The occurrence of a pathological condition, such as cardiospasm of the esophagus, brings the body a reflexive relaxed state of the lower sphincter during swallowing reflexes.
As a result, incoming food in lumps accumulates in the food duct, and expands its upper sections.
This is a pathology that has no age restrictions or gender, so it equally affects all segments of society and gender.
When the first signs of this pathology appear, it is necessary to urgently visit a doctor and undergo the diagnosis prescribed by him with the necessary treatment.
The main and first signs include:
- dysphagia;
- a sharp decrease in body weight;
- pain in the chest compartment (sternum).
In order to correctly diagnose esophageal cardiospasm, the doctor uses instrumental and laboratory diagnostics of the patient’s body.
Therapy for this type of disease is carried out by surgical intervention or by a conservative approach to treatment.
These methods are prescribed and selected by the doctor, depending on the course of the disease and the occurrence of possible complications.
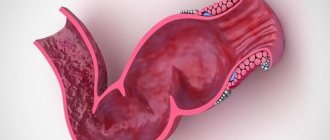
Cardiospasm of the esophagus - characteristics of the disease
This pathology is expressed by the complete or partial absence of the swallowing reflex and contraction of the lower sphincter.
The cause of this condition is a complete failure of the motility of the esophagus.
The spasms resulting from this create stagnation of food contents in the esophagus, which leads to an increase in the upper part and the appearance of an inflammatory state of the digestive organ.
The esophagus changes its shape due to the development of different stages of the pathological condition:
- the initial stage of development of the pathological disease - no changes are observed;
- an increase in the esophagus by 3-4 cm occurs at the second stage of the disease;
- expansion of the esophagus up to 6 cm and thickening of the walls - indicates the third stage of development;
- the fourth stage leads to lengthening of the esophagus and a change in its appearance to a peculiar shape in the form of the English letter S.
The main risk group for this pathology are people with obvious signs of mental disorder, but also different segments of society, regardless of status and age, as well as gender.
In some cases, children begin to suffer from this pathology, in whom this disease usually occurs in a severe form due to a fragile body.
Symptoms
At the initial stage, the signs of the disease are very weak. The erased clinic can last from childhood, and a person can attribute various complaints to completely different diseases. When the disease is already fully formed, the first clinical symptoms appear. They always declare themselves very clearly and intrusively:
- Pale skin.
- Tachycardia.
- Dizziness.
- Noise (ringing) in the ears (hearing loss).
- Sweating.
- Disorientation and confusion.
- Fall in blood pressure.
- Fainting.
- Vomiting blood.
- Vomiting with pieces of food.
- Regurgitation.
- Blood in the stool.
In the acute form of the disease, patients complain of a feeling of a lump in the throat. Patients also experience severe pain, which is similar to cramps. The spasm subsides as soon as the food enters the stomach.
People who have not consulted a doctor for a long time because of their irresponsibility develop nervousness, complexes, and psychological problems, which further aggravates the situation.
Cardiospasm in infants is manifested by vomiting during feeding. Very often the baby chokes while eating. An X-ray with contrast reveals an enlarged esophagus.
Esophageal Disease Clinic
For the initial stage of the disease, certain symptoms of the disease are expressed, and as the pathology develops, they become more noticeable and pronounced. The main and obvious symptom is dysphagia.
This symptom and pathological deviation from the norm is expressed in a violation of the swallowing reflex, which leads to an abundant accumulation of food in the esophageal tube.
In addition, this symptom is characterized by two main features:
- belching with the smell of rotten and fermented food;
- severe bursting pain in the chest caused by an enlarged esophagus.
These symptoms are supplemented by general signs and troubles associated with this pathology:
- severe weakness of the whole body;
- lack of appetite;
- sudden weight loss;
- chronic manifestations of diseases of the human cardiovascular system.
The lack of timely treatment of this pathology brings additional diseases to the patient’s body:
- pulmonary pneumonia;
- abscesses of internal digestive organs and blood vessels;
- pulmonary atelectasis.
When the first signs and causes characteristic of this pathology appear, it becomes the first alarm bell, in which action must be taken without delay.
Timely therapy will save the patient from severe and serious complications.
The course of treatment is prescribed by the attending doctor, according to the diagnostic measures performed. Self-medication in this situation is dangerous to life and health.
Cardiospasm and achalasia of the esophagus
Decreased relaxation of the cardia (the muscle ring that is located between the stomach and the esophagus) leads to stagnation of food in the esophageal tube, disrupting the movement of food into the stomach. Prolonged presence of food in the esophagus causes its expansion above the site of spasm.
First, the muscle layer of the organ thickens, and then the connective tissue grows (especially in the lower sphincter). irritation , swelling appear on the epithelium of the esophageal tube , and as the disease progresses, the development of esophagitis .
Cardiospasm has 4 stages of development and characterizes the degree of damage to the mucous membrane of the esophagus.
Phase 1 is characterized by the unstable appearance of spasms, while the membrane of the muscular organ and the functions of the cardia are not impaired. The lumen of the esophagus is normal.
Phase 2 – attacks become more frequent and become stable. The esophageal mucosa becomes inflamed, and the esophageal tube itself expands.
Phase 3 – scarring changes and persistent significant expansion of the esophagus are observed.
Phase 4 is characterized by stenosis (narrowing) of the cardia, while the esophagus takes on an S-shape, that is, it becomes deformed, lengthens, and esophagitis develops.
In addition, cardiospasm is divided into 3 types, which characterize a violation of the contractile function of the cardiac sphincter.
- Hyperthroat - increased contractile function, which does not correspond to the load on the cardiac sphincter.
- Hypovenous - a decrease in this function below normal.
- Amotylic – motility of the cardiac sphincter is very low or absent.
Each stage of cardiospasm has its own symptoms.
The occurrence and causes of this pathology
Even despite the development of science and medicine, scientists have not yet fully identified the cause of this pathology.
There are opinions that the development of this disease is preceded by the following factors:
- mental disorders;
- stressful situations;
- structural changes in the tissues of nerve endings that are responsible for the reflexes of the body and the esophagus itself.
The development of the above factors creates conditions for malfunction of nerve endings and untimely contraction of the smooth muscles of the esophagus.
Inconsistency in work interferes with the movement of food along the tube channel, which leads to its accumulation and inflammatory disease.
In addition, increasing the tone of the muscular system plays an important role in the development of this pathology and increased tone of the food tube.
Other types of esophagospasm
In medical practice, there are other types of esophageal spasm:
- Nervous - it is characterized by feverish muscle contraction due to mental disorder (depression), sleep disturbances, stress, increased tendency to anxiety, fear. The attack lasts only a few minutes.
- When swallowing, the following symptoms indicate such a spasm: a feeling of a lump in the throat accompanies a panic attack; during convulsions there is a feeling of suffocation; when there are sharp unexpected sounds, vomiting begins; in a neurosis-like state, a spasm can prevent even saliva from being swallowed; attacks of nausea and vomiting are considered frequent accompaniments of neurosis; in the chest area there are pain sensations similar to cardialgia, and their intensity is not constant and varies from insignificant to severe.
- Cardiospasm can be acute or chronic. Acute – characterized by pain in the chest and epigastric region; feeling that a lump of food is lingering over the stomach. However, drinking water does not bring relief. At the end of the attack, regurgitation or belching occurs. With slight excitement, the pain intensifies. Late therapy is dangerous due to sudden weight loss and esophageal vomiting. The development of pneumonia cannot be ruled out. One of the main causes of esophageal spasm, the symptoms of which are described above, is considered to be a long-term ulcerative lesion. The main provocateurs are smoking, inhaling toxic fumes, and drinking strong alcohol.
- Lower sections - with such a spasm, the organ tube expands along its entire length.
- Non-sphincteric - several of its parts are affected simultaneously along its entire length. Individuals complain of regurgitation of mucus, chest pain, and episodes of dysphagia, lasting from a few seconds to several weeks.
Esophageal spasm also occurs with other anomalies. For example, as a symptom it is observed in tuberculosis, syphilis, scarlet fever, inflammation of the pleura or aorta.
General therapeutic measures
Therapy for cardiospasm of the esophagus is carried out conservatively and surgically and depends on the development and complexity of the pathology, symptoms of the disease.
Conservative treatment includes the use of medications, dietary therapy, and adherence to a daily and nutritional regimen.
What medications are prescribed for cardiospasm of the esophagus (achalasia cardia):
- antispasmodics;
- sedatives;
- calcium antagonists;
- agents having the ability to envelop;
- prokinetics.
When starting treatment, dietary measures are prescribed according to table No. 1 prescribed by the nutritionist.
Treatment with folk remedies is also allowed, which includes the use of tinctures, but only with the agreement of the attending physician, since, having a picture of the pathology in hand, he will be able to correct this treatment.
In some cases, to normalize the general condition and improve reflex swallowing, doctors can use minimally invasive methods of therapy, which involves installing a resorbable stent or balloon dilatation.
If there is no improvement in the patient's condition, surgical intervention is used.
Therapeutic measures
After confirming the diagnosis, individuals are interested in the question of how to relieve spasms of the stomach and esophagus. If the exact cause of the disease has not been identified, then doctors do not recommend treating it yourself. Therapy involves the use of:
- medicines;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- diet;
- lifestyle changes;
- medicinal herbs.
If there is an underlying gastrointestinal disease that provokes esophagospasm, then initial treatment should begin with it in order to prevent the occurrence of new attacks. Next, we will consider in more detail how to treat reflex esophageal spasm. For this purpose, drugs of different pharmacological groups are used:
- Antacids, or antacids, protect the mucous membrane of the digestive canal.
- Gastrointestinal motility stimulants - promote the passage of a bolus of food by improving the peristalsis of the muscular tube.
- Antispasmodics – remove spasms.
- Alginates – envelop the mucous membrane, protecting it from aggressive hydrochloric acid.
- Sedatives – a calming effect on the central nervous system.
- Antidepressants, tranquilizers and medications that normalize sleep are prescribed if necessary.
- Analgesics and anesthetics – have a local anesthetic effect.
- B vitamins.
The above medications, doses and treatment regimens are selected by the attending physician individually.
Let's look at how to relieve spasms of the stomach and esophagus with the help of physiotherapeutic treatment. It is aimed at normalizing the functions of the nervous system and includes:
- Electrophoresis with an anesthetic - a direct electric current is applied to the affected organ together with a drug, which helps relieve pain.
- Radon baths - thanks to them, the sensitivity of nerve endings is reduced.
- Galvanization - current is supplied through electrodes with a constant frequency, low strength and low voltage. As a result, the sensitivity of the nerve fibers weakens. This method is especially effective for spasm of the esophagus that occurs against the background of osteochondrosis.
- Warm baths with decoctions of medicinal herbs that have a sedative effect.
- Inductotherapy is the effect of a high-frequency electromagnetic field with a predominance of the magnetic component. The uniqueness of this manipulation is that heat is generated in the muscle layer, which ultimately reduces tone and eliminates spasm of the esophagus. How else can you remove it? Physical activity is especially important, i.e. performing simple exercises aimed at strengthening the spinal column and normalizing the functioning of the central nervous system.
Phytotherapeutic treatment involves the use of medicinal plant materials that have different effects:
- anti-inflammatory – elecampane;
- sedative – peony, valerian, motherwort;
- antispasmodic – chamomile, sage, mint.
Alternative treatments include:
- Acupuncture. The course of treatment is up to ten days, three times a year.
- Medical hypnotherapy.
- Psychotherapeutic methods - sand therapy, autogenic training according to Schultz, art therapy.
Massage of certain points that are located on the midline of the chest is another non-standard way of treating esophageal spasm. How to remove it using this method? The locations of the points are as follows:
- under the cervical fossa;
- between the breasts;
- between the first and second points (at an equal distance from each).
These areas are massaged with the finger bones, making clockwise rotational movements for five minutes. It is noted that when performing this manipulation, the individual experiences severe pain. There is an opinion that this is a normal phenomenon, and after twenty minutes of intense exposure to these points, the pain will completely disappear.
All of the above methods give good results.
Diet therapy
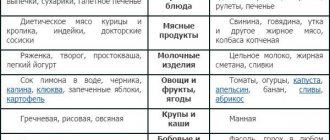
In case of pathology of this disease, dietary treatment is prescribed. Patients suffering from cardiospasm are prescribed dietary food with dietary table No. 1.
Food is consumed in liquid or ground form, in small portions 2-3 times a day.
It is completely forbidden to eat salty, sour, spicy, fatty, and hot foods.
You need to eat slowly, chewing your food thoroughly. Types of foods that it is advisable not to consume or reduce consumption:
- fresh baked goods;
- fermented milk products;
- apples of all types and varieties;
- peaches;
- boiled potatoes;
- meat of fatty varieties and breeds.
After eating food, it is recommended to take a strong and large swallow to improve the passage of food through the esophagus with a glass of warm water.
It is forbidden to eat before bedtime, as this will lead to stagnation in the esophagus and putrefaction of lumps of food.
Symptoms
Most often, the disease manifests itself when eating food, although cases of sudden onset of symptoms of esophageal spasm are very common. The severity of the signs of the disease depends primarily on the type of spasm and the causes that cause it. Atypical contractions of the esophageal muscles accompany:
- Pain in the chest area. May radiate to the back (usually between the shoulder blades), shoulders, neck, lower jaw, arms and ears. Painful sensations can persist for an hour and be intense or manifest themselves in the form of dull pain and discomfort. If pain appears regardless of food intake, then it is worth excluding the influence of other factors (angina pectoris). The pain syndrome is more pronounced against the background of emotional shock.
- Dysphagia (impaired swallowing due to spasm of the esophagus). Occurs when swallowing food and saliva. It can accompany the intake of both solid, coarse, dense food and liquid.
- Feeling of discomfort - heaviness, squeezing in the chest, suffocation, feeling of a “lump” in the throat.
- Belching (with reflux of the contents of the esophagus into the oral cavity - after intense spasms).
- Heartburn.
- Increased salivation.
- Nausea, sometimes vomiting occurs (without an admixture of hydrochloric acid and peptin, since the food did not enter the stomach).
- Regurgitation of food (usually after the spasm ends).
Constant spasm of the esophagus leads to weight loss, and, depending on the individual characteristics of the body, appetite may not disappear.
Damage to the vagus nerve can cause heart rhythm disturbances.
Belching is one of the symptoms of esophageal spasm
Drug therapy for the pathology of cardiospasm of the esophagus
At the onset of the disease, this pathology is amenable to drug treatment. Therapy in this situation is carried out in a complex, and medications and tablets have a wide spectrum of action.
First of all, a certain group of medications has a relaxing effect on the muscles and musculature in the lower part of the esophagus.
This group of drugs includes:
- Dinitrate;
- Nitroglycerine;
- Isosorbitol.
Cardiospasm of the esophagus, treatment requires complete relaxation of the smooth muscles so that food can pass freely through the tube.
For this, myotropic antispasmodics are used. This group includes the following drugs:
- Halidor;
- Papaverine;
- Drotaverine tablets.
These drugs relieve muscle spasms and reduce the patient's pain. Doses of use are prescribed by the doctor, according to the pattern of the course of this pathology.
It all depends on the stage of development of the disease, the severity of the disease, and the individual characteristics of each organism separately.
To speed up the healing process, additional restorative therapy is carried out.
It improves the condition of the immune system and the general condition of the patient's body. What is included in the general health course of treatment of this pathology:
- vitamin groups B;
- vitamin C;
- the use of glucose as a substitute and maintenance of the body.
Therapy takes place with full compliance with dietary nutrition and a gentle diet regimen.
Medicines are selected so that if they get stuck in the duct, they do not cause irritation of the walls of the esophageal mucosa.
In other cases, with the development of serious pathology of cardiospasm of the esophagus, drugs are used by injection. Balloon dilation works well.
Spasm of the esophagus when swallowing, what to do?
You just need to take a bath and add 10 drops of belladonna tincture to it. In addition, do not forget that a simple change of environment and fresh air help quite well in cases of psychosomatic spasms of the esophagus. Therefore, relax more often, go to a resort, swim in the sea and don’t worry about anything. With frequent spasms of the esophagus, food should not irritate the mucous membrane of this organ. In addition, it is imperative to exclude alcohol and carbonated drinks, fatty, fried, spicy or sour foods, because they can cause spasms.
The reasons why esophageal spasm may occur are very diverse. Therefore, treatment of esophageal spasm with drugs should be carried out exclusively as prescribed. Depending on what triggered the diffuse spasm of the esophagus, pain can occur both under the scapula and throughout the entire esophagus.
What is balloon dilatation
The balloon dilatation method is recognized as the most effective way to treat esophageal cardiospasm.
This procedure is performed under general anesthesia. The principle of therapy is to introduce a balloon dilator into the body of a sick person, which is a specially invented device with a balloon at the end of a medical tube.
This action has the ability to stretch the lower food channel of the esophagus. After this event, the process of reflex swallowing improves.
By performing several of these procedures, there is a significant improvement in the swallowing effect. This procedure is carried out in a course and after a certain period of time.
This procedure is unsafe for humans. The main danger is the possibility of damage and rupture of the walls of the esophagus.
If the walls of the mucous membrane of the esophagus rupture, urgent surgical intervention will be required to eliminate the consequences of this rupture.
In some cases, this procedure, if carried out inappropriately, can cause death and accounts for 2-4% of the total dilatation rates.
In addition to this unpleasant moment, mechanical damage to the esophagus can also occur, which will cause internal bleeding into the stomach and duodenum.
Therefore, to avoid side effects and processes, this procedure must be performed only by specialists of high medical rank.
How to relieve esophageal spasm at home?
Also, in such cases, doctors often advise undergoing physiotherapeutic procedures, in particular, a galvanic collar with bromine, darsonvalization of the scalp and epigastric area. Almost always, spasm of the esophagus causes a lot of unpleasant moments for the patient. A person is struck by unbearable pain in the area of the shoulder blades or the back wall of the esophagus for several seconds or tens of minutes.
Surgical treatment of this pathology of cardiospasm
The most recommended operation for cardiospasm of the esophagus is the Geller operation.
What is this surgical procedure? The sequence of actions for this operation:
- between the seventh and eighth ribs the patient’s thoracic region is opened;
- the distal part of the esophagus is separated from the tissues of other organs;
- cut muscles up to 10-11 centimeters long.
This operation is performed at the last stage of the disease and brings positive benefits for the health of the sick person. Sometimes treatment is prescribed using traditional medicine.
Recommendations for patients
If esophagospasm occurs, it is advisable to visit a gastroenterologist. He will prescribe the necessary examinations to exclude its secondary nature. Once confirmed, all efforts are directed toward treating the disease that provokes the spastic state. If the reason lies in a malfunction of the nervous system, then measures are taken to normalize it. Person-centered therapy is most often indicated. In addition, sanatorium-resort treatment in the Crimea and on the Black Sea coast has a good effect.
How to relieve esophageal spasm at home? The following tips will be useful for both segmental and diffuse spasm:
- Give the individual warm water. This simple method helps in most cases. The attack passes, the pain stops.
- If the cause of the spasm is a stressful situation, then the patient is prescribed herbal sedatives.
It is not recommended to use medications on your own, as they all have contraindications and side effects.
Therapy using traditional medicine
Using traditional methods of therapy, you can try to relax the muscle tissue of the larynx. For this purpose, sedatives are used.
The following organics have sedative properties:
- valerian;
- motherwort grass;
- peony grass.
Medicinal decoctions are created from this vegetation. True, failure to follow the rules for preparing tinctures can not only help with this pathology, but also cause serious harm to the body of a sick person, which is why it is better to purchase these drugs at pharmacy kiosks.
Moreover, they do not cost a lot of money and are sold freely. These methods are used for treatment only in conjunction with drug treatment, according to courses prescribed by the doctor.
Inflammatory processes associated with cardiospasm of the esophagus are also relieved with the help of tinctures of the following plants:
- chamomile;
- oregano herbs;
- alder leaves;
- marshmallow root vegetable;
- quince seed.
To increase muscle tone in the lower part of the esophagus, the following tinctures are used:
- Chinese lemongrass;
- ginseng root;
- eleuthorococcus leaves.
Therapy with traditional methods is widely used only at the early stage of the disease.
In other cases, only as an aid to drug treatment.
Why does esophageal spasm occur due to nerves?
Painful sensations, in this case, go away much faster. Dysphagia always appears after or during eating the wrong food. Cold, hot, carbonated, and alcoholic drinks sharply cause spasms of the esophagus.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract that cause esophageal spasm must be cured. To relieve symptoms, it is recommended to take medications immediately before meals. In this case, “No-shpa” will help. 2-3 months after a successful operation and with appropriate drug treatment, you can forget about esophageal spasm. It is not recommended to resort to traditional methods at home. If nothing is at hand, then pine baths have a good effect. They must be taken daily for 10 days. Esophageal spasm will gradually cease to bother you.
Preventive measures against this pathology of the esophagus
To prevent this disease or stop the progression of esophageal pathology, it is necessary to organize a proper and healthy diet.
To do this, you need to review the food menu and turn off rough foods from it, refuse fast food in public catering, eliminate overeating and follow a daily routine.
It should be remembered that early contact with doctors will prevent serious consequences for the health of the victim from this disease pathology.
Strict adherence to the rules and daily routine, playing sports and physical therapy will completely eliminate the possibility of developing this human disease.
Classifications
The disease can begin to develop according to different scenarios, differing in symptoms.
Diffuse spasm of the esophagus makes itself felt by involuntary muscle movements with a frequency of several times from the moment of eating or, regardless of food, several episodes per month.
Segmental spasm spreads to individual areas and manifests itself with increased intensity. Deformation of the esophageal tube occurs. During eating, it happens several times every 30 days.
The neurospastic type of pathology is expressed by spontaneous contractions of a convulsive nature. Caused by excessive emotional outburst, shock, stress, strong feelings. Duration from several minutes to several hours. The degree of expression varies.
The first time an attack occurs, this phenomenon can firmly take hold in a person’s consciousness and in subsequent times manifest itself at the level of a reflex.
Solid spicy food only increases pain and forces the patient to completely refuse to eat. At the same time, the patient may exhibit different types of disease.