To clarify the clinical picture, in the presence of abdominal pain, it is important for the doctor to know their location, intensity, and duration. The phrase “iliac region” used by doctors is not clear to everyone. Therefore, it is worth understanding what it means. In the projection of the iliac region on the right and left are the most important organs from different body systems: digestive, genitourinary, vascular, therefore the presence of pain is evidence of the development of a pathological process in one of them.
The article discusses the most common symptoms and signs of diseases in which abdominal pain is located in the left or right iliac region. Also considered is a list of pathologies that can cause nagging, sharp, aching, dull, throbbing pain in the left or right iliac region, severe and sharp pain, throbbing, burning, cramping, stabbing pain in the left or right abdomen.
Classification of neoplasms in the ilium
Based on the structure and clinical manifestations, the following types of tumors are distinguished:
- bone-forming: enostosis, osteoid osteoma, osteosarcoma, osteoblastoma, osteochondroma, exostosis;
- cartilaginous: enchondroma, chondrosarcoma;
- bone marrow: Ewing's sarcoma, myeloma;
- tumor of vascular origin: hemangioma, hemangiosarcoma;
- other types: fibrosarcoma, lipoblastoma (wen), neuroma.
Osteoid osteoma of the ilium is typical for children and people under 30 years of age. It is small in size (up to 1 cm) and forms a growth that is difficult to distinguish from bone tissue. It is usually discovered accidentally in childhood.
Enostoses are benign tumors, reach 2 cm in size, and have the appearance of nodules. They do not pose a danger in themselves, so therapy is usually not prescribed. The exception is cases when the formation can cause fusion of the bone marrow canal. Enostosis of the wing of the left or right ilium occurs predominantly.
Osteosarcoma is the most common type of bone cancer. It is more common in men over adolescence. It usually affects the lower extremities. Characterized by an aggressive course.
Chondrosarcoma is a neoplasm in the ilium that affects cartilage tissue. It is the second most common type of sarcoma. The course is slow, with late metastases. Grows towards the bone marrow. Older people are more susceptible.
Ewing's sarcoma is predominantly found in the ilium. People under 30 years of age are susceptible to the disease. This is a fast-growing tumor that metastasizes early, and is classified as grade 4 malignancy. Difficult to diagnose due to its similarity to other small cell cancers.
Fibrosarcoma forms in long bones and the pelvis. She has a long asymptomatic period, which makes early diagnosis difficult. Metastases occur in the first 5 years.
In the early stages, the neoplasm in the ilium practically does not manifest itself in any way. Symptoms at the initial stage of the disease include:
- mild dull pain in the pelvis and buttocks, aggravated by walking;
- short-term increase in temperature to subfebrile (37).
As the tumor grows, the symptoms intensify:
- severe pain in the pelvic area;
- lameness;
- an increase in tumor size, which can become noticeable to the naked eye;
- intoxication of the body: weakness, weight loss, fatigue, fever;
- damage to organs in contact with the formation;
- disruption of the functioning of nerves and adjacent vessels.
Appendicitis
Inflammation of the appendix, the vermiform appendage of the cecum, is a fairly common disease, and in most cases requires surgical intervention. There is an acute and chronic form.
Acute appendicitis has 4 types:
- catarrhal;
- phlegmous;
- gangrenous;
- perforated.
The person experiences the following symptoms:
- Pain. In the first hours it may be “blurry” and not have a clear localization. Sometimes it hurts in the pit of the stomach, in the navel area. After a while, the right lower abdomen begins to hurt. If the process is located non-standardly, pain may occur in the pubic area, under the rib. Gradually it intensifies, becomes constant, unbearable, worsens with movement and coughing.
- Nausea and vomiting. May be isolated or repeated.
- Lack of appetite.
- Constipation or diarrhea. Everyone has an individual reaction.
- White coating on the tongue.
- Temperature rises to 38 degrees.
- Weakness.
When examining a patient, a test is often used: the patient should lie on his back with his legs extended. The doctor presses on the navel area and abruptly removes his hand. If the pain becomes stronger, then the diagnosis of appendicitis is correct. Also confirmed is the fact that the patient, lying on the right side, feels a dullness of pain, and on the left - intensification.
Sometimes renal colic is expressed by pain in the right iliac region. This is explained by the fact that a stone or sand is about to come out of the right kidney. Pain is also felt in the lumbar region and radiates to the groin. Moreover, it can be so strong that the patient, unable to tolerate it, turns to a medical institution with a request to relieve the pain.
We suggest you read: How to take Diflucan for pityriasis versicolor
The pathology sometimes gives a complication in the form of pyelonephritis, because the stone damages the mucous membrane of the ureter and kidney. Kidney dehydration (nephrocalcinosis) may also occur.
The reasons for the formation of kidney stones are varied:
- poor nutrition;
- hard water;
- hereditary factor;
- lack of mobility;
- taking certain medications;
- metabolic failure;
- small amount of liquid, etc.
There are connective tissues in the abdominal cavity, in which there are sometimes openings. They may involve certain parts of the intestine. Thus, a hernia may form in the right iliac region. Pains occur (dull, aching, cutting), which subside in a certain position of the body.
There is only one way to treat this disease - surgery, but before that, diagnosis is necessary.
Crohn's disease
A chronic disease in which various parts of the intestine become inflamed, has an immunological cause, and can develop in a child. The disease is always associated with lymphadenitis.
Characteristic symptoms:
- stomach ache;
- lack of appetite;
- nausea, vomiting;
- heat;
- diarrhea;
- weakness.
Treatment is medicinal and surgical.
The inflammatory process in the bursa (a sac of fluid that is located between ligaments, muscles and joints) occurs when playing sports, frequent and repeated stress on the muscles. Pain is felt in the iliac fossa and radiates to the leg or buttock. If the aorta is damaged, an iliofemoral bypass may be prescribed, which allows blood flow to follow a new channel, bypassing the damaged vessel, thanks to the inserted shunt.
General symptoms
Whatever the reasons for the diseases, they all have the same symptoms:
- increased gas formation;
- stool disorder;
- pain;
- loss of appetite;
- vomit.
The pain is localized in various parts of the abdominal cavity: in the pit of the stomach, in the navel area, in the right side of the abdomen. It can be pulling, aching, bursting. Typically, pain decreases after the passage of gas and bowel movements.
The symptoms of the disease are influenced by the degree of development of the pathological process. During exacerbations, intense pain, weakness occur, and blood appears in the stool.
With lesions of the ileum, the process of breakdown and absorption of vitamins, amino acids, and minerals is disrupted. The patient may develop anemia, xerosis (dryness) of the skin and eyes.
What diseases are localized within this area
Pain in the iliac fossa signals a disease. The pain can be constant or periodic, sharp and aching. They can appear during heavy physical exertion, prolonged absence of stool, overeating and for no apparent reason.
Painful attacks in the iliac region most often signal diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. But next to them are the genital and urinary organs, so the cause of the pain may be different.
If you have a stomach ache on the right or left side, you need to see a therapist. If necessary, he will recommend visiting specialized specialists: proctologist, gynecologist, surgeon, gastroenterologist.
After studying the external signs and symptoms, the doctor will make an accurate diagnosis. In some cases, colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy of the intestines, ultrasound of the kidneys, gallbladder, pancreas and pelvic organs, and fibrogastroscopy may be required.
Remember that pain in the lower abdomen may indicate a serious health problem and the need to seek urgent emergency care.
If pain is severe, you should not take analgesics. Many of them effectively reduce sensitivity, thereby making diagnosis more difficult.
The most common diseases that cause pain in the iliac region:
- inflammation of the appendix.
- inflammation of the iliac lymph nodes and retroperitoneal tissue.
- sigmoid colon volvulus.
- gynecological diseases.
- inflammation of the seminal vesicles.
- complications after prostatitis.
- abscesses of the iliopsoas muscle.
- osteochondrosis.
- urological disorders.
- intestinal dysbiosis.
- helminthic lesions.
- inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract.
- femoral and inguinal hernia.
General symptoms of diseases
The ileum, diseases of which can arise for various reasons, almost always makes itself felt by general signs of malaise. These include the following:
- pain syndromes;
- stool disorder;
- rumbling in the intestines;
- increased gas formation.
Quite often, patients complain to their doctors that they have diarrhea for a long time with trips to the toilet up to 4-7 times a day. In this case, undigested food remains may be found in the stool. In the first half of the day, the patient often feels rumbling in the intestines, which usually subsides only in the evening.
The affected ileum sometimes causes pain. They can have different localization (in the umbilical region, to the right of the midline of the abdomen and under the “spoon”) and character (bursting, pulling and aching). As a rule, the intensity of such pain decreases noticeably after the gases that have formed are released.
What does pain in the left side of the iliac region mean?
Painful sensations can signal diseases associated with the gastrointestinal tract. With inflammation of the wall of the large intestine (colitis), aching pain appears with bloating, false urge to defecate, and diarrhea with mucous admixture. These symptoms last from several days to several weeks. If you do not consult a doctor, the disease becomes chronic and occurs with periodic exacerbations.
Colic in the left side, worsening after eating and accompanied by frequent bowel movements, bleeding from the anus, can be caused by ulcerative colitis. To diagnose the disease, histological and endoscopic examination will be required.
Lesions of the sigmoid colon (tumors, bleeding ulcers) are accompanied by a painful urge to defecate and frequent loose stools. There are admixtures of blood and pus in the stool. With congenital elongation of the sigmoid colon (dolichosigma), the same symptoms are observed. The diagnosis of sigmoid colon cancer is based on data from sigmoidoscopy, fibrocolonoscopy and biopsy.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with: Formation of seborrhea of the scalp Measures for the prevention and treatment of seborrhea
Pain caused by intestinal narrowing and ulcers, and nighttime diarrhea may indicate Crohn's disease. With complete narrowing of the intestine, spastic pain, vomiting, and lack of stool occur. Crohn's disease is determined after irrigoscopy, endoscopic examination with biopsy. With intestinal obstruction in the left part of the iliac region, cramping pain occurs at any time, regardless of food intake. It is often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, bloating, and stool retention.
More severe symptoms (lack of stool, sharp pain, difficulty breathing) indicate volvulus of the sigmoid colon or small intestine. To confirm the diagnosis, X-rays and ultrasound examinations of the abdominal organs are performed. If such symptoms occur, seek medical help immediately. There is a high probability of intestinal rupture and the development of peritonitis.
Pain in the left lower abdomen with intestinal cancer is usually poorly expressed. Tumors interfere with the movement of feces, so the disease is accompanied by persistent constipation and bloating. After the passage of stool and gases, the pain temporarily stops. Data on the condition of the intestinal mucosa obtained during colonoscopy help confirm or exclude the disease and clarify the location of the tumor.
Parasites that live in the small intestine can cause pain in the lower left side of the abdomen. Helminthiasis contributes to the development of intestinal obstruction. Pain in the left part of the iliac region occurs with: hepatitis, stomach ulcers, chronic gynecological pathologies, dilated veins in the pelvis, ectopic pregnancy. They are usually accompanied by other symptoms.
Only a specialist can identify the pathology and prescribe treatment.
The cecum is located in the lower right part of the abdomen. A vermiform appendage extends from it. Fecal stones and undigested food clog the entrance to the rectum. Due to the blockage, the appendix swells and stretches. Pathogenic bacteria are involved in this process. Painful sensations during inflammation of the appendix vary in nature and are almost not bothersome at the initial stage.
Please note that inflammation of the appendix is sometimes fatal!
Usually, additional examinations are not necessary to determine appendicitis. But it can be confused with intestinal obstruction, inflammation of the lymph nodes of the intestinal mesentery (mesadenitis), pyelonephritis, ectopic pregnancy, rupture of an ovarian cyst. In some cases, laparoscopy or computed tomography is required to diagnose appendicitis.
Pain in the right lower abdomen is characteristic of inflammation of the ileum (enteritis). It is accompanied by diarrhea, nausea, and the release of undigested food debris. To distinguish enteritis from other diseases, the patient is prescribed an endoscopic and x-ray examination, ultrasound of the pancreas.
Pain in the right side of the iliac region in the presence of stones in the gall bladder, perforated ulcer, pyelonephritis of the right kidney.
Damage to the appendages, uterus and bladder, and genital infections also cause pain in the right lower abdomen. Constant pain in some cases signals the presence of an ovarian tumor. Painful impulses coming from the lower abdomen warn of problems with the seminal vesicles in men or prostatic hyperplasia.
Each of these diseases is serious and can significantly reduce quality of life, and some can lead to death.
Treatment of diseases of the ileum
Crohn's disease and other dangerous illnesses can be fatal. Lymphoid hyperplasia appears against the background of an immunodeficiency state. Proliferative changes are observed on the intestinal walls. They can be transitory and disappear just as easily as they appear. This is how the body reacts to external stimuli. Diagnosis of diseases allows us to find the causes of a person’s illness. If the function of the ileum is impaired, a comprehensive examination will help determine this. The doctor examines the patient and asks what he is complaining about. An accurate diagnosis can be made using the results of stool, urine, blood tests and fiber endoscopy.
Delayed presentation may require surgery. In the first stages of disease development, drug treatment is used. The doctor also prescribes a strict diet. The patient should eat only foods that are quickly and easily absorbed by the body.
You need to include a lot of vitamins in your menu. The patient is prohibited from drinking alcohol and smoking. Addiction to bad habits negatively affects the health of the intestines. Heavy foods are excluded from the diet. The patient is contraindicated in consuming large amounts of salt and fat. He is not recommended to eat bitter, spicy and fried foods. You will need to give up mushrooms and meat and fish, which take a long time to digest.
The diet may include porridge, omelet, tea and compote. An excellent drink for the immune system is rosehip decoction. Sea buckthorn oil will help a lot. 50 ml should be drunk on an empty stomach every day. You can have breakfast only 2 hours after eating. A healing drink can be prepared from flax seeds. A teaspoon of seed is poured into a glass of boiling water. The infusion is left for 30 minutes.
It needs to be stirred from time to time. The drink is drunk on an empty stomach 1 hour before meals. Compliance with the diet and strict doctor’s instructions will help put the patient on his feet. The main thing is to be treated until complete recovery. It is necessary to include in the daily menu products that do not cause discomfort and allergies. If you monitor all the changes in your body, then everything can be corrected. After completing the course of treatment, you can return to normal life.
Establishing diagnosis
Tumor of the ilium on x-ray
The main way to diagnose an iliac tumor is an x-ray. The entire pelvis is examined, pictures are taken in several projections. The presence of a neoplasm will be indicated by: areas of rarefaction in the iliac bones, hypodensity, growth into soft tissues.
We suggest you read: Specifics of the formation of fungal pneumonia in humans
Other methods are also used:
- blood analysis;
- computed tomography (CT);
- MRI with layer-by-layer visualization of the primary tumor;
- scintigraphy;
- Ultrasound;
- radioisotope bone scanning;
- angiography;
- biopsy of tumor fragments.
Diagnostics
Since the disease is characterized by the proliferation of the mucous layer, its localization in the stomach and intestines can be detected using endoscopic methods (FGDS, colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy), as well as during X-ray examination with contrast. During X-ray diagnostics, using contrast distribution, you can determine the degree of proliferation of newly formed tissues. And with endoscopic methods, it is possible to obtain altered tissue for histological examination.
Damage to the endocrine system is characterized by changes in the blood picture with high lymphocytosis. A significant increase in lymphocytes should always alert the doctor.
With a confirmed diagnosis of Lymphofollicular hyperplasia, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations, because abnormally overgrown tissues have a tendency to become malignant. And if this happens, then early detection of the process contributes to a good prognosis.
Therapy methods
Based on the examination results, the doctor prescribes the necessary treatment. In acute appendicitis, urgent surgery is recommended.
Crushing kidney stones
Urolithiasis requires nutritional correction, drinking regimen, and exercise therapy. Surgical intervention is prescribed only for large stones. Urology offers a fairly large selection of therapeutic methods: DLT (remote crushing of stones), endovesical method, ureterolithoextraction, contact lithotripsy, various drugs for dissolving stones and their painless release, antispasmodics.
Crohn's disease is treated with intestinal antibiotics, hormonal drugs, immunosuppressants, biological products, and vitamin complexes. Vitamins must be taken because the intestinal absorption of vitamins from food is impaired. It is important to follow a diet: smoked foods, fried foods, alcohol, fresh milk, borscht, and baked goods are excluded. You need to eat meals in small portions throughout the day.
The operation is performed only in life-threatening cases:
- intestinal obstruction;
- perforation of the intestinal wall;
- peritonitis;
- intestinal bleeding;
- fistula.
During surgery, the affected area of the intestine is removed, then the remaining areas are connected.
Inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs, which also cause pain in the iliac region, are treated with antibacterial drugs, painkillers, and physiotherapy.
In case of ectopic pregnancy, urgent surgery is recommended. For dysbiosis, prebiotics are prescribed. Helminthiasis is treated with anthelmintic drugs.
Cellulitis is opened under anesthesia, an incision is made a centimeter above the inguinal ligament. If the pus has reached the pelvis, the incision is continued to the pubic bone.
The choice of treatment plan for iliac bone cancer depends on the location, structure, size of the formation, the general condition of the patient, his age, and the severity of the medical history.
The main treatment methods are:
- surgical removal of the tumor;
- radiation therapy;
- chemotherapy.
This mainly involves surgery and chemotherapy, since radiation for iliac bone cancer does not have sufficient effect.
The most common treatment regimen:
- removal of the primary tumor by resection of the formation and surrounding tissues;
- removal of metastases;
- chemotherapy;
- irradiation of the lesion if necessary;
- rehabilitation.
Chemotherapy for iliac cancer lasts from 8 months to a year. It has two periods: preoperative and postoperative. The first period lasts several weeks and helps to shrink the tumor to make it easier to remove. The second lasts several months and is carried out to destroy the remaining cancer cells in the body. The chemotherapy regimen is selected individually, based on the characteristics of the tumor and the patient’s condition.
Surgical removal is the preferred treatment method. They try to remove the tumor without damaging it, cutting out the edges right down to the healthy tissue. At the same time, they try to preserve the bone, subsequently reconstructing the defect.
For some types of cancer, surgery is not possible. Ewing's sarcoma is diagnosed at a stage when multiple metastases are present, so new chemotherapy regimens are introduced, total irradiation and stem cell transplantation are performed.
The nature of pain in pathologies of the colon
Weight loss is a sign of colon pathology.
Pain due to pathology of the colon has a unique localization. They are often felt on the side of the abdomen and near the anus.
Less common are unpleasant sensations in the epigastric region, as well as above the navel.
Even in the absence of pain, there will be pain when palpating the area in the iliac region on the right and left.
They become more intense if a person drinks milk or eats a lot of vegetables or coarse cereals. The main character of the pain is aching, accompanied by a feeling of fullness.
If the intestines are freed from gases and feces, the pain subsides. However, immediately before defecation, the pain may become more severe. Sometimes they are cramp-like in nature.
To alleviate the condition, it is recommended to use a heating pad and take enzymes. Pathology of the large intestine can be distinguished from diseases of the small intestine by the absence of the following signs:
- weight loss;
- metabolic disease;
- hypovitaminosis.
However, signs of general malaise are also present. Patients quickly get tired, feel weak, irritable, tearful, and their sleep is disturbed. In general, there are signs of intoxication, which is provoked by frequent constipation.
Preventive measures and prognosis
There is no specific prevention. After treatment, all patients are under the supervision of an oncologist and undergo regular preventive examinations and examinations. It is important to carefully note any changes in health status and monitor the appearance of warning signs.
In the first two years, the patient is examined every 3 months, in the third year - once every 4 months, in the fourth - twice a year, and after five years, visits to the doctor become annual. If complaints arise between examinations, a visit to the oncologist is carried out unscheduled.
The five-year prognosis for pelvic cancer in case of timely treatment is favorable - 80-90%. In the low-risk group (tumor weight up to 70 ml), up to 97% of patients survive. At high risk – up to 40%.
Intestinal tumors
Two types of neoplasms develop in the colon.
Benign and malignant neoplasms very often develop in the colon. At the same time, the championship belongs to the latter.
Many people suffer from colon cancer, and especially rectal cancer.
Moreover, it is the left part that is mainly affected (3/4 of all cases). The largest number of cases are among people over 50 years of age.
The older a person is, the higher the risk of developing this pathology. The following groups of people are considered to be at risk:
- whose diet is dominated by foods rich in animal fats;
- affected by colon polyps;
- those suffering from ulcerative colitis;
- with a family history;
- with a history of colon cancer.
It is almost impossible to detect cancer in its early stages. As a rule, people simply do not pay attention to constipation and minor abdominal pain. The only thing that is alarming is blood in the stool, and even then it can be classified as a manifestation of hemorrhoids.
If the tumor is on the right, the temperature rises, weight goes away, and diarrhea becomes too frequent. If the tumor is on the left, then you will suffer from constipation, the pain will be cramping in nature.
Structure
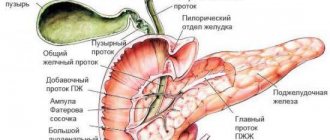
The iliac region is located in the lower part of the abdominal cavity, covering its sides, as well as the lower abdomen. In order to ensure high-quality diagnosis and control over the health of the internal organs of the digestive and genitourinary systems, the ileum is divided into 2 main structural segments. This part of the body has the following structure.
The iliac region consists of the left and right parts
| Name of the structural part of the iliac region | Location in the abdominal cavity |
| Left | This part of the iliac region is located inside the abdominal cavity in the space between the lower left row of ribs and the ilium. |
| Right | The right iliac fossa covers the abdominal cavity from the right side from the lower ribs to the ilium. |
If we look at the anatomical structure of this part of the peritoneum in the pictures, we get the visual impression that the left and right iliac regions are located directly above the lateral part of the pelvic bones or directly above the hip joints.
Both parts of the ileum are located opposite each other and perform a single physiological function as a reservoir for the internal organs of the digestive and genitourinary systems.