Causes of a “lazy stomach”
Functional dyspepsia syndrome is associated with several sources:
- Dietary disorders, expressed in frequent snacking on the go, consumption of dry and “fast” food (fast food), insufficient consumption of liquid foods, including hot liquid foods, excessive consumption of food, large amounts of nutrients in food, especially fat.
- Eating a diet with no or insufficient amounts of minerals and vitamins in food. Such an imbalance of substances in food causes functional deficiency.
- Human age is aggravated by enzymatic deficiency, which is accompanied by longer residence of food products in the digestive organs.
- Neoplasms in the stomach that interfere with the normal digestion of food mass, gastritis, consequences of ulcerative processes and other structural and functional abnormalities.
- Nervous shocks and psycho-emotional stress reduce the secretion of juice in the stomach, which causes low enzymatic activity, resulting in dyspepsia. Impaired production of gastric juice is often a consequence of uncontrolled use of medications.
- Disorders of organs other than the digestive system: systemic renal or liver failure.
Which doctor should I contact?
Antacids will help relieve heartburn.
If you experience discomfort and pain in the stomach, stool problems, nausea and vomiting, you should consult a gastroenterologist. After conducting studies (blood tests, stool tests, FGDS, ultrasound, etc.), the doctor will be able to prescribe treatment, which will include conservative techniques, drug therapy, physical procedures and dietary recommendations.
A lazy stomach is a popular name for insufficient functioning of the digestive organ, referring more to a functional disorder than to a specific disease. In medicine, this concept is known as “functional dyspepsia”. Examinations of the gastrointestinal tract do not reveal any abnormalities; blood, urine and stool tests are within normal limits. However, a person feels heaviness in the stomach area, flatulence, and nausea. Eating a small amount of food makes you feel full.
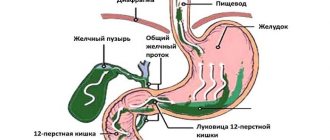
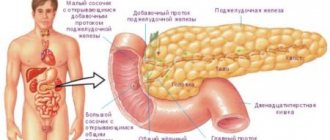
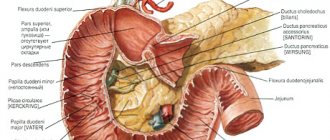
The functions of the stomach include enzymatic grinding of food, rhythmic mixing of the food mass, and peristaltic contractions that promote the movement of food mass into the underlying sections of the digestive system. “Laziness” of the stomach is associated with insufficient implementation of these particular actions.
Symptoms
Signs of a “lazy” stomach are:
- In the gastric region there are unpleasant sensations with a combination of heaviness, which begin to progress after eating food.
- After a meal, a painful sensation may occur in the gastric area.
- Very fast satiety after eating a small portion of food.
- The feeling of mild nausea may intensify and be accompanied by vomiting.
- Flatulence, gas content in the stomach.
In addition to the above general symptoms of functional dyspepsia, there are other signs depending on its type. There are 4 types of dyspepsia:
- Fermentation form, accompanied by a high level of formation of gaseous substances, moving them along with gastric juice and causing rumbling. A person experiences a frequent urge to defecate.
- The ulcerative form of dyspepsia is characterized by the presence of constant or frequent pain.
- The putrefactive form reveals itself as a decrease in appetite, general malaise, and poor health.
- With the pancreatic form, a person has increased irritability, often defecates with loose stools, has stomach rumbling, and a sharp decrease in appetite.
Varieties
Depending on the signs of digestive disorders, experts distinguish the following types of functional dyspepsia:
- fermentative - provoked by the reaction of food with the digestive enzymes of gastric juice, accompanied by a frequent urge to defecate caused by increased gas formation, usually develops with excessive consumption of sweets and kvass;
- putrefactive - develops with excessive consumption of protein dishes, accompanied by lack of appetite, severe weakness;
- pancreatic - accompanied by a deterioration in appetite, stool disorders () and the appearance of excessive nervousness and irritability;
- ulcerative – accompanied by frequent pain in the stomach.
Treatment
If you identify symptoms of a “lazy” stomach, you should not aggravate the functional failure of the digestive organ. A balanced diet with no overeating, multiple small portions of food help normalize gastric digestion of food. Refusal or restriction of food intake that causes irritation of the gastric mucosa (saltiness, spicy foods, citrus fruits and other acidic foods) quickly restores gastric secretion and peristalsis.
The use of medications should be discussed with a doctor after undergoing diagnostic procedures. You should not make a diagnosis on your own without taking into account your general health condition. The doctor may prescribe medications to improve the secretion of digestive enzymes if enzyme deficiency is detected. Detection of Helicobacter pylori in the stomach requires the selection of antibacterial agents.
Answers on questions
What is a “clogged stomach”?
There is no such term in medicine; most likely it is used by the common people. However, a person can feel such a feeling of heaviness in the stomach after overeating, against the background of functional dyspepsia.
Disruption of digestion processes is observed during exacerbation of chronic gastritis and peptic ulcer. In addition to heaviness, a person may be bothered by nausea and belching.
If the feeling of “clogging” of the stomach recurs regularly, it is necessary to undergo an appropriate examination: FEGDS, ultrasound. It is also important to follow the principles of proper nutrition to ease the work of the gastrointestinal tract: eat small portions, 3-5 times a day, avoiding spicy, fried foods, and fast food.
The doctor said that I have impaired gastric motility. What does it mean?
Gastric motility is the sequential contraction of muscle fibers for the purpose of grinding and moving food into the small intestine. If it is disrupted, food is poorly ground into chyme and remains in the lumen of the stomach for a long time, which negatively affects the absorption of vitamins and essential nutrients. In addition, rotting processes are started. Some people also call this condition “sluggish stomach.”
If the motility of the gastrointestinal tract is impaired, the following complaints may appear:
- feeling of heaviness in the upper abdomen;
- discomfort after eating;
- nausea, less often – vomiting;
- belching with a putrid odor.
The diagnosis is confirmed by gastroscopy (FEGDS), in which the doctor detects sluggish peristalsis, cloudy greenish or dark yellow contents in the stomach. Treatment depends on the pathology. Prokinetics are used to normalize motor function.
What could be the reasons for feeling full and quickly getting full of food?
One of the common causes of such complaints is postprandial syndrome as a variant of functional dyspepsia. This disease is a functional disorder in which the gastric mucosa is overly sensitive to distension by food. Diagnosis consists of excluding organic pathology; treatment involves the use of sedatives, antacids and prokinetics.
Rapid saturation with food is also observed in chronic gastritis, stenosis of the stomach or duodenum. Much less often, a premature feeling of fullness can be a sign of a stomach tumor (when it reaches a large size), while it is important to pay attention to other symptoms: sudden weight loss, aversion to meat foods, etc.
Today, you probably won’t surprise anyone with a weak stomach - this is a very common problem, because a large number of people regularly experience feelings of constant heaviness, bloating, nausea and vomiting, as well as other similar unpleasant sensations and problems. How to strengthen your stomach, read further in the article.
Prevention
You can prevent the symptoms of “lazy stomach” syndrome by following simple rules of nutrition and lifestyle:
- daily introduce into the diet foods containing a large amount of fiber (cereals, vegetable dishes, fresh fruits and vegetables);
- limit the intake of fatty and difficult-to-digest foods, do not allow the daily dose of fats (especially animals) to exceed 50 mg;
- do not eat heavily before bed, it is advisable not to eat 2 hours before expected sleep;
- Allow your body to cleanse itself of heavy food one day a week. On a fasting day, you can drink mineral water, eat light food (kefir, broth, juices, etc.);
- Drink still mineral water on an empty stomach and maintain plenty of drinking water throughout the day;
- adhere to an optimal motor regimen with evening walks and physical exercises during the day. Mood and physical activity improve the functioning of the digestive organs;
- limit the consumption of alcoholic beverages, stop smoking;
- learn how to quickly and optimally get out of stressful situations that are a stupor for normal digestion.
A “lazy stomach” will stop frequently giving out whims if you follow the above set of recommendations.
Traditional and folk methods of treatment
Having established the final diagnosis, the doctor decides on treatment methods.
To treat a “lazy stomach” the following is prescribed:
- medications (antibacterial, hepatoprotectors, enzymatic, probiotics);
- maintaining a balanced diet - avoiding fatty, canned, yeast-based foods, semi-finished products, increasing the proportion of fiber in the diet;
- compliance with the rules of eating (full meals throughout the day, chewing food thoroughly), no overeating, no snacking “on the go”;
- getting rid of bad habits;
- increasing physical activity, performing feasible exercises.
In addition, you need to drink at least 1.5-2 liters of clean water daily, which helps cleanse the body and tonify the stomach. It is recommended to eat high-calorie foods for breakfast and lunch, and dinner should be light and not burden the stomach.
Some useful exercises include dancing, walking, climbing stairs or uphill..
Often, for the treatment of the disease, tablets are prescribed to relieve nervous tension.
To eliminate pathology, folk remedies are also popular:
- flaxseed oil or seeds, which can be added to porridges, salads or consumed in their pure form - drink the oil, and chew the seeds thoroughly;
- daily intake in the morning of a mixture of dried fruits (dried apricots, figs, prunes), honey and flax seeds.
It is useful to drink herbal teas and mixtures that improve gastric motility.
Concept of a lazy stomach
A lazy stomach occurs in both adults and children of different ages. This pathological process is usually understood as insufficient functionality of the gastric cavity. In medicine, this disease is called functional dyspepsia. During the study, no deviations were detected. All blood, urine and stool parameters are within normal limits.
But at the same time, the person complains of a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, flatulence and nausea. When you eat a small amount of food, you feel full.
The main function of this organ is the enzymatic grinding of products, rhythmic mixing of the food mass, and peristaltic contractions. The gastric cavity becomes lazy if there is insufficient implementation of all of the above actions.
Pathology in children
Lazy stomach syndrome also occurs in children, even in infants. Doctors believe that the main reason for a “lazy stomach” in a child, unlike in an adult, is errors in the menu.
Negative changes in the activity of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) in children are often observed against the background of excessive consumption of refined foods:
- sweets, pastries, cakes;
- semi-finished products, snacks, carbonated drinks;
- sausages.
Such products reduce the activity of peristalsis. Factors such as malnutrition, excessive food consumption, and irregular meals disrupt the functioning of the stomach.
Other reasons that negatively affect the functions of the gastrointestinal tract in a child are:
- excess emotions (excitement, fear, overwork);
- living in stressful conditions;
- low level of mobility inappropriate for age;
- diseases of the digestive system, intestines, endocrine system.
Symptoms of dyspepsia in children may include:
- refusal to eat;
- belching, which has an unpleasant odor and occurs after eating;
- bowel dysfunction (constipation or diarrhea).
Older children may complain of pain, heaviness in the stomach, and nausea. Sometimes it is enough to change the child's eating habits to make the stomach work.
In a newborn and infant, the disorder is expressed in the form of regurgitation and vomiting.
This most often occurs due to the anatomical and physiological features of the structure of the digestive system and the vomiting center, which receives irritation from different systems of the body.
Constant regurgitation and vomiting, not related to diet and not amenable to antispastic therapy, usually indicate defects in the structure and development of the initial part of the intestine, stomach, and digestive tract.
Causes of a lazy stomach
Lazy stomach syndrome occurs for various reasons such as:
- poor nutrition with snacks on the go, the use of fast foods and processed foods, insufficient fluid intake, high fat and carbohydrate content;
- long-term adherence to a diet lacking mineral components and vitamins in foods;
- age indicators with aggravated enzyme deficiency;
- formation of neoplasms in the gastric cavity. Tumors prevent food from being fully digested;
- frequent nervous shocks, mental disorders or prolonged depression.
The cause of the pathology is diseases of the internal organs of a chronic nature, kidney or liver failure.
It is generally accepted that a sluggish stomach is more common in children aged 9 to 13 years and students. But older people over 60 years old also face this problem.
Causes of the disease
The main reasons for the development of the disease are:
- Poor nutrition, particularly when food consists predominantly of one nutrient;
- Psychological disorders (neuroses, depression, chronic fatigue);
- Gastritis, in which the secretion of hydrochloric acid increases;
- Abuse of medications, especially antibacterial or hormonal ones;
- Violation of intestinal and duodenal motility;
- Lack of physical activity;
- Poisoning of the body with chemicals.
- Other diseases in which illness is normal (allergy to certain foods, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, etc.)
Symptomatic picture
Many patients simply ignore the signs, citing self-recovery of the body. If you have a lazy stomach, the symptoms are characterized by:
- nausea and vomiting;
- quick satiation even with small amounts of food;
- a feeling of fullness and heaviness in the epigastric region;
- discomfort in the solar plexus area after a meal;
- flatulence;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- an increase in the number of bowel movements. Diarrhea may occur;
- loss of strength, weakness, chronic fatigue;
- painful sensations in the abdomen;
- heartburn and belching with sour contents.
In addition, the clinical picture depends on the type of pathology.
In medicine there are:
- fermentation form. If a lazy stomach is detected, the symptoms will be accompanied by increased formation of gases and rumbling. The patient also often complains of a frequent urge to defecate;
- ulcerative form. This type of syndrome leads to constant and frequent pain in the gastric cavity;
- putrefactive form. Manifested by decreased appetite, general malaise, poor health;
- pancreatic form. As a result of the development of such an illness, a person becomes more irritable. He often suffers from diarrhea. In addition to all this, the patient complains of rumbling in the stomach and loss of appetite.
Only an experienced doctor can determine the type of pathological process based on the symptoms of the disease.
Concept and causes of functional dyspepsia
FD refers to periodically occurring pain or a burning sensation in the upper segment of the abdomen, rapid saturation with food, and a feeling of severe fullness in the stomach. Previously, this concept also included: flatulence, vomiting, belching, heartburn, frequent diarrhea (indigestion) and constipation.
The diagnosis of functional dyspepsia is made based on two mandatory criteria:
- The listed symptoms should bother a person for 3 consecutive months, with a total duration of six months.
- Absence of organic damage to the digestive system (as proven by laboratory and instrumental examination methods).
The etiology of functional indigestion is not fully understood, so FD is considered a heterogeneous disease, during which several pathogenetic mechanisms are realized. All of them lead to the appearance of characteristic clinical complaints on the part of the patient.
Diagnosis criteria
Factors that provoke the development of non-organic dyspepsia:
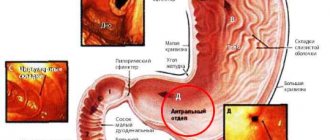
- Impaired motor function in the upper parts of the digestive tube - in the stomach and duodenum. The majority of those suffering from FD exhibit coordination disorders between the antrum and fundus of the stomach, slower distribution and digestion of food; dysfunction of the muscular lining of the stomach during the interdigestive period.
- Visceral hypersensitivity is a significant increase in the sensitivity of the gastric mucosa to stretching by food. Therefore, many patients complain of an earlier feeling of satiety, fullness, and a feeling of fullness in the epigastric region itself.
- – one of the leading factors in the occurrence of functional type dyspepsia.
- . As is known, H. Pylori can provoke not only the development of chronic hyperacid gastritis and peptic ulcers, but also weaken the postprandial motor function of the stomach, disrupt the evacuation of the bolus, and affect the synthesis of hydrochloric acid.
- Recent acute infections of the gastrointestinal tract (in particular, giardiasis and salmonellosis).
- Psychological problems (sleep disorders, depression, anxiety) often act as unique triggers that disrupt the functioning of the central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract.
Since motor dysfunction plays a leading role in the pathogenesis of dyspepsia, this disease is also popularly called “sluggish or lazy stomach.”
Diagnostic measures
If the stomach does not want to function fully, then you need to urgently seek help from a doctor. The doctor will ask about any complaints, conduct an external examination, and then prescribe an examination.
- donating blood for general and biochemical analysis;
- delivery of urine and feces to detect impurities and bacterial agents;
- conducting an X-ray examination using a contrast agent;
- performing ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal organs;
- carrying out manometry and scintigraphy.
Fibro- and phagogastroscopy is considered one of the mandatory types of diagnostics. Such techniques allow you to fully examine the organ from the inside. To identify the cause of a functional disorder, gastric juice is examined. This will help determine the acidity level and take the right measures.
Diagnosis and treatment
Since functional dyspepsia is a diagnosis of exclusion, when characteristic symptoms appear in a patient, a comprehensive examination is indicated.
To confirm the diagnosis, the patient undergoes examinations:
- clinical blood test, general urine test;
- biochemical analysis of peripheral blood;
- coprocytogram;
- sonographic scanning of the abdominal organs;
- FEGDS – fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy, during which morphological changes in the epithelial membranes of the esophagus, stomach and the initial part of the duodenum are excluded;
- for the presence of H. Pylori contamination.
After all possible organic pathology has been excluded, treatment begins.
Note. A history of chronic gastritis or peptic ulcer does not exclude the possibility that the same patient may have functional dyspepsia as an independent disease.
Treatment of patients with FD is always complex and consists of several stages:
- Normalization of lifestyle (improving daily routine, increasing time for rest, eliminating stressful situations and unpleasant communication, including dosed physical activity);
- Getting rid of bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Dietary recommendations: switch to fractional meals, in which you need to eat 6-7 times a day, in small portions. It is important to consume fat-containing foods, fried, spicy and smoked foods as little as possible.
- Prescribing medications.
Drug therapy may consist of several types of drugs:
- PPIs - proton pump inhibitors (Lansoprazole, Omeprazole, Nolpaza). Their main function is to reduce the production of hydrochloric acid by the parietal cells of the gastric mucosa. In some cases, even half the dose of the drug per day is effective.
- H2-histamine receptor blockers (ranitidine, famotidine) are sometimes used together with PPIs. The medicine is used twice a day.
- When H. Pylori is detected, eradication therapy is mandatory. It consists of taking two antibacterial drugs and one antacid for two weeks.
- To normalize motor function, prokinetics (metoclopramide, domperidone) are used.
- Some patients are prescribed sedatives and tricyclic antidepressants in small doses (diazepam, amitriptyline).
Psychotherapy and acupuncture sessions are highly effective.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of a lazy stomach involves complex therapy. It includes:
- taking medications;
- use of traditional methods;
- diet;
- change in lifestyle.
Complex therapy gives more results and allows you to eliminate any cause of the pathological process.
Drug therapy
Drugs are prescribed by a doctor after performing diagnostic measures. When the cause of the pathology is Helicobacter pylori infection, the doctor prescribes antibacterial agents. Often, the regimen includes two medications at once - Amoxicillin and Clarithromycin. They must be taken at the same time.
Diagnosis and treatment of the syndrome
The diagnosis of the underlying disease comes to the fore, which may include various studies:
- detailed blood test (shows the presence of inflammation in the body);
- biochemical study of the patient’s blood serum (most specific for cholecystitis, pancreatitis);
- coprocytogram, bacteriological examination of stool;
- FEGDS – for morphological verification of the diagnosis;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, which includes the liver with the gallbladder and ducts, pancreas, spleen.
Treatment is aimed at the underlying disease and relief of unpleasant symptoms of dyspepsia with the help of diet and medications. It may include antibacterial drugs, pancreatic enzymes, antacids, prokinetics, proteolysis inhibitors, sorbents, probiotics, choleretic drugs and hepatoprotectors.
After complete recovery (for example, with an intestinal infection) or the disease goes into remission, the manifestations of dyspeptic syndrome also disappear.
Preventive actions
A lazy stomach is considered one of the common problems. To avoid the development of such a process, you need to follow some recommendations.
- There are foods high in fiber: baked apples and pears, cereals, stewed vegetables.
- Do not overeat, especially before going to bed.
- Give your body a rest once a week. You need to stop eating heavy foods. On a fasting day, it is better to drink mineral water without gases, kefir, and chicken broth.
- Physical training helps a lot. Every morning before breakfast you need to do special exercises.
- Give up bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Avoid stressful situations. Yoga, water aerobics, and swimming will help you get out of depression.
- Drink fermented milk products at night. This will improve digestion and the state of microflora.
A sluggish stomach leads to fermentation and putrefactive processes. This leads to gradual intoxication of the body and deterioration of the general condition. You should not let the disease progress, but consult a doctor when the first signs appear.
A “lazy stomach,” the symptoms and treatment of which we will consider in this article, is a set of digestive tract disorders that arise due to impaired motility of the stomach. In medicine, this disease is called dyspepsia. The pathology is characterized by pain and discomfort in the upper gastrointestinal tract, rapid satiety, nausea and bloating.
Classification and symptoms of FD
According to the modern classification (FC), functional dyspepsia is divided into 2 types:
- Painful epigastric syndrome (ulcer-like variant).
- Postaprandial distress syndrome (dyskinetic variant).
FD classification
The ulcer-like variant of the disease is characterized by a feeling of intense burning (heat), interspersed with aching or acute pain, which are localized in the upper segment of the abdomen. It is noteworthy that these phenomena do not disappear after bowel movements or the release of gases.
The dyskinetic type of pathology is characterized by a feeling of pronounced fullness in the epigastric zone itself after eating a portion familiar to a person, and earlier saturation due to the low threshold of sensitivity of the gastric wall to stretching by food. All this prevents the normal completion of a meal, eating a full portion, and occurs three or more times a week.
Functional indigestion can occur together with heartburn (as a manifestation), flatulence and bowel dysfunction (which is included in the concept of irritable bowel syndrome).
Reasons for the development of the disease
Lazy stomach syndrome is considered a functional disorder due to the fact that the digestive organ does not perform the necessary functions. Currently, medical specialists cannot say unambiguously what causes the disease. But many attending physicians agree that nervous stress affects the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Nervous experiences can provoke disturbances in the functioning of the stomach and intestines. That is why experienced gastroenterologists, along with medications intended to restore the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, prescribe sedatives.
Causes
So far, gastroenterologists cannot name all the causes of functional dyspepsia. However, their observations show that a condition such as a lazy stomach often develops under the influence of the following factors and causes:
- poor nutrition, overeating, passion for excessively fatty foods;
- chronic diseases of the digestive tract;
- frequent psycho-emotional overload and stress;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- uncontrolled use of medications (especially antibiotics and hormonal drugs);
- hypersecretion of hydrochloric acid;
- Helicobacter pylori infection;
- recent infections of the digestive tract (giardiasis, salmonellosis, etc.);
- smoking;
- coffee abuse;
- drinking alcohol;
- chemical poisoning;
- impaired motility of the upper gastrointestinal tract (stomach and duodenum);
- age-related changes.
In approximately 30-35% of cases, it is not possible to find out the exact cause of functional dyspepsia.
Symptoms of the disease
Immediately after eating, the patient shows the first signs of dyspepsia. In the upper part of the digestive tract, a person begins to experience unpleasant, painful sensations. Some patients note that after a meal they feel fullness and bloating in the stomach, heartburn, nausea and even vomiting occur.
If the symptoms described above appear frequently, and laboratory tests have not shown the presence of other problems with the gastrointestinal tract, then it is necessary to force the “lazy stomach” to function at full capacity. If functional disorders are not treated, the pathological process can develop into a chronic form of the disease.
In addition to those listed, the “lazy stomach” syndrome may have the following symptoms: flatulence, frequent urge to go to the toilet, constant rumbling in the stomach. These symptoms are characteristic of fermentative dyspepsia.
If putrefactive dyspepsia develops in the body, the patient begins to complain of poor health and appetite worsens.
With an ulcer-like “lazy stomach,” the patient complains of severe abdominal pain.
If pancreatic dyspepsia occurs, the following symptoms appear: diarrhea, loss of appetite, nervousness.
What is dyspepsia
The cause of this disease is poor functioning of the stomach, that is, when digesting food, it does not contract, as a result of which the food is not crushed. As a result, the foods that remain in the stomach begin to cause discomfort in a person, manifested in heaviness and other equally unpleasant sensations. With constant poor nutrition, nutritional dyspepsia may occur. This disease can be of several types: putrefactive, fatty or fermentative. If we are talking about the latter type, then this type of disease occurs, as a rule, when a person consumes too many drinks such as kvass, or foods such as sugar, some fruits, honey, legumes, cabbage. As a result, a fermentation process occurs in the stomach.
Putrefactive dyspepsia appears when eating foods that contain protein, for example, pork, lamb, which are digested rather slowly. Often the cause may be not entirely fresh meat. In addition, meat, more precisely, lamb and pork, causes fatty dyspepsia, since it contains refractory fats.
Diagnosis of pathology
A gastroenterologist can make a diagnosis based on a medical examination. Using electrogastrography, the doctor determines functional disorders in the stomach. Using this technique, electrical signals are determined that cause contractions in the stomach and some parts of the intestines. Dyspepsia is characterized by a decrease in electrical activity after eating (with normal values - on an empty stomach).
Additional examinations may also be required: urine and feces analysis, examination of gastric juice for the presence of Helicobacter and acid levels, blood biochemistry, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, etc.
Diagnostics
To carefully examine the gastric mucosa and exclude the presence of organic pathology in it, the patient undergoes gastroscopy.
When identifying signs of functional dyspepsia, which are revealed after analyzing complaints and examining the patient, the doctor must exclude the presence of organic diseases of the digestive system, which may be accompanied by similar symptoms. For this purpose, the patient may be prescribed the following types of diagnostics:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- (FGDS);
- urease test for the presence of H. Pylori contamination;
- stool occult blood test;
- analysis of the gastric mucosa for bacteria;
- daily monitoring of intraesophageal acidity;
- electrogastrography;
- gastric scintigraphy;
- antroduodenal manometry.
If necessary, other techniques may be included in the examination plan: CT, etc.
After excluding organic causes, the diagnosis of “functional dyspepsia” is made if the manifestations that bother the patient are present for a long time and bother about 3 times a year. Manifestations of a lazy stomach do not always occur every day, but they are permanent and change how you feel. In addition, unlike irritable bowel syndrome, with functional dyspepsia, the act of defecation does not bring relief, and the patient continues to feel discomfort.
Treatment of the disease
Lazy stomach syndrome requires complex treatment. The patient is advised to eat often, but in small portions. With this method of eating, food is digested more easily and does not linger in the digestive organ. It is necessary to minimize the consumption of food that irritates the gastric mucosa (spicy and smoked foods, spices and marinades).
Drug treatment can only be prescribed by a gastroenterologist after a diagnostic examination. What to do if the disease is caused by the presence of Helicobacter pylori in the body? The patient is prescribed antimicrobial and antibacterial therapy. In addition, the doctor prescribes medications that affect gastric motility and peristalsis. Antacids and painkillers may be prescribed.
Traditional methods of treatment
Medicines that have anti-inflammatory properties and also coat the stomach can help cope with the disease. To prepare folk remedies that help with dyspepsia, dried fruits, pharmaceutical plants, seeds, etc. are used.
Flaxseeds can make your stomach work. To prepare a medicinal infusion, you need to pour 20 grams of flax seeds into a glass of water (chilled) and leave to infuse overnight. After 12 hours, add grated carrots, raisins and honey to the liquid. The resulting medicinal porridge must be eaten 2 times a day before meals.
Important! Treatment with folk remedies for a “lazy stomach” can only be started after consultation with your doctor. Herbs and plants contain active components that can be harmful, so self-medication can cause severe consequences.
Dried fruits (prunes, dates, raisins and dried apples) have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the stomach. To prepare the medicine, you need to pour boiling water over the dried fruits, steam them, and then grind them into a fine paste. Then add honey there. Drink the mixture on an empty stomach in the morning, and also before going to bed.
A decoction of chamomile, St. John's wort, mint or sage helps to activate the gastrointestinal tract. To prepare a decoction, add 10 grams of dried herb flowers to a glass of boiling water and leave for 30 minutes. Drink instead of tea.
Etiology of the disease
Disturbances can be different, and they depend on the specific cause that caused the disease. But they all boil down to the fact that gastric motility is somehow disrupted.
The organ cannot contract and push food further along the digestive tract. In addition, food lumps are poorly crushed and processed.
Food lingers in the stomach cavity and, accumulating, causes discomfort and a feeling of fullness. In advanced cases, food masses begin to decompose.
Dyspepsia is caused by various factors, based on the nature of which it is divided into 2 types.
Highlight:
- organic dyspepsia, which implies pronounced pathological processes in the digestive system;
- functional dyspepsia, in which structural changes in the digestive tract are not necessarily present.
The organic form of dyspepsia most often occurs as a complication against the background of the underlying current disease of the digestive system (peptic ulcer, reflux, pancreatitis or cholelithiasis), and its treatment is more specific.
Functional dyspepsia is diagnosed when there are no organic lesions in the digestive tract.
The exception is chronic gastritis, in which the activity of the stomach is often disrupted, but no pronounced clinical manifestations of the underlying disease are observed.
Among the main causes of lazy stomach syndrome are:
- improper diet;
- injudicious use of medications;
- stress;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- infection (Helicobacter);
- excessive release of hydrochloric acid;
- disturbances of peristalsis;
- exposure to low frequency ultrasound.
Rules for strengthening the stomach
Let's figure it out together.
So, where should you start every new business first? Of course, by getting rid of old, unnecessary “tails”. Therefore, we strongly recommend that you throw all old, spoiled, expired, tasteless food from your refrigerator into the trash. Remember that all food must be freshly prepared! The refrigerator was cleaned.
Now we cleanse the diet. Eliminate all kinds of spicy, salty, fried and sour foods. It is better to categorically refuse smoked meats. Well, if you can’t do it, use them as rarely and as little as possible. To strengthen the stomach, it is very useful to eat sprouted wheat sprouts and heavily boiled rice porridge. Increase the amount of fresh fruits and vegetables you consume, including carrots. Avoid using mayonnaise as a salad dressing.
Drink as much water as possible - clean, mineral and, of course, still. The average daily water consumption is 2–3 liters, but not everyone can handle this amount, so aim for a minimum of 1.5 liters.
It is very useful to strengthen the stomach with an infusion made from pomegranate peel. In part, this “compote” can replace the usual tea. To prepare a pomegranate drink, you need to take approximately 5 grams of the peel of this fruit and pour half a glass of boiling water. Let the broth brew for at least 20 minutes, and after it cools and steeps, strain. Three times a day you need to drink at least a couple of sips of this remedy.
The most unloved porridge since childhood is incredibly beneficial for our stomach - oatmeal. You need to start every breakfast with oatmeal. You are lucky if you really love this dish, but if not, you should try harder and force yourself. Oatmeal helps remove accumulated toxins from the body, and also stimulates the muscle tissue of the stomach and intestines, which has a beneficial effect on the general condition of the body.
It is recommended to take rice water regularly. This remedy is especially useful for gastritis. Place a spoonful of rice cereal in a container and add 500 ml of boiling water. Simmer over low heat for 40 minutes. Strain the broth. Drink warm, a few sips every two hours. By the way, it can also be used for children as a preventative measure.
Raspberry tea is also beneficial because it strengthens the stomach especially well. To prepare it, you need four tablespoons of crushed raspberry leaves and 500 ml of boiling water. Drink half a mug of this tea four times a day.
To treat indigestion, you need to know its cause, as it can occur for many reasons. This includes the consumption of poor quality or stale food, and excessive consumption of certain foods (for example, fresh plums), and exacerbation of chronic gastritis or stomach ulcers, and much more. And how many of us are unaware of stomach problems in connection with moving to another, especially remote, area? People believe that this happens “due to a change in water”; in fact, climate change and many other factors also play a role here. Today we will talk about traditional methods of treating indigestion.
11 642116
Photo gallery: Traditional methods of treating indigestion
The most effective, and at the same time absolutely safe for health, remedy in this case is black peppercorns. You just need to swallow 6-10 black peppercorns and wash it down with water, preferably boiled. For children, 2-3 peas are enough. No need to chew. This remedy also helps with disorders caused by other reasons. It is convenient because it does not require brewing or other types of preparation, it is found in almost every home and acts surprisingly quickly. So, both at home and in the “travel first aid kit”, this folk remedy is simply irreplaceable.
Nutmeg is also used to treat indigestion. But this remedy is considered very potent, so you should not take more than one nutmeg kernel per day. Even dysentery can be cured with one nutmeg kernel.
For indigestion caused by intestinal infections, dry mustard powder is used. For adults, dilute one teaspoon of powder in ½ glass of cold (namely cold!) water. A repeat appointment is almost never required. For children under 12 years of age, to determine the dose, divide the “adult” dose by 12 and multiply the resulting number by the child’s age. Of course, the child needs to be given something tasty to eat or wash down this medicine. It is strictly forbidden to use mustard for stomach and duodenal ulcers and ulcerative colitis.
Indigestion is also treated with rice water, which is prepared as follows: rinse the rice with water and cook until tender in water in a ratio of 1:5. When the rice is ready, the water in which it was boiled should be drained, cooled slightly, and drunk warm up to two liters per day. Rice also has a binding effect, so it is recommended to eat it during the treatment of indigestion.
To treat indigestion, use an infusion of green tea - the stronger, the better. An infusion that has stood for a day is more effective.
The inner yellow skin lining the chicken stomach should not be thrown away. Dry it and store it, and you will always have a cure for an upset stomach on hand. Grind half the skin of one stomach into powder and brew with a glass of boiling water. After half an hour the medicine is ready. Drink in two doses. In folk medicine, the remedy is considered very effective.
You can also prepare a tincture from walnut partitions for future use. It is prepared like this: remove the internal partitions from 200 grams of walnuts, pour ½ liter of alcohol into a bottle, and let it brew for 3-4 days. Take 5-10 drops diluted in 50-100 ml of warm water 3-4 times a day. The drug is very potent, so you need to stop taking it immediately after the stomach upset stops, otherwise it may lead to constipation.
There are many recipes for herbal decoctions and steams
that help with indigestion. Here are some of them:
Grind one walnut leaf, pour one glass of boiling water, leave for 3-4 minutes and drink as tea.
Linden blossom decoction - 1 tbsp. spoon for 1 glass of boiling water. Leave for 5-10 minutes. Drink warm instead of tea.
Take 1 tbsp. spoon of willow bark, 1 tbsp. a spoonful of chamomile. Pour two cups of boiling water and leave for 10 minutes. Drink 2-3 times a day with honey.
Brew oak bark (5 tablespoons) in one liter of boiling water. Leave for 4 hours. Drink the infusion throughout the day.
Grind the mixture of galangal and burnet and brew 2 tbsp. spoons in boiling water, leave for 20 minutes and drink half a glass every hour with added sugar. Even a severe upset goes away within a few hours. This is a product with strong astringent and bactericidal properties.
Brew 1 tbsp. spoon of pomegranate peel with one glass of boiling water, leave until color appears and drink it all at once, like tea.
If the cause of the disorder is food (especially poisonous mushrooms), it is necessary to cleanse the stomach by inducing a vomiting reaction with large amounts of drink. Then you need to go to bed, be sure to drink a decoction of a mixture of chamomile, St. John's wort and mint. To prepare the decoction, add two glasses of water to the indicated herbs (one tablespoon each), bring to a boil, cool, and strain. Drink half a glass every 2-3 hours.
If an upset stomach occurs due to fear or nervous shock, you need to take soothing decoctions based on mint, chamomile, and calendula. In summer, you can add leaves or shoots of cherries, black currants, and strawberries to the decoction.
If you have an upset stomach, you should drink as much fluid as possible to avoid the possibility of dehydration. It could be cranberry juice, hibiscus tea, green tea.
During treatment and 1-2 days after it, follow a diet. It is better to fast or limit yourself to green tea with crackers. Then porridge, boiled vegetables, compote. Leave sausages, salads and delicacies alone until complete recovery!
We hope that traditional methods of treating indigestion will help you to always be in a good mood and forget about your illness.
When some people say they have a voracious appetite, I don't understand it. My mother told me that as a child I had to be force-fed; I could not remember for days that I needed to eat. I never suffered from this, but as an adult I realized that something was wrong with my stomach.
It turned out that I had low acidity and a sluggish stomach. At one time I was prescribed special digestive enzymes, I took them, but then I decided that I couldn’t rely on outside help all my life and I had to do something myself. I had to watch my diet especially carefully. Fortunately, I am not a particular fan of meat food; I can live on vegetables and fruits for as long as I like. For any stomach disease, it is important not to overeat, eat little and often. I've been used to this for a long time and I like it. But in order for food to be better digested in a lazy stomach, I sometimes eat a special paste for three days at a time: I grate horseradish root, mix it with the same amount of honey and take one teaspoon three times a day before meals. At first I spread the paste on a piece of bread, and when I got used to it, I began to chew the paste without bread.
Chew 50 times - you don’t get sick, 100 times - you live long, 150 times - you’re immortal.
You need to take one or two sprigs of bitter wormwood, two teaspoons of flowers and leaves of St. John's wort, one fresh leaf of indoor geranium, 8 peas of black allspice, 10 pieces of black raisins, one paper bag of black tea (without aromatic additives), one tablespoon of natural honey (or two teaspoons of granulated sugar), pour all 0.5 liters of high-quality vodka. It is more convenient to prepare the mixture in a bottle, because then this bottle must be corked, wrapped in a cotton napkin and placed in a vessel with boiling water. Hold the bottle until the water cools down. After this, remove the bottle, remove the tea bag, cap it again, shake vigorously and place in a dark place to infuse for a month. Strain the finished product and take 2 glasses (about 30-40 g) per meal 2 times a week: drink one glass before meals, the other after.
One bottle is enough for one course of stomach treatment. I can’t say that I regularly used this tincture, but as soon as I felt that food was falling like a stone into my stomach again, I started drinking the tincture. And gradually I got rid of the problems. Now there is no need to take additional medications or enzymes for a long time. I still never overeat, but I no longer experience any discomfort.
There are many reasons for diarrhea. It can be caused by stress, unhealthy diet, infection, poor intestinal absorption, or chronic diseases of the stomach, pancreas, or small and large intestines. It happens that this problem is caused by the protective functions of the body, which is trying to protect its organs from poisoning, thus removing toxins and poisons.
Almost always, diarrhea begins with inflammation of the large or small intestines, so-called colitis and enteritis. It is in them that disruption of digestive processes occurs. The fermentation and putrefactive processes that occur in them are provided by pathogenic bacteria that live in the intestinal tract.
Natural manifestations of diarrhea are seething and rumbling in the stomach, its gurgling, followed by liquid and foamy discharge. It happens that the smell of such feces is very fetid and rotten, which indicates fermentation in the stomach.
When the mucous membranes of the intestines are inflamed, three factors directly influence the development of this unpleasant phenomenon:
- decreased absorption;
- accelerated secretory activity of the intestine;
- volumetric amount of mucus secreted together with feces.
In cases where diarrhea is protracted, only a doctor can prescribe individual treatment. Of course, there are general recommendations that you can use at home. Only initially should you determine what type of diarrhea it is. When fermentative diarrhea is tormented, the best solution is a carbohydrate-free diet, when the main emphasis is on protein foods, such as cottage cheese, meat, eggs, fish. And in the case of putrefactive diarrhea, on the contrary, it will be more effective to refuse protein foods, especially of animal origin. And the main foods that should be consumed for this diarrhea are cereals, vegetables, sugar and fruits. The consumption of certain products should be accompanied by plenty of drinking. We should not forget that all food consumed during treatment must be well boiled and chopped so as not to injure the already damaged mucous membrane of the small or large intestine.
Many of us know enough ways to cure diarrhea at home. Of course, this is effective only in cases where this inconvenience arose due to excessive clogging of the stomach and you want to avoid medications that may not have a good effect on the general condition of the patient.
In the case when a severe blockage of the stomach occurs, it is characterized by the following symptoms: headache, fever, profuse vomiting, unpleasant belching, aching pain in the pit of the stomach and fever. The main thing in this case is to induce a gag reflex, which will help cleanse the body of pathogenic bacteria and remove excess toxins. But it happens that there is practically no vomiting. In this case, the best solution would be to use castor oil, which will help facilitate the elimination process.
There are several traditional home treatment methods that will get rid of diarrhea in a fairly short period of time.
Apple cure
If diarrhea does not have accompanying symptoms such as headache or fever, then treatment with apples can provide quick and effective results. The patient needs to eat one peeled and chopped apple every two hours. You should not refuse such treatment at night. Therefore, the daily consumption of apples should be at least 12 times per day. The main thing at this time is to completely abstain from any food or drink. With this treatment, the patient simply does not feel the need for them. This will not only relieve diarrhea, but will also be an excellent prevention of gastritis.