The cause of cramping abdominal pain is spasms of the smooth muscles of the organs located in the abdominal cavity. A number of diseases can cause such symptoms – from pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract to disorders in the urinary and reproductive systems. Contractions also occur against the background of nervous disorders - paroxysmal pain in the abdominal area can be triggered by severe stress. In women, similar pain in the lower abdomen sometimes occurs during pregnancy or during menstruation. Frequent and prolonged spasms in the peritoneal area are a very alarming symptom, in which a visit to a doctor is mandatory.
The mechanism of spasms
The muscles of the internal organs are constantly in working order, due to which their functioning occurs. Normally, people do not feel the contractile activity of the muscles of the stomach, gall bladder and bile ducts, ureters and bladder, intestines, uterus and fallopian tubes. Everything happens rhythmically, without significant tension, and does not give the person any unpleasant sensations - he does not even notice it. But if the organ becomes inflamed, or an obstacle appears in the path of muscular movement, a spasm occurs, generating paroxysmal pain in the abdomen of varying degrees of intensity - from mild to severe.
The main symptom of spasmodic pain syndrome is its short duration, but when sharp contractions follow one after another, not stopping day or night, this causes considerable suffering. The danger of spasms is, first of all, that they may indicate disturbances in the body’s functioning, leading to the development of serious complications and sometimes death. Therefore, it is important to establish the cause of such symptoms as soon as possible and take measures to eliminate it.
Causes of cramping abdominal pain
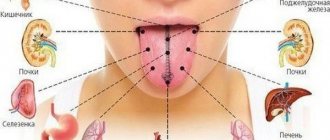
Knowing the location of a person’s internal organs, it is possible to determine the approximate cause of paroxysmal spasms in the abdominal cavity based on their location. If they are concentrated in the upper abdomen, between the hypochondrium and the navel, we may be talking about gastric pathology.
Stomach
Experts divide the reasons why a person may experience severe cramping abdominal pain in the stomach area into two main groups: functional and organic. The first are associated with disturbances in the activity of this organ due to the influence of external factors: intoxication, trauma, stress. Spasms can be triggered by a blow to the stomach, an overdose of alcohol, or severe nervous tension.
The main place among the organic causes of spasmodic pain in the epigastric region belongs to gastritis - inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Depending on the etiology, the pathology is divided into the following forms:
- autoimmune - occurs against the background of atrophic damage to the mucous membrane, accompanied by a decrease in the acidity of gastric juice relative to the norm;
- bacterial - caused by the activity of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which destroys the epithelial cells of the stomach walls;
- stressful – provoked by prolonged nervous tension;
- eosinophilic – allergic.
Symptoms of the disease, in addition to pain, include heartburn, sour belching, nausea, vomiting, and severe thirst.
The consequence of advanced gastritis can be peptic ulcer – deep damage to the gastric epithelium. The disease is more severe than gastritis, and can progress to the state of perforation - the appearance of a through hole in the gastric wall.
Pathologies of other organs
Abdominal cramps can also be caused by:
- Cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder and bile ducts, accompanied by a violation of the outflow of bile. In this case, the person experiences severe abdominal pain and develops diarrhea. Diarrhea can be so severe that the patient literally cannot leave the toilet. Fecal matter becomes discolored because bile does not flow from the inflamed bile duct into the intestines.
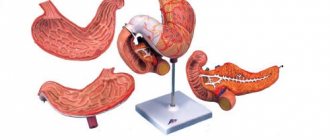
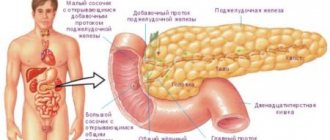
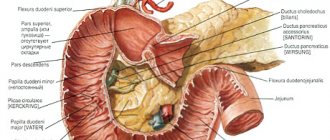
- Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. The pain is localized in the left hypochondrium and radiates to the navel area - there is a feeling that a string is stretched between these two zones.
- Intestinal obstruction - due to impaired peristalsis caused by blockage of the intestinal cavity with feces or a tumor, bloating and asymmetry occur in the peritoneum. The stomach hurts, the temperature rises, nausea and vomiting occur.
- Appendicitis - in the acute form of the pathology, cramping pain spreads throughout the abdomen, without a clear localization. The attacks of nausea and vomiting do not stop.
- Renal colic.
- Kidney stones and urolithiasis.
- Dysentery.
- Rupture of an ovarian cyst.
- Inguinal hernia strangulation.
If during pregnancy there is pain in the lower abdomen, the consequences depend on the period in which these alarming symptoms appear. Up to the 25th week of gestation, it can precede a miscarriage; in the third trimester we are already talking about childbirth. When labor pains continue for several hours and the baby is not born, doctors perform a caesarean section on the woman.
Pain in adults
Pain in the navel area quite often bothers women - it can have various causes, including health hazards, so this condition should not be ignored.
Most often, pulling or cramping spasms in the navel area occur in women during menstruation.
This does not always indicate some kind of pathology in the functioning of the reproductive system - in many cases, painful periods cause hereditary metabolic disorders that increase the sensitivity of the muscular lining of the uterus and its nerve receptors.
This problem is more common in girls than in adult women. Such pain may be accompanied by intestinal upset, diarrhea, and fever.
In especially severe cases, a strong spasm radiates to the right and left and can cause loss of consciousness - the pain is so intense.
Although this problem occurs quite often in women, you should not completely ignore it, dulling the pain with pills, especially if it is very severe.
It is best to consult a doctor, as this syndrome is treatable. In addition, the doctor will be able to identify the reasons why menstruation is so painful and prescribe a medicine that can solve the problem.
Much more dangerous can be cramping pain in the navel area, which occurs suddenly and is very strong.
This condition in women can signal the development of an ectopic pregnancy and requires urgent medical attention.
With an ectopic pregnancy, there is a high risk of rupture of the fallopian tube, which will lead to internal bleeding, which is life-threatening.
READ Bilateral or girdling abdominal pain
In this state, in addition to the spasm, the woman will also experience weakness, chills, often an increase in temperature and an acceleration of the pulse.
The pain is usually felt not only in the navel area, but also on the right and left, spreading to the entire abdominal area. In intensity, painful spasms can be compared to appendicitis.
Appendicitis can cause cramping abdominal pain not only in women, but also in men.
The spasm rather quickly radiates to other areas, radiates to the right and left, as a rule, a person cannot lie on his left side. This condition also requires prompt medical intervention.
In men, as in women, pain in the navel area can be associated with problems of the genitourinary system.
Unpleasant spasms can cause pathologies in the kidneys, inflammation of the bladder, prostate gland, etc.
If cramping spasms occur frequently and are also accompanied by other problems - difficulties with urination or menstrual irregularities in women, then you should definitely consult a doctor, since the problems can be quite serious.
If the pain in the stomach is caused by poor nutrition or poisoning, then it will manifest itself equally in both sexes: a person begins to have diarrhea, vomiting may appear, and the temperature may rise.
This condition is usually not dangerous and can be dealt with on your own.
First aid
If you experience persistent cramping pain in the abdominal area, you should immediately call an ambulance. Before the doctors arrive, the patient must be undressed, unbuttoning the restrictive parts of his clothing - the waistband of a dress, skirt or trousers, shirt collar - and put to bed in a position comfortable for him: on his back or on his side.
If the symptoms suggest an exacerbation of a chronic disease - gastritis, cholecystitis - you can give one or two tablets of No-Shpa. You should not give water, give painkillers or laxatives, give an enema, or apply a cold or hot heating pad to your stomach. During an attack of vomiting, the patient's head must be turned to the side and held in this position to prevent asphyxia due to vomit entering the respiratory tract.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnostic procedures for cramping pain are carried out on an emergency basis and begin with palpation of the abdomen. Then, if necessary, an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity, magnetic resonance and computed tomography are prescribed. If gastritis or a stomach ulcer is suspected, fibrogastroscopy is performed - an endoscope with a miniature camera at the end is inserted into the patient through the mouth, and the doctor can observe the condition of the stomach on the monitor screen. Blood and urine samples are taken at the same time. Therapeutic procedures depend entirely on the results of the examination.
In case of appendicitis, intestinal obstruction, blockage of the bile ducts and rupture of the cystic cavity, the patient is provided with emergency surgical care. In other cases, conservative therapy is carried out, consisting of anti-inflammatory drugs, antispasmodics and other drugs that help relieve spasms.
A necessary condition for the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases is dietary nutrition prescribed by a nutritionist. Fatty, spicy, salty and fried foods are excluded from the patient's menu. Preference is given to buckwheat, rice, oatmeal, turkey, rabbit, chicken, pureed soups with vegetable broth. Dietary nutrition is also necessary to prevent exacerbations of chronic pathologies.
Important! A remedy for heartburn, gastritis and ulcers, which has helped a huge number of our readers. Read more >>>
Paroxysmal stomach pain is a frequent reason to visit a gastroenterologist. They appear in patients of all age categories and are characterized not only by the appearance of spasms, but also by other negative symptoms. Cramping pain in the stomach can last for several minutes, or can continue for several hours; in most cases, it appears on an empty stomach.
Cramping pain caused by gastrointestinal diseases
an increase in temperature to 39°C or higher with diarrhea (especially with bloody discharge in the stool) - this may be dysentery; “acute abdomen”, in which the abdominal muscles are painfully tense and hard to the touch - this may be a sign of intestinal rupture or perforation of the stomach wall as a result of injury, internal bleeding and other dangerous phenomena;
Any pain in the abdominal area should not be ignored. Both men and women should monitor the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract in order to detect in time the onset of the development of various diseases and disorders.
Periodic pain in the stomach occurs against the background of chronic diseases of this organ and is often relieved after the use of medications. But there are other pathologies characterized by cramping pain. Diseases that provoke pain syndrome include:
- Gastritis is characterized by inflammation of the gastric mucosa, accompanied by dyspeptic disorders. Gastritis is characterized by periods of exacerbation. In almost all cases, the spasms occur so strongly that the person is not even able to straighten up to his full height. Often, patients suffering from this disease experience a decrease in appetite and so-called “hunger” pains against this background. Characteristic symptoms in addition are sour belching, heartburn, and putrid odor from the mouth.
- At the initial stage, treatment of aggravated gastritis is a complex of hunger and rest. Only warm drinks in the form of water or tea are allowed. Coffee and carbonated drinks are prohibited for consumption, as they have an irritating, aggressive effect on the inflamed mucous membrane. Foods that cause the secretion of gastric juice are also excluded. These include spicy and salty foods, canned food, cereals consisting of coarse fiber, and fried meat.
- In the drug treatment of gastritis, it is advisable to prescribe sorbents, antispasmodics and antibiotics in the case of a bacterial form of the disease.
- Gastric ulcer is a local pathology of the gastric mucosa as a result of the harmful effects of hydrochloric acid. Cramping pain in this disease usually occurs after eating and subsides after 30-60 minutes. Stomach ulcers are characterized by seasonal exacerbations, usually occurring in spring and autumn. Spasms are always accompanied by belching and heartburn, nausea after eating food. The danger of this disease is represented by the possibility of perforation of the ulcer.
- Nutrition plays a key role in the treatment of stomach ulcers - in small portions 6 times a day. Creamy soups, lean boiled meat and fish, milk porridge, and boiled eggs are recommended for consumption.
- To treat stomach ulcers, antacids and other drugs that coat the gastric mucosa and vitamin B5 are used.
- Appendicitis is a disease of unknown etiology, which is an inflammation of the appendix. The primary symptom of the disease is cramping pain in the epigastric region about a day before the onset of other symptoms, which then moves lower. The cramping pain is accompanied by nausea, vomiting and a sharp increase in body temperature to 38 degrees.
- Treatment of appendicitis involves only surgical intervention, so any delay poses a huge danger to the patient.
- Dysentery is an infectious intestinal disease that causes cramping pain in the stomach. In the future, diarrhea, repeated vomiting, and rapid heartbeat are added to the painful sensations. It is impossible to cope with such a disease at home, since the condition can be aggravated by dehydration. Only inpatient treatment is required.
How does cramping pain in the stomach manifest?
Cramping pain occurs as a result of obstruction of a hollow organ, which is the stomach. This paroxysmal pain is sometimes called colic. Attacks of pain may alternate with painless intervals of varying duration and intensity. The nature of the pain does not depend on the position of the person experiencing it.
There are several types of stomach spasms:
- total (general) – accompanies a disease of the nervous system, occurs infrequently;
- regional (partial) – manifests itself in the form of a spasm of a separate area of the gastric muscles, for example, in a bi-cavitated stomach, which occurs after the healing of an ulcer, tuberculosis scar, gumma;
- limited - diagnosed in case of a disorder of higher nervous activity, as well as after the administration of morphine, systematic smoking, violations of the work and rest regime.
Additionally, there is a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, bloating, a feeling of fullness, nausea, and discomfort in the pit of the stomach.
What causes symptoms such as: cramping abdominal pain
Below are diseases that match your symptoms.
Chronic gastritis
Gastritis – this word refers to a number of diseases of the digestive tract.
Their common feature is inflammation of the inner walls of the stomach. Gastritis can appear in a person completely unexpectedly (acute) or slowly worsen over time (chronic). If this disease is not treated, there is a risk of ulcers and an increased risk of developing malignant tumors of the stomach. Read more- poor appetite
- fever
- stomach ache
- smell from the mouth
- dyspnea
- bloating
- abdominal pain
- constipation
- loss of consciousness
- dizziness
- vomit
- vomiting blood
- weight loss
- belching
- indigestion
- irritability
- lack of appetite
- weakness
- nausea
- cardiopalmus
- diarrhea
- white coating on tongue
- pain in the upper abdomen
Chronic pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis is a disease of the pancreas, which is accompanied by recurrent or constant pain, endocrine and exocrine insufficiency, and pathological changes in the organ.
Read more- pale stool
- fever
- stomach ache
- dyspnea
- bloating
- pop up chair
- abdominal pain
- constipation
- vomit
- fatigue
- weight loss
- back pain
- chronic pain
- cold sweat
- fluid in the abdominal cavity
- smelly stool
- indigestion
- fatigue
- lower back pain
- lack of appetite
- pain
- weakness
- nausea
- thirst
- diarrhea
- chronic fatigue
- heartburn
- abdominal discomfort
- pain in the upper abdomen
Pancreas cancer
Pancreatic cancer is a relatively rare disease, but the number of patients with this pathology is growing.
A malignant neoplasm originates from the epithelium of an organ. Read more- pale stool
- poor appetite
- stomach ache
- itchy skin
- swollen stomach
- abdominal pain
- dark urine
- vomit
- watery stool
- fatigue
- weight loss
- yellow eyes
- aversion to food or drink
- back pain
- depression
- fluid in the abdominal cavity
- indigestion
- jaundice
- fatigue
- lump in the stomach area
- lack of appetite
- pain
- thirst
- diarrhea
- frequent urination
- trembling hands
- heartburn
- pain in the upper abdomen
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an infection of the reproductive organs in women. It is characterized by abdominal pain, especially during urination or sex.
- fever
- stomach ache
- spots on the skin
- fainting
- abdominal pain
- intermenstrual bleeding
- vaginal discharge
- vaginal pain
- vomit
- fatigue
- abdominal tenderness
- back pain
- chills
- hot skin
- problems with conception
- infertility
- fatigue
- lower back pain
- menstrual irregularities
- absence of menstruation
- lack of appetite
- pain
- pain during intercourse
- painful menstruation
- painful urination
- elevated temperature
- lower abdominal pain
- pain in the upper abdomen
Duodenal ulcer
Duodenal ulcer is a chronic and recurrent disease, which is a defect in the intestinal mucosa, the healing processes of which are disrupted or significantly slowed down.
Duodenal ulcers are 4 times more common than gastric ulcers. Read more- stomach ache
- bloating
- abdominal pain
- constipation
- vomiting blood
- fatigue
- belching
- weakness
- nausea
- aching pain in the stomach area
- sharp pain in the stomach area
- pain after eating
- blood in stool
- increased appetite
- heartburn
- pain in the upper abdomen
- aching pain in the abdomen
Functional dyspepsia
Functional dyspepsia is a condition when a patient experiences pain or discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract (most often in the stomach) in the absence of an immediate disease.
Read more- bloating
- constipation
- fast saturation
- nausea
- diarrhea
- abdominal discomfort
- cramping abdominal pain
Salmonellosis
Salmonellosis is an acute intestinal infection of animals and humans caused by Salmonella; an acute infectious anthropozoonotic disease caused by Salmonella and characterized, in general, by the development of intoxication and damage to the gastrointestinal tract. The incubation period ranges from 6 hours to 3 days, averaging 12-24 hours.
- fever
- stomach ache
- abdominal pain
- vomit
- watery stool
- abdominal tenderness
- chills
- hot skin
- myalgia
- pain
- nausea
- diarrhea
- muscle pain
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A (better known as Botkin's disease) is an acute viral liver disease.
The virus is stable and can survive for several weeks at room temperature, several months at 4ºC and for years at -20ºC. The disease is transmitted through the fecal-oral mechanism and is considered the most common intestinal infection. Every year, about 10 million people are infected with the virus. The disease is widespread in developing countries, where the level of hygiene is quite low, and is transmitted by the population in early childhood. Read more- pale stool
- poor appetite
- fever
- stomach ache
- itchy skin
- swollen stomach
- abdominal pain
- unusual color of urine
- dark urine
- vomit
- fatigue
- weight loss
- yellow eyes
- hot skin
- headache
- jaundice
- joint pain
- fatigue
- liver enlargement
- myalgia
- bad feeling
- lack of appetite
- pain
- weakness
- nausea
- elevated temperature
- yellow skin
- body aches
- muscle pain
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is the general name for diseases, significantly different from each other, in which inflammatory damage to the liver occurs.
Read more- pale stool
- poor appetite
- fever
- stomach ache
- itchy skin
- swollen stomach
- abdominal pain
- unusual color of urine
- dark urine
- vomit
- fatigue
- weight loss
- yellow eyes
- abdominal tenderness
- hot skin
- fluid in the abdominal cavity
- breast hypertrophy in men
- jaundice
- joint pain
- fatigue
- liver enlargement
- myalgia
- bad feeling
- lack of appetite
- pain
- weakness
- nausea
- elevated temperature
- yellow skin
- muscle pain
Acute Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis is an acute demarcation inflammation of the pancreas, accompanied by necrosis of pancreatocytes followed by tissue necrosis, dystrophy and secondary purulent infection.
Read more- pale stool
- fever
- stomach ache
- hiccups
- itchy skin
- bloating
- rapid pulse
- swollen stomach
- tachycardia
- abdominal pain
- dark urine
- vomit
- yellow eyes
- anxiety
- aversion to food or drink
- back pain
- chills
- dehydration
- belching
- hot skin
- nervousness
- headache
- indigestion
- heart rhythm disturbances
- jaundice
- low blood pressure
- lack of appetite
- pain
- weakness
- nausea
- diarrhea
- elevated temperature
- sweating
- body aches
- heartburn
Ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus.
Treatment for an ectopic pregnancy may require emergency medical attention. Read more- nausea in the morning
- shoulder pain
- stomach ache
- drowsiness
- spots on the skin
- bloating
- swollen stomach
- fainting
- abdominal pain
- vaginal discharge
- dizziness
- vomit
- woozy
- back pain
- lower back pain
- lack of appetite
- pain
- breast pain
- nausea
- lower abdominal pain
- uterine bleeding
Polio
Poliomyelitis is infantile spinal paralysis, an acute, highly contagious infectious disease caused by damage to the gray matter of the spinal cord by poliovirus and characterized mainly by pathology of the nervous system.
Mostly occurs in an asymptomatic or erased form. Sometimes it happens that poliovirus penetrates the central nervous system and multiplies in motor neurons, which leads to their death, irreversible paresis or paralysis of the muscles they innervate. Read more- poor appetite
- fever
- shiver
- scoliosis
- stomach ache
- rash
- dyspnea
- spasm
- muscle spasm
- muscle stiffness
- bloating
- a sore throat
- abdominal pain
- constipation
- difficulty urinating
- vomit
- watery stool
- weak muscles
- fatigue
- back pain
- suffocation
- cough
- depression
- salivation
- hot skin
- headache
- irritability
- joint pain
- kyphosis
- fatigue
- lethargy
- loss of muscle function
- muscle atony
- myalgia
- bad feeling
- pain
- pain in the neck
- leg pain
- weakness
- nausea
- muscle weakness
- elevated temperature
- runny nose
- muscle pain
Hepatitis D
Hepatitis D, also known as hepatitis delta virus, is an infection that causes inflammation of the liver.
This disease can impair liver function and cause long-term liver problems, including liver scarring and cancer. Read more- pale stool
- poor appetite
- fever
- stomach ache
- itchy skin
- rash
- swollen stomach
- abdominal pain
- unusual color of urine
- dark urine
- vomit
- fatigue
- yellow eyes
- chills
- belching
- hot skin
- fluid in the abdominal cavity
- jaundice
- joint pain
- fatigue
- liver enlargement
- myalgia
- bad feeling
- lack of appetite
- elevated temperature
- yellow skin
- muscle pain
- heartburn
- enlarged spleen
Toxic shock syndrome
Toxic shock syndrome (TSS) is an acute, life-threatening condition that develops rapidly when exposed to a toxin produced by bacteria. The syndrome is based on the body’s reaction to bacterial toxins entering it. These superantigens are so powerful that they lead to the release of huge amounts of anti-inflammatory cytokines - this process has even been called a “cytokine storm.”
- photophobia
- fever
- Red eyes
- seizures
- shock
- stomach ache
- peeling skin
- rash
- dyspnea
- fainting
- abdominal pain
- loss of consciousness
- dizziness
- vomit
- watery stool
- woozy
- chills
- cold sweat
- hot skin
- headache
- joint pain
- labored breathing
- low blood pressure
- confusion
- spasm
- myalgia
- bad feeling
- weakness
- nausea
- diarrhea
- elevated temperature
- yellow skin
- skin rashes
- muscle pain
Q-Fever (Q-Fever)
Q Fever (Q Fever) is an infection caused by the bacteria Coxiella burnetii. The bacteria are most often found in cattle, sheep and goats. It is characterized by general toxic phenomena, fever and often atypical pneumonia.
- fever
- stomach ache
- dyspnea
- a sore throat
- abdominal pain
- watery stool
- fatigue
- weight loss
- chest pain
- chills
- cough
- headache
- jaundice
- myalgia
- nausea
- diarrhea
- elevated temperature
- sweating
- muscle pain
- chest pain when breathing
Colorado tick fever
Colorado tick fever is an acute arboviral disease characterized by two-wave fever, general intoxication, and in some patients the central nervous system is affected. Transmitted through the bite of an infected tick.
- photophobia
- poor appetite
- fever
- Strong headache
- stomach ache
- rash
- abdominal pain
- vomit
- fatigue
- chills
- hot skin
- headache
- fatigue
- myalgia
- lack of appetite
- weakness
- nausea
- diarrhea
- elevated temperature
- muscle pain
- sensitivity to light
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection that may not cause any noticeable symptoms.
Unprotected sex with different partners leads to a greater risk of infection. Read more- fever
- bloody sperm
- stomach ache
- swollen stomach
- tenesmus
- testicular pain
- abdominal pain
- urethral discharge
- dark urine
- vaginal discharge
- vomit
- fatigue
- weight loss
- yellow eyes
- hot skin
- problems with conception
- infertility
- jaundice
- fatigue
- lack of appetite
- pain
- pain during intercourse
- painful urination
- weakness
- nausea
- frequent urination
- elevated temperature
- lower abdominal pain
- pain in the perineum
- burning sensation in the vagina
Esophageal carcinoma
Esophageal cancer is an oncological disease of the esophagus, making up a significant part of all diseases of this organ.
The main symptoms of this disease are: progressive difficulty swallowing (first solid food, then liquid) and unintentional weight loss. Read more- poor appetite
- hoarse voice
- stomach ache
- hiccups
- smell from the mouth
- acidity in the stomach
- swallowing disorder
- tarry stool
- a sore throat
- abdominal pain
- vomit
- vomiting blood
- dark vomit
- fatigue
- weight loss
- aversion to food or drink
- back pain
- pale skin
- chest pain
- cough
- belching
- hemoptysis
- gastrointestinal bleeding
- indigestion
- lack of appetite
- pain when swallowing
- weakness
- elevated temperature
- sweating
- coating on the tongue
- heartburn
- dark chair
- chronic cough
Acetone poisoning
Acetone poisoning occurs when there is a large amount of acetone in your body, which can cause your liver to stop functioning. Acetone is a clear liquid that smells like nail polish remover.
- poor coordination of movements
- Red eyes
- stomach ache
- dyspnea
- drowsiness
- stupor
- fainting
- irritation in the throat
- abdominal pain
- sudden urge to urinate
- vomit
- coma
- hallucinations
- headache
- lethargy
- low blood pressure
- nausea
- incoherent speech
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of type 1 diabetes, and it also sometimes occurs in people with type 2 diabetes.
Read more- polyuria
- fast shallow breathing
- shortness of breath when lying down
- stomach ache
- dyspnea
- stupor
- abdominal pain
- loss of consciousness
- vomit
- fatigue
- coma
- decreased attention
- headache
- hyperventilation
- labored breathing
- fatigue
- low blood pressure
- confusion
- spasm
- myalgia
- lack of appetite
- pain
- nausea
- thirst
- rapid breathing
- frequent urination
Never rely solely on search results to make a diagnosis. Be sure to consult a board-certified physician for diagnosis and treatment.
Possible reasons
Diseases of the digestive system provoke the appearance of colic in the stomach. There are organic and functional disorders of this organ. Gastrointestinal pathologies causing spasms:
- gastritis;
- ulcerative lesions of the gastric mucosa;
- colitis;
- intestinal obstruction.
Additional functional reasons that provoke cramping pain in the stomach:
- side effects of medications;
- intoxications associated with food toxins or alcohol abuse;
- eating disorders;
- smoking;
- neuroses, stressful situations;
- coffee addiction
- allergic reactions to foods or other provoking factors, injuries to the stomach and intestines.
Intussusception
This is the name for the introduction of the overlying intestinal zone into the lumen of the underlying one. Most often, the pathology is observed in children and men. In this case, cramping pain will occur when the final part of the small intestine is inserted into the large intestine.
The reasons are different - helminthic infestation, ingestion of rough food, passage of gallstones, ingestion of a foreign body. The intensity of pain will depend on the degree of entrapment of the mesentery. If it is strong, then the patient quickly develops peritonitis and early necrosis of the intussusception. A person can die without medical assistance within 24 hours.
During contractions, the pain is unbearable, but between them, enlightenment is possible. After 6-12 hours from the onset of this syndrome, bloody discharge from the anus is possible.
What pathologies do stomach cramps indicate?
The nature of spasms differs in each specific case, as it depends on the course of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient.
- Stomach ulcer - attacks almost never appear on an empty stomach; they occur more often after eating, after half an hour to an hour, and subside with the end of digestion of food.
- Pylorospasm - occurs in patients with a weakened nervous system, is characterized by attacks of vomiting and the appearance of a pain symptom after eating; after emptying the stomach, spasms and pain are not felt;
- Pancreatitis - pain during spasm radiates to the right hypochondrium or lower back;
- Dyskinesia of the gallbladder, cholecystitis - the appearance of painful spasms in the epigastric region after errors in nutrition (smoked, salty, fatty, overly sweet foods);
- Gastritis - severe spasms are accompanied by weight loss, vomiting, and sour belching.
- Acute intestinal obstruction - can be caused by a tumor, helminthic infestation, fecal conglomerate after constipation, accumulation of fiber, volvulus of intestinal loops. It is manifested by the inability to excrete gases and feces, bloating, painful spasms of the stomach and intestines, severe vomiting with bile and intestinal contents that acquire a putrid odor.
- Erosion of the gastric mucosa is characterized by prolonged, regularly occurring powerful spasms. The pain appears at night, and may be accompanied by bleeding, which indicates that the process has worsened and become chronic.
Causes of colic in the stomach
Cramping pain can appear due to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: gastritis, ulcers or erosion of the stomach, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the organ, inflammatory processes in the duodenum.
When these diseases worsen, the following factors can provoke pain:
Failure in the diet, when the time of eating has changed sharply, a person overeats or goes hungry for a long time. If the patient does not eat three times, as expected, but once or twice. Colic appears in the stomach if fatty, fried, spicy dishes, with a lot of salt, appear on the menu,- Poisoning with stale food or surrogate alcohol can cause stomach spasms, so a person will begin to experience pain in the abdominal area,
- Pain and colic occur due to allergic reactions and uncontrolled use of medications. Also, the appearance of these symptoms in adults is a large amount of strong tea or coffee drunk during the day, tobacco smoke,
- Cramping pain appears if a person is overweight, in a state of neurosis or prolonged depression,
- In older people, pain appears for organic reasons, this is due to the fact that colic is a consequence of some disease of the digestive tract,
- Functional disorders occur not only in adults, but also in young patients, because they eat mostly snacks and dry foods.
In order to get rid of cramping abdominal pain, you need to identify the main reasons that cause them. After this, begin direct treatment of the disease, rather than eliminating its symptoms.
Cramping pain and diarrhea
The addition of diarrhea to stomach colic indicates the penetration of a viral infection into the body, called “intestinal flu” or infectious gastroenteritis. Its causative agents:
- adenovirus;
- rotavirus;
- astrovirus;
- coronavirus;
- calicivirus;
- norovirus.
Additionally, symptoms such as fever above 37.5⁰, nausea and vomiting, and general weakness may appear. Viruses invade the cells of the stomach and intestines, disrupting the processes of transport and absorption of food.
Viral gastroenteritis is transmitted by the fecal-oral route; most often it affects adults and children, who spend part of their time in large groups. The disease lasts no more than 10 days. Accurate diagnosis is carried out by analyzing the patient's stool and observing the nature of diarrhea.
Another cause of diarrhea along with cramping abdominal pain may be dysentery, an infectious disease caused by Shigella. In this case, the following symptoms will additionally be felt:
- pale skin;
- hyperthermia;
- false urge to defecate;
- the appearance of blood streaks in the stool.
Significance of the symptom
Let's start with the main thing. What is this - cramping pain in the abdomen? Strong contractions of the smooth muscle muscles of a number of hollow organs that are located in the lower part of the peritoneum, the pelvis. This is the uterus (in women), intestinal tract, bladder, ureters, etc. Their smooth muscle muscles contract constantly, helping to propel the contents. However, under normal conditions this process is painless. We do not somehow feel intestinal peristalsis, contraction of the bladder muscles, etc.
Hence, cramping pain will be a rather alarming symptom. He can talk about a lot of things:
- Impaired movement of contents inside a hollow organ.
- Functional dysfunctions in the body.
- Acute stage of the disease, which requires immediate medical attention.
Note that this symptom is also quite subjective. The reason is that people will each have their own degree of sensitivity.
Help with stomach cramps
Any ailment, if it is accompanied by pain and is noted regularly, and not occasionally, requires a thorough examination. In most cases, according to the results of the examination, there is no reason for concern, and a small adjustment of the diet and compliance with the doctor’s recommendations is enough to regain your previous health.
If it is not possible to consult a doctor in the near future, to relieve paroxysmal pain, you need to drink a glass of water at room temperature or another neutral liquid. It is advisable not to eat for 3-4 hours, and if vomiting occurs, abstaining from food lasts up to 6 hours. After the cramping pain stops, it is recommended to limit the following foods in your diet:
- dishes containing coarse fiber;
- freshly baked bread;
- spices, spicy dishes;
- refractory animal fats;
- strong coffee or tea;
- fatty, fried, smoked foods.
It is imperative to follow a diet; you need to eat often, but in small portions, using light, low-fat foods. It is not recommended to eat too cold or too hot food. At night, you can drink a glass of warm low-fat milk.
Antispasmodic drugs will help relieve the intensity of stomach colic: No-Shpa, Drotaverine hydrochloride, Spazmalgon. The drug Iberogast selectively relaxes the muscles of the bottom and body of the stomach and tones the muscles of its bottom, which helps to quickly evacuate the food bolus into the duodenum. It is possible to use traditional methods:
- Mint leaf tea;
- Motherwort juice solution;
- An infusion of a mixture of nettle, St. John's wort, and meadowsweet flowers.
In occasional cases of spasmodic pain in the stomach, massage of the epigastric region helps relieve it.
Reason for urgent hospitalization and prognosis for the development of the disease
In case of an “acute abdomen” that threatens the patient’s life, the prognosis for the development of the situation depends on how quickly the patient is taken to the hospital. Hospitalization is necessary for the following symptoms:
- Cramping pain changes its character and becomes diffuse and constant - suspicion of intestinal obstruction;
- An admixture of blood appears in the stool - suspicion of dysentery;
- The pain lasts for several days, constantly increasing, and is not relieved by antispasmodics;
- Vomiting appears mixed with blood, similar to coffee grounds;
- The stool turns black (“melena”), which indicates gastric or intestinal bleeding;
- Colic is accompanied by severe night pain, from which the patient wakes up;
- Paroxysmal pain occurs in a child, an elderly person, or a patient with a history of chronic diseases;
- Symptoms of colic in the stomach include dizziness, the appearance of delirium, and rapid pulse;
- After an abdominal injury, attacks of stomach cramps periodically appear;
- The patient shows signs of dehydration: the skin is dry and not elastic, the nose is pointed, the eyes are sunken, the urine is dark and there is little of it.
For most conditions that cause paroxysmal stomach pain, the prognosis is favorable. If the diet and nutrition regimen are followed, the health of such patients quickly returns to normal. Untimely diagnosed and treated diseases of the stomach and intestines can affect the condition of hair, nails, skin and teeth.
The consequences of stomach cramps can be the appearance of stomach erosion, atrophy of the gastric walls, ulcerative and oncological lesions of the stomach and intestines. To eliminate the possibility of developing severe pathologies, they should be examined in a timely manner and treated at an early stage.
Cramping pain in the stomach usually does not last long: it appears suddenly and disappears on its own. Cramps spread to the stomach and entire abdominal cavity if intestinal irritation is observed. The symptom may be supplemented by problems with stool and signs of intoxication of the body. Stomach pain with cramps is regularly reported by more than ½ of the world’s population.
Causes
The intensity of cramping pain depends on the characteristics of the human body. The causes of their occurrence are divided into organic and functional. In the first case, the provoking factors of the disease are dysfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract, which affect older people. Functional disorders are associated with metabolic disorders and neurological problems that are common in young people.
The main causes of stomach cramps are diseases of the digestive system. These include:
- peptic ulcer;
- erosive damage to the walls of the stomach;
- intestinal inflammation;
- disturbance of intestinal microflora;
- insufficient production of enzymes.
Factors predisposing to the problem are:
- poor nutrition – irregular meals, consumption of fried and fatty foods, sudden changes in diet;
- intoxication of the body of various etiologies - food, alcohol, toxic;
- excessive consumption of strong drinks - coffee, tea;
- uncontrolled use of medications;
- neurological abnormalities;
- smoking;
- overweight;
- abdominal trauma.
Symptoms of pathology
Stomach pain comes and goes due to obstruction. Such sensations are otherwise called colic, which is characterized by a periodic course. Attacks of spasms alternate with painless periods. Spasms do not change intensity when a person takes a different position.
There are several types of paroxysmal pain in the stomach:
- total – associated with neurological abnormalities and diagnosed in rare cases;
- regional - manifested by spasm of individual muscles of the digestive organ and is detected after peptic ulcers, tuberculosis or gumma;
- limited - manifests itself after the introduction of narcotic drugs (morphine) into the body or with systematic violation of the work and rest regime.
Symptoms requiring hospitalization
If there is severe pain in the stomach area, the patient requires medical attention. The prognosis for recovery will depend on the timeliness of the therapeutic measures provided.
Hospitalization for pathology is required if:
- paroxysmal pain changes its intensity and appears constantly - this may indicate the development of intestinal obstruction;
- mucus and bloody streaks were found in the stool (signs of dysentery);
- the pain is increasing in nature and does not disappear after taking painkillers;
- spasms are complemented by nausea and vomiting mixed with black blood;
- stool becomes black (signs of internal bleeding);
- colic prevents normal rest and affects appetite;
- sharp pain in attacks occurs in children or an elderly person suffering from chronic pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- The patient exhibits symptoms of dehydration: dry skin, pale skin. Reducing the amount of urine excreted, etc.
After professional help is provided, the person will need to self-administer medications, follow a diet, and undergo physical therapy. Untimely elimination of stomach pain negatively affects the condition of the patient’s skin, hair and nails. Among the consequences of the problem are:
- atrophy of the stomach walls;
- oncological formations in the gastrointestinal tract;
- ulcerative lesions of the intestinal walls.
To avoid complications, it is necessary to treat stomach pain when the first alarming symptoms appear.
First aid
If there is a problem, it is important to know what to do: periodic stomach pain can be treated according to different schemes, depending on the causes of their occurrence. To provide first aid you need:
- Provide the patient with rest.
- Ask the victim about the causes of unpleasant symptoms, their intensity and duration.
- In case of strong contractions, give the patient an antispasmodic tablet - Drotaverine or No-Shpa.
- Place the person on their side if they lose consciousness. This will prevent vomit from entering the respiratory tract.
- Perform direct cardiac massage if the patient has no pulse.
In case of severe symptoms of the disease, it is prohibited:
- leave the patient unattended;
- give the victim food;
- put warm compresses on the abdominal area;
- do an enema.
Diet for cramping pain
Important! What to do if you have periodic attacks of abdominal pain? First of all, you need to properly organize your nutrition. It is advisable that the menu be drawn up by a gastroenterologist after studying the test results.
If it is not possible to contact a specialist, then adhere to the following rules:
- drink 200 ml of water;
- refuse to eat for 3-4 hours (if there are signs of nausea and vomiting - for 6-8 hours).
After the cramps begin to subside, you can eat small portions. Exclude from the diet:
- coarse fiber;
- fresh baked goods;
- strong alcohol;
- fatty foods;
- fried foods;
- conservation;
- pickles;
- rich soups;
- spices.
It is advisable that all food eaten be at room temperature. Hot or too cold foods can cause the problem to recur. Before going to bed, you are allowed to drink 200 ml of milk with a fat content of up to 1.5%.
Cramping pain due to abdominal diseases
Organic causes include various diseases of organs located in the abdominal cavity. The most common of them include gastritis and peptic ulcers. Often people neglect to go to the doctor, as a result of which the disease becomes chronic.
Types of gastritis
Gastritis is one of the diseases that is accompanied by cramping pain in the left side of the abdomen. This process is characterized by the development of an inflammatory process in the gastric mucosa.
The main symptoms include:
- heaviness in the stomach;
- heartburn;
- belching with sour contents;
- nausea.
In medicine, there are several types of gastritis:
- Autoimmune type. Occurs due to atrophy of the mucous membrane. Against the background of this process, the acidity of gastric juice decreases.
- Bacterial type. Caused by a bacterium called Helicobacter pylori.
- Fungal or viral type. The cause is thought to be decreased immune function.
- Erosive type. Occurs with regular consumption of alcohol, spicy foods and medications.
- Stress type. Manifests itself as a result of prolonged stress.
- Eosinophilic type. The cause of the pathology is an allergic reaction from the digestive system.
Treatment of gastritis involves following a strict diet, taking plenty of fluids, and using antibacterial and sedatives.
Peptic ulcer disease
Another illness that causes severe and sharp pain in the abdomen is a peptic ulcer of the stomach or intestines. This disease refers to damage to the mucous membrane that occurs as a result of exposure to hydrochloric acid in gastric juice.
Painful sensations usually appear after eating. In case of cramping pain, the patient is hospitalized in a hospital. Therapeutic measures include the use of antibacterial agents, antacids, and pantothenic acid. This group of medications allows you to suppress the activity of bacteria, normalize the composition of gastric juice and heal the mucous membrane.
The patient is also advised to follow a strict diet. Spices and spices, fatty and fried foods are excluded from the diet. Products must be steam and heat treated. Particular attention should be paid to the drinking regime.