Article prepared by:
Vasily Babkinsky
Doctor of the highest category
Acute or chronic anal fissure is a disorder that is not customary to talk about out loud. The disease is in third place among proctological abnormalities in terms of prevalence. Pathology can occur regardless of gender and age group. Needs immediate treatment to reduce the risk of complications. Therapy must be comprehensive. The pathology bothers the patient for at least 4 weeks. Many patients do not know what an anal fissure looks like and ignore the discomfort that is present. People who are sick go to the doctor late.
Anal fissure is one of the most common proctological diseases
Anal fissure
Anal fissure
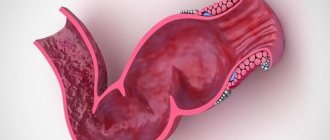
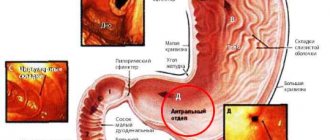
is a defect in the mucous membrane of the anus, usually linear or ellipsoidal in shape, occurring on the wall of the anal canal. Usually located along the midline of the posterior wall. The length of an anal fissure is most often no more than 1 centimeter, however, this is a very serious disease that can have dangerous consequences. Anal fissures are distinguished by the duration of their existence: acute (formed recently) and chronic (long-existing).
Among diseases of the rectum, anal fissures are very common and are the third most common proctological diagnosis after inflammation of the rectum and hemorrhoids. More often, anal fissure occurs in women 25-40 years old (more than 60% of cases). An acute (freshly formed) anal fissure looks like a slit with even, smooth edges. The anal sphincter muscles form the bottom of the fissure. Gradually, granulations form at the bottom and edges, which are covered with fibrin.
A long-existing crack is characterized by compacted edges (due to the growth of connective tissue) with signs of trophic disturbance. A connective tissue tubercle (“sentinel tubercle”) is formed on the inner (sometimes also on the outer) edge of the crack, which can become the basis for the development of a fibrous polyp.
Ointments for the treatment of anal fissures
Anal fissure ointment has a number of very important advantages. She:
- Eliminates pain, burning and itching;
- Restores cells and causes new growth;
- Relaxes the sphincter muscles;
- Helps fight pathogens that cause infection and inflammation of tissues;
- Prevents the development of thrombophlebitis in the surrounding venous ring;
- Stops bleeding;
- Increases the tone of the walls of blood vessels;
- Reduces the size of hemorrhoids;
- Promotes wound healing.
Popular drugs
The modern pharmacological market offers a large selection of various medicinal ointments. Let's look at the most effective ones.
Methyluracil ointment
Methyluracil-based ointment is one of the most common medications used to treat cracks.
Possessing powerful anti-catabolic properties, it stimulates tissue growth, promotes healing and restoration of affected cells, and also strengthens local immunity.
To improve the penetration of methyluracil, lubricate a clean cotton swab with a small amount of ointment and insert it into the anus as deeply as possible.
Important! Methyluracil ointment can lead to the development of an allergic reaction, which is accompanied by burning and itching. As a rule, they go away on their own after some time.
Solcoseryl
Solcoseryl ointment has powerful regenerating and anti-inflammatory properties. This medicine is based on deproteinized calf blood extract, which helps saturate tissues with oxygen and glucose, improves re-epithelialization, normalizes energy metabolism in cells and accelerates the recovery process.
To effectively treat anal fissures, Solcoseryl should be used 1-2 times a day, inserting a cotton swab with this ointment into the rectum.
Important! One of the most important advantages of this drug is its versatility. Solcoseryl has no contraindications and extremely rarely leads to the development of allergies and other side effects. It can be used even during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Levomekol
Antibacterial ointment for cracks in the anus, which has wound-healing properties and prevents wound infection. “Levomekol” has a drying effect, thanks to which the regeneration process occurs much faster, and also relieves itching and pain in the anus. As therapy, this remedy is used for up to 14 days, applied to a cotton swab.
Hepatrombin
It is one of the best medications for the treatment of anal fissure.
The drug copes well with various injuries (especially superficial ones), alleviates the patient’s condition during an exacerbation of the disease, relieves tissue swelling, burning sensation and stinging, and also prevents early blood clotting. Hepatrombin is applied to cleansed skin 2 times a day using a tampon.
Ultraproct
This type of drug is used to relieve inflammation, itching, pain and discomfort. Improvement is observed after the first use of the ointment, which, among other things, promotes the regeneration of damaged areas of the intestinal mucosa. Another important advantage is the presence of a special tip included in the kit, which facilitates the process of introducing the cream into the rectum.
Proctosan
The active components that make up this ointment accelerate tissue healing, dry the damaged surface and relieve inflammation. The kit also includes a special tip.
Troxevasin
"Troxevasin" is one of the most common drugs used to treat external and internal fissures of the rectum. The ointment helps eliminate inflammation, relieve swelling and quickly restore damaged tissue. "Troxevasin" is used in the form of skin applications before going to bed.
Important! The ointment will give the best result if you combine it with other medications.
Nitroglycerin ointment
An effective healing ointment, the active components of which dilate the blood vessels located in the affected area and relieve sphincter spasm. As a result, the patient experiences noticeable relief from pain that occurs during bowel movements.
Fleming's ointment
This homeopathic remedy is effective only at the initial stage of the disease - then it is used in combination with other wound-healing drugs. Fleming's ointment has disinfecting, regenerating and anti-inflammatory properties, without causing any side effects.
Syntomycin ointment
The active component of this ointment is chloramphenicol, which eliminates inflammation and also has an antiseptic, antibacterial and analgesic effect. The product should be used at the first symptoms of cracks - itching, burning and pain in the rectal area.
The duration of treatment and dosage depend on the stage at which the disease is located. Doctors recommend applying Sintomycin after an evening shower. Then you need to lie down so that the ointment penetrates the tissue. If the crack is very deep, you can use a tampon.
Syntomycin ointment has several contraindications. These include:
- Pregnancy;
- Lactation;
- Allergy to chloramphenicol;
- Fungal skin diseases;
- Eczema.
Important! In some cases, this drug can cause adverse reactions - rashes, aplastic anemia, allergies, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia and urticaria.
Heparin ointment
An excellent pain-relieving ointment based on heparin. Helps eliminate the local inflammatory reaction, accelerates the resorption of hematomas and improves the healing process of not very deep cracks. Heparin ointment is prescribed after childbirth, during which a rupture of the anal canal occurs. It is applied to a tampon or linen and inserted into the anus.
Important! This drug should not be used for thrombopenia, ulcerative-necrotic processes and decreased blood clotting.
Vishnevsky ointment
Vishnevsky's ointment contains castor oil, xeroform and birch tar, which has the strongest antiseptic properties. The ointment reduces swelling, accelerates tissue healing and eliminates inflammation. The product should be applied using cotton swabs when the first symptoms appear. The improvement is noticeable after just two sessions.
Important! Vishnevsky ointment can be used during pregnancy.
Ichthyol ointment
It has wound-healing, antiseptic and analgesic effects. The components of the ointment cannot penetrate the bloodstream and harm the baby, so the drug is often prescribed to pregnant and lactating women.
Aurobin
An excellent hormonal remedy with which you can relieve inflammation, relieve pain, reduce the size of nodules and get rid of cracks. The course of treatment is a week.
You can share the article with your friends on a social network:
Source: https://proktoinfo.ru/treshini-zadnego-prohoda/mazi-dlya-lecheniya-treshchiny-zadnego-prokhoda
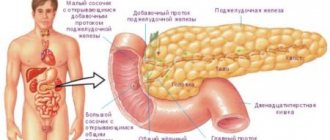
Causes of anal fissure
The most common causes of anal fissures are frequent constipation and diarrhea, hemorrhoids, heavy physical work, sedentary work, alcohol and spicy food abuse, mechanical damage to the mucous membrane of the anal canal by a foreign object or dense feces.
Diseases that contribute to the occurrence of cracks in the anus include inflammation of the large intestine (colitis, enterocolitis, sigmoiditis, proctitis, hemorrhoids). In 70% of cases, anal fissure occurs in people suffering from pathologies of the stomach, small intestine, liver, pancreas and biliary system.
In a similar number of patients, anal fissure is combined with hemorrhoids. Long-existing chronic hemorrhoids contribute to a decrease in the elastic properties of the anal canal mucosa (as a result of pectenosis), which results in a tendency to the occurrence of defects. The pectineal line area of the anal canal wall is most vulnerable to tension.
Factors provoking pathology
The causes and treatment of fissures around the anus in women and men are interrelated. Predisposing and provoking factors are described in the table.
| Predisposing factors | The risk of a disorder increases if you have:
|
| Provoking factors | Often the formation of a crack is caused by:
|
Acute anal fissure in women is usually caused by labor. During this period, the female body experiences real stress. The pelvic organs also suffer. Tissue rupture occurs due to increased pressure during straining. The condition will cause significant discomfort.
In women, a fissure in the anus often occurs and does not heal for a long time due to errors in the postpartum period. Normally, the first bowel movement should occur when using laxatives. The drugs help make fecal matter soft. Weakening medications are required. Feces, passing through the intestines, do not injure it.
In women, the problem may arise during pregnancy and childbirth.
Many patients do not even suspect why anal fissures appear. Another common provoking factor is injury to the intestinal tract. This can happen with constant constipation and anal sex. Increases the risk of straining during difficult bowel movements. The mucous membranes are injured and deep damage occurs.
We have selected useful articles on the topic
Description of Citrobacter and the danger of bacteria to human health
01.05.2019
Rectum: how and why cancer forms
19.06.2019
Initial signs of sigmoid colon cancer
02.05.2019
In order to understand how to get rid of anal fissures, the root cause of the deviation should be established. The pathology may be caused by improper administration of an enema or other medical instruments intended for research. The risk of developing a disorder is increased if there are problems with blood vessels. In this case, the tissues become more susceptible to any damage.
Only a doctor can tell you how to treat microcracks in the anus. The disorder may be a consequence of some other abnormality that requires special treatment.
Cracks can occur as a result of improper administration of the enema.
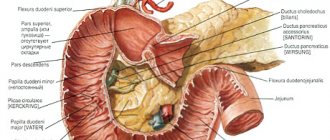
Localization of anal fissure
In the vast majority of cases (85%), an anal fissure occurs on the posterior wall along the midline (at 6 o'clock). This is explained by the specific structure of the anal canal - in this place the blood supply to the sphincter is weakest and the canal wall is most vulnerable when strained during defecation or when foreign bodies penetrate the rectum.
In 8-9% of cases (mainly in women), a fissure can occur on the anterior wall, and in extremely rare cases it is localized on the lateral sides of the anal canal. In 3-4% of cases, a combination of cracks in the anterior and posterior walls is detected.
Anal fissure has a fairly specific clinical picture. With a long-standing fissure, a fairly pronounced pain symptom and tonic spasm of the sphincter after defecation are noted. The spasm may persist for several hours. Sometimes until the next bowel movement.
Tonic spasm is one of the factors in the formation of a vicious circle that contributes to the progression of the fissure: an anal fissure causes persistent spasm, which causes ischemia of the tissues of the walls of the anal canal and interferes with the healing of the anal fissure.
An acute anal fissure is manifested by spasm of the anal sphincter, pain during defecation, and bloody discharge from the anus. Pain is usually the main complaint of patients with anal fissure. Pain occurs at the beginning of defecation, is quite severe, and often persists for a long time. Pain may radiate to the perineum or sacrum. Intense pain in defecation can force patients to postpone this act, which leads to constipation.
Spasm of the anal sphincter is a reflex, associated with an intense pain symptom, tonic spasm is one of the main elements of the pathogenesis of the disease. Spasm caused by pain impairs blood supply, increases pain and interferes with tissue regeneration and healing of the crack.
Bloody discharge from the anal canal is usually scanty (bloody streaks in the stool or traces of blood on paper); they are associated with trauma to the mucous membrane during defecation. If severe bleeding occurs, then we can assume concomitant diseases: hemorrhoids, tumor, etc. An untreated acute anal fissure that has existed for 3-4 weeks becomes chronic. In this case, thickening and compaction of its edges occurs, the formation of a rough scar, and the formation of a “sentinel tubercle” on the inner edge.
Pain, unlike an acute fissure during chronicity, most often occurs after defecation and lasts longer. With prolonged sitting, the pain intensifies. A constant pain symptom significantly reduces the quality of life of patients, causing irritability, sleep disturbances, and neurosis. Patients with chronic anal fissure often have a fear of defecation and often use laxatives.
With prolonged constipation, there may be bleeding from the anus during intense bowel movements. Sometimes the anal fissure becomes suppurated and purulent discharge appears from the anus. With a chronic fissure, the tonic spasm of the sphincter is less intense and does not last long. Anal itching is common. Chronic anal fissure may be accompanied by inflammatory processes in the terminal parts of the intestine: sphincteritis, proctitis, proctosigmoiditis.
Symptoms of the lesion
Signs of a rectal fissure may not be expressed for a long time. Symptoms will become more intense as the defect becomes deeper and more prolonged. Manifestations are also directly related to the form of pathology.
Symptomatic therapy is ineffective. The main deviation needs to be eliminated. Symptoms and treatment of fissures in the rectum are interrelated. Signs help determine the root cause of the disorder.
The main signs of pathology include:
- pain in the anal area;
- itching sensation and discomfort;
- bloody issues.
The intensity of the pain is directly related to the depth of the crack. In the initial stages, the symptom is present only after defecation. If there is no treatment, discomfort will be observed throughout the day. The nature of the symptom can be stabbing, paroxysmal, pulling or burning.
Pain in the anus is one of the signs of pathology
Healing of cracks in the anus must be started urgently in the presence of bloody discharge. In the early stages of the disease, they can be noticed after defecation on toilet paper. Over time, blood appears on the laundry.
The discharge has a deep red color. The color may become darker if the veins have been damaged. The condition requires urgent medical attention.
The patient needs to immediately learn how to cure a fissure in the anus at home if the patient has too much itching in the area of the anus. The symptom is caused by prolonged sitting or wearing uncomfortable underwear.
All of these signs may be present in other proctological diseases. It is for this reason that each patient must undergo a comprehensive diagnosis before starting treatment.
An accurate diagnosis must be made by a proctologist.
The patient may experience pain even at the initial stage for half an hour after bowel movement. It is difficult for a sick person to sit normally. He constantly feels discomfort.
Patients are often interested in how long it takes for a fissure in the anus to heal. The duration directly depends on the severity of the pathology and the degree of its neglect. The defect will disappear only with adequate treatment.
Diagnosis of anal fissure
As a rule, an anal fissure is detected when examining the anus. To carry out the examination, the patient's buttocks are carefully spread apart and the anus area is examined. After spreading the walls of the anal canal, a mucosal defect is revealed. Sometimes (with small cracks deep in the canal), proctologists perform a digital examination, simultaneously noting the existing tonic spasm of the sphincter. Carrying out a digital examination in the presence of a visible crack is not advisable due to possible damage to the mucosa.
For patients with an unhealed anal fissure, severe pain symptoms and a spasmed sphincter, instrumental methods for examining the rectum - anoscopy and sigmoidoscopy - are not performed, or if there are indications (heavy bleeding, suspected proctitis, tumor formations, purulent complications) they are performed using local anesthesia. Sigmoidoscopy to a height of up to 20-25 cm can be performed after the crack has healed to monitor the condition and identify concomitant pathologies.
Diagnostics
An experienced proctologist will be able to determine the appearance of cracks by simply examining the patient’s anus. It looks like a small ulcer. Chronic anal fissure requires more accurate diagnosis. To assess the degree of tissue scarring and muscle spasm, a rectal examination is performed under local anesthesia.
A rectal fissure is sometimes accompanied by inflammatory processes and parasitic infestations. To exclude them, they take a blood test and a coprogram.
Instrumental examinations (anoscopy, rectoscopy, irrigoscopy) are done to fully assess intestinal pathologies. They are performed after healing the cracks or use a drug for anesthesia.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis for this disease does not cause any particular difficulties. Anal fissure is differentiated from incomplete internal rectal fistula. With this pathology, sphincter spasms are not noted, the pain symptom is less intense, the main clinical manifestation is the separation of pus from the anus. Palpation of the mucosal defect is not painful; a depression is found at the bottom (fistula cavity).
It is also necessary to exclude the possibility that the fissure is not a manifestation of rectal infections (syphilitic gumma, tuberculosis, fungal or parasitic infection, rectal damage due to Crohn's disease). To do this, a thorough history is taken, the timing and causes of occurrence, and the features of the course are identified.
Patients with a suspicious history of HIV infection (drug addiction, promiscuity, homosexuality) may suffer from various diseases of the rectum associated with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. The detection of anal fissures in such patients is often accompanied by an unusual clinical picture.
What are hemorrhoids?
For many centuries, almost all diseases of the rectum, manifested by bleeding from the anus, were called hemorrhoids; even the name of the disease, literally translated, means “bleeding.”
Today, the concept of “hemorrhoids” is narrower and refers to a disease manifested by an increase in the venous plexuses of the rectum (cavernous bodies), which are located under the mucosa slightly above the muscles that close the anus.
Enlarged venous plexuses form hemorrhoids. In the case of external hemorrhoids in the quiescent stage, they are visible to the eye as small tubercles with a pale bluish tint to the skin, located around the anus. When hemorrhoids worsen, these formations swell, enlarge, and become purplish-red and even blue-black.
Internal hemorrhoids are characterized by the formation of nodes in the middle and upper part of the rectum. In the early stages, it cannot be determined independently, but later, when the nodes grow so large that they descend through the anus to the outside, even an amateur can diagnose the disease.
Complications of anal fissure
Anal fissures can become infected and complicated by ascending (moving up the intestine) inflammation of the mucous membrane of the terminal parts of the intestine (sphincter, rectum and sigmoid colon). When infection penetrates into the deeper layers, paraproctitis (inflammation of the fatty tissue around the rectum) can develop.
An anal fissure can be complicated by severe heavy bleeding; with regular small blood losses, iron deficiency anemia develops. In men, inflammation can spread to the prostate gland (prostatitis).
Treatment of anal fissure
The main goals of anal fissure therapy: pain relief, relief of tonic spasm of the sphincter, normalization of stool and healing of the fissure. Treatment can be carried out using conservative methods and surgical intervention. A timely visit to a doctor, in case of a fresh (no more than a week) uncomplicated crack with smooth edges, allows you to heal the crack faster and more effectively with the help of therapeutic agents. Conservative therapy is a sufficient measure and leads to cure in 65-70% of cases.
One of the significant factors in the treatment of anal fissure is following a diet aimed at activating intestinal function and facilitating bowel movements. The diet should be nutritious, balanced, rich in plant components and dairy products. It is recommended to exclude spicy, salty and bitter foods, seasonings that irritate the mucous membranes, and alcohol. Beetroot, prunes, apricots, dried apricots and figs have a positive effect on the intestines. Beets can be consumed boiled, along with vegetable oil or sour cream. Fruits need to be steeped in boiling water for a while before eating. This diet helps soften stools and make bowel movements easier.
Therapeutic methods for the treatment of anal fissures are represented by local and general drugs. For local treatment, warm baths with a weak solution of manganese are prescribed (10-15 minutes up to 3 times a day), nitroglycerin ointment to relieve sphincter spasm (use in small quantities, since the absorption of nitroglycerin into the general bloodstream affects cardiac activity and the nervous system) , Botox (botulinum toxin, interrupts the passage of nerve signals into the muscles; when applied locally to the sphincter, it also helps relieve spasms), suppositories and ointments with painkillers (novocaine, lidocaine, anesthesin), melituracil and sea buckthorn oil to speed up healing (also in suppositories or ointments).
General treatment may include taking laxatives and calcium channel blockers (diltiazem, nifedipine) to relieve tonic spasm. In addition, there are methods for treating anal fissures such as infrared coagulation (chronic fissures are treated when there is no spasm and scarring changes occur), laser or radiofrequency coagulation (removal of perianal tissue with a fissure under local anesthesia using a laser or radio waves), drug blockade, surgical treatment.
Indications for surgical treatment: deep chronic fissure with pronounced cicatricial changes in the edges, accompanied by significant spasm, refractory to conservative treatment. In such cases, excision of the anal fissure is performed. Often an anal fissure is accompanied by hemorrhoids. As a rule, in such cases, surgery to remove hemorrhoids (hemorrhoidectomy) with excision of the existing crack is recommended.
The choice of treatment tactics depends on the patient’s condition, the course of the disease, and existing complications. Self-medication and delay in seeing a doctor can lead to the development of complications, and will also make subsequent treatment longer and more unpleasant.
Secondary cracks
Sometimes the cause of anal fissure is various diseases. The first thing that comes to mind is hemorrhoids. varicose veins in the anus and rectum often lead to the formation of cracks. They are usually located in the area of hemorrhoids and outside, around the sphincter.
The cause of secondary fissures may be one of the diseases of the large intestine. As a rule, this happens in cases of severe inflammation or infectious infections in the area.
Treating such cracks separately from other diseases is pointless. As soon as the existing crack begins to heal, there is a risk of developing a new rupture, so you first need to get rid of the disease that caused this illness. And it doesn’t matter whether the anal fissure is internal or external, it will have to be treated in parallel.
Don't be shy about doctors. Only those who do not know the background of these diseases can blush at the word “hemorrhoids” or the expression “anal fissure”. The discomfort they bring into human life is not worth such sacrifices.
An important message from the authors of the portal about HEMORRHOIDS
For quite some time now, the team of our portal has been informing and helping people fight such an insidious disease as HEMORRHOIDS. Many of them entered into this struggle alone more than once and were defeated each time. Hemorrhoids did not go away, but only progressed.
The causes and mechanisms of development of anal fissures are varied. According to most researchers, the most common cause of cracks is mechanical. In this case, not only the consistency of the stool is of great importance, but also the anatomical features of the structure of the male and female pelvis (in the first case, posterior fissures mainly occur, while in women, who are statistically affected more often than men, anterior anal fissures predominate). At the first stage, a defect in the mucous membrane of the anal canal occurs, and then infection, cleansing and healing of the defect occur successively. As scientific research has shown, the main role in the regeneration process is played by local immunity, and the chronicity of cracks is a consequence of dysfunction of the latter. Apparently, in some cases, the root cause of the development of cracks may be inflammatory processes in the anal canal associated with a violation of local immunity. In some patients, vascular changes are a risk factor for developing the disease. Indeed, anal fissures are often combined with hemorrhoids. Eliminating blood stagnation and improving blood flow, that is, the main manifestations of hemorrhoids, contribute to the healing of cracks. The role of neurocirculatory disorders responsible for the occurrence of sphincter spasm remains very significant, although the most unexplored. The possibility of influencing this link in pathogenesis with the help of nitro drugs confirmed the importance of eliminating spasm for wound healing. Further research into the mechanisms of crack formation will help improve treatment results.
Prevalence
Approximately 10-15% of patients who seek help from a proctologist suffer from anal fissures. For many years, this disease has been ranked third in terms of treatment after irritable bowel syndrome and hemorrhoids. More than 60% of patients with anal fissure are women.
Classification of anal fissures
There is no classification of anal fissures. According to the course of the disease, acute and chronic fissures are distinguished. According to localization, they distinguish between the anterior ones, located at 12 o’clock on the watch dial, and the posterior ones at 6 o’clock (coccygeal wall of the anal canal), the latter are found in almost 90% of patients.
Clinical picture of the disease
The most common manifestation of an anal fissure is pain associated with bowel movements. As a rule, it occurs at the time of bowel movement and continues after completion of this process for about half an hour. Such clinical manifestations most often correspond to an acute anal fissure. Sometimes the pain appears with the urge to stool or is constant. Prolonged pain and little effect of analgesic therapy, as a rule, indicate the development of sphincter spasm. The latter itself is capable of increasing pain during defecation, which can lead to a vicious circle, manifested by the development of persistent spasm. Bleeding most often occurs at the moment of formation of an acute crack and is rarely profuse, although even small blood clots may be released on the first day. Subsequently, blood discharge is noted on toilet paper; less often, blood drips into the toilet. With chronic anal fissures, bleeding is often associated solely with bowel movements and rarely causes severe pain and spasm. As with hemorrhoids, the blood lost is often scarlet in color. When interviewing patients, it is possible to identify the fact of stool disorders, but it should be remembered that diarrhea leads to cracks no less often than constipation. No less dangerous in terms of the occurrence of cracks is “heavy” coarse stool, caused by ingesting a large amount of coarse fiber without a sufficient amount of liquid. In modern conditions, when collecting anamnesis, the possibility of anal sex should be clarified, which allows not only to establish the cause of the disease, but also to take measures to exclude the specific nature of the lesion. Before examining a patient, you should remember a few strict rules. The order of diagnostic procedures must be strictly observed, which always begins with an examination, which cannot be carried out in a standing position. Digital examination of the anal canal should be carried out using a gel containing lidocaine, starting manipulation from the side of the healthy wall. The absence of visual signs of the disease is not a reason to refuse digital examination and further treatment of a patient with a presumptive diagnosis. The detected changes should be interpreted taking into account the duration of the disease and the treatment performed.
When examining the anus, the patient should be correctly identified. Inspection in the lateral position requires great skill and is a necessary measure. It is preferable to conduct the examination on a gynecological chair or in the knee-elbow position with a good inward bend of the back. The last technique allows you to spread the buttocks well, in addition, you should slightly stretch the skin, and then a defect can be found on the transitional mucosa, sometimes extending to the skin. The length of the crack usually does not exceed 1 cm, although in some cases the defect can reach the length of the anal canal. With an acute fissure, the defect may be oval in shape, superficial, with smooth edges; in some cases, the bottom of the fissure may be the sphincter. The atypical lateral location of the cracks, especially in combination with the multiple nature of the lesions, most often corresponds to improper sexual contact. In the case of a chronic fissure, scars can be found, sometimes with manifestations of hyperkeratosis, the edges of the fissure are raised, its bottom is smooth, sometimes shiny, covered with “varnish granulations.” An infected crack has a dull bottom and undermined edges. The study of the anal reflex, despite the simplicity of execution, is difficult in terms of interpreting the results obtained. The results of a digital examination also largely depend on individual skills, but in any case, forced insertion of a finger into the anal canal is unacceptable. At a minimum, with an acute fissure, it is possible to detect pain in the wall of the anal canal and the manifestation of spasm at the time of its examination, especially pronounced when the dentate line zone (the border of the rectum and the anal canal) is involved in the process. With sufficient experience, it is possible to identify a defect in the mucous membrane, in the case of compaction of the edges of the crack, and detect a sentinel tubercle or hypertrophied anal papilla. Additional visual examination of the anal canal using a mirror or anoscope is carried out by proctologists.
Complications of anal fissure
The most common complications of anal fissure include the development of persistent sphincter spasm, usually accompanied by disruption of the defecation process, sometimes leading to coprostasis. Acute paraproctitis is much less common; sometimes the fissure becomes the cause of an incomplete internal fistula of the rectum. Massive intestinal bleeding occurs extremely rarely, mainly in cases of traumatic development of the fissure.
Differential diagnosis
Clinical manifestations of anal fissure do not differ in the specificity of symptoms. In case of an acute fissure or its complications, the differential diagnosis is made with acute hemorrhoids, paraproctitis, cryptitis, and rectal prolapse. It should be remembered that cryptitis and hemorrhoids are often combined with an anal fissure. Therefore, to carry out a differential diagnosis, one should rely not only on a careful history taking and digital examination (requiring great skill), but also on a visual examination using an anoscope or a rectal speculum. If a deep fissure with undermined edges, similar to an ulcer, is detected, damage to the anal canal by Crohn's disease, specific sexually transmitted infections, or the development of a tumor of the anal canal should be excluded. In patients who have had anal intercourse, injury to the sphincter, rectum, or the presence of a foreign body should be excluded. In case of any treatment of a patient with a fissure to a therapist or general practitioner, in addition to the prescription of simple conservative treatment, he should receive a referral for a consultation with a proctologist.
Conservative treatment
The choice of treatment for anal fissure is usually determined by the stage of the disease or the nature of the complications that have developed. The diet for patients with fissure excludes the consumption of alcohol, spices, and fried foods. As a rule, a protein-plant diet 3 is recommended (a high-fiber table with increased fluid intake to achieve a soft stool consistency). In patients with chronic constipation or “sheep feces”, it is permissible to recommend taking petroleum jelly or liquid paraffins for the period of treatment, but not more than three weeks. In patients with concomitant diseases of the colon, such as irritable bowel syndrome, diverticular disease or nonspecific colitis, the diet should be aimed at normalizing stool.
Patients should pay special attention to performing hygienic measures. During the acute period of the disease, a non-hot shower should be recommended 2-3 times a day and always after stool; in this case, it is necessary to wash not only the skin of the perineum and anus, but also the anal canal itself. In cases where water procedures are not available, the use of special wet sanitary napkins should be recommended.
If a fissure is combined with hemorrhoids, drugs containing bioflavonoids (diosmin and hesperidin) should be prescribed to treat the latter.
Local therapy
The purpose of local treatment is to relieve inflammation, stimulate repair processes and analgesia. To solve the first two problems, we can recommend Posterizan Forte ointment (or candles of a similar name). The drug contains a suspension of E. coli culture and hydrocortisone. E. coli metabolites can enhance local immune responses, accompanied by the release of cytokines, especially intraleukin-1. In addition, a suspension of bacterial culture causes the formation of specific immunoglobulin A, which forms a delicate film on the intestinal mucosa, acting as a local protective barrier. Hydrocortisone, which is the second component of the drug, helps to quickly suppress inflammation and accelerates the processes of tissue regeneration induced by a suspension of Escherichia coli culture. The ointment should be administered using a special applicator while lying down. The drug is prescribed 2 times a day, and in case of severe inflammatory process, for example in patients with nonspecific colitis, the frequency of administration can be increased taking into account the frequency of stool. The maximum duration of treatment, as a rule, does not exceed three weeks. If it is necessary to continue therapy, it is possible to use suppositories or Posterizan ointment containing exclusively a suspension of bacterial culture.
Among the drugs that have an analgesic and reparative effect, Relief Advance suppositories should be recommended. The composition includes 10.3% benzocaine, which has a rapid analgesic effect, in addition, shark liver oil containing fat-soluble vitamins, free fatty acids, squalene and alkylglycerol, which are powerful reparants, which allows them to be recommended even for use in the postoperative period in patients who have undergone intervention for cracks, the frequency of administration is 3-5 times a day. In patients with difficulty defecating, suppositories can be prescribed immediately before stool. In the absence or disappearance of pain, you can switch to using suppositories or Relief ointment without painkillers. The drug is highly effective, well tolerated and rarely produces adverse reactions, which allows its use even at all stages of pregnancy. Conservative treatment of patients with severe pain or sphincter spasm, as well as in cases of relapse of the disease or combination with nonspecific colitis, should be carried out by a proctologist, since the risk of complications or chronicity of the fissure in these patients is extremely high. The use of nitro drugs for the treatment of fissures accompanied by spicter spasm is hampered by the lack of official drugs approved for use for a new purpose.
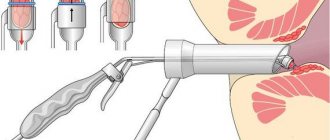
Surgical treatment of fissure
Indications for surgical treatment of anal fissure arise in case of chronicity of the process. In this case, it is important to assess the adequacy of the conservative treatment performed, as well as the nature of local changes. Quite often, patients equate the healing of an anal fissure with the disappearance of its clinical manifestations, which is a very common misconception. Therefore, the disappearance of symptoms of the disease is not a reason for refusing to re-examine the patient. In addition, in some cases, healing may be accompanied by the formation of a very rough scar or “sentinel” tubercle, that is, a small bulge of the mucous membrane at the base of the crack. Persistent sphincter spasm also indicates the lack of effect of conservative treatment. In all such situations, the patient should be referred to a proctologist to decide on the choice of further treatment method. In this case, minimally invasive manipulations include a blockade with an anesthetic and hormones or Botex injections. The use of the latter is an extremely expensive treatment method. Surgery for anal fissure involves excision of the tissue defect followed by open management of the wound until complete healing. In cases where there is a pronounced spasm of the sphincter, excision of the fissure is complemented by dosed dissection of the sphincter, the so-called lateral submucosal sphincterotomy. The duration of disability in the postoperative period is determined by the rate of healing of the postoperative wound and depends on its size and individual characteristics of regeneration. As a rule, it takes 3-4 weeks until the wound is completely epithelialized. Relapses after surgery are very rare.
Literature
- Fundamentals of coloproctology edited by Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, prof. Vorobyova G.I. Rostov-on-Don: Phoenix Publishing House. 2001.416.
McNally P.R. Secrets of gastroenterology trans. from English M.-S.-Pb: ZAO “Publishing House BINOM” “Nevsky Dialect”. 1998. 1023 p.
K. E. Mayat
,
Candidate of Medical Sciences European Medical Center
,
Moscow
A disease characterized by the appearance of linear breaks and damage to the mucous membrane of the rectum is called anal fissure. The pathology can occur in both sexes, but most often it affects women of childbearing age.
Prevention and prognosis of anal fissure
Prevention of anal fissure consists of proper nutrition, an active lifestyle, and timely treatment of diseases accompanied by stool disorders. Regular walks, walking, and physical exercise help prevent congestion in the pelvic area.
An anal fissure that is quickly identified and treated conservatively in a timely manner is completely cured in 60-90% of cases. Inadequate treatment, self-medication, and delay in seeing a doctor contribute to the chronicity of the fissure, which worsens the prognosis and may lead to the need for surgical treatment. Surgical excision of the anal fissure leads to recovery in the vast majority of cases.
LiveJournal