The presence of a high temperature after appendicitis surgery indicates the possible development of complications. One of the most effective and common methods of treating appendicitis is its removal, that is, appendectomy. This method of treatment raises many concerns among people, since questions immediately arise about the possible negative course of the operation and its consequences, as well as questions about the level of qualifications and experience of the specialists performing such operations.
Of course, there are cases where a certain type of disease can manifest itself as another disease, which can lead to disastrous mistakes, but the current level of medical care excludes this. The technical equipment of medical institutions with modern equipment allows for high-quality and quick diagnosis of the disease and establishment of the best type of treatment.
Preoperative period
There are 2 forms of appendicitis - acute and chronic.
There are several forms of the disease - chronic and acute appendicitis. The most common acute form of appendicitis occurs when the patient needs immediate medical attention, namely in the first 4 hours of exacerbation.
Untimely treatment can lead to serious consequences, since changes occur inside the inflamed appendix (perforation), then the appendix ruptures, which is accompanied by the release of all its contents into the abdominal cavity, which in turn leads to a serious complication - peritonitis.
Before carrying out a planned operation, ensure that all possible threats are eliminated, which leads to different durations of the operation. Preparation for appendicitis surgery occurs in the following sequence:
- As noted earlier, when the appendix is inflamed, it is very important to receive prompt medical attention. Therefore, when entering the hospital, you need to quickly go through the registration process, which means it is very important to prepare all the necessary documents in advance. Then the patient is admitted to a specialist, who interviews him and conducts a general examination, accompanied by palpating, tapping the corresponding areas of the abdominal cavity, and also conducts x-rays and other laboratory tests. Removal of the appendix is carried out only after all the circumstances have been clarified.
- An appendectomy is performed under anesthesia, so the anesthesiologist is obliged to establish the patient’s basic parameters (height, weight), as well as find out all the details about his state of health - the presence of chronic diseases, the state of the cardiovascular system, the presence of allergies. In some cases, before surgery, the patient is given a drip of isotonic solutions, which reduces the level of intoxication. At the end of the preparatory stage, the required area of skin is shaved and disinfected.
Read: Signs of esophageal cancer, you can’t miss them...
Pathological causes
If complications develop, the patient's body temperature will be above 38 °C. In this case, such a high indicator lasts more than 5 days. The reason for this condition may be:
- infection of the wound surface during surgery. Such situations can arise both through the fault of medical personnel and in cases of pus in the appendix;
- damage to organs adjacent to the appendix during surgery;
- massive blood loss;
- contamination of the postoperative suture;
- the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- development of inflammation of the peritoneum or general blood infection;
- the addition of a respiratory viral infection due to a sharp decrease in immunity;
- violation by the patient of the diet recommended by the attending physician.
When such complications develop, measures to eliminate them are taken urgently. This may include intensive drug therapy, repeat surgery, or transfer of the patient to the intensive care unit.
Surgery and postoperative period
The operation to remove the appendix is performed under general anesthesia.
Let's consider the process of surgery for appendicitis, as well as the postoperative recovery period.
The operation to remove the inflamed appendage of the cecum is performed under mandatory anesthesia - this can be a tight infiltrate, conduction block or general anesthesia.
Creeping infiltration has many advantages - it has a quick effect on the nerve ending, there is no need to find the injection site for the solution, and the ability to perform operations in poorly equipped institutions.
But this method also has a disadvantage - the need for frequent use of novocaine. The method of conduction anesthesia is difficult to perform, but it is characterized by speed and reliability, as well as the need to use a small amount of solution.
The anesthesiologist determines the required dose of drugs for each patient individually. Then premedication is carried out to reduce the patient’s anxiety with the help of special medications, induction, which is the first phase of anesthesia, artificial respiration (intubation) is provided, and finally the patient is removed from anesthesia. In some cases, muscle relaxants are used during anesthesia to immobilize the patient.
Surgery for appendicitis consists of several stages. First, the abdominal wall is dissected and the entire cavity is examined, then the organ itself is removed, after which the edges of the wall are sutured with absorbable threads, and the skin of the abdomen is tightened with interrupted sutures. If appendicitis is accompanied by peritonitis, the cavity is cleaned and drainage is installed, which helps remove pus.
The manner in which the appendectomy process was performed affects the patient's subsequent recovery. So, on the first day of the postoperative period, specialists detoxify the patient, he is under constant medical supervision, since complications may occur (bleeding, paresis of the intestines and bladder).
It must be remembered that during this period the doctor must be informed of any ailments. After discharge, it may happen that the stitches come apart, in which case it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance and wait for its arrival in a lying position.
Read: Intestinal lymphoma: symptoms that should alert you
The video will tell you why there is a high temperature after appendicitis removal:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CjzDHoBT3Ek
How is postoperative inflammation treated?
Normally, the highest temperature after surgery occurs in the first days, and then it gradually decreases to 37 and returns to natural values. If the doctor sees that recovery is going well and the temperature is leveling out, no prescriptions or manipulations are carried out. If within 10 days there is no tendency to normalize the temperature, you need to find out the reason for this reaction of the body and eliminate it. To do this, it is enough to do a general blood test and ultrasound to see if there is inflammation and where it is localized.
Once the reason for maintaining a high temperature for more than 10 days has been established, treatment is carried out, which includes:
- Antibacterial therapy with antibiotics, which the doctor selects based on which microorganisms are the causative agents of inflammation.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy with NSAIDs (Ibuprofen).
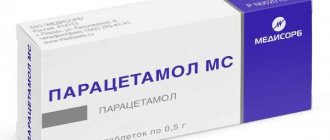
- Symptomatic treatment of high fever with antipyretics (Aspirin, Paracetamol).
All treatment should be prescribed by a doctor, and the progress of recovery should also be monitored. Under no circumstances should you try to cure postoperative inflammation on your own.
A normal temperature 10 days after appendicitis is removed is an important parameter for recovery, which is why a patient with a high temperature cannot be discharged from the hospital. Usually everything is managed with a course of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, after which the number on the thermometer drops to 37 or below. If such treatment does not lead to the desired results, the attending surgeon can perform a repeat operation so that not on the monitor of an ultrasound machine, but with his own eyes, he can see what is happening at the site of appendicitis removal.
The presence of a high temperature after appendicitis surgery indicates the possible development of complications. One of the most effective and common methods of treating appendicitis is its removal, that is, appendectomy. This method of treatment raises many concerns among people, since questions immediately arise about the possible negative course of the operation and its consequences, as well as questions about the level of qualifications and experience of the specialists performing such operations.
Of course, there are cases where a certain type of disease can manifest itself as another disease, which can lead to disastrous mistakes, but the current level of medical care excludes this. The technical equipment of medical institutions with modern equipment allows for high-quality and quick diagnosis of the disease and establishment of the best type of treatment.
High temperature in the postoperative period
The cause of elevated temperature is weakened immunity.
It must be remembered that the presence of a high temperature after surgery for appendicitis indicates an inflammatory process in the body.
Moreover, if the temperature increased in the first time after the operation and was of a short-term nature, then this condition is normal and indicates that the body is resisting.
This temperature is normalized independently or with the help of special procedures. A fever is considered dangerous and requires immediate medical intervention if it lasts up to 1 month and is accompanied by vomiting, dysbacteriosis, constipation, sweating, partial or complete loss of consciousness, and abdominal pain.
The main reasons for the increase in temperature are weakened immunity, postoperative stress of the body, as well as the process of absorption of decay products that occur with a perforated gastric ulcer: manifestation, surgery and treatment.
During the operation, hyperthermia of the body occurs, that is, the amount of fluid in the body decreases, and the wound releases fluid. The patient’s condition upon admission to the hospital plays an important role, since the more severe it was, the greater the likelihood of an increase in temperature.
Reasons for rising temperature
Treatment of acute appendicitis is always a surgical operation to remove the appendix. Intervention in the body, its integrity, is an unnatural process that disrupts the functioning of organs and cells. The body reacts by increasing its temperature. In most cases, such a reaction is a variant of the norm, since the immune system after surgery for appendicitis begins to produce a large number of leukocytes to neutralize possible viruses and pathological conditions. As a rule, when damaged tissues heal, a reaction in the form of an increase in temperature is considered normal.
It is not recommended to lower the temperature below 38C, so as not to disrupt the body’s healing process. Moreover, doctors are concerned when a person’s body temperature does not increase. This indicates that the immune system is very weak, which means that adverse reactions, complications, and inflammatory diseases are possible. The absence of hyperthermia after abdominal surgery can especially lead to serious health problems.
Experts note that overheating in the human body begins at the stage of the inflammatory process in the appendix of the cecum. This is a symptom indicating an inflammatory process, acute appendicitis. Therefore, after removal, the symptom persists for several days.
But in some cases, long-term persistence of fever indicates pathology.
- A strong temperature jump over a short period of time for no apparent reason. Sometimes such a reaction indicates an allergic reaction when introducing certain drugs or the ingress of pathogenic microflora that is actively reproducing.
- Hyperthermia as an immune response to the introduction of a drainage system after surgery. If it goes beyond a certain time, it is considered a pathology and requires drug treatment.
- Complications during surgery resulting in damage to internal organs.
- Excessive blood loss during surgery.
- Infection during surgery.
- A patient with ARVI during the postoperative period. The patient's body's defenses after removal of the appendix are aimed at recovery. Against the background of reduced immunity, any ARVI is tolerated more severely by the patient, longer, and longer treatment is required.
- The patient does not follow a diet after the appendix has been excised. If you ignore the diet prescribed by the doctor, disturbances in the functioning of the intestines, and even inflammatory processes, are possible.
An increase in temperature after removal of the appendix lasts about a week and is considered normal and part of the recovery phase. But if the time frame is not met and the fever persists after a week, additional blood, urine and other tests are necessary, at the discretion of the specialist. Tests are necessary to establish the exact cause of fever, diagnosis, and timely treatment.
The main reasons for the duration of postoperative hyperthermia
Let's consider the main reasons for the increase in temperature some time after the operation:
- Establishing drainage may be one of the reasons for the increase in temperature, since this is how immunity manifests itself. In this case, the temperature will normalize on its own after removing the drainage. Drug temperature reduction is used only if necessary.
- Sepsis and inflammation of internal organs may be an indicator of severe hyperthermia after surgery for appendicitis. In this case, antibiotics are used, or surgery may be performed to remove the pus.
- Viruses and infections. After the operation, the patient’s body is weakened, immunity is reduced, so during this period there is a high probability of contracting any infectious disease.
In such situations, it is important not to self-medicate, but to urgently consult a specialist for medical advice.
Why does it rise and how long does it last?
High temperature after removal of appendicitis, like any other surgical intervention, is a natural reaction of the body to a damaging factor. This happens due to the following reasons:
- A sharp decrease in the body's defenses as a response to stress resulting from damage to soft tissues by surgical instruments. During any surgical treatment, the body uses all internal resources, including the immune system, to restore damaged tissue.
- The formation of a large number of tissue breakdown products that have a toxic effect.
- Fluid loss due to bleeding during surgery.
- Drainage of the postoperative field to improve the outflow of wound secretions. In this case, the pyrogenic reaction will be caused by the presence of a foreign body.
How long a high temperature can last depends on the method of surgery.
Duration of postoperative hyperthermia
With purulent appendicitis, the temperature rises.
The complexity of the operation is of great importance for the subsequent increase in temperature.
Read: How to treat pinworms in children: causes of the disease, symptoms, prevention
One of the methods of performing appendicitis surgery is laparoscopy, in which, instead of large incisions, small holes are used through which the operation is performed.
With this method, a slight increase in temperature may occur for 3 days, but in most cases the temperature does not increase. During a normal operation for appendicitis, the temperature can rise to 38 degrees, and then return to normal within 3-5 days.
With purulent appendicitis, the temperature rises even before the operation and may persist after the operation. Such appendicitis is accompanied by peritonitis, the temperature can last up to several weeks and antibiotics can be used to recover the patient. It must be remembered that a temperature after surgery above 38 degrees can indicate serious complications, so you must urgently seek medical help.
Read along with this article:
- Reasons for the appearance of elevated body temperature after...
- How does appendicitis surgery work and how long does it last?
- On which side is appendicitis located and how does its inflammation manifest?
- Postoperative period for gangrenous appendicitis,…
- Chronic appendicitis: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods
- Acute appendicitis: causes, types, symptoms
- Laparoscopy for appendicitis: indications, advantages,…
- Appendicitis in children: signs, symptoms and help for the child
- Appendicitis and its symptoms, treatment and possible consequences
Classification of fever
Fever is classified based on 2 criteria - the characteristics of temperature fluctuations and the degree of rise. The doctor must take all this data into account to determine whether an increase in temperature is normal after removal of the appendix or whether the pathology is progressing.
Classification by lift level:
- Subfebrile. It stays between 37 and 37.5°C. In the postoperative period, such indicators are considered normal. They are an “indicator” of the active functioning of the immune system. This type of hyperthermia does not need to be treated.
- Febrile. It is located at the level of 38-39°C. This type of hyperthermia indicates the development of secondary inflammation. The patient's condition usually worsens. If necessary, antipyretic drugs are given (as prescribed by a doctor).
- Pyretic. This type of hyperthermia is simply called fever. The patient is literally “on fire.” Indicators exceed 39°C. In most clinical cases, this sign indicates the presence of inflammation of a local or generalized type. It is necessary to stop hyperthermia. In addition, doctors may decide to carry out antibiotic therapy or even repeat surgery.
- Hyperpyretic. The most dangerous type, which can lead to death in the absence of qualified and timely assistance. Temperature exceeds 40°C. Emergency intervention is required, since this indicator is usually a sign of a generalized infectious process or even sepsis.
Classification according to temperature fluctuations:
- Constant hyperthermia. This type is more characteristic of low-grade or febrile temperatures. The presence of persistent fever usually indicates the development of a chronic type of inflammatory process. Indicators change by no more than one degree in 24 hours.
- Laxative. This type is typical for diseases with suppuration. The indicators are different and do not last long. During the day, the temperature usually fluctuates by 1-2 degrees.
- Intermittent. This type is characterized by sharp temperature jumps from high values (38-39°) to normal. Such changes are usually recorded once a day. After 2-3 days the same situation repeats itself again.
- Returnable. Over the course of 2-3 days, an increase in temperature is observed, then it decreases to normal. This type of fever is characterized by cyclicity. The situation is repeated 2 to 5 times during the entire period of illness.
- Hectic. Characterized by sudden changes in temperature up to 5 times in one day. This type of fever is very dangerous for the patient. It exhausts him and depletes the body's strength. Hectic fever usually accompanies viral or bacterial infections, sepsis and purulent pathologies.
- Wavy. A characteristic feature is a gradual increase and gradual decrease in temperature (over several days).
- Atypical. There is no pattern in temperature changes. Also, hyperthermia cannot be associated with any objective reasons.
- Perverted. By evening the temperature becomes even lower than it was in the morning.
- Sharp wavy. The attacks of fever are short, there are no breaks between them.
- Recurrent. Fever makes itself felt again after remission.
A short fever with low levels does not pose a threat to human health or life. Concerns should be caused by hyperthermia, which is observed for more than ten days and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- prolonged constipation;
- pain in the abdomen, especially in the surgical area;
- nausea, vomiting;
- the appearance of pathological impurities in the stool - streaks of blood, mucus;
- chills and cold sweat;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- dizziness;
- disturbance of consciousness.
If any of these signs are detected, you should inform your doctor. He will assess the condition and intensity of these symptoms and prescribe a treatment plan, which may involve the use of both conservative and surgical techniques.
Signs of the development of pathological hyper- and hypothermia
Surgeons are aware of the level of blood loss, which means they can control this process. With the development of acute temperature reactions due to blood loss, the patient is also accompanied by pale skin and cold sweat, and possibly an increase in heart rate and the number of breathing acts.
Most often, during an appendectomy, loops of the large or small intestine, as well as blood vessels, are damaged, against which the temperature initially rises in the postoperative period, but along with the level of loss of red blood cells, it begins to fall.
Such conditions are immediately recorded by the supervising doctors, as this is reflected in the dynamics of the general blood test. General weakness, nausea, and pale skin appear. Clots of dark blood are found in the stool, indicating bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract. Repeated surgery with suturing of hemorrhagic areas solves this problem.
The first symptoms of appendicitis
Anatomical changes in the rudimentary appendix, its location, the form of development of the disease, the duration of the inflammatory process, the age of the patient and other conditions determine the first symptoms of appendicitis. Constant stabbing or dull pain in the abdomen, occurring suddenly without reason, in the afternoon (in most patients) is the main symptom of pathological inflammation of the appendix in its classic location.
- Mildronate - instructions for use. Indications for taking the drug Mildronate in capsules, tablets and injections
- Silicone shoe pads: anti-chafing inserts
- Oven potatoes with cheese: recipes
Initially, the pain occurs near the navel, then moves higher (epigastric region). Pain sensations gradually change. They become pronounced, intense, localized in the lower abdomen on the right (in the iliac region) . When walking, coughing, laughing, attacks of acute pain intensify. Positioning on the right side or on the back alleviates the patient’s condition. With an atypical location of the appendix, the symptoms are different:
- Retrocecal inflammation (the process is located behind the cecum) occurs in 6-25% of cases. The main symptom of the pathology is diarrhea with mucus and high fever. Pain may be absent or occur throughout the abdomen. In most cases, unpleasant symptoms are localized in the lumbar region. The pain radiates to the right leg.
- Pelvic localization is more common in women - 21% of cases, in men - 11%. Frequent loose stools with a lot of mucus and difficulty urinating are characteristic symptoms. Other signs of inflammation appear vaguely. Pain occurs in the lower abdomen and radiates to the umbilical area.
- The left-sided location occurs with a mirror position of the internal organs or increased intestinal motility. The clinical picture is similar to that of ordinary appendicitis, but the symptoms appear on the left side.
- The subhepatic location of the process during inflammation gives pain in the right hypochondrium.
The clinical picture of the disease is different with empyema. This is a rare form of inflammation of the appendix. Symptoms of the pathology increase slowly. Deterioration in health and increase in temperature occurs several days after the onset of the inflammatory process. In this case, mild pain in the place where the appendix is located occurs immediately.
Normal test values
A blood test for appendicitis in people depends not only on the disease, but also on age, as well as time of day.
However, no differentiation depending on gender is observed.
Normal values depending on age (per liter of blood):
- 1-3 days – 7-32*109;
- 3 days-12 months – 6-17.5*109;
- 12-24 months – 6-17*109;
- 2-6 years – 5-15.5*109;
- 6-16 years old – 4.5-13.5*109;
- 16-21 years old – 4.5-11*109;
- men from 21 to 50 – 4.2-9*109;
- men over 50 – 3.9-8.5*109;
- women from 21 to 50 – 3.98-10.4*109;
- women over 50 – 3.7-9*109.
Although blood tests for appendicitis in adults do not show a strong difference, the range of values in women is wider.
After all, the number of leukocytes depends on the day of the menstrual cycle. Therefore, after 21 years of age, patients are most often divided by gender.
In blood tests in children, not only in cases of appendicitis, the level of leukocytes is increased. At a young age, when the immune system is not sufficiently developed, quite a lot of infectious agents enter the body.
To fight them, more white blood cells can be produced. This allows you to train the body's defenses.
In addition to the number of leukocytes, attention is also paid to the ratio of their varieties:
- Neutrophils – 55%.
- Lymphocytes – 35%.
- Monocytes – 5%.
- Eosinophils – 2.5%.
- Basophils – 0.5-1%.
Even if the total amount is within the normal range, but the proportions are not observed, this may be a sign of inflammation.
Therefore, a blood test is performed for appendicitis in children not only before surgery, but always after. Often, the doctor may order a collection of material after 1-2 weeks to monitor the patient’s well-being.
Postoperative peritonitis
The patient's condition worsens gradually over 2–3 days after surgery. Consciousness is confused, lethargy, weakness, drowsiness are noted, fever appears (body temperature 38–39 ° C and above), diffuse abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting of dark green contents without a feeling of relief. Breathing is frequent, shallow, tachycardia is observed (increased heart rate). The tongue is dry, covered with a brownish coating.
Patients have no bowel movements, the amount of urine excreted decreases, the stomach is swollen, although gases are poorly passed. During palpation of the abdomen, tension in the muscles of the abdominal wall, soreness and a positive Shchetkin-Blumberg sign (increased pain after the pressure on the abdomen ceases) are determined.
After a short preoperative preparation, an emergency operation is performed (sanation of the abdominal cavity, surgical treatment of the wound). Infusion therapy is required and antibiotics are prescribed. For the purpose of detoxification, plasmapheresis and hemosorption may be required.
prostudnik.ru
Infiltration and abscess of the abdominal cavity
An inflammatory infiltrate after surgery for appendicitis forms if:
- the exudate accumulated in the abdominal cavity is not completely removed;
- fibrinous deposits remain on the peritoneum.
The occurrence of infiltrates is associated with insufficient sanitation of the abdominal cavity during surgery if the patient has peritonitis, complicating appendicitis.
The clinical picture is characterized by an increase in body temperature to 38–38.5 °C, weakness, loss of appetite, and pain on palpation of the abdomen. Treatment uses antibacterial therapy and cold applied to the infiltrated area.
Suppuration of the abdominal cavity infiltrate is accompanied by an increase in size and increased pain. The patients' condition worsens, weakness, chills, and fever with sudden changes in temperature appear. For treatment, an abscess is punctured under ultrasound guidance or the purulent cavity is opened and drained, followed by the prescription of antibacterial drugs.
Abscess formation in the wound area
Infection of a surgical wound in patients with normal immune reactivity causes the formation of an abscess. There is constant pain in the wound area, which is often pulsating in nature and intensifies when trying to change the position of the body or palpate the affected area. If subcutaneous fatty tissue is involved in the process, an infiltrate forms and the skin around the wound turns red. Palpation of the wound may be accompanied by the release of pus between the skin sutures. Body temperature rises to 38–39 °C, the fever is constant or characterized by sudden changes. Patients are concerned about weakness, headache, and loss of appetite.
If infection is detected early, antibacterial therapy is prescribed, but conservative methods are considered insufficiently reliable and complement surgical treatment.
The sutures are removed, the abscess cavity is opened, washed, and tamponade is performed. During daily dressings, the condition of the wound is assessed (cleaning of pus, appearance of granulations).
Prevention of complications after appendicitis removal
Is it possible to avoid fever after appendectomy? In many ways, everything depends on the individual characteristics of the body and the state of the immune system.
The first day after surgery, low-grade fever is present in 90% of cases. To avoid complications in the future, you need to follow the following doctor’s recommendations:
- If there is inflammation, be sure to take antibiotics.
- Follow a diet. Avoid constipation or diarrhea.
- Follow all instructions of specialists.
- Do dressings.