A gallbladder attack is characterized by acute pain in the area where it is located and can be triggered by many reasons. Most often, this condition in the form of biliary or biliary colic is caused by various pathologies such as cholelithiasis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis or cholangitis. The appearance of colic may be the result of eating certain foods. To get rid of such attacks and prevent their occurrence in the future, it is necessary to find out the cause of their occurrence and carry out treatment.
A little about hepatic colic
According to medical statistics, a gallbladder attack in adults most often occurs as a result of a violation of the outflow of bile during cholelithiasis, provoked by obstruction of the organ duct with formed stones. This condition is accompanied by prolonged intense pain in the right hypochondrium and repeated vomiting. The intensity of the pain symptom largely depends on the size of the stone and its location. In the absence of an inflammatory process and when the stone is located in the body or bottom of the gallbladder, pain does not occur. If the stone is located closer to the neck of the organ, pain of minor intensity may be felt. The formation or reaching of the gall bladder ducts by a stone causes blockage with a sharp disruption of the outflow of bile and is always accompanied by sharp, prolonged pain until the stone moves from its place.
Hepatic colic is closely related to disorders of the gallbladder and in almost 75 percent of patients is the onset of cholelithiasis. Hepatic colic with its repetitions is observed in every ten patients with cholelithiasis. With age and as the asymptomatic nature of cholelithiasis develops, the likelihood of hepatic colic increases. Fifteen years after the formation of gallstones, attacks occur in a quarter of patients.
The cause of the formation of hepatic colic is most often an irritating factor in the form of eating fatty and spicy foods, which promotes spastic contractions of the walls of the gallbladder and the advancement of stones into its ducts. As a result of obstruction, the free outflow of bile is disrupted, which results in an increase in intravesical pressure, accompanied by severe pain.
Hepatic colic can manifest itself during physical overexertion, at the time of increased psycho-emotional state, during the period of bearing a child. In some cases, the factor that provokes the development of hepatic colic is not determined. A third of patients note the appearance of attacks at night. In the case when the manifestation of colic occurs against the background of inflammation, one can judge the acute form of calculous cholecystitis.
Treatment options
In the hospital, an attack of the disease can be relieved quickly, and it will take 10 days to relieve inflammation. When stones pass out, surgical intervention is necessary. There is a problem when the gallbladder is closed and the ducts are blocked. There is only one way out - removal of the diseased organ. The extreme method helps save the patient’s life, because specialists try in any way to ensure the preservation of organ function, even resorting to endoscopic techniques.
A puncture is made in the abdomen, experienced surgeons insert an endoscope, and with the help of ultrasound the process of removing stones from the ducts is completely visible. The organ is saved.
Follow-up diet
During a relapse, to make life easier for the patient, fasting is required for a couple of days. You can drink mineral water and green tea without sugar. As general health improves, the patient may be offered lean broths and viscous porridges. You should eat small meals often. Coarse fiber contained in raw vegetables is prohibited.
Food is only steamed and boiled. A strict diet excluding junk food is indicated for the future. It is based on dietary meats, steamed and pureed, low-fat fish, dairy products, and sweet fruits. Non-acidic juices are recommended, you can drink still mineral water, berry fruit drinks, mint and green tea.
Traditional medicine to help with cholecystitis
Many herbs can reduce pain: choleretic decoctions and infusions. Such properties include: yarrow, chamomile, immortelle, leaves and buds of birch. You can use herbs only after consulting a doctor. Some herbs dilute bile, while others stimulate its formation and expel it.
There are known ways to take one spoonful of vegetable oil on an empty stomach.
Rowan juice is useful. You need to drink 100 g three times a day.
Grate horseradish root 200 mg. Pour four glasses of hot water. Place in the refrigerator for a day. It is advisable to strain and reheat before use. Drink 50 g before meals three times a day.
Plantain decoction: you will need one tablespoon of seeds or leaves, pour boiling water. Leave for 15 minutes, take small sips within an hour. The benefits of beets in the fight against disease have been proven. Boil the peeled vegetable until the consistency of the broth resembles syrup. Drink 1⁄4 cup of the decoction before meals.
Oatmeal jelly has good results. Pour boiling water over half a kilogram of oat grains and leave for half an hour. Strain and consume 0.5 cups three times a day. Another way is to cook jelly from oatmeal, add milk, and bring to a boil. Add honey. Drink a glass three times during the day, warm.
When the first symptoms appear, it is advisable to seek professional help in order to prevent complications of various types. It is also important to adhere to a strict diet. Although the patient will not neglect this requirement. The attacks are so strong that the person cannot find a place for himself.
The causes of stagnation in the gallbladder are:
- Bacterial infections;
- Anatomical features of the structure of the organ;
- Stones in the bile ducts;
- Changes in the chemical composition of bile.
In order to promptly recognize and stop an attack of acute cholecystitis, it is necessary to clearly know the causes of this disease, its characteristic symptoms, the mechanism of development and the correct algorithm for assistance.
Causes of an attack of cholelithiasis
Attacks of cholelithiasis are usually caused by certain factors, the influence of which causes painful symptoms. Typically, the following conditions can cause such symptoms:
- Late diagnosis and establishment of cholelithiasis;
- Having excess weight;
- Failure to comply with the principles of healthy eating;
- Lipid and cholesterol disorders;
- Taking hormonal drugs;
- Unfavorable heredity.
Most often, an attack of cholelithiasis can occur in people belonging to a certain risk group, which includes people with diabetes, elderly patients and those who are overweight. In order to prevent the development of an attack and prevent it, it is necessary to be able to identify the symptoms of its approach.
Causes of the attack and the mechanism of its occurrence
Several etiological factors for the occurrence of acute cholecystitis can be noted:
- It is often preceded by disturbances in the diet: large feasts, eating large amounts of fried and fatty foods, dry snacks. In this regard, in some sources cholecystitis is designated as a “holiday disease.” Sweetened carbonated drinks and alcohol have a particularly negative effect on the functioning of the gallbladder.
- Obesity is another cause of pathology. Closely related to this factor is the belief that, based on gender, cholecystitis is a female disease, because it is women who, more often than men, cannot refuse food. It is important to note that a sharp decrease in body weight during weight loss does not benefit the body, but, on the contrary, often causes the formation of stones inside the gallbladder and subsequent exacerbations of the disease.
- Age. The risk group for this factor in the occurrence of inflammation in the gallbladder includes elderly patients. The older a person is, the higher the likelihood of developing the disease, which is associated with the accumulation of large amounts of bad cholesterol and toxins, which slow down the metabolic process and provoke disruption of the functioning of many organs.
As a result of the influence of causative factors, metabolic failures occur in the body, which leads to disruption of the functioning of the gallbladder, inflammation, the formation of stones and thickening of bile. As a result, the structure of the walls of the gallbladder changes and an attack of acute cholecystitis develops.
Symptoms of an attack
Symptoms of a gallbladder attack depend on the stage and form of the disease. Usually, when it approaches, patients feel pain on the right side under the ribs. Many of them experience disorders in the digestive system, nausea and vomiting.
Also, symptoms of an attack with biliary colic occur in the following situations:
- In the presence of exacerbation of cholelithiasis, symptoms manifest as pain in the right side, which occurs when the principles of a healthy diet are not followed. The condition is complicated by fever with an increase in temperature to 40 degrees, chills with profuse sweating.
- In the chronic form of cholecystitis, there is a feeling of discomfort in the right hypochondrium, aching pain after eating fatty foods, itching of the skin and a slight increase in temperature.
- Impaired contractility of the gallbladder, as well as a decrease in the patency of its ducts, leads to paroxysmal pain caused by increased pressure from the accumulation of bile. When pressure decreases, patients feel aching pain. During such attacks, the temperature can rise to 38 degrees.
- Inflammation of the bile ducts causes an attack of severe pain that can put the patient in a state of shock. Some patients may experience itchy skin, chills with a body temperature of up to 40 degrees, and increased sweating.
- In the presence of malignant neoplasms, it is also possible to experience paroxysmal pain in the right side with a slight increase in temperature up to 38 degrees.
Currently reading: Where is the gallbladder in a person, photo and how does it hurt?
These symptoms are usually not clearly expressed, since at the beginning of the development of diseases, attacks are periodic and occur only when the diet is violated and in the presence of factors that can lead to exacerbations.
Experts identify several common symptoms that precede an attack of biliary colic:
- An increase in paroxysmal pain in the right side and in the epigastric region;
- Sudden profuse sweating;
- Cardiopalmus;
- The appearance of a sharp headache;
- Stool instability in the form of alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- Sleep disturbance in the form of insomnia.
The resulting reflex spasms are accompanied by nausea with a large amount of saliva, vomiting containing bile, and a feeling of bitterness in the mouth. The pain that occurs during a spasm lasts up to six hours, and the skin and mucous membranes at this time acquire a jaundiced tint.
In the case of acalculous cholecystitis, the attack occurs abruptly, and when it subsides, it does not relieve the pain, which becomes permanent.
Signs of illness
The development of the disease occurs slowly, and at the initial stage it does not manifest itself in any way for a long time. First, several stones up to 0.5 mm in diameter form in the bile ducts, which reduce the lumen of the ducts and impede the exit of bile fluid.
When the stones increase in size and begin to move into the intestines, the first and sure sign of the disease appears - hepatic colic.
As the disease progresses further, symptoms appear:
- Pain localized in the right side. At the initial stage, it is short-lived and has a paroxysmal character. Over time, its manifestations increase in intensity and duration.
- Bloating and abdominal tension.
- Flatulence.
- Temperature increase.
- Diarrhea.
- Digestive problems.
- Constant feeling of nausea.
- Vomit.
- Belching.
- Development of arrhythmia.
- Rapid breathing with incomplete inhalations and exhalations.
- Change in skin color - becomes pale.
- Sweating increases.
- Weakness, malaise, fatigue.
The named signs of pathology appear singly or all at the same time, and they cannot be called specific. Using them, it is difficult to diagnose this disease and prescribe adequate treatment. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis by conducting examinations.
First aid for an attack of cholelithiasis
During an attack of cholelithiasis, you can help the patient alleviate his condition on his own at home, but this should be done only after an ambulance is called.
First aid in this case involves the following procedures:
- It is necessary to provide the patient with complete rest;
- All this time, the patient with an attack must remain in bed;
- To alleviate the condition, you can put a warm heating pad on the right hypochondrium;
- If possible, it is recommended to place the patient in a bath of warm water.
Until the doctor arrives, you must remain close to the patient and help him carry out the recommended procedures. To reduce a severe pain attack, it is recommended to give an analgesic along with an antispasmodic in the form of No-Shpa and Spasmalgon. The ambulance doctor will give the patient an intramuscular injection with one of the painkillers. Despite the fact that with the arrival of a doctor, the severity of the symptoms of a gallbladder attack can be eliminated at home, the main treatment should take place under the supervision of doctors in a hospital setting.
What to do during an attack
Attacks occur at different intervals and have varying degrees of manifestation. For some people, the pain lasts 3-5 minutes, for others it lasts for hours. But no matter how long it lasts, emergency help is called, and before it arrives, try to improve your well-being on your own.
First aid for an attack of illness:
- Stopping feeding. You need to fast for the first 12 hours, and then drink rosehip infusion and eat soup made from fresh vegetables.
- Taking antispasmodics and drugs that dilate blood vessels.
- Maintain complete peace.
- Warming your feet with a heating pad.
- Sitting in a bath with a water temperature of 37-39 degrees (up to 20 minutes) and drinking warm water.
It is not recommended to leave the patient alone during an attack because of the likelihood of vomiting or fainting.
You cannot refuse hospitalization, since the situation may require emergency surgery.
Treatment in hospital
There are several types of medical care for attacks of gallstone disease:
- Medication.
- Surgical.
- Physiotherapeutic.
- Sanatorium-resort.
The essence of medication is to relieve pain and inflammation, and prevent the development of complications. Therapy is effective for stones less than 1 cm in diameter. For this purpose, 4 groups of drugs are used:
- Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs: Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen.
- Antipyretics: Paracetamol.
- Painkillers: Pethidine, Pentazocine.
- Antispasmodics: “Papaverine”, “Drotaverine”.
For stones larger than 1 cm, the doctor recommends surgery to remove them. There are 2 types of intervention:
- Closed cholecystectomy. The operation is performed using a laparoscope, is safe for the patient, and less traumatic. After it, surgical scars are hardly noticeable.
- Open cholecystectomy . A surgical procedure in which the gallbladder is removed through an incision made in the abdominal cavity.
The type of surgical operation is determined by the surgeon based on the size of the stones and their location.
Physiotherapeutic treatment involves shock wave extracorporeal lithotripsy. Stones are removed using a shock wave if there is no inflammation. After crushing, they are excreted naturally.
Sanatorium-resort assistance consists of:
- moderate physical activity, when patients are recommended to walk at a slow pace;
- drinking mineral waters of low or medium mineralization;
- oxygen-nitrogen baths (daily for up to 15 minutes for a course of 5-7 days).
In the sanatorium, the climate and special dietary food also influence the patient’s recovery.
What is the danger of the condition
As practice shows, an attack is considered a dangerous phenomenon. If a person does not consult a doctor in a timely manner, he faces consequences that negatively affect the general condition of the body.
While the stones are small, painkillers can help relieve pain. But when the number of stones increases, they increase in diameter, and moving along the ducts, they clog them.
This condition leads to:
- peritonitis;
- cholangitis;
- acute cholecystitis;
- secondary pancreatitis;
- cirrhosis;
- jaundice;
- choledocholithiasis;
- empyema of the bladder.
The listed diseases are a prerequisite for the development of:
- diabetes mellitus;
- Crohn's disease;
- gout
There are frequent cases of stones piercing the membrane of a bladder. The consequence of this phenomenon is severe pain shock. Another undesirable complication is dehydration. Conditions that provoke it are diarrhea and vomiting.
How to help yourself at home?
Often a situation arises with the development of an attack while the patient is at home alone. In this case, you must immediately call an ambulance and, while waiting for the arrival of specialists, try to alleviate your condition on your own. To do this, it is recommended to take a warm bath, then apply a cold compress to your right side. You should not eat or drink anything during an attack, and to reduce pain, you can lightly apply pressure to the place where the pain is felt most strongly, while trying to maintain shallow, shallow breathing.
Patients at risk of developing attacks of cholelithiasis or biliary colic should know exactly what not to do in this situation:
- Do not apply a hot heating pad to the abdominal area;
- Until the cause of the pain is determined by doctors, you should not take choleretic medications;
- It is not recommended to take any folk remedies based on medicinal plants;
- In some cases, with severe pain, it is recommended to apply ice, but this can only be done for a short time and in exceptional cases.
In general, until the ambulance arrives, you must refrain from taking any medications, and taking painkillers is only permissible in case of unbearable pain. Otherwise, the symptoms of the disease will be dulled and it will be more difficult for the doctor to make a diagnosis. You need to be especially careful with drugs that have a choleretic effect. When stones move along with bile in the case of cholelithiasis, their sharp parts can cause damage to the gallbladder or its ducts, which is a serious complication that can be fatal.
Currently reading: What is gallbladder deformation - ICD 10 code and how to treat it
Causes of acute cholecystitis
The cause of the attack may be a calculus that has blocked the duct
Acute cholecystitis begins to actively develop when an obstruction occurs in the path of bile outflow from the gallbladder. E. coli is often the culprit of the pathology. Staphylococci and other bacteria are also dangerous. Their entry into the gallbladder is accompanied by severe pain.
An attack of illness can occur due to the following reasons and conditions:
- improper diet, snacks on the run, dry food;
- abuse of fatty and spicy foods, fast food, sweets, carbonated drinks, alcoholic drinks;
- inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity;
- fasting, strict mono-diets;
- pressure on the abdomen (for example, the wrong size jeans belt cutting into the flesh);
- developmental anomaly or bending of the gallbladder;
- deformation, compression, displacement of ducts due to injury, tumor, inflammation of nearby organs;
- stones inside the bubble;
- lack of physical activity;
- overweight;
- stress, nervous exhaustion, depression;
- disruptions in the functioning of the biliary tract;
- atherosclerosis;
- pancreatitis;
- diabetes;
- viral hepatitis.
Watch a video about acute cholecystitis:
- sharp, ever-increasing pain in the right side under the ribs, radiating to the shoulder, shoulder blade and lower back on the right side;
- belching, nausea, vomiting with bile and blood;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- chills, fever;
- bloating;
- lemon-yellow skin tone, whites of the eyes;
- darkening of urine;
- bowel dysfunction;
- tachycardia;
- lethargy, drowsiness.
When palpating the right side, the pain worsens. If the patient gets worse, his temperature and pulse jump even more. After an attack of vomiting, the expected relief does not come.
The most dangerous attack is calculous cholecystitis, which occurs when stones are moved. When the bile ducts are blocked, a person begins to suffer from severe biliary colic. This condition is fraught with death.
If the migration of stones disrupts the integrity of the walls of the gallbladder, then its contents, along with the infection, will enter the abdominal cavity. The most likely outcome will be peritonitis.
In this case, the patient’s condition will worsen significantly, he will become very pale and weakened, the pain will become unbearable, and the pressure will drop sharply. With such symptoms, self-medication is not only useless, but also dangerous. You need to call an ambulance as soon as possible.
Gallbladder attack in a child
When there are disorders in the gallbladder, bile stagnation occurs, which, if this condition develops in children, manifests itself with insufficiently pronounced symptoms. Typically, a child may experience a gallbladder attack with hypertonic, hypotonic or mixed forms of congestion.
Hypertensive stagnation, caused by increased contractility of the gallbladder and ducts, is usually accompanied by acute pain in the right hypochondrium, most often occurring after increased physical activity of the child. In this case, children may experience nausea, vomiting, frequent bowel movements and diarrhea, loss of appetite, accompanied by headaches and weakness. This form is more often found in teenage children.
The hypotonic form of bile stagnation with an attack of colic in children is less common, as it is caused by a decrease in the contractility of the gallbladder ducts and its walls. As a result, the liver enzyme accumulates, stretching the walls of the gallbladder, which is accompanied by pain.
The mixed form contains symptoms of these two conditions. Usually the child loses his appetite, but does not lose weight, but, on the contrary, gains weight due to swelling of the limbs and face. In this case, the skin suffers; the child scratches the skin vigorously, leaving scratches on it. Severe itching causes anxiety, his character changes, he becomes capricious and nervous. If an accurate diagnosis is not determined in a timely manner, since such symptoms are often mistaken for manifestations of allergies, then the disease enters an advanced stage.
Asymptomatic and dyspeptic forms of the disease
Some people have stones in their gallbladder, but patients do not have any complaints. This form of the disease is called asymptomatic (latent). Experts consider it as a period of cholelithiasis, because, according to statistics, after about 10 or 15 years, 30-50% of people experience symptoms of the disease and complications.
Another form of cholelithiasis is dyspeptic. Sick people complain of functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. The following symptoms are observed (they usually occur after eating, especially if fried, fatty, spicy foods, or alcoholic drinks have been consumed):
- feeling of heaviness in the epigastrium and right hypochondrium;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- heartburn;
- excessive accumulation of gases in the intestines;
- unstable chair.
Diagnostic measures
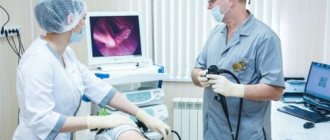
When you see a doctor with a gallbladder attack, he examines the patient’s medical history, conducts an examination using palpation of the abdomen, and also gives a referral for laboratory tests and ultrasound. To exclude the possibility of a malignant neoplasm or inflammation of the gallbladder, a minimally invasive diagnostic method is used - laparoscopy.
Ultrasound is no less important in diagnostics, since with the help of this study it is possible to detect changes in the condition of the organ itself and its ducts. When examining blood, special attention is paid to existing deviations of its indicators from the norm, as this serves as evidence of dysfunction of the gallbladder. When the level of direct bilirubin increases, the patient is assumed to have hemolytic anemia, and cases of increased indirect bilirubin make it possible to suspect the development of cholelithiasis, an inflammatory process in it, damage to its ducts, injury or an existing neoplasm.
An increase in AST or ALT in the analysis increases the likelihood of developing hepatocyte necrosis, and an increased amount of alkaline phosphatase indicates pathological changes in the gallbladder that are chronic in nature.
After the diagnosis, the doctor begins to eliminate the causes that caused the attack of gallbladder colic.
Prevention and prognosis
A healthy lifestyle is the best prevention of most diseases
Primary prevention consists of a number of measures to prevent the formation of gallstones. This is facilitated by a properly selected diet. The patient is recommended to lead an active lifestyle, jogging, yoga - to the best of his ability, but regularly.
If you have gallstone disease, it is dangerous to go on strict diets: sudden weight loss can cause migration of stones and gallbladder dysfunction. To reduce the risk of an attack, the attending physician may suggest surgery while the disease is not yet in the acute stage.
With proper and timely treatment of cholecystitis, the prognosis is positive. Even after removal of the gallbladder, the liver does not stop producing bile, but sometimes postcholecystectomy syndrome develops. Initially, after surgery, patients often experience soft, frequent stools, but for most they soon return to normal.
In the acute form of the disease, as well as in emergency surgery, the prospects are much worse. If you do not seek medical help at all, you can die due to extremely serious complications.
An attack of cholecystitis can be manifested by symptoms of varying intensity, it all depends on the form and stage of development of the disease. As you know, cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder. It can be acute and chronic, acalculous and calculous (with the formation of stones). And if exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis does not pose a direct threat to health, then an acute attack accompanied by biliary colic is a dangerous condition that requires urgent medical attention.
Treatment of cholelithiasis
When treating cholelithiasis, conservative and surgical methods are used, depending on the nature of the disease and the degree of its development.
Typically, therapeutic methods using medications are used first. In this capacity they carry out:
- Dissolution of gallstones using special medications;
- The use of extracorporeal wave lithotripsy;
- Prescribing a strict diet.
If the treatment does not bring the expected result, then the patient is treated with one of the methods of surgical treatment of cholelithiasis - cholecystomy, which can be classical or use laparoscopy. The method that will be more appropriate in a particular case is chosen by the attending surgeon.
Cholecystomy is required for the following conditions:
- In the case of several neoplasms in the gallbladder;
- With frequent repetition of attacks of biliary colic;
- If there are stones in the biliary tract;
- With the development of biliary pancreatitis.
Urgent surgery is performed in the presence of certain dangerous violations:
- In case of a complicated course of the disease in the form of peritonitis;
- With the structure of the bile ducts with their narrowing;
- In case of formation of a purulent focus;
- In the presence of biliary fistulas.
The choice of treatment depends on many reasons. Some patients, despite the indications, are contraindicated for surgical intervention. The reason for refusal may be the patient’s advanced age, as well as existing chronic diseases. Another situation is envisaged with patient intolerance to pharmacological drugs, when the only treatment option is surgery.
Currently reading: Symptoms and treatment of cholelithiasis (calculous cholecystitis)
How to relieve an attack of cholecystitis
In case of a sharp exacerbation of cholecystitis, you need to call an ambulance. Depending on your general health, age and other circumstances, the consequences of an attack may vary. The seriousness of the situation does not allow you to try to cope with cholecystitis on your own. However, you can alleviate the condition of a loved one even before the doctor arrives.
First aid at home
When sharp pain literally paralyzes, the first thing to do is to provide the person with peace by placing him in a horizontal position. Apply cold to the right side. If there is a urge to vomit, give a few sips of plain still water or mint tea without sugar.
You can relieve pain during an attack with a No-shpa or Baralgin tablet.
An attack of cholecystitis cannot be completely cured at home. Even if after the measures taken the pain began to subside, this does not mean that the crisis will not happen again. Only after an ultrasound examination will it become clear whether there are gallstones. If the answer is positive, surgery is inevitable. If there are no stones, after a few days the doctor will send you home, prescribing appropriate treatment.
What will the doctor prescribe?
An acute attack of cholecystitis with the presence of gallstones ends with cholecystectomy - removal of the bladder.
If it is possible to manage with conservative treatment, to relieve the attack, the doctor will prescribe:
- analgesics and antispasmodics (Analgin, No-shpa, Drotaverine) to relieve pain;
- antibiotics (Azithromycin, Ampiox, Furazolidone) to destroy pathogenic microflora;
- glucose solution (in droppers) to reduce intoxication.
After relief of the condition, the following are prescribed:
- choleretic agents (Allohol, Cholenzym, Holagol) to free the gallbladder from stagnant bile;
- stones are dissolved using drugs such as Ursofalk, Ursosan;
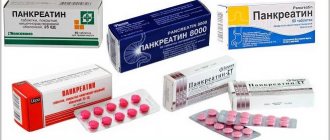
- digestive enzymes (Pancreatin, Festal);
- hepatoprotectors (Essentiale, Antral).
It is forbidden to drink choleretic drugs without a doctor’s recommendation. This is dangerous due to repeated exacerbation of cholecystitis.
Diet after an attack
Since inflammation of the gall bladder is largely associated with poor nutrition, cholecystitis will also have to be treated with diet. Immediately after an attack, complete fasting with plenty of fluids is indicated for 2-3 days. It is advisable that it be still water or unsweetened mint tea.
Over time, the diet is replenished with lean broths, homogeneous viscous porridges, and vegetable purees. All food should be boiled or steamed.
Raw vegetables are considered heavy food during the recovery period.
Food served must be warm (neither hot nor cold). The number of meals increases to five, but portions become smaller. You should eat your last meal a few hours before bedtime.
Drug therapy
Drug therapy is aimed at reducing the severity of spasm, for which M-anticholinergic blockers in the form of Atropine or Platifilin, as well as antispasmodics, are used. To reduce pain symptoms, analgesics in the form of Baralgin or Pentalgin are usually prescribed. For very severe pain, Promedol can be used. An equally important task remains the dissolution of stones with the help of medications in the form of Ursofalk or Ursosan. This method is justified if the age of the stones does not exceed three years, they contain cholesterol and are no larger than 5 millimeters in size.
Why does an attack occur?
Patients suffering from this disease often notice a sharp deterioration in their health after holidays and feasts. This is due to the following factors:
- Drinking large amounts of alcohol.
- Passion for fatty, salty, smoked and spicy foods, carbonated water, desserts, fast food.
- Binge eating.
- Gaining excess weight due to poor diet.
As a result of the influence of these factors, the bile becomes too thick, an inflammatory process occurs in the tissues of the organ, and stones form. The patient develops an acute attack of cholecystitis. Treatment of symptoms at home involves the use of drugs that help normalize the process of bile outflow.
Help in hospital
If there is a severe attack of biliary colic, the patient is placed in a hospital where his condition will be alleviated and the development of dangerous complications will not be allowed. To do this, the patient is prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antipyretic and painkillers, as well as opioids. Opioids are stronger analgesics that can relieve pain during an attack.
Often, the condition of a patient with a gallbladder attack requires immediate surgical assistance to remove large stones from the bile ducts, since this condition is life-threatening.
First aid
If you experience symptoms of a gallstone attack, you should urgently call a doctor. Before the specialist arrives, the patient should be given first aid:
- ensure rest (bed rest is recommended);
- give a heating pad (it must be placed on the right hypochondrium);
- suggest taking a warm bath.
At the time of an attack of cholelithiasis, it is allowed to give medications: antispasmodics (“Drotaverine”, “No-shpa”) in combination with analgesics (“Spazmalgon”, “Baralgin”). You can wait for the doctor to arrive. The specialist will tell you how to relieve an attack and administer the necessary medications in a certain dose:
- “No-shpu” (intramuscular 2 ml);
- "Papaverine", 2% (intramuscular 2 ml);
- "Baralgin" (intravenously 5 ml);
- "Atropine", 0.1% (subcutaneous 1 ml).
Other dangerous conditions may be hidden behind the symptoms of an attack of gallstone disease. To confirm the diagnosis, you will need to do a detailed blood test, ultrasound or fluoroscopy. If indicated, specialists will perform the following activities:
- cleaning the bile ducts;
- surgical removal of existing stones and gallbladder.
Complications of cholelithiasis and concurrent diseases
The presence of cholelithiasis without taking timely measures can lead to serious complications at any time. As the disease progresses, the size of the stones increases and their advancement can lead to blockage of the bile ducts, causing the following dangerous conditions:
- Biliary liver cirrhosis;
- Development of jaundice;
- Inflammation of the gallbladder in the form of cholecystitis;
- Formation of cholangitis.
When the ducts are blocked, the pain becomes constant and becomes quite intense. The metabolism and further existence of the patient depend on the complications of cholelithiasis that arise.
Description
Cholecystitis is an inflammatory disease that develops in the gallbladder and is accompanied by pain. Bile collects in the gallbladder. After eating, the bladder contracts and bile is released into the intestines. It is required to activate enzymes involved in the digestion of food. Cholecystitis disrupts this order.
Exacerbation of cholecystitis develops when the outflow of bile from the bladder is disrupted, which causes its stagnation. The pathology is characterized by the formation and movement of stones. Stones can block the bile ducts, causing bladder rupture and peritonitis, which can be fatal.
Proper nutrition
To prevent gallbladder attacks, patients with cholelithiasis should adhere to the prescribed diet and not violate it. Its composition should minimize the content of fat and cholesterol, and fiber-rich foods should be consumed as much as possible. The daily menu can include lean meat and fish, cereals, fresh fruits and vegetables, as well as fermented milk products and vegetable oil.
Alcoholic drinks, spicy and fried foods with a high fat content, natural milk, tea and coffee, as well as red meats should be excluded from consumption.
Following a diet will not dissolve existing stones, but with proper nutrition, colic attacks occur less frequently and are less painful.
Nutritional Features
An attack of cholelithiasis, the symptoms of which are known to every gastroenterologist, is familiar firsthand to many people. However, not everyone thinks about prevention. Changing your daily menu will greatly help in preventing attacks of gallstone disease.
First, you should avoid refractory fats. Due to insufficient bile supply, the activity of a special enzyme, lipase, decreases. This, in turn, leads to a deterioration in the breakdown and absorption of fats. People feel pain, cramping, and bloating. Only butter and vegetable oils are allowed.
Secondly, you should exclude rye bread, mushrooms, peas, beans, nuts, millet, chocolates, coffee, cocoa, and pastry from your menu. These products cause aggravation, because their digestion requires tension in the enzyme systems of the human body.
Prevention
As a preventative measure aimed at preventing gallbladder attacks, doctors recommend adhering to certain rules:
- Eat often and in small portions;
- Prefer clothes that do not tighten the stomach;
- Go for the night no earlier than two hours after eating;
- Do not lift heavy objects and avoid bending;
- Raise the head of the bed a few centimeters;
- Avoid foods prohibited by your doctor;
- Do therapeutic exercises, exercises aimed at strengthening the abdominal muscles.
If an attack with characteristic symptoms occurs, timely consultation with a doctor plays a very important role in recovery. Only a specialist will be able to identify the cause of the pain and choose the necessary methods to eliminate it.
Types of pathology
There are several types of inflammatory process in the gallbladder:
- Spicy. It is characterized by pronounced signs. The disease develops over several days.
- Chronic inflammatory process. It proceeds slowly, without pronounced manifestations. Often occurs as a result of the lack of adequate treatment for acute pathology.
In addition, there are the following types of disease:
- Calculous cholecystitis. Develops in the presence of stones and pus in the gallbladder, thickening of the walls.
- Catarrhal. It manifests itself as a slight compaction of organ tissue. It is not accompanied by a disturbance in the process of bile discharge or a change in its composition.
- Phlegmonous. It manifests itself as a pronounced inflammatory process, accumulation of pus. It poses a threat to the patient's life and requires immediate assistance.
- Gangrenous. Accompanied by tissue death. Leads to rupture of the walls of the organ, the development of acute inflammation in the abdominal cavity.
How to eliminate an acute attack of cholecystitis, symptoms?
Treatment at home in some cases helps to get rid of the signs of the disease. But if the patient is in serious condition, he needs hospital therapy and possibly surgery.
Reviews
Dear readers, your opinion is very important to us - therefore, we will be glad to see your feedback on first aid and treatment of a gallbladder attack in the comments, this will also be useful to other users of the site.
Lydia:
When I had my first attack of biliary colic, I didn’t think about cholelithiasis. I thought it was my stomach that reacted that way. But the disease was already discovered on an ultrasound, and now I’m following a diet.
Olga:
I didn’t know that an attack of pain could be mitigated by the same No-Shpa, I endured it. The pain, of course, was severe, but it passed quickly.
How to relieve an attack of cholecystitis
An attack of cholecystitis requires emergency care. Let's look at step-by-step actions that will help you relieve an attack at home:
- The first thing you should do is call an ambulance.
- Place the patient in a horizontal position.
- Apply ice to the abdominal area.
- Antispasmodics will help relieve pain.
- Mint tea or still mineral water will help eliminate nausea.
- If you vomit, be sure to drink mineral water.
First aid
When an attack of cholecystitis occurs, measures must be taken immediately to alleviate the pathological symptoms. First aid must be competent so that your health does not worsen. First you need to call an ambulance, because you won’t be able to get rid of the pathological condition on your own.
While the doctors are traveling, it is necessary to lay the patient horizontally. To make you feel better, you can give an antispasmodic - for example, No-shpu or Drotaverine. If possible, it is better to refuse medications until medical specialists arrive.
Ice can be applied to the abdominal area, but it must be wrapped in a cloth. To reduce nausea, you can use mint tea. After bouts of vomiting, it will be useful for the patient to drink non-carbonated mineral water, taking small sips.
Treatment
An attack of cholecystitis is most often eliminated surgically. Surgery will be required if the attack of cholecystitis cannot be stopped or peritonitis occurs. If the patient's condition is advanced, they resort to lavage of the abdominal cavity.
Conservative treatment consists of the use of antibacterial drugs, antispasmodics and detoxification agents.
Drug treatment can:
- Suppress the activity of pathogenic microorganisms. This goal is achieved through the use of antibiotics.
- Eliminate symptoms. Choleretic agents, dietary nutrition and duodenal intubation increase the intensity of bile outflow.
One of the main conditions for the effectiveness of therapy is adherence to a special diet . For the first few days after an exacerbation of cholecystitis, experts recommend fasting. During this period, only mint tea is allowed. If the patient prefers mineral water, then drink it warm and without gas.
After 3 days, when the patient feels better, the following are introduced into the diet:
- puree soups,
- weak broths,
- viscous boiled porridge.
Meals should be fractional, small portions, food pureed. Raw vegetables, which contain coarse fiber, are temporarily excluded from the diet. Preference is given to the steam method of processing products, boiling and baking.
Also prohibited are:
- "fast carbohydrates"
- salty,
- pickled,
- smoked,
- fatty,
- baking,
- sugar-sweetened carbonated drinks,
- seasonings, spices,
- alcohol.
Allowed to eat:
- lean varieties of fish and meat,
- steamed omelette
- vegetable salads dressed with oil,
- low-fat dairy products,
- sweet berries, fruits.
Drinks can be varied with diluted non-acidic juices, rosehip decoction, herbal tea, fruit drinks, and compotes.
How does the disease manifest itself?
Gallstone disease is a pathological process of stone formation in the gall bladder and bile ducts. Gallstone disease can be asymptomatic for a certain period of time. In such cases, the patient learns about the existence of stone deposits during an abdominal ultrasound, which may be performed for a completely different reason.
For example, an incidental finding during an ultrasound may be an echogenic suspension in the gallbladder, from which, under unfavorable circumstances, stones will later form.
In other cases, the first symptom of gallstones is biliary colic. The main manifestation of biliary colic is severe paroxysmal (paroxysmal) pain in the right hypochondrium. The pain can reach the right shoulder blade and also move to the spine. A painful attack occurs due to a stone blocking the flow of bile. Colic lasts from a few minutes to several hours, after which it gradually goes away.
Associated symptoms may include:
- nausea,
- uncontrollable vomiting,
- bloating,
- subjectively felt interruptions in the functioning of the heart.
The diagnosis of cholelithiasis is based on a typical clinical picture: biliary colic with nausea and vomiting. Jaundice, itching, discoloration of urine and feces are additional symptoms indicating the origin of the pain.
Performing instrumental studies, such as abdominal ultrasound (sometimes abdominal radiography), can confirm the diagnosis and accurately determine the location of the stones. In the diagnosis of gallbladder diseases, laboratory tests are used (transaminases, GGT, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin concentrations divided into fractions).
For more information about how to detect the disease in time, whether it is necessary to remove the gallbladder if stones are present, and how to avoid complications, read the article about cholelithiasis.
Also read answers to questions about gallstones that our expert hepatologist often asks. Your question may already be answered!
Some people have stones in their gallbladder, but patients do not have any complaints. This form of the disease is called asymptomatic (latent). Experts consider it as a period of cholelithiasis, because, according to statistics, after about 10 or 15 years, 30-50% of people experience symptoms of the disease and complications.
Another form of cholelithiasis is dyspeptic. Sick people complain of functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. The following symptoms are observed (they usually occur after eating, especially if fried, fatty, spicy foods, or alcoholic drinks have been consumed):
- feeling of heaviness in the epigastrium and right hypochondrium;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- heartburn;
- excessive accumulation of gases in the intestines;
- unstable chair.
Basic nutrition rules for patients
An important component of therapy is diet.
A patient who has been diagnosed with gallbladder inflammation is allowed to consume the following foods:
- First courses based on milk or vegetable broth.
- Dishes made from lean meat, fish and poultry, baked or steamed.
- Omelettes made from egg whites.
- Dairy products with low fat content.
- Non-acidic fruits and berries.
- Mild vegetables.
- Pasta, cereals.
- Biscuits, crackers, croutons.
- Jam made from sweet fruits and berries.
- Greens (parsley, dill).
- Cinnamon and vanilla.
- Dried fruits, marmalade, candies without cocoa and chocolate.
Patients are prohibited from using:
- Fried, spicy, salty, pickled, sour and fatty foods.
- Sauces (mayonnaise, adjika, ketchup, mustard).
- Dairy products are high in lipids.
- Mushrooms.
- Egg yolks.
- Beans, peas.
- Coffee, chocolate, cocoa, sparkling water.
- Alcohol-containing products.
- Confectionery, baked goods.
- Vegetables, herbs, fruits and berries with a spicy and sour taste.
Complications
When the first signs of acute cholecystitis appear, it is important to immediately consult a specialist or call a doctor at home to provide first aid. Already on the first day of exacerbation of the pathological process, serious complications can arise. Including:
- acute pancreatitis,
- perforated or destructive cholecystitis,
- obstructive jaundice,
- biliary fistulas,
- subhepatic abscess,
- peritonitis,
- empyema,
- gangrene.
More details need to be said about peritonitis. This is an inflammatory process that covers the peritoneum. With peritonitis, the patient complains of pain in the abdomen, which sharply increases with pressure. The patient is bothered by vomiting, which contains food remains. After some time, the vomit takes on a characteristic greenish color.
The general health of the patient with peritonitis also deteriorates sharply:
- the skin turns pale,
- a whitish coating forms on the tongue,
- belly gets bigger
- body temperature rises.
Symptoms
Cholecystitis can occur in chronic and acute forms, and the disease can be either acalculous or with the formation of stones. The symptoms of an attack are pronounced, so it is impossible not to notice it.
It all starts with severe and sharp pain in the right hypochondrium. It resembles an attack of pancreatitis - the pain radiates to the shoulder, lower back, and shoulder blade. If you press on the right hypochondrium, then the unpleasant sensations will immediately become stronger.
Other symptoms of an attack of cholecystitis may be observed:
- Bloating and excessive tension in the abdominal area.
- Decreased blood pressure, severe weakness, dizziness.
- Yellow tint to skin and eyes.
- Bitter taste in the mouth, nausea.
- Vomiting of bile, without relief.
- Stomach upset, increased gas formation.
- A sharp increase in body temperature.
- Tachycardia. The pulse is more than 120 beats per minute.
- Heavy sweating.