Types of disease
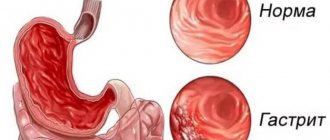
Hypertrophic gastritis - what is it? In order to understand this issue, you need to consider what types of diseases can be found. The main distinguishing feature is the type of deformation of the gastric mucosa.
- Gastritis Menetrier - large folds of various sizes form on the mucous membrane. Depending on their appearance, nature and clinical course, this type is further divided into dyspeptic, pseudo-tumor and asymptomatic forms.
- Hypertrophic granular gastritis is characterized by the presence of cysts on the gastric mucosa.
- Warty gastritis is diagnosed when warts form on the mucous membrane.
- Polypous gastritis indicates the presence of polyps.
Growths located on the gastric mucosa can be either single or group.
Diagnostics
First of all, a visual examination is carried out by a doctor. The patient talks about his complaints and provides a medical history for study. Using palpation, the doctor will determine the localization of pain and may at this stage suggest the presence of hypertrophic gastritis.
To confirm the diagnosis, the following examination methods are used:
- acidity level test;
- general and biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- stool culture tank;
- histology;
- cystology;
- enloscopy;
- laparoscopy;
- fluoroscopy;
- Ultrasound.
A comprehensive examination helps determine the cause and type of disease. If there is a suspicion that hypertrophic gastritis is caused by the Helicobacter bacteria, then additional examination is carried out.
- stool analysis - determines Helicobacter antigen in the body;
- respiratory tests;
- fibrogastroscopy – study of the mucous membrane using a special optical instrument.
After the results are obtained, the doctor can prescribe effective treatment. It is worth noting that treating hypertrophic granular gastritis is more difficult than regular gastritis.
Causes of formation of hypertrophic gastritis
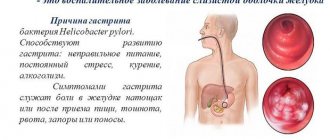
In order to prescribe correct and effective treatment, a specialist must first correctly determine the cause of gastritis.
Most often, inflammation of the gastric mucosa occurs due to the bacteria Helicobacter pylori. It attaches to the surface of cells and, during its activity, increases the acidity of gastric juice, which becomes more aggressive and causes irritation. However, many doctors argue that Helicobacter pylori is not the main cause of gastritis, but only a provoking factor. This is due to the fact that the bacterium can be found in 90 percent of the population, but gastritis is not diagnosed in everyone.
Another reason due to which hypertrophic gastritis of the stomach can develop is reflux. During this pathology, a disruption of the digestive system occurs, which is characterized by the reflux of the contents of the duodenum back into the stomach. The greatest danger in this case is bile, which dissolves the outer protective shell. After this, hydrochloric acid actively affects the walls of the stomach, forming severe chemical burns. Such conditions become favorable for the appearance of gastritis.
Disturbances in the functioning of the digestive canal may be a consequence of a disorder of the autonomic nervous system. From this we can conclude that the development of gastritis can also be influenced by nervous overload, stress, overexertion and emotional surges.
Hypertrophic gastritis quite often appears due to improper diet and consumption of junk food. The body is negatively affected by undereating, overeating, frequent snacking, fatty, smoked and pickled foods.
Increased acidity of gastric juice, leading to the development of gastritis, occurs due to the consumption of large amounts of spices, spicy foods and some medications.
Main symptoms
Hypertrophic gastritis can occur in people of different ages, but most often this disease manifests itself between the ages of 30 and 50 years. In order to timely determine the development of the disease, you need to know its main symptoms:
- aching pain in the stomach, which is accompanied by cutting attacks;
- if gastritis is accompanied by increased acidity, then a person develops hiccups;
- the main signs of the disease are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or constipation;
- increased salivation is observed;
- appetite decreases or is absent altogether;
- There is heaviness and bloating in the abdomen.
Symptoms
Symptoms of hypertrophic gastritis can be found not only in the adult population. Sometimes the disease affects even young children. Hypertrophic gastritis can be distinguished from other forms of gastritis by the following symptoms:
For the prevention and treatment of gastritis and peptic ulcers, our readers recommend a proven gastric collection
from gastrointestinal diseases. Read the doctors' opinions. >>
- Painful sensations in the epigastric region that take on an aching character. The pain may occur intermittently and be replaced by cutting attacks.
- Heartburn. This symptom occurs in people who have been diagnosed with hypertrophic gastritis with high acidity.
- Feeling of nausea, partial salivation and vomiting.
- Bloating, feeling of fullness in the abdomen.
- Poor appetite or its complete absence.
- Weight loss.
- Abnormal stool.
- A feeling of heaviness and discomfort that occurs after eating.
Granular form
The most common type of hypertrophic gastritis remains granular. It is characterized by the presence of small protrusions on the surface of the mucous membrane. This form of the disease can only be determined through diagnosis. Some doctors are of the opinion that granular gastritis is not a type of pathology, but just its initial stage of development.
The main symptoms of granular gastritis include nausea, vomiting, pain in the epigastrium, weakness and poor appetite. To determine it, the doctor prescribes fibrogastroduodenoscopy to the patient.
Diagnosis of the disease
A gastroenterologist treats hypertrophic gastritis. In order to make a correct diagnosis, he resorts to the following methods:
- First of all, an anamnesis of the disease is collected, which indicates the possible cause of the disease and the patient’s complaints.
- Then the specialist palpates the abdomen. This is necessary in order to determine the primary signs of the disease.
- The next step is to examine the skin and visible mucous membranes.
- In order to visualize and examine the upper part of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum, many specialists resort to the use of fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS). During this procedure, a probe is inserted into the patient's stomach and intestines, which allows the condition of the internal organs to be assessed.
- During FGDS, various types of tests are often taken, which include collecting bile and pinching off particles of growth on the mucous membrane.
Diagnosis and treatment
Before prescribing treatment, the patient must undergo a complete diagnostic examination. It includes the following mandatory measures:
Inspection
- taking anamnesis;
- palpation of the abdomen;
- examination of mucous membranes and skin for the presence of pathological changes, rashes, etc.
Instrumental research
- esophagofibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- biopsy;
- acidotest.
Analyzes
- coprogram;
- blood sampling;
- Analysis of urine;
- biochemistry.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to cure completely. However, when this disease occurs, symptomatic therapy is indicated, which is aimed at suppressing pain and normalizing the patient’s general condition.
A mild form of the disease requires outpatient treatment. The patient is prescribed the following treatment:
- Taking medications that reduce stomach acidity;
- Taking antacids;
- Use of blockers;
- Diet;
- No excessive physical activity.
If there is no result from such treatment, doctors decide on surgical intervention - removal of formations from the surface of the gastric mucosa.
After surgery, the patient should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Compliance with a strict, gentle diet, which involves taking mostly light and pureed food;
- No heavy lifting or strenuous exercise;
- Avoid nervous conditions and stressful situations.
Important: Following the diet during the postoperative period should last at least 6 months. You should also remember about the temperature of the food you eat - it should not be too cold or too hot.
Prognosis for recovery
With proper and timely treatment, the prognosis for recovery from hypertrophic gastritis is quite positive. However, it should be remembered that a complete cure for the disease is impossible. The patient may experience periods of exacerbations and remissions. Main. Avoid complications of the disease.
Source: netuyazvi.ru
Diagnosis of the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori is a bacterium, in the presence of which the main treatment of the disease may not bring the desired result, and the disease turns into chronic hypertrophic gastritis. The following methods are used to identify bacteria:
- Laboratory analysis of feces.
- A respiratory test, which involves the patient taking a special drug and after a certain time breathing into a device that shows the presence of bacteria.
- Also, an analysis for Helicobacter pylori can be taken during an FGDS.
Treatment
In mild cases of the disease, treatment of hypertrophic gastritis is carried out on an outpatient basis, that is, at home. If there are complications, therapy is carried out under the supervision of a doctor, that is, in a hospital. The following medications are usually used to treat gastritis:
- The “antacids” group - these drugs have a rich composition and include aluminum, calcium, bismuth salts and magnesium. The action of the medications is aimed at reducing acidity in the stomach. Once in the body, drugs envelop the entire surface of the internal organ, due to which its walls have time to recover.
- Proton pump blockers - these drugs are responsible for eliminating the inflammatory process and reducing pain. The desired effect is achieved by blocking the receptors that produce hydrochloric acid.
- If the bacteria Helicobacter pylori is present in the body, the patient is prescribed antibiotics to eliminate foreign microorganisms.
In cases where conservative medicine does not bring results, it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention, during which growths are removed from the gastric mucosa or partial removal of the internal organ occurs.
Diagnostics of deviations
The disease requires drug treatment. Therapy is selected only after an accurate diagnosis has been made. This cannot be done at home, so the patient must visit a medical facility. The doctor will conduct an initial examination and tell you exactly whether there is a need to see a gastroenterologist.
When diagnosing, you will need to donate blood for tests.
One of the most important studies is gastroscopy. With this diagnostic method, the doctor visually examines the stomach. This happens thanks to a special tube with a video camera. The procedure helps determine the location of the inflammatory process and determine the extent of damage. The examination allows you to see injured areas only on superficial tissues.
The patient is given an appointment for:
- X-ray;
- probing;
- PH-metry;
- blood analysis;
- stool examination;
- laparotomy (if cancer is suspected or differential diagnosis with Ménétrier's disease);
- biopsy.
Diagnosis is carried out using fibrogastroduodenoscopy
A stool test is necessary to detect occult blood. It may be present when there is significant damage to the stomach. The doctor measures acidity. With gastritis of the hypertrophic type, indicators are usually elevated.
Laparotomy is necessary when the condition is advanced and the gastrointestinal disease develops into cancer. A biopsy helps detect malignant cells and Helicobacter pylori infection. It is impossible to establish an accurate diagnosis without special examinations.
Diet
It is worth remembering that hypertrophic gastritis can be cured only by adhering to a gentle diet, and further maintaining such a diet will help avoid relapses:
- Food must be warm; cold or hot foods can harm the body.
- You should eat in small portions, 5-6 times a day.
- It is not recommended to consume fatty foods, semi-finished products, pickled and smoked foods, butter dough, strong tea and coffee, soda and alcohol.
- It is best to give preference to pureed cereals, fermented milk products, lean meat and fish, dried fruits and eggs.
Treatment of pathology
For mild gastritis, treatment is carried out conservatively. It is generally recommended to follow a diet high in proteins and vitamins.
Drug treatment is carried out using the following medications:
- Antibacterial (if bacteria are present) - Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav, Clarithromycin.
- Anticholinergic (reducing protein loss).
- Enveloping and astringent (to eliminate heartburn).
- Painkillers (to relieve pain attacks).
- Enzymatic (to improve digestion) - “Panzinorm”, “Festal”, “Mezim Forte”.
In addition, for diarrhea, probiotics and prebiotics are prescribed - “Bifiform”, “Linex”, “Enterol”, “Acipol”.
In the complicated form of gastritis (when bleeding, pain, swelling is present), the disease requires surgical intervention. In this case, the overgrown tissue is removed. When there is a risk to the patient's life, a complete or partial gastrectomy (excision of the stomach) may be used.
Diet for hypertrophic gastritis
The main condition for the treatment of hypertrophic gastritis is compliance with a special gentle diet.
With hypertrophic gastritis, it is very important to follow the principle of fractional nutrition - food intake is carried out in small portions, at least 5-6 times a day.
After the operation, the patient should eat food during the first six months only in pureed form and in compliance with the temperature regime (food should not be too cold or too hot).
| Prohibited products include | Recommended for use |
| strong coffee and tea, chocolate | pureed cereal soups |
| mushrooms | cottage cheese (non-sour), cheeses (low-fat and mild) |
| alcohol | lean meats (rabbit), poultry (boiled turkey, skinless chicken) and fish |
| sausages and canned goods | lean beef as mince for cutlets |
| fatty meats, poultry and fish | steamed omelette or soft-boiled eggs |
| sour cream | white bread (only yesterday's bread) |
| hot seasonings and sauces | oatmeal porridge |
| brown bread, pastry products | jelly |
| grape | dried fruit compotes |
For gastritis, an apple is considered a useful product. Thanks to the pectin it contains, the functioning of the entire digestive tract improves. During the acute phase, it is recommended to consume the apple baked.
Also, for gastritis, it is recommended to drink milk with a spoon of honey. It helps with gastritis with high acidity. An important condition for this is to consume the mixture warm, preferably before bedtime. Milk helps reduce acidity and coats the mucous membrane, and honey, thanks to the microelements and vitamins it contains, has an anti-inflammatory effect on the patient’s body as a whole.
Treatment with folk remedies
Therapy with traditional methods is allowed only at the rehabilitation stage. To restore the damaged gastric wall, aloe juice, medicinal herbs, honey and other folk recipes are used.
Potato juice is used as an enveloping agent that has a beneficial effect on the gastric mucosa; it can be used to eliminate erosions and small ulcers on the surface of the mucosa. To obtain the product, squeeze the juice from several potatoes and drink half a glass 30 minutes before meals. In addition, it is good to drink this remedy on an empty stomach, 1 glass an hour before breakfast. Duration of therapy is 10 days.
Drinking mineral water helps reduce stomach acidity and suppress the effects of hydrochloric acid. The effect of mineral water depends on its temperature; when it is necessary to reduce acidity, drink warm water. It is recommended to drink 1 glass of mineral water at one time.
When increased synthesis of gastric juice is required, mineral water is drunk cold in the amount of 0.5 cups, and should be drunk very slowly. When drinking water, you should rid it of gases by shaking or heating it a little. The duration of the course of therapy is a month.
Sea buckthorn oil is considered another powerful remedy in the treatment of atrophic gastritis, as it has wound-healing, anti-inflammatory and enveloping effects. It should be consumed to heal ulcers and erosions before meals, a dessert spoon at a time.
The use of flax seeds as a decoction helps restore the mucous membrane, protects and envelops it. To prepare the remedy, use 1 tbsp. Pour a spoonful of flaxseed into hot water and boil for 5 minutes, then leave to infuse for about 2 hours. The strained broth is consumed before meals, 1 tbsp. spoon. You can also use another recipe to prepare the product: mix 1 tbsp. spoon of flax seeds with 0.5 liters of hot water, leave for several hours. Drink a glass of the strained product 1 hour before meals.
If your stomach has high acidity, it is recommended to drink 1 glass of warm boiled water before breakfast. In addition, it is recommended to use a decoction of the following herbs: St. John's wort, chamomile, yarrow - 2 tbsp. spoons, celandine - 1 tbsp. spoon. 1 tbsp. A spoonful of this mixture is poured with boiling water and left to cool. You should drink the resulting infusion 5-6 times a day before meals, a quarter glass. Course – 2 months.
Fresh cabbage juice helps with low acidity. It should be consumed slightly warmed, half a glass 1-2 times a day.
Disease prevention
In order to avoid the occurrence of hypertrophic gastritis, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- nutrition should be correct, balanced and healthy;
- it is necessary to give up cigarettes and alcohol;
- try to be at rest as often as possible;
- Any digestive disorders must be treated promptly and not neglected.
Hypertrophic gastritis is one of the most severe forms of this group of diseases, so its treatment will require the patient to strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations, which include taking medications, giving up bad habits and following all the rules of a healthy diet.
Prognosis and prevention
The disease is not cured quickly - you will have to be patient. But if you follow a diet, take prescribed medications and, as an addition, use traditional methods approved by your doctor, then the disease will subside. Otherwise, bleeding in the stomach may develop, sometimes leading to the death of the patient. As a preventive measure, eat right, lead a healthy lifestyle, and treat all diseases of the digestive system in a timely manner.
Source: uvasgastrit.ru