General rules
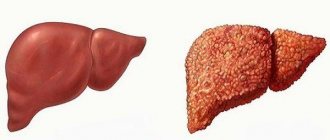
Among the types of hepatitis, hepatitis C is the most dangerous. significantly higher than with hepatitis A. In 75% of cases it becomes chronic, and 20-40% of patients suffer from liver cirrhosis , and in 1-4% hepatocellular carcinoma . hepatitis C virus RNA is detected in a patient’s blood for 6 months, we can talk about a chronic form of the disease. The disease is potentially fatal. Progressive liver damage often occurs without symptoms and appears at the stage of cirrhosis , when treatment is no longer effective.
The main route of transmission is through blood, which is why the disease is spreading due to syringe addiction and the reusable use of unsterile needles. Other routes of infection are also possible: hemodialysis , blood transfusion, damage to the skin with unsterile needles, transmission through saliva and during sexual intercourse. When a virus enters the body, two options are possible:
- Acute hepatitis (icteric or anicteric form) with mandatory clinical symptoms of hepatitis (liver enlargement, intoxication, asthenic and dyspeptic syndromes ).
- Asymptomatic form - there are no complaints or symptoms characteristic of hepatitis.
Acute manifest forms are mild, moderately severe and severe. In some cases, a protracted course is observed: with prolonged jaundice and an increase in enzymes in the blood. The asymptomatic form is the most common, but is not detected in the acute period. Patients are unaware that they have an infection and serve as a source of infection for others. Subsequently, subclinical forms may end in recovery or develop into chronic hepatitis.
Recovery is observed in 15-25% of all cases of acute hepatitis, in other cases there is a transition to a chronic form. In the chronic course, clinical manifestations are insignificant: increased fatigue, weakness, bad mood, there may be a decrease in appetite, nausea after fatty or spicy foods. In the chronic form with high activity, the disease has a wave-like character - periods of exacerbation are replaced by remission. Repeated exacerbations end in transition to viral cirrhosis of the liver .
Treatment and diet for hepatitis C
Treatment for hepatitis C is expensive and the likelihood of recovery is low. For treatment, it is recommended to use Roferon A (interferon alfa-2a). Interferon therapy is indicated for patients from 18 to 60 years of age, in the presence of a constant increase in the levels of ALT and HCV RNA in the blood. 3 million IU is administered 3 times a week for a year if HCV RNA disappears after 3 months from the start of treatment. If detected after 3 months of treatment, it is not advisable to continue therapy. Treatment with IFN alpha is most effective when the level of viral RNA is low and the presence of moderate histopathological changes in the liver according to biopsy results.
In addition to interferon alpha-2a, ribavirin can be used . There are several treatment regimens: IFN alpha, ribavirin in combination with IFN alpha, ribavirin alone, corticosteroids with ribavirin.
And interferon therapy is absolutely effective in 35% of patients, in 65% of cases it contributes to the positive dynamics of liver transaminases and in 29% has a supporting effect. However, 50-90% of patients experience a re-exacerbation after withdrawal. Pegasys can be considered very promising . Long-term removal of it from the body makes it possible to prescribe it once a week. Official medicine is against using fasting treatment for viral hepatitis. This is due to the fact that:
- The liver does not receive nutrients and may lose 50% of its volume. It is a metabolic , so patients experience profound metabolic disorders.
- During fasting, toxins from the intestines are absorbed and pass through the liver.
- The viral load is increasing.
- Prolonged fasting in cirrhosis can contribute to the development of hepatic encephalopathy.
It should be borne in mind that there is no confirmed data on the high effectiveness of fasting for this disease. Isolated cases of improvement in health status cannot be taken into account. Certain restrictions and exclusion from the diet of foods and foods that are harmful to the liver are considered a therapeutic diet, not fasting.
Factors such as alcohol abuse and poor diet greatly accelerate the process of liver damage. What diet should be used for hepatitis C? Patients should follow Diet No. 5 during remission, and during exacerbation - No. 5A . The range of products in this option corresponds to Diet No. 5, but it involves more thorough culinary processing - boiling and mandatory mashing or pureeing. The diet is applied for 2-4 weeks, and then the patient is transferred to the main table.
The general principles of nutrition for patients are:
- Providing complete protein (1.0–1.2 g per kg of weight).
- An increase in its content in fatty hepatosis . It has been noted that with viral hepatitis C there is pronounced fatty degeneration of hepatocytes.
- Protein restriction in liver failure in the stage of decompensation and threatening coma.
- Adequate fat content up to 80 g/day.
- Providing complex carbohydrates (they should make up 50% of the energy value) through the consumption of cereals, cereals, vegetables and fruits.
- Enrichment of the diet with vitamins ( group B , C , folates ).
- Control of salt content (limit to 8 g, and for edema and ascites - up to 2 g).
- Inclusion of specialized products in the diet (protein composite mixtures for protein correction of the diet).
The diet should not contain foods that irritate the bile ducts, as well as poorly digestible refractory fats. Patients with chronic hepatitis C are characterized by weight gain, which is due to increased calorie intake due to animal fats and large amounts of simple carbohydrates, so they are limited in their diet.
The diet for hepatitis C should contain a sufficient amount of protein, since its consumption reduces catabolic processes (decomposition), normalizes the patient’s immune status and improves liver function. Eating adequate amounts of protein is essential for muscle maintenance and liver cell regeneration.
The patient's diet is enriched with lipotropic products - they improve metabolic processes in the liver cell and prevent the development of fatty degeneration. This is lean beef, milk, whey, cottage cheese, soy, soy flour. Food is steamed, stewed, boiled or baked and served warm 5 times a day. In the basic diet, food is not crushed.
The diet must contain a sufficient amount of vitamins (group B, folic and lipoic ).
Sources of folic acid: lettuce, onions, parsley, beans, beans, lentils, broccoli, cauliflower and Brussels sprouts, regular cabbage, carrots, corn, watermelon, tomatoes, pumpkin, beets, asparagus. Lentils contain almost half of the daily value. Fruits include oranges, lemons, mineole, pears, apples, raspberries, currants, apricots, strawberries, bananas, kiwi, grapes, pomegranate, papaya. It contains: buckwheat, wheat and rye, but the amount decreases during cooking. The vitamin will be fully absorbed if you eat sprouted grains.
Lipoic acid is contained in beef, all types of cabbage, green peas, bell peppers, pumpkin, beets, onions, cassava, eggplant, rice, buckwheat, oatmeal, beef, sour cream, fermented milk drinks, eggs, pomegranate, apricots, persimmons, cherries, oranges, apples, plums, quinces, figs, black currants, mulberries, blackberries, hazelnuts, almonds, cashews.
For patients with chronic liver diseases, the supply of selenium, copper, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus is important, and in case of cirrhosis - also zinc. It has been established that zinc deficiency increases the phenomena of hepatic encephalopathy . You need to include foods with these microelements or supplement them by taking mineral-vitamin complexes.
Sources of selenium include seafood, Brazil nuts, whole grains, wholemeal flour, poultry liver, beef and pork liver, wheat bran, rice, wheat, corn.
Magnesium can be obtained by eating sesame seeds, cashews, almonds, Brazil nuts, bananas, dried apricots, prunes, grapefruit, mangoes, melons, soybeans, black beans, peanuts, leafy vegetables, pumpkin, artichoke, chard, halibut, snapper, and flounder.
High calcium content in dairy products, citrus fruits, sesame seeds.
Copper, together with vitamin C, reduces the activity of viruses and is especially important for hepatitis. Sources of copper are soybeans, hard cheeses.
Known sources of zinc include seafood, beef, animal liver, wheat bran, kohlrabi, peanuts, pine nuts, Brazil nuts, walnuts, poppy seeds, sesame seeds, pumpkin seeds and sunflower seeds.
Most patients with liver disease have vitamin D . This vitamin is produced in the body under the influence of solar radiation. But for patients with hepatitis, solar radiation can be harmful. It can worsen the course of the disease and reduce the effectiveness of antiviral treatment if the patient receives it. In addition, riboverine and sofosbuvir cause photosensitivity (sun allergy), accompanied by rash, itching and even sunburn. In this regard, you should avoid prolonged exposure to the sun and take sunbathing before 10 a.m. after 6 p.m. Sunscreen with SPF 30 and protective clothing must be used.
Vitamin D can be obtained from food. These are herring, cod and halibut liver, sour cream, salmon, mackerel, fermented milk products, cottage cheese, butter. Sometimes you can afford these high-calorie foods.
For hepatitis, you can arrange fasting days: apple (up to 1.5 kg per day), vegetable (the same amount of raw vegetables, can be partially replaced with fruits), cottage cheese (norm 500 g), kefir (1.5 liters per day).
In case of liver cirrhosis with symptoms of liver failure, the amount of protein in the patient’s diet is limited. This is necessary to prevent encephalopathy.
The patient should consume mainly vegetable protein (green peas, legumes, quinoa, nuts, seeds, sesame). At the same time, protein mixtures with branched amino acids are introduced into the diet. An increase in carbohydrates in the diet due to simple and complex ones is also shown.
The use of dietary fiber is provided (cereals, wholemeal bread, vegetables, fruits, bran). Soluble dietary fiber (fruits, vegetables, dried beans, lentils, soy, oatmeal, rice, barley, nuts, seeds) and poorly absorbed disaccharides (lactulose) affect nitrogen metabolism in the intestines and are useful for liver failure. The use of zinc supplements is also important.
For mild encephalopathy, protein restriction is introduced for a short time. The amount is limited (50-75% of the age norm) to prevent cerebral edema. With progressive deficiency in a precomatous state, animal protein is completely excluded and fats are sharply limited/excluded. The patient should receive easily digestible carbohydrates in sufficient quantities: fruit and berry juices, tea with sugar, infusion of dried fruits, jelly and compotes.
Patients are prescribed parenteral nutrition, and the drinking regime is under strict control, as ascites and edema . Effective nutritional support includes enteral nutrition: docasohexaenoic acid and structured lipids, branched chain amino acids. This makes it possible to ensure normal nutrition and improve the quality of life of patients.
During the period of recovery from a coma, protein is gradually introduced into the diet and its amount is increased. A long stay on a protein-free diet does not ensure normal reparative processes in the liver. Mild ascites, which does not cause much discomfort during breathing and movement, often does not require salt restriction. In more severe cases, salt is limited to 1-2 mmol/kg body weight.
Hepatitis C: what can you eat and what can’t you eat?
During the course of treatment for hepatitis C, you should adhere to certain nutritional principles:
- Eat around the same time.
- Split meals into 5-6 times (less is better, but more often).
- read calories. More than 2,500 calories per day are allowed.
- Products can be baked, boiled, steamed. Frying in a frying pan costs nothing.
- The food you eat should be neither too cold nor too hot. It's best if they are at room temperature.
- The volume of water you need to drink per day is 1.5-2 liters.
- The amount of salt eaten per day should not exceed one teaspoon.
- It is necessary to limit the consumption of fats and fast carbohydrates and increase the percentage of protein and vitamins.
As the disease progresses, it is worth helping him in the process of assimilation of food. At this time, all food should be pureed, crushed and homogenized.
Authorized Products
Proper nutrition during remission includes:
- Lean meat and poultry (beef, chicken, turkey, veal should be preferred; pork can be consumed in limited quantities), prepared by boiling and baking after boiling. For variety, you can prepare dishes from minced meat (cutlets, zrazy, quenelles, meatballs, casseroles).
- Low-fat fish, which should be included in the diet more often than meat, since it is easier to digest. Fish dishes are also prepared boiled and baked. They use cod, blue whiting, pike perch, pollock, navaga, pike, and hake.
- Sour cream or milk sauces for meat, fish and vegetable dishes. These sauces are used for baking.
- Soups with vegetable broths. They are prepared with cereals, pasta or vegetables. During the period of remission, the components of soups are not crushed, and the diet is expanded to include borscht and cabbage soup, which can be cooked with Savoy cabbage if white cabbage causes bloating. A prerequisite for preparing first courses is not to use fried vegetables and limit the amount of tomato paste.
- Gray and white bread, maybe rye and with bran. Any bread is consumed dried. Patients can eat biscuits, biscuits, and baked pies made from soft dough.
- Many vegetables (excludes radishes, garlic, mushrooms, green onions, pickled vegetables). They are consumed raw or stewed. You can make puree from green peas. Green peas are a light protein food that, unlike dishes made from mature legumes, does not cause bloating. You can add non-acidic sauerkraut to vinaigrettes, and season dishes with dill and parsley.
- Fruits and berries in any form. The only condition is that they must be ripe. Dried fruits are useful for patients because they contain microelements necessary for this disease. Compotes, jelly, and jelly are prepared from fruits.
- Moderate amount of sweets. There may be meringues and meringues, marmalade, caramel, candies without chocolate, natural marshmallows, jam and honey.
- Eggs are consumed in the form of omelettes or soft-boiled.
- Butter (20-30 g), as it is highly digestible and contains fat-soluble vitamins. It is necessary to limit refractory fats due to the fact that they are poorly absorbed and cause the development of fatty liver degeneration. It is very important to consume vegetable oils, which enhance bile formation and bile secretion. Unsaturated fatty acids in vegetable oils activate lipolysis (fat breakdown) and improve cholesterol metabolism. You can use any unrefined oils (olive, cottonseed, soybean, sunflower, flaxseed, corn). They are added in their natural form to dishes. The amount depends on tolerance - usually 2-3 tbsp. l.
- Low-fat dairy products, which have a lipotropic effect, should be present in the diet daily. In addition, they provide the patient with calcium. You can consume kefir, yogurt without additives, acidophilus, yogurt, low-fat cottage cheese and milk as part of your meals. Sour cream is used as a seasoning for dishes.
- Any cereals from which porridges, casseroles with vegetables and cottage cheese are prepared.
- Weak green tea, herbal tea, still water, vegetable and fruit juices, rosehip infusion.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| parsley | 3,7 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 47 |
| iceberg lettuce | 0,9 | 0,1 | 1,8 | 14 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
| dried figs | 3,1 | 0,8 | 57,9 | 257 |
| dried apricots | 5,2 | 0,3 | 51,0 | 215 |
| dried apricots | 5,0 | 0,4 | 50,6 | 213 |
| prunes | 2,3 | 0,7 | 57,5 | 231 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| noodles | 12,0 | 3,7 | 60,1 | 322 |
| buckwheat noodles | 14,7 | 0,9 | 70,5 | 348 |
Bakery products | ||||
| bran bread | 7,5 | 1,3 | 45,2 | 227 |
| whole grain bread | 10,1 | 2,3 | 57,1 | 295 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| milk candies | 2,7 | 4,3 | 82,3 | 364 |
| fondant candies | 2,2 | 4,6 | 83,6 | 369 |
| fruit and berry marmalade | 0,4 | 0,0 | 76,6 | 293 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
| Maria cookies | 8,7 | 8,8 | 70,9 | 400 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
Dairy | ||||
| kefir 1.5% | 3,3 | 1,5 | 3,6 | 41 |
| Ryazhenka | 2,8 | 4,0 | 4,2 | 67 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 1% | 16,3 | 1,0 | 1,3 | 79 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken breast | 29,8 | 1,8 | 0,5 | 137 |
| boiled chicken drumstick | 27,0 | 5,6 | 0,0 | 158 |
| boiled turkey fillet | 25,0 | 1,0 | — | 130 |
Eggs | ||||
| soft-boiled chicken eggs | 12,8 | 11,6 | 0,8 | 159 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| flounder | 16,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 83 |
| pollock | 15,9 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 72 |
| cod | 17,7 | 0,7 | — | 78 |
| hake | 16,6 | 2,2 | 0,0 | 86 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| peach juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,5 | 40 |
| plum juice | 0,8 | 0,0 | 9,6 | 39 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Diet for acute hepatitis
It was already mentioned above that in the acute form there are more restrictions than in the chronic form. During an exacerbation, the liver does not produce a sufficient amount of bile and performs other functions poorly. In this regard, it does not need to be overloaded. It is recommended to eat in very small portions, adhering to the fractional principle. At the same time, nutrition must be correct; harmful foods should be excluded from the diet.
In the acute period of hepatitis C, animal fats are completely contraindicated. They need to be completely removed from the menu. The exception is butter, but it should also be consumed in small quantities. But the amount of vegetable fats, on the contrary, should be increased. They help normalize lipid metabolism. In addition, vegetable fats reduce cholesterol levels.
It is imperative to include a large amount of protein in your diet. It is found in meat, fish, poultry, and eggs. Fast carbohydrates are needed, but they should be consumed only in the first half of the day. It is important to eat a lot of vegetables, as they contain healthy fiber and saturate the body with necessary substances: vitamins and microelements.
As for drinking, it should be plentiful. Naturally, with hepatitis there can be no talk of alcoholic beverages. Alcohol has an extremely destructive effect on the liver, even in small doses, so you should avoid it completely.
The method of preparing food is important. Products can be cooked traditionally or steamed. It is also recommended to grind food into purees.
The main dishes included in the diet for hepatitis C are porridge, vegetable soups, and boiled vegetables. You can use juices, jelly, fruit drinks, compotes as drinks.
Fully or partially limited products
- Fried foods, since heat treatment of fats produces oxidation products that have an adverse effect on the liver.
- Highly extractive dishes (stews, broths).
- Products with any chemical additives.
- It is forbidden to consume fatty meat and fish, cooking fats, goose and duck meat, sausages, canned food, smoked meats, lard, salted fish, full-fat milk, cottage cheese and cream. All these products are difficult to digest and put a lot of stress on the liver.
- Fresh bread, yeast baked goods, cakes and pastries with butter cream, puff pastry.
- Products containing essential oils and oxalic acid.
- Foods high in cholesterol .
- Kvass, legumes and white cabbage (if poorly tolerated), as they can cause flatulence .
- Hard-boiled and fried eggs, as in this form they are difficult to digest.
- Spicy seasonings and sauces.
- You should not drink black coffee, cocoa and chocolate.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| peas | 6,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 60 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| chickpeas | 19,0 | 6,0 | 61,0 | 364 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
| marinated mushrooms | 2,2 | 0,4 | 0,0 | 20 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| peanut | 26,3 | 45,2 | 9,9 | 551 |
Snacks | ||||
| potato chips | 5,5 | 30,0 | 53,0 | 520 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| vareniki | 7,6 | 2,3 | 18,7 | 155 |
| dumplings | 11,9 | 12,4 | 29,0 | 275 |
Bakery products | ||||
| buns | 7,9 | 9,4 | 55,5 | 339 |
| Rye bread | 6,6 | 1,2 | 34,2 | 165 |
Confectionery | ||||
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
| shortbread dough | 6,5 | 21,6 | 49,9 | 403 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 4.5% | 3,1 | 4,5 | 4,7 | 72 |
| cream 35% (fat) | 2,5 | 35,0 | 3,0 | 337 |
| whipped cream | 3,2 | 22,2 | 12,5 | 257 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| parmesan cheese | 33,0 | 28,0 | 0,0 | 392 |
Meat products | ||||
| fatty pork | 11,4 | 49,3 | 0,0 | 489 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| salmon caviar granular | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| salmon | 19,8 | 6,3 | 0,0 | 142 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| salmon | 21,6 | 6,0 | — | 140 |
| trout | 19,2 | 2,1 | — | 97 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| dry red wine | 0,2 | 0,0 | 0,3 | 68 |
| vodka | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 235 |
| beer | 0,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 42 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| soda water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| cola | 0,0 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 42 |
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| sprite | 0,1 | 0,0 | 7,0 | 29 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| tomato juice | 1,1 | 0,2 | 3,8 | 21 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Prohibited Products
The diet for hepatitis A prohibits foods that force the liver to work harder, cause increased bile production and significant secretion of the pancreas.
Products that irritate the stomach and promote increased gas formation and fermentation in the intestines are also not welcome. All these products (extractives, purines, refractory fats, fried foods) create additional stress on the affected organ and should be excluded.
The list of prohibited products includes:
- fresh bread, pastries, especially muffins, fatty and fried pies, pancakes, pancakes;
- strong and rich broths from meat, fish, poultry, mushrooms and soups made from them, as well as okroshka;
- fatty and stringy meats: pork, old beef, lamb, poultry, chicken with skin;
- fatty fish: salmon, tuna, halibut, mackerel, cod, smelt, sardines.
- any canned fish and meat, all types of sausages, meat and fish snacks;
- smoked and salted foods (ham, herring, etc.);
- pork, lamb lard, margarine, mayonnaise, spreads;
- all types of poultry, except chicken, offal;
- eggs, hard-boiled or fried;
- seasonings: pepper, horseradish, mustard, vinegar;
- vegetables: green onions, garlic, sorrel, radish, radishes, spinach, legumes, as well as pickles and pickled vegetables;
- caviar, mushrooms in any form, especially salted and pickled;
- strong tea, coffee, cocoa, sweet carbonated drinks, especially cold ones;
- ice cream, pastry creams, cakes, pastries, chocolate;
- high-fat milk, cream, sharp and salty cheeses;
- all dishes prepared by frying.
Menu for hepatitis C (Diet)
It is not difficult to create a food menu for the week, since the list of permitted foods is wide. The patient can be offered snacks (salads of raw and boiled vegetables, seasoned with vegetable oil or low-fat sour cream, grated carrots, vinaigrettes, green peas with pickled peeled cucumbers, jellied fish or meat). Alternating protein dishes diversifies the diet.
It is useful for patients to eat pumpkin, which is very useful for liver diseases. It normalizes liver function, prevents liver obesity and has a choleretic effect. Pumpkin pulp contains large quantities of polysaccharides - pectins , which play the role of an enterosorbent - they absorb toxic substances, plant poisons and heavy metals. You can include boiled, stewed and baked pumpkin with apples or cottage cheese in your diet.
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Diet goal
The diet for hepatitis C is prescribed for the following purposes:
- liver protection;
- normalization of the functioning of this organ;
- elimination of inflammatory processes;
- normalization of metabolism;
- prevention of cirrhosis.
Under no circumstances should you give up your diet, as this can lead to serious negative consequences. In general, the same rules apply here as in the case of other hepatitis, but the diet may undergo changes. The menu is adjusted if a person is also sick with other diseases. Changes are also made if we are talking about a pregnant woman or a minor patient.
For acute and chronic hepatitis, different diets are used. In general, they are not too different, but during an exacerbation you have to adhere to a much greater number of restrictions than during the chronic course of the disease.
Recipes
The dishes of the fifth table are quite varied and this diet can be compared with a common table, but in comparison with it, this therapeutic diet does not include the consumption of fried foods. Remember that the main thing is low-fat and non-fried foods. A quick breakfast option can be milk porridge, omelettes, boiled eggs or cottage cheese with dried fruits.
Light snacks can consist of baked pumpkin and baked apples, juice with cookies, pumpkin porridge or carrot-pumpkin puree with dried fruits. Below are options for first and second lunch courses. Use vegetables more widely: cauliflower, Savoy or Brussels sprouts can be cooked in milk or sour cream sauce, vegetable stew, potato roll with peas and carrots, cabbage rolls with vegetables, zucchini stuffed with vegetables and rice.
Using modern technologies, many dishes can be prepared in a slow cooker - this will save time and diversify your diet. In it you can make low-fat casseroles and muffins from healthy oat or buckwheat flour with dried fruits. You can choose simple recipes for dishes that require little time to prepare.
First meal
Cauliflower soup
Potatoes, carrots, sweet peppers, cauliflower, butter.
Place diced potatoes into boiling water. After 10 minutes, add carrots, bell peppers, cabbage disassembled into inflorescences and bay leaves. Cook until the vegetables are ready, add salt and a little green onion. Before serving, add butter.
Oatmeal soup with milk and prunes
Oatmeal, water, milk, salt, prunes.
Boil oatmeal in water, mash, add salt (add sugar for dessert). Add milk to the desired consistency, heat again, add prunes and let it brew. At the end add butter.
Second courses
Fish soufflé
Beat the boiled pollock or hake fillet in a blender, add butter, semolina and egg yolks. Knead well, add a little salt and fold in the beaten egg whites. Place in pan and bake.
Steamed fish with vegetables
Hake fillet, cauliflower, zucchini, green beans, carrots, butter. Chop vegetables randomly. Place vegetables, fish fillets in a steaming dish, add bay leaf and salt. Steam, pour melted butter over the finished dish and sprinkle with lemon juice.
What not to eat if you have hepatitis
Prohibited foods for hepatitis are those that negatively affect the liver, worsening its condition. The hardest thing for the liver to cope with is alcohol and its derivatives; they must be completely abandoned.
One of the functions of the liver is to cleanse the blood of toxins and harmful chemicals, so while following a diet you need to avoid complex industrial products with artificial colors, flavors, and preservatives. It is best to eat home-cooked meals.
Refractory fats place a greater burden on the liver. Their use is reduced to zero.
List of foods that should not be consumed:
- alcoholic drinks, sweets with liqueur and rum;
- animal fats;
- fatty meats, fish, broths based on them;
- canned fish and meat;
- smoked meats;
- pickles, marinades;
- fast food products;
- baked goods;
- chocolate;
- coffee, carbonated sweet water;
- hot spices.
During periods of exacerbation, it is not allowed to eat cold or too hot food; after cooking, food is served in crushed form.
Since hot spices are prohibited, some are interested in whether it is possible to eat garlic if you have hepatitis. Garlic is a healthy product for the liver, as it prevents cell destruction and stimulates the secretion of bile. But it is recommended to consume no more than 3 g of garlic per day.
Reviews and results
Patients with liver disease should adhere to a diet constantly, given that the disease tends to progress. This healthy diet does not burden the digestive organs and does not cause deterioration of the condition. Reviews from patients once again confirm this. The food is nutritious and quite varied, so patients do not consider themselves disadvantaged in anything.
- “...Hepatitis C was discovered by accident. I was worried about fatigue, I was constantly tired and nothing made me happy. She was tested and found to have elevated liver enzymes. I repeated the tests for three months and the third time they showed the presence of hepatitis. I know that I am incurable, although they offer very expensive treatment. You need to maintain a healthy lifestyle, no alcohol, diet and moderate physical activity. I have a more fruit and vegetable diet. Be sure to eat low-fat cottage cheese, oatmeal, carrots, beets, a lot of pumpkin and chicken every day, drink flaxseed oil and freshly prepared juices. I allow myself soaked herring and natural brewed coffee. Ban on smoked, fried and fatty foods”;
- “... The doctor said that with hepatitis C you need to constantly adhere to a diet. Given my weight, she is not overweight. I eat everything boiled or baked. I add herbs (fresh or dried) and sometimes a little pepper to my dishes. The food is complete and you don’t have to go hungry, you just need to find recipes for dietary dishes. If I eat dishes with seasoning, then I don’t feel very good. Although saffron, turmeric, anise, cinnamon and ginger are actively used in Indian medicine, including for hepatitis. Of course, my diet does not include fatty, smoked or fried foods. I bought myself a slow cooker and now I cook everything in it. My family thinks that I eat bland food, but I’m already used to it. I believe that following a diet helps maintain good health, although it involves additional hassle and time.”
Hepatitis C: causes and consequences
One of the most complex and dangerous diseases of our time is hepatitis C. No one is officially talking about a pandemic, but statistics claim that there are currently more than 500 million carriers of this virus registered in the world.
It is extremely difficult to detect the disease at an early stage, since the acute phase is practically asymptomatic. And the chronic form may require treatment for several months or even years. With such long-term therapy using potent drugs that often negatively affect the immune system, proper nutrition and a diet appropriate to the patient’s condition are a prerequisite.
Is it possible to follow a diet for patients with hepatitis C?
Dietary nutrition for hepatitis C is encouraged. You should avoid new-fangled diets aimed at reducing body weight. Treatment table No. 5 for men and women is designed to reduce the load on the liver, without excluding vital substances necessary for the healthy functioning of the body: protein, healthy fats, omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, fat-soluble and water-soluble vitamins, amino acids, antioxidants .
Conventional diets, which simply limit the diet and are so loved by many women, may not have a therapeutic result. They often aggravate the course of the pathological process and can cause exacerbations. Therefore, it is recommended to discuss the selection of an individual diet with your doctor and nutritionist. For concomitant chronic disorders, a specialist will help you adjust your diet in such a way as to reduce the risks of hepatitis C and not aggravate the course of associated pathological processes. Any amateur activity can be disastrous and worsen your well-being, clinical picture, and prognosis.
Diet and nutrition for toxic disease in adults
Diet changes are necessary for people with decompensated cirrhosis, which is characterized by such extensive scarring (fibrosis) that the organ does not function properly.
It is necessary to get enough calories during therapy. Anorexia is a symptom associated with a progressive pathological process in the liver. If your lack of appetite lasts for several days or weeks, you may not be eating enough calories.
Meat, milk, nuts and cheese are good sources of protein. It is an essential nutrient and absolutely necessary for building cells and maintaining health.
People with toxic hepatitis are able to digest moderate amounts of protein. Its excess can lead to brain disease, since products of its incomplete breakdown accumulate in the blood and spread through the vessels.
Some people with this disorder may not get enough fat-soluble vitamins and essential minerals. A doctor or nutritionist can determine the level of microelements using tests and prescribe special medications as needed. Or use the standard method: a balanced diet.
The liver is an incredibly important organ. One of its functions, in addition to detoxification, is the production of bile, which the body uses to break down fats.
However, depending on the extent of organ damage, insufficient amounts of bile are produced. One solution is to simply eat low-fat foods.
Foods that are prohibited for toxic hepatitis:
- legumes and mushrooms;
- high-calorie dairy products (yogurt, cottage cheese, sour cream);
- carbonated drinks, coffee, strong black tea;
- fatty varieties of fish, meat and poultry;
- cocoa and chocolate;
- confectionery and sweets;
- canned sausage;
- nuts and ice cream;
- smoked and pickled delicacies;
- various seasonings and sauces;
- salt (no more than 10 grams per day);
- spinach, sorrel, garlic;
- eggs (no more than one per day);
Example of a diet and menu for the week.
Monday:
- Breakfast: oatmeal with dried fruits, green tea.
- Snack: any fruit and 100 g biscuits.
- Lunch: fish soup, buckwheat with chicken meatballs and salad.
- Snack: dried fruits and yogurt.
- Dinner: baked apple with honey, raisins and cinnamon.
- Second dinner: a cup of yogurt or milk.
Tuesday:
- Breakfast: cottage cheese casserole with tea.
- Snack: fruit salad and a few pieces of bread.
- Lunch: vegetable soup, mashed potatoes with steamed cutlets.
- Snack: fresh biscuit or crackers with tea.
- Dinner: rice with boiled fish.
- Second dinner: herbal tea or yogurt with waffle cookies.
Wednesday:
- Breakfast: one egg omelet with milk and vegetables.
- Snack: Fruit or vegetable juice with crackers or stale bread.
- Lunch: pickled vegetables, wheat porridge with meatballs.
- Snack: tea, any fruit.
- Dinner: boiled or baked chicken with vegetables.
- Second dinner: yogurt and banana.
Thursday:
- Breakfast: green tea and vegetable salad.
- Snack: 200 g cottage cheese with sour cream.
- Lunch: milk soup with buckwheat, pasta with meat sauce.
- Snack: a handful of dried fruits or any fruit.
- Dinner: baked potatoes and vegetable salad dressed with sour cream.
- Second lunch: tea or yogurt, biscuits.
Friday:
- Breakfast: cottage cheese and dried fruits, tea.
- Snack: dry biscuit and juice.
- Lunch: beet soup, barley porridge with steamed cutlets and vegetable salad.
- Snack: fruit juice with crackers.
- Dinner: boiled fish with rice.
- Second lunch: a cup of yogurt or green tea.
Saturday:
- Breakfast: fruit salad and herbal tea.
- Snack: any fruit, tea or juice.
- Lunch: vegetable soup with croutons or stale bread, buckwheat meatballs with cabbage.
- Snack: any fruit and juice.
- Dinner: baked chicken with vegetables and low-fat hard cheese.
- Second dinner: yogurt or tea.
Sunday:
- Breakfast: herbal tea, oatmeal with honey.
- Snack: cottage cheese with fruit.
- Lunch: chicken noodle soup, mashed potatoes with steamed beef cutlet, vegetable salad.
- Snack: any fruit and tea with crackers.
- Dinner: steamed fish with vegetables.
- Second dinner: yogurt with waffle cookies.
Despite such a large list of restrictions, patients can come up with a tasty, varied and most importantly healthy menu that will help restore the damaged organ.
www.verywell.com
medicalformat.com
General recommendations
The diet for chronic hepatitis C is aimed at improving the functioning of the digestive tract and reducing the load on the organ affected by the disease. The patient's menu implies compliance with the following daily chemical composition of products:
- about 100 grams of proteins, most of which should be of animal origin;
- 80 grams of fat;
- 400 grams of carbohydrates;
- no more than 4 grams of table salt.
The patient's diet should be designed in such a way that he receives 2400 calories per day.
In addition, the following general recommendations should be taken into account:
- the patient should eat frequently – 4–5 times a day, but in small portions, with an interval between meals of 2–3 hours;
- dishes should only be consumed warm;
- the consistency of the food should be liquid or puree;
- the menu should include only boiled, steamed or oven-baked food without a fried crust.
By following such dietary recommendations, you can not only improve the patient’s well-being, but also speed up the recovery process or prolong the period of remission if we are talking about a chronic form of the disease.
What does the menu consist of for alcoholic epilepsy?
Seizures caused by drinking alcoholic beverages develop at a late stage of abuse. This reveals chronic alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis.
The body's ability to break down and absorb fats and fat-soluble vitamins is impaired. The liver does not produce enough bile, so heavy foods are not digestible and are excreted almost unchanged (steatorrhea).
Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, vegetables and fruits, are the best sources of glucose, the body's main fuel, as well as minerals that are deficient in inflammatory organ damage and are simply essential in the diet.
Alcohol is particularly depleting of B vitamins, which can cause brain damage caused by Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome.
For alcoholic epilepsy and hepatitis, it is necessary to consume foods rich in proteins: from 2000 to 3000 calories per day, to restore damaged cells. The main thing is that there is no excess, as it forms ammonia, which is toxic to the body.
Ascites, the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity, is a potentially life-threatening complication of alcoholic liver disease.
Salt intake should be limited to 2000 mg per day because it increases fluid retention. Canned soups, smoked meats and ketchups contain a lot of sodium chloride, so you should avoid them.
www.livestrong.com
Nutrition for liver cirrhosis
Many people with this diagnosis want to know how to change their eating habits to maintain health. The main rule is that a properly selected diet is beneficial for almost everyone, and is especially true if there is cirrhosis due to hepatitis.
Good foods include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and proteins in proper amounts. In addition, it is recommended to take a daily multivitamin during your diet.
Depending on the severity of cirrhosis, some people may not be getting enough key minerals and fat-soluble vitamins (K, A, D, and E) that the body needs.
There are two things that should be avoided with this pathology: alcohol and fatty foods. For people with cirrhosis, regardless of the cause, alcohol-containing drinks must be excluded from the diet completely and forever.
With a high fat content in food, digestive problems may occur. The body breaks them down using bile, which is produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder.
However, it is important not to avoid fat completely because the body requires a certain amount to function normally. Suitable foods in the diet for liver cirrhosis and hepatitis: nuts, avocados, fish and vegetable oils.
In the compensation stage of the disease, patients must replenish protein. Its increase in the blood can not only prevent fatty degeneration of the gland, but also has a positive effect on the restoration and regeneration of liver cells. In this case, the patient should eat more food rich in proteins: fish, dairy products and lean meat.
Typically, people with this disease have very low levels of zinc and magnesium, so it is recommended that the diet include foods rich in these microelements: lean meat, eggs, fish, apples, peanuts and champignons.
The following foods are prohibited: hard foods, beer, pickles, fried foods, desserts, and foods containing artificial colors, preservatives, and additives.
Vegetables such as cauliflower, bok choy, cabbage, peas and beans are rich in fiber. They help remove toxins from the body, positively affecting the functioning of the liver, so you can eat them often, but within reasonable limits.
Patients with cirrhosis and symptoms of ascites (fluid accumulation in the abdomen) and edema should follow a minimally low-sodium diet. Daily salt intake should be within 2 g.
You should also avoid any medications that are hepatotoxic (damage the liver).
www.verywell.com
www.cirrhosis-treatment.net
Diet during treatment and after hepatitis C
During therapy, it is recommended to adhere to a strict diet. The diet is expanded after the course of treatment has ended. If there is a history of other chronic pathologies, including human immunodeficiency virus, or complications of hepatitis in the form of fibrotic changes or cirrhosis of the liver, the diet is constantly followed.
For patients with any form of hepatitis, treatment table No. 5 is recommended, which supports and restores the liver, reduces the load, and ensures the supply of all necessary vitamins, minerals and amino acids. To achieve the best result, maintain a balance of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, and be sure to introduce a large amount of fiber. This ensures the normal functioning of the liver detoxification phases and prevents digestive disorders.