For various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, a comprehensive examination is required. If the bacterium Helicobacter pylori is detected in the stool, then gastritis, ulcers, duodenitis and other more serious diseases are diagnosed. It is also necessary to regularly collect stool to determine the number of pathogenic microorganisms during drug therapy, so that it is possible to monitor the positive dynamics of therapy.
In what situations is it prescribed?
It is required to submit stool for analysis in case of various pathological disorders in the digestive system. The bacteria Helicobacter pylori is determined by several methods, each of which is used for different disorders. A PCR stool antigen test should be taken in the following cases:
- stomach ulcer;
- the formation of erosions in the duodenum and other organs of the gastrointestinal tract;
- atrophic process in the mucous membrane;
- polyps and neoplasms;
- gastroesophageal reflux, characterized by the reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus;
- genetic predisposition to various pathologies of the abdominal organs.
PCR testing of stool is the most accurate method for monitoring the state of gastric microflora during treatment with antibacterial drugs.
Pathogenic microflora provokes stool disorders.
You can also take an immunological test, carried out in the following cases:
- broken stools, heartburn, discomfort and other pathological manifestations of digestive tract dysfunction;
- before taking a course of antibiotics;
- iron deficiency anemia or thrombocytopenia of unknown origin;
- genetic factor;
- the presence of infection in the immediate environment.
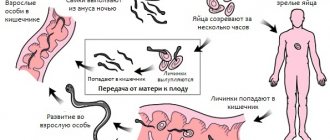
Helicobacter during pregnancy: danger to the fetus and treatment methods
The pathogenic bacterium does not affect the course of pregnancy and the condition of the child
This is interesting: Antidepressants. List of the best drugs of the new generation, tricyclic, herbal, with and without prescription
During pregnancy, the gastrointestinal tract is subject to heavy load. In this case, heartburn, pain in the epigastric region, etc. are very often observed. The risk of developing an ulcer is very high, so the expectant mother should be examined to identify this infection in order to avoid possible violations.
It is better to carry out the examination in the first months, since diagnosis becomes more difficult as the period increases. Non-invasive research methods are used for diagnosis. An effective diagnostic method for determining Helicobacter is gastric intubation. The procedure is carried out in a gentle way. Endoscopy is performed in rare cases and with great caution, as the pressure on the uterine organs increases.
Treatment of helicobacteriosis during pregnancy and lactation is prohibited due to the possible negative effect of antibiotics on the fetus.
Among the drugs that are allowed are Phosphalugel and Maalox. Among antispasmodics, Drotaverine, Baralgin, Papaverine can be used only with the permission of a doctor.
If Helicobacter pylori infection actively manifests itself during gestation, then the symptoms of toxicosis are pronounced and appear very early. Toxicosis can be observed up to 5 months. A pregnant woman should adhere to a special diet and exclude from her diet foods that irritate the gastric mucosa. Diet No. 1 is prescribed during the acute period. It is prohibited to consume fatty meats and fish, rich broths, smoked foods, cabbage, spinach, radishes, etc.
Preparation: what do you need to know?
A stool antigen test for H. Pylori may give false results if the following recommendations are not followed:
- A few days before the laboratory procedure, they refuse to take antibacterial and laxative medications. If it is impossible to stop therapy, then doctors warn about it.
- It is necessary to collect material for examination in pre-washed containers; it is better to use a sterilized container, which is purchased at a pharmacy. It is strictly prohibited to use stool after an enema or use of drugs with a laxative effect to test for Helicobacter pylori. In such cases, the reliability of the results is low.
- The collected material is delivered to the laboratory no later than 12 hours after collection. If it was not immediately possible to pass a diagnostic test, the material is stored for 24 hours at a temperature of 2-8 degrees.
- A repeat stool test for Helicobacter pylori is taken a month after antibiotic therapy.
H. pylori antigen in feces
Biological material can be studied in different ways.
| Method | Dates | Decoding the results |
| PCR | 1 working day |
|
| Bakposev | from 6 to 12 days |
|
| ELISA | Material – venous blood, during the working day, urgently within 2 hours |
|
We recommend reading:
The use of prostaglandin preparations in gastroenterology
Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to learn a lot about a person’s health status from his biological fluids: blood, urine, feces.
By examining stool, you can find out whether the bacterium H. pylori, which can cause gastritis, stomach ulcers and provoke cancer pathology, has settled in the body.
Feces for the presence or absence of this microbe can be studied in three ways: cultural, immunological, and the most reliable and widespread method - the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
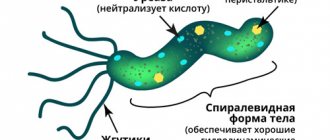
The bacterium itself is extremely rarely found in feces in its usual S-shape entirely. The large intestine and feces are not a favorable environment for the microorganism, therefore, when it enters them, it can take on a round coccal form, occasionally occurring in feces in this form.
The cultural method involves sowing part of the test material onto a nutrient medium in which the bacteria will feel good and begin to multiply.
Colonies grow, which are analyzed, stained with special reagents and examined under a microscope. In this way, pathogenic microbes are literally grown for the purpose of further study.
In addition to detecting the bacterium itself, the method allows one to determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to a particular antibiotic. If, when adding a drug, the growth of the colony continues - H. pylori is resistant to the antibacterial agent, and if the microorganisms die, it makes sense to prescribe this drug to the patient for the purpose of treatment and eradication, the bacteria are sensitive to it.
The cultural method is very reliable, but only if the S-form of the microbe is found in the biological material taken. The method has its drawbacks, and for this reason is not very widespread:
- The research period takes from 6 to 12 days
- Expensive media for sowing Helicobacter bacteria
- Specific conditions for media that ensure colony growth that are difficult to reproduce in the laboratory
- Rare occurrence of S-shaped bacteria in feces suitable for growth under nutrient conditions (coccal forms are not studied)
- The patient's feces can be subjected to immunological research, which allows identifying not the microorganism itself, but its parts - antigens.
- For this:
- Special antibodies are used aimed at detecting a foreign antigen - parts of a bacterium, its metabolic products, genetic material.
- Interacting with a foreign agent, antibodies form a specific complex, which is determined by enzyme immunoassay.
- This method of studying feces is rarely used in Russia; not many laboratories are equipped with the necessary reagents and necessary tests.
- But in the future, it is possible to include this method of detecting Helicobacter as screening tests: studying broad groups of the population for infection with the bacterium.
- This is the most common method for testing feces for this bacterium and is highly accurate.
- The essence of the method is as follows:
- A section of bacterial DNA is isolated from the patient’s biological material, which is then artificially duplicated many times on a special apparatus, which is how the genetic code of H.
pulori - When the genomic fragment of a microbe reaches a sufficient size, it is compared with the reference one and a conclusion is made about the microorganism under study: whether it is Helicobacter or another pathogen.
- A positive PCR test means the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection in the human body: the bacterium is present in the stomach, its DNA fragments were found in the stool and coincided with the reference ones.
Advantages of the PCR method:
- High accuracy: even a small amount of genetic material is enough for research with a high percentage of confidence, approaching 99%.
- Speed of research. 2 days is enough for analysis, but there are express methods that allow you to establish a diagnosis in a few hours.
- Painless. The method is atraumatic and non-invasive. Allows you to examine small children, elderly, debilitated patients for whom FGDS with biopsy and other endoscopic manipulations are contraindicated.
- For an accurate result, it is not necessary to detect DNA fragments of exactly S or helical forms; parts of coccal microbes (most common in feces) are also suitable for analysis.
PCR diagnostics have significantly more advantages than disadvantages. The disadvantages include:
- Relatively high cost of analysis.
- Preservation of microbial DNA fragments in feces and after eradication. Even if the treatment is successful and the bacterium is absent from the body, after some time DNA fragments are found in the biological material and a stool test for Helicobacter may give a positive result. Therefore, in order to monitor cure, PCR diagnostics is recommended no earlier than 1 month after the end of therapy.
- Special expensive high-tech equipment, which requires trained and trained personnel to operate.
All diagnostic studies carried out with patient feces refer to in vitro manipulations - “in vitro”, “in glass”, outside the human body.
They have fairly high accuracy and information content if they pursue the goal of detecting a microbe.
When studying the antibacterial sensitivity of microbial colonies on nutrient cultures, it was revealed that the most suitable drugs for bacteria in vitro “did not work” and turned out to be ineffective in treating the patient.
The results of in vitro studies of bacterial sensitivity to antibiotics are not always accurate.
The information content of a diagnostic test depends not only on the study chosen, the quality of the equipment and the qualifications of the personnel, but also on how the patient prepared for the analysis.
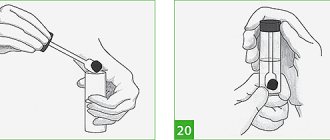
Feces for research must be collected correctly:
- After defecation, part of the fecal matter must be placed in a sterile container for collecting biological material, which must be purchased in advance from a pharmacy or laboratory.
- Prevent the ingress of blood, urine, saliva, pus and other foreign impurities into the biological material, which are likely to distort the results of the analysis.
- The container with the contents must be tightly closed and delivered to the laboratory no later than 4-5 hours before the study.
In addition to observing the technical aspects of collecting material for analysis, for several days before donating stool, you must follow the following recommendations:
- A week before the test, stop taking antibiotics.
- For three days, do not drink alcohol, foods high in fiber, or those that can color stool: beets, drinks with dyes.
- Do not use rectal suppositories or ointments, do not use laxatives.
Compliance with the above rules will allow the laboratory diagnostic doctor to assess the patient’s health status as accurately as possible and draw the right conclusions during the analysis.
PCR - diagnosis of feces is the most reliable of all three methods described above, it is to some extent inferior only to biopsy endoscopic examination.
PCR analysis of feces rarely gives false-positive results, is highly specific, and allows one to examine the DNA material of commonly encountered coccal forms of Helicobacter in feces.
The reliability of the cultural and immunological method is lower than PCR. These methods are prone to false-positive results, but in combination with other methods of detecting Helicobacter pylori, they are an excellent tool for making a diagnosis.
If Helicobacter pylori antigen or a DNA fragment of the microorganism under study is detected in the stool, this means that:
- The person is infected with H. pylori.
- Eradication therapy is not effective enough and the microbe has not disappeared from the gastrointestinal mucosa.
- Less than a month has passed after therapy and antigens of dead pathogens remain in the stool.
To exclude a false positive result after undergoing an anti-Helicobacter therapy regimen (when the test is positive and the human body does not contain H. pylori), you should not rush to find out the effectiveness of the treatment, but wait at least one month after its completion.
If the treatment of the bacteria is successful, 1 month after eradication, antigens and DNA of the microbe are not detected in the stool. The examination result is negative.
If antigens are detected during the initial analysis, the doctor will recommend that the patient undergo a course of special therapy aimed at destroying H. pylori.
The result of therapy directly depends on a correctly designed treatment regimen. To determine the sensitivity of microorganisms to certain types of antibacterial drugs, special fecal tests are used. Each technique has its own advantages and disadvantages. To obtain accurate results, it is recommended to conduct several tests.
The doctor prescribes a specific test for helicobacteriosis. The specialist takes into account the individual clinical picture of the patient’s health status. You can get tested for Helictobacter pylori yourself if you suspect a functional deviation of the digestive tract.
Molecular analysis reveals the specific DNA of the bacterium. The code is duplicated on a special device. When the bacteria reaches the desired size, it is compared with ethanol. If parts of the DNA match the original, then the test result is positive (Helictobacter pylori infection has been detected). The technique is characterized by a high degree of information content.
Features of the event
PCR is the main molecular diagnostic method
Polymerase chain reaction testing of stool reveals DNA and RNA of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. The technique refers to molecular biology, as a result of which DNA fragments of a pathogenic microorganism are increased many times in size. Stool analysis is carried out for PCR using the following means:
- Primer. Helps to detect and identify the required fragment.
- Polymerase. An enzyme that copies a fixed section of a DNA chain.
- DNTP. Chemicals needed to build a new chain.
- Sample for analysis.
- Buffer solution. Through the liquid, the most approximate condition for the polymerase chain reaction is created.
Using the PCR method, it is possible to accumulate specific sections of DNA in geometric progression; as a result of the procedure, more than 100 million of the same are obtained from 1 molecule. Using this laboratory method for examining stool, it is possible to determine the presence of Helicobacter pylori even in a small volume. If a circuit does not form during diagnosis, then the test result is negative.
The advantage of the PCR method is its automation, in which a person takes minimal participation in the examination.
Culture technique
Helicobacter pylori can be detected by bacteriological culture of stool. The diagnostic method refers to microbiological methods. The resulting material is placed in a special environment that is favorable for the growth of bacteria. After a certain period of time, the grown culture is studied using a microscope. In laboratory research, staining and other methods are used to help correctly identify the colony. In addition, an antibiotic sensitivity test is performed, making it easier to choose treatment against Helicobacter pylori.
Stool ELISA
During diagnosis, the reaction of antibodies to Helicobacter pylori is determined in this way. Reveal No. is possible through a specific connection between bacteria and antibodies. The procedure uses a chromogenic substrate; if the reaction is positive, a colored product is noted, the quantitative content of which is determined by spectrophotometry. Helicobacter ELISA is used most often, since this method of examining stool gives a more reliable result and is carried out quickly.
Helicobacter pylori: blood test, normal
To identify this bacterium, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is used. Its essence is to determine the concentration of antibodies in plasma to Helicobacter. When a pathogen enters the internal environment of the body, complex immune processes occur that are aimed at removing a genetically foreign protein compound, which is Helicobacter.
In cases where the infectious agent has already entered the body, but the immune system has not yet had time to respond to it, laboratory testing can produce false negative results. Also, when the bacteria is eliminated, antibodies to it may still be detected for some time (pseudo-positive reaction). Taking into account this pattern, a fractional determination of the level of immunoglobulins is carried out:
- Ig M are the largest, but make up only 10% of the total number of immunoglobulins. These antibodies can be detected earlier than Ig G.
- Ig A - they are detected not only in the blood, but also in gastric juice or saliva, which indicates significant activity of the pathological process.
- Ig G is a class of immunoglobulins, which makes up 75% of all types.
These protein substances appear a month after the infection enters the stomach. The concentration of igg is directly proportional to the activity of Helicobacter pylori infection. In addition, weakly positive results occur a month after treatment and complete recovery from helicobacteriosis.
The standard of analysis is the absence of Helicobacter pylori infection in the body. When the level of all immunoglobulins increases, an active infectious process is indicated. In this case, when assessing the results, total antibodies are taken into account.
Decoding
You can take a stool test to determine Helicobacter pylori at Invitro, Sinevo and other laboratories, which will help you correctly interpret the tests received. The table shows the indicators that are needed to decipher the results of laboratory diagnostics:
| Method | Dates | results |
| PCR | 5-6 hours – 2 days | Negative if no genotype of the microorganism is detected |
| Positive with diagnosis of helicobacteriosis | ||
| Bakposev | From 7 to 10 days | 0 - Helicobacter pylori bacteria were not detected |
| S - sensitivity to the specified antibacterial substance | ||
| R—antibiotic resistance | ||
| I - moderate sensitivity | ||
| ELISA | 24 hours | Negative, in which the presence of bacteria is not confirmed |
| Positive with Helicobacter pylori growth |
Results
- there are several ways to determine Helicobacter in stool using a laboratory method;
- each analysis option has its own advantages and disadvantages;
- To obtain the most accurate results, it is recommended to take several tests of different types;
- feces for analysis are collected taking into account a number of rules;
- a few days before the procedure, coarse fiber, fried, fatty foods, hot spices and seasonings, alcohol and any orange or red fruits are excluded from the diet;
- the container for feces must be sterile (pharmacy containers are the best option).
Video on the topic: Why is the Helicobacter pylori bacterium dangerous?