Hepatitis C is an infectious disease that occurs as a result of infection with the hepatitis virus and leads to damage to liver cells. In approximately 70-80% of cases, acute hepatitis develops into a chronic form.
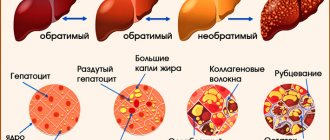
This disease is insidious because of its complications - if treatment is not started in time, liver cirrhosis may develop, and in the most advanced cases, liver cancer. Healthy liver cells are replaced by connective tissue, as a result of which the organ ceases to perform its functions and dies.
A timely course of antiviral therapy leads to recovery in 50-90% of cases and negates the risk of developing liver cirrhosis. Although hepatitis C is a disease with extensive symptoms that requires long-term treatment, it is important to know that it is not a death sentence. You can live with the virus, only complications are extremely dangerous (see how long people live with hepatitis C).
According to WHO, 150-185 million people in the world are infected, 350,000 die annually from complications caused by hepatitis C. In Russia, official statistics are still not kept and experts suggest that about 2.5% of the population are carriers of the virus, which is 5-7 million Russians is an epidemic that has been kept silent for a long time. Those who have the disease are the tip of the iceberg, there are 5-6 times more carriers of the virus who do not suspect that they are infected and are sources of infection, since the virus does not manifest itself in any way. They find out about this by chance before surgery, during pregnancy, etc.
When to start treatment
Hepatitis does not always require immediate treatment, since in 5% of cases complete self-healing of hepatitis C is possible due to the body's powerful immune response. In this case, only specific antibodies remain in the blood. That is, the immune system completely defeats the virus and its reactivation does not occur, even with a significant decrease in immunity in the future.
Therefore, when a virus is detected in the blood, only a specialist can determine whether the patient needs active therapy and what treatment methods should be used. This is very individual and depends on a number of factors:
- Age
- Paula
- Duration of the disease
- Virus genotype
- Process duration
- Genetic predisposition to fibrosis formation (rapid development of liver cirrhosis)
The last point is especially important for the selection and prescription of therapy methods. To determine the tendency to rapid development of cirrhosis, an analysis is carried out for the following immunogenetic markers:
- cytokines
- immunoregulatory proteins
- fibrogenesis factors
Having determined the risk factor for the development of cirrhosis, you can begin prescribing therapy. The higher the risk factor, the sooner treatment should be prescribed. With the advent of methods for determining the risk factor for the development of cirrhosis, diagnosing liver damage has become much easier.
Previously, the tendency to develop liver fibrosis was assessed by the presence in the patient’s family of patients with liver cirrhosis. Treatment of hepatitis is by no means free and requires large financial expenses.
What is hepatitis C
The disease is recognized as viral, the causative agent is HCV.C - the most severe form of hepatitis, which is dangerous due to genetic variability. The high ability to mutate causes the risk of developing new species. Scientists identify 7 main genotypes; each group can contain up to 40 subspecies. Hepatitis acts by entering the liver through the blood. The virus is destructive to the cells of this organ, causing its damage, which leads to cirrhosis or liver cancer. The source of the disease is recognized as active patients, patients with a latent form are carriers of the virus.
The condition for hepatitis C disease is that the pathogen enters the bloodstream through parenteral or instrumental infection. This can happen in the following cases:
- when sharing manicure and shaving accessories;
- when applying a tattoo or piercing with instruments contaminated with the patient’s blood;
- when using one injection syringe;
- during transfusion;
- during a procedure on a hemodialysis machine;
- sexually (the probability of unprotected contact is 3-5%);
- from mother to child (about 5% of cases, often during childbirth).
At the initial stage, hepatitis is difficult to detect, because symptoms can also be attributed to other diseases. Once the virus enters the body, it first goes through an incubation period. Further up to the acute stage, its symptoms are similar to the flu state:
- activity decreases;
- appetite decreases;
- headache;
- nausea, weakness;
- fast fatiguability.
The difficult process of the disease progresses with further complications. The disease can be detected at a late stage by more serious symptoms:
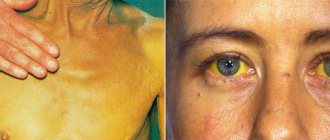
- yellowness of the skin;
- hair loss;
- anemia, urine darkens and feces become discolored;
- nausea, vomiting;
- painful sensations appear in the right hypochondrium;
- depression may develop;
- Clinical blood tests show an increase in the amount of bilirubin; liver function tests provide specific markers.
Cost of hepatitis C treatment in Russia
Treatment of this insidious virus is currently very expensive. It requires from 50 thousand to 700 thousand rubles, depending on the type of virus, the treatment period is from 3 months to a year. Genotype 1b is especially difficult to treat and relapses occur in half of the cases. Treatment with more effective new drugs is even more expensive - 40-100 thousand dollars for a course of therapy.
For example, a weekly ampoule of 1 drug alone for genotype 1 costs 7-10 thousand rubles. plus 3-4 thousand per month for tablet forms of drugs. In total, a patient needs 500-700 thousand rubles for a course of treatment, taking into account paid analyses, studies and tests (see the cost of hepatitis C treatment in Russia is equal to the price of a foreign car or an inexpensive apartment in a small city).
In many regions of the country in 2007–2009, a federal state system operated. the free treatment program for chronic hepatitis C, in order to take advantage of it, one had to go through a lot of bureaucratic procedures, so only 5-10% of the country's needy citizens could be treated for free. But since 2010, funding has ceased and now this program continues to operate only for the treatment of patients with hepatitis C in combination with HIV infection. Patients have dark humor about this: “to get free treatment for hepatitis, you need to catch HIV somewhere.”
The situation today is not the best with the introduction of modern diagnostics, for example, the latest liver fibroscanning study (Elastometry) is close in effectiveness to a liver biopsy, and most importantly, it is completely painless for the patient. However, even in Moscow there are only 7-8 such non-invasive devices (fibroscans). This is in the capital, but what about the regions? It’s good if there is at least one in the regional center. And it’s not even about the cost of the device - a fibroscan is cheaper than a good ultrasound machine (for comparison, a good ultrasound machine costs about 200 thousand euros, a fibroscan 130 thousand euros).
What does the cost of treatment depend on?
All patients, without exception, are concerned about the question: how much does treatment for hepatitis C cost?
The cost of therapy varies depending on many factors. The first cost is a thorough diagnosis, which provides comprehensive information (how much the organ is affected). Based on the results of tests and hardware diagnostics, the hepatologist selects medications and develops a dosage regimen - dosage and course duration. The general health of the patient, the state of his immune system, the presence or absence of concomitant diseases, and physical characteristics (gender, weight, age) are also important.
The first genotype of the virus is the most resistant to drug therapy, so it is more expensive to cure than the others.
The main cost item is the cost of the drugs themselves. In addition, it is important how the body responds to therapy; it may be necessary to create other schemes, and this will involve additional costs.
Prices for medicines are quite high. However, there is the option of choosing domestically produced analogue drugs or generics, which, with a properly developed treatment regimen, are no less effective, but are several times cheaper.
Hepatitis C treatment protocol according to the European Association for the Study of the Liver
In the treatment of chronic hepatitis C there is no single standard of treatment; each case is purely individual. Treatment is prescribed after a thorough analysis of the following factors:
- Degree of liver damage
- Presence of concomitant diseases
- Potential risks of adverse events
- Probability of success
- Patient's readiness to begin therapy
The most effective treatment for viral hepatitis C today includes complex antiviral therapy with ribavirin and interferon. These drugs are general genotypic, that is, they are effective against all genotypes of the virus.
The difficulty with treatment is that some patients do not tolerate interferon well, and the drug is not widely available. The cost of treatment for hepatitis C is not affordable for everyone, so many patients simply do not complete treatment and the virus develops resistance to the drugs they are taking. If the patient subsequently starts a new course of therapy with resistance to antiviral drugs, there will be no effect from the treatment.
People are more likely to show positive signs of response to hepatitis C combination therapy:
- European race
- Female
- Weight less than 75 kg
- Age under 40
- Low insulin resistance
- No signs of severe liver cirrhosis
Most doctors use a combined treatment regimen for hepatitis, the so-called dual therapy - a combination of interferon, which actively fights the virus, and ribavirin, which enhances the effect of interferon.
The patient is administered short-acting interferon daily or once every three days, and long-acting interferon (pegylated interferon) in combination with ribavirin (used daily in tablet form) once a week. Depending on the type of virus, the course is 24 or 48 weeks. Genotypes 2 and 3 respond best to therapy - treatment success is 80-90%.
For genotype 1, combination therapy is successful in 50% of cases. If the patient has contraindications to combination therapy, interferon-alpha monotherapy is prescribed. In this case, the course of therapy lasts 12-18 months. Long-term monotherapy with interferon-alpha reduces the viral load in 30-50% of cases.
Drug therapy
Until about 20 years ago, hepatitis C was an incurable disease, but today there are a large number of reliable medications. At the same time, new drugs for hepatitis appear literally every year, so treatment regimens are constantly changing.
At first, such drugs were very expensive, but today on the market you can find a large number of generics that almost completely copy foreign drugs, but are much cheaper than the originals.
Typically, treatment therapy lasts about 12-24 weeks. The main medications for treatment are Interferon-alpha, Ribavirin, Pegasys, Daclatasvir, etc. Often these drugs are prescribed in combination, since there are several types of hepatitis C virus, and a particular drug is effective only against a specific subtype of the virus.
These drugs are available in the form of tablets and injection solutions. They are quite expensive, but in other countries their cost is much higher.
These pills must be taken in strict accordance with the treatment plan developed by the doctor. Almost all medications have a lot of side effects:
- From the respiratory system – cough and deterioration of breathing;
- From the nervous system - depressive disorder, sleep disturbance, weakness, problems concentrating, headaches, increased fatigue, etc.;
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract - vomiting, nausea, problems with bowel movements, abdominal cramps and loss of appetite;
- Allergic reactions - redness of the skin, itching, small rashes on the skin and hair loss.
There is no need to be afraid of side effects, since upon completion of treatment they go away without any dangerous consequences for the body.
The doctor, at his discretion, may prescribe additional medications for symptomatic treatment. For example, in the case of a skin rash, antiallergic drugs may be prescribed that effectively fight the rash. If side effects occur, you can stop treatment only after consulting your doctor.
In what cases is combination therapy with interferon and ribavirin contraindicated?
There are categories of people for whom combined treatment of hepatitis C is contraindicated:
- children under 3 years of age
- pregnant women
- people with organ transplants
- people with individual intolerance to ribavirin and interferon
- patients with an overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism)
- patients with heart failure, decompensated diabetes mellitus, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, coronary heart disease and heart failure
Drugs with proven effectiveness
Let's take a closer look at medications whose effectiveness in treating hepatitis C leaves no doubt.
- Essentiale forte N. Allows you to restore the integrity of the walls of liver cells, hepatocytes, by incorporating essential phospholipids contained in the preparation. Positive dynamics are achieved due to the similarity of the composition of the active substances with the lipids of cell membranes. Thus, the medicine prevents liver intoxication. Contraindicated for children.
- Hepatosan. A drug of animal origin binds toxins that damage the liver, removing them out. Promotes the restoration of liver cells, activating metabolic processes. It is permissible to take as prescribed by a medical professional when carrying a child or breastfeeding.
- Phospholip. The medicine stabilizes the functioning of the liver, restoring cell membranes. Removes harmful substances that poison the body. Children under fifteen years of age are prohibited from using the drug.
- Heptral. Taking the tablets ensures the restoration of hepatocytes and normalizes bile outflow. Patients taking the drug note a decrease in pathological symptoms - pain, itching, yellowness of the skin.
- Hepa-merz. The medicine helps remove a toxic substance - ammonia. Usually used as a prophylactic agent. The effectiveness of the drug is high, as is the cost. Incompatibility with the following medications has been proven: Diazepam, Meprobamate, Vincamine.
- Galstena. Homeopathic medicine. Usually prescribed as part of complex therapy. The product protects the liver by restoring hepatocytes. The medicine is used to treat all liver and bile diseases.
Above is an overview of the most common remedies, the effectiveness of which has been proven. However, even their use is possible only if prescribed by a doctor.
Side effects of combination therapy
To date, combination therapy with interferon and ribavirin is the most successful in the treatment of hepatitis C genotypes 2 and 3. However, these drugs have a number of side effects that you need to be aware of:
- Anemia
The use of ribavirin can lead to anemia, a decrease in the number of red blood cells. The level of drop in hemoglobin is directly related to the dose of ribavirin. In clinical studies, hemoglobin levels decreased significantly in 15-22% of patients. Why this happens is still unknown. Reducing the dose of ribavirin has a negative effect on treatment, so patients with anemia are prescribed iron supplements.
- Thyroid dysfunction
Pegylated interferon leads to dysfunction of the thyroid gland. It can cause both increased and decreased activity of the thyroid gland. During treatment and the next six months, it is necessary to monitor the functioning of the thyroid gland, since antiviral therapy can lead to irreversible impairment of its functions.
- Hair loss
Antiviral therapy may lead to moderate hair loss. This is very noticeable when washing or combing your hair. Hair loss is a temporary symptom; after completion of therapy, hair growth resumes (see causes of hair loss in women).
- Flu-like symptoms
At the beginning of therapy, flu-like symptoms may appear. The patient begins to experience headache, chills, fever, weakness, and muscle pain. Typically, such symptoms appear 2-24 hours after the interferon injection. By the middle of the course of treatment, the intensity of side effects usually decreases. The severity of side effects can be reduced by injecting interferon at night. Double therapy leads to dehydration, so it is recommended to drink more water, eat a balanced diet and do light exercise.
- Insomnia
Many patients undergoing combination therapy complain of insomnia (see how to fall asleep quickly). You should immediately inform your doctor about this, since insomnia significantly worsens the quality of life and leads to irritability, increased anxiety and depression. It is recommended to strictly observe a sleep schedule (go to bed and wake up at the same time), resort to moderate physical activity, eat right, take herbal sedatives (valerian, motherwort, lemon balm, mint). If the above remedies are ineffective, the doctor prescribes sleeping pills.
- Depressive state
Most often, patients refuse therapy due to the appearance of neuropsychiatric symptoms, in particular depression. It occurs at any time, in almost every 3 cases, usually its symptoms appear in the first month of therapy - depressed mood, apathy, insomnia, loss of appetite, irritability, decreased libido, thoughts of suicide, feelings of hopelessness and hopelessness.
A person stops enjoying things that previously brought joy. Depression is treated with a combination of drug therapy (antidepressants) and non-drug therapy (psychotherapy). The main medications prescribed by a doctor for depression in hepatitis C are fluoxitin (Prozac), paroxitin (Paxil), sertraline (Zoloft), citalopram (Celexa) - serotonin reuptake inhibitors.
- Increased irritability
Pegylated interferon (Pegintron) injections may cause irritation. To reduce discomfort, apply ice to the skin and treat it with alcohol before the injection. Interferon for injection should be at room temperature.
- Labored breathing
Interferon and ribavirin therapy may cause problems with your lungs (such as difficulty breathing). If a cough occurs, a thorough examination should be performed to exclude pneumonia and fibrosis. Difficulty breathing may result from anemia caused by ribavirin.
- Vision problems
Some patients may develop rhinopathy. However, this requires risk factors such as hypertension or diabetes.
Free drugs in Russia
Treatment for hepatitis C is expensive and not available to every Russian. The state provides free relief from the disease as part of the state program. First, you will need to obtain a referral to a regional hepatology center that provides similar services. To do this, the patient needs to perform the following steps:
- visit a therapist;
- pass the prescribed tests;
- wait for confirmation of hepatitis.
Completing the above actions does not guarantee receiving a referral and taking a free course of medication. Priority is given to:
- seriously ill patients;
- people suffering from drug addiction, alcohol addiction;
- AIDS patients.
For a free course of therapy, the drugs Interferon and Ribavirin are mainly used. In exceptional cases, interferon-free treatment is prescribed.
The role of hepatoprotectors in the treatment of hepatitis C
Regardless of the chosen method of therapy, the treatment regimen for hepatitis C includes hepatoprotectors - drugs of natural or synthetic origin that increase the liver’s resistance to pathogenic factors, restore its structure and have a positive effect on its functions.
They do not have an antiviral effect, but are indispensable in supporting liver cells, accelerating their regeneration. Hepatoprotectors are made on the basis of silymarin, immortelle, solyanka kholmovoy, artichoke or cattle liver extract (Legalon, Karsil, Hofitol, Progepar, Hepatosan, etc. see the list of all hepatoprotectors with an assessment of their effectiveness).
The action of hepatoprotectors is aimed at:
- restoration of homeostasis in the liver
- stimulation of liver cell restoration processes
- normalization of liver activity
- increasing liver resistance to adverse factors
Hepatoprotectors
As an adjuvant treatment, your doctor may prescribe hepatoprotectors for hepatitis C. These medications do not destroy harmful viruses, but they can protect liver cells from further damage. Substances of both natural and synthetic origin are used as hepatoprotectors.
Using a combination of hepatoprotectors with hepatitis pills, it is possible to restore damaged liver cells and destroy all copies of the harmful virus.
The main hepatoprotectors for hepatitis C are Heptor, Hepa-Merz, Karsil, Legalon, milk thistle extract, Rezalut, Hepatamine and others. Tablets should only be prescribed by your doctor. In some situations, the use of hepatroprotectors is useless: for example, the hepatitis virus is seriously weakened and cannot damage liver cells. Sometimes such treatment is contraindicated due to the risk of side effects.
A new stage in the treatment of patients infected with genotype 1 of the virus
Over the past ten years, the “gold standard” in the treatment of hepatitis C has been the use of double combination therapy, the effectiveness of which:
- in general, this method of therapy is 60-70% effective
- in relation to the 2nd and 3rd genotypes - by 90%
- in relation to the 1st - only 40-50%.
With the advent of new generation antiviral drugs - Boceprevir and Telaprevir, treatment has become more successful - 70-80% of cases. Treatment of hepatitis C with a new method has been available in Russia since 2013. Thanks to the use of new drugs, specific enzymes of the virus are blocked, preventing it from multiplying.
Patients need to know that Telaprevir and Boceprevir:
- Used to treat patients only with the first genotype of the virus
- The drugs are prescribed only in combination with ribavirin and peginterferon as part of triple therapy
- Taken orally, Boceprevir from the second month of therapy, Telaprevir - from the 12th week. The duration of therapy is individual in each case
- 60% effective in the stage of compensated liver cirrhosis
Contraindications and disadvantages of triple therapy:
- High price
- Increased number of side effects - skin reactions, anemia, taste disturbances
- Therapy is not possible if there are contraindications to ribavirin or interferon
Approximate cost of treatment
There can be no talk of specific figures for the cost of treating the disease, since they cannot be applied to absolutely every patient.
Based on pharmacy prices of drugs, we will consider the approximate amounts that a patient will have to pay for hepatitis C treatment in Russia.
The cheapest option for combination antiviral therapy is the traditional regimen, using conventional interferon (Reaferon) and ribavirin. The course of therapy ranges from 24-48 weeks (can increase to 72 weeks).
So, to treat genotypes 2.3 on average you will need:
- 18 packages - 84 injections of Reaferon (injections every other day) with a dosage of 3 million, 1,200 rubles each = 21,600 rubles;
- 14 packs of Ribavirin (tablets/capsules every day) with a dosage of 200 mg for 300 rubles = 4200 rubles.
The minimum cost for a course of treatment was 25,800 rubles. Control tests will help check the effectiveness. The total amount will be about 30,000 rubles.
Genotype 1 requires more intense therapy, and material costs increase accordingly. In addition, the drugs are used in higher dosages and the course of treatment is longer:
- 36 packages of Reaferon with a dosage of 5 million, 1500 each = 54,000 rubles;
- 34 packs of Ribavirin = 10,200 rubles
Total, 64,200 is the minimum cost of treatment for hepatitis C genotype 1.
Often therapy is intensified for the first 12 weeks by administering interferon injections every day. So, plus 8 packs * 1500 = 12,000 rubles.
Another plus will be payment for control examinations. The total will be more than 80,000 rubles.
Treatment with pegylated interferons
For more effective and gentle therapy, pegylated interferons are used.
There are 3 pegintreferon drugs registered in the Russian Federation:
- Pegasys (peginterferon alfa 2a) produced in France;
- PegIntron (peginterferon alfa 2b) – Merck, Germany;
- Algeron is a complete analogue of PeGintron, Biocad, Russian Federation.
The prices for these medications for hepatitis C are not low, but they also need to be administered into the body according to a different scheme than regular interferon (on average three times less).
Pegasis and Algeron cost about 5,000 rubles per injection. An average course of therapy for genotype 2.3 requires a minimum of 140,000 rubles - this is only for peligated interferon. And for therapy of genotype 1 – 280,000 rubles.
Pegintron costs 7,000 rubles for 1 injection. The minimum course of treatment for genotype 2.3 will be 196,000 rubles, for genotype 1 – 392,000 rubles.
Clinical studies have shown that peginterferon alfa 2a, 2b are almost identical in effectiveness.
Triple therapy
The most problematic groups of patients are patients with hepatitis C genotype 1, liver cirrhosis, as well as those who have not responded to therapy or have had a relapse of the disease after successful therapy.
In this case, a third component is added to the combination of interferon (peginterferon) and ribavirin - a viral protease inhibitor.
First generation protease inhibitor drugs, which are registered in Russia, have been used since 2013:
- Insivo (Telaprevir) - Vertex, USA;
- Victrelis (Boceprevir) - Schering Plow, Singapore.
The course of treatment is 24-72 weeks.
The cost of Insivo tablets with a dosage of 375 mg is 60,000 rubles for 42 pieces. A monthly course costs approximately 830,000 rubles.
Victrelis capsules with a dosage of 200 mg - 50,000 rubles for 336 pieces. Monthly course – 220,000 rubles.
Despite the effectiveness of the regimen, all the disadvantages of chemotherapy remain, to which serious side effects have been added. Tolerability was recorded even more difficult than with traditional antiviral therapy. Currently, hepatitis C is rarely treated using this regimen.
Interferon-free therapy
An innovative direction of antiviral therapy is the treatment of the disease without the use of interferon, and sometimes even without ribavirin.
Registered direct acting drugs in Russia:
- Simeprevir "Janssen-Cilag" INTERNATIONAL N.V., Belgium - a second-generation hepatitis C virus protease inhibitor. Prescribed 1 tablet per day (150 mg). The approximate cost of the course is 2,500,000 rubles.
- Daklinza (Daklatasvir) Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, USA. Take 1 tablet per day with a dosage of 60 mg. The minimum cost of treatment is 600,000 rubles.
- Sunvepra (Asunaprevir) Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, USA. The cost of the course is 60,000 rubles.
- Vikeira Pak (ritonavir-boosted paritaprevir, ombitasvir, dasabuvir) “Abbwy Ireland” NL. B.V., Ireland. The cost of the course is 800,000 rubles.
- Sovaldi (sofosbuvir) Gilead Sciences, Ireland. The cost of a 12-week course is 800,000 rubles.
All approximate amounts are calculated for a minimum course of treatment (12 weeks), excluding the cost of peginterferon and ribavirin. Each of the drugs can be combined with other antiviral agents. The most effective combination is selected by the attending physician.
The cost of therapy with these drugs is not affordable for many patients with hepatitis C. However, there are generic drugs made in India and Egypt, which are more affordable and no less effective. They are not commercially available; you will have to order them from manufacturing countries via the Internet.
It is possible to cure hepatitis C; the main thing is to start antiviral therapy in a timely manner. This process is lengthy, labor-intensive, and requires significant financial costs. The cost of therapy depends on many factors and ranges from 30,000 rubles per course to several million. In Russia, there is a state program for the treatment of hepatitis C, under which theoretically it is possible to undergo therapy for free. However, patients mostly have to rely on their own financial resources.
Features of treatment of hepatitis C in children
Hepatitis C in children occurs with a higher percentage of complications - international studies have revealed that more than half of children with chronic hepatitis C show signs of liver fibrosis.
Therefore, the sooner you start therapy, the less likely it is to develop liver cirrhosis. For the treatment of children, pediatricians recommend the use of interferon monotherapy. Combination therapy is carried out only in case of low interferon effectiveness. The earlier the disease is detected and treated, the lower the risk of complications.
Absolute contraindications to inferon therapy in children:
| Relative contraindications to infernotherapy in children:
|
What treatment do doctors prescribe for hepatitis C?
Only a qualified doctor has information about how to treat and cure hepatitis C. Doctors can prescribe different treatment regimens for chronic hepatitis C, depending on the degree of development of the disease and the financial capabilities of the patient. Treatment of the disease is always carried out on an outpatient basis. The exception is the severe form of acute hepatitis C. The basis of therapy is antiviral medications.
Diet
Treatment of a disease with medications will be meaningless without measures to change the patient’s lifestyle. In addition to medications, diet is an important component of hepatitis C treatment. The goals of the diet are to exclude from the diet foods that cause the liver to work overload, as well as to get rid of the negative symptoms that accompany gastrointestinal disorders. A diet for chronic hepatitis involves avoiding hot, spicy, fatty, fried, pickled, salty foods and canned food.
Alcohol, coffee, cocoa, and sweet carbonated drinks are contraindicated. Meals should be fractional, the number of meals per day should be 5-6 times. Preference is given to boiled or steamed dishes.
It is necessary to consume water in significant quantities - at least 2-3 liters per day. Water, on the one hand, helps remove toxins from the body, and on the other hand, it allows you to restore the volume of fluid that the patient loses due to vomiting and diarrhea.
- lean meats,
- low-fat soups,
- boiled vegetables,
- porridge with milk,
- vegetable and fruit juices (primarily those containing large quantities of beta-carotene, for example, carrot, pumpkin).
It will also be useful to consume butter and vegetable oils and eggs in reasonable quantities.
Healing procedures
Therapeutic exercises can also be one of the ways to treat hepatitis. Physical exercise prevents blood stagnation and promotes the removal of toxins from the body, which facilitates the functioning of the liver and improves the overall tone of the body. Water procedures - baths, contrast showers - have similar effects.
Extracorporeal hemocorrection
The extracorporeal hemocorrection procedure allows you to reduce the viral load on the body and increase the effectiveness of antiviral therapy. This is a type of plasmapheresis - purification of part of the blood through a special filtering device that removes pathogenic elements.
Hemocorrection cleanses the blood of harmful elements and reduces the level of viral load hundreds of times, which doubles the effect of drug therapy. It is aimed at eliminating extrahepatic signs of hepatitis, such as itching, joint and muscle pain, and kidney failure. The procedure improves laboratory blood parameters and reduces the severity of side effects from antiviral therapy. Hemocorrection is indicated for patients:
- with active inflammatory process in the liver
- with an enlarged liver
- with an enlarged spleen
- with fever
- with low effect of antiviral therapy
- with extrahepatic symptoms of hepatitis
Extracorporeal hemocorrection is only part of the complex therapy for hepatitis C. But this procedure has a beneficial effect on the treatment process, increasing the effectiveness of antiviral therapy and neutralizing their toxic effect on the body.
Treatment rules
There are a number of rules that must be followed for successful treatment of the disease.
- Eliminate alcohol from your life three months before therapy, during treatment and after it.
- Ignore stress and nervous tension.
- For patients with a history of cirrhosis, physical activity is prohibited.
- You should stop taking any other medications for the period of therapy. If hepatitis C is present in the body chronically, then it is necessary to consult with a specialist about the method of treating a parallel disease.
- Dieting. Along with drug treatment, it is recommended to adhere to proper nutrition. Spicy, fried, fatty and smoked foods are excluded to avoid stress on the liver. It is necessary to include fruits, vegetables, lean meats, grains and fish in your diet. It is advisable to steam food and eat it in small portions in 6 meals.
- Avoid active exposure to the sun. Limit your trips to the solarium and sauna.
- Monitor the condition of the body by regularly taking tests once a month.
In addition to acute and chronic forms of the disease, there is an inactive phase of hepatitis C. Even if an inactive form of the disease without changes in the liver was detected in the body, treatment must be completed. Dormant hepatitis requires the same treatment and use of the same medications as acute hepatitis. Treatment regimens change over time. Until recently, it was based on the use of Interferon and Ribavirin. Nowadays, there has been a breakthrough in the field of medicine. Indian pharmacists offer replacements for drugs with an extensive side list with generics.
Balanced diet and healthy lifestyle
A healthy lifestyle, giving up bad habits and a special diet are not a panacea for all diseases. But by adhering to them, you can significantly increase the effectiveness of therapy, reduce the load on the liver and minimize the risk of developing cirrhosis.
There is no special diet for patients with hepatitis C. Patients are advised to adhere to diet No. 5, recommended for pathologies of the biliary tract and liver (see what you can eat with cholecystitis). Following the principles of a healthy diet will normalize impaired liver function. Basic nutritional principles recommended by many European medical authorities. centers that should be followed after treatment:
- Drink enough fluid (6 to 8 glasses per day)
- Avoid alcohol completely
- Try to make your diet varied
- Avoid fasting
- Eat small meals 5-6 times a day
- Limit your intake of foods high in sugar
- Eat fresh vegetables and fruits
- Avoid trans fats (canned foods, sweet baked goods, fast foods)
- Avoid saturated fats (ice cream, red meat, whole milk, fried foods)
- Enrich your diet with fiber
- Add vegetable fats (nuts, seeds, legumes) to your daily menu.
- Eliminate sorrel, fatty fish and meats, cocoa, chocolate, pastry, smoked meats, meat broths and decoctions, and spices from your diet.
Moderate physical activity is very important. Physical exercise will help overcome chronic fatigue, insomnia and depression. Before starting exercises, consult your doctor, he will help you choose the right set of exercises and the right load. Start with simple steps - walks in the fresh air, give up the elevator, walk a few stops to work. Optimal types of loads:
- Walking, swimming
- Dancing, Bodyflex (for women)
- Pilates, Yoga
Features of treatment for pregnant women
The acute form of the disease can be dangerous both for the fetus and for the woman herself. The use of medications can harm the development of the baby in the womb, so it is important to be treated under medical supervision. During pregnancy, the use of plant-based hepatoprotectors (Essentiale, Hofitol, Karsil) in combination with a special gentle diet is indicated. Ursodeoxycholic acid can be used in the second and third trimester of pregnancy, but if indicated, it can also be used in the first.
A pregnant woman should eat 4-5 times a day, dividing food into equal portions. It is worth consuming natural products; dyes and preservatives will increase the load on the liver damaged by the virus. The diet involves excluding the following foods from the diet:
- carbonated waters and sweet drinks;
- cocoa and chocolate;
- fatty dairy products, meat, fish;
- smoked and fried foods;
- mushrooms;
- fresh bread, muffins, cookies.
Ursodeoxycholic acid in the treatment of hepatitis C
Ursodeoxycholic acid was isolated from the bile of the Chinese brown bear in 1902. The structure of the acid is identical to endogenous tertiary bile acid, which is synthesized in the human liver from chenodeoxycholic acid. Unlike other acids, it is non-toxic and more hydrophilic.
The use of acid affects the composition of bile acids - ursodeoxycholic acid becomes the main component of bile. Clinical studies have established that a drug based on ursodeoxycholic acid reduces bilirubin levels, reduces transaminase activity and reduces the frequency of relapses. By including ursodeoxycholic acid in the course of therapy, you can reduce weakness, irritability, and fatigue. The drug completely eliminates skin itching.
These drugs include: Ursofalk, Ursosan, Urosliv, Ursodez, Urdoxa, Livodex.
The role of hepatoprotectors
Hepatoprotectors are mandatory in the treatment regimen, along with antiviral treatment of hepatitis
Hepatoprotectors are mandatory in the treatment regimen, along with antiviral treatment of hepatitis. Especially in the case of a chronic diagnosis. They allow the patient to return to an active life. The disease is deadly. It can be acquired through blood. Millions of people in all parts of the globe are diagnosed with this disease, hundreds of thousands of whom die every year. Only with proper treatment do patients have a chance to live. The most important thing is to start treatment at the initial stage of the disease, immediately after infection.
Patients suffering from Hepatitis C, in fear for their lives, are trying to find effective drugs against the disease. Experienced specialists can help defeat a dangerous virus. After a thorough analysis of the severity of the disease based on all the research results, they prescribe the correct treatment that gives life to the patient.
Hepatoprotectors play an important role in treatment. Pharmacists offer this group of drugs in large quantities. They are aimed at protecting and regenerating the cellular structure of the liver, which bears the brunt of the disease. Treating the virus with these medications is a vital necessity. The drugs differ in price, effectiveness and safety for the body.
New treatments
Sofosbuvir and daclatasfavir
New drugs for the treatment of hepatitis C - sofosbuvir and daclatasfavir - have successfully passed clinical trials in the United States. The drugs turned out to be effective even in cases where triple therapy failed.
Sofosbuvir and daclatasfavir are equally effective for the 1st, 2nd and 3rd genotypes of the virus - clinical trials in which 211 people took part showed that the drugs were successful in 98% of cases. Sofosbuvir and daclatasfavir, unlike ribavirin and interferon, do not cause as many side effects. During trials, side effects such as nausea, headaches and fatigue were found.
Sofosbuvir is approved by WHO, and daclatasfavir is still in clinical trials. According to study leader Mark Sulkowski, daclatasvavir will also soon be approved, marking a new era in hepatitis treatment. Of course, this hepatitis C treatment program is not free, but requires significant financial costs.
Ledispavir and sobosfuvir
In April 2013, the third phase of trials of sobosfuvir and ledispavir came to an end. In 97% of patients, after 12 weeks of therapy, the virus was not detected in the blood. Treatment drugs have shown effectiveness against all genotypes of the virus. There were no serious side effects found in half of the patients.
In the group of patients taking ribavirin with ledispavir and sobosfuvir, the cure rate was 100%, but the side effects were much worse. The purpose of further trials will be to study the optimal duration of therapy and the advisability of using ribavirin. Ledispavir is currently undergoing clinical trials. It will probably be approved soon.
Author:
Selezneva Valentina Anatolyevna physician-therapist
New drugs for hepatitis C
Progress in the search for cures for hepatitis C does not stand still. New drugs make it possible to act directly on the virus, preventing its replication. For this ability they are called direct antiviral drugs (DAAs). DAAs have a number of advantages over standard combination therapy:
- They can reduce the duration of antiviral therapy to 12-24 weeks;
- DAAs have fewer side effects and contraindications;
- Increase SVR
The first antiviral drugs to undergo clinical trials and become actively used in treatment were the HCV protease inhibitors, boceprevir and telaprevir. The list of such drugs is constantly expanding, miravirsen and sofosbuvir, etc. have been added to it.
Recovery and vitamin complexes
During the acute course of the disease, the body experiences a lack of vitamin B12. An insufficient amount of this microelement leads to long rehabilitation. Filling the gaps of the necessary component occurs with the help of medications. But only a doctor can prescribe the choice of drug, its dose and course of administration. Take advantage of consultation to avoid unwanted consequences.
Increasing the amount of beef or pork liver in the diet replenishes the daily dose of vitamin B12.
To maintain good health and help the immune system while the body is recovering, it is necessary to use vitamin complexes . They play an important biological role. To get the best results from treating viral hepatitis, doctors often prescribe the following medications:
- Alphabet. These multivitamins help restore damaged cellular structure of the liver.
- Leviron Duo. It eliminates the feeling of discomfort and pain under the right rib. Increases appetite, eliminates drowsiness and lethargy.
- Hepatrin detox. Necessary for cleansing the liver of toxins that destroy the organ.
- Omega-3. Created to support liver function.
Vitamins, of course, do not cure hepatitis; this also requires additional medications. But for successful recovery they are indispensable. Before using any vitamin complex, you should consult a specialist. Based on the characteristics of the body and the course of the disease, he will choose the best option.