Advantages of Ranitidine over similar drugs
The main advantage of Ranitin is its low cost and proper therapeutic effect. The following advantages of the medicine are also noted:
- the medicine can be purchased at any pharmacy and used for a long time;
- during treatment, the concentration of hydrochloric acid is normalized;
- Ranitidine has a long-lasting effect: at least 11-13 hours, half-life – 120 minutes;
- normalizes acidity;
- The tablets can be used before or after meals, at the discretion of the patient.
If for some reason (hypersensitivity reactions, allergies, ineffectiveness) the medicine is not suitable, the doctor will select a replacement remedy.
What about the price?
In most cases, each person first pays attention to the price of the drug, and then makes a decision: to buy it or try an analogue whose price is much lower. For peptic ulcers, treatment is carried out using several medications. And in this case, the patient tries to minimize his financial losses. And the question of what is cheaper - Ranitidine or Omez, becomes more relevant than ever.
The average cost of Ranitidine in pharmacies does not exceed 100 rubles. And the average cost of Omez is about 300 rubles. Naturally, in this case too, the plus is clearly not in favor of the last resort.
But with all the above advantages, the prescription and recommendations of the attending physician play a huge role. But asking him a question about the interchangeability of these drugs is very possible. Since there is a chance that in a particular case such a replacement will not affect human health.
Comparison of Ranitidine with other drugs: doctor's opinion
According to doctors, the basic means of complex therapy for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are drugs with antiulcer and antisecretory properties. A prominent representative of this group of drugs is Ranitidine. Many drugs with this active ingredient from various manufacturers have been registered in Russia: Atsidek, Ranisan, Rantak, Ulkodin, Ranison, Ranx, Zantac, Zantin.
Experts say that replacement may be required if Ranitidine causes undesirable reactions (headache, nausea, vomiting, hair loss, bowel movements, liver dysfunction, arrhythmia). An analogue is also required for patients who are contraindicated in taking Ranitidine: patients under 14 years of age, pregnant and lactating women, people with liver or kidney dysfunction, or individual intolerance to the active or excipients.
Modern gastroenterology considers Ranitidine an outdated medicine, in comparison with medications that contain famotidine and which are classified as proton pump blockers. Doctors are trying to prescribe more modern drugs because they are better tolerated by patients, cause fewer unwanted reactions in the body, and exhibit more pronounced therapeutic properties.
Ranitidine or Famotidine: which is better?
Famotidine is a cheap substitute for ranitidine. Both drugs help block H-2 receptors that recognize histamine. The main difference is the composition. The drugs belong to the same pharmacological group and prevent the release of acid into the stomach. Medications that include famotidine contain a smaller amount of active substance (40 m), while one tablet of ranitidine contains 150 mg. Ranitidine is absorbed more quickly than famotidine, but exhibits its pharmacological effect later.
How to take Omez and De-Nol. Which is better and more effective
Almost any disease of the gastrointestinal tract must be treated comprehensively. Today on the pharmaceutical market there are all kinds of drugs for gastrointestinal diseases. Depending on the symptoms, the doctor prescribes one or another medicine. The most popular among them remain Omez and De-Nol. But which of these two drugs is right for you, only a doctor can determine.
Both drugs are used in the treatment of gastrointestinal pathologies. In fact, the two drugs belong to different pharmacological groups. Omez is a proton pump inhibitor that inhibits the increased production of gastric juice. De-Nol, in turn, is an antiseptic intestinal, astringent and wound healing agent.
Omez or De-Nol, which is better to drink for problems with the gastrointestinal tract - this is a serious question. Both medications are aimed at eliminating the symptoms of stomach diseases. These include pain of varying degrees, nausea, abdominal discomfort, etc.
These medications belong to different groups of drugs. They can be taken together, combining their healing properties. But most often, depending on the symptoms, the doctor prescribes one of these remedies.
The doctor prescribes De-Nol if you are diagnosed with an ulcer with the bactericidal activity of Helicobacter pylori. The drug has an astringent and anti-inflammatory effect, has a beneficial effect on the gastric mucosa and increases mucus production.
The form of release of the drugs is also different. The basis of Omez is omeprazole, in De-Nol it is bismuth subcitrate. The release form also differs. De-Nol is produced in the form of tablets, Omez - in the form of capsules.
In addition, there are differences in the price of the issue. The cost of Omez is lower. On the Russian market it’s about 170-180 rubles for thirty capsules. A package of De-Nol in 58 tablets can be purchased for 550-560 rubles. In any case, the cost of the latter is higher, regardless of the larger number of tablets.
The indications for use of both drugs are similar, but there are still some differences. The doctor prescribes an antiulcer drug based on omeprazole to the patient in the following cases:
- inflammation of the gastric mucosa;
- the presence of ulcerative lesions of the organ, the appearance of which has a different etiology;
- reflux disease;
- prevention of inflammation of the gastric mucosa (usually prescribed as a complex treatment so that other medications do not harm the organ).
Taking Omez is strictly prohibited in case of individual intolerance to the components that make up the drug. Also, the product is not recommended for children under 3 years of age.
Omez is produced in the form of capsules. In the case of a child or an elderly person who cannot swallow the capsule whole, the contents of the tablet are dissolved in a small amount of water and drunk. The standard treatment regimen involves taking the medication once a day, but, as mentioned above, sometimes the treatment regimen is adjusted.
Depending on the disease and severity, as well as on the patient’s age and individual characteristics, standard treatment can be adjusted by the doctor.
Any side effects occur quite rarely. The list of side effects is standard: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, pain in the abdominal area.
De-Nol is necessary for the treatment of gastric or duodenal ulcers. It has an astringent and antiseptic effect, and an anti-inflammatory effect. The active component of the active substance, as we said above, is bismuth tripotassium dicitrate. Here are a number of indications for which De-Nol is used as treatment:
- functional dyspepsia;
- ulcerative lesions of the stomach or duodenum, which are caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori;
- gastritis, which is caused by bacteria.
Unlike medicines based on omeprazole, De-Nol has more contraindications. These include individual intolerance to the active substance, carrying a baby, and breastfeeding. The product should not be taken by children under 4 years of age.
De-Nol should be taken with caution by people who have kidney failure, and only as prescribed by a gastroenterologist.
The antiulcer drug is drunk at least 3 times a day. Like other capsules, De-Nol is washed down with plenty of clean water. Consume it before meals, mainly 40 minutes before the upcoming meal. For children, the product is dissolved in water or tea. Also, under no circumstances should the drug be taken with dairy products.
Possible side effects include an allergic reaction and vomiting. This usually occurs when the dosage of De-Nol is not observed. In other cases, no side effects are observed. The course of treatment is 2 months. Then a break is taken, and the treatment is extended as prescribed by the doctor.
Any doctor in the field of gastroenterology will confirm that gastritis, ulcers, or any other pathology of the gastrointestinal tract must be subject to complex therapy, otherwise the treatment will become ineffective.
The main purpose of Omez is aimed at inhibiting the production of gastric secretions. The active components of the drug produce a protective film, which has a beneficial effect on the mucous membrane of the organ.
De-Nol, in turn, is also prescribed for the treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. After a few days of taking De-Nol in complex therapy, the components of the drug produce substances that form a protective film on the gastric mucosa, thus preventing the bacteria Helicobacter pylori from developing.
To prevent diseases, experts recommend using De-Nol.
These two remedies can be taken together. This is evidenced by the recommendations of doctors. But you still need to strictly monitor the duration of taking medications that only a doctor prescribes.
Reception scheme
Omeprazole in combination with De-Nol is a powerful complex against gastrointestinal diseases. At the same time, you need to know how to take them correctly in order for the treatment to have a positive effect.
After confirming the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes complex therapy. Omez is taken 20 mg. no more than twice a day. De-Nol - 1-2 tablets twice a day. It is important not to increase the dosage prescribed by your doctor.
De-Nol and Omez are prescribed simultaneously for severe symptoms of the disease. For both drugs to work properly, you need to take them correctly. Omez is drunk 30 minutes before De-Nol. This therapy is most effective in the treatment of chronic diseases. Therefore, the drugs are often prescribed to be taken together, and the chances of recovery are significantly increased.
If vomiting, nausea and dizziness occur after taking the product, consult a doctor immediately.
Patient reviews
I have had chronic gastritis since childhood. During the acute stage, she was treated with standard medications - she took anticoagulants and proton pump inhibitors. Omez was my salvation. However, the doctor said that there would be improvements in just a couple of days, which in itself is strange. And I decided to change doctor.
After diagnosis, I was diagnosed with bacterial gastritis, which, naturally, needs to be treated differently. The doctor prescribed me to take De-Nol. I took the course. I forgot about gastritis! It's been 4 years already. A good remedy. She underwent a thorough medical examination before the planned operation. They examined me from head to toe and found an ulcer.
I was shocked, because I never had a stomach ache! The doctor immediately prescribed therapeutic treatment. I was prescribed to take Omez and De-Nol at the same time. Both drugs performed well. No side effects were found. The ulcer was cured in just two months. It took a long time to treat a stomach ulcer; De-Nol and Omez were prescribed.
There were no improvements. It even seemed to me that it was only getting worse. The doctors were shocked how the medications helped everyone, but not me. By the way, I had a bacterial ulcer. The doctor asked me to stop taking the medications one by one and look at how I was feeling. First I stopped taking Omez and immediately noticed that I felt better.
It turned out that the active component of the drug simply did not suit me.
It is impossible to compare Omez and De-Nol, since the two products have completely different pharmacological properties. To effectively cure an ulcer and choose individual treatment, be sure to consult a doctor.
Ranitidine
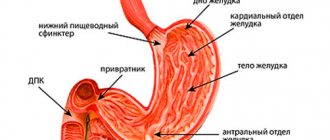
The principle of action of the drug is based on blocking histamine receptors located in the gastrointestinal mucosa. This reduces the formation of hydrochloric acid. Ranitidine is taken as a course. When taken simultaneously with enveloping agents, the effectiveness of the drug is reduced.
Ranitidine is indicated in the following cases:
- Peptic ulcer or erosion of the stomach and duodenum;
- Prevention of disease beyond exacerbation;
- Gastritis accompanied by high acidity;
- Heartburn;
- Reflux esophagitis;
- Stomach operations.
Among the disadvantages, it should be noted that rapid addiction to the drug requires a constant increase in dosage.
After stopping Ranitidine, the secretion of gastric juice increases sharply. Side effects include possible allergic reactions, as well as increased gas production and soft stools.
What do the reviews say?
So, Omez or Ranitidine - which is better? Reviews from many people who have taken these drugs are controversial, because for several decades they have both been helping people with stomach diseases. According to patient reviews, Ranitidine is an excellent remedy that has helped many with peptic ulcers. It is very effective and copes well with pain.
But the drug "Omez" in this case is in no way inferior. It also perfectly fights pain, and its duration of action is almost twice as long as that of Ranitidine.
Omeprazole
Regulates the proton pump, which is responsible for regulating the production of gastric juice. It has a prolonged effect by reducing the activity of enzymes and peptides.
The use of the drug is recommended for:
- Gastric ulcer;
- When treating Helicobacter pylori;
- Reflux esophagitis;
- Gastrinoma;
- Formation of a hole in the esophagus (hernia);
- Preparation for surgery and the period after it;
Contraindications are similar to Ranitidine.
Differences between Omeprazole and Ranitidine
Despite the similarity of action, there is still a difference between Ranitidine and Omeprazole:
- Mechanism of action. Both drugs are antisecretory agents that affect the secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. But if Ranitidine simply blocks its formation, Omeprazole is able to neutralize the already formed acid, which more effectively affects the healing of damaged gastric mucosa and significantly speeds up recovery;
- Release form. Omeprazole is available in powder form for injection, as well as in the form of enteric capsules and tablets. Ranitidine exists only in tablet form;
- Acceptable age of the patient. Omeprazole is allowed to be taken from 5 years of age, while Ranitidine is only allowed from 12 years of age;
- Ranitidine is quickly addictive; Omeprazole does not have this drawback. However, there have been cases where the patient did not respond to taking Omeprazole. In cases, it is recommended to prescribe treatment with Ranitidine;
- It has been established that the antisecretory effectiveness of Omeprazole is 2-10 times higher than the similar effect of Ranitidine.
Omeprazole and De-Nol: how to take at the same time? What's better? — updated 03.19
These medications are prescribed for lesions of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT).
The drugs are similar: their action is aimed at eliminating irritation of the gastric mucosa and reducing acidity. Medicines eliminate pathogenic (hostile) flora in the stomach by normalizing the production of gastric acid, which promotes the proliferation of bacteria. Both significantly reduce infection by helicobacter pylori bacteria (a spiral-shaped bacterium that parasitizes the lining of the stomach and intestines);
The substance omeprazole inhibits the production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach and suppresses the development of infectious flora. Easily tolerated by patients. Rarely causes allergic reactions.
Used for the treatment of acid-dependent gastrointestinal lesions:
- ulcerative gastric manifestations, regardless of the cause of their occurrence, including the use of certain medications;
- inflammation of the gastric mucosa (gastritis) at any stage of the disease;
- benign changes in the pancreas (Zollinger-Ellison syndrome).
The drug eliminates peptic ulcers (ulcers resulting from an increased concentration of gastric juice) of the gastrointestinal tract against the background of high acidity, eliminates dyspeptic symptoms - reduces pain in disorders of the digestive process.
Contains bismuth tripotassium dicitrate, which protects the walls of the gastric mucosa by stimulating the formation of new cells. Reduces the level of pepsin (a component of gastric juice) in the body, minimizing its irritating effect. It is well tolerated and has no characteristic side effects.
It has an antimicrobial (against Helicobacter pylori) and anti-inflammatory effect, restores the protective layer of the mucous membrane.
The main diseases for which the drug is prescribed:
- any form of peptic ulcer caused by Helicobacter pylori;
- damage to the intestinal walls, disturbances of peristalsis (contraction) from excess acid in gastric secretions;
- gastritis and duodenitis (damage to the mucous membrane of the duodenum);
- pain syndromes caused by functional reasons;
- irritable bowel syndrome, manifested over a long period of time with a predominance of diarrhea.
De-nol is taken as a course, prescribed on the eve of surgical interventions, during operations under general anesthesia for prophylaxis.
Reception is possible during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
De-nol is prescribed to children from 4 years old, the dosage of the drug is calculated based on body weight.
Although these drugs are prescribed for the same diseases, there is no point in comparing them, since they belong to different pharmacological groups: De-nol is a gastroprotector (provides mechanical protection of the mucous membranes), which has a local effect on the gastric mucosa, Omeprazole is a proton pump inhibitor, absorbed into the blood (blocks the activity of cells that synthesize hydrochloric acid).
Omeprazole produces a cumulative effect: after a course of treatment, the balance of the chemical composition of gastric secretions is maintained for a long period.
De-nol is valid only during the period of use. It is effective when mucosal lesions have already occurred.
De-nol has a number of qualities that are unusual for Omeprazole:
- promotes the regeneration of the lining tissues of the gastrointestinal tract, stimulates their growth;
- has a healing and soothing effect - envelops and heals ulcers;
- relieves inflammatory processes in the abdomen;
- eliminates increased gas formation.
Omeprazole only creates conditions for normal secretion of gastric juice, eliminates the cause of pain, and not the symptoms themselves.
Treats:
- GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease, characterized by the release of excess acid into the esophagus);
- ulcers caused by stress and after taking NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
Medicines have various restrictions: for Omeprazole it is up to 4 years of age. The medication is prescribed with caution to patients if there is impaired liver function. Patients may have hypersensitivity to the components of the drug. De-nol is better tolerated and is considered safer. The remedy can be taken during pregnancy, breastfeeding, and is used to treat babies.
Omeprazole is suitable for providing quick help to a patient with ulcerative lesions: it is administered intravenously for a faster effect in advanced forms. De-nol is not available in solutions for injection.
Shared use enhances the therapeutic effect, accelerates the healing process, and destroys Helicobacter pylori.
Ranitidine
The drug blocks histamine receptors in the gastrointestinal mucosa (on basal cells), reducing the production of hydrochloric acid, hence the antiulcer effect. A course of treatment is recommended. The dose should be increased if you drink alcohol or smoke. The effectiveness of the drug decreases when combined with enveloping agents.
- Treatment of the acute stage of gastric and duodenal ulcers, as well as for prophylactic purposes during remission.
- Gastritis with high acidity.
- Heartburn due to stress and poor nutrition.
- Reflux esophagitis.
- Preparation for gastroscopy.
- Surgical interventions on the stomach.
- Children under 12 years old.
- Pregnancy and lactation.
- Hypoacid gastritis.
- Individual intolerance.
What is the difference between ranitidine and omeprazole?
Disadvantages include the rapid development of tolerance to standard doses. After discontinuation of the drug, a sharp increase in secretion is observed.
Side effects include: allergic and dyspeptic reactions (flatulence, stool disorders), etc.
Omez
The medicine is produced as capsules and lyophilized powder, on the basis of which an infusion solution is prepared. The basic component of Omez is omeprazole.
Gelatin capsules (20 mg) are packaged in boxes of 10-30 pieces. The lyophilisate is placed in bottles with a volume of 40 mg.
Manufacturer Omez - Dr. Reddy's, India. Price – from 85 to 264 rubles.
Omez is considered an antiulcer drug that inhibits proton pump function.
Indications:
- Gastrointestinal ulcer
- NSAID gastropathy
- Reflux esophagitis
- Hypersecretory pathologies
- Surgical interventions on the gastrointestinal tract.
Contraindications – hepatic or renal dysfunction, pregnancy, hypersensitivity, childhood, lactation.
The lyophilisate is administered intravenously over half an hour. Dose 20-60 mg per day.
The dosage of capsules for ulcers is 20 gm. The drug is taken twice a day. Therapy time is from 2 to 8 weeks. In other cases, the dose may vary from 10 to 120 mg per day.
Taking Omez sometimes causes digestive, nervous, and allergic disorders. Other consequences of treatment with omeprazole:
- Gynecomastia
- Formation of granular formations in the stomach
- Leukopenia
- Atralgia
- Skin rash
- Pancytopenia
- Hyperhidrosis
- Alopecia
- Myalgia
- Erythema and more.
Omeprazole
It is an inhibitor of the proton pump, which regulates the concentration of gastric juice. Reduces the activity of peptides and digestive enzymes, thereby providing a prolonged effect. An integral part of Helicobacter pylori eradication.
The difference between omeprazole and ranitidine is that the former not only blocks acid secretion, but also neutralizes its excess. This helps heal erosions and restore damaged cells.
- Stomach and duodenal ulcers.
- Combination therapy for Helicobacter pylori.
- Reflux esophagitis.
- Hyperacid gastritis.
- Gastrinoma.
- Hernia of the diaphragm (esophageal opening).
- Gastropathy after taking NSAIDs.
- Preparation for surgery and postoperative period.
- Contraindications and side effects are similar to ranitidine.
Which is better and conclusions
Studies have shown better effectiveness of omeprazole, compared with ranitidine, in the healing of ulcers and the duration of remission after taking high doses of NSAIDs. In addition, it does not require an increase in dosage. Antisecretory activity exceeds H2-blockers by 2-10 times.
Contraindications and side effects
Both types of medications are prohibited from taking during pregnancy and lactation, as well as in case of impaired renal and liver function. Side effects when taken are rare; as a rule, negative aspects appear in the case of individual intolerance to the drug.
Diseases of the digestive system are widespread everywhere. They require a long period of treatment and lifestyle adjustments. Omez and De-Nol occupy a key place in basic therapy. They belong to different pharmacological groups and influence individual parts of the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal diseases.
To understand the effect of taking these drugs together, it is necessary to understand what each drug is individually.
Omez is a well-known representative of the group of proton pump inhibitors. Its main effect - reducing the acidity of gastric juice - is due to its ability to reduce the production of hydrochloric acid.
The following indications for use of the drug are available:
- duodenal or gastric ulcer;
- GERD – gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- conditions associated with increased secretion of gastric juice with high acidity;
- eradication of Helicobacter pylori;
- when taking NSAIDs - for the prevention of mucosal erosions and peptic ulcers;
- prevention of the development of aspiration pneumonitis (Mendelssohn syndrome);
- prevention and treatment of dyspepsia.
Note! According to modern data, Omez can be prescribed in childhood. Its effectiveness in this group of patients has been proven in the treatment of GERD and peptic ulcers.
Omez capsules have a characteristic appearance: the trade name is on each shell on a transparent background
Taking the drug may be accompanied by a number of negative symptoms:
- headache;
- pain in the abdominal area, often accompanied by dyspeptic symptoms;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- bloating.
Less commonly, undesirable symptoms may appear from the hematopoietic, immune, respiratory, urinary and reproductive systems. Muscle weakness, dermatitis, and disruption of the sensory organs may occur. In the presence of concomitant osteoporosis, bone strength decreases.
De-Nol
De-Nol is a branded drug produced in the Netherlands. The active ingredient is bismuth tripotassium dicitrate.
The drug has the following therapeutic effects:
- reduces the manifestations of the inflammatory process;
- has an astringent effect - as a result of biochemical reactions and interaction of the drug with tissues, a protective protein film is formed on the surface of the latter;
- causes the death of Helicobacter pylori;
- increases the formation of prostaglandin E, which, in turn, reduces the secretion of hydrochloric acid by the cells of the gastric mucosa and increases the secretion of mucus and bicarbonate;
- triggers cytoprotective mechanisms, increasing the resistance of the mucosa to aggressive factors;
- stimulates tissue regeneration;
- reduces the activity of the gastric enzyme pepsin, which can negatively affect the wall of the digestive tract.
The formation of a protective film is due to the formation of chelate compounds with a protein substance. It prevents the development of erosions and ulcerative defects.
De-Nol fights Helicobacter pylori
The product is used in the presence of the following pathologies:
- peptic ulcer;
- exacerbation of chronic gastroduodenitis and gastritis;
- irritable bowel syndrome, in case of predominance of diarrhea;
- various types of functional dyspepsia.
The medication is well tolerated. In some cases, it causes a number of side effects. From the gastrointestinal tract we are talking about nausea, diarrhea or constipation and vomiting. On the part of the skin – itching and rashes. For the nervous system, the drug in high doses can be toxic, even leading to the development of encephalopathy.
The combined use of Omez and De-Nol is included in many treatment regimens for diseases of the digestive system. They are used as basic drugs in the treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract with different mechanisms of development.
For gastritis
One of the first symptoms of gastritis, an inflammatory process in the stomach, is pain. It is accompanied by belching and heartburn. Proton pump inhibitors and bismuth preparations are effective both when taken once and as a component of long-term therapy.
Their prescription for gastritis is due to the following features of the drugs:
- Omez, by reducing the secretion of hydrochloric acid, reduces the damaging effect of the aggressive factor on the inflamed gastric mucosa.
- De-Nol, like Omez, is an important component of anti-Helicobacter therapy, along with antibiotics. It is Helicobacter pylori, according to official studies, that is the key etiological factor in most cases of gastritis. Additionally, bismuth tripotassium dicitrate has an anti-inflammatory effect, protects the organ wall and stimulates rapid tissue restoration.
- The combination of drugs provides a comprehensive effect on the pathogenesis of the disease. This helps to achieve stable long-term remission or recovery.
Carrying out eradication of the microorganism, eliminating aggressive factors, including high acidity, is a reliable way to treat hyperacid gastritis. In the presence of low acidity, taking Omez is not indicated. De-Nol can be included in the complex therapy of hypoacid gastritis.
For ulcers
Ulcerative lesions of the stomach and duodenum are one of the main indications for the simultaneous use of these two drugs.
The disease can be caused by a number of factors:
- Helicobacter pylori invasion;
- taking medications - Aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, glucocorticosteroids, sympatholytics (reserpine alkaloid);
- excessive stress loads.
If the pathology is caused by the activity of a microorganism, De-Nol will be used as a component of etiotropic therapy. In all cases, with the development of an ulcer, the bismuth preparation is also indicated as a cytogastroprotector, due to its property of forming a protective film.
Note! Omez reduces the production of the main aggressive factor that aggravates the course and prognosis of peptic ulcer disease - hydrochloric acid. It is also a drug of three-component and four-component anti-Helicobacter therapy.
For gastroduodenitis
The development of an inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum is called gastroduodenitis. Currently, the number of patients diagnosed with this type of pathology is gradually increasing.
Like gastritis, gastroduodenitis can be accompanied by an increase and decrease in the acidity of gastric juice.
According to the same principle, the doctor decides to prescribe the joint use of proton pump inhibitors and De-Nol, as well as other medications indicated in this case.
For gastric erosion
An important effect of omeprazole in the event of erosions of the gastric mucosa is the rapid relief of pain. Erosion is a defect in the surface layers of the organ wall. Omez promotes faster tissue regeneration.
Stomach erosion can transform into peptic ulcer
It is known that Helicobacter pylori often takes part in the process of launching the pathogenetic process, as a result of which erosions are formed. Therefore, De-Nol will be effective not only as a gastroprotector, but also in the fight against microorganisms.
Understanding how compatible certain drugs are with each other is necessary to achieve the desired result of therapy.
Note! Medicines can enhance or weaken the effect of substances when taken together and even distort their effect on the body.
Often they simply do not interact with each other and do not intersect in any way in their mechanisms of action. Both Omez and De-Nol are usually combined with a number of drugs.
With antibiotics
One of the main reasons for the development of pathologies of the stomach and initial parts of the intestines is the invasion of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. De-Nol and Omez are present in treatment regimens aimed at getting rid of this microorganism.
They are combined with the following antibiotics:
- Clarithromycin;
- Amoxicillin;
- Metronidazole;
- Tetracycline.
If a negative result is obtained after testing for Helicobacter pylori, the use of antibiotics is not advisable.
Duspatalin
If there is a spasm in one or more parts of the gastrointestinal tract, a special group of drugs called antispasmodics is used. One of its representatives is Duspatalin. It not only helps relax smooth muscles, but also has an analgesic effect.
If there are indications for the simultaneous use of proton pump inhibitors, Duspatalin and De-Nol, their combined use is possible in the absence of negative reactions to the drugs.
Ranitidine
Ranitidine is a drug that is an alternative to Omez. The secretion of hydrochloric acid is influenced by a number of factors. Omeprazole inhibits the work of hydrogen-potassium adenosine triphosphatase, ensuring proton transport. The latter are necessary to maintain the acidic environment of the stomach at the proper level.
But if the pH level goes outside the normal range and becomes overly aggressive, it needs to be adjusted. Ranitidine reduces histamine production. The latter acts on the H2 receptors of secretory cells, stimulating the production of highly acidic gastric juice. Ranitidine is an antagonist of these receptors.
As a rule, in order to achieve the desired pH, it is enough to influence one of the mechanisms.
Ranitidine serves as a substitute for Omez in case of intolerance to the latter
In a situation where the use of Ranitidine is indicated, simultaneous use of De-Nol is permitted for the same reasons as its combination with proton pump inhibitors.
Almagel
Another group of drugs used for high stomach acidity are antacids. The active ingredients of Almagel - aluminum and magnesium hydroxide - neutralize the acidity of gastric juice.