Tuberculosis.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Pneumonia.
- Children's infectious diseases - measles, rubella, mumps and chickenpox.
- Tumors of various types.
Frequent stressful situations can provoke inflammation of the nasolacrimal duct. It’s not for nothing that people say that all diseases are caused by nerves.
Blockage of the tear ducts (dacryocystitis) is an inflammatory process. It affects the tear duct, which is located between the nasal septum and the inner corner of the eye. As a result of the blockage, pathogenic microorganisms can accumulate. Their activation leads to the onset of inflammation and disruption of fluid outflow.
Diagram of the lacrimal duct
Most often, obstruction of the tear duct occurs due to the following reasons:
- Congenital pathology of patency. The defect appears at birth and may disappear in the first months of life. However, sometimes it may remain. In this case, it is necessary to pierce the lacrimal canal.
- Non-standard development of the skull and face.
- Infectious diseases and inflammatory processes.
- Surgical operations performed on the eyes.
- Injuries and damage to the face. Misaligned bones can interfere with the normal flow of fluid.
- Tumors on the face. Formations that arise in the nasal bones and lacrimal sac can block the canal. This happens if the tumor increases in size greatly.
- Medicines for external use. Some eye drops cause obstruction of the tear ducts.
- Medicines for internal use. Obstruction occurs as a side effect of taking certain medications.
- Irradiation. If a person has suffered from cancer during treatment, the risk of blockage increases significantly.
The first signs of bowel cancer
It is advisable to identify the first signs of intestinal cancer using instrumental methods of visual examination of the walls of the large intestine, by probing or by radiation methods, without penetrating into the body.
The basis for prescribing instrumental or laboratory tests are:
- at-risk groups;
- age over 40 years, but there are cases of the disease at a younger age;
- the presence of some signs indicating damage to the gastrointestinal tract against the background of any other symptoms, for example, a combination of disorders of the heart and excretory functions against the background of intestinal dysfunction.
A very important role during this period is played by the competent oncological alertness of the general practitioner, because in 70-90% of cases people turn to the general practitioner in the early stages of the disease, often for reasons that have no apparent relation to cancer.
The doctor usually thinks about the possible layering of oncology when the following subjective sensations appear or intensify in the patient (at least three at a time), including:
- general weakness;
- fast fatiguability;
- pain in a certain anatomical area of the abdomen (see intestinal anatomy above);
- progressive weight loss;
- slight but persistent increase in body temperature;
- blood or mucus in stool;
- dark (black) stool;
- pallor of the mucous membranes and skin;
- lack of relief after effective therapeutic procedures.
Naturally, these signs are not an accurate indication of cancer; one should always take into account the patient’s suspiciousness, individual pain sensitivity threshold, and other clinically important parameters for diagnosis. When the doctor confirms the patient’s complaints, the diagnosis is clarified on the basis of clinical, instrumental and laboratory studies.
It is inappropriate to list the primary macro- and microscopic changes in the intestinal walls that diagnosticians detect during examinations in this article, since such knowledge is purely professional.
Possible consequences
If dacryocystitis is not treated, it can lead to serious consequences. The most commonly observed complications are:
- constant watery eyes;
- spread of infection to healthy tissue. This can lead to orbital cellulitis, sinus thrombosis, meningitis or general blood poisoning;
- chronic inflammation of the tear ducts;
- atony of the lacrimal ducts.
The infection can quickly spread to the ENT organs. The consequence of this may be sinusitis, otitis media and other infectious diseases.
Dacryocystitis is often observed in weak and premature babies. But such a disease can also occur in adults as a complication of various infectious diseases.
Signs of Colon Cancer
Colon cancer (in medicine the wording “colon” is used) manifests itself:
- pain in the abdominal area (in the hypochondrium, displaced to the right or left side) that is dull or aching in nature
- bloating, seething, feeling of fullness; due to the specifics of the colon (predominantly water is absorbed), stool liquefaction and diarrhea occur
- Intestinal obstruction often occurs (a feeling of acute pain, attacks of nausea and vomiting, which may contain feces fragments in its composition
- signs of accumulation of fluid (ascites) in the abdominal cavity may appear, excessive pressure of which contributes to the dysfunction of all intra-abdominal organs.
Signs of colon cancer
Indicates colorectal cancer:
- the appearance of false urges to empty the bowel (they are called tenesmus)
- discharge from the anus in the form of pus, mucus or blood
- attacks of severe pain in the perineal area and slightly higher in the abdomen may precede or accompany the act of bowel movement (caused by nerve damage)
- if muscle structures are damaged, there is an inability to retain gases or feces
- Constipation and prolonged presence of waste products in the rectal cavity can result in general intoxication of the body (headaches, increased fatigue, weakness) or an inflammatory process.
- due to the close location of the last section of the intestine and the organs of the genitourinary system, formations can affect the functioning of the latter (inflammation of the bladder, urinary incontinence).
Treatment methods
Rectal cancer
The basic treatment for patients with rectal cancer is surgery. In the early stages of the disease, partial removal of the organ is possible with maximum preservation of functionality without the use of combined methods. In this case, the size of the neoplasm does not exceed 3 cm, and the disease affects no more than 30% of the circumference of the organ.
If the tumor is located in the middle, lower parts of the intestine, in most cases a total resection is performed (mesorectumectomy, when the organ itself, the anal canal, the sphincter are cut out, a colostomy is applied - a part of the colon is surgically removed for intestinal drainage). More gentle surgical formats involve partial tissue extraction.
The main consequence of removal of the colon is a lifelong change in style and quality of life (strict diet; the bone breaker plays the role of the anus, and the colon takes on the functions of the rectum: the accumulation and retention of feces). The intervention is carried out using laparoscopy (through punctures in the abdominal cavity) or in the format of “open” operations, when an incision is made in the abdominal cavity.
During the treatment of stage 2-3 cancer, it is imperative to use the capabilities of chemotherapy (radiation) at gamma therapeutic units. If the tumor is motionless and has grown into neighboring organs and tissues, resection or removal of the tumor is impossible in most cases. In this case, patients are prescribed radiation and chemotherapy. After 6-8 weeks, an MRI of the pelvis is recommended to assess the operability of the tumor. Then either radical surgical treatment or supportive (palliative) therapy and continued radiation therapy are performed.
It is important to remember that the intervention should be carried out as soon as the tumor and metastases become operable, because prolonged exposure to chemotherapy treatment has a toxic effect on the liver and masks some of the metastases that cannot be seen during laparoscopy. During the period after intestinal surgery, special attention is paid to restoring metabolism and eliminating nutritional deficiencies.
At the end of surgical treatment, complications may occur: pain, perforation (formation of a through hole in the wall of the colon), bleeding, intestinal obstruction. To monitor health status, regular observation is necessary: for the first 2 years - once every six months, then - once a year. Specialists conduct clinical and laboratory tests, colonoscopy, lung x-rays, abdominal ultrasound, and CT scans.
Advice: nutrition after intestinal surgery for oncology should be therapeutic, making the digestion process more efficient, enhancing the role of the intestines. Food is taken strictly according to the clock, according to a certain diet, and this promotes emptying. It is better to exclude strong tea, coffee, rice, white bread, cottage cheese, slimy soups, jelly from the menu, and agree on the best option for your menu with your doctor.
Signs of small intestine cancer
Cancer of the small intestine (in medicine the wording “small intestine” is used) is manifested mainly by dyspeptic symptoms:
- intestinal spasms, nausea and vomiting, heartburn, belching, change in taste
- pain occurs in any area of the abdomen
- The patient has no appetite and has an aversion to food
- If there is bleeding, the stool may turn dark.
The doctor may be alerted to any manifestation of a disturbance in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract that does not go away after normalizing nutrition and following a diet. If symptoms persist, a more detailed examination is necessary.
Symptoms of bowel cancer in women and men
Signs of intestinal cancer in men and women with this course are practically no different. Later, if the tumor progresses and spreads to neighboring organs, the prostate is the first to be affected in men, and the vagina is the first to be affected in women; the rectal space and anal canal are also affected.
In this case, the patient begins to experience severe pain in the anus, coccyx, sacrum, and lumbar region; men feel difficulty during urination.
If it is oncology, the clinical outcome is not always favorable. Malignant neoplasm appears in women after 35 years of age; in the primary form, it does not spread metastases to the uterus. First, the patient experiences general weakness throughout the body and classic signs of dyspepsia, then specific signs of an intestinal tumor appear. This:
- recurrent pain during bowel movements;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle;
- blood in stool;
- impaired urination;
- sudden weight loss, lack of appetite;
- blood impurities in the daily urine sample;
- aversion to fried, fatty foods.
Late stages of colon cancer are characterized by the addition of general symptoms to local ones. Signs of intestinal cancer appear:
- The skin becomes dry and pale.
- Frequent dizziness and headaches.
- Weakness and fatigue of the patient.
- Unreasonable weight loss and exhaustion.
- Damage to other systems and organs of the body.
- Low presence of blood in the body, low level of protein in it.
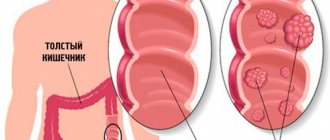
Stages
In intestinal cancer, the stages of the pathological process are determined based on several parameters, including the intensity of growth of the primary tumor, the severity of symptoms and the presence of metastases to distant organs. In medical practice, the most often used classification takes into account 4 stages of the oncological process. Some clinicians also distinguish stage 0, which is characterized by the presence of a cluster of cells that have an atypical structure and the ability to rapidly divide.
- At stage 1 of the pathological process, malignant degeneration of the existing tumor begins, which is accompanied by its rapid increase in size. The formation has not yet left the wall of the affected area of the intestine. Metastases to regional lymph nodes and no pain are observed. During this period of cancer development, patients may periodically show signs of mild eating disorders. A colonoscopy at this stage of tumor formation makes it possible to identify it.
- At stage 2, the malignant formation reaches a size of 2–5 cm. It grows to the entire depth of the intestinal wall. There are still no signs of the onset of tumor metastasis. The severity of disorders of the digestive system is aggravated. Any instrumental research methods can identify a neoplasm.
- At stage 3 of the oncological process, there is an increase in the activity of cells with an atypical structure. This leads to a rapid increase in the size of the existing tumor. It begins to spread beyond the intestines, affecting nearby lymph nodes and internal organs. Symptoms of damage to the gastrointestinal tract become pronounced.
- Stage 4 of intestinal cancer is considered the most dangerous. It is characterized by rapid growth of tumor tissue and metastasis to distant organs. The severity of symptomatic manifestations of the pathological process becomes critical. In addition, the human body is poisoned by toxic substances released by the tumor. Disruptions in the functioning of all body systems are increasing.
Classification
Dacryocystitis can be primary (congenital dacryocystitis in children) and secondary, acquired as a result of another disease or external influence. Secondary dacryocystitis is of two types:
- Acute dacryocystitis is a sharp, aggressive course with the formation of a purulent sac, swelling, lacrimation, and fever, requiring immediate medical intervention.
- Chronic dacryocystitis in adults is a sluggish process with vague symptoms and minor discomfort. It has a wave-like change in symptoms from an acute attack to a chronic course.
According to the form of inflammation, they are divided into:
- catarrh of the lacrimal ducts;
- stenosing form;
- phlegmon of the lacrimal sac;
- empyema.
There are several clinical forms of inflammation of the lacrimal sac:
- spicy;
- chronic;
- dacryocystitis of newborns.
Acute dacryocystitis in adults can be in the form of an abscess or phlegmon. The difference lies in the nature of the spread of inflammation - with an abscess, the inflammatory infiltrate is limited to the connective tissue capsule, and phlegmon has a diffuse nature of inflammation.
Depending on the etiology, the following forms of inflammation of the lacrimal sac can be distinguished:
- bacterial;
- viral;
- parasitic;
- traumatic.
Some authors separately identify dacryocystitis as chlamydial in nature, but it can also be attributed to the bacterial form of the disease.
Inflammation of the nasolacrimal duct can be acute or chronic. In the latter case, periods of exacerbation and remission of the disease alternate. In adults, this condition is often observed with swelling of the nasal mucosa.
If treatment is not carried out, the pathological process can affect healthy tissue. If pus enters the circulatory system, it can be life-threatening. Sometimes so much pus accumulates that it thins the skin and breaks out on its own.
Metastases
Colon cancer most often metastasizes to the liver; there are frequent cases of damage to the lymph nodes of the retroperitoneal space, the peritoneum itself, abdominal organs, ovaries, lungs, adrenal glands, pancreas, pelvic organs and bladder.
- When an intestinal cancer metastasizes to the liver, the prognosis depends on the stage of its development, the severity of liver damage, the number of malignant neoplasms, as well as on the general condition of the patient. The average life expectancy for 50% of such patients is six to nine months.
- Half of patients with stage IV colon cancer who have a single metastasis in the liver are able to live another 2-2.5 years. The five-year survival rate is less than one percent.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing bowel cancer in the early stages of the disease is extremely important, since the disease is characterized by a slow progression, and timely measures can completely eliminate bowel cancer if it has not gone too far. The diagnosis is made after the following studies:
- X-ray diagnostics of the intestines (irrigoscopy). It is an X-ray examination of the intestinal walls after the administration of an X-ray contrast agent through an enema, for which a barium suspension is used.
- Retromanoscopy. The examination of a section of the intestine from the anus to a depth of 30 cm is carried out with a special device that allows the doctor to see the intestinal wall.
- Colonoscopy. Examination of the intestinal area from the anus to a depth of 100 cm.
- Laboratory examination of feces for occult blood.
- CT and MRI can determine the location of the tumor, as well as the presence or absence of metastases.
Tear duct surgery in adults
Doctors can diagnose blocked tear ducts in patients of any age. Most often in adults, the procedure is performed for diagnostic purposes. Using this method, it is possible to determine the percentage of passive patency of the lacrimal ducts (in some cases, the diagnosis is carried out several times).
Problems with patency in adults are more difficult to eliminate than in infants. In this case, neither probing nor massage helps. Due to the tightly formed tissues, the only way to restore tear flow is repeated rinsing.
If a thick film blocks the tear ducts, as a rule, simple rinsing is not prescribed. In the appropriate situation, surgical intervention is advisable. As in the case of newborns, the patient is given antibiotics after the procedure to prevent complications.
Therapeutic measures begin with vitamin and physiotherapy, the purpose of which is to reduce the density of the infiltrate. For this purpose, UHF and dry heat are used.
In the abscess form of acute dacryocystitis, the abscess is opened after the appearance of fluctuations. Next, antibacterial therapy is started, which consists of washing the abscess cavity or lacrimal sac with antiseptic solutions (hydrogen peroxide, furatsilin, dioxidine, etc.).
At the same time, broad-spectrum antibacterial agents belonging to the group of cephalosporins, penicillins, and aminoglycosides are administered parenterally. Only after the inflammation has subsided is dacrystorhinostomy performed - an operation to create an opening. Through which the lacrimal sac and the nasal cavity will communicate.
In newborns, treatment includes several stages, such as massage of the lacrimal sac, rinsing the canal and probing it both retrogradely and through the lacrimal openings. This set of measures must be carried out gradually over a period of approximately 10-12 weeks.
Chronic dacryocystitis, as well as acute, is treated surgically to create a path for the outflow of tear fluid. Modern ophthalmic surgery has minimally invasive methods for treating this disease, based on the use of laser or endoscopic techniques.
Sometimes methods such as bougienage and balloon plastic surgery of the lacrimal sac are used. The technique of this operation consists of inserting a probe into the stenotic or obliterated nasolacrimal canal, with the help of which a balloon is inserted into the cavity of the bag - then it is inflated and thereby expands the canal.
The prognosis for recovery in the absence of complications of dacryocystitis is usually favorable. Lack of timely treatment leads to the development of pathologies such as orbital phlegmon, thrombophlebitis, cavernous sinus thrombosis, inflammatory diseases of the brain and its membranes.
When an infection of other localizations occurs, the prescription of antibiotics is required, which are administered parenterally. It is possible to attract specialists of the relevant profile.
The disease does not manifest itself particularly clearly in the first stages. Classic symptoms are swelling and a feeling of fullness in the lacrimal sac.
After some time, continuous lacrimation, a feeling of constant discomfort and mild pain occur. When pressing on the area of the lacrimal sac, fluid or pus may be released.
Without appropriate and timely treatment, simple catarrhal dacryocystitis in adults can develop into an abscess - purulent melting of tissue. This is an extremely serious disease that can lead to loss of vision or sepsis of the entire body.
In the initial stages of the disease, cure is possible using conservative methods. Regular massage of the lacrimal sac, and the introduction of antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and vasoconstrictor drugs into the lacrimal sac and nasolacrimal duct.
If the disease turns out to be advanced, then surgical intervention can only be an effective way to treat dacryocystitis in adults.
Operations used for this pathology: bougienage - restoration of the tear flow through the nasolacrimal duct. The second type of operation is dacryocystorhinostomy. Its essence is the formation of a new communication between the lacrimal sac and the nasal cavity.
The following causes of tear duct blockage in adults can be identified:
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the duct, as well as the face and skull;
- infectious diseases of the eyes and nasopharynx;
- tumors of the facial part of the skull;
- surgical interventions on the organ of vision;
- radiation therapy for oncological diseases;
- abuse of eye drops;
- side effects of certain medications.
Due to a violation of the outflow of fluid, there is an increased proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. An inflammatory process occurs in the lacrimal sac - dacryocystitis.
- Bougienage. This method is the most gentle. If the procedure is carried out on time, this will help avoid surgery to remove the lacrimal sac. Under local anesthesia, special probes called bougies are inserted into the canal through the lacrimal opening. They remove the obstacle and expand the lumen of the canal.
- Balloon plastic. Under local anesthesia, a conductor with a balloon containing liquid is inserted into the canal. It is placed at the site of narrowing. Gradually pressure is supplied to the cylinder. The stenotic area expands.
- Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy. During the surgical procedure, a flexible endoscope with a camera is inserted into the tear duct. With its help, a small incision is made on the affected area. The operation will be available to patients who do not have allergic reactions. The duration of the rehabilitation period is up to 8 days. The advantages of such an operation are that after it is performed there are no visible scars left on the skin and the tear ducts are not damaged.
- Balloon dacryocytoplasty. This is a safe surgical intervention that is performed even on children under one year old. Specialists insert a thin conductor into the tear duct. It contains a bottle with a special liquid. At the site of blockage, a pressure balloon expands the problematic area of the tear duct and helps clear it. Local anesthesia may be used during the procedure. After surgery, you may be prescribed to use antibacterial drops.
Sometimes these procedures have to be repeated after an interval of several days.
Surgery is usually prescribed in difficult cases. The operation has the following types:
Carrying out balloon dacryocytoplasty
Treatment
Every person should understand that traditional methods of treatment cannot cure cancer. Such drugs can only reduce the intensity of symptoms, but they do not affect the growth of malignant cells. If you suspect intestinal cancer, it is much more prudent to seek help from a specialist who will help get rid of the pathology in its initial stages.
Modern medicine is capable of providing effective therapy for intestinal cancer, but one very important condition is necessary - the pathology must be detected at an early stage. If cancer is diagnosed in late stages, only half of patients have a chance of getting rid of the disease. This is unfortunate because today less than a quarter of patients receive timely care. Therefore, in our country over 35,000 people die every year from intestinal cancer.
Surgical methods
If the tumor was detected at an early stage, it can be removed surgically, followed by complete restoration of intestinal patency. After this, the intestines will be able to fully perform their functions, and, accordingly, the possibility of defecation naturally remains. And this circumstance allows the patient to live comfortably even after surgical treatment.
However, in some cases, foci of the malignant process are located in such a way that restoration of full intestinal patency after their removal is impossible. With this development of events, the surgeon brings the end of the healthy intestine to the abdominal surface. This surgical process is called a colostomy. After this, the patient is forced to use disposable colostomy bags, which at least partially ensures a normal existence.
Radiation therapy and chemotherapy
The technique of influencing the process using ionizing radiation and chemicals makes it possible to prevent metastasis, as well as stop tumor growth for a long period. This technique can be used both in the postoperative period and in the absence of surgical treatment.
How to treat dacryocystitis
Dacryocystitis is treated mainly comprehensively. The treatment regimen is determined by the doctor, based on the results of studies and tests. Adults and children are prescribed antiseptic solutions for washing the canals and antibacterial drugs that prevent the spread of infection.
Drugs
For dacryocystitis, eye drops and ointments with an antibacterial effect must be prescribed. The following medications are most often prescribed:
- Levomycetin drops. The active substance of this drug has a detrimental effect on a number of pathogenic microorganisms. Thanks to these inexpensive eye drops, it is possible to quickly eliminate conjunctivitis and other infections of the visual organs.
- Phloxal. This drug is often prescribed to newborns diagnosed with dacryocystitis and other eye infections. The medicinal solution is dripped into the eyes several times a day, after which the tear duct is gently massaged.
- Tobrex. A powerful antibiotic that is active against many pathogens. Tobrex can be prescribed to treat adults and children.
For dacryocystitis, various ointments can be prescribed. Such drugs have a viscous structure and remain on the eye mucosa longer. The doctor may prescribe Levomycetin or Tetracycline ointment. Floxal and Tobrex ointment helps a lot.
Medicines are placed 1 cm behind the lower eyelid. 2-3 eye treatments are required per day. After the procedure, close the eyelids and actively move the eyeball so that the medicine spreads evenly.
Before using eye drops and ointments, the mucous membrane is washed. To do this, you can use a solution of Furacilin, Miramistin or a weak solution of boric acid. Eye rinsing is carried out several times a day. For each eye, take a separate cotton pad, pre-moistened in a warm solution.
Massage
Newborn babies with dacryocystitis must be prescribed an eye massage. Thanks to such procedures, the gelatin film is broken and patency in the canal is restored.
Before the massage, the baby's eyes are washed well to remove pus. It is recommended to carry out procedures frequently. Some mothers adapt to massage movements while feeding their baby.
Massaging the tear ducts is not difficult. An ophthalmologist will show you whether the techniques are performed correctly.
- The baby is placed on a changing table or bed, previously covered with a diaper.
- An adult warms his hands and lubricates his index fingers or little fingers with neutral baby cream, this will make sliding easier.
- Place a finger on the inner corner of the eye and make pushing movements with it. It is very important to calculate the force, since strong pressure can damage the cartilage tissue. First, move the finger downwards, then change the direction.
- After the massage, antibacterial drops prescribed by the doctor are dripped into the baby's eyes.
To achieve a positive result, eye massage should be done for at least 2 weeks. It is advisable to carry out this procedure about 10 times a day.
If massage of the tear ducts does not help for a long time, the doctor gives a referral for probing. This is a safe procedure that is performed on newborns under local anesthesia.
Folk remedies
Dacryocystitis can be treated with a number of folk recipes. These methods often complement drug treatment prescribed by a doctor.
- Squeeze the juice from aloe leaves, mix it half and half with warm water and use the composition to wash the eyes.
- You can make lotions with aloe. To do this, the leaves are crushed, the pulp is wrapped in two layers of gauze and applied to the eyelids for 10 minutes. This procedure is recommended to be carried out after a massage of the visual organs.
- Brew a tablespoon of eyebright herb in a glass of water. The resulting decoction is infused, filtered and used to wash the mucous membrane.
- Prepare a chamomile decoction from a tablespoon of plant material and a glass of water. The herb is poured into a thermos and poured boiling water, left for an hour, after which it is used for compresses on the eyelids. You can take chamomile bags, pour 1/3 cup of boiling water over them, leave for 10 minutes, cool slightly and apply to your eyelids.
- Thyme is good for eye diseases. A strong decoction is prepared, which is used warm for lotions.
To eliminate inflammation of the eyelids and reduce swelling, grated fresh potatoes are applied to the eyes. Such lotions should be kept for at least 10 minutes.
Non-traditional treatment methods are especially helpful in the early stages of the disease. If the inflammation of the tear duct is severe, then surgical intervention is most often necessary.
If conservative treatment does not give effect for a long time, then surgical intervention is resorted to. In young children, tear ducts are often probed. It is noteworthy that for babies under 3 months the operation is performed under local anesthesia. For children older than this age, surgery is often performed under general anesthesia.
In older children and adults, treatment boils down to the creation of an artificial tear duct, through which fluid from the eye will flow into the nose. If dacryocystitis is very severe in adults, their lacrimal sac is removed.
If there is a lot of pus in the lacrimal sac and there is a possibility of its rupture, the surgeon performs an autopsy. After the pus drains, the cavity is washed with disinfectant solutions. After which the wound is sealed with a bactericidal plaster.
Operations are most often performed using a laser. In this case, there is less likelihood of complications developing, and healing occurs faster.
Treatment of pathology in a child involves watchful waiting. It takes time for the nasolacrimal ducts to mature, strengthen and develop. In this case, massage of the lacrimal ducts and lacrimal sac is used during each feeding of the child.
Treatment of dacryocystitis in adults combines conservative means, traditional medicine, home methods and surgery. Therapy depends on the patient’s age, form, stage, severity of dacryocystitis, as well as its underlying cause.
If there is a large accumulation of pus in the lacrimal sac, as soon as the plug begins to come out, all the contents are evacuated into the nose, and the swelling also disappears. If the process is not complicated, then the disappearance of the symptoms of dacryocystitis, tearing when dropping drops into the eye, and the appearance of a bitter taste in the mouth will be a sure sign of recovery.
Dacryocystitis can go away on its own with the use of massage exercises. This is especially true in childhood; with the help of massage, the tear outflow pathways that have not yet fully opened are broken through.
Conservative treatment is used for the chronic form of the disease, narrowing or stenosis of the lacrimal system. If there is an obstruction or blockage, acute dacryocystitis will not be cured by drops or ointments. In this case, specialist intervention is necessary, including surgery.
Treatment begins with washing the lacrimal canals with a bactericidal agent, this can be Chlorhexidine, Furacilin, peroxide, Dioxidin, or simply saline sodium chloride solution. Next, to prevent the spread and multiplication of the infection, antibacterial agents are prescribed.
Ointments and drops for dacryocystitis:
- "Ciprofloxacin";
- "Miramistin";
- "Dexamethasone";
- "Tobrex";
- "Floxal";
- tetracycline ointment;
- gentamicin ointment;
- Vishnevsky ointment.
Along with medications, it is recommended to perform a special massage for dacryocystitis.
If the process is not resolved, surgical intervention is resorted to.
Forecast for life
How long do you live after treatment for colon cancer? In medicine, the term “five-year survival rate” is accepted; this is statistical data indicating the number of patients who lived more than 5 years after treatment with a positive result. The indicator depends on many factors, primarily on the stage of cancer at which treatment began:
- Stage 1 – about 95% of patients live more than 5 years.
- Stage two – about 75% of patients live more than 5 years.
- Stage three – about 50% of patients live more than 5 years.
- Stage four (with the presence of metastases) – about 5% of patients live more than 5 years.
You need to understand that all of these are very average indicators, which additionally depend on many related factors:
- patient's age,
- the state of his immune system,
- the presence of concomitant pathologies.
And the main thing to remember is that the likelihood of completely overcoming bowel cancer exists regardless of the stage at which it was diagnosed. At the same time, time is both a partner and an enemy of the patient. If you use it rationally, the result of therapy is quite likely to be positive.
Prevention
To prevent the development of cancer, you must:
- Immediately treat precancerous diseases that cause inflammation of the large intestine (most often it develops due to colitis and Crohn's disease).
- People whose family history is burdened with cases of intestinal cancer need to be periodically examined in a specialized clinic.
- Include as many vegetable and fruit dishes as possible in your diet. Their high content of dietary fiber and plant fiber will contribute to the rapid and effective cleansing of the intestines.
Clinical forms of chronic dacryocystitis
- simple catarrhal dacryocystitis
- stenosing dacryocystitis
- empyema of the lacrimal sac
- phlegmon of the lacrimal sac
Acute dacryocystitis in adults, as a rule, is not an independent disease, but an exacerbation of a chronic process.
The most common pathogens are bacteria, viruses, and parasites. A frequent provoking factor for dacryocystitis in adults can be trauma to the eyeball.
The cause of dacryocystitis in adults is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nasolacrimal duct. As a result, the membrane thickens and the outflow of fluid stops. The tear accumulates in the lacrimal sac, and conditions are created for infection by pathogenic flora.