Causes
A non-functioning gallbladder means that it has completely lost its functionality. The causes of the pathology can be both diseases and changes in the organ itself, and problems with the bile ducts.
The main reasons are considered to be:
- Cholelithiasis (cholelithiasis). The bladder becomes clogged with stones, which leads to the onset of the inflammatory process. It happens when cholelithiasis is ignored for a long time; in such cases, the disabled organ is a complication of stone deposition. The stones form solid neoplasms, the organ is filled with stones, and bile “does not fit” in it. As a result, the gallbladder becomes nonfunctional.
- Flowing obstruction. The bladder is connected to the ducts by a vessel through which bile passes. The presence of stones or scars in this area can cause a blockage in the passage of bile.
- Porcelain organ. This is a pathology in which bladder dysfunction is provoked by metabolic disorders. Due to a metabolic failure, growths appear on the walls of the bladder. As their size increases, they cover the tissue of the organ and it hardens. Because of this, it stops contracting and loses other functions.
- Shriveled gallbladder. Sclerotic processes lead to tissue deformation, the bubble becomes tissue-like and fits tightly to the liver. Shrinking of the organ causes it to appear deflated.
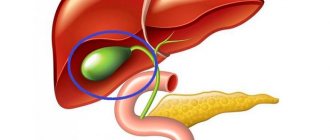
Disabled gallbladder: what is it?
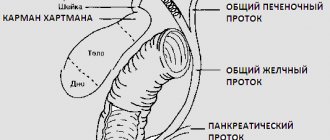
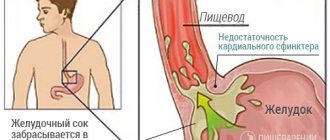
A disabled gallbladder is said to occur when bile does not flow into or out of its cavity. In such a situation, bile enters the duodenum through the common bile duct, bypassing the organ. The main cause of gallbladder dysfunction is cholelithiasis. Mechanisms of occurrence of pathology in cholelithiasis:
- Filling the gallbladder cavity with stones. Occurs during a long course of cholelithiasis. The walls of the organ are so stretched by the stones that they cannot contract.
- Obstruction of the cystic duct. A stone can block the exit of the gallbladder. Less commonly, this occurs when the lumen of the cystic duct is blocked by thick, putty-like bile. A factor that further contributes to this is inflammation of the neck of the gallbladder.
- Sclerosis of the gallbladder wall. Consequence of long-term chronic cholecystitis that was not treated. The gallbladder becomes wrinkled. Its muscle fibers are replaced by connective tissue that are not capable of contraction.
- Calcification of the gallbladder. Calcium deposition in the walls of the organ. One of the medical terms for pathology is “porcelain gallbladder.” The danger largely lies not in the disappearance of the function, but in the high probability of the formation of oncopathology.
Obstruction of the cystic duct can be caused not only by stones, but also by tumors. Obstruction of patency occurs when the duct is compressed from the outside or the lumen is blocked from the inside. In rare cases, a disabled gallbladder is a consequence of a congenital pathology. For example, with underdevelopment of an organ. Sometimes the cessation of bladder function without organic pathology is caused by a severe disorder of its motility.
The progression of congestion in the gallbladder leads to degenerative phenomena in its wall. The pathology can be permanent or temporary. The longer the gallbladder is in a disabled state, the greater the likelihood that its function will not resume after the organ’s patency is restored.
Symptoms
A disabled gallbladder is often the result of advanced cholelithiasis and associated pathologies. Therefore, the symptoms are similar to those that appear in advanced stages of cholelithiasis.
The main ones are:
- severe pain syndrome;
- flatulence;
- bloating;
- problems with stool, often diarrhea;
- heartburn;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth after eating and in the morning.
Vomiting after eating is a symptom that requires urgent medical attention; it is usually associated with blockage of the bile ducts due to a large number of stones and concretions.
Symptoms when the gallbladder is turned off may be mild. Sometimes painful sensations can be mistaken for inflammation of appendicitis. And also due to a violation of the outflow of bile, it enters the blood, which causes yellowness of the skin and increased color of urine. Some people perceive such symptoms as signs of jaundice.
Clinical picture
The symptoms of gallbladder pathologies are not always pronounced. For a long time, a person may not even realize what is actually happening in his body.
When the pain begins, he thinks that it is jaundice or inflammation of appendicitis, but in fact the situation is a different pathology.
When there is a shutdown of the bile-storing organ, there may be such manifestations as pain in the hypochondrium region, increased flatulence, heartburn, bloating, stomach problems, fever, attacks of vomiting, hepatic colic, and an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, there is a risk of losing the integrity of the walls of the organ, as well as starting an inflammatory process.
As a result, pus will enter the cavity of the abdominal surface, which can lead to peritonitis. Without medical intervention, this process can be fatal.
Consequences for humans
If the gallbladder has stopped functioning, this is a sign that the digestive system has been suffering from ongoing inflammatory processes for a long time. Gallstone disease is easily treated in the initial stages, when stones have just begun to form, there are few of them. But when the bladder has already lost the ability to accept and secrete bile, the stage of cholelithiasis is severe.
The fact that the consequences are truly dangerous is due to their irreversibility; most violations cannot be restored.
When the inflammatory process affects the walls of the bladder, their integrity is compromised. They can become hard as stone or, conversely, deplete when the organ shrinks. If pus has already accumulated inside the bladder, then due to the weakness of the walls it leaks outside the organ and enters the abdominal cavity. The consequence of this is often intensively developing peritonitis. Peritonitis can result in death.
If you seek medical help in time, you can return the walls of the bladder to their previous tone. This requires complex treatment, which includes medication and diet therapy. They are often prescribed for life, but this is the only way to resume the functioning of the organ.
Fact. Strong, intense inflammatory and purulent processes that last for a long time can turn off the gallbladder. Therefore, a favorable outcome and complete recovery are unlikely.
Guide to therapeutic actions
If the first signs of the disease are detected, you need to contact a doctor who will prescribe a course of treatment, regardless of the stage of the pathology.
It is worth considering that in the presence of this pathology, it is necessary to undergo surgical intervention associated with the removal of the gallbladder organ. The procedure is called cholecystectomy.
Proper surgical intervention is presented in several types: laparoscopy or abdominal surgery.
In the first case, the consequences for the body will not be very pronounced. If laparoscopy is prescribed.
It is carried out in the form of several incisions, the punctures are miniature, and therefore this type of surgical intervention is tolerated quite well by patients with gallbladder diseases.
Doctors try to make every effort to preserve the organ, but this is not always possible, and therefore, if the gallbladder is not able to recover with the help of treatment, it poses a danger to humans.
In such cases, specialists decide to completely remove it. If the gallbladder is disabled, what to do and what course of treatment to choose should be decided exclusively by an experienced doctor, who is based on the results of the diagnosis of the patient’s body.
It may be that for the purpose of recovery and treatment, therapeutic or medicinal treatment is prescribed, and retrograde cholangiopancretography is performed.
This procedure is prescribed if there are stones or known plaque. They can be broken down using special preparations.
The doctor, first of all, prescribes medications that should help the body strengthen its immune system. These are drugs that have a tonic effect.
Also included here are products with a choleretic effect. Thanks to them, it is possible to remove signs of inflammation, spasms and pain, and improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
If the duct is blocked by a stone, the doctor will prescribe a remedy to dissolve the formation.
But when the gallbladder is disabled due to the lack of tone in the muscle layer of tissue, you need to use medications and a special diet.
All methods of treatment, including alternative medicine or recipes for natural infusions, healing decoctions, are best discussed with the treating specialist; self-medication can have a detrimental effect on the patient’s subsequent condition.
You need to understand that the same remedy is not able to give the desired result for two completely different degrees of development of the disease.
Health is no joke, as WHO statistics once again prove.
Diagnostics
Any dysfunction of the biliary system requires urgent diagnosis. It is impossible to assess the condition of the gallbladder without instrumental studies. And also a disabled organ is accompanied by severe inflammatory processes, which also need to be diagnosed.
The examination usually begins with an ultrasound. Previously, if bladder dysfunction was suspected, an x-ray was prescribed, but this method of examination is less effective. The main task of ultrasound is to assess the condition of the organ, it can be:
- completely disabled;
- malfunctioning;
- normally functioning.
On the screen, the specialist sees stones and other formations located inside the bladder.
Sometimes ultrasound reveals signs of cancer, more often this happens in older people over 60 years of age. In this case, an urgent referral of the patient to oncologists is required.
In addition to ultrasound, other examinations are prescribed to help decide what to do for the patient and what treatment tactics to prescribe. They may be:
- palpation – to assess pain when touching an inflamed organ;
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- cholecystography with the introduction of a contrast agent;
- duodenal sounding.
Therapeutic diet
Nutritional therapy is always recommended in combination with other means and methods against this disease. The diet has the following features:
Eat often, in small portions (up to 300 g).- Do not fry dishes, but boil, stew, steam.
- Consume more plant foods, less animal fats.
- Do not forget about choleretic products, especially vegetable and fruit juices.
- Season vegetables with vegetable oil to stimulate bile drainage.
- Eat more foods with vitamin C.
- In the acute phase of the disease, eat only liquid, semi-liquid food, and pureed foods.
- Reduce the amount of salt and sugar in your diet.
- Drink at least 3 liters of fluid per day.
There are foods that the diet completely prohibits from eating when the gallbladder is disabled. These include beef fat, lard, lamb fat, as they are too heavy to digest, as well as ketchup, mayonnaise, marinades, and mustard. In the initial period after the operation, the menu is meager and mainly vegetarian (vegetables and fruits with an abundance of essential oils are also prohibited - radish, rhubarb, onions, garlic, and the like). Then throughout your life you should limit the amount of mushrooms, high-calorie foods, fatty fish, fried and spicy foods.
The patient can eat dried bread, jelly and compotes, fermented milk foods, eggs (sometimes only without yolks), and soups without frying in low-fat broth. Semi-viscous porridges are useful - buckwheat, oatmeal, barley, baked fruits and vegetables. But you can only eat ripe fruits - watermelons, melons, apples, pears and others. Sour, unripe fruits are prohibited for consumption. Not everyone can eat cabbage and legumes, which increase gas formation and irritate the mucous membrane of the gallbladder. We must also not forget that diet, despite its importance, will never cure the disease completely, so if necessary, you will still have to decide on surgery or conservative treatment.
Treatment methods
There are two main methods of treatment for a disabled gallbladder: surgical and medicinal. Surgical intervention is required in cases where it is clogged with stones. Then an operation to remove the stones is prescribed. If the tissues of the organ are depleted, irreversible processes of death have begun, and complete removal of the bladder may be necessary.
Recently, laparoscopy has been used to remove an organ - this type of surgery is less traumatic and the rehabilitation period is shorter.
If the patient seeks help on time, the walls of the bladder can still be restored and functionality restored; drug therapy is prescribed. It is determined individually by the attending physician, who takes into account the patient’s condition, ultrasound results, the likelihood of recovery, and the degree of the inflammatory process.
Signs of gallbladder disease
The following groups of drugs are usually prescribed:
- antispasmodics;
- analgesics;
- fluoroquinols;
- cephalosporins;
- vitamins;
- alkaline mineral waters.
Their use is aimed at reducing the inflammatory process, eliminating pain, and restoring the gallbladder. Fluoroquinols and cephalosporins help dissolve stones and remove them naturally. However, if there are a large number of stones and/or large stones, pus, and other complications, such drug therapy will not only be ineffective, but will also aggravate the inflammatory process. Therefore, drug treatment is rarely used and is often preceded by surgery.
What to do if your gallbladder is disabled?
For diagnosis, you should undergo a complex examination - cholecystography, since ultrasound does not provide a complete picture of the pathology. The doctor must find out the reason why the gall bladder is turned off, and then decide what to do. There is no point in preserving an organ if it is clogged with stones, deformed, or has a lot of scars and adhesions. Such an organ will never work again, so an operation is performed - abdominal or laparoscopic cholecystectomy to remove the gallbladder.
If the cystic duct is blocked by a stone, you can try to push it back using special tools. Drugs are often prescribed that can dissolve stones, but they do not always help. Reduced organ tone is stimulated with medication, and, as a rule, the effect is positive. In case of pathology, it is mandatory to prescribe a diet in accordance with available medical recommendations. Diet is also urgently needed for patients after surgery to remove an organ.