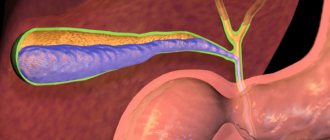
Cholecystitis is one of the most common diseases of the digestive system, consisting of inflammation of the gallbladder wall.
The main causes of cholecystitis are infection and bile stagnation. These reasons are interconnected and can enhance each other's effects. Stagnation of bile creates favorable conditions for the development of infections that cause inflammation of the gallbladder and ducts, and inflammatory processes, in turn, increase stagnation of bile.
The causative agents of the disease are, as a rule, various microbes - streptococci, staphylococci, E. coli and others that enter the gallbladder through the bile ducts from the intestine, as well as through the blood and lymph flow. Pathological processes in the gallbladder are closely interrelated: chronic cholecystitis can lead to the formation of gallstones, and at the same time, cholelithiasis is very often the cause of cholecystitis.
A number of factors (age, female gender, impaired motor skills and tone, gallbladder, impaired outflow of bile, concomitant diseases of the intestines, liver and pancreas, the presence of foci of chronic infections, unbalanced diet and sedentary lifestyle, as well as obesity, diabetes, pregnancy) increase risk of developing chronic cholecystitis.
Cholecystitis can occur in both acute and chronic forms.
Causes of the disease
The leading causes of the occurrence and development of acute or chronic inflammation of the gallbladder are bacterial infection and bile stagnation. Infection in the gallbladder can enter from the lumen of the duodenum or along with blood or lymph. The development of infection is facilitated by impaired bladder emptying.
The cause of the outflow disturbance may be congenital deformation of the cervical part of the gallbladder and cystic duct, as well as biliary dyskinesia (impaired neuro-reflex and humoral regulation of bile duct motility). Biliary dyskinesia is a fairly common functional disorder in children, especially those who have disrupted diet, study and rest, and who are subject to frequent nervous stress at home and at school.
The inflammatory process in the wall of the gallbladder leads to disruption of its function, stagnation of bile and changes in its physicochemical properties, which, in turn, maintains inflammation and contributes to the transition of acute inflammation to chronic, as well as stone formation.
Cholecystitis is predisposed by a sedentary lifestyle and rare, plentiful intake of food rich in protein and fat. The risk of acute cholecystitis also increases during pregnancy, when, due to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, the evacuation of bile into the duodenum is disrupted. In addition, this disease is promoted by chronic constipation, excess weight, frequent accumulation of gases in the intestines, as well as roundworms and lamblia located in the bile ducts. Doctors consider women with the so-called “four Fs” to be a high-risk group - fat, over 40, who have children and who suffer from gas (in English fat, fortyish, fertile, flatulent).
Hereditary predisposition plays a decisive role in the occurrence of cholecystitis. It can be triggered by metabolic disorders, allergic factors, circulatory disorders of the gallbladder wall (with diffuse connective tissue diseases, atherosclerotic vascular lesions, etc.). Quite often, cholecystitis develops against the background of gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, pancreatitis, and a tumor process in the abdominal cavity.
Inflammation of the gallbladder: causes
Any disease is already the result of your lifestyle. Yes, all responsibility lies on your shoulders. Of course, other ailments (that is, as a consequence of another disease) or other malfunctions in the body can also contribute to inflammation of the gallbladder. But their percentage is small. Therefore, let's study in detail what can lead to cholecystitis.
- Like any other organ of the digestive system, the gallbladder is directly dependent on nutrition. In an era of such abundance and variety of delicious products, unfortunately, one cannot be sure of their usefulness. Smoking, pickling or the so popular chips (we will, of course, not give the whole list), as well as fatty, fried foods do not have the best effect on our health.
- Who doesn't like to have a sandwich at work? And with the same smoked sausage (the composition of which is very questionable). Dry milk also leads to inflammation of the gallbladder.
- Overeating is also mentioned in the Bible and is one of the seven deadly sins. More precisely, there it is interpreted as gluttony. Eating large quantities of food, and even not the healthiest food, will lead to a change in the chemical composition of the contents of the gallbladder.
- Doctors insist that the last meal should be at least 2 hours before bedtime. Because food must have time to be digested. By the way, I remember the proverb: “dine like a beggar.” Yes, the last meal should not be heavy, fatty or take a long time to digest in the stomach. Otherwise, stagnation of bile will begin to form, which will then come out, as they say, sideways.
- Now let’s highlight such an aspect as a sedentary and sedentary lifestyle. And it’s even worse if you are overweight. Although, as a rule, as a result of all of the above, you are not far from overweight.
- Now let’s touch on an aspect that does not depend on your lifestyle (well, partially) - this is hormonal imbalance. Why partly, because most often this happens to pregnant women. But such a reason (although rare), also occurs among the male population.
- Constant stress, strong feelings and other disorders in the nervous system will lead not only to gastritis or stomach ulcers, but will also help cause inflammation of the gallbladder.
- One of the main factors is excessive drinking and smoking!
- Weakened immunity or any infections in the body affect the production of bile. By the way, health deteriorates with age, so the chances of developing cholecystitis double.
- It is impossible not to note the genetic predisposition. Yes, those whose parents suffered from a similar illness were a little less fortunate. It is important to monitor your diet and health from the beginning, especially if there is a heredity to this.
- And, of course, any disorders and decline in immunity that are associated with other diseases. For example, HIV or diabetes will naturally cause cholecystitis.
Classification
In gastroenterology, there are several classifications of the disease, each of which is of great importance, giving specialists the opportunity to attribute certain clinical manifestations to a specific type of disease and choose rational treatment tactics. Taking into account the etiology, two types of cholecystitis are distinguished:
- Calculous
. Stones are found in the organ cavity. Calculous cholecystitis accounts for up to 90% of all cases of the disease. It may be accompanied by intense symptoms with attacks of biliary colic or be asymptomatic for a long time. - Non-calculous
(stoneless). Accounts for 10% of all cholecystitis. It is characterized by the absence of stones in the lumen of the organ, a favorable course and rare exacerbations, usually associated with nutritional errors.
Depending on the severity of symptoms and the type of inflammatory-destructive changes, cholecystitis can be:
- Spicy
. Accompanied by pronounced signs of inflammation with a violent onset, vivid symptoms and symptoms of intoxication. The pain is usually intense and wave-like. - Chronic
. It manifests itself as a gradual, slow course without pronounced symptoms. The pain syndrome may be absent or aching and of low intensity.
Based on the severity of clinical manifestations, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Easy.
It is characterized by a low-intensity pain syndrome lasting 10-20 minutes, which is self-limiting. Digestive disorders are rarely detected. Exacerbations occur 1-2 times a year and last no more than 2 weeks. The function of other organs (liver, pancreas) is not changed. - Moderate weight.
The painful sensations are persistent with pronounced dyspeptic disorders. Exacerbations develop more often than 3 times a year and last more than 3-4 weeks. Changes in liver function are noted (increased ALT, AST, bilirubin). - Heavy
. Accompanied by pronounced pain and dyspeptic syndromes. Exacerbations are frequent (more than once a month), long-lasting (more than 4 weeks). Conservative treatment does not provide significant improvement in well-being. The function of neighboring organs is impaired (hepatitis, pancreatitis).
According to the nature of the course of the inflammatory-destructive process, they are distinguished:
- Relapsing course
. It manifests itself as periods of exacerbation and complete remission, during which there are no manifestations of cholecystitis. - Monotonous flow
. A typical sign is the absence of remissions. Patients complain of constant pain, discomfort in the right abdomen, upset stool, and nausea. - Intermittent flow.
Against the background of constant mild manifestations of cholecystitis, exacerbations of varying degrees of severity periodically occur with symptoms of intoxication and biliary colic.
Symptoms of acute cholecystitis
This form of the disease goes through three stages in its development, each of which has its own clinical picture:
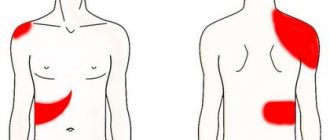
- Catarrhal cholecystitis is manifested by constant severe pain in the right hypochondrium, radiating to the right half of the body - the shoulder blade, shoulder, and right surface of the neck. At the beginning of the disease, pain can be paroxysmal. Vomiting of stomach contents often occurs. Bile is almost always found in vomit. The temperature is low-grade, the pulse is normal.
- With phlegmonous cholecystitis, inflammation penetrates deep into the wall of the gallbladder, affecting not only its mucous membrane, but also the underlying layers. The pain in this form is much more intense and intensifies with changes in body position, breathing, coughing, and straining. Vomiting is repeated, temperature is high (38-39°C). The pulse increases to more than 100 beats per minute. The abdomen is swollen and painful when palpated.
- With gangrenous cholecystitis, which often occurs in older people, general symptoms come first. The pain subsides somewhat, but this is only apparent well-being. The reason for the decrease in pain is the death of nerve receptors under the influence of an infection that penetrates the entire thickness of the gallbladder wall. The patient's condition sharply worsens, he becomes lethargic and lethargic. The phenomena of general peritonitis—inflammation of the peritoneum, resulting from the spread of infection from the gallbladder into the abdominal cavity—are increasing. The temperature is high, there is strong tachycardia, it is sharply swollen, painful on palpation in all parts, and tense. This is an extremely dangerous form of the disease, often leading to a tragic outcome even with proper treatment.
Calculous
The formation of a solid sediment in the form of stones in the gall bladder leads to the appearance of calculous cholecystitis. The disease mainly affects adults over 40 years of age. Women are susceptible to it more often than men. With rare exceptions, children get sick.
Concretions - stones of various shapes and diameters can be located both in the gallbladder and in the ducts, thereby complicating the outflow of bile, which causes an attack of biliary colic and a chronic inflammatory process. Stones form against the background of changes in the basic composition of bile, and also as a concomitant pathology with gastrointestinal diseases.
Factors that increase the risk of stone formation may include:
- violation of diet;
- excessive consumption of foods high in animal fats;
- inactive lifestyle;
- heredity.
The leading research method when symptoms of calculous cholecystitis appear is ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal organs. Other research methods are prescribed according to indications. As a rule, surgery is required to remove the gallbladder, since the presence of stones in it leads to constant inflammation.
In case of chronic cholecystitis, the operation is carried out as planned, in case of acute cholecystitis - in an emergency. Existing methods of drug treatment aimed at dissolving stones are not justified.
Exacerbation of gallbladder inflammation
Exacerbation of inflammation of the gallbladder is very dangerous. The worst thing is that the disease can appear suddenly. That is, a person is at home or on vacation, and an extra dose of alcohol or sudden stress can provoke a number of similar symptoms, which we will indicate below.
IMPORTANT: The person must be hospitalized immediately. And before the ambulance arrives, it is necessary to provide first aid and at least slightly relieve the patient’s pain.
- The symptoms are slightly similar to ordinary inflammation.
- The person's right side suddenly seizes. Moreover, the pain is incredibly sharp and strong to such an extent that it is difficult for a person to take a breath.
- The patient constantly feels sick and even vomiting cannot relieve this feeling completely. Moreover, vomiting may be bloody (but not always).
- The temperature jumps sharply and the patient shudders.
- He feels tired and sleepy. Which, in principle, is typical for the exacerbation of any disease with high fever.
- Also, belching, diarrhea (or constipation) and yellowing of the skin appear. Moreover, the last symptom becomes visible even to the naked eye.
- It is also important to take into account that the patient may have not just a bitter taste in the mouth, but a metallic taste.
How you can help:
- The first thing to do is to immediately call an ambulance.
- Then gently help the patient into a horizontal position.
- If you have any painkiller on hand, you can give it. Regular No-shpa is perfect.
- It is advisable to place a bag of something cold on your stomach. Ice, of course, would be ideal.
- If the patient experiences bouts of vomiting, help him cope with them by turning his head to the side.
- To slightly reduce the feeling of nausea, give the victim strong mint tea.
IMPORTANT: There are two types of exacerbation - with the formation of stones (calculous cholecystitis) or without them (that is, a non-calculous disease). The first can also be caused, for example, by shaking on the road. Which will lead to blockage of the bile ducts with a stone. In the second case, the cause of exacerbation is often infection in the gallbladder. But in both cases, it is necessary to urgently take the patient to the hospital.
Non-calculous
Inflammation of the gallbladder against the background of obstructed outflow of bile without cholelithiasis is called acalculous cholecystitis. This disease is always combined with hepatitis, inflammation of the bile ducts and pancreas.
Non-calculous cholecystitis can develop under the influence of:
- Microbial infection of the gallbladder;
- Corrosion of the mucous membranes of the organ by pancreatic enzymes;
- Circulatory disorders in the walls of the gallbladder.
Non-calculous cholecystitis is manifested by typical and atypical symptoms:
- Typical form. The disease is characterized by dull, monotonous pain in the right hypochondrium forty to ninety minutes after eating, driving off-road or carrying heavy objects. The pain increased in the sitting position and calmed down in the lying position. The pain is combined with heartburn, nausea and belching;
- Cardialgic syndrome. Dull pain in the precordial region, arrhythmias and extrasystoles that occur after eating. The electrocardiogram shows a negative T wave, smoothed QRS waves;
- Esophagic syndrome. Persistent heartburn, dull pain and sensation of a foreign body behind the sternum. Temporary dysphagia (difficulty swallowing food);
- Intestinal syndrome. Abdominal bloating with non-localized pain and persistent constipation.
Chronic noncalculous cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder that occurs as a result of microbial infection, accompanied by the proliferation of connective tissue and stagnation of bile without the formation of stones.
Penetration of microflora into the focus of pathogenesis occurs along an ascending or descending path, or lymphogenously:
- The ascending path is from the intestine to the neck of the bladder and higher. Promotes dysfunction of the sphincter, which prevents the reverse flow of bile from the intestine;
- The descending path is when the infectious agent circulates in the bloodstream. Some sources call it the “hematogenous” route of infection;
- Lymphogenic. Lymph is a biological fluid of the body that is involved in many functions, including neutralizing inflammatory reactions. In case of massive purulent infections (genitourinary, respiratory, digestive), lymph fails to cope with its role and becomes a factor in the transmission of infection.
The development of the pathogenesis of chronic acalculous cholecystitis is accompanied by a loss of contractile and absorptive functions of the gallbladder, which leads to stagnation (occlusion) of bile, thickening of the walls and shrinkage of the organ.
Inflammation of the gallbladder: symptoms and signs
Some may be wondering, how do people who have had their gallbladder removed live? After all, they continue to lead the same lifestyle. In fact, no, such representatives need to constantly monitor their diet (but more on that a little later).
- Of course, the first indicator will be pain. It is impossible to say unequivocally what pain is caused by inflammation of the gallbladder. Because it can be dull and aching, and after eating food (especially too fatty or fried), the pain in the right side has a bursting character. It can also be caused by stress or physical activity.
- Keep in mind! The pain may not be clearly localized in the liver area, which is often confusing. Pain may radiate to the neck, under the shoulder blade or to the right shoulder.
IMPORTANT: Inflammation of the gallbladder ducts or a dense clot of bile can cause sharp and acute pain.
- The person experiences nausea or even vomiting. Against this background, appetite disappears, the patient begins to lose weight.
- This is also facilitated by the resulting diarrhea, although in some cases prolonged constipation occurs (this, as they say, is a personal matter).
- Bitterness in the mouth is a dangerous signal that indicates a visit to the doctor as soon as possible.
- The temperature during inflammation of the gallbladder, as with any infection, reaches 38-39 °C.
- There is also bloating and unpleasant (bitter) belching.
- With increased bile production, yellow skin color and even yellowing of the eyeball are possible. As a rule, such a symptom occurs with severe degrees of the disease.
IMPORTANT: Women get sick twice as often as men. And, basically, the disease worsens after 40 years.
Symptoms of chronic cholecystitis (if we call the disease in scientific or medical language).
- The pain syndrome in this case intensifies several times and has a very wide area. It can radiate into the chest, under the shoulder blades and to the left side. If we speak clearly and clearly, then the whole body can hurt, below the head and above the waist. By the way! The pain can be localized in the area of the heart (yes, it looks like heart pain), the heartbeat quickens and its rhythm is disturbed.
IMPORTANT: Attacks of vomiting can be with bile!
- Dry mouth appears, and the patient is constantly thirsty. By the way, many people note that they crave smoked and fatty foods (exactly what you absolutely cannot eat).
- Symptoms of the gallbladder in women manifest themselves in the tension of premenstrual syndrome. Frequent headaches, mood swings, and possibly swelling of the face and limbs may occur.
IMPORTANT: Patients are often also diagnosed with vegetative-vascular dystonia. That is, there is weakness, sweating, increased heart rate, sleep disturbance and emotional instability.
There are also symptoms that depend on the form of the disease:
- The catarrhal form of inflammation is characterized by:
- an increase in the size of the gallbladder
- white coating on the tongue
- the appearance of serous secretion in the organ
- increased salivation
- constant nausea and vomiting, especially after eating
- temperature
- About purulent cholecystitis he says:
- also nausea and vomiting
- pain in the abdomen that gets worse with breathing, coughing, or even changing position
- body temperature can reach 40 °C
- severe intoxication of the body
- as well as gurgling in the stomach and slight bloating
IMPORTANT: This type of cholecystitis is very dangerous and can lead to rupture of the walls of the gallbladder itself.
- Gangrenous inflammation is different:
- increased irritability and nervousness
- dry mouth
- rapid breathing and heart rate
- but the pain is not so strong and sharp
- there is bloating and muscle tension
Attack of cholecystitis
Attacks are characteristic of both primary cholecystitis and exacerbations of the chronic form of the disease. Harbingers of attacks are discomfort in the stomach after eating fatty, spicy foods or alcohol.
Symptoms of an acute attack of cholecystitis:
- Sharp cramping pain in the right hypochondrium, epigastrium or navel;
- Nausea and vomiting, gas belching, bitter taste in the mouth;
- Low-grade or febrile body temperature (37-38 0 C or 38-39 0 C).
How to relieve an attack of cholecystitis?
To relieve an attack of cholecystitis it is necessary:
- Call an ambulance;
- Lie in bed and apply cold to your stomach;
- Take an antispasmodic (papaverine, no-shpa) and an analgesic (analgin, baralgin);
- To reduce nausea, drink mint tea or still mineral water at room temperature;
- If there is vomiting, ensure that the vomit is collected for analysis.
Inflammation of the gallbladder in children
Children's symptoms are similar to the adult symptoms described above, but may differ slightly. And it’s important – acute forms of cholecystitis are extremely rare in children!
- The baby may also experience nausea, vomiting and poor appetite.
- Which leads to irregular bowel movements (or, on the contrary, diarrhea may occur) and weight loss
- Pale skin and dark circles under the eyes are observed
- The baby often complains of abdominal pain and becomes restless at night (and therefore does not sleep well)
- Often capricious, which is natural for an unhealthy baby
- Possibly constant thirst and dry mouth (take care to stay hydrated)
- And, of course, elevated temperature, as a result of intoxication of the body
Complications
The presence of any cholecystitis is always fraught with the possible development of complications. Some of them are very dangerous and require immediate surgical intervention. Thus, as a result of cholecystitis, patients may experience:
- pericholecystitis (transition of inflammation to nearby tissues and organs);
- cholangitis (spread of inflammation to intra- and extrahepatic bile ducts of different sizes);
- blockage of the bile ducts;
- “porcelain” gallbladder (the result of deposition of calcium salts in the wall of the bladder);
- empyema of the gallbladder (purulent inflammation);
- necrosis of the wall (necrosis) of the gallbladder due to inflammation and pressure on it from stones (stone);
- perforation of the wall (formation of a hole in it) as a result of necrosis, as a result its contents end up in the patient’s abdominal cavity and leads to inflammation of the peritoneum (peritonitis);
- the formation of fistulas between the bladder and the intestine, the bladder and the renal pelvis, the bladder and the stomach (the result of necrotic changes in the gallbladder wall;
- “disabled” (non-functioning) gallbladder;
- secondary biliary cirrhosis (a consequence of prolonged calculous cholecystitis);
- gallbladder cancer.
Why does cholecystitis occur?
Microorganisms spread into the gallbladder from foci of acute or chronic infection through contact, with blood or lymph flow. Cholecystitis is an inflammatory disease. The infection enters the gallbladder most often from the intestine through the bile ducts, but can also from other foci (tonsillitis, periodontal disease) through the blood and lymph flow. And various predisposing factors:
- obesity,
- decrease in gastric acidity,
- biliary dyskinesia,
- intestinal dysbiosis,
- constipation
contribute to the development and chronicity of the disease.
Diagnostics
A gastroenterologist treats cholecystitis. In the chronic form of the disease, it will be useful to consult a nutritionist. A physical therapist may provide additional assistance.
To make a diagnosis, the following activities are carried out:
- taking anamnesis;
- examination of the patient;
- laboratory examinations;
- instrumental studies.
Laboratory research:
- General blood analysis. Reveals signs of inflammation.
- Biochemical blood test: total bilirubin and its fractions, transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, cholesterol. Their moderate increase is observed.
- Blood sugar. For the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus.
- General urine analysis. For differential diagnosis with kidney diseases.
- Feces for worm eggs. To identify Giardia, Ascaris.
- Microscopic and bacteriological examination of bile.
- Immunoenzymatic blood test for giardiasis.
- Fecal elastase analysis 1. To diagnose pancreatitis.
The following diagnostic methods are used:
- Ultrasound diagnostics. It is carried out to detect signs of pathologically altered gallbladder tissue, in some cases, stones;
- Holegraphy. An X-ray examination method that complements ultrasound. Used to identify hidden pathologies of the gallbladder;
- Probing of the duodenum. Used to sample the contents of the small intestine.
The best way to determine the presence of the disease is early research. Most often, identifying certain deviations in the chemical composition of bile may only require adherence to a non-strict diet.
Inflammation of the gallbladder: treatment
The first thing I wanted to note (more precisely, it is very important to know) is the treatment of chronic cholecystitis. The easiest and fastest way (let's say) to relieve inflammation of the gallbladder, which has an acute or chronic form, is to remove it. Acute cholecystitis requires drug treatment.
- Of course, antibiotics will be the most effective for inflammation of the gallbladder. They can only be prescribed by a doctor based on your tests. By the way, you will definitely need to undergo: Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity
- take a general urine and blood test, of course
- undergo an extended biochemical blood test
- and also take an x-ray of the abdominal area
IMPORTANT: Levomycetin is not recommended for inflammation of the gallbladder, since it disrupts protein metabolism in the microbe itself.
- Most often, antibiotics are prescribed such as Cefazolin, Ampicillin, Erythromycin, Cephalexin and the like.
IMPORTANT: Do not self-medicate! If your doctor has prescribed you to take certain medications, you must strictly follow all recommendations. Do not try to replace them, for example, with cheap analogues, without consulting your doctor. We have listed only popular drugs in this area, but everyone has their own personal predispositions and requirements.
- And further! When taking antibiotics, do not forget to drink yogurt or, for example, Linex.
IMPORTANT: Drugs for inflammation of the gallbladder should enhance the secretion of bile, but at the same time reduce its viscosity.
- For these purposes, doctors prescribe medications based on natural ingredients, for example, Gepabene or Hofitol.
- It is also important to monitor the functioning of the digestive system. And to normalize it, they can prescribe, for example, Mezim, Pancreatin or Creon.
- For women (before menstruation) or patients with vegetative-vascular dystonia, valerian or motherwort may be prescribed.
IMPORTANT: Treatment with auxiliary drugs lasts at least two months. But only a doctor can indicate how everyone should take medications, their regimen and duration!
- Antipyretic drugs and medications to strengthen the immune system may also be prescribed. Don’t forget that you need to remove toxins from the body, so another course of detoxification medications may also be prescribed.
How to treat cholecystitis?
Since the cause of cholecystitis is an infection, if there are signs of its exacerbation (pain, fever, changes in blood tests), antibiotics are prescribed, but it is better to entrust this to a doctor, who ideally has the results of bile culture on hand.
But at home you can and should be treated with the following means:
- Follow a diet. During an exacerbation, you can generally fast for a day or two, but at the same time drink weak tea, juices or fruit drinks diluted with water 1:1, or still mineral water. Then add puree soups and porridges, then low-fat cottage cheese, boiled meat and steamed fish, and after 5-7 days you can switch to a gentle, but completely physiological diet, excluding fried foods, fatty foods, such as goose or cream cakes, smoked and spicy foods. seasonings (for example, horseradish or mustard). It is better to eat often, every 3 hours, but little by little.
- For pain, take antispasmodics. This is a traditional no-spa (2 tablets three times a day, but no more, read the side effects in the annotation and make sure that this is a serious drug and an overdose is unacceptable), papaverine (can be taken in suppositories - many note that the effect is even better than from tablets), duspatalin 1 tablet 2 times, 20 minutes before meals.
- The choice of choleretic drugs depends on the motility of the biliary tract.
In general, the basis for the treatment of acute and chronic non-calculous cholecystitis is complex drug and diet therapy. In case of a frequently recurrent calculous form of the disease or when there is a threat of complications, surgical intervention on the gallbladder is resorted to.
Treatment of chronic cholecystitis
Treatment of a chronic process without the formation of stones is always carried out by conservative methods, the main of which is dietary nutrition (diet 5 - fractional meals with a sufficient amount of liquid, mineral water). If there are gallstones, limit hard work, physical overload, and bumpy driving.
The following drugs are used:
- Antibiotics, most often broad-spectrum or cephalosporins
- Enzyme preparations – Pancreatin, Mezim, Creon
- Detoxification – intravenous infusions of sodium chloride, glucose solutions
- NSAIDs – sometimes used to relieve inflammation and pain
Choleretic drugs are usually divided into:
- Choleretics are drugs that enhance the formation of bile. Preparations containing bile and bile acids: allohol, lyobil, vigeratin, cholenzyme, dihydrocholic acid - hologon, sodium salt of dehydrocholic acid - decholin. Herbal preparations increase the secretion of bile: flakumin, corn silk, berberine, convaflavin. Synthetic drugs: osalmide (oxafenamide), hydroxymethylnicotinamide (nicodine), cyclone, gymecromone (odeston, holonerton, cholestil).
- Cholekinetics are divided into: promoting the secretion of bile and increasing the tone of the gallbladder (magnesium sulfate, pituitrin, choleretin, cholecystokinin, sorbitol, mannitol, xylitol) and cholespasmalytics, reducing the tone of the biliary tract and sphincter of Oddi: drotaverine hydrochloride, no-spa, olimethine, atropine, platiphylline, aminophylline, mebeverine (duspatalin).
During periods of exacerbation, herbal medicine is very widely used; in the absence of allergies to it, decoctions of chamomile, dandelion, peppermint, valerian, and calendula are used. And during periods of remission, it is possible to prescribe homeopathic treatment or herbal medicine, but with other herbs - yarrow, marshmallow, tansy, buckthorn.
It is very important to follow a strict diet after an exacerbation of cholecystitis, then the symptoms gradually subside. In addition to the diet for gallstones and cholecystitis, it is also recommended to periodically apply tubages with xylitol, mineral water or magnesium; physical therapy is effective - electrophoresis, reflexology, SMT therapy.
In case of calculous chronic cholecystitis with pronounced symptoms, it is recommended to remove the gallbladder, the source of the growth of stones, which can pose a threat to life if they move. The advantage of chronic cholecystitis with stones from acute calculous cholecystitis is that this operation is planned, it is not an emergency measure and you can safely prepare for it. Both laparoscopic surgery and cholecystectomy from a mini-access are used.
When surgery is contraindicated, sometimes with chronic cholecystitis, treatment may consist of the method of crushing stones - shock wave lithotripsy; this extracorporeal procedure does not remove stones, but simply crushes, destroys them, and often causes them to re-grow. There is also a method for destroying stones using salts of ursodeoxycholic and chenodeoxycholic acids; in addition to the fact that this therapy does not lead to a complete cure, it is also quite long in time and lasts up to 2 years.
Nutrition and diet
During the period of severe exacerbation of cholecystitis, patients are recommended to undergo treatment in a hospital - therapeutic or gastroenterological, adherence to bed rest, and a state of psycho-emotional rest. After the elimination of pronounced signs of exacerbation, the patient’s regimen is expanded to general.
During an exacerbation, in the first two days, only warm liquids are prescribed (weak sweet tea, fruit and vegetable juices diluted with water, still mineral water) in small portions up to 1.5 liters per day and several crackers. As the pain subsides and the general condition improves, the dietary table expands. Recommend:
- pureed soups from vegetables and cereals,
- porridge (oatmeal, rice, semolina, buckwheat),
- jelly, mousse, jelly, low-fat cottage cheese,
- lean boiled fish,
- pureed and boiled meat, steamed cutlets (veal, chicken, turkey, rabbit),
- white crackers.
Food is taken in fractional portions 5-6 times a day.
During an exacerbation period, it is recommended to carry out fasting days 1 day a week:
- cottage cheese - kefir day. 900g kefir for 6 doses, 300g low-fat cottage cheese for 3 doses and 100g sugar;
- rice - compote. 1.5 liters of compote prepared from 1.5 kg of fresh or 240 g of dry fruits for 6 servings, rice porridge cooked in water from 50 g of rice - for 3 servings.
After stopping the exacerbation of cholecystitis, a diet is prescribed, table No. 5, which is the main one for this disease.
Patients are recommended:
- milk, fruit, vegetable broth soups with cereals, noodles;
- boiled meat, steam cutlets, meatballs (beef, rabbit, chicken, turkey);
- low-fat varieties of sea or river fish, boiled or baked, without crust;
- eggs, up to 1-2 per day – soft-boiled, in the form of steam omelettes;
- dairy products: low-fat milk, cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt, yogurt, butter (limited);
- vegetables boiled, baked, partially raw. Potatoes, beets, carrots, tomatoes, cucumbers, pumpkin, sweet peppers, eggplants, cauliflower, zucchini;
- fruits and berries. Pears, melons, bananas, peaches, apricots, watermelons, sour apples;
- porridge – buckwheat, oatmeal, rice, semolina, with the addition of milk, if tolerated;
- sweet dishes - marshmallows, marmalade, honey, jams, preserves, jelly;
- flour products - wheat and rye bread, yesterday's bread, white bread crackers, dry unsweetened cookies.
You need to eat food in small portions, slowly 5-6 times a day. Long breaks between meals and fasting are not recommended. Breakfast is required, dinner 2-3 hours before bedtime, not much. The amount of liquid is not limited. A large amount of food, taken once, disrupts the rhythm of bile secretion, causes spasm of the gallbladder and provokes pain.
In case of chronic cholecystitis, it is necessary to increase the consumption of foods that improve the flow of bile and reduce cholesterol levels:
- rich in dietary fiber (bran, vegetables, fruits, berries). The bran is pre-steamed and added to dishes, 1-1.5 tablespoons 3 times a day;
- rich in magnesium salts (buckwheat and oatmeal, dried fruits, bran);
- containing essential polyunsaturated fatty acids, phospholipids, vitamin E (corn, olive, sunflower and other oils);
- containing lactic acid bacteria (fermented milk drinks, cottage cheese).
Products not recommended
- with a high content of animal fats (fried foods, fatty fish, pork, lamb, duck, sausages, smoked meats, mayonnaise, creams, cakes, pastries);
- raw onions, garlic, radishes, sorrel, spinach, mushrooms, bean dishes (peas, beans);
- cold and carbonated drinks, concentrated juices, coffee, cocoa, alcoholic drinks.
Folk remedies
Traditional treatment for acute and chronic cholecystitis involves the use of herbal decoctions.
The most widely used collection for cholecystitis is according to N. G. Kovaleva:
- calendula officinalis (aerial part),
- dill (seeds) – 10 g, white birch (leaves) – 10 g,
- forest cudweed (grass) – 10 g,
- common juniper (fruit) – 10 g,
- chamomile (flowers) – 20 g,
- wild strawberries (berries) – 20 g,
- white rose (petals) – 20 g,
- horsetail (shoots) – 30 g,
- corn silk – 30 g,
- brown rose hips (crushed fruits) – 40 g.
5–6 g of the collection are brewed with 500 ml of boiling water, infused and taken 50–150 ml 3 times a day for 10–15 minutes. before meals. The taste of the infusion is bitter, the smell is pleasant.
In recent years, preparations containing essential oils (in particular German ones - Rovahol and Enatin) have found widespread use in the treatment of patients suffering from diseases of the gallbladder and biliary tract. As a choleretic agent, you can use black radish juice, 1 tablespoon 3 times a day before meals for 10–20 days.
The choleretic effect of polyhydric alcohols (sorbitol, mannitol and xylitol) has been convincingly proven. Sorbitol stimulates the production of endogenous cholecystokinin, increases the bacterial synthesis of vitamins B1 and B2, and enhances the absorption of vitamin B12. Sorbitol can be used in the form of a 10–15% solution of 50–75 ml 3 times a day instead of magnesium sulfate. Xylitol is also prescribed in a similar dose.
For chronic cholecystitis
Drinking mineral waters of low and medium salinity with a predominance of bicarbonates, sulfates, chlorine, magnesium, sodium, and calcium is widely prescribed. Use water at thermal (35–42 °C) or hyperthermal (42–50 °C) temperatures.
Mineral waters stimulate bile secretion, secretion, decrease in viscosity and liquefy it. Drink water in the amount of 3 ml per 1 kg of body weight in small sips. More often they use Essentuki No. 4, 17, 20, Smirnovskaya, Borzhom, Slavyanovskaya.
If cholecystitis is complicated by gastritis with high acidity, then mineral water is given 1–1.5 hours before meals, with gastritis with normal or low acidity - 40 minutes before meals. before meals. The course of treatment with mineral waters is 1–1.5 months. with a break between the next course of 3–6 months.
Inflammation of the liver and gallbladder
The liver and gall bladder are like two puzzles of one picture. The work of one depends on the functionality of the other and vice versa. In this case, liver disease entails inflammation of the gallbladder, and not vice versa.
- There are two forms of hepatitis - acute and chronic. In the first case, the patient may not even catch those important signals from the body. After all, the symptoms are very similar to the common flu. That is why treatment is often delayed and severe.
- With chronic hepatitis, the symptoms are known to many and are obvious. These include yellowing of the skin and eyeball, brown urine, and discoloration of stool.
IMPORTANT: If treatment is not started in time, the patient will begin to develop cirrhosis of the liver. That is, a complete restructuring of the organ cells occurs and its functionality changes.
- If we talk about the reasons, they also lie in poor diet and unhealthy lifestyle. But liver disease more often occurs against the background of the development of infection in the body and the entry of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Treatment requires emergency care. By the way, during an examination it often becomes clear about the disease based on the size of the liver. When it becomes inflamed, it increases in size.
Surgical treatment
Removal of the gallbladder is carried out in case of advanced cholecystitis, ineffectiveness of conservative treatment methods, or calculous form of the disease. Two techniques for organ removal have found widespread use: open and laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Open surgery is performed for complicated forms, the presence of obstructive jaundice and obesity.
Videolaparoscopic cholecystectomy is a modern, low-traumatic technique, the use of which can reduce the risk of postoperative complications and shorten the rehabilitation period. In the presence of stones, non-surgical crushing of stones using extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy is possible.
Rehabilitation
Physiotherapy and spa treatment is an important component of comprehensive rehabilitation of patients. Inductothermy and a UHF electric field are used as thermal procedures to correct hypertonicity of the gallbladder and have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. The course of treatment is 12-15 procedures, daily. In order to stimulate the emptying of the gallbladder, a low-frequency pulsed current is prescribed. To reduce dyskinetic phenomena, electrophoresis of 5% novocaine, 2% papaverine is recommended.
To normalize the functional state of the nervous system, a galvanic collar according to Shcherbakov and electrophoresis with bromine are used. For the same purpose, coniferous, oxygen and carbon dioxide baths are prescribed. Sanatorium-resort treatment is indicated no earlier than 2-4 months after an exacerbation of cholecystitis. Patients are sent to balneo-mud resorts: Essentuki, Zheleznovodsk, Truskavets, Morshin.