Giardiasis is one of the most common forms of parasite infestation. Giardia is a simple microorganism that affects the intestines and parasitizes in the human body for a long time, which negatively affects overall health.
In the first stages, infection is discovered by chance, since it is not accompanied by severe symptoms. A blood test for Giardia is the most reliable way to find out about the invasion.
What to do in such a situation? To get started, we recommend reading this article. This article describes in detail methods of controlling parasites. We also recommend that you consult a specialist. Read the article >>>
Giardia
Blood test for lamblia in children and adults
When the first signs of infection appear, you should consult a doctor. During the examination, he evaluates the clinical picture and chooses the optimal method for diagnosing the disease.
Indications for a blood test are:
- attacks of nausea, vomiting;
- long-term bowel dysfunction;
- flatulence, pain, bloating;
- general fatigue;
- unstable psycho-emotional state;
- development of allergic reactions in the form of a rash;
- change in the structure of feces.
The first signs of invasion may appear only a month after infection. Carrying out an analysis during this period can already indicate damage to the body by the parasite. However, due to the absence of symptoms, a person does not go to a medical facility, which significantly complicates the diagnostic process.
Quite often, the symptoms of invasion are confused with other diseases, and a person begins to self-medicate, which not only aggravates the problem, but also complicates further therapy and the recovery process.
Giardia cysts: what they look like, treatment and tests, what to do if there are Giardia cysts in the stool
- What are Giardia cysts and what do they look like?
- How cysts enter the body
- Analysis for Giardia cysts in stool and blood
- Giardia cysts in an adult
- Giardia cysts in children
- It is possible to defeat parasites!
Giardiasis is a fairly common disease that occurs in every 4 patients with infestation. The main cause of infection is non-compliance with hygiene rules. It is provoked by Giardia, cysts that enter the body and settle in the intestines.
Have you been trying to get rid of PARASITES for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to get rid of parasites by taking every day...
Read more "
The initial stage of infection does not have pronounced symptoms; you can find out about the invasion by chance during a routine examination or at the chronic stage.
What are Giardia cysts and what do they look like?
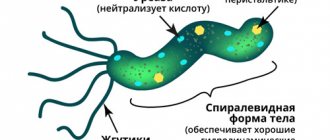
Giardia cysts are eggs from which a parasite is formed during further development. They are distinguished by their oval, pear-shaped shape. At the active stage of development, 4 nuclei are visible in them, flagella are absent, so they are motionless.
After penetration into the body, they move into the digestive system, and the mobile phase of development - the trophozoite - begins. Cysts acquire 8 flagella, which allow them to attach to the intestinal walls and multiply in it.
The parasite can reproduce only in the small intestine. If they enter the large intestine, development takes on a passive form - the local environment negatively affects the vital processes of Giardia. Adult active individuals acquire a protective shell and turn into cysts that can be found in feces.
Such a person does not develop infection, but he is a carrier of the parasite.
How cysts enter the body
Giardiasis is more common in children than in adults. Giardia habitat:
- animal body;
- water pipes;
- public places;
- dirty food.
Invasion occurs through contact with animals, visiting public bodies of water, and failure to comply with personal hygiene rules. Chlorination of water has a detrimental effect on the parasite and reduces the risk of infection.
After entering the body, Giardia affects the intestines, causing many negative consequences.
Infection occurs through consumption of thermally untreated, unwashed food and contaminated water. A child can become infected while playing in a sandbox.
Giardia cysts can be found on household items, toys, and dirty hands. Contact between a healthy person and an infected person causes infection.
Analysis for Giardia cysts in stool and blood
To diagnose an invasion, stool and blood tests are prescribed. Stool examination is carried out several times, since cysts are released with some frequency, they cannot always be detected in stool.
No special preparation is required to collect biomaterial. It is important to exclude the possibility of mixing feces with urine. The feces are placed in a sterile container and sent to the laboratory.
Blood collection is carried out only in a medical institution. It allows you to detect the presence of antibodies to Giardia, refute or confirm infection.
ELISA is one of the most reliable methods for detecting parasites; it is prescribed to both adults and children.
Giardia cysts in an adult
After infection, some time passes and the person experiences symptoms of the disease. The incubation period can last 1-3 weeks. Typically, signs of infection appear in the form of dysfunction of the digestive system.
The acute phase of infection lasts about a week and then the chronic phase begins.
You will be surprised how many parasites will come out if you drink a glass of regular...
Parasites will leave the body in 3 days! You just need to drink on an empty stomach...
| Symptoms | Treatment |
At the chronic stage there is:
| Treatment is carried out only by a doctor, excluding self-medication. Therapy includes three stages:
|
Giardia cysts in children
Giardia infection in children can cause serious pathological conditions. Therefore, the disease cannot be ignored - if any negative symptoms appear, contact a medical institution to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate methods of therapy.
| Symptoms | Treatment |
As the disease progresses, the child will experience the following symptoms:
| Treatment of giardiasis in children is not much different from treatment in adults:
|
The lack of adequate, timely treatment causes the development of:
- vitamin deficiency;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- intoxication;
- delays in child development (mental, physical);
- autoimmune, allergic diseases;
- a significant weakening of the body’s protective functions, which is why the child is more likely to encounter colds and viral diseases.
Compliance with preventive measures and doctor’s instructions significantly reduces the risk of relapse and speeds up the recovery process.
Giardia cysts, after penetration into the human body, cause the development of many pathological conditions. The treatment process is complicated if a person ignores the disease or engages in self-medication, which is aimed only at eliminating the symptoms, and not the cause that provokes them.
If you suspect Giardia infestation, it is better to consult a doctor to make an accurate diagnosis and choose effective therapy.
- Dispensed without a doctor's prescription;
- Can be used at home;
- Clears parasites in 1 course;
- Thanks to tannins, it heals and protects the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, and skin from parasites;
- Eliminates rotting in the intestines, neutralizes parasite eggs thanks to the F molecule.
A certified remedy recommended by helminthologists for getting rid of parasites at home. It has a pleasant taste that children will like. Consists exclusively of medicinal plants collected in environmentally friendly places.
?Expert opinion about the drug.
There is a discount now. The drug can be obtained free of charge.
How to take it
Having received a referral for a blood test for Giardia, the patient is sent to the laboratory, where blood is drawn in the volume required for the study.
Various factors, such as smoking, can affect test results. Venous blood is required for analysis. The sampling is carried out in the laboratory.
A week before the tests you need to exclude from the diet:
- smoked, sweet, fried, salty and spicy foods;
- Do not drink tea, coffee, any carbonated drinks or alcohol.
Before taking blood, it is better to warn the laboratory technician about possible negative reactions to the test, for example, possible loss of consciousness.
How to take a stool test for Giardia
The simplest single-celled organisms lead to many diseases and do not leave us for a second. Very often such organisms live in our intestines. There is the most favorable place for their existence. In the intestines, parasites obtain all the necessary vitamins and minerals, taking them from our body. Giardiasis, caused by single-celled protozoa, is no different from others. They are called Giardia. This is a disease of dirty hands, since it is Giardia that enters our body. Very often, the disease affects the children's body, but does not bypass adults.
The insidiousness of giardiasis is that it is often confused with other diseases. This is a dangerous disease in which toxic and allergic reactions, asthma, abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract, growth retardation and psychological development develop.
To detect infection, special laboratory tests are performed.
Fecal analysis for Giardia
Regardless of where it is found, in the body of adults or children, everyone, without exception, is prescribed a stool test for Giardia. It is important to pass it correctly. With its help, you can identify parasites and determine the form of the disease.
There are situations when donating feces is simply necessary:
- Diarrhea, allergies.
- Gastrointestinal diseases.
- Dysbacteriosis.
- Dermatitis, urticaria, eczema.
- Asthma, bronchitis.
- Immunodeficiency.
- Hypotrophy.
Giardia cysts in feces
Cysts are a temporary form of microorganisms.
Many protozoa are capable of existing in this form for several years. Giardia can be found in vegetative form in feces; this happens because, when it enters the intestines, it immediately turns into a cyst. With giardiasis, parasites negatively affect the intestines. This leads to his frustration. One of the symptoms is constipation, which abruptly gives way to diarrhea. It is in case of diarrhea that tests are recommended. During constipation, the stool is dense and it is impossible to determine whether cysts are present in the mass. What cysts look like in feces is shown in the photo.
Test methodology
Like any diagnosis, stool analysis is carried out according to certain rules. The effectiveness of the results depends on this. Preparation for stool donation is carried out in many stages. The sample should appear naturally, without the aid of laxatives or enemas. The freshness of the analysis is of great importance. If more than six hours have passed since the bowel movement, the microbiological composition of the stool changes and this may affect the result.
Preparing for tests - recommendations:
- Before the date of the test, you need to follow a diet for 3-5 days. Limit yourself from foods that contribute to gas formation, constipation, and diarrhea.
- It is necessary to stop taking medications and activated carbon. It is also not necessary to conduct X-ray contrast studies.
- Women during menstruation are not advised to undergo tests.
Collect excrement for analysis: rules
Before collecting the sample, you must urinate, wash the perineum very thoroughly with soap, and wipe dry. If urine or water gets into the stool, such a sample will not be suitable for analysis. You need to pay a lot of attention to personal hygiene, since chemical elements from underwear or clothing can get into it. To defecate, you need to take clean and dry dishes. Many people place cling film over the toilet and then collect the sample in a clean, airtight container. You can take a plastic or glass jar, put about a teaspoon of feces, close it carefully and take it to the laboratory.
Where can I get tested?
There are many places to get tested. Most often, attending physicians give a referral to the nearest laboratory. Such tests can be done at a diagnostic center, clinic, or commercial laboratory. Private clinics are a paid option, but faster and more convenient, since you don’t have to wait in lines for a long time, but simply make an appointment at a time convenient for you. Although for some it is better to stand in line, getting the tests done is free. Only you can decide where to get tested.
How is Giardia isolated in feces during analysis?
Tests: feces for antigen, PCR method. These are the main ways to identify parasites of this type. If cysts or eggs were found in the stool, this is a direct confirmation of the diagnosis. But it also happens that Giardia is not always found in feces. In such cases, when signs of the presence of parasites exist, but are not determined by tests, doctors recommend donating stool once a week for a month.
Stool test for Giardia antigen
Analysis of stool for antigens will allow the identification of Giardia fragments in samples. To carry it out you need a small amount of feces. The results of the examination are accurate, but to be completely sure, you will need to test for the presence of antigens about four more times.
Antigens are not only released in feces. When examining the composition of the blood, Giardia cysts are also detected. An antigen is an immunoenzyme formation that resists foreign bodies entering the human body.
Sometimes they are present in the blood or stool even if a person is not infected. Strong immunity reacts by releasing antigens even when transit cysts or eggs enter the body, which immediately come out without infecting the person.
PCR research
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis is a common and accurate method.
PCR helps identify individual genes in Giardia DNA. Even if there is no cyst discharge, he will still detect their presence. Using PCR analysis, the source of infection is detected in the patient’s body and the type of invasion is determined.
Stool testing using the PCR method is informative and effective. PCR is an experimental method during which foreign bodies are isolated from a substance. Diagnostics are available in specialized laboratories that practice this analysis.
The Invirto laboratory network successfully engages in PCR research in the field of parasitology. You can view the price list for PCR diagnostics on the company’s website.
Tests for invasion at Invitro
For tests, you can always contact the Invitro medical laboratory.
An individual approach to each patient, quick and accurate results are guaranteed. There is no need to tire yourself out with long queues, but simply come at a convenient time. Affordable prices, qualified staff, the latest technologies at your service.
Among different methods and means, everyone chooses the one that suits him best. But we must remember that no matter what parasite settles in our body, we must undergo a full examination and devote maximum time and attention to the problem. To prevent this from happening, you need to take care of your health.
1parazit.ru>
Blood test for antibodies to Giardia
Blood ELISA involves testing the antigen-antibody reaction. For analysis, blood is also taken from a vein and mixed with Giardia antigens. During the reaction, you can determine the presence of antibodies (IgG, IgM, IgA), which are produced to fight the parasite.
The analysis is highly accurate (about 90%). The results will be presented in the following diagram:
| IgM+, IgG-, IgA- | No antibodies |
| IgM-, IgG+, IgA- | The presence of immunity developed to the pathogen |
| IgM+, IgG-/+, IgA-/+ | Exacerbation of invasion |
| IgM+, IgG+, IgA+ | Chronic form of infection |
| IgM- | Recovery |
If antibodies with an IgG marker are detected in the blood, one cannot claim infection. The immune system will produce these antibodies for some time (1-6 months) after recovery; they can be detected in the blood.
Diagnosis of giardiasis - what tests to take
At the moment, there is no 100% method for detecting Giardia in the human body, so it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination.
The diagnostic search begins with an analysis of complaints, examination of the patient, and assessment of the clinical picture. There are no specific symptoms of giardiasis; the disease disguises itself as intestinal disorders, can provoke allergic reactions, and also causes a disturbance in the general condition (weakness, decreased performance, drowsiness).
Important! A reliable diagnosis can only be made based on laboratory data!
Types of tests for Giardia
There are a number of studies that help diagnose giardiasis. Let's look at each analysis in more detail.
Microscopic examination of stool for cysts
It is the first diagnostic method. It is included in the mandatory standard of examination before planned admission to a hospital or children's educational institutions and is called feces for eggworm.
The test may give a negative result because cysts are released cyclically. In order to obtain a reliable result, feces must be taken 3 days in a row. A repeat three-day test is done after 10 days if the results are negative.
The laboratory uses the formalin-ether enrichment method to preserve the parasite in feces. In loose stools, vegetative forms can be identified that live for 30-60 minutes. Cysts persist in processed stool for up to 10 days. The sooner the laboratory receives biomaterial for testing, the higher the risk of detecting a microorganism.
Stool test for giardia lamblia antigen
It is based on identifying specific molecules (antigens) that are present only in Giardia. Monoclonal antibodies to the GSA-65 antigen are used. The method is popular in the Helix laboratories network; it makes it possible to detect the disease during the “silent” period, when cysts are not released.
Examination of stool for dysbacteriosis
With giardiasis, the intestinal flora changes. The number of fungi (candida) increases; they work in symbiosis with Giardia. Candida synthesizes B vitamins, which parasites feed on. E. coli is displaced, and the analysis shows a decrease in it.
Bile examination
It is carried out during duodenal intubation. Microscopic analysis shows the presence of vegetative forms. The method may give a questionable result if the parasites are in the lower parts of the small intestine, so it is complemented by other types of diagnostics. Currently not used due to its complexity and low evidence.
Small intestine biopsy
Shows structural changes in the organ, allows you to detect vegetative forms of Giardia. The negative point is the high cost of the method. It is used if there is a suspicion of a malignant process in the small intestine (immunohistochemical analysis).
Enterotest: what is it?
The essence of the method is to swallow a gelatin capsule, inside of which there is a nylon thread. In the stomach, the capsule dissolves, the thread is exposed and enters the small intestine with the bolus of food, where vegetative forms of Giardia settle on it. The thread leaves the body naturally and is then examined microscopically.
Serological test (ELISA)
Blood is taken from a vein on an empty stomach, centrifuged, and the presence of antibodies to Giardia in the serum is determined. Total antibodies (immunoglobulins M and G) are determined.
Explanation of the results obtained:
- Immunoglobulins (Ig) M are an early fraction of antibodies that are synthesized in the first 10 to 14 days from the moment of infection. A positive result indicates an acute process. Over time, their number decreases and IgGs are synthesized to replace them.
- Immunoglobulins G are produced later and remain in the blood for a long time (up to 6 months). They are the most significant.
- An increase in the level of IgM and IgG can indicate an exacerbation of a chronic process, re-infection.
The higher the level of antibodies in the blood, the more pronounced the degree of the infectious process.
The result may be weakly positive when there are antibodies, but there is no Giardia in the body (with a negative PCR test). This is due to a cross-reaction in the presence of other protozoan parasites (intestinal amoeba, blastocysts) in the body.
Important! The level of antibodies depends on the state of the immune system! When it is weakened, antibodies may be absent.
PCR – polymerase chain reaction
Allows you to identify the genetic material of a microorganism in stool. It is the most accurate in terms of effectiveness (98%). It is used extremely rarely in the diagnosis of giardiasis.
PCR analysis for Giardia
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) - examination of stool or venous blood. This analysis can be prescribed in combination with an ELISA blood test, which significantly increases the reliability of the results. PCR is aimed at identifying DNA fragments of the parasite and is used to study the dynamics of treatment.
The patient needs to collect a morning portion of stool. This must be done before hygiene procedures in the morning after waking up. To eliminate the possibility of urine and feces mixing, the bladder should be emptied in advance.
The feces are placed in a sterile container, closed and sent to the laboratory for testing (within 8 hours). The analysis does not require a special diet.
Defecation should occur naturally without the use of laxatives.
Types of tests to determine Giardia infection
The presence of Giardia in the body can be checked using stool or blood tests.
Stool studies are carried out in two directions:
- For protozoan eggs . The cheapest but least informative test. Indicates the presence of cyst larvae in the lower part of the large intestine. Since the release of cysts occurs in waves, the test may give a false negative result if carried out during an unfavorable period. Such an analysis costs between 230-425 rubles.
- For Giardia antigens . During the test, it is not larvae that are detected in the stool, but specific molecules - antigens that are present in Giardia cells at any period of their life. A very informative analysis, the cost of which ranges from 740 to 920 rubles .
A blood test checks for the presence of antibodies to Giardia. There are two possible test options:
- Analysis for total antibodies . It will be positive in the presence of acute or chronic forms of giardiasis. Even if the disease has already been cured, this test will still give a positive result for several years. The cost of such a study will be about 420-660 rubles
- IgM antibody test . It will give a positive result only in the presence of an acute disease, when the body is actively fighting the pathogen. This test is not carried out in all laboratories and costs between 420-580 rubles .
Preparation for analysis
A week before blood sampling, you need to follow a diet enriched with light, quickly digestible foods.
On the day of blood sampling, the patient is prohibited from eating and smoking; he can only drink still water - each factor can affect the final result.
It is recommended to stop taking medications a few days before the tests; if this is not possible, you need to notify your doctor. This will allow you to make a reliable diagnosis.
You need to enter the office without haste - increased physical activity provokes the release of certain substances into the blood that can distort the test results.
Price and where to rent
The cost is affected by the region where the laboratory is located and the type of blood test for Giardia. In the Invitro laboratory, the cost of testing for Ig antibodies with markers M, A, G is 115 UAH.
Diagnosis of giardiasis is complicated by the asymptomatic course in the early stages of invasion. Various diagnostic methods are used to detect the parasite. A blood test is considered the most reliable. It is not recommended to start treatment on your own, without being examined by a doctor. Self-medication can cause serious complications.
It is possible to defeat parasites!
Antiparasitic Complex® - Reliable and safe removal of parasites in 21 days!
- The composition includes only natural ingredients;
- Does not cause side effects;
- Absolutely safe;
- Protects the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, skin from parasites;
- Removes waste products of parasites from the body.
- Effectively destroys most types of helminths in 21 days.
There is now a preferential program for free packaging. Read expert opinion.
Interesting to know:
Bibliography
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Brucellosis. Parasites. Link
- Corbel MJ Parasitic diseases // World Health Organization. Link
- Young EJ Best matches for intestinal parasites // Clinical Infectious Diseases. — 1995. Vol. 21. - P. 283-290. Link
- Yushchuk N.D., Vengerov Yu.A. Infectious diseases: textbook. — 2nd edition. - M.: Medicine, 2003. - 544 p.
- Prevalence of parasitic diseases among the population, 2009 / Kokolova L. M., Reshetnikov A. D., Platonov T. A., Verkhovtseva L. A.
- Helminths of domestic carnivores of the Voronezh region, 2011 / Nikulin P. I., Romashov B. V.
An article for patients with a doctor-diagnosed disease. Does not replace a doctor's appointment and cannot be used for self-diagnosis.
The best stories from our readers
Topic: Parasites are to blame for all troubles!
From: Lyudmila S. ( [email protected] )
To: Administration Noparasites.ru
Not long ago my health condition worsened. I began to feel constant fatigue, headaches, laziness and some kind of endless apathy appeared. Problems also appeared with the gastrointestinal tract: bloating, diarrhea, pain and bad breath.
I thought it was because of the hard work and hoped that it would go away on its own. But every day I felt worse. The doctors couldn’t really say anything either. Everything seems to be normal, but I feel like my body is not healthy.
I decided to go to a private clinic. Here I was advised, in addition to general tests, to get tested for parasites. So in one of the tests they found parasites in me. According to doctors, these were worms, which 90% of people have and almost everyone is infected, to a greater or lesser extent.
I was prescribed a course of antiparasitic medications. But it didn’t give me any results. A week later, a friend sent me a link to an article where some parasitologist shared real tips on fighting parasites. This article literally saved my life. I followed all the advice that was there and after a couple of days I felt much better!
Digestion improved, headaches went away and the vital energy that I so lacked appeared. To be sure, I took the tests again and no parasites were found!
Anyone who wants to cleanse their body of parasites, no matter what types of these creatures live in you, read this article, I’m 100% sure it will help you! Go to article>>>
Still have questions? Ask them in our Anonymous group on VK
How to get rid of parasites in a week. The answer is here!
A reliable and effective remedy for combating worms. Removes all parasites in 21 days.
Go to website
Reviews
Read online
Symptoms that 100% indicate parasites! Take the Test.
How to rid your body of life-threatening parasites before it’s too late!
Read more
Website
To get a consultation
The doctor tells how to quickly get rid of parasites for adults and children!
A parasitologist explains what effective methods exist to combat helminths.
More details
Read completely
Comments
Search for cures for parasites
Other tests
We recommend reading
Nemozol or Vermox: which is more effective for pinworms and ascariasis
1 week ago 05/14/202005/14/2020ecoliv94
Measures and rules for the prevention of helminthiases in adults and children
1 week ago 05/14/202005/14/2020ecoliv94
Diagnosis of parasitic diseases: laboratory research methods
1 week ago 05.13.202013.05.2020ecoliv94
Should I take Vermox before or after meals? Instructions for use
1 week ago 05.13.202013.05.2020ecoliv94
Human parasites
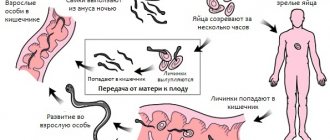
The source of infection is a person infected with Giardia. Transmission of infection occurs through the fecal-oral route. The main factor of transmission is water, but transmission can also occur through food products, on which Giardia cysts remain viable for 6 hours to 2 days; contact transmission from person to person is also possible. Giardia can cause serious intestinal diseases in humans, both in the form of epidemics and in sporadic cases. Children are more susceptible to Giardia infestation; their disease occurs with more pronounced clinical signs.
Invasion of the small intestinal mucosa by Lamblia intestinalis can give a different clinical picture: from an asymptomatic course to allergic symptoms and diarrhea syndrome, which is especially severe with severe immunosuppression. Giardia infection may spontaneously disappear after 6 weeks or may persist for years. By colonizing the mucosa of the small intestine, Giardia trophozoites penetrate the epithelium and cause a systemic immune response.
According to clinical studies, antibodies to Giardia antigens are detected in 39 - 42% of patients with gastrointestinal pathology. In 89 - 92% of them, giardiasis is confirmed by a positive result of testing samples of feces or duodenal contents for the presence of Giardia cysts. There is a problem of cross-reactions of Giardia antigens with other parasitic and somatic antigens, which give false-positive results, therefore, to increase the reliability and reliability of the diagnosis of Giardiasis, a comprehensive examination is necessary.
Giardiasis: causes, symptoms and diagnosis of the disease
Giardiasis is one of the most common parasitic diseases in humans.
According to WHO, about 200 million people become infected with Giardia every year. Clinical manifestations of giardiasis are recorded in almost 500 million patients per year. The disease is widespread.
What is Giardia?
The causative agent of giardiasis in humans is the well-known protozoan organism Lamblia intestinalis, which settles in the small intestine and causes digestive disorders.
In humans and animals, Giardia exists in two forms. In the form of a vegetative form (such lamblia are called trophozoids), they are found mainly in the upper parts of the small intestine, and when they enter the large intestine they turn into cysts (spore form), which are excreted into the external environment with feces. Giardia in the form of cysts can remain in a “preserved” state for a long time and only when favorable conditions occur turn into trophozoids.
Once in the intestine, Giardia turns into trophozoids, attaching to the surface cells of the mucous membrane and sucking nutrients from it. Their life cycle is from three to forty days. Despite the fact that this is a fairly short period, the disease can last a very long time, since repeated self-infection occurs all the time. As a result of the long-term existence of Giardia in the body, a syndrome of chronic endogenous intoxication is formed. With reduced immune defense, this can lead to damage to almost all organs and systems of the body.
How does infection occur?
There are three main routes of transmission of giardiasis:
Most often, infection occurs when drinking poorly treated tap water or water from open reservoirs. In the contact-household route, entry into the body occurs through household items contaminated with cysts: linen, toys, dishes. Infection is also possible by consuming food products infected with cysts, especially without heat treatment (vegetables, berries, fruits).
How does giardiasis manifest in adults?
The incubation period of the disease lasts 1-3 weeks. As a rule, giardiasis occurs without any symptoms. With a large number of parasites inside the human body, the disease occurs with severe clinical symptoms and has an acute or chronic course.
In the acute form, the disease begins with the appearance of loose, watery stools without mucus and blood. Pain appears in the epigastric region. A large amount of gas is formed, bloating the intestines, and belching is observed. Patients experience decreased appetite, nausea, vomiting, and a slight increase in body temperature.
In most patients, the symptoms of the disease disappear spontaneously within 1-4 weeks. Then the disease becomes chronic, which is periodically manifested by bloating, pain in the epigastric region, and loose stools.
All patients with giardiasis show signs of vitamin deficiency: pale skin, blue under the eyes, pockets in the corners of the mouth, allergic rashes.
How dangerous is giardiasis for a child?
In children, giardiasis develops much more often and is more severe than in adults.
Modern epidemiological studies have shown that about 30% of preschool children are infected with Giardia. Moreover, in most cases, giardiasis in a child manifests itself with symptoms that mimic other diseases and make it difficult to identify the true cause of the disease.
Once in the child's intestines, Giardia begins to actively multiply, using the nutrients the child needs for growth. As a result, there is a lack of vitamins in the body, which inhibits the normal development of the child.
During their life, Giardia also releases a number of toxic substances. This leads to severe allergization of the child’s body and suppresses his immunity. For this reason, one of the common manifestations of giardiasis in children are: atopic dermatitis, bronchial asthma, chronic dry cough and frequent colds.
What are the consequences of giardiasis?
Giardiasis can aggravate the course of any other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract combined with it. It masks them and contributes to the occurrence of allergic reactions.
Situations are quite common when the diagnosis of giardiasis hides such chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract as inflammation of the pancreas, dyskinesia (impaired motor activity) of the gallbladder, inflammation of the intestines of various types, etc.
The nervous system is often affected. Patients complain of general weakness, fatigue, irritability, shallow sleep, disturbing dreams, headaches, and dizziness. The development of hypotensive crises with fainting is possible. Vegetative-vascular dystonia and arrhythmia are quite common.
In chronic giardiasis in children and adults, skin lesions are detected: pallor, uneven skin color (“multi-colored skin”), damage to the red border of the lips. The severity of the lesions varies: from mild peeling and dryness to severe cheilitis with cracks and jams.
Due to the discovery of Giardia in the child's stool and the appearance of characteristic complaints, additional examination is required in order to identify hidden chronic inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
How is giardiasis diagnosed?
The variety of clinical manifestations of giardiasis and the absence of symptoms characteristic only of this disease require mandatory laboratory confirmation of the diagnosis. The material for research is feces and duodenal contents. Only trophozoids are found in the duodenal contents, only cysts are found in formed feces, and trophozoids and cysts are found in liquid and semi-formed feces.
Currently, a number of methods are used to diagnose giardiasis, which differ in sensitivity, specificity and general availability. The independent laboratory INVITRO offers a wide range of studies to detect the presence of Giardia in the human body.
The most accessible method of laboratory diagnosis of giardiasis is scatological examination. When conducting research, it is necessary to remember that cysts in stool cannot always be detected. Intermittent excretion of cysts in feces requires repeated examination of feces, as well as the use of other laboratory research methods.
In patients with clinical manifestations of giardiasis, but with a negative fecal examination, it is advisable to examine the duodenum or upper jejunum. As a rule, it contains a large number of Giardia, including trophozoids (they are visible in fresh smears).
Analysis of failures in identifying Giardia in the study of feces made it possible to systematize the main reasons for false negative results. These include:
- incorrectly collected research material;
- submission of stool to the laboratory while taking medications that damage the morphology of parasites;
- errors of laboratory research;
- examination of feces during the so-called “silent” period, when the excretion of Giardia cysts stops (8-14 days).
Giardia can be detected in 76% of patients if these causes are eliminated during the first stool examination. After the second study, the probability increases to 90%.
The most reliable method for diagnosing giardiasis is duodenal biopsy. Indications for duodenal biopsy are:
- typical clinical picture of giardiasis;
- negative result of scatological studies;
- one of the pathological symptoms (for example, edema and segmentation of the jejunum during endoscopic examination);
- pathological lactose tolerance test (i.e. the presence of abnormal bacterial flora during aspiration of intestinal contents);
- absence of secretory Jgd;
- hypogammaglobulinemia (deficiency of one of the types of proteins in the human body - gammaglobulin);
- achlorhydria (lack of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice).
Immunological methods (ELISA method for detecting Giardia lamblia antigen) have recently been widely used throughout the world to diagnose giardiasis. Such test systems have very high sensitivity and specificity, and allow the simultaneous detection of both cysts and trophozoids in stool samples. Typically, G lamblia is detected in 50-70% of patients after a single stool analysis. After three-fold analysis - in 90%.
Detection of antibodies of the total classes IgA, IgM, IgG to Giardia antigens (serological methods) is an indirect method for laboratory diagnosis of giardiasis. Can be used as an additional diagnostic method to determine the body's immune response to the introduction of a pathogen.
Source: www.invitro.ru