Hemorrhoids are a fairly common disease among residents of large cities who have crossed the thirty-year mark. It appears unexpectedly, at first accompanied by only barely noticeable symptoms that can be confused with the consequences of dietary errors. As the disease progresses, its manifestations become more and more unpleasant. However, a modern office worker, even if bleeding occurs, cannot find time to visit a doctor and goes to the pharmacy in the hope that the next suppository, on the advice of the pharmacist, will cure the disease.
Gradually the disease starts. External ones are added to the internal nodes, the inflammatory process becomes permanent. The patient is occasionally bothered by itching, burning, a feeling of fullness in the intestines even after going to the toilet, and a little later a nagging pain appears, which intensifies at the time of defecation. At this stage, a person may decide to visit a doctor who will have to treat already chronic combined hemorrhoids. But even in this case, it can be dealt with by choosing the right therapeutic course.
Stages of development
Hemorrhoids progress gradually. Several years pass from the appearance of the first symptoms of the disease to the fourth stage.
| Stages of disease development | Symptoms |
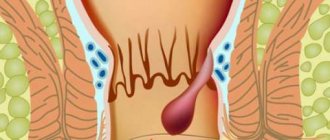
| First stage | The first nodes are located inside the rectum. At first they don't show themselves at all. A little later, the patient experiences a feeling of fullness, the presence of a foreign body, insufficient bowel movement, and over time, burning, itching, and slight bleeding are added. |
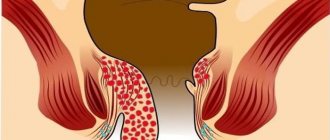
| Second phase | Hemorrhoidal cones begin to come out, but spontaneously set back. During defecation, a person becomes more tense than usual. Traces of blood on linen and toilet paper are constantly recorded. At this stage, the disease takes on a combined form. |
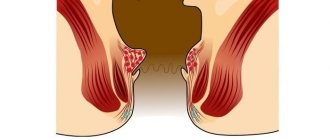
| Third stage | The knots come out and do not retract back, but they can still be set by hand. Constipation becomes constant, the inflammatory process progresses due to the loss of nodes. The itching and burning do not stop, and bleeding is observed during each act of defecation. |
| Fourth stage | The most difficult period is when hemorrhoids go from combined to external form. Knots fall out constantly and are rarely fixed inside. Frequent heavy bleeding is observed. |
At different stages of its course, hemorrhoids have specific treatment options. If in the first two stages you can get by with taking systemic drugs and using local remedies, then combined hemorrhoids of the 3rd degree involves treatment using minimally invasive surgical interventions, such as ligation, cryodestruction, sclerotherapy. At the fourth, advanced stage, hemorrhoidectomy is performed - abdominal surgery.
What is the disease
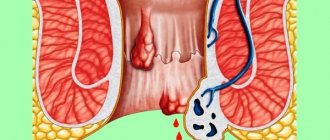
Hemorrhoids are a proctological disease. Is a varicose expansion of hemorrhoidal veins. This occurs due to stagnation of blood in the venous vessels of the lower rectum. Over time, the walls become much thinner due to constant pressure, and this is very bad. After all, in the future it leads to the formation of nodes and bleeding.
There are several types:
- acute (sharp development of pathology with large nodes that can protrude beyond the anus, accompanied by severe pain and severe bleeding);
- chronic (the disease develops over a long period of time, is accompanied by pain and minor bleeding; upon examination, hemorrhoidal spots and small nodes are observed).
Reasons for the development of pathology
There are several reasons for the occurrence and development of hemorrhoids. It does not appear out of nowhere; there are always negative factors that provoke the progression of the disease. The main reason is a family history of venous diseases. If they were recorded among close relatives, you need to be doubly careful, following some rules.
| Cause of hemorrhoids | Prevention measures |
| Poor nutrition | Eating vegetables, fruits, avoiding spicy, fatty and smoked foods will help normalize digestion and avoid constipation. |
| Insufficient water consumption | By increasing the volume of clean water consumed to two liters per day, a person normalizes his metabolism and puts his digestion in order. |
| Heavy physical activity | By refusing to lift weights and strength sports, a person will protect himself from an unpleasant illness that can complicate life. |
| Excessive stress response | By reacting more calmly to irritants, you can protect yourself from many gastrointestinal diseases. |
| Sedentary lifestyle | By moving more and doing simple exercises from the school physical education course, you will be able to prevent the appearance or development of hemorrhoids. |
| Pregnancy and childbirth | Even in this case, it is quite possible to prevent the disease from developing. By changing your diet, adding walking to your daily activities, consuming enough liquid, and performing combined Kegel exercises, a woman will protect herself from hemorrhoids. |
If the necessary measures were not taken when symptoms of the disease appeared, the treatment was not agreed with the doctor and was irregular, the disease progresses. Chronic combined (mixed) hemorrhoids of 2-3 degrees require more serious, systematic therapy, which will be selected by a proctologist after conducting the necessary diagnostics.
Treatment of mixed hemorrhoids
Treatment for combined hemorrhoids depends on the stage of the identified pathology. Conservative, minimally invasive and classical surgical techniques are used. The onset of pathology can be compensated by prescribing a diet and a complex of therapeutic exercises. The diet and exercise therapy are selected only by the doctor on an individual basis. But the patient is always shown to follow the general simple rules:
- exclusion from the diet of foods and drinks that cause constipation or diarrhea: for example, alcohol, coffee, soda, spicy, fatty foods, seasonings, spices, sauces;
- refusal to lift weights: for a woman, weighing more than 2 kg is already heavy;
- when working sedentarily, get up every hour and walk a little;
- on the advice of a doctor, always have on hand a drug to relieve pain, inflammation, and priming: three in one;
- It is imperative, at any opportunity, regardless of location, to perform Kegel exercises to train the pelvic floor muscles.
Medications
Treatment of combined hemorrhoids is complex. The goal is to relieve symptoms and prevent the development of complications or exacerbations. If we are talking about surgery, then medications are designed to facilitate and speed up preparation for surgery and significantly alleviate the patient’s condition during the rehabilitation period.
Pathogenetic therapy includes systemic and local drugs:
- phlebotonics: Detralex, Venarus, Phlebodia 600, Troxevasin, Troxerutin, Antistax;
- antispasmodics: No-Shpa, Spazmalgon, Spazgan;
- NSAIDs: Diclofenac, Indomethacin, Nise, Xefocam, Ketorol;
- enzymes: Festal, Mezim, Creon, Pancreatin;
- dysbiotics: Bactisubtil, Bifiform, Hilak-forte.
Locally prescribed:
- anesthetic suppositories and ointments with local anesthetics: suppositories with belladonna, anesthesin, lidocaine, novocaine;
- suppositories with antispasmodics: Proctosan, Neo-Anuzol;
- combination drugs: Posterizan;
- antithrombotic external agents: Geparoid-Zentiva, Lyoton-gel, heparin ointment, Hepatrombin G;
- as hemostatic agents: suppositories with adrenaline, Natalsid (in severe cases, parenteral hemostatics are used simultaneously - Etamzilat, Dicynon).
The effectiveness of minimally invasive therapy
In the case of combined (mixed) hemorrhoids, minimally invasive therapy is used at all stages of the disease:
- starting with the first, sclerotherapy is indicated: a sclerosant is injected into the node, which causes the replacement of the lump tissue with connective tissue fibers, when the nodes are still small in size and do not fall out, but blood is released; in the later stages, the procedure is used to stop bleeding;
- latex ligation – constriction of the cavity base with a latex ring is used at any stage and is correlated with the number of affected nodes and their size;
- infrared, laser, electro-, cryo- and radiofrequency coagulation is the doctor’s choice for combined hemorrhoids;
- disarterization - a method of alternately ligating the vessels feeding the lump under ultrasound control - is the most effective, practically does not cause relapses, but is expensive, requires special equipment and physician skills, and is not widely used in the Russian Federation.
Combined advanced hemorrhoids of the third or fourth stage without minimally invasive techniques at the first stage are sometimes impossible to cure even with classical hemorrhoidectomy.
Surgery
Surgical intervention for chronic combined hemorrhoids is prescribed only if conservative therapy and minimally invasive techniques are ineffective. A closed or open classic hemorrhoidectomy according to Milligan-Morgan is performed with complete excision of the nodes and mucosa. Or a gentle Longo operation is performed while preserving the mucous layer.
Symptoms of the disease
Typically, stage 3 chronic combined hemorrhoids are more severe than just submucosal or subcutaneous hemorrhoids. The inflammatory process begins either in internal formations or in external bumps, so exacerbations occur much more often.
Symptoms of this form of the disease are:
Discomfort in the anus
- Feelings of severe and often unbearable itching and burning in the anorectal area.
- The feeling of the presence of a foreign object, which appears due to the inflammatory process in the internal nodes.
- Presence of bleeding. Traces are found on toilet paper or linen.
- Pain during defecation.
- Hemorrhoids prolapse outward.
- As the disease develops, constant pain and a feeling of heaviness appear in the intestines.
How to treat chronic combined hemorrhoids 2, 3, 4 degrees
Mixed or combined hemorrhoids occur due to the location of hemorrhoids both inside and outside.
At the initial stage, it is difficult to identify the problem of discomfort and take appropriate measures. This is due to the fact that hemorrhoids occur slowly and take a long time to move from one stage to another. With combined hemorrhoids, the patient may feel more discomfort than with the internal or external type of this disease. This is due to the fact that during remission of internal hemorrhoids, external hemorrhoids may worsen. And vice versa. With combined hemorrhoids, increased thrombus formation can significantly worsen the patient's condition.
Combined grade 2 hemorrhoids are the initial stage of this disease. There are three degrees of development in total.
Almost every person faces a disease such as hemorrhoids. This is the most common ailment in proctology. More than 40 percent of all patients of a proctologist come to the doctor with the problem of hemorrhoids. This disease is the main disease of people who have pathologies of the rectum. However, society does not want to talk about this problem, tries not to pay attention to it, avoids answering and does not seek help. So let's at least first understand what hemorrhoids are.
Hemorrhoids are a disorder in the size of hemorrhoids, in which the patient feels discomfort in the anal area, such as itching, sensitivity, burning, bleeding, pain during bowel movements and prolapse of hemorrhoids. The question of surgical removal of hemorrhoids arises when there is thrombosis, bleeding and other symptoms.
- The first stage includes internal hemorrhoids. With this development of the disease, the patient feels itching in the anus and slight discomfort during bowel movements.
- The second stage includes hemorrhoids with prolapse of hemorrhoids during defecation. At this stage, the patient experiences itching of the anus, pain during bowel movements, burning inside the rectum and bleeding.
- The third stage includes prolapse of hemorrhoids during physical exertion. This degree of hemorrhoids can be determined visually and by touch.
- The fourth stage or acute hemorrhoids. Prolapse of hemorrhoids and the impossibility of their reduction. Treatment is carried out only surgically.
Diagnostics
It is impossible to cure hemorrhoids without diagnostics, which can be done by visiting a proctologist.
First, he will perform a digital rectal examination, which will allow:
- determine the condition of the internal lining of the rectum;
- assess the tone of the anal sphincter;
- find out how ready the rectum is for other diagnostic procedures;
- assess the condition of hemorrhoids, which in the combined form of the disease can be located both outside and inside the rectum;
- detect polyps;
- detect thrombosis.
After performing a digital rectal examination, the doctor may conduct an additional examination using an anoscope. The procedure is accompanied by unpleasant sensations; if there are cracks, bleeding may occur.
To confirm the diagnosis of chronic recurrent combined hemorrhoids of the 3rd degree, it will be necessary to undergo an examination using a colonoscope - an optical fiber tube that allows you to see the intestinal walls from the inside. You need to prepare for this procedure in advance - do an enema or take special laxatives.
The sigmoidoscopy method involves the use of a special instrument inserted into the rectum, thanks to which the doctor receives data on the presence of:
- internal hemorrhoids;
- neoplasms;
- thrombosis;
- fistulas.
Another popular diagnostic method is irrigoscopy. This X-ray examination is carried out after the administration of a contrast agent; it allows you to detect tumors, find out their size and exact location.
What are the stages of hemorrhoids?
We usually use sclerotherapy and infrared photocoagulation for ongoing bleeding from internal hemorrhoids. Especially if the patient has low hemoglobin due to hemorrhoidal bleeding, then after sclerotherapy and photocoagulation we achieve a temporary stop of bleeding. After normalization of the patient’s hemoglobin levels, we prescribe radical surgery.
In addition to the above treatment methods:
To treat the initial stages of hemorrhoids, we also use disarterization of hemorrhoidal arteries under Doppler control. The essence of the operation is to stitch the vessel feeding the internal hemorrhoid. As a result of disruption of blood flow to the hemorrhoidal node, the latter decreases and blood flow stops. The suturing of the arteries occurs under the control of Doppler ultrasound. We often use this technique as an auxiliary part during radical operations.
Therapeutic measures
Coloproctologist
Treatment of acute combined hemorrhoids should include several stages, at each of which both medications and physical procedures, hirudotherapy, and Kegel gymnastics are used. Systemic drugs are used, which are convenient, reliable and help relieve symptoms of the disease in a short time. They are taken orally, which is a big plus because you can take the pill at work, making it easier to stick to your medication schedule.
To relieve the symptoms of combined hemorrhoids, it is also necessary to simultaneously use an ointment that works externally and suppositories that act on the internal nodes. It is important not to forget about hygiene procedures - cool baths, replacing toilet paper with wet wipes or washing.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine
If hemorrhoids have acquired a combined form, treatment with traditional methods is impossible, it will not bring any effect. Moreover, if a person decides to abandon conservative therapy in favor of home remedies, he will waste time. In this case, the disease will progress, and, ultimately, only a surgeon can cope with it.
However, if combined hemorrhoids are in remission, traditional medicine can be used as a preventative measure. Cool sitz baths with decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, knotweed, nettle, burnet) should be continued after the symptoms subside. Chilled compresses with aloe, dandelion, and yarrow will also not cause harm and will prevent the exacerbation of the disease.
Insulin injection: how to give an insulin injection
Sometimes a person becomes a home nurse or nurse out of necessity.
For example, you have to perform various types of injections at home. Then, in particular, there may be a need to perform a subcutaneous injection. This article will tell you how to do it correctly. How to give subcutaneous injections is taught in all sorts of courses, but you can master this simple technique yourself, for both women and men. With a fairly calm and careful approach, problems should not arise at all.
Injections are given subcutaneously for the reason that, due to the good blood supply to the subcutaneous fat layer, medications are absorbed better and faster here. Accordingly, the effect of drugs introduced into the body is thus more effective than when administered orally. Up to two milliliters of solutions are usually injected subcutaneously.
Subcutaneous injections are made with a needle with the smallest diameter. Obviously visible large vessels should be avoided. The most suitable places for subcutaneous injection are the outer humeral surface and the outer femoral surface. Sometimes subcutaneous injections are performed in the subscapular space or the lower part of the axillary region. In these places it is easiest to grab the skin into a fold, and the risk of damage to large blood vessels is minimal.
Subcutaneous administration of the drug provides a longer effect of the drugs than with intravenous injection. The exception is cases of insufficient peripheral circulation.
Technique for performing subcutaneous injections
First of all, you need to wash your hands well with soap and wear surgical gloves. Next, the following actions are performed:
- You should choose the right syringe for injection. Subcutaneous injections are usually performed with a two-milliliter syringe. The ampoule with the drug is also treated with alcohol, after which a cut is made with a special nail file that comes with the medicine and the tip of the ampoule is broken off. If the medicine is in a bottle with a metal cap and a rubber stopper, then the upper part of the cap should be removed, the surface of the rubber stopper should be treated with alcohol and pierced with a needle. If the drug is in powder, then it should be dissolved through the same needle. The medicine is drawn into the syringe by pulling back the plunger. It is necessary, after the medicine has completely entered the syringe, to remove excess air by slowly and carefully pressing the plunger with your finger. Continue pressing until a stream of solution emerges from the needle. The syringe is held with the needle up, and to collect air bubbles at the outlet, you need to lightly tap the syringe with your finger. The intended site where subcutaneous injections will be made is treated with alcohol. First, a large area is treated with a cotton swab, and then the injection site is treated directly with another swab, also soaked in alcohol. The skin should be grabbed in a fairly thick fold and pulled upward. Quickly but carefully, the needle is injected into the base of the resulting skin fold and inserted into the fat layer. By slowly pressing on the syringe plunger, the medication is squeezed under the skin. With the same quick and sharp movement, the needle is removed from under the patient’s skin, and the injection site is lightly massaged and again treated with alcohol.
Sometimes subcutaneous injections are given in the abdomen. To give the injection correctly, you should mentally draw a figure eight on the patient’s stomach, with its center at the navel.
Injections are made into one of the rings of this figure eight. All other actions are performed almost the same as in the example described above. It should only be taken into account that the skin in this area is very delicate, and all actions must be carried out as carefully as possible to avoid bruising. The figure eight ring changes with each subsequent subcutaneous injection into the abdomen.
The abdominal area is the most commonly used site for insulin injections.
Nurses, however, give insulin injections in other places - buttocks, thighs, upper arms.
When injecting, it is important to remember that each subsequent injection must be at least 3 centimeters from the previous one.
If this is not taken into account, skin thickening and scars may form at the injection sites!
I understood what to do, but here’s how. syringes are ready. Should the entire length of the needle be inserted into the belly? and on the Internet someone writes that it should be inserted at an angle of 45 degrees, others perpendicularly. eh.
Maybe you have some tricks? Or does everything come with experience?
Thank you!!
I inject at 90 degrees, the whole needle to the end
The main thing is to find “your” place. For some it is more comfortable below the navel, for others (like me) closer to the sides
It's not scary at all))))))
Don’t torment your husband, you can do better yourself!
I collect the fold and first lightly poke it a couple of times in different places to find the least sensitive point
Then I carefully and slowly press the needle into it
And then I also inject the medicine very slowly.
I didn’t have any tricks, I just read the instructions and injected. Different drugs inject differently, for example Puregon at 90 degrees, but Clexane at 45, I don’t know why this is so. But I personally didn’t care, because I tried to overcome my fear. The first time I sat with a syringe in my hand for half an hour))) and then I injected myself and immediately thought, what a fool - it doesn’t hurt at all!
Are you pressing in slowly?!?!?!
I'll try)))) but really I still have a barrier.
Yesterday it seemed painful to me ((((and after it there were painful sensations
//fb. ru/article/20294/kak-delayutsya-ukolyi-podkojno
//bogmark. com. ua/hypoderm/
//elhow. ru/zdorove/pervaja-pomocsh/kak-kolot-v-zhivot
//www. babyplan. ru/otvety/_/kak-pravilno-delat-ukol-v-zhivot-r16623
Complications and prevention
If you do not pay due attention to your health, chronic hemorrhoids in your medical history can lead to dire consequences. At the fourth stage of development of the disease, bleeding becomes so severe that it leads to severe anemia, which is the reason for hospitalization of the patient in a hospital. Persistent inflammation in the anorectal area can lead to loss of bowel control and fecal incontinence.
Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor in time when the first symptoms of hemorrhoids appear, and after the course of treatment, do not forget about preventing new exacerbations - follow a diet, give up bad habits, do Kegel exercises, walk more and exercise.
Precautionary measures
- If you have been prescribed several injections, then they should all be given at a distance of 3 cm from each other. Otherwise, you may end up with thickened skin as well as scars. In addition, each time you need to use a new syringe and the necessary medications. If you are afraid to give injections in the stomach yourself, ask someone from your family or use the services of a professional nurse. It is worth noting that an injection in the stomach can be made with a syringe of the smallest diameter to a depth of 1.5 cm, and no more than 2 ml of the drug can be injected. Thus, the drug quickly dissolves in the subcutaneous tissue of the abdomen without causing any harmful effects. To prevent bruising after the injection, cotton wool with alcohol must be pressed to the injection site and held for several minutes. You can also lightly massage the injection site to quickly distribute the drug under the skin. Remember to wear gloves, as otherwise you may get an infection under your skin. Experts recommend not transferring the syringe from one hand to another during the injection.
Here's how to give injections in the stomach. Read more:
- If you have been prescribed several injections, then they should all be given at a distance of 3 cm from each other. Otherwise, you may end up with thickened skin as well as scars. In addition, each time you need to use a new syringe and the necessary medications.
- If you are afraid to give injections in the stomach yourself, ask someone from your family or use the services of a professional nurse.
- It is worth noting that an injection in the stomach can be made with a syringe of the smallest diameter to a depth of 1.5 cm, and no more than 2 ml of the drug can be injected. Thus, the drug quickly dissolves in the subcutaneous tissue of the abdomen without causing any harmful effects.
- To prevent bruising after the injection, cotton wool with alcohol must be pressed to the injection site and held for several minutes. You can also lightly massage the injection site to quickly distribute the drug under the skin.
- Remember to wear gloves, as otherwise you may get an infection under your skin.
- Experts recommend not transferring the syringe from one hand to another during the injection.
- wash your hands (wear gloves);
- treat the injection site sequentially with two cotton balls with alcohol: first a large area, then the injection site itself;
- take the syringe in your right hand (“place” it in your hand - hold the needle cannula with the 2nd finger of your right hand, hold the cylinder from the bottom with the 3rd-4th fingers, and hold the cylinder from the top with the 1st finger);
- gather the skin with your left hand into a triangular fold, base down;
— insert the needle at an angle of 45° into the base of the skin fold to a depth of 2/3 of the length of the needle, hold the needle cannula with your index finger;
— move your left hand to the plunger and inject the medicine (do not transfer the syringe from one hand to the other);
- Apply a clean cotton ball with alcohol to the injection site.