What it is
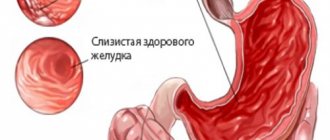
Some growths look like smooth rounded compactions and have a stalk, while others are characterized by a wide base. Hyperplastic polyps of the esophagus, which consist of epithelial cells, occur when its tissue increases. These neoplasms extremely rarely turn into cancerous tumors, but if detected, they must be removed.
Adenomatous polyps that form from glandular epithelium are dangerous for humans, since their growth is dangerous due to degeneration into a malignant neoplasm.
A seal on a long stalk hangs down into the pharynx if it is located in the upper part of the esophagus. Sometimes not one red polyp appears on the mucous membrane, but several.
Esophageal polyp - treatment
If an esophageal polyp is detected, treatment is only surgical
. It must be removed; there is no other way.
Indications for immediate surgery:
• progressive growth;
• bleeding;
• high risk of malignancy.
Removal of a polyp is carried out depending on its location, size and type.
1. A long-pedunculated polyp is removed using an esophagoscope
. Electrocoagulation of the pedicle and vessels is then performed to prevent further bleeding. The entire manipulation lasts several minutes. The wound surface and organ functions are restored within a few days.
2. If a formation on a thick stalk is detected, it is technically impossible to remove it using a fiberscope. In addition, there is a high probability of malignancy in such growths (especially if it is a hyperplastic polyp) during such manipulations. If the esophageal polyp has a wide base, treatment should be surgical.
The operation is performed using an open method
depending on the section of the esophagus where the polyp was detected. Most often, the incision is made on the neck, because typical location is the upper third of the esophagus. The tumor is cut off and the incision site is sutured. The removed tissues are sent for histological examination. If malignancy has not occurred, the specimen shows a picture of a simple polyp with elements of inflammation in the connective tissue and edema.
3. According to statistics, large formations rarely become malignant
. If this happens, the esophagus is removed.
4. If polyposis is detected in the lower part of the esophagus and in the stomach and if it is impossible to remove it using the fiberscopic method, abdominal surgery with an abdominal incision is performed. Such surgical interventions are always done with great attention and caution, since any detected tumor is considered a potential cancer. For this purpose, during therapeutic procedures, attempts are made to avoid contamination of the surrounding tissues of the tissue being removed.
Removing the growth as soon as possible after its detection makes it possible to prevent the need for extensive operations in the future. Relapses after treatment are rare.
Causes
Various factors contribute to the appearance of growths that are attached to the lining of the digestive tract with a base or stalk. Among them, doctors identify chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane.
On this topic
- Digestive system
Differences between sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 9, 2020
Polyps form when the walls of an organ are injured, which happens if a person often consumes spicy and rough foods, sour and carbonated drinks.
They provoke damage to the shell and the appearance of growths on it:
- stress and overexertion;
- unfavorable environment;
- genetic predisposition;
- long-term medication use.
Irregular eating, poor diet, and the presence of reflux often lead to the development of polyposis. The risk of the disease increases in people who abuse alcohol and lead a sedentary lifestyle.
Esophageal polyp - causes
Why an esophageal polyp occurs - the reasons for this are still unknown.
The presence of certain diseases is considered predisposing factors. These include: • chronic esophagitis;
• GERD – gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Play a role:
• condition of the esophageal wall - microtrauma of the mucous membrane after ingestion of rough food, certain medications;
• genetic predisposition;
• excessive alcohol consumption;
• chronic stress;
• bad ecology.
Symptoms
A person usually does not feel the presence of a polyp in the esophagus up to 1 cm. If a small lump, as detected on an x-ray, begins to grow, fall out, rise, fall, become pinched, move into the mouth, or spread to other organs, the first signs appear in the form of:
- difficulty swallowing foods;
- discomfort and pain in the sternum;
- nausea and heartburn;
- the presence of a lump in the throat;
- increased secretion of saliva.
On this topic
- Digestive system
The role of hormonal contraceptives in the development of liver hemangioma
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 6, 2020
When the growth presses on the trachea, it becomes difficult for a person to breathe. Nausea after eating.
The patient loses his appetite and loses weight sharply. Due to constant irritation, erosion or a bleeding ulcer occurs on the polyp. This leads to anemia, which is accompanied by weakness and increased heart rate.
Esophageal polyp - signs and diagnosis
If there is a polyp in the esophagus, there are no signs characteristic of this particular pathology.
Therefore, it is impossible to independently determine the existing growth. It is diagnosed as a finding during examinations of the stomach: • EGDS - esophagogastroduodenoscopy;
• contrast fluoroscopy.
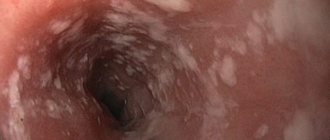
1. When examining the esophagus with an esophagoscope, a round or oval bright red formation is detected. When touched with an instrument, bleeding occurs.
2. When performing contrast fluoroscopy, a polyp less than 1 cm in size appears as a compacted fold of the mucous membrane.
If the dimensions are more than 1 cm, a filling defect of a round shape with clear contours is determined.
The absence of signs in an esophageal polyp that would indicate its existence is explained by its small size. The functions of the esophagus are not impaired, the general condition remains satisfactory. In addition to its small size, it is characterized by slow growth. Therefore, it can exist asymptomatically for a long time. Dysphagia, a problem with swallowing that occurs periodically, should alert you. But when the spasm decreases, the swallowing process is restored, since the polyp cannot completely block the lumen of the esophagus - its size does not allow it.
The polyp is constantly irritated by ingested food and moves under its influence. As a result, the leg of the polyp stretches, and the polyp itself gradually grows. There is further difficulty in swallowing food, slowing down its passage through the esophagus and even delay.
When the formation reaches enormous sizes, with an existing esophageal polyp, the signs of a tumor manifest themselves with a clear clinical picture. A large polyp can fall down, blocking food from entering the stomach, or rise up and enter the oral cavity, causing:
• difficulty swallowing food;
• pain when swallowing;
• nausea and vomiting after eating;
• chest discomfort;
• difficulty breathing associated with compression of the trachea;;
• sudden weight loss.
When a polyp exists for a long time, it is constantly irritated by rough food. Over time, it becomes covered with erosions and can ulcerate. This leads to bleeding. If there is a slight loss of blood every day, which a person may not be aware of, anemia gradually develops. Weakness, shortness of breath, and palpitations occur.
Diagnostic methods
The presence of a polyp in the esophagus is detected using fluoroscopy. If the growth is less than a centimeter, it is just a compaction. When its size is larger than this value, the neoplasm acquires a rounded shape and has boundaries.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy
To determine the condition of the mucosa, another method of instrumental research is carried out. Using an esophagoscope with a video camera at the end, they not only detect polyps in the esophagus, but also remove these growths. Fibrogastroduodenoscopy helps stop bleeding and perform chemical coagulation.
The procedure is prescribed when a person suffers from:
- constant nausea;
- heartburn and belching;
- problems with bowel movements.
On this topic
- Digestive system
What causes thickening of the intestinal wall
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 3, 2020
During the manipulation, the patient is placed on his left side, with his knees bent. After administering anesthesia, the doctor inserts a probe through the mouth, filling it with air, detecting lumps and growths.
If degeneration of the tumor is suspected, a piece of tissue is cut off and sent for histology. Sometimes there is a need for chromoscopy. During this procedure, the lining of the esophagus is stained, which allows for a better view of the polyps.
Methods of surgical treatment
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, treatment requires immediate removal of the tumor. Conservative therapy is not effective, while wait-and-see tactics can lead to tumor degeneration into a malignant formation or damage to the vessels of the esophageal wall and the development of bleeding. A complicated course is considered to be the spread of tumor cells to other parts of the gastrointestinal tract, causing diseases of the stomach or intestines. The growth of the polyp is dangerous due to compression of surrounding organs, including the trachea, which causes respiratory disorders of varying degrees.
Treatment
When the tumor begins to grow rapidly and bleed, surgery is performed. Surgical intervention is necessary when there is a possibility of polyp degeneration.
Small growths are removed using an esophagoscope. A device with a video camera is inserted into the esophagus. An electrical loop is passed through it. The image is sent to the monitor, which allows you to clearly see the excised polyp.
After removing the growth, the doctor cauterizes the small vessels and its base. The wound heals quickly, no blood flows. Five days after coagulation, the esophagus completely copes with its functions.
On this topic
- Digestive system
Irrigoscopy or colonoscopy
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 3, 2020
If a polyp with a diameter of more than a centimeter is detected, an incision is made in the neck, the protrusion is eliminated, tissues located nearby are excised, and the edges of the wound are sutured.
Growths with a long stalk are removed in a few minutes; polyps with a wide base cannot be cut out using an esophagoscope; an open operation is required, which traumatizes the tissue, but reduces the possibility of the spread of abnormal cells.
If a polyposis is detected, when several tumors need to be removed, a strip operation is started, and part of the growth is sent to study the structure.
The pathology cannot be treated with medications and folk remedies. Conservative therapy, herbal decoctions, and sea buckthorn oil are used only in addition to the surgical method.
Sometimes the stalk of the polyp is excised with special scissors and a wire loop. This method is often abandoned because healthy tissues are injured.
Is an esophageal polyp dangerous and how to treat it?
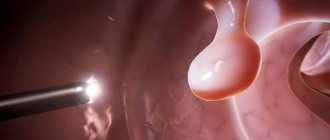
An esophageal polyp is a small, pedunculated neoplasm of a benign nature. Based on epithelial cells.
It is considered a rare but dangerous disease, occurring more often in middle age in the male population.
It is located in any area, but the most common location is the upper region of the esophagus or near the cardia of the stomach.
Description of the disease
The polyp has a thin stalk or a wide base. Narrow, located near the stomach, can lead to pinching. When the formation is located near the larynx, the growth may fall out into the pharyngeal cavity. Then the person suffers from pain, a feeling of “coma” and dysphagia appear.
In appearance, the polyp is red in color and has a smooth or lobed structure. During diagnostic procedures, instruments may cause bleeding. The growth is up to 1 cm in size, small enough that it is detected by chance. With significant diameters, when they grow quickly and aggravate a person’s condition, the only solution is to remove the polyp.
Neoplasms are divided according to their pathogenesis. When they occur due to an increase in the number of healthy cells, this is a hyperplastic type. A large number of pathological tissues indicates a neoplastic growth. Inflammation occurs in places where the integrity of the tissue is damaged.
The process of degeneration into a malignant formation occurs from localization. Often, it is broad-based growths that are susceptible to malignancy, especially if they are large.
Causes
The reasons for the formation of a polyp are not yet fully understood. There are only predisposing culprits for the development of pathology:
- inflammation of a chronic form that occurs in the mucous membrane of the esophagus - esophagitis;
- reflux disease, as a result of which gastric juice enters the esophagus due to cardia insufficiency in the muscle tissue of the gastric sphincter;
- periodic injury to the walls of the esophagus, resulting in microtraumas. This happens with constant intake of rough, mucosal-stimulating foods and certain medications;
- genetic predisposition.
There are also secondary causes of polyps in the esophagus, they are:
- constant stress;
- improper, unbalanced diet;
- alcohol abuse when gastrointestinal diseases appear;
- physical inactivity – changes in the body’s functioning during inactive movements;
- unfavorable ecological environment.
When making a diagnosis, some causes are determined from the patient during the process of collecting anamnesis. This is necessary to eliminate etiological factors and reduce the likelihood of the formation of new growths.
Symptoms
It is worth noting that with polyps in the esophagus, the symptoms will be directly determined by the size of the tumor. But as the tumor grows, the clinical picture will be supplemented with new signs and intensify.
Recommended: How can you test your esophagus to get accurate results?
Growths of significant size may not express themselves for a long time and may appear unexpectedly during the examination of other organs during endoscopy or radiography. In rare cases, a small polyp can have pronounced manifestations.
The main signs of polyps are as follows:
- dysphagia – difficulty passing food and pain when swallowing;
- increased salivation;
- weight loss;
- nausea;
- sensation of a foreign body in the chest area;
- belching of air or particles of undigested food;
- pain and discomfort appear when eating food.
In most cases, the polyp does not completely block the lumen of the esophageal tube, but, having a long stalk, is able to push it into the cavity of the stomach and pharynx. When the formation blocks the lumen of the larynx, asphyxia or sudden death is possible.
Surgery
When choosing a treatment method for polyposis, they are based on the data obtained during the histological examination. The protrusion is eliminated with extreme care to prevent contamination of nearby cells with pathological tissues.
A growth of less than 1 cm is removed with low trauma:
- The generally accepted method of elimination is endoscopic. The procedure involves the following: an esophagoscope is inserted into the esophagus, through which an electrical loop is passed. The device has light and optics, this helps to more clearly recognize the disease and transmit what is received to the screen monitor. Such control allows the doctor to better excise the tumor.
- After surgical treatment, electrocoagulation is performed - the damaged capillaries and leg are cauterized. This manipulation is needed to reduce blood loss and eliminate bleeding that appears in the postoperative period. The wound that appears at that location heals already on the 5th day after the operation. The organ gradually resumes functioning.
Removal of large formations over 1 cm, where the size occupies a third of the esophagus, is done using the open method due to the high likelihood of malignancy. The procedure involves the following:
- An incision is made in the front of the patient’s neck, opening the esophagus;
- the doctor evaluates the features of the polyp;
- excises protrusion and nearby tissues;
- sews up the wound.
Benign tumors of the largest size are effectively removed by esophagotomy or partial/complete resection of the esophagus. This is necessary due to the high risk of malignancy. Malignant formation requires final excision of the growth along with the esophagus. In addition, advance and further chemotherapy, and possibly radiation, will be required.
After any type of removal, a biopsy of the collected tissue is performed.
Traditional treatment
Traditional methods of treatment will be effective when identifying a polyp at the initial stage of development. In other circumstances, alternative therapy is used as an additional or preventive measure, prescribed along with surgical and drug treatment.
The most effective recipes:
- 25 g of celandine are poured into 0.5 liters of boiled water. Use before meals 3 times a day. The same decoction can be used for microenemas;
- you need to squeeze the juice out of burdock, but not the old one. You will need 3 courses of 30 days each with an interval of 1 month;
- You will need 50 g of spruce needles, add 250 ml of boiled liquid to them, then add 10 g of dried hops. Put on fire until it boils, consume 250 ml once for 3 days, take a break for 6 days, and so on 3 times;
- you can take 25 g of sea buckthorn oil on an empty stomach daily;
- Combine 1 kg of melted butter and 1 kg of natural honey and mix well. The composition is stored in the refrigerator, use 25 g on an empty stomach in the morning. Complete therapy when the product runs out.
Before using folk recipes, you should definitely consult with a specialist, especially when it comes to the presence of esophagitis in children; incorrect actions can worsen a person’s situation.
Often, after the operation to excise the growths, the patient returns to normal life, and nothing bothers him. However, an important condition is examination at least once a year to prevent relapse.
Small esophageal polyps are successfully eliminated with the least likelihood of recurrence of the disease. For people who have had larger growths removed, observations are carried out especially carefully and for a long time.
For malignant tumors, the prognosis is less favorable and depends on the stage of the cancer.
The information on our website is provided by qualified doctors and is for informational purposes only. Don't self-medicate! Be sure to consult a specialist!
Rumyantsev V. G. Experience 34 years.
Gastroenterologist, professor, doctor of medical sciences. Prescribes diagnostics and carries out treatment. Expert of the group for the study of inflammatory diseases. Author of more than 300 scientific papers.
Source: https://gastrot.ru/pishhevod/polip
Possible complications
Growths that form on the mucous membrane of internal organs are not as safe as they seem. They are injured when solid foods pass through the esophagus, and the leg grows. It becomes difficult for a person to swallow drinks and eat food.
A polyp, which is located near the larynx, sometimes falls into it, causing pain and a feeling of the presence of a lump.
The growths that form where the esophagus meets the stomach often become pinched, closing the lumen in it. They bleed and increase in size to 10–20 cm in diameter.
Due to compression of the respiratory tract by the polyp that has formed near the larynx, the person begins to experience a lack of oxygen and suffocation develops.
Esophageal polyp: why it occurs and how to get rid of it
It is important to know! An effective remedy for gastritis and stomach ulcers exists! To be cured in 1 week, it’s quite simple... Read more
The appearance of neoplasms in the upper part of the digestive system is an uncommon occurrence, but it may indicate serious abnormalities in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
An esophageal polyp is a fairly rare benign formation consisting of epithelial cells. The polyp is formed as a result of the proliferation of the epithelial layer of the esophageal wall and hangs from it, having a stalk and a wide base.
Polyps in the esophagus can be localized in any part of the esophageal tube and in any part of the gastrointestinal tract. Representatives of the stronger sex, in the age group of 35-70 years, are more susceptible to the disease. The pathology is characterized by an asymptomatic course, which often leads to the growth of the formation and a significant deterioration in the patient’s quality of life.
Types and characteristics of polyps
Esophageal polyp ICD 10: diagnosis code D13.0
This neoplasm of the esophagus is classified in medicine by origin:
- Hyperplastic polyp of the esophagus - is formed due to the proliferation of normal, healthy tissue. This species is practically not prone to degeneration into a malignant formation. Hyperplastic polyps often occur in people who lead an unhealthy lifestyle, neglect proper nutrition, and prefer fast food and smoking.
- A neoplastic polyp of the esophagus (what causes polyps to arise is already clear) develops from pathological cells. This type of esophageal polyp can be either benign or cancerous.
- Inflammatory is localized directly at the site of inflammation, where the integrity of the organ tissues is compromised. There is a high probability of an inflammatory growth occurring against the background of esophagitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the esophageal tube.
Often the esophageal polyp is located near the cardia, in the upper third of the esophagus. Due to this location, the growth can fall into the pharynx. The polyp of the cardia of the esophagus (cardiac region) received its name due to its special location, in close proximity to the heart.
Polyps on the esophagus are not dangerous as long as they are small in size and not numerous in number.
These compacted growths can be multiple and spread to neighboring internal organs; this phenomenon is called polyposis .
The process of polyp spread is considered to be started if the neoplasms begin to systematically increase in size.
Polyps on the esophagus: causes of appearance and development
The causes of this neoplasm are very diverse, but the fundamental prerequisite is the presence of an inflammatory process or any concomitant pathologies of the upper parts of the digestive system. Let's consider a complete list of factors for the development of the disease:
- chronic inflammation of the esophageal mucosa - esophagitis ;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- microtrauma of esophageal tissue due to consumption of rough food, large amounts of spices and seasonings, aggressive chemicals;
- malfunction of the esophageal sphincter, which causes reverse reflux of bile;
- a sedentary lifestyle, leading to a weakening of muscle tone and the appearance of tumors;
- genetic factor;
- regular stress;
- bad environmental situation.
What causes esophageal polyps, the symptoms of which will be studied further? The exact reasons for the formation of growths in the esophageal canal are not fully understood, however, the above predisposing factors have a direct impact on the appearance of tumors in the esophagus.
Polyp in the esophagus: symptoms
However, even minor delays in the treatment of these tumors can lead to cell transformation and the appearance of cancer, so it is important to pay attention in time to even the slightest manifestations of this pathology:
- dysphagia - a violation of the swallowing process, is a primary alarming sign, the polyp reduces the esophageal lumen and prevents the normal passage of food masses;
- feeling of discomfort behind the sternum;
- pain while eating;
- feeling of nausea and frequent gag reflexes;
- spasms of the esophageal walls;
- decreased appetite and, as a result, noticeable weight loss;
- increased irritability of the patient, against the background of the inability to fully eat.
Forecast
After removing a small polyp, the wound quickly heals, the esophagus performs its functions normally, and no serious complications arise for the body.
A person will simply have to be examined regularly to eliminate the risk of a new growth forming. This should be done at least once a year. The medical staff observes the patient for a long period when a large diameter polyp is removed.
If surgery is not done in a timely manner, the lump grows, begins to bleed, and sometimes an oncological process develops. Then it is difficult to cure the disease.
Benign tumors are excised using an esophagoscope or resorting to resection of the esophagus. Cancerous growths are removed along with the organ, after which chemotherapy and radiation are prescribed.
The prognosis for recovery largely depends on the stage of the disease and the spread of the oncological process.
Esophageal polyp - prevention
In terms of treatment, the diet is ineffective.
For esophageal polyps, prevention primarily includes diet. Dietary nutrition is prescribed to prevent the formation of new ones and reduce trauma to existing esophageal polyps, as well as after surgery. Goals pursued when prescribing a diet:
• reduction of esophageal injuries from eating rough dry food;
• rapid epithelization of damage to the epithelium of the esophageal mucosa;
• normalization of the evacuation function of the esophagus;
• prevention of GERD.
To accomplish these tasks it is necessary:
• steaming food and grinding it to a puree consistency;
• frequent divided doses in small portions (at least 5 times a day);
• observing meal times;
• in the absence of contraindications - drink up to 1.5 liters of liquid per day.