Natural childbirth
If during childbirth a woman has tears in the vagina, or she has had an episiotomy (dissection of the tissue of the perineum), doctors cannot do without stitches.
In such cases, spastic constipation is most often observed: the intestines are in a compressed state, sometimes accompanied by abdominal pain. What to do?
- A young mother should not sit (only stand or lie down); it is also not recommended to push.
- Take antispasmodic drugs.
- Follow a special diet that improves intestinal motility.
Diet after childbirth
A woman’s diet in the first 2-3 days should consist only of liquid food: still mineral water in large quantities, broths. Then, gradually, the young mother should switch to more solid foods, limiting the consumption of bread and flour products.
The main thing is that the food contains a large amount of fiber - it actively helps the intestines work and eliminates problems with stool. As you know, fiber is found in vegetables and fruits. Considering that almost all women breastfeed their babies, and it is extremely important not to cause allergies in the baby, choose “universal” fruits and vegetables. Moreover, this list may change depending on the season.
Vegetables and fruits, universal for nursing and non-breastfeeding mothers:
- Zucchini, pumpkin, broccoli, boiled carrots, eggplant, beets.
- Apples, pears, bananas, plums, currants, gooseberries, cherries.
Figs and prunes have a beneficial effect on intestinal function in the first days after childbirth (but you should be extremely careful with plums). And also olive or sunflower oil (1 tbsp per day). It is worth reassuring nursing mothers suffering from constipation: an imbalance in intestinal function does not affect the quality of breast milk.
And non-breastfeeding mothers can resume their normal diet within a week after giving birth.
After natural childbirth, constipation due to fear is common. Until the stitches heal, the young mother thinks that something might happen during a bowel movement. This is not true: if doctors performed an operation and stitched for 6 days, this does not mean that you have to endure it and not go to the toilet until everything heals! If a woman cannot cope with her fears, nurses in the maternity hospital will help give a cleansing enema.
What reasons?
There are a number of main factors that answer the question of why pain appears in the intestines after childbirth:
- Change in function due to gestation - a large uterus puts pressure on the vessels and muscles of the gastrointestinal tract, causing relative ischemia (circulatory failure) and impaired peristalsis (wave-like movements that move food forward), but such problems disappear after a few weeks.
- Weakness of the pelvic floor muscles - these muscles stretch and lose tone during pregnancy, and then are a risk factor for constipation, since they are unable to fully perform their function when straining.
- Hemorrhoids are a common complication of the very process of passing a child through the pelvis during pushing, and subsequently causes pain and discomfort during bowel movements, which forces the woman to restrain herself.
- Sutures after episio- or perineotomy are another factor that causes pain and, as a result, excessive caution when emptying or ignoring it as much as possible.
- Epidural (spinal) anesthesia - performed during a caesarean section can provoke disruption of the digestive tract, which delays natural recovery over time.
- Antibiotics - disrupted microflora leads to the fact that the internal organs involved in the digestion of food begin to work poorly.
- Less common causes include various chronic diseases, consumption of fatty and spicy foods, and smoked foods.
Read also: When hormones return to normal after childbirth: background and its restructuring
In this article we will look at the most common symptoms accompanying them - constipation or disorder.
Constipation
Often it all starts with a delay in bowel movements, which is easy to determine by the characteristic symptoms. After just a couple of days, the following signs appear:
- difficulty or complete absence of stool after 3 days from the last time;
- the need to make significant efforts and increase the total amount of time to go to the toilet;
- flatulence;
- feeling of heaviness, nausea;
- paroxysmal pain in the lower left corner and/or abdomen;
- general malaise, weakness, insomnia.
But don’t rush to run to the pharmacy for medications, since in most cases, intestinal restoration after childbirth can be corrected with a banal diet and adherence to certain nutritional rules:
- regularity of eating: 3 main meals and 2 small snacks, all in small portions;
- the correct ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates;
- 2-3 hours before bedtime – dinner;
- drinking regimen – 8 glasses of water per day (this is 1.6 l);
- no overeating: make it a rule that after feeling your stomach is half full, wait 10 minutes and evaluate this feeling again (during this time the food reaches the stomach and the receptors provide true information);
- among drinks you should give preference to still table water, cranberry juice,
- you should limit the consumption of coffee and strong tea, industrial lemonades and sweet carbonated drinks;
- food should be low-fat, broths, fruits and vegetables, whole grain porridges, fermented milk products are recommended, and prunes, beets, plums and raisins are especially useful.
Diarrhea
If constipation is not something special, then you should pay close attention to intestinal upset after childbirth. Normally, it may be present as a consequence of a psycho-emotional state - a reaction to stress in the form of childbirth, since there is significant worry about the condition of the baby. This condition is popularly called “bear disease.”
At the same time, the mother does not have nausea, fever, vomiting or malaise. In other cases, these are alarm bells as a consequence:
- infectious diseases;
- poisoning with poor quality food;
- allergies.
Read also Why is the navel brown or black during pregnancy or after childbirth?
In case of food poisoning, diarrhea is one of the consequences of dysbiosis, which disrupts the functioning of the intestines after general intoxication and disruption of the local microflora attacked by toxins. It is worth noting that they are also transmitted to the child through milk, so in this, as in other cases, a visit to the doctor should not be postponed until later.
The most dangerous cause is an infectious disease, since it can also affect the health of the baby - you can simply infect him.
In the case of ordinary poisoning, the body is affected by the toxins of already dead bacteria, while in an infection they are alive and multiplying inside you.
But the mildest is an allergic reaction, since most often it is caused by some product due to enzyme deficiency (for example, gluten deficiency) or intolerance to some food and is treated by excluding it from the diet.
C-section
A caesarean section has a worse effect on the functioning of the intestines than a natural birth, since during the operation the woman is given a certain drug that “inhibits” the functioning of the intestines. This causes atonic constipation. For atonic constipation, a certain drug is used that stimulates intestinal function.
As a consequence and extreme degree of atonic constipation, a woman may experience bloating and bloating. This happens if the uterus ruptures during childbirth, or if the woman in labor had peritonitis.
Sometimes complications caused by a long stay under anesthesia contribute to the occurrence of atonic constipation. But now Russian clinics are pursuing a policy aimed at ensuring that young mothers immediately begin to move actively after giving birth: this affects the functioning of the intestines - it begins to function much better. So, 6-8 hours after a cesarean section, the woman is asked to get up and walk around - more and more every day.
Epidural anesthesia
Epidural anesthesia is used for both natural childbirth and caesarean section. By and large, it does not affect intestinal function in any way. But sometimes mild intestinal atony is possible due to the effects of the administered anesthetic drug: peristalsis worsens, the intestines become sluggish, food passes with difficulty.
Speaking about the timing of restoration of intestinal function, it is difficult to predict anything, since this is an individual process. But still, on average, within 7-10 days the young mother’s body recovers. In general, as soon as a woman starts eating something, the intestines activate their functions.
It is worth remembering that in addition to constipation, intestinal problems such as diarrhea or disruption of intestinal microflora are extremely rare, but still occur. Diarrhea, that is, diarrhea, loose stools, occurs only when a woman overdoes it with “relaxing” foods. It's easy to prevent this: stick to a postpartum diet.
The microflora may be disrupted if the woman in labor has undergone cleansing enemas. Such a process of cleansing the intestines is still not natural. To bring everything back to normal and prevent dysbiosis, the doctor will prescribe drugs with bifidobacteria that normalize intestinal function.
Digestive system disorders after childbirth
- During pregnancy, the mode and structure of intestinal functioning changes. When the impact of the uterus after childbirth on all organs of the gastrointestinal tract decreases, the intestines need some time to get used to their normal position.
- Pregnancy and childbirth inevitably lead to changes in hormonal levels. This cannot but affect the functioning of all internal organs and systems, including the gastrointestinal tract.
- If the birth took place by caesarean section, then anesthesia was necessarily used. Drugs used for pain relief also always affect the digestive system.
- In some cases, a course of antibiotics is prescribed after childbirth. They can cause intestinal dysbiosis. To eliminate this problem, special medications are often prescribed.
- Postpartum hemorrhoids are often the cause of intestinal dysfunction. If a woman had it before childbirth, then after childbirth it may worsen. In this condition, sometimes everything is accompanied by pain when visiting the toilet.
- The abdominal muscles weaken during childbirth, which contributes to the development of constipation. Also, the normal process of bowel movement can be hampered by sutures in the perineum.
- Tissue ruptures in the genitals and sutures placed on them provoke spasms of all adjacent organs. Because of this, constipation and intestinal pain often occur.
Why does my stomach hurt?
Abdominal pain after childbirth is caused by natural or pathological processes. If you understand the reason, you can eliminate the pain or avoid unnecessary worries.
Gynecological reasons
Pain in the lower abdomen after childbirth usually occurs as a result of contraction of the smooth muscles of the uterus. For a short time after the baby is born, the hormone oxytocin is synthesized. It is necessary to cause contraction of the uterine muscles. When the organ shrinks, the woman feels pain similar to that experienced during contractions, only less intense.
The stronger the pain, the faster the organ will return to its previous size. How long it takes to recover depends on the individual characteristics of the body. One week after natural childbirth, pain, as a rule, no longer bothers you.
Breastfeeding affects the production of oxytocin. During lactation, the hormone prolactin is synthesized, which accelerates the production of oxytocin, therefore, the uterus contracts faster, which causes cramping pain when breastfeeding a newborn.
If a woman has had a cesarean section, the uterus contracts much more slowly than after a natural birth, since the necessary hormones were not synthesized during labor. It may take two months for the uterus to regain its previous size and take its place in the abdominal cavity.
During the operation, blood vessels, muscles, and nerve endings are damaged; naturally, a scar is formed on the uterus, which can also hurt until healing
After childbirth, many muscles hurt, including the legs, abdomen, lower back, and chest. This is natural, since they experience extreme stress when pushing the baby out. A young mother may confuse muscle pain with pain in the stomach or intestines. The muscles stop hurting a couple of days after giving birth.
Severe pain in the lower abdomen after childbirth occurs due to a pathological process. For example, due to rotting of the placenta that has not left the uterus. Perhaps the pain is the result of inflammation of the walls of the uterus or appendages due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms during strip surgery.
The pathology is accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen, febrile temperature, and bloody discharge with pus. If the integrity of the uterus is damaged, pus leaks into the abdominal cavity (peritonitis), which is fraught with serious consequences.
If girdling pain appears after childbirth, affecting the back and lower abdomen, then it is possible that the reason for this is displacement of the vertebrae. The pain increases after physical activity and can occur even months after childbirth.
Digestive dysfunction and gastrointestinal pathology
Pain in the lower abdomen after childbirth is caused by deterioration in the functions of the gastrointestinal tract.
Discomfort felt:
- with accumulation of gases or feces in the intestines;
- during the inflammatory process;
- when moving stones.
The stomach often hurts after childbirth due to changes in the diet of the nursing mother. If a woman consumes little fiber and dairy products, this contributes to impaired intestinal motor function. As a result, food stagnates and provokes increased gas formation and the formation of fecal stones, which leads to painful sensations.
Stomach pain after childbirth and if a young mother forgets to eat on time.
During pregnancy, digestive function is disrupted as the growing uterus compresses or displaces organs, which impairs blood circulation in them. Pregnant women often experience cystitis, cholecystitis, gastritis, and pancreatitis. If the disease has become chronic, it can recur during stress caused by childbirth, as well as due to non-compliance with the prescribed diet.
During pregnancy, stones often form in the gall bladder, pancreas or kidneys, as hormonal levels change, physical activity decreases and the water-salt balance is disturbed. The passage of stones can be triggered by taking certain medications, vibration, or heavy physical activity.
When the stone moves, a sharp cramping pain occurs on the left or right (depending on where it was formed), which moves to the thigh.
If the stone does not pass through the ureter, but gets stuck in it, then renal colic appears, which is accompanied by disruption of the digestive system.
After the birth of a child, the uterus, which compresses the intestines, may not contract for another week, so the pain in the lower abdomen does not subside immediately. Restoration of normal bowel function will occur within a week or two after birth.
Since after childbirth the tone of the intestinal muscles is reduced, the ability to absorb gases decreases. Therefore, after eating certain foods (potatoes, milk, black bread, fruits and vegetables), increased gas formation leads to abdominal pain, belching, a feeling of heaviness and fullness.
To restore normal bowel function, it is recommended to drink herbal decoctions of fennel, chamomile, dill or caraway. They help speed up the passage of gases.
Digestive disorders can be caused by hormonal imbalances
If a woman gives birth by caesarean section, she is given spinal anesthesia, which affects the functioning of the digestive tract. The disorders are neuralgic in nature. Digestive function is restored without treatment some time after childbirth.
The functioning of the intestines is influenced by the microflora that inhabits it. If dysbiosis develops after antimicrobial therapy, constipation and flatulence occur, which provokes abdominal pain. The natural bacterial flora of the intestine speeds up digestion, promotes the absorption of certain substances, and prevents the growth of pathogenic bacteria.
It can be restored with special preparations containing bifidobacteria or by increasing the consumption of fermented milk products.
Sometimes the stomach hurts for a long time after childbirth due to a change in its location. With this pathology, a woman feels pain in the abdomen during physical activity, running. If the prolapse of the stomach is significant, then it puts pressure on the duodenum, which prevents the passage of food, resulting in nausea, belching, and constipation.
Gastroptosis appears due to diets, extreme thinness, and childbirth. This happens due to the fact that when carrying a child, the abdominal wall muscles and ligaments stretch and lose the ability to hold the stomach in place.
The occurrence of pain is caused by distension of the stomach and the mobility of food masses along the gastrointestinal tract. The pain disappears if you lie on your back and lift your stomach up.
Often a change in the position of the stomach is accompanied by prolapse of other organs, then the corresponding clinic is added
Restoring the size and location of the stomach is possible only with the help of proper diet, massage and maintaining good physical shape. Gymnastics helps strengthen the abs and torso muscles; it should be done daily.
Signs of a pathological process
If the stomach hurts severely, for a long time and constantly, and the discomfort does not leave women even a month after giving birth, then we can talk about the presence of some pathological processes in their body.
Why does the lower abdomen hurt after childbirth and severe pain occur when urinating? In such a situation, we can talk about the presence of any infectious diseases affecting the genitourinary tract.
Often the cause of abdominal pain in young mothers is the remnants of the placenta that were not removed during childbirth.
The placenta attaches to the lining of the uterus and begins to decompose, poisoning the woman’s body with toxic substances.
This disease is common in women who have had a caesarean section. Endometritis is an infectious disease that takes a long time to treat.
Additional symptoms of endometritis are bloody vaginal discharge, saturated with clots of pus.
If your left or right side hurts after childbirth, then you need to consult a doctor and ask him to check your body for the presence of inflammation of the appendages.
If you experience pain and discomfort in the abdomen after childbirth, this can be explained by both physiology and pathological reasons. It is important to identify them in time, because some require treatment, while others can be dealt with quickly and independently. During the birth of a child, a woman’s body, muscles and internal organs experience significant overload, so it takes time for them to fully recover.
To reduce the likelihood of complications, you need to undergo a gynecological examination 5 days after birth.
Even during pregnancy, you need to reconsider your diet, exclude fatty, floury, salty, spicy, sweet, pickled, smoked foods. This measure will protect the gastrointestinal mucous membranes from irritation and reduce the likelihood of exacerbations.
When attending “pregnant school”, pay special attention to pushing, because during contractions many women push incorrectly, which leads to the development of hemorrhoids.
By following these simple rules, you can reduce the risk of postpartum abdominal pain.
If after childbirth the stomach hurts for a natural reason, this condition is not characterized by additional symptoms. In the presence of a pathological process, pain can have a different nature and be accompanied by changes in the general condition.
Endometritis
During the first day, discharge from the genital tract should become brown, mucous, and less and less reminiscent of blood. But sometimes the bleeding does not decrease, but suddenly increases. At the same time, nagging pain appears in the lower abdomen. Additional signs are the following:
- temperature increase;
- signs of intoxication;
- purulent discharge from the genital tract;
- signs of uterine subinvolution;
- tachycardia.
These symptoms are characteristic of postpartum endometritis. The condition most often develops after a cesarean section, but can also occur as a result of natural childbirth. Endometritis is an infectious postpartum complication and requires immediate medical attention.
The cause of endometritis and subinvolution is a violation of contractility, which is associated with retention of parts of the placenta or fetal membranes. While they are in the uterus, it is not able to contract normally, which means the pathological process will progress.
Endometritis threatens to turn into parametritis - inflammation of the periuterine tissue, pelvioperitonitis - damage to the pelvic part of the peritoneum, peritonitis - an infectious-inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity. In this case, abdominal pain will only increase.
Symphysitis
In some cases, only a radiologist together with a traumatologist can determine why the lower abdomen continues to hurt even in the long term after childbirth. The cause is often symphysitis - separation of the bones of the pubic symphysis.
The prerequisites for the appearance of this pathology are associated with physiological reasons. The same progesterone is to blame, as well as the hormone relaxin secreted by the placenta. It leads to softening and divergence of the symphysis pubis. This is necessary so that the birth canal can adapt as much as possible to the parameters of the fetus.
Normally, the distance between the two bones of this joint does not exceed 1 cm. The symphysis pubis is a semi-movable joint. This means that a minimum amount of displacement of its surfaces relative to each other is allowed. During the birth of a child, the joint may diverge by an additional 5-6 mm.
Degrees of discrepancy:
- 1st degree – discrepancy 5-9 mm;
- 2nd degree – 10-20 mm;
- Grade 3 – more than 20 mm.
Postpartum pain caused by symphysitis most often appears 2-3 days after birth. A woman lying in bed cannot raise her legs; walking causes pain. An accurate diagnosis can be made only after X-ray diagnostics.
Postpartum abdominal pain may be associated with a more common cause. The intestines do not always quickly return to normal after pregnancy and childbirth. Sometimes it takes a while to get it going. But all this time, feces will accumulate, expanding the sigmoid colon and rectal ampulla. This is accompanied by a nagging, aching, bursting pain in the abdomen, which manifests itself approximately a week after delivery. If measures are not taken in a timely manner, constipation will become extreme.
For some women after childbirth, going to the toilet is associated with a certain fear of damaging the existing sutures on the perineum or hemorrhoids. At the same time, stagnant processes in the intestines are aggravated: liquid from the stool is gradually absorbed back into the intestines, it becomes dry and can lead to greater damage to the lower part of the intestines.
The presence of stool disorders harms not only the digestive tract. This leads to displacement or compression of the uterus, disrupts the outflow of lochia and can lead to subinvolution.
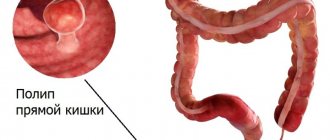
Placental polyp
Retention of parts of the placenta in the uterine cavity will most likely lead to bleeding in the early postpartum period. But sometimes small parts, microscopic chorionic villi allow the uterus to fully contract, and signs of pathology appear after a long time.
The clinical picture appears after 4-5 weeks. Pain in the lower abdomen is not a characteristic sign of pathology; bleeding comes first, resulting in a decrease in hemoglobin, weakness, dizziness, and tachycardia. Uterine pain after childbirth appears after infection and the development of endometritis. Further, the clinical picture will develop according to the classic pattern of uterine inflammation.
Osteochondrosis
During pregnancy, a woman's posture changes. This is due to weight gain and its redistribution to the abdominal area. If the pregnant woman did not use a special support bandage, the pain syndrome will be severe.
After delivery, not everything immediately falls into place. Sometimes during pregnancy, compression of the nerve plexuses occurs, and after childbirth this can manifest itself as signs of osteochondrosis or neuritis. Pain in the lower abdomen will be combined with irradiation into the abdominal cavity.
The rehabilitation period after the birth of a child lasts a month or two months. During this time, the mother's body gradually restores its functions, returning to its usual state.
During this period, many women complain to their doctors that they have pain in their left side, right side, stomach or lower back. The nature of these pains has been studied, all of them can be relieved.
If a month after the birth of the child has not yet passed, then most likely the cause of nagging, short-term and sharp pain is contractions of the uterus.
In the process of bearing a child, this organ was subjected to enormous stress. Other organs in the abdomen have also been under severe stress and require a long recovery period.
On average, the pain produced by uterine contractions can last a month or a little more. In the third month after pregnancy, a woman should forget about all unpleasant sensations.
The physiological causes of pain after childbirth cannot be treated with medication.
They can only be softened with the help of antispasmodics, but taking them during feeding is strongly not recommended.
If you are not breastfeeding your child, then you can safely take drugs such as “No-Shpa”, “Drotaverine”, “Bral” and so on.
How to smooth out discomfort in the stomach after childbirth? If you want to alleviate the pain, lie on your back or side and pull your knees towards your chest.
Women who have had a caesarean section should carefully treat the external seams on the body with brilliant green or iodine.
It is best to obtain more thorough recommendations regarding the treatment of the suture from the doctor who delivered the child.
You can get rid of uterine pain by carefully performing a specially designed set of exercises.
Remember: intense physical activity can cause internal sutures to separate, so do therapeutic exercises smoothly and slowly.
If abdominal pain is caused by pathological causes, the help of a specialist is necessary. The gynecologist examines the woman and prescribes the necessary diagnostic measures. Based on the results obtained, the doctor draws up a treatment regimen.
But what if the unpleasant sensations are natural? You can cope with discomfort if you follow simple recommendations:
- Perform exercises that accelerate the contractile activity of the uterus;
- Avoid sedentary activity;
- Switch to a balanced diet.
It should be remembered that the success of treatment depends entirely on eliminating the factor that causes pain.
Read more about the physiological causes of abdominal pain
The rehabilitation period after the birth of a child lasts a month or two months. During this time, the mother's body gradually restores its functions, returning to its usual state.
During this period, many women complain to their doctors that they have pain in their left side, right side, stomach or lower back. The nature of these pains has been studied, all of them can be relieved.
If a month after the birth of the child has not yet passed, then most likely the cause of nagging, short-term and sharp pain is contractions of the uterus.
In the process of bearing a child, this organ was subjected to enormous stress. Other organs in the abdomen have also been under severe stress and require a long recovery period.
On average, the pain produced by uterine contractions can last a month or a little more. In the third month after pregnancy, a woman should forget about all unpleasant sensations.
Photo:
Useful article? Share the link on VKontakte
The physiological causes of pain after childbirth cannot be treated with medication.
They can only be softened with the help of antispasmodics, but taking them during feeding is strongly not recommended.
If you are not breastfeeding your child, then you can safely take drugs such as “No-Shpa”, “Drotaverine”, “Bral” and so on.
How to smooth out discomfort in the stomach after childbirth? If you want to alleviate the pain, lie on your back or side and pull your knees towards your chest.
If you have severe pain not only in your stomach, but also in your lower back, then wrap it in a warm shawl or put a heating pad under your side.
Women who have had a caesarean section should carefully treat the external seams on the body with brilliant green or iodine.
It is best to obtain more thorough recommendations regarding the treatment of the suture from the doctor who delivered the child.
You can get rid of uterine pain by carefully performing a specially designed set of exercises.
Remember: intense physical activity can cause internal sutures to separate, so do therapeutic exercises smoothly and slowly.
Photo:
Treatment
If pain in the lower abdomen after childbirth is due to pathological causes and is not normal, the doctor will prescribe treatment. It will depend on what kind of disruptions occurred in the woman’s body after the birth of the baby.
- If after childbirth your stomach hurts a lot due to the placenta remaining in the uterus, this problem can be solved with the help of surgical treatment. Blood clots and placenta particles are scraped out to avoid postpartum infection. After this, antibacterial therapy is prescribed.
- If severe pain in the lower abdomen is caused by beginning and developing endometritis, complex conservative treatment will be required. It includes antibacterial, infusion, detoxification, sedative, desensitizing and restorative therapy, and the use of uterine contractions. To limit inflammation, a therapeutic and protective regimen is prescribed to normalize the central nervous system. You will also need good nutrition, which will contain a lot of proteins and vitamins.
- If a lot of time has passed, and the pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the spine, makes itself felt (this may be after 3, 4 months), you need to contact a specialist to check whether the vertebrae were displaced during childbirth). In this case, manual therapy will be required.
- If peritonitis has been diagnosed, immediate surgery is required.
- For problems with the gastrointestinal tract, doctors usually recommend a special diet. Since pain in the lower abdomen due to this reason can manifest itself 1 or even 2 months after childbirth, a woman needs to include more dairy products and those rich in fiber in her diet from the very beginning.
So the treatment of such painful sensations after childbirth is determined by the reasons that caused them. But what to do if unpleasant, cramping abdominal pain after childbirth is the norm (caused by natural contractions of the uterus), but prevents you from enjoying the birth of your baby in the first days after the long-awaited birth? A few helpful tips will help you deal with them.
Gastrointestinal problems
After childbirth, a woman may experience worsening gastrointestinal diseases, especially if they already existed before pregnancy. And in this case, a woman may complain that her stomach hurts after childbirth. A change in the nature of food can lead to spastic pain in the gastroduodenal area. Then it is recommended to adjust your diet and replace forbidden foods with others.
It often happens that during the postpartum period a woman loses her appetite and her taste buds weaken. Eating by force, if necessary, and the occurrence of constipation after childbirth can also provoke stomach pain. Therefore, during pregnancy, and especially after childbirth, nutrition should be balanced, and food should be taken without long breaks in order to avoid such troubles.
It is worth distinguishing when pain in the lower abdomen after childbirth is caused by natural processes, and when it is pathological changes. If pathological symptoms appear, it is important to consult a doctor in time to receive timely and competent treatment.
What causes stomach pain after childbirth?
Why does my stomach hurt after childbirth? There may be several reasons for such a malaise - a change in diet, a history of chronic diseases, gastroptosis.
Chronic pain
During pregnancy and after the birth of a child, all chronic diseases in a woman become aggravated, and new ones are identified.
Gastroptosis
During pregnancy, a woman's stomach shifts slightly; it seems to be shifted by the growing uterus. When childbirth occurs, the stomach is initially displaced. A little later, his activity is restored, he returns to his previous place. But due to weakened abdominal muscles and weakness of the ligaments that support it, prolapse of the stomach can occur. Most often, women who have given birth more than once encounter it.
Gastroptosis is a condition when the stomach cavity descends relative to a conventional line that runs in the place of the upper part of the wings of the iliac bones located in the pelvis.
Quite often it occurs in women during postpartum recovery. Most of all, irritable bowel syndrome occurs in women who have undergone an episiotomy or given birth to their babies by cesarean section.
The disease is accompanied by constipation and diarrhea. This problem is psychological. Mostly, it goes away on its own, but you may need the help of a doctor.
These are the main causes of stomach pain after childbirth. When a woman breastfeeds, her eating patterns change. Perhaps she overeats, or, on the contrary, her appetite decreases.
In any case, the body will recover over time, you just have to follow a diet and eat healthy foods.
Stomach problems after childbirth
Heartburn
Another sign that indicates indigestion is heartburn. During an attack, a burning pain is felt in the chest area, which often rises to the throat. Heartburn occurs due to the reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus. To eliminate the problem, antacid drugs are used that protect the gastric mucosa from the action of hydrochloric acid and bile. Antacids are divided into 2 types:
• Absorbed – quickly show effectiveness, the therapeutic effect does not last long. They neutralize hydrochloric acid and produce carbon dioxide, which causes flatulence and belching. In addition, carbon dioxide can trigger the re-release of hydrochloric acid.
• Non-absorbable - these are local drugs, the therapeutic effect of which lasts for a long time. During the neutralization of hydrochloric acid, carbon dioxide is not formed. Some non-absorbable antacids have an absorptive effect, absorbing toxins.
Doctors often prescribe non-absorbable antacids to lactating women to relieve heartburn: Maalox, Phosphalugel, Almagel.
Peptic ulcer
Common gastrointestinal pathologies include peptic ulcers, during which the mucous membrane of the stomach or duodenum becomes covered with ulcers. To treat ulcers in lactating women, gastroprotectors are used - drugs that increase the resistance of the gastric and duodenal mucosa to various irritating substances. Breastfeeding mothers are allowed to take Sucralfate and Misoprostol. These drugs improve microcirculation in the mucous membranes, neutralize hydrochloric acid, and increase the volume of mucus produced.
In any case, if you experience stomach problems after childbirth, you should first consult a gastroenterologist.
Possible pathologies after childbirth
Pain syndrome may occur due to the following conditions:
- fragments of the child's place remain in the fallopian tubes;
- an inflammatory process develops, localized in the uterine mucosa - there are many reasons, and if 2 weeks after birth the lower abdomen hurts, then perhaps this is a symptom of inflammation;
- inflammation in the uterine appendages;
- the inflammatory process has spread from the reproductive organs to the peritoneum - if you ignore the primary symptoms and attribute the unpleasant sensations to the postpartum condition, then similar complications can be expected.
If the pain is accompanied by additional symptoms: purulent discharge from the vagina or breasts, fever, swelling, etc., then most likely a serious infection has developed in the body. Any of the conditions requires contacting a gynecologist, and a woman should protect herself from possible infection.
In addition, some women are faced with such a pathological condition as discrepancy of the pubic bones. This phenomenon occurs during pregnancy, and during childbirth there is a risk of tissue rupture. After some time, inflammation may occur in the damaged area. The disease is called symphysitis, which requires mandatory complex therapy.
Etiology of physiological pain
The painful condition is characteristic of premenstrual syndrome. Abdominal pain sometimes occurs during ovulation. In women who have not given birth, pain occurs before the onset of menstruation; in women who have given birth, pain occurs after it. The reasons lie in excessive stretching of the walls of the uterus and arise as a consequence of past illnesses.
Help is to take painkillers. Colic can be quite severe; it is necessary to exclude peritonitis of the abdominal organs.
Pregnancy and painful sensations are a physiological condition for a woman and it is associated with the fact that the growing uterus puts more and more pressure on neighboring organs - the intestines, kidneys, and bladder. Acute pain radiating to the lower back and lower back in the first trimester indicates an unfavorable course of pregnancy.
If paroxysmal colic appears in the lower abdomen, you should immediately seek help. These are dangerous symptoms; there is a threat of miscarriage or spontaneous abortion.
The physiological category includes pain that occurs due to excessive tension in the abdominal muscles or sprain of the ligaments that hold the uterus in a certain position.
After childbirth, an inflammatory process sometimes occurs in the uterus due to the penetration of microbes. The temperature may rise, and purulent vaginal discharge may occur. Therefore, after childbirth, it is mandatory to inspect the uterus for possible remnants of the placenta and blood clots.
The recovery period after childbirth for women does not always go smoothly. The body needs some time to recover from such “stress”. After childbirth, contraction of the uterus causes pain. Severe cramping pain after childbirth is associated with stimulation by the child of the nipple during breastfeeding. The pain also increases due to pressure from nearby organs, for example, a full bladder.
Aches and pains after childbirth as a result of a caesarean section are understandable. The cause of this pain after childbirth is the presence of clots in the uterus or injury to the pubic bone. If the symptoms increase, the temperature rises, the woman requires immediate consultation and help from a doctor.
Restoring the intestines after childbirth
As soon as the baby is born, the mother's uterus decreases in size, and the abdominal organs begin to get used to the new condition. Gynecologist Alexander Shlychkov talks about how to eat properly and what rules are best to follow in the first days after childbirth.
By the end of pregnancy, the intestines are in a compressed state. This significantly complicates the passage of food and may be one of the causes of constipation during pregnancy. Usually in the maternity hospital, women in labor are given cleansing enemas (to prevent involuntary emissions from the intestines during delivery).
It is important! Water in large quantities is simply necessary in the first days after childbirth. It restores the water balance of the intestines and normalizes its functioning.
Natural childbirth
If during childbirth a woman has tears in the vagina, or she has had an episiotomy (dissection of the tissue of the perineum), doctors cannot do without stitches. In such cases, spastic constipation is most often observed. the intestines are in a compressed state, sometimes accompanied by abdominal pain.
When to see a doctor
The duration of the period of pain depends on individual characteristics and the speed of uterine involution. In most cases, during the first two weeks, the physiological discomfort associated with feeding the baby gradually decreases. The pain no longer appears at every feeding; its intensity decreases. When the uterus contracts completely, this symptom will disappear.
But there are signs that indicate a possible pathological process. If they appear, do not delay your visit to the doctor:
- temperature may be low at first and then rise to 39°C;
- disturbance of general well-being - weakness that does not go away after rest;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen that is constantly present;
- chills as a symptom of fever;
- headache;
- bloody discharge from the genital tract (it may intensify and change in character from mucous to more liquid, reminiscent of scarlet blood);
- cramping pain resembling spasms, after which blood clots are released;
- absence of stool for more than two days;
- inability to lift your heels off the bed when lying down;
- change in gait to a waddling, “duck” gait;
- sudden onset of bleeding over a long period after discharge from the hospital.
With a placental polyp, bleeding is usually intense and begins a month or two after the birth of the child. At the same time, it can be differentiated from menstruation: during menstruation, the nature of bleeding changes daily, it becomes less intense. In the case of a placental polyp, the discharge is scarlet and only intensifies.
You can contact a gynecologist for any changes that a woman considers different from physiological.
Possible reasons
If the lower abdomen hurts after childbirth, this phenomenon can be due to both physiological and pathological reasons. If you determine in a timely manner why this happens and what causes these pains, they can either be avoided altogether or reduced to a minimum. Among the most common causes, doctors name the following factors.
- Nagging, cramping pain in the lower abdomen after childbirth is caused by the body’s active production of oxytocin. This is a hormone that provokes active contractions of the uterus. During this period, her muscles are in good shape, as this organ returns to its former shape and size (read more about the restoration of the uterus here). This is the main cause of pain in the lower abdomen after the birth of a baby.
- The second factor that explains why the stomach hurts after childbirth is breastfeeding. During lactation, a woman’s breast nipples become irritated, and this provokes even greater production of oxytocin. Accordingly, the uterus begins to contract even stronger and more actively, causing pain.
- Severe abdominal pain after childbirth that does not stop after a month is already a serious pathology, the causes of which can pose a danger to the health and life of the young mother. And one of them is the remains of the placenta in the uterus. It simply might not have been completely removed from there after the birth of the child. In this case, its particles become stuck to the wall of the uterus. This provokes the formation of blood clots and the process of rotting.
- The next reason is endometritis (inflammatory process of the uterine mucosa). It is most often diagnosed in women who gave birth not naturally, but by cesarean section. During this operation, infections and microbes often enter the uterus. As a result, after childbirth, the lower abdomen hurts greatly, the temperature rises, and there is bloody discharge with purulent clots.
- Salpingo-oophoritis (postpartum inflammation of the appendages) is another cause of discomfort after the birth of a baby. If it is present, at first there are mild but nagging pains in the lower abdomen, which do not go away over time.
- If the pain is unbearable and is accompanied by high fever, the cause may lie in peritonitis - a dangerous infectious disease that will require immediate treatment.
- If the lower abdomen and lower back hurt, radiating to the spine, we may be talking about a postpartum injury, namely, a displacement of the vertebrae. As a rule, such sensations can be disturbing even six months after childbirth, and they usually manifest themselves during physical activity or when walking, when a large load is placed on the spine.
- Sometimes a woman may find that her lower abdomen hurts a month after giving birth: the cause may be improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Most often this happens due to a lack of dairy products and fiber in her diet. This leads to fermentation and gas formation processes, which create unpleasant painful sensations in the abdominal area.
- If the pain in the lower abdomen after childbirth is characterized by burning and rawness, this is due to the process of urination, which returns to normal within 3-4 days after the birth of the child. Over time, these unpleasant sensations pass.
- In some cases, the stomach may hurt due to severe divergence of the hip joint during labor. The process of its recovery can be quite long - up to 5 months, depending on the individual characteristics of the woman’s body.
This is why after childbirth the stomach hurts, just like during menstruation: everything is explained by normal or pathological physiological processes occurring in a woman’s body. If they are short-lived and pass quickly, there is no need to worry or panic. If a week has passed since giving birth and the pain still persists, you should definitely consult a doctor. You may need to undergo a course of treatment to avoid complications.