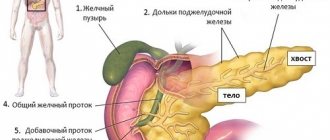
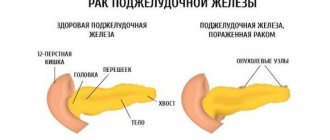
General information
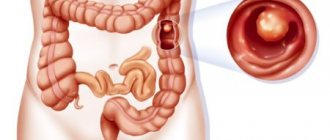
Peritoneal carcinomatosis is one of the most common diseases that arise as a result of metastatic lesions of other cancerous tumors, regardless of their location.
Scientists believe that the source of damage to the abdominal organs in this case is mutated cells. They are separated from the primary focus of the pathological process and penetrate into other organs through the serous fluid.
The result of this process is the formation of a malignant tumor on the abdominal organs. According to statistics, the disease is diagnosed in 30% of patients with established cancer pathology.
Carcinomatosis has a poor prognosis, as it is practically untreatable. It is possible to improve the patient’s condition and prolong life only with the help of an integrated approach.
Treatment of peritoneal carcinomatosis in Israel
Treatment of peritoneal carcinomatosis in Israel is:
- high-quality examination of patients using the latest diagnostic techniques;
- highly effective therapy with innovative drugs;
- unique methods of surgical treatment;
- struggle to achieve results even among seriously ill patients.
Timely diagnosis allows you to achieve the best results in the treatment of peritoneal carcinomatosis.
↑ Top | Applying for treatment ↓
Classification
Experts classify diseases based on the location of metastatic lesions. There are three main forms.
P1
There is only one focus of the pathological process. It does not go beyond its borders and is characterized by local defeat.
This form is more treatable than others, since the mutated cells do not affect surrounding tissues.
P2
When conducting research, the presence of several pathological foci is established. They can have different locations and sizes.
A distinctive feature of the P2 form is that the metastases do not unite with each other. The areas of tissue between them are healthy.
P3
It has an aggressive course, accompanied by severe symptoms. It is characterized by the presence of multiple foci that merge with each other and form conglomerates.
As a result, a secondary tumor of a malignant nature begins to form.
Experts also use a technique for determining the lesion index. For this purpose, the scores for the measured lesions are summed up. They can vary from 0 to 3. In total, experts identify 13 areas where metastases form.
Symptoms by localization
To some extent, symptoms that become more and more clearly evident as the tumor grows indicate the localization of maxillary sinus cancer:
- Invasion into the nose and nasopharynx indicates posterior localization. The tumor becomes noticeable during rhinoscopy as a small pinkish formation of a loose structure that bleeds at the slightest touch. Accordingly, very often the patient has severe nosebleeds, bloody marks in the runny nose, and unpleasant sensations in the nose.
- Invasion into the eye socket. If the tumor located in the upper part of the maxillary sinus grows upward, then it gradually reaches the mucous membrane of the eye through the ethmoidal labyrinth, simultaneously affecting the optic nerves. Accordingly, paralysis of the motor nerve, severe visual disturbances due to disruption of the optic nerve, severe pain or lack of innervation in the ocular zone may develop.
- Invasion into the upper jaw. It is possible when the cancer in the maxillary sinus is lower localized. This leads to severe toothaches, swelling of one or both cheeks, severe inflammation, loosening and loss of healthy teeth. If the trigeminal nerve is damaged, severe pain in the facial area or a complete lack of sensitivity in the cheek area may occur.
- Germination into the pterygopalatine fossa. Usually occurs with lower posterior localization of the tumor. Quickly affecting soft tissues, the tumor affects the maxillary nerve, which provokes very severe pain, deformation of the face and upper lip, swelling and swelling in the cheek area.
But these are only general cases and their characteristic symptoms. In fact, cancer of the maxillary sinus can give a very different clinical picture, which largely depends on the structure and size of the tumor, its exact location in the nasal cavity and the individual characteristics of the body.
Causes
The main cause of the development of abdominal carcinomatosis is primary cancer. Mutated cells penetrate the peritoneal organs when the disease is at clinical stage 3 or 4.
Mutated cells, after being separated from the main formation, enter the blood and lymph and spread throughout the body.
Thus, secondary damage occurs, and over time their number increases. As the pathological process spreads through the tissues, they merge with each other. A secondary type of tumor begins to form.
Also, the causes of carcinomatosis are considered to be germination of the main formation into the walls of the peritoneum and improperly performed surgical intervention.
A distinctive feature of the disease is the damage to large areas of tissue at once, which complicates treatment and worsens the prognosis.
Symptoms and signs
Signs of carcinomatosis appear depending on the location of the primary tumor. Most often, ascites is observed, which in certain cases is the only manifestation with which patients present.
But often the clinical picture is clearly expressed. Symptoms include a sharp weight loss, an increase in abdominal volume, and dull, sharp pain.
During the examination, a violation of the digestive process is determined, which may be accompanied by constipation or diarrhea. Nausea and vomiting occur.
On this topic
- Oncogastroenterology
Feces for stomach cancer
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 6, 2020
Already at stage 2, pronounced signs of intoxication by the decay products of the primary formation are observed. These include fatigue, weakness, increased sweating, and increased body temperature.
When the metastatic lesion reaches a large size, it can be felt through the skin. But the signs of a primary neoplasm are more pronounced.
How is cancer detected?
Most often, a tumor of the maxillary sinus is discovered at an early stage by chance, when a strange darkening appears on an x-ray. It is worth paying close attention to, even if symptoms characteristic of cancer are still completely absent. And even more so if the patient regularly experiences:
- cloudy greenish-gray mucous nasal discharge;
- morning runny nose with traces or blood clots;
- recurrent nosebleeds;
- difficulty breathing or congestion in one of the nasal passages;
- neuralgic pain of the facial nerves;
- severe headaches, mainly in the evening and at night;
- damage to the optic nerves, visual impairment;
- a sharp drop in immunity, frequent acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections;
- loss of appetite, noticeable weight loss for no apparent reason;
- changes in body temperature, possible low-grade fever;
- constant inflammatory processes in the maxillary sinuses.
In this case, one x-ray is absolutely not enough to make an accurate diagnosis. It is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination, since cancer of the maxillary sinus can be so insidious that it is not detected even by histological studies.
How is diagnostics carried out?
First of all, the specialist conducts an examination and palpation examination of the abdominal cavity. In later stages, this makes it possible to establish the presence and location of a secondary tumor. In order to clarify the diagnosis, a number of instrumental research methods are prescribed.
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs
Ultrasound examination is prescribed to detect changes in the walls of the peritoneum. The procedure allows you to quickly identify a large lesion and quickly obtain the necessary data.
But in case of carcinomatosis, the technique is not the main diagnostic method, since it is not always informative.
Laparoscopy
The procedure is performed using a special device called a laparoscope. At one end there is a camera and lighting fixture. The image is transferred to the monitor.
With the help of laparoscopy for carcinomatosis of the abdominal cavity, a specialist is able to visually examine the mucous membranes and take a sample of pathologically altered tissues for further cytological examination.
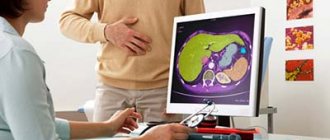
CT or MRI
Tomography is prescribed to determine the presence of foci of the pathological process, their number and area of distribution.
Magnetic resonance and computed tomography are one of the most informative methods for detecting metastatic lesions, as they allow layer-by-layer scanning.
MSCT and photodynamic therapy are used as additional diagnostic methods. The patient will also have to undergo a blood test.
Treatment methods
When carcinomatosis is diagnosed, therapy is carried out comprehensively. Patients are prescribed not only surgery, but also chemotherapy and drug treatment.
Operation
First of all, the primary tumor and lymph nodes affected by the pathological process are removed.
Surgery can prevent the mutated cells from spreading and causing new lesions.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy drugs are also used to treat metastases in the abdominal cavity. Today the intraperitoneal method is used. This is a modern method of treatment in which drugs are injected into the abdominal cavity using hot air.
The injected solution circulates continuously, destroying cancer cells within an hour. This technique allows you to reduce the risk of side effects and increase the effectiveness of therapy several times.
Drug therapy
In case of cancer, the use of medications does not bring a positive effect. Drugs are used only to relieve symptoms.
Painkillers are often prescribed. But with carcinomatosis, the painful sensations are strong and only a narcotic analgesic helps to relieve them.
In order to improve the digestion process, medications are prescribed aimed at maintaining perilstatics, restoring the functioning of the intestines, stomach and other gastrointestinal organs.
On this topic
- Oncogastroenterology
First signs of rectal cancer recurrence
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 3, 2020
If there are changes in the composition of the blood, intravenous administration of detoxification drugs is prescribed. This allows you to relieve signs of intoxication and improve your condition.
The patient is also prescribed diuretics, which are used to remove excess fluid from the body. All medications are selected individually.
Prices
| Disease | Approximate price, $ |
| Prices for examinations for stomach cancer | 5 730 |
| Prices for diagnosing Crohn's disease | 3 560 — 4 120 |
| Prices for diagnosing gastrointestinal cancer | 4 700 — 6 200 |
| Prices for hepatitis C diagnostics | 5 700 — 6 300 |
| Prices for treatment of Vater's nipple cancer | 81 600 — 84 620 |
| Prices for colorectal cancer treatment | 66 990 — 75 790 |
| Prices for treatment of pancreatic cancer | 53 890 — 72 590 |
| Prices for treatment of esophageal cancer | 61 010 — 81 010 |
| Prices for treatment of gallbladder cancer | 7 920 — 26 820 |
| Prices for treatment of nonspecific ulcerative colitis | 5 670 |
| Prices for treatment of stomach cancer | 58 820 |
| Prices for diagnosis and treatment of gallstone disease | 9 000 — 11 950 |
| Prices for the treatment of gastroenterological diseases | 4 990 — 8 490 |
| Prices for diagnosing Crohn's disease | 5 730 — 9 590 |
| Prices for treatment of viral hepatitis C and B | 5 380 — 7 580 |
| Prices for treatment of gastrointestinal cancer | 4 700 — 6 200 |
| Disease | Approximate price, $ |
| Prices for thyroid cancer screening | 3 850 — 5 740 |
| Prices for examination and treatment for testicular cancer | 3 730 — 39 940 |
| Prices for examinations for stomach cancer | 5 730 |
| Prices for diagnosing esophageal cancer | 14 380 — 18 120 |
| Prices for diagnosis and treatment of ovarian cancer | 5 270 — 5 570 |
| Prices for diagnosing gastrointestinal cancer | 4 700 — 6 200 |
| Prices for breast cancer diagnostics | 650 — 5 820 |
| Prices for diagnosis and treatment of myeloblastic leukemia | 9 600 — 173 000 |
| Prices for treatment of Vater's nipple cancer | 81 600 — 84 620 |
| Prices for treatment of colorectal cancer | 66 990 — 75 790 |
| Prices for treatment of pancreatic cancer | 53 890 — 72 590 |
| Prices for treatment of esophageal cancer | 61 010 — 81 010 |
| Prices for liver cancer treatment | 55 960 — 114 060 |
| Prices for treatment of gallbladder cancer | 7 920 — 26 820 |
| Prices for treatment of stomach cancer | 58 820 |
| Prices for diagnosis and treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome | 9 250 — 29 450 |
| Prices for leukemia treatment | 271 400 — 324 000 |
| Prices for thymoma treatment | 34 530 |
| Prices for lung cancer treatment | 35 600 — 39 700 |
| Prices for melanoma treatment | 32 620 — 57 620 |
| Prices for treatment of basal cell carcinoma | 7 700 — 8 800 |
| Prices for the treatment of malignant skin tumors | 4 420 — 5 420 |
| Prices for treatment of eye melanoma | 8 000 |
| Prices for craniotomy | 43 490 — 44 090 |
| Prices for thyroid cancer treatment | 64 020 — 72 770 |
| Prices for treatment of bone and soft tissue cancer | 61 340 — 72 590 |
| Prices for treatment of laryngeal cancer | 6 170 — 77 000 |
| Testicular cancer treatment prices | 15 410 |
| Bladder cancer treatment prices | 21 280 — 59 930 |
| Prices for cervical cancer treatment | 12 650 — 26 610 |
| Prices for treatment of uterine cancer | 27 550 — 29 110 |
| Prices for treatment of ovarian cancer | 32 140 — 34 340 |
| Prices for treatment of colon cancer | 45 330 |
| Prices for lymphoma treatment | 11 650 — 135 860 |
| Prices for kidney cancer treatment | 28 720 — 32 720 |
| Prices for breast reconstruction after cancer treatment | 41 130 — 59 740 |
| Prices for breast cancer treatment | 26 860 — 28 900 |
| Prices for prostate cancer treatment | 23 490 — 66 010 |
Possible consequences
Despite the fact that carcinomatosis is a complication of a cancerous tumor, it can also lead to certain consequences. They develop when the pathological process is widespread or in case of damage to the peritoneal leaves.
The most common complication of the disease is ascites, in which fluid begins to accumulate in the abdominal cavity.
Against the background of decreased immunity, patients experience frequent infectious diseases of internal organs, leading to the formation of interintestinal ulcers.
In addition, patients experience adhesive disease and peritonitis, which can take a purulent form.
Forecast
Carcinomatosis develops against the background of existing cancerous lesions of other organs and tissues, which worsens the prognosis.
In the case when the disease is diagnosed in a timely manner, and the pathological process affects a small part of the abdominal cavity, specialists are able to prolong the patient’s life for several years through surgical removal. But the final prognosis is established only after removal of the primary tumor.
Death occurs several months later if the pathological process affects most of the peritoneum. Modern treatment methods do not allow for recovery, but are used only to alleviate the patient’s condition.
That is why it is necessary to undergo diagnostic procedures prescribed by a specialist in a timely manner and regularly visit a doctor.
Probability of recovery
The level of development of modern medicine is such that in most cases, a diagnosis of cancer is no longer a final death sentence, as it was half a century ago. Laser surgery, new chemotherapy techniques, and ultra-modern radiological equipment make it possible to successfully treat even tumors in hard-to-reach locations.
At the first and second stages, cancer of the maxillary sinus is completely curable with timely initiation and proper treatment. Therefore, it is important here not to miss the moment when it begins to manifest itself with signs uncharacteristic of a common acute respiratory infection or sinusitis.
Unfortunately, there are still widespread fears about traditional methods of treating cancer that force people to turn to psychics and other “traditional healers” for help, to search for “home remedies for cancer” on the Internet, etc.
Yes, in isolated cases it works, but those for whom these methods did not help will not tell you about it - the disease won, ending their lives. Therefore, it is better to overcome your fear and trust the doctors.
The success of treatment of the third stage of maxillary sinus cancer largely depends on both the type of tumor and the area of its localization. The likelihood of a complete cure for an inoperable tumor is much lower, and if it is possible to completely remove it surgically, the patient’s chances increase significantly.
Stage 4 cancer can be completely cured only in 1-2% of cases, with very favorable circumstances and a strong positive attitude of the patient himself. At this stage, the biggest problem is multiple metastases affecting internal organs and a greatly weakened immune system by the disease.
A doctor’s vast experience and sensitive intuition are needed to select the optimal course of treatment, diet, give general recommendations and constantly motivate the patient to recover.