What is the difference between a carrier and a patient with hepatitis C?
Carriers of a viral infection are people who have traces of the pathogen in their bodies—antibodies or virions. In most cases, the infection is chronic with mild to moderate inflammation of the liver.
For a very long time, hepatitis C does not manifest itself in any way, which is due to the absence of pain receptors in the liver. It follows from this that people with a latent course of the disease can also be classified as virus carriers.
Many people do not understand what it means to be a carrier of the HCV virus. According to most hepatologists, HCV carrier is a vaguely worded concept that does not reflect:
- nature of inflammation;
- characteristics of the disease;
- prognosis for recovery.
In general, a person with HCV markers without obvious signs of liver inflammation is considered a carrier of hepatitis C. Patients with HCV are people with pronounced symptoms, which manifest themselves when the liver is damaged by hepatoviruses.
In medical practice, gastroenterologists and hepatologists do not use the concept of virus carriage. Conventionally, all patients with hepatitis C are divided into 2 groups - with acute and chronic inflammation of the liver. In this case, the severity of symptoms directly depends on the intensity of inflammatory reactions in the parenchyma.
Treatment methods
You already know what hepatitis C is and how this disease threatens not only the carrier, but also the people around him. For this reason, taking into account possible unfavorable directions of events (progression of the disease, its development into a chronic form or further deterioration of the patient’s condition), appropriate treatment measures may be required.
We suggest you read: Side effects of dexamethasone injections
In order to defeat the disease or put it into remission, doctors use an integrated approach, which involves the following techniques:
- Antiviral therapy;
- The use of drugs that have a beneficial effect on the liver and support its functions;
- Immunotherapy;
- Special gentle diet;
- Limiting physical activity and long rest.
Due to the fact that hepatitis is a disease of viral origin, treatment methods primarily focus on the use of antiviral drugs (often in combination). The course of therapy with such medications, their frequency and duration of use is prescribed by a doctor; it can last up to 10-12 months.
Hepatoprotectors are used as drugs used to improve liver function. They increase the protective properties of the organ and its resistance to pathogenic factors, and also have the function of restoring the structure of tissues and cells.
Dieting means completely giving up bad habits, especially drinking alcohol. As for diet, there is no clear diet, but the patient is strongly advised to abstain or reduce to a minimum the intake of fatty, fried, smoked, spicy, as well as excessively salty and sour foods.
To summarize all that has been said, it is worth noting that even if it is impossible to completely cure hepatitis C, following the doctor’s instructions and completing a full course of therapy, 97% of patients experience positive dynamics and the person returns to normal life. In addition, hepatitis C is not a death sentence; many carriers of the virus live long and happy lives with it, so there is no need to despair.
08-05-2019 – Medist
Share with friends on social networks
If a carrier of hepatitis C does not show any signs of the disease, then the virus in his body is in a latent state. Most doctors believe that such patients do not need to be treated - this can provoke the aggression of the virus, and then the disease will rapidly progress. However, a person should not hope for a quiet life - he must constantly undergo examinations so that doctors can observe the dynamics of antibodies and transaminases to the blood.
To prevent the disease from entering the active stage, an infected person needs to take maximum care of his health - do not drink alcohol, do not smoke, follow diet No. 5, and switch to gentle work. Doctors pay special attention to those categories of patients who have such serious illnesses as diseases of the cardiovascular system, diabetes, and thyroid dysfunction. Their body is weakened, so an exacerbation of the hepatitis virus can occur at any time.
Today, drugs for hepatitis C have already appeared in the world with an effectiveness close to 100%. The modern pharmaceutical industry has created drugs that have virtually no side effects. Many patients receive the first results in the form of relief of symptoms and a decrease in viral load within a week of use. Read more about generics for hepatitis C here.
It is not advisable to treat inactive hepatitis B, since the slowly developing pathological condition is not accompanied by severe clinical symptoms and destruction of the hepatic parenchyma. But carriage is a reversible process, which, when exposed to negative factors and a decrease in immune defense, can be reactivated over time, so the virus carrier cannot be called completely healthy.
Particular attention in dynamic monitoring is paid to the viral load (determining the amount of DNA of the infectious agent in 1 ml of serum). To control this criterion, virus carriers undergo a quantitative test twice a year. It must be carried out throughout your life. An increase in quantitative test results is direct evidence of the disease transitioning to an active form, which must be treated urgently.
Patients with any form of chronic hepatitis C require constant medical supervision
Patients with any form of chronic hepatitis C, including virus carriers with minimal infection activity, require constant monitoring by a doctor. This is necessary for:
- monitoring the course of the disease, since the activity of the process may change;
- determining indications for starting antiviral therapy;
- timely detection of complications.
The examination, which is carried out at least once every 6 months, includes tests for transaminase activity and the content of viral RNA in the blood. If indicated, a liver biopsy or non-invasive methods for determining the degree of liver fibrosis, for example, elastometry, are prescribed.
Hepatologists
Make an appointment
Omarova Khadizhat Gadzhievna Gastroenterologist, Hepatologist 67 reviews Price: 2000 rub. Rating: 9.5/10
Make an appointment
Mikhailoshina Elena Vladimirovna Gastroenterologist, Hepatologist 76 reviews Price: 2600 rub. Rating: 9.5/10
Make an appointment
Kovaleva Tatyana Anatolyevna Pediatrician, Hepatologist, Infectious disease specialist 133 reviews Price: 3800 rub. Rating: 9.5/10
All hepatologists »
Carriage with and without symptoms
A carrier of the hepatitis virus may not be aware of the presence of virions in the body for a long time. In 90% of cases, pathology is detected by chance during a routine examination before surgery or diagnosis of other diseases.
Virus carriage does not affect a person’s health in any way, but there is always a risk of acute liver inflammation.
If RNA-containing viruses are present in the body, local and general symptoms of hepatitis are often absent. Sometimes HCV carriers complain of:
- fatigue;
- decreased intellectual abilities;
- joint pain;
- loss of appetite;
- attacks of nausea.
During chronic and acute hepatitis, there is a latent phase during which there are no external symptoms of infection. The disease disguises itself as other pathologies, so it is not easy to detect. In case of intense inflammation of the liver, the following occurs:
- fast saturation;
- apathy;
- dyspepsia;
- discomfort in the right side;
- short-term jaundice.
The incubation period for hepatitis is 2-23 weeks. In rare cases, it lasts up to 26-27 weeks. In 95% of patients, the acute phase occurs in an anicteric form, so the symptoms are scanty. Very often, inflammation in the liver becomes chronic. In 90% of cases, virus carriers can only be identified through laboratory testing.
Functional liver tissue lacks nerve endings. When it is inflamed, a person is not bothered by pain, which is why hepatitis is also called the gentle killer.
In 60% of cases, chronic hepatitis is detected in the laboratory 6-7 months after the first symptoms - malaise, weakness, digestive disorders.
What test results indicate carriage of the hepatitis C virus?
Analysis for hepatitis carriage is carried out using serological methods and PCR diagnostics. If hepatitis C is suspected, the following is prescribed:
- ALT test;
- blood test for anti-HCV;
- polymerase chain reaction for viral RNA.
If antibodies to the causative agent of hepatitis are detected, it is still impossible to confirm its presence in the body. According to statistics, self-healing occurs in 15-30% of cases of HCV infection. Therefore, to confirm the diagnosis, additional studies are performed - ultrasound of the abdominal organs, liver biopsy.
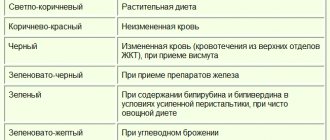
Determination of the activity of the infectious process in the liver with hepatitis C
| Intensity of inflammation | Level of antioxidant activity, rel. units | ALT relative to reference values | Ceruloplasmin activity, rel. units | Knodel index |
| insignificant | 13-18 | – | – | 1-3 |
| low | 24.4-33.5 | less than 5 | 46.5-57.9 | 4-8 |
| moderate | 15.5-24.3 | 5-10 | 38.0-46.4 | 9-12 |
| high | 15.4 | to 10 | up to 38 | 13-18 |
By the presence of antibodies in the blood (anti-HCV IgM), it is possible to distinguish a carrier of the virus from a patient with hepatitis. If IgM is not detected by analysis, and ALT is within the normal range, we are talking about virus carriage.
Diagnostics
It is not possible to determine the carriage of hepatitis C by visual examination; the patient does not have a typical clinical picture. Diagnosis is carried out in a laboratory.
Many pathogenic microorganisms are found in human tissues without causing clinical symptoms. Therefore, it is important to undergo an annual medical examination with laboratory tests.
This is interesting: Quantitative determination of hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA by PCR
There are several methods for determining the pathogen, each of them can be false negative or false positive. Therefore, the doctor prescribes several tests. For analysis, blood is taken from a vein, examining it on semi-automatic analyzers.
| Methodology | Description |
| Antibody determination | Immune cells (antibodies to hepatitis) aimed at fighting against the pathogenic microorganism are determined in the biological fluid. They can only be detected 1-3 months after infection from a carrier, so repeated analysis is necessary |
| PCR | Determination of the genotype of the virus and its components. The reproduction rate and activity of hcv are studied. The technique is used to make a diagnosis and determine the effectiveness of treatment (if it is prescribed correctly, the concentration of the pathogen decreases) |
| Biopsy | Informative method. Detects hcv RNA, inflammation, fibrotic disorders, scarring, degree of cell death |
| UAC | Detects deviations in biological fluid; by testing, the doctor may suspect a disease. Leukocyte counts are increased, platelets are decreased |
| Biochemistry | Determination of liver enzyme levels to diagnose liver damage. The higher the indicator, the more active the process of necrosis and liver dysfunction |
| Coagulogram | With hepatitis C, hepatic prothrombin, which is involved in blood clotting, decreases. Therefore the process slows down. Blood does not clot, wounds bleed for a long time |
If HCV is detected in the patient’s body, the test is repeated to prevent medical errors. A carriage determined in two or more tests is considered correct.
An ultrasound and CT scan of the liver are performed to diagnose hypertrophy (enlargement), necrosis or scarring of the tissue.
Can a carrier infect another person?
Hepatitis carriers with minimal intensity of liver inflammation do not complain about their health. But regardless of the concentration of RNA viruses in the blood, they spread the infection. Viral particles are transmitted in several ways:
- parenterally through infected blood;
- during sexual intercourse through seminal fluid and vaginal discharge.
Patients with indolent (chronic) hepatitis pose the greatest danger to others. The virus can survive for a long time on hygiene items and medical instruments.
Sources of viral infection are people with latent and active hepatitis, carriers of HCV. In most cases, infection occurs during tattooing, piercing, and dental services.
Rules for inactive media
Doctors recommend that hepatitis B carriers follow certain rules to reduce the likelihood of infecting other people:
- Maintain good hygiene and do not let other people use your personal belongings (razors, toothbrushes, etc.);
- Give up bad habits. Medical research shows that tobacco and alcoholic beverages weaken liver function, which can lead to increased growth of harmful viruses;
- Periodically undergo a full medical examination to understand how the virus develops and what danger it poses to you and the people around you. If necessary, you should undergo full medical treatment to finally defeat hepatitis B.
Life expectancy of virus carriers
Carriage of hepatitis C poses a threat to both the carrier and those around him. Under certain conditions, the virus is activated, which can lead to liver inflammation. But virus carriage itself does not affect human health in any way.
The life expectancy of HCV carriers depends on many factors:
- method of acquiring carrier status;
- lifestyle;
- immune status;
- age;
- gender;
- concomitant chronic diseases.
In 1/3 of virus carriers, the disease enters the active phase 45-50 years after the infection enters the blood. In another 30% of HCV carriers, the duration between acute inflammation and cirrhotic changes in the liver is 15-20 years. With rapid progression of hepatitis, appropriate immunostimulating or antiviral therapy is prescribed.
HCV carriers who do not follow medical recommendations put themselves at serious risk. Drinking alcohol, smoking and other bad habits negatively affect the functioning of the immune system. When the body's resistance to infections decreases, virions quickly divide, which leads to acute inflammation of the liver. The course of hepatitis in such patients is complicated by cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma already 5-7 years after activation of the virus.
Who is a virus carrier?
A carrier of the hepatitis C virus – what does this mean for the patient and others? The definition makes it clear that the human circulatory system contains the body of the causative agent of a dangerous pathology. Upon contact with it, infection occurs. At the same time, the patient himself may completely lack any external manifestations of the disease, and he can lead a full-fledged lifestyle.
Attention! A person who carries the hepatitis C virus not only poses a danger to others, but is also considered sick himself. After all, the absence of a clinical picture is due only to the ability of the immune system to contain the disease.
It should be understood that sluggish symptoms do not indicate a “dormant” disease; it still progresses, albeit very slowly. In carriers, irreversible changes in hepatocytes also gradually occur.
While an effective vaccination has been developed against the type B virus, which avoids infection, there is no vaccine against hepatitis C. A vaccine cannot be created due to the increased mutagenicity of the virus. Even after complete recovery, there is always a risk of re-infection, since the antibodies produced do not react to other mutated strains.
Is this type of carriage treatable?
Virus carriage is a reason to get quality treatment. Timely destruction of the hepatitis causative agent leads to complete recovery.
In the fight against HCV carriage, interferon-free treatment regimens are most effective. Direct antiviral drugs are well tolerated by carriers and patients with acute and indolent hepatitis.
Various treatment methods are used to combat infection:
- Immunotherapy. To increase the body's resistance to viral infection, HCV carriers are prescribed interferon drugs in combination with Ribavirin. The duration of 1 course is 25 days. If resistant strains of the virus are identified, it is extended to 48 days. Depending on the indications, basic therapy includes antihistamines, enzymes to improve digestion and detoxification agents.
- Antiviral therapy. In modern hepatology, interferon-free treatment regimens are increasingly being used. Direct antiviral medications are much less likely to cause adverse reactions and increase the chances of completely eliminating the infection in the host’s body. The therapy includes Daclatasvir, Sofosbuvir, Ledipasvir, Grazoprevir and their generics. Medicines interact with the nucleic acids and proteins of the pathogen, preventing them from copying themselves.
To reduce the load on the liver, carriers of the virus should adhere to table No. 5 according to Pevzner. As part of diet therapy, refractory fats and foods that stimulate the production of liver enzymes are limited - canned vegetables, smoked meat.
With proper and timely treatment, complete recovery can be achieved. Ignoring the problem is dangerous due to the activation of HCV and the transition of inflammation to a chronic form.
Does the virus carrier require treatment?
If the carrier has only antibodies to hepatitis C, and there is no virus in the body, he does not require treatment. Doctors will insist on periodic examinations and monitoring of health status to exclude errors in diagnosis. If the patient is a carrier of the virus, then it is extremely important to undergo comprehensive antiviral treatment.
Although there are no symptoms of the disease at this stage, they may appear in the near future. The likelihood that the virus will never become active and the body will overcome the disease on its own is extremely low. Over time, the disease will become chronic. Its result is cirrhosis of the liver or liver cancer and the death of the patient.
Until recently, hepatitis C was considered incurable. Now the situation has changed dramatically. Western scientists have developed drugs that act directly on the virus. They work in two directions - they reduce its activity and prevent mutations within the body.
In this way, a sustained virological response can be achieved within 12 weeks. Patients who already have symptoms of the disease and carriers of hepatitis C should undergo similar regimens.
According to statistics, approximately 30% of HCV carriers experience complete disappearance of the virus without therapy. That is, the immune system itself reacts to the virus and secretes antibodies that stop the carriage of HCV. This is possible before the onset of the disease or at the stage of acute hepatitis C. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends treating HCV at any stage.
After the acute form, the disease enters the chronic stage. In this case, treatment is necessary, because chronicity means the inability of the immune system to cope on its own. Untreated hepatitis C leads to diseases that can be fatal. Most often, the liver suffers from cirrhosis, fibrosis or cancer.
According to WHO recommendations, the main treatment is a course of 2-4 months with the prescription of direct antiviral drugs. These are Sofosbuvir, Ledipasvir, Daclatasvir, Pibrentasvir and their analogues. By acting directly on the pathogen, these drugs reduce the viral load, which reduces damage to the liver.
However, in addition to the cost of drugs, there is another limitation - therapy is not prescribed to children under 12 years of age who are HCV carriers.
To alleviate the condition, vitamins and sorbents are prescribed to improve the functioning of the immune system and relieve symptoms of intoxication.
A separate case is the treatment of HCV during pregnancy. The risk of transmission of the virus from a mother with HCV carriage to the fetus is very low, about 3-5%, so the health of the unborn child is not at risk. The real danger is taking medications for the virus that have a negative effect on the fetus. During pregnancy, doctors should suspend treatment for hepatitis C unless there are serious reasons (exacerbation or worsening of the woman's condition).
The doctor monitors the multiplication of the virus based on test results and, if necessary, prescribes drugs to suppress the virus. It is noteworthy that even after treatment, when the Australian antigen is not detected in the blood, the risk of developing liver necrosis and cirrhosis still exists.
Rules of caution for hepatitis C carriers
Carriers of a viral infection should remember the possibility of infecting other people with hepatitis. To prevent infection of family members and others, it is necessary:
- inform doctors about virus carriage before carrying out diagnostic measures or taking blood;
- use barrier contraceptives during sexual contact;
- warn tattoo parlors and dentists about HCV carriage;
- use only personal hygiene products.
When planning pregnancy, hepatitis C carriers should be aware of the risk of infection of the fetus. Infection occurs during delivery or in utero, since virions can cross the placental barrier. The probability of transmission of infection from mother to fetus is 7-10%.
Possible complications of virus carriage
Carriage is fraught with activation of the virus at any time, intense inflammation of the liver and the transition of hepatitis to a sluggish form. When inflammation becomes chronic, the prognosis for recovery worsens. In case of severe disease, complications arise:
- aplastic anemia;
- neuritis;
- liver scarring;
- abdominal dropsy;
- portal hypertension;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- hepatocellular carcinoma.
In 90% of cases, death from hepatitis occurs as a result of cirrhotic changes in the liver or carcinoma.
How to live with a person with HCV
People living with someone who has HCV should always be aware of the risk of infection. To avoid hepatitis infection, you need to:
- exclude close contact with the carrier - kissing, sex without barrier contraceptives;
- hide personal hygiene products from children - razors, toothbrushes;
- provide first aid for injuries only with rubber gloves.
If others and HCV carriers follow medical recommendations, the risk of contracting the infection is reduced to zero. To avoid complications, relatives of patients with hepatitis should be tested annually. Timely completion of interferon-free therapy in most cases leads to recovery.