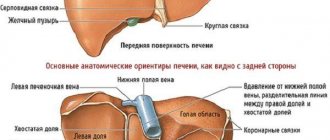
Biliary cirrhosis - what is it?
Hepatic biliary cirrhosis is a chronic disease that gradually progresses and is manifested by the replacement of healthy organ tissue with fibrous formations. For a long period the pathological condition is not suspected. In later stages, small liver signs, portal hypertension, and hepatic encephalopathy occur.
The disease begins to be suspected after an ultrasound scan and blood tests. For complete clarification, a liver biopsy is necessary. The patient is shown a gentle and correct lifestyle. If there is a terminal stage, a liver transplant is necessary. Pathology is a serious disease that requires careful monitoring.
What is the danger of the disease
Women over 40 years of age are at risk for morbidity, especially if there is a hereditary aggravating factor. Men are less likely to suffer from the disease.
The causes of primary biliary cirrhosis are still not known for certain. The essence of the disease is damage to mitochondrial liver inclusions. Making a diagnosis in the early stages is very complicated, because the diseased organ does not make itself felt until the pathology reaches serious development.
You can suspect something is wrong only through blood tests if a person periodically does blood biochemistry.
Stages of liver pathology
Pathology is divided into two types, depending on the root cause. There are primary and secondary biliary cirrhosis. The disease also has 4 stages of development:
- The first degree is manifested by rare attacks of cholestasis, when bile is less well evacuated from the gallbladder. Usually the course is asymptomatic, so people rarely seek help from a doctor. At this stage, the disease is discovered by chance during an annual preventive examination. The name of the stage is ductal.
- The second degree is characterized by pathological disorders in the functionality of the bile ducts. There is a violation of their patency. As a result, the liver becomes inflamed, and healthy tissue is replaced by fibrous inclusions. The name of the stage is ductular.
- When the third degree of pathology occurs, sclerosis of the hepatic ducts occurs, which causes the death of liver cells. Fibrous tissue gradually replaces hepatocytes. Liver cells are rapidly destroyed. When the third stage develops, the patient usually already feels unwell, which becomes the reason for contacting a doctor. The name of the stage is fibrosis.
- The terminal stage is characterized by cirrhosis, the patient feels a severe deterioration in health. At this stage, urgent medical measures must be taken, otherwise the person will die.
The only working and radical treatment measure is a liver transplant.
Causes
Modern gastroenterologists are inclined to believe that primary biliary cirrhosis is associated with autoimmune disorders in the body. The disease has a connection with heredity; if someone in the family has it, then there is a high probability of manifestations in children and relatives. Autoimmune disorders such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis, Sjögren's syndrome, and rheumatoid arthritis are also associated with autoimmune disorder.
Predisposing factors contributing to the appearance of liver diseases include any disturbances in the function of the gallbladder - deformation of the bile ducts, cholelithiasis, the presence of a liver tumor, enlarged lymph nodes in the liver, the appearance of cysts in the bile ducts, a history of purulent cholangitis.
Some types of bacteria can trigger an unfavorable autoimmune process. If the patient has contracted a gram-negative infection, which can trigger the appearance of mitochondrial antigens, causing primary biliary cirrhosis. The secondary form of the disease develops exclusively against the background of those diseases that provoked the deterioration of the condition - atresia and stones in the biliary tract, cancer of the extrahepatic biliary tract, cystic fibrosis or common bile duct cyst.
Signs of pathologies
As a rule, liver disease is accompanied by skin symptoms. It is, first of all, a yellowish tint. In addition, the patient experiences heartburn and feels nauseated. There is a sharp, extremely unpleasant odor of sweat. Therefore, typical cases do not cause difficulties in diagnosis.
In most cases, a doctor can already visually suspect liver disease. Skin symptoms and the patient’s discomfort give the doctor an idea of the nature of the pathology.
The main signs of liver diseases are:
- pain, discomfort in the organ area;
- liver enlargement;
- general malaise, weakness;
- headache;
- impairment of thinking and mental abilities;
- swelling;
- increased sweating;
- jaundice;
- skin itching;
- rash;
- increased tendency to bleeding, fragility of blood vessels;
- symptoms of hypovitaminosis;
- changed color, character of feces, unstable stool;
- the presence of a venous pattern on the abdomen;
- weight loss;
- increased abdominal size;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- temperature reaction;
- cracks in the tongue, white or brown coating on it.
Clinical manifestations
Depending on the form of liver cirrhosis, the symptoms will differ slightly. With primary biliary cirrhosis, the following symptoms occur:
- Periodic itching of the skin. Mostly unpleasant sensations occur during night sleep and intensify upon contact with irritating substances - a woolen blanket or after taking a shower. Intermittent itching can last a long time. If the patient ignores this symptom for a long time, the clinical picture will worsen over time.
- The skin turns dark brown. The area of large joints and armpits darkens mainly. Over time, the entire body surface becomes brown.
- Flat plaques and several neoplasms appear on the eyelids. These formations are called xanthelasmas and occur predominantly in the chest, palms, buttocks and elbows.
- Often, against the background of biliary liver pathology, the spleen increases in size.
- Then the classic symptoms appear, indicating a hepatobiliary disorder - pain in the right hypochondrium, discomfort in the muscles, a bitter taste in the mouth in the morning, and a slight increase in body temperature.
When the disease rapidly progresses, all of the above symptoms increase. The patient's appetite almost completely disappears, and the itching of the skin increases significantly. Itchy sensations are associated with excess levels of bilirubin in the blood. In pigmented areas of the skin, the phenomenon of hyperkeratosis occurs, and severe swelling also occurs. The finger phalanges narrow.
Pain in the right hypochondrium becomes unbearable and against the background of this phenomenon, varicose veins of the esophagus and stomach occur. A severe complication is accompanied by internal hemorrhages. Hypovitaminosis develops, since the absorption of vital microelements and vitamins is difficult. There is also an enlargement of the lymph nodes, accompanied by serious disruptions in the digestive system.
In the secondary form of biliary cirrhosis, the following complaints arise:
- The itching of the body intensifies so much that even with the initial course of biliary cirrhosis, constant discomfort occurs.
- My right side constantly hurts. On palpation, the specialist notes pain and thickening of the liver structure.
- The skin, oral mucosa and sclera become bright yellow, stool becomes discolored, and urine darkens.
- Body temperature rises to 38 degrees.
- In the secondary form, complications from biliary cirrhosis occur much earlier and manifest themselves in the form of liver failure and portal hypertension.
Weight loss and persistent fatigue are common signs that should alert the patient. At the slightest deterioration, you should seek treatment from a doctor.
Causes of spots
The appearance of spots on the skin indicates problems with internal systems, usually due to diseases of the liver, digestive organs, kidneys, hormonal imbalances and endocrine glands. Other accompanying factors aggravate the problem and the skin takes on an increasingly unaesthetic appearance. Common pigment spots can spread over almost the entire surface of the human body, especially in areas exposed to the sun.
Under the guise of a harmless pigment spot, a malignant formation may be hidden, which is important to identify at the initial stage and begin treatment.
Rash, papules, acne and pustules under normal conditions occur more often with liver diseases in the form of an allergic rash. Minor hemorrhages (hemorrhagic rash) occur due to decreased blood clotting and a neglected, clogged liver. Yellow plaques form on the arms, legs, armpits and eyelids. There are also red rashes, if they disappear when pressed - this is parmal erythema. In addition, this includes urticaria and psoriasis.
Asterisks (telangiectasia)
Liver stars (vascular branches) appear for various reasons. In healthy people, often during pregnancy, they quickly disappear and are not as pronounced. In women they are formed as a result of hormonal dysfunction, and in men - due to venous insufficiency. They are also located on mucous membranes: in the nose, on the lips, in the stomach, esophagus, and pharynx. In this case, they can be classified as a chronic type of hereditary predisposition. If the red vascular spiders become brighter and the number increases, you should urgently seek medical attention. This may indicate neglect of internal organs, cirrhosis or viral hepatitis, as a result of which filtration processes in the liver are reduced, blood vessels lose their elasticity and stagnation forms in them.
Combinations of skin manifestations
The stars can also be combined with white spots on the arms and buttocks, which are more clearly visible when exposed to cold. Sometimes small vessels located in a chaotic order are simultaneously visible on the hands. This is called the "money bill" symptom because the subcutaneous layer becomes like a dollar bill laced with silk threads.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment methods for the disease are selected individually. The treatment regimen depends on the type of biliary cirrhosis and the stage of development. Usually, diet and medication are indicated in the initial stages. If end-stage biliary cirrhosis occurs, an organ transplant is necessary. Since the disease is serious and dangerous, a careful approach to treatment is required, both from the doctor and the patient himself. Unauthorized deviations from the assigned scheme are unacceptable.
Traditional therapy
When primary biliary cirrhosis occurs, the patient has severely increased bilirubin in the blood, cholesterol and alkaline phosphatase. Medicines with hepatoprotective and choleretic properties are used. A product based on ursodeoxycholic acid copes well with the task. Examples - Ursohol, Ursosan. Such drugs remove bile, reduce bilirubin levels and, in the case of biliary cirrhosis, slow down the rate of breakdown of hepatocytes.
Among hepatoprotectors, essential phospholipids, lecithin, choleretic agents based on immortelle sandy, corn silk, artichoke extract are also used (examples - Flamin, Essentiale-N, Hofitol). A product based on silymarin, Karsil, helps in the fight against the destruction of liver cells. These medications must be taken constantly, but in order. The course of treatment must be prescribed by a doctor. Medicines that help relieve itching - histamine blockers, Galoxin, Colestipol. When ascites develops, diuretics are prescribed.
Treatment is also aimed at normalizing the patient’s well-being. The patient is prescribed vitamin and mineral complexes that need to be taken daily. It is important to receive the required amount of fat-soluble vitamins E, D3, K, A. They are prescribed to the patient as single medications. Statins are indicated to lower cholesterol levels. If it is possible to reduce the indicators with diet, it is better to take statins as a last resort, since they have a hepatotoxic effect.
Surgical intervention
With the development of the fourth stage (cirrhosis itself), only liver transplantation will help. A donor must be sought in advance, even if there is a milder stage, because the disease inevitably progresses. Patients usually tolerate surgery well, as it significantly increases the chances of survival.
In addition to transplantation, other types of surgery may be prescribed, especially if biliary cirrhosis is secondary:
- Removal of the gallbladder. It is necessary to carry out only if the pathology is caused by cholelithiasis.
- Surgical removal of a benign or malignant tumor. This is done without fail, since the tumor compresses the liver, blocking the bile outflow, which interferes with the treatment of cirrhosis.
- Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. This type of intervention is carried out to reduce pressure in the portal vein by reducing the amount of circulating blood. This will eliminate internal bleeding and prevent the occurrence of abdominal swelling - ascites.
Traditional medicine recipes
It is not recommended to refuse a liver transplant or conservative drug treatment. Self-medication can be dangerous and fatal. Among home methods, you can use choleretic and hepatoprotective herbs. Each prescription should be discussed with your doctor.
To improve the function of the liver and gall bladder, it is useful to drink infusions, teas based on chamomile, dandelion leaves, corn silk, and sandy immortelle. It is not recommended to make alcohol tinctures, since alcohol loads the liver, reducing the functions of the damaged organ.
The classic scheme for preparing a decoction looks like this:
- A tablespoon of dry collection is poured with 200 ml of boiling water.
- The mixture is brought to a boil in a water bath for 10 minutes.
- Then the broth is filtered.
- When the drink has cooled, it is taken immediately after meals several times a day.
If no improvement is observed, traditional therapy should be abandoned.
Diet therapy
A nutritional plan for correcting the condition of biliary cirrhosis is important. Without changing your diet, the effect of conservative treatment will be reduced. The patient should eat fractionally, in small portions, excluding large amounts of animal fats, protein and harmful foods. Fried, fatty, spicy and salty foods are prohibited. It is necessary to give up baked goods, confectionery, coffee, smoked foods, semi-finished products and canned food.
The basis of the diet is porridge with water. Sources of fats are vegetable, in limited quantities. Protein foods are not fatty and are also limited. The patient switches predominantly to a plant-based diet with a predominance of carbohydrates. You can eat fruits and vegetables.
Rash with cirrhosis of the liver: types and photos of rashes
Rash is common in liver cirrhosis. The liver is an endocrine gland, the largest in size. It plays a big role for the body, performing a number of important functions:
- The barrier function is one of the main ones; substances entering the body and formed in the process of vital activity are neutralized by liver cells and excreted from the body with feces.
- The direct intrasecretory function is the formation of bile, which is involved in the digestion process.
- Synthesis of proteins, fats and carbohydrates to build new body cells.
- Formation of blood proteins - albumin, synthesis of glycogen.
- Maintaining hemostasis – blood clotting factors are formed in the liver.
There are many liver diseases and some of them progress to cirrhosis. This is a life-threatening condition in which irreversible structural changes occur in the form of fibrosis and the formation of nodes. The gland decreases in size and its surface acquires a lumpy structure. It can be viral, alcoholic and stagnant. The most common cause of cirrhosis is prolonged alcoholization of the body.
What will I learn about? The content of the article.