How is the treatment carried out?
Combination of drugs
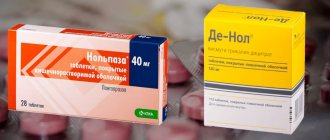
De-Nol for gastritis and ulcers must be taken simultaneously with drugs that reduce the production of hydrochloric acid.
Omez is usually prescribed (the active ingredient is omeprazole). The pharmacological group of this drug is a proton pump inhibitor, that is, an antisecretory drug. Omez and De-Nol, acting in combination, promote rapid healing of the mucous membrane.
In addition, Omez enhances the effect of some antibacterial drugs.
The regimen for taking these medications is prescribed by the attending physician; we only note that Omez can be taken once a day, its effect is quite long-lasting. At the same time, this remedy is used even with normal and even low acidity, only the dosage changes. In any case, Omez must be taken to help protect the mucous membrane from the action of hydrochloric acid while undergoing treatment.
Remember that Omez is a prescription drug and should not be taken without a doctor’s prescription, as this can mask a malignant process in the stomach, which also leads to increased acidity. Before taking any medications, you must undergo a comprehensive examination. Omez is usually prescribed in the morning before meals, sometimes at night.
At the same time, a broad-spectrum antibiotic is prescribed, often combining different drugs with each other (indications for use depend on the results of tests for Helicobacter). The course of treatment is at least 7 days and cannot be interrupted, otherwise the bacteria may develop resistance to this substance, after which it will be much more difficult to get rid of it.
An antibiotic such as amoxicillin or clarithromycin is active against Helicobacter. If it does not help, levofloxacin is included in the treatment regimen.
Metronidazole is also used - it is not an antibiotic, but an antimicrobial drug, the indications for its use are the same.
To restore the microflora, which will certainly be disrupted by the antibiotic, special preparations containing probiotics are used (Bifiform, Acipol and others).
Interaction with other drugs:
- The tablets should be taken thirty minutes before taking other medications or eating;
- the drug weakens the effect of tetracycline - sometimes this antibiotic is included in the treatment regimen (for example, with intolerance to amoxicillin), but its dosage is increased;
- You should not take it at the same time as other medications containing bismuth, as this increases the likelihood of side effects.
Some people believe that you should not drink milk while taking De-Nol. There is no such data in the official literature. Milk, if it is well tolerated, can be drunk with meals, but you should not take pills with it (keep a break of half an hour). For the drug to help, alcohol, strong tea, carbonated drinks, and coffee are prohibited during treatment.
How to use?
If there are no contraindications, the drug is prescribed according to two regimens: either 4 times a day, 1 tablet, or 2 times, 2 tablets. For children from 4 to 8 years old, the dosage is calculated based on body weight (8 mg per 1 kg per day). From 8 to 12 years old you need to take half the dose. The dosage must be strictly observed; you cannot drink the drug as soon as your stomach hurts, unlike antacids.
De-Nol, like Omez, is included in all modern treatment regimens for stomach ulcers, and doctors’ reviews of the drug are very positive. However, sometimes you can hear questions about why the drug did not help in treatment. This may be due to various reasons.
The compatibility of Clarithromycin with Metronidazole has been clinically proven, but both drugs, while destroying pathogenic microorganisms, do not affect the level of acid secretion.
But for diseases such as ulcers or erosive gastritis, it is important not only to destroy Helicobacter pylori, but also to protect the gastric mucosa from additional damage from hydrochloric acid.
For this purpose the following is additionally prescribed:
- Proton pump inhibitors. The secretory activity of the glands is suppressed and the acidity of gastric juice is reduced. Omeprazole, Clarithromycin and Metronidazole are usually prescribed. Omeprazole must be taken once a day, and antibiotics must be taken according to an individually selected doctor regimen;
- Gastroprotectors. Envelops the gastric mucosa, protecting the gastric mucosa from damage and accelerating the healing of erosions and ulcers. The treatment regimen may look like this: De-Nol, Metronidazole and Clarithromycin. Instead of De-Nol, other bismuth-based drugs may be prescribed: Vikalin, Ulcavis or Novobismol.
Taking Metronidazole and Clarithromycin together allows you to quickly destroy pathogenic bacteria, but to obtain the necessary therapeutic effect, you must take medications to protect the gastric mucosa along with antibiotics. If this is not done, then antibacterial therapy will be ineffective.
Found a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl Enter
Modern medical methods of treating gastric and duodenal ulcers have four different schemes in their arsenal.
1-, 2-, 3-, 4-component treatment regimens for peptic ulcer
Monotherapy and each of the subsequent therapeutic protocols that provide effective treatment of peptic ulcer disease, 2, 3, 4 component regimens, are used today for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori. The goal of treatment is to relieve symptoms. and provide conditions for rapid scarring.
1-component treatment regimen for peptic ulcer
A 1-component treatment regimen involves the use of:
- de nola,
- macrolides,
- semisynthetic penicillin,
- metronidazole.
It is effective in only 30% of episodes of gastric and duodenal ulcers, so experts prefer monotherapy to complex drug treatment methods.
2-component treatment regimen for peptic ulcer
The 2-component treatment regimen for gastric and duodenal ulcers has several variations: for example, a specialist prescribes a combination:
- de-nol and metronidazole;
- de-nol and amoxicillin.
It gives results only half the time. Often failure is due to the resistance of the pathological flora to metronidazole. According to medical studies, between 1991 and 1995 alone, the effectiveness of metronidazole fell by more than half.
3-component treatment regimen for peptic ulcer
The “classic” 3-component treatment regimen for gastric and duodenal ulcers also has several options:
- de-nol, metronidazole, tetracycline;
- de-nol, metronidazole, amoxicillin.
Those. The two main components that remain unchanged are de-nol and metronidazole. And the duo can be supplemented with either synthetic penicillin, or macrolides, or tetracycline, or fluoroquinolones. The effectiveness of trivalent ulcer therapy is estimated at 70%.
In addition to antibacterial therapy, its combination with antisecretory drugs - omeprazole and H2 blockers - gives good results. The use of omeprazole allows you to increase the effectiveness of the three-component regimen to 95%, and reduce the use of antibiotics to 2 times a day. The use of ranitidine or its combination with bismuth increases the effectiveness of therapy to 94%.
4-component treatment regimen for peptic ulcer
To completely eliminate resistance to antibiotics and metronidazole, it is preferable to use quadrivalent therapy. Only 5% of patients subsequently return to the doctor with relapses.
TREATMENT SCHEMES FOR GASTRITIS B AND Peptic Ulcer
Treatment regimens for gastritis B
bismuth preparation (colloidal bismuth subcitrate, or bismuth gallate or bismuth subsalicylate) 120 mg 4 times a day (dose in terms of bismuth oxide) together with
tetracycline 500 mg 4 times a day plus metronidazole 250 mg 4 times a day or tinidazole 500 mg 2 times a day
• One-week quad therapy. allowing to achieve eradication of Helicobacter pylori strains resistant to known antibiotics.
Schemes using histamine H2 receptor blockers as an antisecretory drug.
Scheme 1. Ranitidine 300 mg/day or famotidine 40 mg/day amoxicillin 2000 mg/day metronidazole (tinidazole) 1000 mg/day for 7-14 days
Note. In patients with sharply reduced secretory function, bismuth (the drug de-nol 240 mg twice a day) can be used instead of acid secretion inhibitors.
Treatment regimens for gastric and duodenal ulcers
Regimen No. 1: omeprazole (Losec, Omez and other analogs) 20 mg 2 times a day in the morning and evening - no later than 20 hours - with a mandatory interval of 12 hours, clarithromycin (Klacid) 250 mg 2 times a day, metronidazole (Trichopol and other analogs ) 500 mg 2 times a day at the end of meals.
Regimen No. 2: omeprazole (Losec, Omez and other analogues) 20 mg 2 times a day in the morning and evening - no later than 20 o'clock - with a mandatory interval of 12 hours, amoxicillin (Flemoxin Solutab, Hiconcil and other analogues) 1 g 2 times a day at at the end of the meal, metronidazole (Trichopolum and other analogues) 500 mg 2 times a day at the end of the meal.
Regimen No. 3: pylorid (ranitidine with bismuth citrate) 400 mg 2 times a day at the end of meals, clarithromycin (clacid) 250 mg 2 times a day or tetracycline 500 mg or amoxicillin 1 g 2 times a day, metronidazole (trichopolum and other analogues) 500 mg 2 times per day at the end of meals.
Recovery in 95% of patients.
Regimen No. 1: ranitidine (Zantac and other analogues) 300 mg 2 times a day or famotidine (gastrosidine, quamatel, ulfamide) 40 mg 2 times a day morning and evening (no later than 20 hours) with a mandatory interval of 12 hours, potassium salt of dibasic citrate bismuth 108 mg 5 times a day after meals, metronidazole 200 mg 5 times a day after meals, tetracycline hydrochloride 250 mg 5 times a day after meals.
Recovery in 85-90% of patients.
After the end of combined eradication therapy (eradication - eradication, from radix - root), continue treatment for another 5 weeks for duodenal and 7 weeks for gastric ulcers using one of the following drugs: ranitidine (Zantac and other analogues) 300 mg at 19-20 hours, famotidine (gastrosidine, quamatel, ulfamide) 40 mg at 19-20 hours.
Treatment regimens for gastric and duodenal ulcers using nitrofurans.
Regimen No. 1. De-nol 240 mg 2 times a day for 1 month. Metronidazole 400 mg 3 times a day for 7 days. Amoxicillin 500 mg 3 times a day for 7 days.
Regimen No. 2. De-nol 240 mg 2 times a day. Furazolidone 100 mg 4 times a day. Amoxicillin 500 mg 4 times a day. Take all medications within 14 days.
Regimen No. 3. De-nol 120 mg 4 times a day. Metronidazole 400 mg 4 times a day. Tetracycline 500 mg 4 times a day. Take all medications within 7 days.
Regimen No. 4. De-nol 240 mg 2 times a day. Furazolidone 100 mg 2 times a day. Clarithromycin 250 mg 2 times a day. Take all medications within 7 days.
Regimen No. 5. De-nol 240 mg 2 times a day. Metronidazole 400 mg 2 times a day. Clarithromycin 250 mg 2 times a day. Take all medications within 10 days.
Regimen No. 6. De-nol 120 mg 4 times a day. Clarithromycin 500 mg 2 times a day. Take all medications within 7 days.
Regimen No. 7. De-nol 120 mg 4 times a day. Metronidazole 500 mg 3 times a day. Tetracycline 500 mg 4 times a day. Take all medications within 7 days.
Add proton pump blockers (proton pump inhibitors) to the regimen, which reduce the production of hydrochloric acid in the gastric mucosa: omeprazole (omez) 20-40 mg 2 times a day or lansoprazole 30 mg 2 times a day or pantoprazole 40 mg 2 times a day or mesoprostozol or Losek. They must be taken for 4-6 weeks for duodenal ulcers and 6-8 weeks for gastric ulcers.
In addition to proton pump blockers, it is necessary to take H2 receptor blockers (histamine): ranitidine 150 mg 2 times a day or famotidine 20 mg 2 times a day or cimetidine 200 mg 2 times a day.
Rules for the use of anti-Helicobacter therapy
1. If the use of a treatment regimen does not lead to eradication, it should not be repeated.
2. If the regimen used did not lead to eradication, this means that the bacterium has acquired resistance to one of the components of the treatment regimen (nitroimidazole derivatives, macrolides).
3. If the use of one and then another treatment regimen does not lead to eradication, then the sensitivity of the Helicobacter pylori strain to the entire range of antibiotics used should be determined.
4. If bacteria appear in the patient’s body a year after treatment, this should be regarded as a relapse of the infection, and not a reinfection. If the infection recurs, it is necessary to use a more effective treatment regimen.
The effectiveness of eradication treatment should be assessed four to six weeks after the end of treatment. If eradication is not achieved, then combination treatment is necessary with the inclusion of four drugs (based on either secretion blockers or de-nol) using tetracycline up to 2000 mg per day, amoxicillin up to 2000 mg per day, furazolidone up to 400 mg per day.
| Drugs | % eradication |
| 2-component circuits: | |
| omeprazole amoxicillin | 40-70 |
| omeprazole clarithromycin | 60-75 |
| 3-component circuits: | |
| omeprazole amoxicillin metronidazole | 88-91 |
| omeprazole amoxicillin clarithromycin | 85-90 |
| omeprazole clarithromycin metronidazole | 86 |
| omeprazole clarithromycin tinidazole | 87-95 |
It was noted that omeprazole, although it does not have antibacterial properties, can lead to a decrease in the number of bacteria (especially vegetative forms) in the antrum of the stomach. At the same time, their number may increase in the body and fundus of the stomach.
This effect of omeprazole is associated with its influence on the pH of the environment: a significant increase in the pH in the antrum leads to a disruption in the metabolism of ammonium produced by Helicobacter, which leads to the death of the microorganism. In the acid-producing zone of the stomach, the pH cannot increase sharply; favorable conditions remain here for the persistence of Helicobacter.
Omeprazole plays a great role in the phenomenon of its “movement” from the antrum to the body and fundus of the stomach. In the fundus, bacteria transform into vegetative forms and begin to multiply, which makes it possible for them to be exposed to antibiotics. In addition, omeprazole, by changing the pH of the stomach to 5.0 or higher, increases the bactericidal properties of these drugs.
De-nol requires an acidic environment for dissolution, and the effect of antibiotics in such an environment is reduced. All this forced the replacement of de-nol omeprazole in anti-Helicobacter combination therapy.
Alternative 2- and 3-component treatment regimens have appeared, which include the antisecretory drug omeprazole.
Multicenter studies have shown that a 3-drug regimen containing omeprazole, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin (or metronidazole) results in
eradication of Helicobacter more than cases. In alternative regimens, H2 blockers can be used as an antisecretory drug. In particular, there is evidence of the high effectiveness of a 3-component regimen containing ranitidine.
Table 4
| Drugs | % eradication |
| ranitidine metronidazole amoxicillin | 71 |
| ranitidine de-nol amoxicillin | 61 |
| ranitidine de-nol clarithromycin | 85 |
Based on ranitidine, a combination drug PILORID was created, which is a combination of ranitidine and bismuth citrate.
This drug has antisecretory activity due to ranitidine and a protective anti-Helicobacter effect on the mucous membrane due to bismuth. Indicated for the treatment of duodenal and gastric ulcers, as well as an anti-Helicobacter drug for anti-relapse therapy.
The drug causes scarring
ulcers in 65-90% of cases after 4 weeks of treatment. Monotherapy with pilorid is not accompanied by Helicobacter eradication. By combining it with antibiotics, eradication can be achieved in 80% of cases.
The best anti-Helicobacter effect is obtained by combining pylorid with clarithromycin at a dose of 1000-1500 mg per day (82-94% eradication).
Due to the emergence of Helicobacter strains resistant to metronidazole (and possibly other antibiotics), a 4-component treatment regimen (omeprazole de-nol tetracycline metronidazole) is recommended. Using this scheme, it is possible to achieve eradication of the pathogen up to 95%.
Regimens containing omeprazole can reduce the duration of anti-Helicobacter therapy to 7 days, as well as the frequency of antibiotic dosing - up to 2 times a day, which increases the tolerability of treatment and makes it more acceptable for patients.
1. The degree of eradication is at least 80%2. Short course (7-10 days)3. Simple dosing regimen of drugs (reducing the frequency of administration)4. No side effects5. Affordable price
With all treatment options, a patient suffering from peptic ulcer disease requires clinical observation. Constant monitoring and timely prevention reduce the risk of complications and allow you to maintain your ability to work.
Return to main page.
Return to the KUNSTKAMERA.
Often, treatment of ulcers and gastritis requires an integrated approach. "De-Nol", "Amoxicillin" and other drugs are taken together to ensure a comprehensive effect on the problem. So, a complex treatment scheme may be as follows:
- drink De-Nol twice a day half an hour before meals;
- twice a day you need to drink 500 mg of Clarithromycin;
- Amoxicillin is taken according to the same schedule, but 1000 mg each.
Sometimes a slightly different scheme is used to treat ulcers and gastritis:
- drink De-Nol twice a day half an hour before meals;
- take 500 mg of Tetracycline four times a day;
- in a similar dosage, but three times a day, drink Metronidazole;
- Omeprazole, Lanzoprazole or other proton pump inhibitors are taken according to the instructions.
If you decide to undergo complex treatment using the drug "De-Nol", taking the medication should continue for 1-2 weeks. Complex therapy should not be stopped abruptly. After completing the course, taking De-Nol can be continued for up to 8 weeks. This will speed up the regeneration of the mucous membrane.
Can I take it at the same time?
The drugs can be taken together.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Wc2q3S36WWU
Their compatibility is positive, i.e. They:
- enhance each other’s therapeutic effect;
- accelerate the onset of the effect;
- inhibit the growth of bacteria that cause gastropathy;
- eliminate symptoms of diseases faster.
Thus, joint therapy is aimed at all parts of the pathology:
- bacteria;
- excessive production of hydrochloric acid;
- dyspeptic symptoms;
- erosive and ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane.
Hydrochloric and bile acids, pepsin thoroughly digest ingested food products. However, these active ingredients of digestive juices act aggressively on the walls of the stomach. Its mucous membrane is protected by a reliable defense mechanism. But when it fails, inflammation develops. It is also enhanced by the pathogenic microorganisms Helicobacter pylori, which become active in a weakened organ.
The most common pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract are erosions and ulcerative lesions of the stomach. There are medications that reduce the degree of aggressiveness of the acidic environment and suppress the proliferation of pathogenic flora. The most effective today are Omeprazole and De-Nol. The combination of these drugs from the group of gastroprotectors eliminates even severe gastrointestinal inflammation.
Omeprazole (Russia) is prescribed together with De-Nol (Netherlands) for acute forms of gastritis and ulcers, exacerbations of chronic gastrointestinal pathologies. These medications act on the affected organs of the gastrointestinal tract in different ways. The therapeutic effect of taking them together is much higher than when treating them separately.
However, De-Nol significantly weakens the effect of Omeprazole. Therefore, it is necessary to maintain a time interval between doses of drugs of 1-1.5 hours. You cannot prescribe treatment with them yourself. With a mild form of gastritis and a negative test for Helicobacter pylori, Omeprazole alone is most often sufficient. The decision to take these medications together should be made only by your doctor.
Any doctor in the field of gastroenterology will confirm that gastritis, ulcers, or any other pathology of the gastrointestinal tract must be subject to complex therapy, otherwise the treatment will become ineffective.
The main purpose of Omez is aimed at inhibiting the production of gastric secretions. The active components of the drug produce a protective film, which has a beneficial effect on the mucous membrane of the organ.
De-Nol, in turn, is also prescribed for the treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. After a few days of taking De-Nol in complex therapy, the components of the drug produce substances that form a protective film on the gastric mucosa, thus preventing the bacteria Helicobacter pylori from developing.
To prevent diseases, experts recommend using De-Nol.
FREQUENCY OF N. PYLORI ERADICATION DURING ANTIBACTERIAL THERAPY
| Drugs | % eradication |
| Monotherapy: de-nol metronidazole amoxicillin | 18,6 |
| 2-component regimen: de-nol metronidazole de-nol amoxicillin | 48,2 |
| 3-component circuit: de-nol metronidazole 1 tetracycline 2 amoxicillin | 93 73 |
However, a 2-component regimen, like monotherapy, does not allow achieving 100% success in getting rid of Helicobacter pylori infection. One of the reasons is the development of resistance to metronidazole.
This led to the creation of a 3-component circuit, called the “classical” one. Its mandatory components are de-nol and metronidazole; the third component may be semisynthetic penicillins (amoxicillin), tetracycline, macrolides (erythromycin, clarithromycin), fluoroquinolones. The 3-component scheme in most cases allows to achieve Helicobacter eradication in 80-100% of cases.
The main factor determining the effectiveness of this regimen is the duration of use of antibacterial drugs (but not de-Nol). Both the 2-week and 4-week regimens are equally effective - 81%. Reducing the duration of treatment to 7 days reduces the eradication rate within 59-64%, and to 4 days - to 35-45%.
The duration of 3-component combination antibacterial therapy should be 14 days. Longer treatment is more often accompanied by the development of side effects - nausea, vomiting (25%), diarrhea (19%). With the introduction into practice of treating patients with peptic ulcers, OMEPRA-
REGIMENS OF PRESCRIPTION OF ANTI-HELICOBACTER MEDICINES
| A drug | Doses | Duration |
| De-nol | 120 mgx4 times | 7 days |
| Metronidazole | 200 mg x 4 times or 400 mg x 2 times | 7 days |
| Tinidazole | 500 mg x 2 times | 7 days |
| Amoxicillin | 500 mg x 4 times or 1000 mg x 2 times | 7 days |
| Clarithromycin | 2500 mg x 2 times or 500 mg x 2 times | 7 days |
| Omeprazole | 20 mgx 1 or 2 times | 7 days |
To enhance the effectiveness of antibiotics in an acidic environment, antisecretory drugs (H2 blockers, omeprazole) are prescribed.
But this is not enough. Only combined antibacterial therapy allows eradication of Helicobacter in 70-80% of cases.
The basis of this therapy is a combination of de-nol (taking into account its bactericidal effect) and metronidazole (due to its high stability in an acidic environment). This combination turns out to be more effective than others.
table 2
Indications for use
De-Nol tablets have proven themselves well. The instructions contain comprehensive information about the method of use and dosage. So, adults should take 1 tablet four times a day. The first 3 doses are taken half an hour before meals, and the last one before bedtime. It is also acceptable to take 2 tablets twice a day, half an hour before meals.
Children under 12 years of age are prescribed 2 tablets of the drug daily. As in the previous case, eating is possible half an hour after taking the medicine.
A different scheme works for children under 8 years old. The daily norm is defined as 8 mg per kilogram of the child’s body. The number of doses is equal to the number of tablets (or their parts) that meet the norm.
The composition of the drug "De-Nol" determines the fact that treatment should last 4-8 weeks. In the next 2 months, treatment with any other drugs that contain bismuth is prohibited. To make the fight against pathogenic bacteria that provoke erosive changes more effective, it is permissible to combine De-Nol with antibacterial agents.
Joint use of “de-nol” and “omez”
Treatment regimens for diseases of the stomach and intestines often include both drugs, which are supplemented by the prescription of one or two antibacterial agents.
It is important to understand that medications have fundamentally different effects on the gastric epithelium. One helps reduce the production of hydrochloric acid. While the other has a regenerative, anti-inflammatory effect, helping to destroy pathogenic bacteria.
"Omeprazole": difference from other drugs, how to take it at the same time as an antibiotic for abdominal pain?
Cost of the drug
These tablets can be bought at any pharmacy without a prescription. Release form in packs of 56 and 112 pieces.
Approximate cost 550-650 rubles. If you are planning a long-term appointment, it is more profitable to buy a large package; it will cost about 950 rubles and will last for a month.
These are approximate data; you can find out exactly how much the drug costs by calling the pharmacy. You can look for a more affordable analogue with the same active ingredient - Novobismol, but sometimes it is not available.
Negative reviews
Treatment with the same drug may have different effects on patients. Thus, there are a number of negative reviews about the drug “De-Nol”. The most significant are the following:
- the result does not occur immediately, and significant relief is noted only after 2 months from the start of treatment;
- in case of serious problems with the gastrointestinal tract, De-Nol itself may be ineffective and requires taking an additional set of medications;
- in the first 5-10 days of treatment, side effects described in the instructions may be observed;
- some patients note a metallic taste in the mouth;
- high price;
- long course of treatment;
- the tablet is difficult to break in half and into smaller pieces, which is required when treating small children, and therefore the medicine simply crumbles and deteriorates;
- given the high cost and popularity of the drug, there are many fakes on the market;
- in some cases, 2 or more courses of treatment may be needed for complete recovery;
- immunity from re-infection with Helicobacter pylori is not formed;
- During treatment with De-Nol, dairy products should not be consumed.
Admission rules
When taking medications in one regimen, it is worth remembering the following nuances:
- Omeprazole is taken thirty minutes before the intended meal;
- The bismuth preparation should be consumed forty minutes after finishing the meal.
Differences in joint treatment of different groups of drugs. How to use “omez” for gastrointestinal pathology?