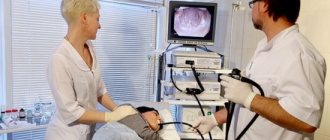
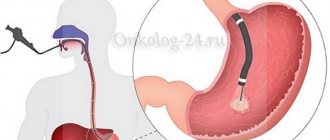
Esophagogastroduadenoscopy (EFGDS) is one of the most effective ways to diagnose diseases of the stomach, esophagus and duodenum. Unfortunately, during this procedure most patients experience serious discomfort. It is for this reason that many are trying to find an effective alternative to gastroscopy of the stomach. Thanks to the achievements of modern science, such techniques have actually been developed.
About esophagogastroduadenoscopy
It is very difficult to overestimate the importance of this research method. Thanks to it, the following diseases of the digestive system can be identified in the early stages:
- esophagitis;
- gastritis;
- duodenitis;
- ulcers and erosions;
- benign and malignant neoplasms;
- polyps;
- gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- diaphragmatic hernia and other types of gastrointestinal pathology.
Such a high information content of the technique is due to the fact that it allows visualization of the mucous membrane of the digestive tract.
Effective methods for checking the stomach and signs of possible diseases
Experts recommend examining the stomach not only for alarming symptoms, but also for preventive purposes. Stomach cancer is the fourth most common cancer among cancers and the second most common cause of death after lung cancer.
Unfortunately, this disease can occur without symptoms for a long time, which is what determines the lethality of stomach cancer: it is detected at one of the last stages. Other stomach diseases can also be dangerous due to gastric bleeding and precancerous conditions. In order not to miss anything, doctors recommend visiting a gastroenterologist at least once a year, and also monitoring your diet.
Stomach check: appointment for examination
Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and heartburn are signs of stomach diseases
The condition of the whole organism as a whole depends on the functioning of the stomach. It is in the stomach that the process of digesting food begins, on which the further functioning of the intestines depends. If food is digested incorrectly or incompletely, metabolism may be disrupted and the pancreas, liver, and intestines may suffer.
Quite often, pathological processes in the stomach are accompanied by various symptoms that require medical attention. It is very dangerous to start treatment on your own; before starting any medications, you need to check your stomach.
You should immediately consult a doctor and undergo an examination if the following symptoms appear:
- Periodic abdominal pain. Stomach pain can occur at different times of the day and is usually localized in the upper abdomen. They can be strong cutting, dull, aching, cramping. When pain appears, an examination of the stomach is necessary, since it can be a sign of a variety of diseases. When visiting a doctor, you need to clarify how long ago the pain began, how often it appears, at what time (at night, in the morning, before or after meals, etc.), and also describe the nature of the pain.
- Nausea and vomiting. Nausea can occur for various reasons: from liver disease and gastritis to psychological stress. Vomiting is essentially the body's defense mechanism when the contents of the stomach are expelled. This is how the body protects itself from the absorption of toxic substances, but sometimes vomiting is associated with a disease, especially if it is periodic. Vomiting may indicate an inflammatory process in the stomach, an ulcer. The appearance of black vomit indicates internal bleeding and requires immediate hospitalization of the patient.
- Heartburn. Heartburn is considered by many to be a minor symptom that appears after eating certain foods. But persistent and severe heartburn can be a symptom of the disease. With heartburn, some of the gastric juice enters the esophagus, causing a burning sensation. This symptom often appears with gastritis with high acidity.
- Dysphagia. A very serious symptom that requires mandatory examination. With dysphagia, it is difficult for a person to swallow food, he experiences pain when swallowing, and food enters the nasal cavity. This may be due to the high acidity of gastric juice, which, when entering the esophagus, damages it, causing a narrowing of the lumen.
Methods for checking the stomach
Gastroscopy is an effective method for examining the stomach
There are many methods for examining the stomach, but FGDS remains the most informative. Only this method of examination allows us to evaluate the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach and accurately make a diagnosis.
Each examination method has its pros and cons. If there is a lack of information, they can be combined:
- History taking and palpation. With such an examination, the doctor can only guess which part of the stomach (and whether it is the stomach) is damaged and determine the location of the pain. The undoubted advantage of this method is its accessibility, speed and non-invasiveness. However, it is impossible to obtain complete information about the state of the stomach in this way.
- Ultrasound. The ultrasound examination method is painless, fast, inexpensive and does not require internal insertion of probes and devices. However, an ultrasound of the stomach will help identify only large formations in it, for example, tumors and polyps. It is impossible to assess the condition of the mucous membrane using ultrasound.
- CT and MRI. Both of these methods are painless and can be performed using a contrast agent. CT and MRI cannot be called cheap examination methods, but they are non-invasive, quite fast and informative regarding the structure and neoplasms. It is again impossible to see and evaluate the condition of the gastric mucosa.
- Gastroscopy. This is an endoscopic examination method in which a thin tube is inserted into the throat and advanced all the way to the duodenum. This method is quite unpleasant and requires some preparation, but it is very informative and is often combined with a biopsy. During the procedure, polyps can be removed and tissue taken for examination. Many people try to avoid this method of examination and in vain. A more informative procedure to assess the condition of the stomach does not yet exist.
- Probing. Most often, the purpose of intubation is to obtain a sample of gastric juice for research. As with FGDS, a thin tube is inserted through the patient's mouth, but it is impossible to assess the condition of the gastric mucosa.
The doctor should choose a method for examining the stomach after assessing the patient’s complaints. There is no need to refuse the examination for fear of pain and complications. All procedures are carried out by specialists and are not accompanied by severe pain.
Description of the procedure
The technique of esophagogastroduadenoscopy involves performing the following sequential manipulations:
- Preparing the patient for the study.
- Choosing a method of pain relief (most often, it is sufficient to use a spray that reduces the sensitivity of the oral cavity and pharynx, thereby reducing the severity of the gag reflex).
- Using an endoscope to pass through the digestive tract through the esophagus, stomach to the duodenum. During this test, your doctor may perform a diagnostic biopsy and sometimes remove small polyps that may develop into cancer in the future.
- Observe the patient for 20-30 minutes to exclude the development of complications.
After this procedure, many patients report experiencing unpleasant sensations. During the study, it is extremely important to follow absolutely all the instructions of the doctor and nurse.
When to see a doctor
Under no circumstances should you delay your illness. If even just once you feel unwell and suddenly have pain in the abdominal area, you should immediately consult a doctor. The most popular symptoms remain:
- nausea;
- loss of appetite;
- vomit;
- discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract.
If you experience the following symptoms, then you should definitely not postpone your visit to the doctor. Unpleasant sensations in this area are formed locally. And by finding these “hot spots” you can even determine the diagnosis. Pain below the ribs indicates damage to the inlet of the stomach.
It may also mean that the esophagus is damaged. Pain in the upper right part of the stomach to the navel is most likely pangastritis or intestinal pathology. Ulcers and cancer are very difficult to identify. To do this, you need to pass specialized tests.
About discomfort during gastroscopy of the stomach
An analysis of surveys conducted in healthcare institutions among patients undergoing endoscopy shows that most of them experience certain unpleasant sensations during this procedure. Among the most common complaints are the following:
- Gag reflex (of varying severity depending on the individual characteristics of the person and the anesthetic used) during gastroscopy.
- Non-critical breathing difficulties during the examination.
- Feelings of bloating in the abdomen during gastroscopy (caused by the supply of air to the stomach and intestines to straighten their walls in order to improve visualization of the mucous membrane).
- Tingling in the abdomen during the day after the study (caused by the same additional introduction of air into the gastrointestinal tract).
- Slight soreness in the throat after the examination (most often disappears in the morning after endoscopy).
However, the severity of all these symptoms varies greatly depending on the individual patient, the anesthesia used and the equipment used.
Danger of stomach pain
Like any disease, pain in the gastrointestinal tract can develop into more serious diseases. Usually such pains are symptoms of gastritis and stomach ulcers. If you have stomach pain, your doctor may make the following diagnoses:
- Acute gastritis is an acute inflammation of the gastric mucosa.
- An ulcer is a trophic formation in the gastric mucosa.
- Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas.
- Esophagitis is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the esophagus.
- Stomach cancer.
- Ulcerative colitis is a chronic disease of the intestinal mucosa.
How to properly prepare for research?
First of all, it is recommended to seek advice from a general practitioner or gastroenterologist. They will conduct a general examination, palpation of the abdomen, and also collect anamnesis. Before undergoing this diagnostic procedure, the patient should find out what tests are needed for gastroscopy of the stomach. Most often, therapists and gastroenterologists refer a person for the following clinical and laboratory tests:
- general blood analysis;
- biochemical blood test (ALAT, AST, total and conjugated bilirubin, amylase, electrolytes);
- blood glucose.
In addition to taking tests, it is very important to undergo the necessary preparation immediately before esophagogastroduadenoscopy. It means refusing to eat any food for at least 6 hours before the test.
When to consult a proctologist?
If you have any doubts about which doctor to go to if you have prolonged stool retention, you should first visit a therapist.
In what cases is it necessary to visit a proctologist:
- anal fissures;
- burning, pain, constant discomfort in the area of the colon and outlet;
- suspicion of neoplasms – polyps, tumors;
- haemorrhoids.
A consultation with a proctologist begins as standard. The doctor interviews, prescribes tests, and performs a rectal examination. Based on the results, drug therapy and procedures are prescribed to help restore normal bowel movements. If neoplasms are detected, surgery is considered.
Doctor's consultation includes:
- Preliminary survey of the patient, detailed anamnesis collection.
- Examination of the patient with palpation of the abdominal wall.
- Diagnostics (ultrasound, FGDS).
- Taking tests (blood, stool, urine).
- Selection of effective treatment.
- Adjusting your diet. Selecting an appropriate diet.
- Constant monitoring and control over the progress of treatment.
Analogues of gastroscopy
The stomach, esophagus and duodenum are quite difficult organs to study. The most informative method for diagnosing his diseases is esophagogastroduadenoscopy. Thanks to this type of study, the endoscopist is able to study in detail the morphological structure of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, during EGD, a specialist can perform a biopsy (take a sample of a changed area of the mucous membrane) and subsequently send it for pathohistological examination.
No other research method is capable of providing equally complete information about the state of the digestive tract. At the same time, there are a number of diagnostic procedures that can help identify most diseases of the stomach, esophagus and duodenum. As a result, the following research methods may become an alternative to gastroscopy:
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- X-ray examination using barium suspension.
- Capsule EGDS.
- Ultrasound examination of the stomach.
Each of these methods has both advantages and disadvantages.
When is emergency medical attention required?
There are conditions when you cannot do without urgent medical help:
- sudden acute pain;
- the person’s behavior has changed (he suddenly became lethargic, apathy appeared);
- sudden vomiting with pain;
- lack of stool for several days;
- a person refuses to eat;
- weakness, accompanied by cold sweat, pale skin, rapid pulse;
- fever (high temperature);
- the wall of the abdomen is very tense, as if stiff.
If any of these symptoms appear, you must immediately call an ambulance.
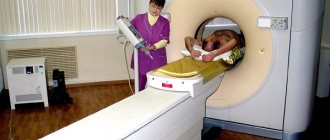
Magnetic resonance imaging
This diagnostic procedure is currently one of the most popular among both patients and doctors of various specialties, including gastroenterologists. As a result, it is often positioned as a good replacement for gastroscopy of the stomach. Its undoubted advantages are the following:
- has no side effects;
- does not cause discomfort during the examination, unlike gastroscopy;
- allows the specialist to obtain a layer-by-layer display of the structure of the stomach, esophagus and intestines;
- the radiologist can see not only the internal cavity of the stomach, but also its outer wall, which makes it possible to identify neoplasms with exophytic growth, which are extremely difficult to diagnose diseases.
Unfortunately, magnetic resonance imaging cannot be considered a full-fledged analogue of gastroscopy of the stomach, since it does not allow a detailed assessment of the condition of the mucous membrane and taking a tissue sample for pathohistological examination. In the process of improving the methods of magnetic resonance imaging, it is likely that this type of diagnosis will be able to compete with classical esophagogastroduadenoscopy.
Visit to a therapist or gastrologist
If you have already previously visited a therapist who has sent you to see a specialized doctor, then you need properly selected treatment, since gastritis and other gastrointestinal diseases are a very serious problem, and this should not be joked about under any circumstances.
Diagnostics
Well, you are already at an appointment with a gastroenterologist. Experts recommend using special expressions to describe your condition and pain. Pain in this area may be:
- piercing;
- cutting;
- pulling;
- aching;
- twitching;
- pushing.
In addition, pain in the stomach area is not always associated with digestion. These may be disturbances in the functioning of the liver or gall bladder. And only a doctor can determine what the problem is.
Surveys
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo an examination. If a gastroenterologist diagnoses you at your first appointment, you need to think about whether this doctor is really a specialist in his field?
Usually, at the first appointment, the doctor will find out about your diet, the nature of stomach pain or other unpleasant sensations. Next, the specialist recommends undergoing a digestive system examination. After all, only a deep study of the problem can correctly diagnose and cure the body in a short period. Among the most popular examinations are:
- basic tests (blood, urine, etc.);
- fibrogastroscopy - examination of the stomach using an endoscope;
- biopsy of the stomach and intestines (if indicated);
- Ultrasound of internal organs.
At the first symptoms of gastritis or a stomach ulcer, a gentle diet and medications that can remove the signs of the disease are prescribed.
In addition to the main types of examinations, a specialist may prescribe additional types of symptomatic studies:
- Breathing test - the patient breathes into a special bag that is evacuated. After this, the air in the bag is examined for the presence of harmful microorganisms.
- Analysis of gastric juice - the analysis is taken using a specialized rubber device - a probe.
- X-ray of the gastrointestinal tract.
The first stage of treatment involves a specialized diet. The patient should refuse fatty, spicy, i.e., foods harmful to the stomach. In addition to diet, medications are prescribed that can relieve pain. They do not cure the disease, but only make it easier to tolerate the disease.
At the second stage, after a full examination, the specialist prescribes specialized drugs that fight the inflammatory process of the stomach and intestines.
X-ray with barium suspension
This diagnostic method is used less often than others. This is due to the fact that such a procedure has limited information content and is accompanied by irradiation of both the patient and the medical personnel performing it. This alternative to gastroscopy allows you to obtain data on:
- patency of the esophagus and stomach;
- the presence or absence of large tumors on the mucous membrane of the digestive tract;
- contractile function of the stomach.
Naturally, this technique also cannot serve as an alternative to gastroscopy of the stomach, but it has its own diagnostic value and scope of application.
How to become a gastroenterologist?
Every doctor knows which doctor treats the intestines. At the same time, many of them would not mind specializing as a gastroenterologist in the future. Any general practitioner can apply for it. To do this, he must either pay for the training himself or receive a referral from the health care institution in which he works or plans to work.
Another option, but much less likely, is to pursue a residency in gastroenterology. Today there are practically no places in it. Institutes and universities are trying to graduate generalists, that is, therapists and general practitioners.
Capsule endoscopy
Currently, when discussing the question of whether there is an alternative to gastroscopy of the stomach, this diagnostic technique is most often mentioned. Its advantages are:
- no discomfort during the study;
- the possibility of obtaining information about the condition of the mucous membrane of the digestive tract.
However, this method is not without serious disadvantages, the main ones being the following:
- high cost of the procedure;
- the likelihood of missing pathology, since during the study not the entire surface of the mucous membrane is examined, but only those parts of it that are captured by the camera lens;
- the impossibility of taking a sample of altered tissue for further pathohistological examination and establishing an accurate diagnosis.
As a result, today capsule gastroscopy is not a panacea for detecting diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Currently this method is very expensive and ineffective. It is quite possible that in the process of improving this diagnostic procedure, most of its shortcomings will be eliminated and it can become a good alternative to gastroscopy of the stomach.
Associated diseases
Specialists in this category treat the digestive tract. A person may have problems ranging from the esophagus, where chewed food ends up, to diseases in the rectum. The patient should contact this specialist if problems such as:
- pathology in the work of the sphincters, which are located between the border of the stomach and esophagus;
- diseases of the esophagus: the presence of polyps, achalasia, dilated veins in the esophagus, diverticula;
- diseases in the stomach: ulcers, gastritis, papillitis, erosion, tumors, polyps;
- diseases of the pancreas: pancreatic necrosis, pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, diabetes mellitus, cyst, oncology;
- pathology in the duodenum;
- diseases occurring in the spleen: cyst, abscess, malignant neoplasms;
- pathology of the rectum and anus;
- intestinal diseases: colitis, duodenitis, adhesions, enteritis, obstruction, ulcers, flatulence, tumors, worms, dysbacteriosis;
- various liver diseases, pathologies in the gallbladder and biliary tract: cholecystitis, hepatitis, Gilbert's syndrome, oncology, cirrhosis of the liver, curvature of the biliary tract.
Today, a gastroenterologist is one of the most sought-after specialists. Due to the constant bustle, snacking, poor quality products, sedentary lifestyle and poor environment, diseases of the digestive system are one of the most common.
Gastroenterologists treat diseases such as:
- hepatitis (A, B, C, E and D);
- glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, nephropathy, crystalluria;
- gastritis, peptic ulcer;
- dyspancreatism;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- infections, the source of which is the gastrointestinal tract;
- urolithiasis and cholelithiasis;
- toxoplasmosis;
- intestinal dysbiosis
Intestinal dysbiosis is a violation of the natural microflora of the organ. Beneficial bacteria in the intestines not only affect the process of absorption of nutrients, but also stimulate the immune system of the human body. With dysbacteriosis, beneficial intestinal bacteria die, which leads to the development of pathogenic microflora.
The answer to the question of which doctor treats dysbiosis is quite predictable: a gastroenterologist. A highly specialized doctor deals with the intestines inside and out. A gastroenterologist can even treat a number of infectious diseases, but he does not have the right to hospitalize a person with a similar diagnosis in the gastroenterology department. Hospitalization in this case is allowed only in the infectious diseases department.
Typically, dysbiosis is treated in several stages. At the first stage, complete cleansing of the intestines occurs. Gastroenterologists prescribe intestinal cleansing using sorbents. Laxatives and enemas are extremely rarely prescribed, the effect of which is currently controversial. On the one hand, they help remove the pathogenic environment from the body, on the other, they also destroy beneficial bifidobacteria and lactobacilli.
After the intestinal cleansing has occurred, the gastroenterologist individually selects medications. Here everything depends on the state of the intestines at the time of treatment. If the population of beneficial bacteria has not been affected, then the gastroenterologist will prescribe prebiotics - chemicals that are not distorted during the digestion process. Once in the intestines, they serve as a source of nutrition for bifidobacteria and lactobacilli.
In cases where the strain of beneficial bacteria has suffered great damage, as happens in cases of taking antibiotics or enemas, it is necessary to replenish the losses with the help of probiotics, which include beneficial lacto- and bifidobacteria. Without being broken down in the gastric juice, they directly enter the intestines. Typically, within two weeks of taking live bacteria, there is a significant improvement in bowel function.
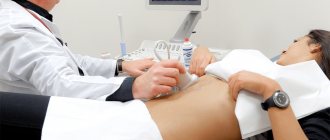
Ultrasonography
Many patients believe that an excellent option to replace gastroscopy of the stomach is an ultrasound of the abdominal organs. Unfortunately, this is not entirely true. This technique does not allow a detailed study of the condition of the stomach. At the same time, it has a number of positive aspects, the main ones being the following:
- It is completely safe.
- Does not require serious preparation (except for refusing food for 4-6 hours before the test).
- There are no contraindications for its implementation.
- The method does not require serious financial expenditure.
- Allows one to suspect the presence of many malignant neoplasms of the digestive system.
As a result, this technique cannot be a good option for replacing gastroscopy of the stomach, but due to its advantages it is used very often.
In what cases should you consult a doctor?
A mandatory visit to a doctor is necessary when:
- pain appeared for the first time;
- you feel discomfort (not pain) in your stomach for several days. If pain occurs, do not wait more than 1 day, but go to the hospital;
- suffers from flatulence for more than 2 days;
- when urinating, you feel a burning or stinging sensation, and it has become frequent;
- upset stool for more than 1 day;
- you feel pain, and at the same time there is a rise in temperature;
- irradiation of pain to the neck, shoulders in the chest area;
- During pregnancy, any abdominal pain requires immediate consultation with a doctor.