Mixed gastritis is an ambiguous form of the disease, in which the symptoms and processes of different types of inflammation of the stomach are combined. This type of disease deserves special attention because it is very difficult to choose a treatment for it - while eliminating some symptoms, doctors are faced with the manifestation of signs of another form. Mixed gastritis, the symptoms and treatment of which often change and require adjustment, can occur in any person.
General rules
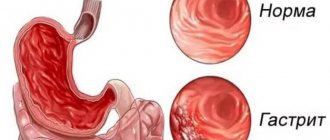
The group of chronic gastritis is morphologically characterized by inflammatory/dystrophic processes in the gastric mucosa (GM) with a disorder of secretory and motor function and various clinical manifestations. Chronic gastritis in its structure .
There are various classifications of chronic gastritis (Sydney, Houston, classification of the IX International Congress of Gastroenterologists), which are based on various factors. Among the many forms of chronic gastritis, mixed gastritis is distinguished based on etiology: atrophic multifocal pangastritis according to one classification or A and B gastritis/pangastritis according to another.
Chronic mixed pangastritis is characterized as multifocal, less often diffuse atrophic gastritis of the antrum/fundus of the stomach and damage to the coolant by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori (HP), which is detected in 60-70% of cases. This form of gastritis is characterized by preserved/moderate secretory insufficiency with a normal/less commonly reduced number of antral cells.
In complex therapy of mixed gastritis, diet is an integral/most important component of complex treatment. A diet for mixed gastritis of the stomach is prescribed taking into account the form of the disease (exacerbation, remission), the acid-producing function of the stomach (hyper/hypoacid gastritis), the patient’s condition, and test data on the presence of HP.
The basic diets for mixed gastritis are therapeutic Table No. 1 ( 1A , 1B ) according to Pevzner (for normal/hyperacidity of gastric contents and, accordingly, Table No. 2 for hypoacid gastritis. However, regardless of acidity indicators, if the patient is diagnosed with Helicobacter pylori-associated chronic gastritis, treatment begins with eradication therapy.In this case, before prescribing it, it is necessary to establish the HP status (high/moderate/low degree of infection, urease test activity, level of inflammation).
The diet for mixed gastritis with high acidity should be chemically/mechanically/thermally gentle on the gastric mucosa. Nutrition according to Diet No. 1 should be complete/balanced with a limitation of foods that promote the production of gastric juice, as well as indigestible/irritating dishes and products that irritate the gastric mucosa.
The amount of salt is kept to a minimum (5-8 g/day), dishes are prepared by boiling or steaming and lightly baked without a fried crust. Frequency of meals - up to 6 times. It is recommended to drink milk at night. It is recommended to take Borjomi mineral water, heated to 45°C, an hour before meals.
Excluded from the diet are sausages, fatty meats (fatty pork, goose, duck meat, lamb), mushrooms, smoked meats, legumes, rye bread, cabbage, radishes, fresh baked goods, fried foods and seasonings and spices (red and black hot pepper , garlic, onion, mustard, horseradish).
The basis of the diet should be: boiled lean meat ground in a meat grinder (chicken/quail meat, rabbit), mucous/semi-ground porridges (oatmeal, rice), low-fat fish (cod, hake), soups with vegetable broth, low-fat cottage cheese, freshly squeezed cabbage juice, fruit/berry drinks from non-acidic fruits and berries (apples, raspberries, strawberries). To reduce secretory activity/excitability of the stomach, patients with high acidity need foods containing easily digestible carbohydrates (sweets, sweets, honey, sugar, jam) in their diet.
Diet for mixed gastritis of the stomach with reduced secretory function - Table No. 2 , and outside the period of exacerbation - Table No. 15 . The diet may contain dishes of varying degrees of grinding and temperature treatment - stewed, boiled, unbreaded fried dishes, baked without crust, chopped dishes containing fiber. The diet includes: lean boiled meat, meat broths and broth-based soups that stimulate the secretion of gastric juice, low-fat fermented milk products, fish, vegetable dishes with “non-aggressive” vegetables - salads/purees from beets, carrots, zucchini, potatoes, spinach , juices/decoctions of sweet fruits, rosehip juice, dried fruit compotes. Products that are difficult/long to digest and irritate the gastric mucosa (animal fats, fatty meat products, smoked foods, hot seasonings, canned foods) are excluded. Fortified drinks (decoction of parsley roots, rose hips, plantain juice) are useful.
In case of a mild exacerbation of mixed chronic gastritis, Diet No. 1 should be followed for 2-3 months, after which the patient is transferred to a common table with a restriction (excluded) from excessively spicy dishes, seasonings, and sauces.
Causes of infection
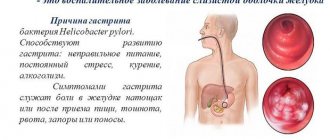
In 95% of cases, the cause of the disease is the bacterium Helicobacter Pylori. Infection occurs through the fecal-oral or contact-household route. The toxins released by the bacterium destroy the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum.
The following factors also act as catalysts for the development of the disease:
- weakened immune system;
- poor quality and irregular nutrition;
- bad habits;
- frequent stress;
- uncontrolled use of medications;
- exposure to toxic substances on the body.
The risk group includes people who are overweight and lead an inactive lifestyle.
Authorized Products
Therapeutic nutrition for mixed chronic gastritis with normal/high acidity involves the inclusion in the diet of:
- Not fried soups with vegetable broth/potato broth with the addition of pureed vegetables, boiled cereals (buckwheat, semolina) or white rice, seasoned with low-fat cream/garden herbs/butter. Or cream soups with the addition of thoroughly pureed chicken meat and whipped with a blender to the consistency of puree soup.
- Boiled/steamed chicken/turkey meat without skin, tongue and beef liver, lean beef. After pre-boiling the meat, it can be baked in the oven.
- Low-fat types of white fish in the form of cutlets, meatballs, meatballs, zraz.
- Dairy products (fresh cottage cheese, milk and low-fat cream, mild grated cheese, sour cream and curdled milk), low-fat herring, chicken eggs in the form of a steamed omelet/soft-boiled, low-fat ham, liver pate, milk sausage, jellied fish.
- Stale (yesterday's) wheat/dried bread, biscuits.
- Rice, semolina, buckwheat/oatmeal, noodles or pasta as a side dish.
- Vegetables (young peas, cauliflower, beets, potatoes, carrots), boiled, pureed. Butter/vegetable oil - only for ready-made dishes.
- Sweet berries/fruits in boiled and baked form - jelly, compotes, purees, jelly, marshmallows, non-sour jam, marshmallows.
- Fruit juices from permitted fruits, rosehip decoction, weak coffee/tea with milk, mineral water.
What is gastritis?
Gastritis is a collective medical term meaning various inflammations of the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus. It is believed that up to 80% of gastrointestinal diseases are gastritis in one form or another. Its development can be provoked by chronically poor nutrition, bad habits, genetic predisposition and even infection.
At the same time, modern medicine believes that the key reason for the development of gastritis is not nutrition at all, but a bacterial infection. The bacterium Helicobacter pylori settles in the lower esophagus, stomach, duodenum and moves inside the mucosa, forming microchannels into which hydrochloric acid (the basis of gastric juice) enters. More than half of the world's inhabitants are carriers of this bacterium¹.
Despite the infectious nature of the disease, diet for gastritis also plays an important role - for example, you should not eat spicy, sour or fermentable foods. Smoking and drinking alcohol (especially beer) is prohibited. On the other hand, with a properly designed menu, you can significantly reduce the symptoms of gastritis and normalize the functioning of the stomach.
Diet for acute gastritis
Exacerbation of gastritis can be caused by several reasons, including alcohol, poor diet, allergic reaction to food components and taking medications (for example, large doses of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). Acute gastritis can also occur due to consumption of stale meat and dairy products.
In severe cases (especially if there is dark blood in the vomit and almost black stool), it is recommended to seek medical advice. In mild cases, exacerbation of gastritis can be cured by following a strict diet with a minimum amount of solid food and switching to viscous and mushy foods. The diet should contain exclusively vegetables, cereals, vegetable oils and lean meat.
What can you eat for acute gastritis:
- viscous and well-cooked porridges (rice, oatmeal, buckwheat)
- boiled or stewed vegetables, vegetable puree
- jelly from berries, fruits and dried fruits
- a small amount of boiled meat, smashed in a blender
How to make a diagnosis
First, a patient with unpleasant symptoms consults a gastroenterologist. In some clinics, the first thing they do is visit a therapist to get a referral to a specialized specialist. In private clinics, as a rule, this approach is not required.
At the appointment, the doctor conducts an initial examination, learns from the patient about the time of onset of symptoms and previous factors. Be sure to draw up a picture of existing chronic diseases. However, only an instrumental examination with histological analysis (tissue sampling for subsequent biopsy) provides a complete picture of the disease.
The main examination method is FGDS. This is a procedure involving immersion of a special probe into the stomach through the oral cavity. A miniature camera shows the condition of the mucous membrane. Additionally prescribed:
- blood chemistry,
- submitting stool to determine bacteria,
- breath test to determine the presence of Helicobacter pylori,
- analysis of urine and gastric juice.
Only on the basis of all the described tests and examinations can an accurate and reliable diagnosis be made for further treatment.
Nutrition for gastritis
Proper nutrition for gastritis depends on whether there is increased or decreased acidity of gastric juice. In the first case, it is recommended to avoid foods that stimulate the production of hydrochloric acid, while in the second case, these foods will be useful in the diet. Note that in practice, gastritis with high acidity is more common.
In addition, for any type of gastritis, you should not eat foods that cause mechanical and thermal damage to the stomach - primarily crackers and excessively hot foods. Carbonated drinks, hot spices, and excess salt are prohibited. The diet should consist of predominantly liquid and mushy food, taken warm in small portions.
What not to eat if you have gastritis:
- excessively hot and cold foods
- rough foods that can damage the stomach
- fermentable foods
- heavy fatty foods
- most spices (including bell pepper)
- most sauces (mayonnaise, ketchup, mustard)
- carbonated drinks
- alcoholic drinks
- strong tea, coffee and chocolate
What can you eat?
Nutrition for gastritis should be based on the consumption of fresh vegetables (they are alkaline in nature and reduce the acidity of gastric juice), natural products (well-cooked whole grain cereals), lean meat and eggs. Pasta and a small amount of fresh bread are acceptable, but it is better to avoid sweet pastries, cookies and crackers. Food must be chewed thoroughly.
Note that with gastritis with low acidity of gastric juice, you can eat a small amount of fruits (primarily citrus fruits) and some dairy products (for example, cottage cheese and cheese) - whereas with gastritis with high acidity they are not recommended. At the same time, milk is useful if there is excess acid production, but is prohibited if there is insufficient acid production (it lowers the acidity of the stomach).
Symptoms
Among the general symptoms, it is necessary to point out phenomena from the nervous system:
- general weakness;
- headache;
- apathy;
- tendency to hypochondria (fear of getting several diseases).
On the part of the secretory function, at first there are signs of hyperchilia (increased secretion of hydrochloric acid and enzymes), due to irritation of the glands, often with large secretion of mucus. Subsequently, the secretory apparatus is depleted, the secretion of hydrochloric acid decreases or the acid disappears altogether.
Typically, the atrophic process first affects the main cells that secrete enzymes, then pepsin (an enzyme that breaks down proteins) disappears, and later rennet (which curdles dairy products in the stomach). Due to the accumulation of mucus and inflammatory swelling of the walls, the motor function of the stomach decreases. Poorly digested food causes intestinal diseases.
The clinical expression of mixed gastritis depends on the type of disease. Thus, the symptoms of the acute course of the disease are:
- significant pain in the stomach area;
- increase in abdominal size;
- attacks of nausea, which often end in vomiting;
- the occurrence of belching;
- rapid satiety and a feeling of fullness in the stomach.
The main sign of the chronic type of disease is a decrease in appetite with low acidity, or an increase in cases of increased stomach acidity. Other symptoms occur only after eating. These include:
- feeling of nausea and pressure in the stomach;
- the appearance of heartburn;
- the occurrence of constipation, which may be followed by diarrhea;
- formation of an unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- soreness in the heart area.
Due to the fact that the disease manifests itself in a large number of different symptoms, treatment of the disease will consist not only of taking medications aimed at eliminating the manifestations of diffuse type gastritis. Therapy will also consist of following a diet according to a menu specially prepared by the doctor and using traditional medicine.
Inflammation of the gastric mucosa of mixed type is characterized by a chronic course. Periods of exacerbation and remission are typical for it. In the latter case, there is no clear clinical picture. At the same time, the patient is confident that he has fully recovered.
However, errors in diet, alcohol abuse and smoking can provoke an exacerbation. It is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Pain in the stomach area, which is aching and bursting in nature. Discomfort occurs on an empty stomach or after eating.
- Nausea and vomiting, heartburn. If the erosive type of gastritis predominates over other forms of the disease, blood may be present in the vomit.
- Intestinal disorders: diarrhea, flatulence, constipation.
With a prolonged course of the disease, complete disruption of digestion occurs. Vitamin deficiency gradually develops, manifested by hair loss and brittle nails. The person begins to lose weight, and purulent rashes appear on the skin throughout the body.
Menu and diet for gastritis
The menu presented below represents nutritional recommendations for gastritis with high acidity of gastric juice. To ease the work of the stomach, food should be taken 5-6 times a day, avoiding long breaks. Also, if you have gastritis, it is not recommended to skip breakfast, and you should have dinner no later than 2-3 hours before going to bed.
When choosing food products, preference should be given to fresh and natural food, while dry snacks, ready-made meals, semi-finished products and canned food should be excluded. Legumes (from peas to lentils) and other products that provoke gas formation (onions, cabbage, radishes) pose a separate danger - they should not be consumed if you have gastritis. For the same reason, rye and yeast products are prohibited.
Menu for gastritis: example 1
- Breakfast: rice porridge with raisins in milk, weak warm tea
- Second breakfast: smoothie with milk, banana and chia seeds
- Lunch: baked fish with a side dish of stewed vegetables
- Afternoon snack: oatmeal, dried fruit compote
- Dinner: pureed vegetable soup, steamed chicken cutlets
- Before bed: a glass of warm skim milk
Menu for gastritis: example 2
- Breakfast: oatmeal with dried fruits and milk, tea
- Second breakfast: smoothie with milk, peach and flaxseeds
- Lunch: chicken broth with pasta and carrots
- Afternoon snack: fluffy omelette with milk
- Dinner: Sweet potato puree, meatballs
- Before bed: a glass of warm skim milk
Eating red meat for gastritis is not prohibited, but it is better to give preference to lean beef, finely chopped or minced - you can use it to make cutlets, meatballs, or simply lightly fry and add to porridge (buckwheat and quinoa). Frying is also not prohibited, but it is important to use only a small amount of vegetable oil and not to eat the dish too hot.
The diet for gastritis is based on avoiding foods that cause mechanical and thermal damage to the stomach (rough, excessively hot foods) and eating foods that are easy to digest. We are talking about alkaline vegetables in stewed, baked and boiled form, various compotes, as well as lean meat (chopped or minced). If you have gastritis with high acidity, you can drink milk; if you have low acidity, it is prohibited.
- Gastritis (Symptoms, Pain, Home Remedies, and Cure), source
- WebMD: What Is Gastritis?, source
- Gastritis Diet: What to Eat and What to Avoid, source
What can and cannot be eaten with gastritis? - nutrition rules
Therapeutic nutrition for gastritis reduces discomfort and pain in the stomach caused by inflammation. A properly selected menu contributes to the effectiveness of therapeutic measures and normalization of digestion. The diet for gastritis of the stomach includes treatment tables No. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5. The choice of a specific menu depends on the level of acidity and the phase of the disease. Table No. 1, 4, 5 have several options. In the number of the main diet, they are designated by letters and are used based on the severity of symptoms and the period of the disease (acute, subsiding, chronic form).
Diet principles
Organizing proper nutrition for gastritis means completely revising your diet and eliminating foods that irritate the gastric mucosa. Preference is given to steamed and boiled dishes. For any type of gastritis, it is forbidden to eat fried, fatty foods.
Therapeutic diets for people with various diseases were developed in 1929 by the Soviet scientist I.M. Pevzner. The system includes 15 main tables with clarifying options and unloading periods.
Nutrition for gastritis of the stomach is organized taking into account the following rules:
- optimal food temperature 200–500°;
- meals are taken at the same time, 5–6 times a day;
- avoid overeating;
- when choosing a diet, take into account concomitant diseases;
- exclude alcohol, smoking;
- refuse smoked, pickled, spicy foods;
- have dinner 2–3 hours before bedtime;
- chew food thoroughly;
- refrain from snacking on the run;
- You can drink 30 minutes after eating;
- cook the food well.
This regimen has a beneficial effect on the regeneration of the mucous membrane. The menu for gastritis of the stomach should be varied and include a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals. The patient should not starve.
List of useful products
A therapeutic diet for patients with gastritis necessarily includes enveloping foods and components that restore damaged mucosal cells. Food should contain a lot of B vitamins. These elements are often lacking in gastrointestinal diseases. Healthy foods to eat for all forms of chronic gastritis:
- oatmeal is a source of fiber and antioxidants;
- vegetable oils – contain fatty acids, tocopherol;
- milk (if well tolerated, does not cause bloating);
- fermented milk products – normalizes intestinal function due to the high content of bacteria responsible for strong immunity;
- ripe bananas – stimulate the production of protective mucus, rich in B vitamins and magnesium;
- berries - are absorbed better than fruits; when the production of secretory fluid increases, non-acidic varieties are chosen;
- rice – has absorbent properties;
- potatoes - helps to improve metabolism; the juice of the raw vegetable is used for medicinal purposes.
Proper drinking regimen will help alleviate the condition during exacerbation and discomfort. The liquid improves peristalsis of the gastrointestinal tract and dilutes excess acid in the stomach. The volume of clean water without gases in the daily diet should be at least 1.5 liters.
Treatment options
The disease is treated by a gastroenterologist. Independent attempts to eliminate the disorder are dangerous and can lead to the development of complications.
The mixed form of gastritis always requires complex therapy. Its main goal is to eliminate the causes of inflammation of the stomach. Treatment involves the use of medications and a special diet.
Medication
The basis of drug therapy is antibiotics to suppress the activity of Helicobacter Pylori. These may be drugs from the group of cephalosporins, fluoroquinols, aminoglycosides. The doctor most often prescribes 2 or more drugs, which is due to the high resistance of the bacteria to most modern drugs.
To relieve the symptoms of gastritis, the following medications are also indicated:
- Antacids (neutralize the effect of hydrochloric acid in the stomach).
- Enzymes (normalize microflora in the stomach, restore the digestive process).
- Prokinetics (improves peristalsis).
- Analgesics (relieve pain, relieve spasms of smooth muscles of organs).
- Preparations with an enveloping effect (promote the healing of erosions).
- Vitamin complexes, immunomodulators (help restore the body's strength after an inflammatory process).
The name of the drugs, their dosage and duration of use are determined by the doctor. The specialist must take into account the patient’s clinical picture, the severity of the pathology and the presence of concomitant health problems.
Features of nutrition with high acidity
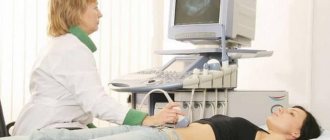
The gastroenterologist selects a diet after ph-metry - a diagnostic procedure in which the acidity level of gastric contents is measured. It is usually performed during endoscopy.
Symptoms of gastritis with high acidity are heartburn, pain under the ribs between meals. When inflammation of the stomach is provoked by excessive production of secretory fluid, table menu No. 1 is recommended.
To normalize the pH level, a person follows a strict diet. Any menu errors can cause discomfort and pain. The list of allowed dishes consists of products that restore the mucous membrane and reduce stomach acidity:
- liquid porridge;
- lean soups;
- side dishes - mashed potatoes, boiled vegetables, durum wheat pasta, well-cooked buckwheat, rice;
- low-fat meat and fish meatballs, meatballs;
- cheese;
- veal-based sausage;
- dairy products;
- sweet fruits, berries;
- stale bread, crackers;
- cheese casserole;
- jelly, soufflé;
- for dessert - honey, pastille, marmalade, seedless raisins, dry cookies.
The diet must include butter and vegetable oil. Main courses of meat and fish during the period of remission can be prepared in whole pieces.
Vegetables are consumed boiled. Fresh onions and garlic irritate inflamed mucous membranes, so they should not be eaten if you have gastritis. When boiled, these vegetables are allowed in small quantities.
It is useful for people diagnosed with hyperacid gastritis to drink milk jelly and dried fruit compote. The list of permitted drinks also includes weak tea and rosehip decoction.
What not to eat if you have gastritis
- salo;
- dumplings;
- liver;
- mushrooms;
- margarine, spreads;
- fast food;
- Rye bread;
- heavy cream;
- coffee;
- chocolate;
- spices;
- fresh fruits (except bananas, sweet apples, pears);
- radish;
- ice cream;
- confectionery;
- baking;
- canned food;
- carbonated drinks;
- salty cheeses;
- lollipops;
- marinades.
If the disease worsens, you need to limit the consumption of pasta, seafood, seeds, and nuts. If inflammation of the stomach is combined with diseases of the liver and gall bladder, eggs are consumed as components of dishes. Eating them separately, in the form of an omelet, is undesirable if you have a combination of gastrointestinal diseases.
Categorical prohibition
With any type of stomach inflammation, some dishes must be excluded from the diet forever. These are foods that cause gastritis.
Their use can lead to irreversible consequences. The list is presented:
- Alcoholic drinks, given their leading role in the occurrence of pathology.
- Spicy seasonings that irritate the mucous membranes, cause heartburn and belching, aggravating inflammation.
- Semi-finished products - containing artificial additives and flavor enhancers, such as monosodium glutamate, which cause irritation of the gastric epithelium.
- Carbonated drinks, especially colored ones, have a negative effect on the production of hydrochloric acid.
Attention!
Regular consumption of harmful foods increases the risk of developing stomach inflammation, causing irreversible changes in the mucous membrane of the organ, ulcers and atrophy of the epithelium.
Allowed products for hyperacid gastritis
To normalize the acidity level, treatment is combined with a special diet that excludes foods that increase the production of secretory fluid in the stomach.
Diet therapy significantly accelerates the healing process for superficial focal gastritis. As a rule, minor damage to the mucosa can be cured with the help of a treatment menu and medications in 10–14 days. In case of deep lesions, it is recommended to eat properly for the rest of your life.
List of foods that you can eat for gastritis with high acidity:
- Flour products. It is allowed to eat yesterday's bread made from wheat flour, long-lasting cookies (“Maria”, “Zoological”).
- Cereals. Rice, buckwheat, and rolled oats are considered especially beneficial for the stomach.
- Vegetables in the form of puree. It is recommended to make salads from grated vegetables.
- Eggs. They need to be boiled well. You should eat eggs no more than 3 times a week.
- Dairy products. They neutralize excess acid in the stomach.
- Hard and curd cheese.
- Meat. The most useful varieties for gastritis are turkey and rabbit.
- Fish. Low-fat varieties are suitable - pollock, cod, pink salmon, flounder, hake, pike.
- Dessert. Allowed sweets include honey, jelly, marshmallows, marmalade, and marshmallows. For baked goods, you can make cottage cheese casserole.
- Still mineral water.
Traditional methods
Alternative medicine recipes are used as an additional therapeutic measure. However, before starting such treatment, it is necessary to consult a doctor, since some decoctions and herbs can only aggravate the course of the disease.
One of the available methods for treating mixed gastritis is potato juice. It normalizes stomach acidity and eliminates the bitter taste in the mouth.
To prepare a folk medicine you will need 1 large fruit. It must be washed well, peeled and chopped on a plastic grater. The resulting mass must be squeezed through gauze. The result is about 50-70 ml of liquid. You can add 1 tsp to potato juice. starch. It is recommended to take this remedy twice a day.
If mixed gastritis is diagnosed, treatment with potato juice is 14 days. If necessary, it can be repeated after taking a break of 1 month.
Healing with honey
A mixture of honey, butter and aloe juice is also used in the treatment of mixed gastritis. To prepare the medicine you will need to take 200 g of each ingredient. It is recommended to first keep aloe leaves in a dry and dark place or refrigerator for several days, and only then squeeze out the juice.
The mixture should be taken at a dose of 20-30 mg 20 minutes before meals. It is best to store it in the refrigerator, and must be reheated before each use.
Various mixtures based on medicinal herbs are excellent in the fight against mixed gastritis. The most commonly used are St. John's wort, calendula, plantain and wormwood in a ratio of 3:1:1:1. The mixture in the amount of 75 g should be poured into 0.3 liters of boiling water and left in a water bath for about 20 minutes. Take 50 ml infusion 4 times a day before meals.
Propolis tincture
You can purchase a ready-made tincture or make it yourself at home. To prepare it, pour 60 g of propolis into 0.5 liters of diluted alcohol. The mixture is left for a week in a warm place, stirring occasionally. It is recommended to take the medicine before meals, diluting 10 drops with a glass of water.
Features of the diet for hypoacid gastritis
In people with low acidity, the digestion process is difficult due to a lack of enzymes. Signs of this pathology are poor appetite, weight loss, pale skin, vitamin deficiency.
Rough food provokes an exacerbation. People with hypoacid form of gastritis should not consume:
- peeled fruit;
- berries with seeds - raspberries, strawberries, gooseberries;
- pure milk.
The list of products for gastritis with high acidity is approximately the same as for the hyperacid form. There are also differences in diet. If you have low acidity, you can consume:
- sour fruits, vegetables and berries (citruses also belong to this group);
- salted cucumbers;
- tomatoes;
- fruit juices.
Particular attention is paid to grinding food. It is advisable to take food in a calm environment and chew it thoroughly. With low acidity, there may be intolerance to meat, milk, eggs. In this case, foods that cause discomfort are excluded from the diet so as not to provoke complications of gastritis.
To increase acidity levels, follow a diet based on increasing the production of gastric juice. Digestive enzymes - Festal, Pancreatin, Creon - are often taken along with permitted products.
Diet during exacerbation of the disease
The menu is based on table No. 1a. Restrictions are observed for 5–7 days. When the symptoms subside, the diet is expanded. If acute gastritis is accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea, the body needs increased fluid intake. Regidron powder dissolved in water helps restore the water-salt balance. If the active phase of the disease is accompanied by pain and constipation, table No. 1b is recommended.
The menu for acute gastritis includes liquid and pureed dishes that promote healing of the stomach walls:
- slimy soups with rice and rolled oats;
- steamed cutlets, soufflé with chopped meat;
- viscous porridge;
- jelly;
- weak tea.
Diagnostics
Before starting treatment, the doctor directs the patient to the necessary diagnostic measures. First of all, the doctor listens to all the patient’s complaints and palpates the abdominal cavity. After this, a blood test is taken, as well as stool and urine tests. If necessary, gastroscopy of the stomach is performed.
Ultrasound examination helps to see how the stomach works at the moment. If pathologies are suspected, the patient is sent for an X-ray examination and MRI of the stomach. All these diagnostic studies require special preparation, with which a gastroenterologist will assist.