What is Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium that is present on all surfaces and objects. She is not afraid:
- freezing;
- drying;
- exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- chlorine-containing compounds;
- antiseptics.
Staphylococcus aureus is killed by boiling for an hour. Resistant to antibiotics. Immunity to it is not developed, so re-infection is possible. Shows its pathogenicity under certain conditions. It is localized and actively multiplies in the digestive canal. The enterotoxins it produces lead to serious conditions.
How to treat the infection?
If a bacterial infection with Staphylococcus aureus is confirmed, all therapeutic measures should be aimed at combating the disease. In a favorable environment, this microorganism multiplies very quickly, displacing beneficial microflora and leading to tissue poisoning with the products of its vital activity.
What needs to be provided:
- Mandatory use of antibacterial drugs after identifying the sensitivity of this strain.
- Strengthening the body's natural immune forces by taking special medications and vitamin complexes.
- Acceleration of metabolic processes occurs not only through drug therapy, but also through maintaining sufficient water regime and removing toxins and decay products of these bacteria from the body.
- The use of special bacteriophage viruses, the action of which is selective. This is a more gentle option, but for severe cases of infection it is necessary to provide suitable combinations with antibacterial drugs.
- Dietary nutrition should be as gentle as possible, but fully meet the body's needs. A minimum of effort should be spent on digesting food, so the priority is a puree-like consistency and eating foods warm.
Folk remedies for the treatment of bacterial infection must be agreed with the attending physician and do not cancel the main treatment. Herbal decoctions are usually used to strengthen the body and promote recovery. Vitamin preparations and detoxifying recipes also help well.
Antibiotics for intestinal staphylococcus
Symptoms of this pathological condition can persist for 14 days. If you choose the right effective therapy, you can improve the patient’s well-being in the shortest possible time. Bacterial colitis is treated with antibiotics. The choice of a specific drug depends on the patient’s diagnostic results. During treatment with antibiotics, it is important to follow the recommendations of doctors, namely:
- Do not self-medicate. Before taking the medicine, consult your doctor.
- The medicine is selected exclusively by the doctor.
- Follow the prescribed schedule.
- Do not exceed the dosage.
- Do not interrupt the course of treatment even if your overall health has improved.
- If the patient misses even one dose, the attending physician should be informed.
- To avoid the emergence of resistant strains of staphylococci, it is necessary to take a responsible approach to the process of antibiotic therapy.
If staphylococcal foodborne illness is diagnosed, then an antibiotic is not prescribed. The doctor uses antistaphylococcal toxoid to treat the patient. Gastric lavage is performed. The patient is given an intravenous infusion (glucose, Regidron). To reduce the risk of developing intestinal dysbiosis, experts recommend using antifungal drugs (Diflucan, Nystatin) in parallel with an antibiotic. Immune regulatory treatment is carried out.
In the process of treating this pathological condition, the doctor prescribes a drug that has a complex effect on the human body. In some cases, the doctor prescribes medications from several groups:
- Those that activate antibody production. Under such conditions, a resistant environment to golden coccal cells is formed.
- Medicines that destroy the disease.
- Antiseptic and antibiotic.
- Drugs that speed up metabolism. Under such conditions, the effectiveness of drug therapy is enhanced and the patient’s recovery process is accelerated.
Therapy for Staphylococcus aureus is carried out using:
- "Anatoxin." After using the drug, the production of natural antibodies is activated. They help fight coccus bacteria.
- Bacterial lysates. After using Imudon and Bronchomunal, local immunity is strengthened. Therapy with such drugs is the most effective.
- Vaccination can build immunity against coccal bacteria.
- “Bacteriophage” is a drug that destroys pathogenic cells.
- After using antistaphylococcal immunoglobulin, antibodies are supplied to the body that resist Staphylococcus aureus.
- The immunoglobulin drug has a detrimental effect on harmful bacteria.
- Medicines that include aloe.
- To reduce the risk of developing an infectious disease, it is recommended to use the ointment “Supirocin”, “Bactroban”, “Baneocin”.
- The Chlorophyllipt solution has a strong antibacterial effect.
Before carrying out treatment, it is recommended to consult a doctor - this will reduce the risk of complications. The dosage is determined by the doctor, depending on the individual clinical picture. The antibiotic treatment regimen is prescribed by the doctor. Staphylococcus aureus in the intestines is a serious pathological condition that can be fatal.
What is a staph infection
Staphylococcus is a spherical bacterium that in hollow organs (intestines, ureter, nasal passages) can create multilayer colonies, displace the normal microflora of the mucous membranes and cause serious diseases that threaten the patient’s life.
A feature of the infection is its resistance to antibiotics.
One type of staphylococcus, namely aureus, is considered a hospital bacterium. The use of antiseptics in medical institutions, as well as the unreasonable or incorrect (incomplete course) use of antibiotics has led to the fact that the bacterium has developed resistance (immunity) to antibacterial agents. This fact complicates and makes it difficult to fight it.
With extensive colonization by the bacterium, an infectious disease develops, the clinical manifestations of which will depend on the affected organ.
The danger of staphylococcus lies in the release of toxins that poison the body, causing symptoms of intoxication. Bacteria also have a suppressive effect on the human immune system, which allows them to multiply quickly and unhindered. From the intestines, staphylococcus can penetrate the blood, spread throughout the body and colonize internal organs (kidneys, brain, lungs). Then meningitis (inflammation of the meninges), pneumonia (pneumonia) or sepsis (blood poisoning) develops. Each of these conditions threatens the patient's life.
Staphylococcus aureus in children: treatment regimen - how to treat, how to cure
Local forms of staphylococcal infection are treated at home. Hospitalization is indicated in cases of generalization of the process with sepsis, meningitis, endocarditis, or if surgical treatment of purulent-necrotic skin lesions - boils or carbuncles is necessary.
Antibiotics are prescribed to the patient after receiving the results of a microbiological examination of the discharge from the pharynx or nose. Patients are prescribed:
- Semi-synthetic penicillins – “Ampioks”, “Oxacillin”;
- Combined penicillins – “Amoxiclav”;
- Aminoglycosides – “Gentamicin”;
- Cephalosporins - Cefepime.
Currently, there are microbes whose enzymes destroy these drugs. They are called MRSA - methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Only a few antibiotics will help cope with such strains - Vancomycin, Teicoplanin, Linezolid. "Fuzidin" is often prescribed with "Biseptol".
Antibiotics should be used only as prescribed by a doctor. Antibacterial therapy must be justified and thoughtful.
Irrational use of drugs:
- Destroys healthy microflora of the body,
- Has a detrimental effect on the functioning of internal organs,
- Harmful to health
- Provokes the development of dysbacteriosis,
- Complicates the course of staphylococcal infection.
Bacteriophages
Bacteriophages are biological weapons against bacteria. These are viruses that act very specifically, attack harmful elements and do not have a negative effect on the entire body. Bacteriophages multiply inside bacterial cells and lyse them. Having destroyed dangerous bacteria, bacteriophages die themselves.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2Z_TIGYfJi0
To destroy Staphylococcus aureus, the bacteriophage is used locally or orally for 10-20 days, depending on the location of the pathology. To treat purulent skin lesions, lotions or irrigations with liquid bacteriophage are used. It is injected into the articular or pleural cavity, vagina, uterus, taken orally, instilled into the nose and ears, and given enemas with it.
Immunostimulation
- Autohemotransfusion is the intramuscular injection of a patient’s own venous blood. This procedure is widely used to treat furunculosis. After intramuscular injection, the blood is destroyed, and the breakdown products stimulate the immune system.
- Subcutaneous or intramuscular administration of antistaphylococcal antitoxic serum or intravenous administration of antistaphylococcal plasma.
- Herbal immunostimulants - Schisandra, Echinacea, Eleutherococcus, Ginseng, Chitosan. These drugs normalize energy and basal metabolism, have an adaptogenic effect - help cope with stress and stress.
- For patients with severe signs of immune dysfunction, synthetic immunomodulators are indicated - “Polyoxidonium”, “Ismigen”, “Timogen”, “Amiksin”.
- Vitamin therapy.
Surgical intervention consists of opening abscesses and boils, excision of necrotic tissue, removal of purulent contents and foreign bodies, drainage of lesions to create unimpeded outflow of pus, and local administration of antibiotics. Often, surgeons remove the source of infection itself - a catheter, artificial valve or implant.
ethnoscience
Folk remedies complement the main drug treatment of pathology.
Heat treatments can only be used during the recovery period.
Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus in the intestines involves a set of the following measures:
- Suppression of pathogenic activity of the pathogen.
- Restoring immunity.
- Stimulates metabolism.
- Treatment of concomitant diseases.
- β-lactam antibiotics. This includes drugs based on amoxicillin, oxacillin, cephalexin, cefazolin and others.
- Macrolides. Substances based on erythromycin and clarithromycin.
- Lincosamides. Medicines based on clindamycin.
To restore immunity, in most cases adaptogens, synthetic immunomodulators and antistaphylococcal immunoglobulins are used.
Restoring normal metabolism is achieved by using multivitamins.
The “fight” against staphylococcal infection is aimed at:
- suppression of pathogen activity;
- improvement of immunity;
- stimulation of metabolic processes;
- treatment of chronic diseases that weaken the body.
The choice of treatment method is made based on the results of a stool analysis. If the number of CFU (colony-forming units) of the pathogen is no more than 1*104, then the risk of developing complications of the infection is small. Therefore, only stimulating drugs are prescribed - immunomodulators, vitamins.
If the number of CFU is not more than 10*104, then drug treatment is supplemented with antibacterial drugs. It is very important to choose the right antibiotic. This can be done by timely diagnostic measures and tests.
If the number of CFU is more than 100*104, then sepsis has begun in the tissues of the body, and therefore massive therapy will be required, the successful use of which is possible only in the intensive care unit.
The most effective remedy is considered to be staphylococcal bacteriophage. This is a virus that destroys certain bacterial cells. The bacteriophage is used for the treatment and prevention of purulent inflammation of any location and for intestinal dysbiosis.
If Staphylococcus aureus is detected in the intestines, the bacteriophage is prescribed three times a day 1 hour before meals. The dose of the drug is calculated individually, taking into account the weight and age of the patient. It is also used rectally in the form of a suppository once a day.
Staphylococcal bacteriophage has no contraindications for use. However, pregnant women and women during lactation can take the drug only as prescribed by a doctor. This is the most gentle treatment option for staphylococcal intestinal infections in this group of patients.
Bacteriophage is often included in combination therapy and is prescribed together with antibacterial agents. Ceftobiprole, cubecin, levofloxacin, linezolid, vancomycin are recognized as the most effective against Staphylococcus aureus. However, gastroenterologists try to prescribe such drugs only as a last resort.
At the same time, drugs that stimulate the immune system are prescribed. In milder cases, herbal adaptogens are recommended, such as tincture of Rhodiola rosea or Schisandra chinensis.
When severe symptoms are observed, which are accompanied by antibiotic resistance of the identified strain of staphylococcus, synthetic immunomodulators are prescribed, and sometimes the use of anti-staphylococcal immunoglobulin is indicated. To stimulate metabolism in the body, multivitamins are prescribed, and diet is also recommended. However, like any disease, staphylococcal intestinal infection can be prevented.
To identify Staphylococcus aureus in the intestines, you need to take a bacterial culture test, which will help confirm or deny the presence of this bacterium and determine its strain. Based on the result of the analysis, the patient is prescribed antibiotics and bacteriophages, which should only be prescribed by a doctor, since this pathogen has its own mechanism of resistance to a number of antibacterial agents.
Identify the bacterium St. aureus in the intestines can be done by culture of pathological material (vomit or feces). A cultural study will confirm (or refute) the presence of this microorganism, determine its strain and the degree of sensitivity to popular antibiotics.
Staphylococcus aureus can also be detected in bacterial cultures of absolutely healthy people. If its quantity does not exceed 103 CFU/g, and the person does not have any signs of infection, therapy is not carried out.
Staphylococcus aureus can be cured only if an integrated approach to treatment is followed. It includes:
- complete eradication of the pathogen from the body;
- restoration of normal intestinal microflora;
- increasing immune defense.
In addition to the main treatment, folk remedies will help get rid of the pathogen.
Etiotropic therapy
Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus in the intestines always begins with its direct destruction through the use of suitable antimicrobial agents or bacteriophages.
The drugs of choice are semisynthetic penicillin antibiotics and cephalosporins. The administration of special “medicinal” viruses - bacteriophages, which rid the body of staphylococci and can even be used to treat infants, is also effective.
In addition to etiotropic therapy, it destroys infection in the body by:
- rehydration agents (Rehydron and water-salt solutions);
- for indomitable vomiting - Cerucal and other antiemetic drugs;
- sorbents - Polysorb, Enterosgel, Polyphepan, Smecta;
- probiotics – Bifiform, Lactobacterin;
- multivitamin complexes;
- natural herbal antiseptics – Chlorophyllipt.
Prescribing immunomodulatory drugs will help increase the body's defenses and help the body defeat the disease. The following drugs are currently most common:
- Immunal;
- echinacea tincture;
- Dibazol;
All of them have a natural herbal composition and have virtually no side effects.
Medical nutrition
In addition, following a diet will allow you to get rid of Staphylococcus aureus and restore intestinal function faster. Food should be gentle and easily digestible, contain a minimum of chemical additives and flavor enhancers (including salt and spices). During treatment and 1-2 months after it, it is recommended to avoid:
- fried and fatty foods;
- hot and sour marinades, smoked meats;
- alcohol and carbonated drinks;
- coarse fiber foods.
Principles of treatment
To rid the body of bacteria, it is necessary to take antibacterial agents to which it is highly sensitive. The choice of antibiotic is determined by the doctor after bacterial sensitivity testing. It is also necessary to take immune boosters so that the body resists the bacteria.
It is advisable to drink a vitamin-mineral complex to normalize metabolic processes. It is imperative to normalize the intestinal microflora. For local treatment, enemas are used.
Most often, Staphylococcus aureus is sensitive to semisynthetic penicillins and cephalosporins. Therefore, the doctor prescribes Amoxiclav, Azithromycin, Linezolid.
In addition, the doctor prescribes the use of bacteriophages, which can eliminate bacteria in the body, and if you combine their use with the use of nitrofurans (Ersefuril), then this is an almost 100% guarantee of getting rid of pathological bacteria. It is noteworthy that this scheme can also be used in relation to infants.
It is very important to restore the water-salt balance in the body; as a result of vomiting and diarrhea, it is disrupted, which significantly weakens the patient and leads to the development of other pathologies. Therefore, Regidron is prescribed.
To cleanse the body of toxins with which a pathogenic microorganism poisons it, Smecta, Polysorb and others are prescribed. Probiotics must be taken in a course of at least 30 days - this can be Bifiform, Linex, and so on.
Sometimes antihistamines are prescribed (Zyrtec, Zodak, Cetrin), because allergic reactions can accompany dysbacteriosis, especially for children. For intestinal cramps, you can take Papaverine, and to stop diarrhea, you can take Loperamide.
It is clear that it is impossible to completely restore the body without following a diet. All food should be low-salt, not fatty, light and not traumatic to the intestines. You should not eat spicy foods or foods that contain coarse fibers.
How to cure Staphylococcus aureus
As it turns out, Staphylococcus aureus is a very tenacious creature and this bacterium is often quite difficult to fight. But whoever searches will find, and it turns out there is a working way to cure Staphylococcus aureus in the intestines in a week.
Intestinal dysbiosis caused by Staphylococcus aureus cannot be cured by taking bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, trying to normalize the composition of the intestinal microflora; in any case, we were not able to defeat staphylococcus within two months of using bacteriophages and bifidobacteria. The staphylococcus bacterium is very tenacious and aggressive, so drug therapy in combination with colonization of the intestines with friendly microflora is necessary.
As an allergist with 40 years of experience told me, in such advanced cases they used gentamicin, a rather dangerous antibiotic with very strong side effects. Although gentamicin is not absorbed from the intestinal lumen and the risk of side effects is negligible, you should still not use this antibiotic.
Currently, an excellent drug has appeared for the treatment of intestinal infections in infants - Enterofuril. I used Enterofuril suspension, which has a wide spectrum of antimicrobial action and is not absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. But the main advantage of Enterofuril is that it does not affect normal intestinal flora.
Therapy is aimed at:
- Suppress the activity of the parasite.
- Boost immunity.
- Stimulate metabolic processes.
- Treat chronic pathologies that weaken the body.
Medicines
Staphylococcus aureus in feces determines the choice of treatment methods. At CFU (colony forming units) value:
- Up to 1 in 104 vitamin preparations and immunomodulators are used, since the likelihood of serious complications is very low.
- At 10/104 there is a need for antibiotics.
- Above 100 to 104 they speak of sepsis, which cannot be dealt with without massive therapy carried out in an intensive care unit.
The most effective means of destroying staphylococcus in the intestines include the corresponding bacteriophages, that is, viral particles that destroy pest cells. With their help, intestinal dysbiosis and purulent infections are treated, regardless of location. Take the drug 3 times a day an hour before meals. The dosage is determined by the doctor, taking into account the age and weight of the patient.
In addition, rectal use of the bacteriophage is possible. Viral drugs are considered the most delicate treatment options for intestinal infections in pregnant and lactating women, but medications can only be taken as prescribed by a gastroenterologist.
Bacteriophage is often part of a combination treatment along with antibiotics. Among the latter, the most effective are Vancomycin and Levofloxacin. They are prescribed in extreme cases, since their use leads to the following consequences:
- All intestinal microflora is destroyed.
- High resistance to antibacterial compounds develops.
- Difficulties arise in the process of getting rid of toxic infection.
At the same time, treatment of Staphylococcus aureus is carried out by taking drugs to enhance immunity. For mild conditions, adaptogens are provided in the form of tinctures of medicinal plants such as Schisandra chinensis and Rhodiola rosea.
Synthetic immunomodulators, in particular antistaphylococcal immunoglobulin, are prescribed for severe symptoms characteristic of antibiotic-resistant strains of the pathogen.
Folk remedies
Serve as an adjunct to drug treatment. They can be taken only after agreement with the doctor. Among the most popular:
- Composition of 4 tbsp. l. mixture of echinacea and burdock, 1 liter of boiling water. Cook for 20 minutes. Drink 250 ml 3 times a day until the symptoms of infection disappear, then 1 tbsp. for 3 days.
- Blackcurrant puree (about 500 g). Take on an empty stomach. The course of treatment is 3 days.
- A decoction of apricot pulp and chamomile. Drink before bed.
Intestinal infections are accompanied by intoxication of the body, disturbances in energy and protein metabolism, electrolyte balance, and a decrease in the level of vitamins. Therefore, the diet includes:
- Boiled or steamed meat and fish.
- From lactic acid products, cottage cheese.
- Pasta, porridge, potatoes.
- Berries, vegetables, fruits.
- Drinks include mineral water, juices, tea with lemon or milk.
In this case, you will have to limit the consumption of saturated broths, coffee, sauces, and exclude the following products:
- Lard, fatty meat and fish.
- Rye bread.
- Fried foods coated with flour and breadcrumbs.
- Beans, cabbage.
- Alcoholic drinks.
- Canned food, smoked meats, spices.
Staphylococcus aureus is a special type of bacteria that actively parasitizes the child’s body. It underlies normal microflora and has a positive effect.
Under the influence of provocateurs, in particular secondary infection, hypothermia or weakening of the body's protective functions, the microbe begins to actively parasitize.
Staphylococcus aureus lives in the throat, localizing mainly on the mucous membranes. Its colonization is observed in the nasal cavity and other organs, in particular the intestines. Under the influence of provocateurs, infectious and inflammatory processes develop.
Staphylococcus aureus is considered the most dangerous parasite. It can cause serious illness and complications.
Almost every person on the planet is a carrier of a dangerous microbe. Sore throat and severe inflammation are associated with parasitism of this representative of the pathogenic microflora. Discomfort in the nasopharynx persists as long as favorable conditions for parasitism are “observed.”
Description of the bacterium
Staphylococcus aureus is a type of gram-positive bacteria. They can develop without air access and at almost any temperature.
Most people (according to various sources, from 25 to 40%) are permanent carriers of this bacterium. It is Staphylococcus aureus that causes purulent-inflammatory processes in the body, and in approximately 25% of cases it is the causative agent of nosocomial infections.
The bacterium received its name due to its corresponding color, visible under a microscope. Active growth and reproduction in the body occurs with a decrease in immune defense.
Bacteria of this genus cause a wide range of diseases, mainly on the skin or upper respiratory tract. The use of penicillin-based antibacterial agents, effective at the dawn of its discovery, is gradually losing its relevance.
Microorganisms have developed a kind of immunity, so infections of this type are now treated with synthetic antibiotics or bacteriophages.
Selection of antibacterial agents
In most cases, with rapid progression of the disease and high fever, antibiotics are immediately prescribed. Moreover, most often doctors do not wait for the results of bacterial culture, so they do not know whether Staphylococcus aureus is in the intestines of the baby. The symptoms of the disease suggest that it may be caused by the uncontrolled proliferation of pathogenic microflora, which must be stopped.
Many strains of this microorganism are resistant to penicillin and cephalosporin antibiotics. In an ideal situation, it is necessary to prescribe the drug only after receiving test results, which will indicate which drugs the detected microorganisms are sensitive to.
Statistics show that in almost 70% of cases, glycopeptides and carbapenems help if Staphylococcus aureus was detected in the child’s intestines. Treatment consists of taking drugs such as Vancomycin, Imepinem, Meronem.
If the causative agent is unknown, then, as a rule, cephalosporins of the first and second generations are prescribed. Many strains exhibit moderate sensitivity to them. Drugs such as Cefuroxime, Cefamandol, and Cefazolin are prescribed. To increase efficiency, they are used in combination with aminoglycosides. These are drugs such as “Neomycin”, “Amikacin”, “Isepamycin”, “Streptomycin”.
Statistics show that in almost 70% of cases, glycopeptides and carbapenems help if Staphylococcus aureus was detected in the child’s intestines. Treatment consists of taking drugs such as Vancomycin, Imepinem, Meronem.
Symptoms
The first symptoms of staphylococcal infection may appear almost immediately after discharge from the maternity hospital (if the child is infected in the maternity hospital). Newborns experience:
- bloating and intestinal colic;
- frequent foul-smelling stools (mixed with mucus and greens);
- sometimes there may be an increase in body temperature;
- violation of the child’s general condition (prolonged crying, refusal to eat, lethargy or restlessness).
Signs of dehydration in a newborn and a child up to one year old include crying without tears, dry lips, tongue and oral mucosa, and a sunken large fontanelle. Such phenomena require urgent hospitalization of the child in a hospital.
The temperature increase with staphylococcal gastroenteritis can be over 38 degrees
Features of the disease in infants
In children under one year of age, staphylococcal infection occurs as a toxic infection or gastroenterocolitis (inflammation of the stomach and small intestine). The main symptoms will be:
- weakness, lethargy, refusal to eat;
- fever (increased body temperature over 38.5 degrees);
- headache or dizziness;
- nausea and uncontrollable vomiting;
- frequent loose stools with admixtures of greens, mucus, blood, foam;
- abdominal pain, bloating.
It is important to know that frequent vomiting and diarrhea (loose stools) lead to dehydration of the child’s body, which is dangerous for his life. The baby's sudden drowsiness will also be a threatening condition; this may indicate incipient stupor (a harbinger of coma). In case of any of these conditions, you should immediately consult a pediatrician or infectious disease specialist.
Causes of the disease
The most well-known and effective preventive measures include:
- vaccination with antistaphylococcal serums;
- strict adherence to personal hygiene rules, because Staphylococcus aureus is transmitted by dirty hands and contaminated food;
- timely care of wounds, since staphylococcus “populates” previously affected areas;
- balanced nutrition, regulation of the amount of incoming nutrients. Residents of large cities should
- take a full course of vitamins for a year, since the toxic substances that enter their body significantly reduce
- absorption of vitamins and minerals from food;
- sports and hardening of the body perfectly stimulate the immune system, reducing the risk of developing diseases several times,
- the causative agent of which is staphylococcus.
Today, Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most thoroughly studied and frequently encountered microorganisms. However, even despite this “notoriety,” staph infections are still very difficult to treat. This is a consequence of the fact that staphylococcus is very variable and quickly becomes resistant to the action of many antibiotics. Therefore, it is very important not to self-medicate, but to visit a doctor when the first symptoms appear.
Staphylococcus aureus: culture
Outbreaks of bacterial gastroenteritis are often associated with poor food quality in restaurants and canteens.
Bacteria can enter the intestines with food and cause illness within 12 hours.
Staphylococcus can also be easily transmitted from person to person. An infected person spreads the bacteria by touching foreign objects.
Food production workers with skin infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus are especially at risk.
Risk factors:
- Eating raw foods (fish, oysters, unwashed fruits and vegetables). There is also a risk of infection from eating undercooked meats and eggs. It is necessary to control the quality of the products consumed.
- Impaired immune function. This may be due to HIV infection, organ transplantation, diabetes, cancer and other conditions.
- Skin infections caused by staphylococcus. In this case, improper hygiene can lead to bacteria entering the intestines.
Recent studies have identified risk factors associated with certain medications. Proton pump inhibitors used to treat gastritis and peptic ulcers may increase the risk of bacterial gastroenteritis. This is due to a decrease in stomach acidity and a corresponding violation of the protective properties.
Staphylococcus aureus: culture
Read: How to treat thrush in men: causes, symptoms and treatment of the disease
Therapeutic measures and prevention
Staphylococcus in a child's stool is a cause for concern
It is better to start treatment of bacterial gastroenteritis in the early stages of the disease. Symptoms may persist for several weeks. It is especially important to reduce the intensity of vomiting and diarrhea to avoid excessive fluid loss.
Read: Rectal candidiasis: what is this disease, its symptoms and treatment methods
It is also necessary to actively replenish fluid loss. If the patient's condition is serious, fluid is replenished in a hospital setting by intravenous administration of electrolyte solutions.
Some medications help reduce diarrhea. Antidiarrheals increase the time between trips to the toilet and prevent the formation of loose stools. Intestinal antibiotics may be prescribed to treat bacterial infestation.
Such drugs help to quickly remove pathogenic organisms from the intestines and reduce the effect of toxins on the walls of the organ. It must be remembered that only a doctor can prescribe antimicrobial treatment, since such drugs can cause complications.
Additional therapeutic measures:
- Drink fluids frequently throughout the day. It is also important to restore electrolyte balance, so soups and broths will be useful.
- Consumption of foods containing potassium. For example, bananas.
- Complete exclusion of physical activity and rest.
- Dietary measures. It is important to give up sweets, too salty and peppery, fried and fatty foods. In the first days of infection, it is best to consume broths and cereals.
Preventive measures include adequate hygiene and proper diet. Eating proven and safe foods will eliminate the risk of bacteria entering the intestines.
Problems for infants
When assessing laboratory tests, one must remember that there is nothing to worry about if Staphylococcus aureus was detected in the intestines of an adult in a concentration not exceeding 103.
The situation is a little different with young children. In the first year of life they should not have this microorganism. After a year, they look at the quantitative indicator and use it to determine the seriousness of the situation.
Naturally, one cannot ignore the situation when Staphylococcus aureus was discovered in the intestines of a baby. Symptoms of the development of the disease may be the following: watery or mucous mushy stools, repeated up to 15 times a day, regurgitation, vomiting, bloating. If such signs are present, the baby must be examined.
If the pathogenic microorganism mentioned above is detected, they speak about the possibility of fecal-oral transmission of infection from the mother or from medical personnel. Infection from environmental objects is also possible. After all, Staphylococcus aureus can live on them for up to 50 days. You can get rid of it only by treating surfaces with disinfectants.
The causative agent of infection
Intestinal microflora contains many bacteria that have a positive effect on the body, help in the digestion of food, the production of enzymes, protect the mucous membrane from irritation, and participate in the absorption and production of vitamins. But there are also bacteria that belong to the group of opportunistic organisms. They do no harm, but under certain conditions they begin to become active and multiply, causing a number of diseases. These include Staphylococcus aureus. It got its name because of the golden pigment, which can be seen under a microscope. Externally, these bacteria have the shape of a ball, gather in a group, resembling a bunch of grapes.
Staphylococcus is a gram-positive bacterium that is highly resistant to environmental conditions. Stays on objects and food for a long time. Boiling or other means of disinfection have a detrimental effect on them. During its life, staphylococcus releases endotoxins, which cause symptoms of food poisoning and severe intoxication.
According to medical observations, about 40% of the adult population are carriers of this bacterium, but not everyone suffers from intestinal infections. The reason for this is a decrease in the immune system and an increased concentration of staphylococcus in the intestines. If we talk about children, in the first days after birth their intestines are completely sterile. Colonization by bacteria occurs in stages. At this moment, it is important to ensure that pathogenic microorganisms do not become infected along with the “beneficial” bacteria.
Important! Normally, Staphylococcus aureus should not be present in the child's intestines.
About 27 species of staphylococcus are known, 14 of which are present in the human body and only 3 are considered hazardous to health. Staphylococcus aureus also belongs to the dangerous category, which can provoke the development of many diseases: from skin rashes to kidney inflammation, intestinal infections and meningitis. Given the danger of the bacterium, when it is detected, it is necessary to take treatment measures.
What does Staphylococcus aureus look like?
Prognosis and possible complications
The prognosis for the presence of Staphylococcus aureus is related to the degree of the disease (mild, moderate, severe) and the effectiveness of the selected treatment. If the mucous membranes and skin are mildly affected, the prognosis is favorable. With massive intestinal infection and the development of purulent sepsis, 50% of patients cannot be saved. Possible complications of staphylococcus include infectious-toxic shock conditions, sepsis, coma and death.
The presence of an insidious and extremely unpredictable bacterium in the intestines can lead to serious consequences, including:
- Chronic diseases of the digestive system.
- Infectious-toxic shock conditions.
- Sepsis, osteomyelitis.
- Pneumonia, sore throat.
- Cystitis, urethritis.
- Meningitis, endocarditis, coma.
It should be remembered that Staphylococcus aureus is the most dangerous microorganism for humans, since one of its serious complications is sepsis. Spreading through the blood, the bacterium affects vital human organs and causes extremely severe inflammatory processes.
- endocarditis;
- meningitis;
- toxic shock syndrome;
- urethritis, cystitis;
- stomatitis;
- sore throat, pneumonia;
- osteomyelitis;
- coma.
Staphylococcus in the intestines can cause dangerous complications. Complications are usually a consequence of improper or untimely treatment of the disease. Young children and the elderly are more susceptible to complications.
Frequent complications:
- Kidney failure.
- Anemia due to loss of blood in the intestines.
- Brain infection.
- Acute intestinal motility disorders.
The risk of complications also increases with chronic infection.
Pathogen classification
The most dangerous type of staphylococcus is definitely Staphylococcus aureus. This species is capable of creating large colonies on the mucous membranes and skin of humans, and under favorable conditions, provoke inflammatory processes of a purulent nature.
There are also less aggressive types of pathogen, for example, epidermal. If Staphylococcus aureus initially has a negative effect on the human body, then this species can exist quite harmlessly on the mucous membranes and skin, without causing any pathological consequences, however, if it penetrates the blood (through wounds and minor skin lesions), it becomes a serious problem - it provokes inflammation of the heart membrane and causes blood poisoning.
As for the saprophytic bacterium, it is the least dangerous for humans. This type of staphylococcus constantly lives on the mucous membranes and skin, and under favorable conditions it can provoke cystitis and kidney problems.
Routes of infection
Staphylococcus aureus in the intestines is a “hospital” infection. Penetrates through injured skin and mucous membranes. Uncontrolled proliferation of bacteria is observed against the background of stress, unbalanced nutrition, intestinal dysbiosis, pathologies of the endocrine system, and diabetes.
Severe forms occur in older people and children. The risk group includes infants who have spent a long time in the maternity hospital. Staphylococcus aureus enters the newborn's body through the blood when cutting the umbilical cord, through cracks in the nipples, through medical instruments, and through contact with carriers of the infection.
Staphylococcal intestinal infection is transmitted through medical instruments, food, blood, respiratory tract and breast milk. People with low or weakened immunity are susceptible to infection: patients who have undergone chemotherapy, long-term antibacterial treatment, surgery and serious injuries.
You can become infected by using unsterile medical devices (hemodialysis, ventilators), through scratches, wounds, sneezing or coughing. Staphylococcus enters the intestines directly with meat, dairy products, eggs, cream pies and cakes, causing signs of severe poisoning due to a huge dose of enterotoxin.
Staphylococcus aureus is quite contagious. Its entry into the intestinal tract can occur in various ways.
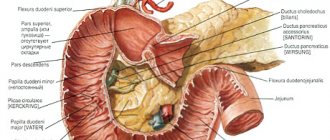
Table: Paths to hit St. aureus in the gastrointestinal tract
| Mechanism of infection | Description |
| Nutritional | Eating food that was stored incorrectly (with non-compliance with temperature conditions); |
| Contact |
|
| Artificial |
|
| Non-specific |
|
Prevention
To avoid intestinal infection with the St. aureus, it is important to follow a few simple rules:
- Maintain personal hygiene.
- Wash your hands before eating and after using the toilet.
- Eat a healthy and varied diet, often include fresh dairy products in your diet, which saturate the gastrointestinal tract with beneficial lactobacilli.
- Seek medical services only from trusted institutions.
In general, the prognosis for staphylococcal intestinal infection is quite favorable. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner and follow all his recommendations, complete recovery usually occurs after 10-12 days.
Traditional medicine recipes
How to treat staphylococcal intestinal infection using alternative medicine? Our review contains the most effective and popular recipes.
Herbal infusion
Ingredients:
- fireweed leaves - 3 tsp;
- chamomile flowers – 2 tsp;
- hop cones – 2 tsp;
- fragrant mint – 2 tsp;
- calamus root – 1 tsp;
- meadowsweet (leaves) – 1 tsp.
- dill seeds – 1 tsp.
Mix and grind the above ingredients to a powder. 2 tbsp. l. pour a liter of boiling water over the raw materials and leave in a thermos overnight (at least 7-8 hours). In the morning, strain and take half a glass throughout the day. Fresh infusion must be prepared daily. The course of treatment is 3 months.
Ingredients:
- golden thorn - 1 tbsp. l.;
- water – 1 l.
Place the dried golden thorn herb in a linen bag and place it in a saucepan with water boiling over low heat. Cook for 30-40 minutes until the broth turns a rich yellow color. Cool, strain through a strainer and take in unlimited quantities for 10 days.
Herbal infusions and decoctions have their contraindications. Treatment with folk remedies should be agreed with your doctor.
How can the diagnosis be confirmed?
Diagnosis of staphylococcal infection includes:
- Analysis of stool for dysbacteriosis. It shows which microorganisms and in what quantities inhabit the intestinal mucosa. Normally, there should be no Staphylococcus aureus in the intestines. When it appears, you need to start treatment. The analysis also helps determine the patient’s treatment tactics. If the number of bifidobacteria is reduced, then drugs containing them are prescribed. If there are few lactobacilli, then lactose-containing drugs are prescribed.
- If other foci of staphylococcal damage are suspected, an X-ray examination of the lungs, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, and blood culture for sterility are prescribed.
- To determine the general condition of the patient, but not to confirm the diagnosis of staphylococcal infection, the following tests may be prescribed:
- Clinical blood test. It may show an inflammatory process in the form of leukocytosis (an increase in the number of leukocytes in the blood) and a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left. Leukopenia (decrease in the number of white blood cells) will indicate reduced immunity in the child;
- A general urine test allows you to detect the penetration of infection not only into the intestines, but also into the genitourinary system. Protein, leukocytes, and bacteria may appear in the urine;
- biochemical blood test. With staphylococcal infection, there is often a decrease in the amount of protein in the blood (hypoproteinemia), which indicates impaired liver function;
- stool analysis for coprogram will show changes in the functioning of the intestines or pancreas. Mucus, streaks of blood, and bacteria may appear in the stool.
Possible complications of staph infection
- Infectious-toxic shock is a condition that develops with severe intoxication of the body and is manifested by a sharp decrease in blood pressure and loss of consciousness;
- Sepsis is blood poisoning. Treatment should be carried out in an intensive care unit.
Streptococcal meningitis is a complication with high mortality
Staphylococcal intestinal infection in children
Bacteria belonging to the genus Staphylococcus always live around us. Sometimes they do not cause any harm to the human body, but in some cases they can cause infectious diseases, in which various organs and tissues are involved in the inflammatory process. In this article we will talk about staphylococcal intestinal infection in childhood.
The role of staphylococcus in the occurrence of intestinal infections in children
Staphylococcus that enters the gastrointestinal tract of a child can cause an infectious process, the clinical picture of which is quite varied. In total, there are three types of staphylococci, each of them can cause illness in a child: aureus, epidermal and saprophytic staphylococcus.
The distinctive features of these bacteria are that they are located in clusters in a smear, have the shape of a ball, do not have mobility, cannot form spores, and do not have flagella.
The pathogenicity of staphylococci is due to the fact that they secrete several toxins and enzymes that attack human tissue. In addition, these bacteria are very resistant to the influence of environmental factors, so they remain viable for a long time on objects, in food and in the external environment. However, banal boiling and exposure to disinfectants is destructive to them.
Sometimes entire families or groups (in organized groups) suffer from an intestinal infection associated with infection with staphylococcus, but isolated cases of the disease also occur. Dangerous bacteria enter the child through the mouth. How severe the symptoms will be depends on the age of the children and whether they have significant health problems.
How can you get a staph infection?
You can become infected with a staphylococcal intestinal infection from a person who is already sick with it or is a carrier of the bacteria (that is, he does not have obvious symptoms of the disease, but is dangerous for others). The role of domestic animals in the spread and transmission of infection among people has been described, but this source of infection is recognized as a secondary source.
You can become infected with a staphylococcal infection in different ways: in everyday life, through contact, during conversation, with food, etc. The most dangerous food products for children and adults in relation to staphylococcal infection are the following: milk and dairy products, confectionery, cakes and pastries with cream.
Diarrhea, fever and other symptoms of staph infection
Hemorrhoids kill the patient in 79% of cases
Staphylococcal intestinal infection in children occurs in different forms: food toxic infection, enteritis, enterocolitis. The latent period of the disease lasts from 8 hours to 3-5 days.
- Food poisoning (gastritis, gastroenterocolitis)
This form of the disease usually affects older children. Already on the first day of illness, the child is worried about intoxication and diarrhea. The stool is loose and frequent, and may contain mucus and blood. In some cases, a hemorrhagic rash appears (similar to small skin hemorrhages); it disappears in children without leaving a trace.
If the child is examined by a doctor on time and receives full treatment, then within a couple of days there will be no trace of intoxication left, and by the end of the week we can already talk about recovery. Complications are not typical for this form of the disease.
- Enteritis (inflammation of the small intestine) and enterocolitis (inflammation of both the small and large intestines)
This form of infection can be primary (when bacteria enter the digestive tract directly) and secondary (that is, develop when the pathogen enters from other inflammatory foci). Young children are more often affected.
Primary enteritis and enterocolitis are more common in children who are over six months old. Moreover, many children are bottle-fed or mixed-fed.
Staphylococci enter the children's body mainly through food. But some parents note the presence of catarrhal symptoms in the child at the very beginning of the disease.
This may indicate that the pathogen entered the intestines from the nasopharynx.
Typically, children suffer from this form of infection mildly, without complications. The main symptoms are diarrhea and abdominal pain (baby anxiety). Recovery takes a long time. At this time, the baby may periodically experience unstable stool.
Newborns have their own characteristics of staphylococcal infection. They usually become infected with dangerous bacteria while still in the maternity hospital, and they often get staphylococcus from their mother. Symptoms develop towards the end of the first month of life.
Diarrhea comes to the fore; impurities of greens, mucus, and sometimes blood are found in the stool. Abdominal pain and false urge to defecate are not typical.
It is also worth paying attention to the constant low-grade fever in newborns, although there is no obvious reason for its increase.
Secondary enterocolitis and enteritis in children develops when staphylococcus enters the intestines through the bloodstream from other lesions. This form of the disease is severe, the child experiences severe intoxication. Symptoms from the intestines (diarrhea, vomiting and regurgitation) are intertwined with symptoms from other organs.