Thick bile is not yet a disease, but it can lead to such a serious condition as the formation of gallstones. At first, sediment only forms, which accumulates and forms persistent stones. Subsequently, they can enter the bile ducts, block the outflow of bile and provoke acute cholecystitis. This condition is urgent and requires urgent surgical intervention, consisting of cholecystectomy.
Gallbladder filled with stones
Functions of bile
Bile is needed by the body to digest food. The substances contained in this liquid contribute to the change from one type of digestion to another. In addition, bile is necessary for the emulsification of fats and the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. Bile also contains large molecular compounds that cannot be excreted from the body through the kidneys.
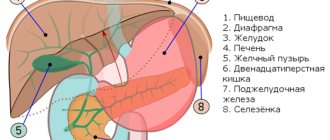
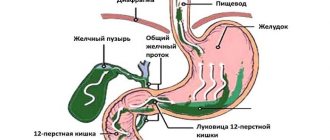
The stage of digestion itself, in which bile participates, occurs in the duodenum. Bile synthesis begins in liver cells. After this, it gradually collects in the intrahepatic bile ducts and enters the gallbladder.
The bladder consists of several layers: mucous, muscular and serous. The exit from the bladder is limited by a muscle ring - the sphincter, which opens when eating. During food intake, the muscle layer of the bladder becomes toned, and the sphincters that close the exit to it open, so that bile can enter the duodenum and participate in digestion.
Due to various pathological processes associated with changes in the chemical composition of bile, it can stagnate, increase its density and become thick.
Causes of thickening of bile secretions
When food enters the stomach, the gallbladder begins to contract, due to which bile also enters the stomach through the ducts. This process, which ensures proper digestion (breakdown and absorption) of food, is possible only if the bile secretion has a normal consistency and there are no obstacles in its path.
There are many factors that provoke an increase in bile viscosity:
- Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract or pancreas;
- Increased cholesterol levels . It occurs due to excess intake of fatty, spicy, smoked foods, as well as marinades. Low-density lipoproteins (the so-called “bad” cholesterol contained in these products) saturate the bile, leading to its thickening, and subsequently to the formation of clots (biliary sludge) and calculi (stones).
. Nutrient deficiency is directly related to increased bile viscosity.
Strict unbalanced diets- Constant stress . It has been proven that the likelihood of increased bile viscosity is higher in choleric people. In stressful situations, the gallbladder contracts (even to the point of spasm) and its ducts narrow. The outflow of bile slows down and stagnates, which leads to the formation of sand or clots.
- Uncontrolled use of medications . The risk of bile thickening is higher in patients who take various medications for a long time or independently increase the dose taken, without taking into account existing contraindications.
- Physical inactivity . Thickening of bile secretion due to its stagnation most often develops in people leading a sedentary lifestyle (seamstresses, drivers, office workers), as well as in patients with excess body weight.
Why does bile become thick?
An increase in the thickness of bile can result from several reasons, both pathological and physiological in nature:
- Functional disorders (dyskinesia);
- Organic pathology (tortuosity, stenosis of the bile ducts);
- Physiological reasons associated with loss of fluid by the body. When the water balance is normalized, bile dilution occurs almost immediately.
Bile thickens automatically when it stays in the gallbladder for a long time. This is due to the fact that the mucous layer begins to attract liquid, increasing the concentration of large molecular compounds. As a rule, this effect can be observed with functional disorders in the functioning of the gallbladder, when excessive tension or relaxation of the muscle layer occurs. This pathology is commonly called dyskinesia of the bile ducts.
Dyskinesia can be of hypertonic or hypotonic type. In the first case, a violation of the outflow of bile occurs due to a lack of coordination in the muscular apparatus of the biliary tract. Normally, the muscle layer of the bladder wall should contract and the sphincter should open, but with pathology, both contractions occur. As a result, bile cannot exit and enter the duodenum. With the hypotonic type, the opposite happens - the muscle layer of the bladder does not shrink and does not give a “push” for bile to enter the digestive tract.
How to thin bile
If thick bile is diagnosed, it is important to avoid stone formation. At the initial stage, it is enough to change your diet and food preferences:
- give up fatty and spicy foods;
- reduce the consumption of animal fats and vegetable oils;
- Maintain a drinking regime (at least 2 liters of clean water per day).
To maintain the functioning of the gallbladder, doctors select drugs that help produce enzymes. The process of digesting food is easy, without pain and an unpleasant taste of bitterness. Natural based medicines are the most effective. They contain plant extracts and dried animal bile, relieve bloating and pain.
Tubage helps stop a painful attack. During the procedure, a probe with a drug is inserted into the duodenum, which removes bile and prevents its accumulation in the ducts. The bubble is cleared of salts and clots and restores function.
At the initial stage, herbal treatment helps improve the structure of bile. The most useful for thinning and improving digestion: lingonberries, turmeric, tansy, artichoke. But remember that extracts have a choleretic effect, so they are dangerous in the formation of stones.
Symptoms
Symptoms of thick bile in the gallbladder directly depend on the initial disease. Most often, dyskinesia leads to stagnation and increased density of bile. Despite the common name, hypotonic and hypertensive dyskinesia are two different pathologies with differences in pathogenesis and symptoms.
With the hypotonic type, the pain will have a pulling and aching character. Some patients have no pain, but instead there is a bursting feeling of discomfort in the right hypochondrium. Increased gas formation in the intestines is also often observed. A characteristic sign of this disorder is the normalization of the patient’s condition after taking choleretic drugs.
With hypertensive dyskinesia, the pain will be more intense, stabbing in nature, and localized in the right hypochondrium. As a rule, pain is observed almost immediately after eating fatty foods. They are spastic in nature, similar to biliary colic. Sometimes the pain radiates to the area of the right shoulder blade, right arm or lower jaw.
Typical localization of pain in biliary colic
Species diversity of sludge
There are several criteria by which pathology in adults and children is classified. A child's predisposition to thickening of bile may be genetic.
Based on the composition, the following types of sludge are distinguished:
- Microlithic. In this case, small inclusions appear that can move depending on the position of the body. The bile suspension contains cholesterol crystals, protein, calcium salts, and fats.
- Putty-like bile. Consists of clots. Their movement can be noticed during an ultrasound examination, that is, biliary ultrasound. It studies the bile inside the bladder and duct. Biliary fluid is the scientific name for secretion.
- Mixed sludge. It has a consistency reminiscent of both previous types. Bile clots are combined with a suspension of grains of cholesterol, proteins, and salts.
Typically, one component predominates in the composition of bile:
- calcium salts;
- cholesterol crystals;
- bilirubin compounds.
Bilirubin is a pigment in bile. The substance is red-brown. The color is due to the function of bilirubin. The compound utilizes destroyed red blood cells. Bilirubin accumulates in bile during intoxication of the body.
Depending on which components predominate in the sludge, the doctor prescribes a specific treatment.
According to the mechanism of development of the pathology, the syndrome is divided into:
- To primary. Flakes form independently without the presence of other pathologies.
- Secondary. The cause of the disease is disruption of the gallbladder and other concomitant diseases. Signs (symptoms) of bile clots in the gallbladder appear against the background of cholelithiasis or pancreatitis.
A sharp weight loss also leads to sedimentation of bile. In the case of secondary pathology, thick bile in women and men “gives” symptoms characteristic of acute forms of the disease. The temperature may rise, pain and nausea become intense.
Diagnostics
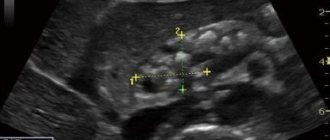
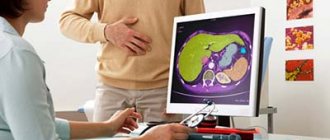
Thick bile is very clearly visible during an ultrasound examination. Normally, bile has reduced echogenicity and visually on the monitor resembles water, blood or other fluid in the body. However, if the outflow is disrupted, the bile begins to acquire a lighter shade, which indicates its compaction. Ultrasound can also assess the patency of the biliary tract and the presence of stones in the gallbladder. It must be remembered that ultrasound should be performed on an empty stomach and it is advisable to not consume foods that promote gas formation a few days before the examination.
Stagnant bile on ultrasound examination
There is also a special test that allows you to evaluate the density and composition of bile - duodenal intubation. The examination is painless, but very unpleasant. The end of the probe is placed on the root of the patient's tongue and, using swallowing movements, is pushed to the stomach. After this, the patient is placed on the right side so that the probe can enter the duodenum, where bile is collected.
How it manifests itself
Did you feel discomfort in your right side under your ribs? This is the first hint to visit a specialist. But there are a few more symptoms that are better to be aware of:
- insomnia and a feeling of causeless anxiety;
- attacks of nausea and even vomiting on an empty stomach;
- swelling and pain in the throat and neck area;
- discomfort and itching in the feet, mainly during the day;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- excessive activity of a person, previously not characteristic of him.
Each symptom of the above is a reason to go to the doctor. And he will already prescribe the necessary examinations to make a diagnosis. Most likely the following will be carried out:
- examining and listening to patient complaints;
- ask questions about the presence of similar pathologies in other family members;
- feels the stomach to understand the degree of pain;
- prescribe blood, urine and stool tests;
- blood biochemistry;
- Ultrasound will assess the condition of the organ;
- probing to determine the amount of bile;
- CT and MRI.
Treatment
How to liquefy bile in the gallbladder? The basis of any treatment is lifestyle modification and it is advisable to start with lifestyle correction. To begin with, the patient can be advised to lose excess weight and begin to lead an active lifestyle. Physical exercise helps improve digestion and blood circulation in the organs in the gastrointestinal tract, which has a beneficial effect on motility in the gallbladder.
Diet
Normalization of nutrition is the basis in the treatment of many gastroenterological diseases. The diet for stagnation of bile in the gallbladder consists of several important points:
- Food must be taken in small portions and fractionally, at least 6 times a day. It is best to divide the standard portions into two and spread the intake throughout the day;
- It is forbidden to go hungry. When the number of meals is reduced, bile begins to stagnate, which leads to its thickening;
- Food should be balanced, contain fats, proteins and carbohydrates. It is best to give preference to vegetable fats (sunflower, olive, pumpkin);
In addition to normalizing nutrition, it is also recommended to consume foods that dilute bile (rose hips, spinach, cabbage, tomatoes, beet juice).
How is thickened bile secretion treated?
Depending on the stage of the disease, the medical professional prescribes a treatment plan. In some situations, therapy allows the patient to be treated at home, on an outpatient basis; in other cases, a person requires medical supervision and inpatient treatment.
If large stones and a large amount of suspended matter are diagnosed in the gallbladder, this problem cannot be solved conservatively - surgical intervention is necessary. As a rule, such operations are performed endoscopically, through a small puncture of the peritoneum. But if the disease is extremely advanced, complete removal of the gallbladder is possible.
In situations where thickening of bile has not yet caused serious harm, three most important categories related to therapeutic treatment can be distinguished: pharmaceuticals, supporting traditional medicine recipes and diet. Let's talk about all three components of therapy in more detail.
Pharmaceutical products for the treatment of thick bile
Pharmaceutical drugs prescribed by doctors for the treatment of the gallbladder, in which thickening of bile is observed, are divided into three large groups: synthetic choleretics, hydrocholeretics and bile-thinning herbal agents.
The group of synthetic choleretics (SC) includes drugs that stimulate the motor and secretory function of the gallbladder, providing a choleretic effect. The main function of such drugs is to prevent the formation of congestion in the organ and enhance bladder peristalsis.
Table 2. Drugs of the CX group
| Name | Action | approximate cost |
| "Nikodin" | Choleretic, bile-thinning agent. Increases the secretory function of the liver and gall bladder. Anti-inflammatory, bactericidal effect, facilitating the release of bile into the intestines. | 100 rubles for 10 tablets |
| "Odeston" | Strengthens the synthesis of bile, accelerates its evacuation into the intestinal lumen. Relieves spasms of the walls of the bile ducts, reduces cholesterol, increases the volume of bile secretion produced. | 400 rubles for 20 tablets |
| "Oxafenamide" | Restores the functions of the liver and gall bladder, relieves spasms, reduces cholesterol, and increases the flow of bile secretions. | 70-100 rubles for 50 tablets |
| "Cyqualon" | Helps to enhance the formation and separation of bile, relieves inflammation, and prevents the formation of stones. | 160-190 rubles for 20 tablets |
Hydrochoderetics (HC) include waters with a special mineral composition (magnesium, sulfate ions, sodium), which reduces the absorption of fluid in the gall bladder and equalizes osmotic pressure. A mineral water with this composition dilutes bile without causing harm to neighboring organs and the body as a whole. These include: Essentuki 4 and 17, Borjomi, Narzan, Arzni.
Herbal remedies (RS) contain the necessary substances, vitamins, phytoncides, trace elements and essential oils needed by the gallbladder to restore functionality. They stimulate the liver, help activate gallbladder motility, relax the muscles of the bile ducts, thin bile, and improve intestinal motility.
Table 3. Drugs of the MS group
| Name | Action, composition | approximate cost |
| "Allohol" | Stimulates muscles and enhances the secretory function of the gallbladder and ducts, choleretic. Contains condensed bile, freeze-dried garlic, nettle leaves, activated carbon, calcium. | 70-90 rubles for 25 tablets |
| "Holenzym" | Choleretic effect, normalizes digestive processes, facilitates the digestion of fats, carbohydrates and proteins. Contains condensed bile, dried pancreatic gland powder, powder of dry crushed membranes of the small intestine of cattle. | 200-250 rubles for 50 tablets |
| "Vigeratin" | Effectively protects the liver and gallbladder, dilutes bile, and prevents the development of anemia. Contains cattle liver extract and pancreatin. | 100 rubles for 50 tablets |
| "Holiver" | Increases bile secretion, has antiseptic properties, removes toxins. Contains medical bile extract, artichoke, turmeric. | 300 rubles for 100 tablets |
| "Hologon" | Treats inflammatory processes of the gallbladder and ducts. Choleretic. Strengthens the secretion of bile and reduces its viscosity. Contains dehydrocholic acid. | 70 rubles for 10 tablets |
| "Liobil" | Strengthens the outflow of bile, the secretory function of the gallbladder, relieves inflammation, stimulates the breakdown and absorption of fats. Contains bovine liver enzymes. | 150-170 rubles for 100 tablets |
In addition, the following medicinal herbs are classified as choleretic, which can be purchased at a pharmacy and brewed according to the instructions:
- Tansy;
- Buckthorn;
- Birch buds;
- Corn silks;
- Rose hip;
- Immortelle;
- Tatarnik;
- Hop.
Traditional methods of treatment
If the use of ready-made pharmaceutical preparations is more related to the classical treatment of condensed bile, then combined herbal and vegetable decoctions, as well as vegetable oils, are recipes from alternative medicine specialists. Here are several recipes that have proven themselves among thousands of patients struggling with bile thickening.
One of the effective and gentle ways is to use olive oil. To use it, you should purchase olive oil without refining, first pressing. The oil is drunk in the morning, before breakfast, in the amount of a tablespoon. Olive oil contains fat-soluble acids that help normalize cholesterol metabolism.
An herbal mixture made from dandelion roots, corn silk, wormwood, plantain, and chicory has an effect that improves bile flow. Dry ingredients are taken in equal proportions and then mixed. Pour a tablespoon of raw material into a glass of boiling water and leave for about 20 minutes. After cooling, the infusion is filtered and consumed one third of a glass half an hour before meals three times a day.
Another good recipe is made using beets. A medium-sized fruit is poured with three liters of water and boiled until the liquid becomes a second less - that is, until it evaporates to one liter. Then the beets are pulled out, grated and boiled in the same water for another quarter of an hour. The finished broth is cooled, filtered and drunk in a glass five times a day.
Diet for bile stagnation
We mentioned above that a properly composed menu is an important part of the entire treatment. In order for more bile to be produced and for it to spread well through the intestines, it is necessary to include saturated vegetable oils in the diet: olives, peanuts, corn, walnuts. They are good for seasoning vegetable salads and porridges.
Among the products there are also those that provoke the secretion of bile secretion and prevent its thickening, as well as prevent the formation of stones. These include grapes, cabbage, tomatoes, spinach, and carrots. Compliance with the drinking regime plays a significant role. Thickening of bile often occurs due to general dehydration of the body, so every day you need to drink at least one and a half liters of pure water, rosehip decoction, and unsweetened freshly squeezed juices.
Like any disease of the gastrointestinal tract, bile stagnation requires the exclusion of unhealthy, heavy foods from the menu: smoked foods, spicy foods, fatty and fried foods. It’s not easy for even a healthy person to digest them, and if you have problems with the gallbladder, such a menu can even provoke a sharp deterioration in your condition. You need to build your diet on vegetable or fish soups, vegetable salads, light side dishes (rice, broccoli, stew). The meat should be lean, boiled or steamed.
What to do and how to treat thick bile?
Such a pathological condition associated with stable circulation of bile in the ducts requires complex treatment. For this purpose, both traditional medicines are used, and a special diet is formed that helps dilute the bile. Let's consider all areas of the therapeutic course that restores the normal consistency of bile secretion.
Drugs
Modern pharmacology offers three main groups of medications designed to thin bile that is too thick. These are choleretics, synthetic hydrocholeretics and extracts of medicinal plants. The latter contain a completely natural biochemical formula and have a minimum number of side properties and contraindications.
The following drugs are used in medical practice:
- Holenzyme;
- Allohol;
- Digestal;
- Oxafenamide;
- Enzistal;
- Panzinorm.
Which particular remedy to choose for treating a patient, its dosage and the duration of the therapeutic course are determined exclusively by the gastroenterologist who is seeing the patient.
Each clinical case is individual, so some people may need 10 days to restore the normal consistency of the bile secretion, while another person with a more complex case of the disease will need at least 1 month for the thickness of the bile to return to normal. Self-treatment is strictly prohibited, as it can cause an exacerbation of the disease and a deterioration in the general condition of the digestive system.
Bile thinning foods
There are certain types of foods that help thin bile that is too thick, while others, on the contrary, have the opposite properties. Patients with concentrated and viscous bile are recommended to adhere to the following menu:
- fresh vegetable salads with plenty of parsley, dill and other herbs, seasoned with sunflower oil;
- cereal porridges cooked in water without adding butter;
- oven-baked fruits;
- stewed cabbage or vegetable stew;
- chicken broth, which is used with gray, slightly stale bread or crackers;
- not strong green tea with sugar;
- lean chicken breasts, steamed or boiled in lightly salted water;
- berry jelly, rose hip compote, chamomile tea;
- pasta made from durum wheat.
Before creating a dietary menu, it is recommended to have a preliminary consultation with your doctor. It is possible that the doctor will advise you to include additional foods in your diet, which will also help thin the thick bile. The main thing to remember is that fatty, fried, smoked and protein foods make the bile secretion too concentrated and viscous.
Similar articles:
Causes
To understand why the bile in the gallbladder thickens and what to do in this condition, you need to briefly familiarize yourself with its causes. The liver is an important organ not only for digestion - it neutralizes and removes decay products from the body, affects the status of the immune system, the condition of the skin, hair, nails and the general tone of the body.
The gallbladder is a small muscular sac containing bile. This substance is necessary for the complete digestion of fats. It enters the main biliary duct, then into the duodenum. In the digestive tract, its remains break down into substances that are excreted in urine and feces. They give color to these physiological secretions.
In order for the system to work normally and bile thickening does not occur, the following is necessary:
- good condition of the gallbladder walls;
- proper and regular nutrition;
- eating foods that contain low fat content;
- normal weight;
- sufficient physical activity;
- absence of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
If all these factors are present, the bile in the bladder does not form clots and has a liquid consistency necessary for rapid release into the cavity of the duodenum. The reasons that cause thickening of bile secretion are as follows:
- constant nervous overload;
- the predominance of fatty, spicy, smoked and other foods in the diet, which leads to depletion of bile secretion;
- lack of physical activity;
- obesity;
- natural weakness of the muscle wall of the bladder;
- anatomical defects of the main bile duct or the bladder itself;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- pathology of endocrine organs;
- medications that cause thickening of bile.
Constant stress causes involuntary spasm of the smooth muscles of the bile duct. This leads to stagnation of the contents, loss of appetite, weight loss, and the appearance of other symptoms of a nervous system disorder. Moreover, the normal secretion of bile does not just stop for some time - clots begin to form in it, its consistency is more putty-like than liquid.
Without the proper range of movements, not only the tone of the body muscles decreases, but it also becomes sluggish, loses turgor and the gall bladder. The biliary secretion enters the common bile duct (main bile duct) in insufficient quantities, part of it remains unclaimed, it does not have time to be released into the intestine.
The reasons for the appearance and retention of excess weight (obesity) is the consumption of large quantities of foods containing a lot of fat and carbohydrates. The predominance of fatty meats, fish, mayonnaise, sweet and flour products in the diet, combined with low physical activity, leads to stagnation of thick bile in the liver ducts and gall bladder.
In this condition, only combined measures, including special medications, herbs, diet, and physical activity, will help to liquefy the bile in the gallbladder.
Anatomical curvature of the duct, weakness of the muscular wall of the gallbladder lead to dyskinesia - improper contractile function, insufficient production and incomplete release of bile in the digestive process. Stagnation occurs, thickening of the bile secretion and symptoms of liver disorder appear. The combination of these factors with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract leads to significant digestive disorders. Gastritis, pancreatitis, duodenitis, colitis, esophagitis and other combined diseases of this body system can negatively affect the regularity and quality of bile excretion into the duodenum.
Pathology of the endocrine system is widespread even in young patients, and women are affected more often than men. The tone of the gallbladder is affected by diseases of the pancreas, thyroid gland, and female genital organs. Diseases such as diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis or hypothyroidism do not leave their mark on the liver. In women, diseases of the digestive system, including disorders of bile secretion, develop during periods of hormonal changes: during menopause, fluctuations caused by disruptions in the menstrual cycle.