What tumor markers exist?
Markers do not necessarily indicate malignant tumor processes.
Such substances are natural to the body. The values increase during pregnancy, when the pregnant woman feeds the fetus. Intestinal tumor markers are usually divided into precise specific and rough nonspecific proteins. These substances are detected in cancer of the heart, kidneys, intestines and brain. With their help, they think about the presence of a malignant tumor, but it is impossible to indicate the exact location.
The group includes:
- Alpha fetoprotein (AFP) is a glycoprotein that also appears during gestation.
- LASA-P – liver antibodies to malignant tumors.
- Tu M2 PK – using Tu protein, the metabolic rate of cancerous tissues is determined. The indicator is considered a marker of choice; it is used to determine pathological growth in the body.
Such studies are not very specific. With their help, they determine the growth of cancer in the gastrointestinal tract, lungs, and nervous system.
Remember, deviations from the norm do not provide complete confidence in malignant growth. If there is a suspicion of an increase in oncological values in the blood and body fluids, a thorough examination by specialists is required.
The group includes substances characteristic of the pathology of a particular organ. For example, for the stomach, liver or rectum. Their detection makes it possible to indicate the location of cancer with a high degree of probability. When the intestinal tract is damaged, the following indicators are most often detected:
- Carcinoembryonic antibodies (CEA) are a protein of cancer of the initial parts of the intestine. By assessing the results of the identified values, it is possible to predict and control the growth of small intestinal tumors. Decoding of CEA indicators is carried out to analyze the quality and success of treatment.
- CA 72-4 - this protein is often tested for detection in conjunction with cancer antibodies. The protein can be detected in tumor tissues of the large and sigmoid intestines in the small cell type. Increased antigen values also indicate colorectal cancer.
- CA 125 – The main indicator of cancer of the thick sigmoid part.
The detection of antibodies and proteins in the indicators indicates particularly malignant growths in the digestive tract.
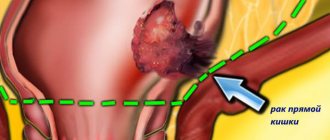
Cancerous tumor in the intestine
Tumor marker for colon and rectal cancer - types, preparation, meaning
To carry out laboratory diagnostics correctly, the patient must be prepared in advance. He needs to be warned that the test will be taken on an empty stomach. The day before performing the laboratory procedure, the patient must give up fatty, fried foods and foods with high concentrations of various flavor enhancers, preservatives, stabilizers and dyes.
Every year, at least 8 million people die from cancer of the digestive tract, with intestinal cancer being the second most common cause.
Such indicators are associated with late diagnosis of the disease, when the tumor is no longer operable and metastases spread throughout the body.
It is possible to detect cancer at the very beginning and increase the chances of recovery using a specific analysis for intestinal tumor markers. It allows not only to confirm or exclude the presence of a malignant tumor, but also to determine its type, location, monitor the progress of treatment and predict relapses in the future after surgical removal.
Therefore, at the first signs of dysfunction of the digestive system, accompanied by constant weakness, alternating constipation and diarrhea, bleeding after defecation, an increase in ESR in the general blood test, weight loss and a temperature within 38⁰C, there is a need to take tests for intestinal cancer.
This is how medicine refers to special protein compounds produced in response to the development of a malignant tumor or by cancer cells themselves in the process of life.
Normally, their concentration is low, but in cancer cases it increases already at the first stage of the process.
If the results of the initial screening for intestinal tumor markers are positive, then a full comprehensive examination is required to confirm the diagnosis.
In this case, cancer markers are divided into:
- nonspecific – allowing only to detect the presence of a neoplasm;
- specific - their presence informs not only that cancer exists, but also its location.
Once the diagnosis is made and confirmed, tests are done regularly to monitor the development of the tumor.
It is necessary to understand that tumor markers should be studied only in conjunction with other tests. In this case, the oncologist should decipher the results. These tests help in primary screening diagnosis and further monitoring of the disease, however, the diagnosis is not made based only on the results of tumor markers.
Main article: What are tumor markers, how much can you trust them, types, how to get tested correctly
Today, more than two hundred types of tumor tumor markers are known, but only five are important for laboratory diagnosis of colorectal cancer.
Based on their concentration and combination, one can judge the localization of the source of the disease, monitor the dynamics during the treatment process, make predictions and determine the likelihood of relapse.
Knowing the names of intestinal tumor markers and their values within normal limits, it is possible to monitor the effectiveness of treatment, the appearance of metastatic foci and the risk of disease relapse.
Abbreviated as CEA, it is not detected at all in a healthy person or is contained in an insignificant concentration of up to 5 ng per ml. It is produced by the body only during intrauterine development and ceases to be produced after birth.
That is why its presence in the blood plasma in large volumes suggests the presence of a rectal tumor. However, an increase in the level of carcinoembryonic antigen is also characteristic of heavy smokers and people suffering from inflammatory diseases.
For this reason, additional laboratory and instrumental diagnostics are required.
The information value of this tumor marker for intestinal cancer is very high, since it is it that is always determined in the colorectal form, that is, it is specific.
Specific numerical indicators make it possible to judge the growth and size of the tumor, that is, the stage of the cancer process.
Once treatment is prescribed, it allows you to monitor its effectiveness and adjust the course, and after recovery, regular studies help predict a relapse long before its clinical manifestation.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Asd fraction 2 - use in oncology
It is a nonspecific tumor marker for intestinal diseases, since it is also detected in the blood in the case of pancreatic and esophageal cancer. Its concentrations also increase with pancreatitis, cholestasis, and cirrhosis of the liver. When the location of the tumor has already been determined, based on the results of the analysis for the CA 19-9 antigen, one can judge its operability and make predictions:
- up to 1000 units per ml – about 50% of patients can be operated on with a subsequent favorable outcome;
- above this indicator - only 5% have a chance of success of surgical treatment;
- more than 10,000 U/ml of this type of intestinal tumor marker in cancer indicates the presence of distant metastases and the futility of surgery.
Normally, the antigen content should not exceed 40 units per milliliter.
Tumor marker CA 242
Another carbohydrate compound characterized by a higher level of specificity. It is secreted by cancer cells of tumors of the same localization as CA 19-9, but makes it possible to more reliably detect colorectal cancer at an early stage.
It is of great importance for predicting relapse of the disease after treatment, since the concentration of the antigen begins to increase several months before clinical signs. With negative results for tumor markers for rectal and colon cancer, the values do not exceed 30 IU/ml.
Tumor marker CA 72-4
This substance also belongs to glycoproteins, the presence of which in the body is normal only for the period of intrauterine development. If, as a result of the analysis, its quantity exceeds the value of 6.9 units per ml, then we can judge the presence of a malignant tumor:
- intestines
- ovaries
- lungs
- stomach
Therefore, intestinal tumor marker 72-4 alone is not enough to reliably determine colorectal cancer (assessed in combination with CEA indicators). In addition, it is detected in benign formations and ordinary ovarian cysts, some liver diseases, and rheumatism.
Tumor marker Tu M2-RK
The tumor marker ptu m2-rk (tumor pyruvate kinase type m2 enzyme) does not differ in organ specificity. This test cannot determine the location of the tumor.
It reflects the nature of metabolic processes in the cells of malignant neoplasms, allowing one to draw conclusions about the presence of cancerous degeneration, its metastases, and also predict postoperative relapses.
A stool sample is required for laboratory testing.
To test for the presence of tumor markers-glycoproteins, you need blood, which should be donated in the morning and strictly on an empty stomach. That is, the last meal should be no less than 8 hours before taking the sample. It is also undesirable to drink sweet drinks the night before and take one of the B-group vitamins - B7. The latter distorts the result of the analysis for identifying the CA 72-4 antigen.
It is forbidden to drink alcohol (at least 48 hours before the test). The day before diagnosis, you should avoid heavy physical activity. Before donating blood (one hour), you should refrain from smoking.
The Tu M2-RK enzyme is isolated from feces for laboratory research, so you also need to prepare for this test for tumor markers for intestinal cancer.
A small amount (about a tablespoon by volume) of feces is placed in a special sterile container and delivered to the laboratory.
It should be borne in mind that laxatives or an enema should absolutely not be used for defecation - the material must be obtained naturally.
The timing of tests for different tumor markers for colorectal cancer differs:
- results for antigens CA 19-9, CA 242 and CEA will be ready within 24 hours;
- detection of glycoprotein CA 72-4 will take from 3 to 7 days;
- Stool examinations last a week.
The conclusions issued in the laboratory make it possible to decipher information about the results.
It is no coincidence that a comprehensive analysis of several tumor markers is prescribed for the diagnosis of malignant neoplasms. Even the most highly specific antigen is not 100% accurate and more information is required.
So, how to “read” a tumor marker in combination with others:
- elevated levels of glycoproteins CA 19-9, CA 72–4 and CEA suggest gastric cancer;
- the most specific CA 242 in combination with CA 19-9 and CEA is highly likely to indicate rectal cancer;
- Tu M2-RK enzyme in combination with high concentrations of CEA, CA 19-9 and CA 242 – colon tumor.
However, the presence of indications for studying the level of tumor markers and their positive result is not a death sentence. It is impossible to draw any conclusions on your own based on this information alone without a thorough comprehensive examination, since antigens appear in the body during a variety of diseases.
What tumor markers are used to diagnose stomach diseases?
For the diagnosis of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, the tumor marker CA 72-4 (Cancer Antigen), which is a complex of protein and oligosugars, is most useful. Its norm is considered to be up to 6.9 U/ml, thus, an increase in the analysis of gastric tumor markers from 7 U/ml and above can be considered a basis for further screening examination.
Cancer antigen 72-4 is the main indicator for diseases of the stomach, but to verify the diagnosis, a comprehensive study and identification of other tumor markers are required. The fact is that the tumor marker CA 72-4 can often increase in ovarian cancer, which casts doubt on the diagnosis of stomach cancer. To confirm his assumption, the doctor prescribes a test for:
- CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen);
- CA 19-9;
- CA 50.
A combined increase in these markers will with high confidence indicate gastric pathology.
An increase in tumor markers in the blood can be observed during infectious diseases, against the background of inflammation. This is a nonspecific manifestation of a systemic inflammatory response (as is an increase in ESR or CRP), which should not cause increased concern. Some time after recovery, it is better to get tested again, and most likely all the indicators will return to normal.
Any oncological process does not manifest itself clinically until a certain point, however, thanks to the accuracy of laboratory tests, it can be suspected in the early stages. Depending on the tissue of the tumor, tumor markers may be different in different cases, but most often a pattern can be observed.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How genital (genital) herpes is transmitted - routes of transmission, how you can become infected, when you are contagious
The concentration of tumor marker CA 72-4 may increase with:
- gastrointestinal cancer, 40%;
- lung cancer, 36%;
- ovarian cancer, 24%.
An increase in CA 72-4 in pancreatitis, cirrhosis of the liver, rheumatic diseases and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract with a relatively benign course (gastric or duodenal ulcers, various gastritis) should also be considered a nonspecific reaction of the body.
Classification
To determine the nature of the pathology, there are types of intestinal tumor markers:
- specific;
- nonspecific.
Tumor markers of the first group show the location of intestinal cancer and the degree of damage to the organ. An increase in the concentration of nonspecific proteins reveals the presence or absence of a malignant neoplasm.
Specific
Tumor markers of the first group of substances for rectal cancer include:
- carbohydrate antigen;
- carcinoembryonic antigen;
- tumor marker of choice.
An increased concentration of carbohydrate antigen determines the initial stage of development of cancer of the rectum, colon, pancreas, ovarian region, and gall bladder. If the amount of tumor marker CA 242 exceeds the norm, an immunological study is performed to detect the development of a neoplasm. The increased concentration of carcinoembryonic antigen determines the degree of organ damage in rectal cancer, formation parameters, and the dynamics of tumor growth.
The study of tumor markers makes it possible to evaluate the progression of pathology, the effectiveness of prescribed treatment, and the likelihood of disease relapse. To detect small cell cancer in the lungs and colon, an analysis is done to detect the amount of specific proteins CA 72-4.
The tumor marker of choice determines the nature and rate of progression of the cancer tumor. Determination of metabolic processes and the level of metabolism of malignant cells reveals the spread of tumors of the stomach and intestines. The amount of Tu M2-PK proteins gives an idea of the presence of oncology, the degree of progression of the pathology, and the spread of metastases.
Nonspecific
Tumor markers of the gastrointestinal tract that do not provide information about the location of tumor formation are:
- AFP;
- CA 19-9;
- CA 125;
- CYFRA 21−1;
- SCC;
- LASA-P.
An increased concentration of the tumor marker alpha-fetoprotein, CYFRA 21−1, diagnoses the presence of cancer of the rectum and respiratory system. An indicator of the carbohydrate antigen CA 19-9, exceeding the norm, indicates the development of an internal pathological process without establishing the localization of malignant cells.
CA 125 – the presence of cancer of the sigmoid process, the ovarian region. The level of concentration of the squamous cell tumor marker SCC determines the formation of a tumor in the rectal canal. An increase in LASA-P indicators indicates damage to other parts of the digestive system.
When to take it
The study of gastrointestinal tumor markers is carried out using blood, urine and feces. You have to choose the most suitable option. If you do not want to donate blood, it is permissible to choose another medium. In this case, the diagnostic range of markers will be lower. The most common method is a blood test. For a good and accurate value, you should follow a diet for a number of days, and on the day of the procedure, come with an empty stomach in order to donate blood with the correct result.
The last meal is taken no later than 12 hours before the expected delivery. It is necessary to remember this rule. Many doctors recommend not eating the night before the test. A couple of days before the appointed date, give up sweet foods. Juice, sugary sodas and tea will compromise the accuracy of the test.
Blood is not suitable for analysis if a person takes B vitamins. This is critical if the test targets markers like 72-4. It is better to stop taking the drug the day before the test. In case of urgent need, the time is reduced to 8 hours.
The study of the Tu M2 PK marker is considered special. For research, the biological medium is stool analysis. Enemas and the use of laxatives are contraindicated. Due to its specificity, the result takes longer to determine than a blood test. The waiting time is 4 – 10 days.
Limitations in the use of the tumor marker method are highlighted. Examination of blood taken for nonspecific indicators gives incorrect ideas about the structure of morbidity. High values of individual indicators do not necessarily indicate tumor-like growths. Tumor markers for intestinal cancer are also isolated during inflammatory and structural changes in organs, and they are not associated with the spread of malignant neoplasms.
It is extremely difficult to identify a tumor in the digestive organs. The reason for the difficulties is the meager and vague symptoms of many clinical types of cancer at the initial stage. For laboratory determination, the values of cancer proteins are looked at. Determining the critical values of complex proteins at the beginning of the disease will increase the chances of successful treatment and longevity.
For individuals diagnosed with a malignant tumor, tumor markers are useful in assessing the effectiveness of therapy. During the therapeutic course, repeated measurements of oncotic proteins show the effect of the drugs used in a particular case. There are no identical diseases, just like there are no identical people. Therapy is required to be comprehensive and tailored to the patient.
Cancer oncoprotein shows intestinal cancer long before noticeable changes in the body begin. Various biological media and liquids are used for detection. Tests of saliva, urine, and stool can determine the presence of altered proteins.
Changes in the functioning of the digestive system are called dyspepsia. Similar phenomena include a feeling of heaviness after eating, heartburn, and nausea. These are stomach symptoms. Intestinal pathology causes bloating and constipation. The presence of flatulence and rare stools is considered a pathology of the intestinal canal.
We suggest you read: Is it necessary to remove pus from tonsils?
What are tumor markers?
Tumor markers are specific proteins that appear in the body as a result of the manifestation of activity by both tumor and healthy cells located next to the malignant formation.
They function as unique markers in the body, by the increased number of which it is possible to identify the area of the intestine susceptible to cancer. Malignant tumors, including gastrointestinal cancer, are diagnosed in the majority of patients who seek medical help. The danger of this disease lies in the difficulty of diagnosing it at an early stage.
Symptoms often appear too late. Occasionally, during a preventive examination, it is possible to suspect a pathology, then the patient is referred for tests. By analyzing tumor markers for intestinal and rectal cancer based on their level, the doctor can determine the disease, its nature and stage.
Tumor markers are certain types of proteins found in the blood. They can also be present in a healthy person, only in small quantities, not exceeding normal levels.
Malignant tumors promote the production of the corresponding protein, which leads to an increase in the concentration of tumor markers.
When colon cancer tumors appear, tests make it possible to clarify the location of the pathology and determine the stage of the disease.
Among the proteins that indicate problems with the gastrointestinal tract, there are 2 groups:
- Specific – identifying tumor formations in a specific place in the body.
- Nonspecific - detect oncology, but do not record localization.
The first group includes the following tumor markers:
- Carbohydrate antigen (CA 242) - shows cancerous pathology of the colon, rectum or pancreas at an early stage. The study makes it possible to determine how the tumor will behave over the next five months.
- Carcinoembryonic antigen - is responsible for detecting oncology in the rectum. Analysis of the study results allows us to talk about the nature of the cancer, the dynamics of the increase in tumor size, and calculate the period of disease progression. Using CEA, oncologists evaluate the effectiveness of therapy and determine the risk of relapse.
- SA 72-4 is prescribed as an addition to REA. This tumor marker is found in malignant cells of the lungs and colon if small cell cancer occurs. Colorectal pathology is also determined using this antigen.
- Tu M2-RK (the second name is the tumor marker of choice) - allows you to identify all metabolic processes occurring in cancer cells. This type of study is prescribed for specific metabolic indicators. It helps to identify oncological tumors of the gastrointestinal tract, including carcinoma.
The group of nonspecific markers includes the following indicators:
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) - manifests itself as an increase in the content of α-fetoprotein, which indicates the appearance of a tumor-like neoplasm in the rectum and sigmoid colon.
- CA 19-9 is a marker that determines cancer pathologies of the large intestine, bile ducts and bladder itself, esophagus, and pancreas.
- CA 125 - using this indicator, the pathological process that has arisen in the sigmoid colon, leading to the formation of a tumor, is determined.
- CYFRA 21-1 - high values for this marker indicate the presence of a malignant lump in the rectum.
- SCC - helps to detect the presence of cancerous pathologies of the anal canal.
- LASA-P - increased antigen content gives a signal about the suspected occurrence of a malignant process in other parts of the intestine.
Thanks to research to determine cancer markers, it is possible to identify the disease before the first manifestations and symptoms. However, it is important to consider that exceeding the normal limits of the level of antigen concentration in the blood itself does not guarantee the presence of oncology.
If the patient’s tests show alarming results, he is offered additional examination to confirm or refute the preliminary diagnosis.
To determine the level of tumor markers, the patient donates blood as the biomaterial being studied. The sample collection procedure is carried out early in the morning. It is important that the patient does not eat for eight hours prior to the test. To get clear answers, doctors recommend refraining from drinking coffee, tea and juices, replacing them with water.
The results of the study will be ready a day or two after the collection of biological material. Tests to determine the level of protein antigen CA 72-4 are carried out taking into account the possible intake of biotin, since a daily dosage exceeding 5 mg will violate the veracity of the results. It is then recommended to postpone the study for 8 hours until the drug is removed from the body.
The level of Tu M2-RK is determined by analyzing stool. The specificity of this procedure is the prohibition of extracting biomaterial by enema or with the assistance of laxatives. Feces are obtained exclusively naturally. Results are issued after 7 days.
Tumor markers for stomach and intestinal cancer are detected by private or public laboratory workers. To do this, you must provide your biological material.
Before proceeding to donate blood, the patient must carefully follow the recommendations issued by the oncologist for the allotted time to ensure reliable results. Measures to prepare for the procedure are as follows:
- For a week, exclude fried, smoked, fatty and sweet foods from your diet.
- Drink only water, neglecting other drinks.
In the morning, on an empty stomach, the patient must report to the laboratory, where a nurse will draw blood from a vein. Within a week, the biomaterial is studied, then the results are generated and presented. If a person was previously diagnosed with neoplasms of various natures, then monitoring for tumor markers should be carried out on a regular basis.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fmbe5svRrUw
Experts do not make conclusions about the presence or absence of cancer based on one individual marker, since such a statement may not always be accurate. To make a diagnosis, the results of combined studies are often taken into account. Eg:
- CEA and CA 242 indicators reveal malignant pathological formations of the stomach.
- The CEA marker, together with CA 19-9, is responsible for the diagnosis of rectal cancer.
- The combination of CEA, CA 242 and CA 19-9 is required when it comes to determining the presence of colon cancer.
To detect pyruvate kinase, an enzyme produced by malignant cells of the gastrointestinal tract, a study of the tumor marker Tu M2-RK is carried out.
In some cases, an increased concentration of antigens may signal the presence of other pathologies in the body. For example, a high concentration of CEA often indicates disorders in the venous system. Such signs are also characteristic of Crohn's disease and cirrhosis of the liver.
The results of each biochemical analysis are checked using additional studies (ultrasound, magnetic resonance or computed tomography).
Having received the test results in hand, you should take into account when studying the indicators that the data can be interpreted in different ways. It all depends on the laboratory in which the research was carried out. Different clinics use different measurement systems, so it is important to compare the obtained figures with generally accepted standards:
- CA 72-4 - does not exceed 6.3 IU/ml.
- CA 19-9 - up to 40 IU/ml.
- CA 242 - in the range of 0-30 IU/ml.
- CEA - no at all (0 IU/ml).
In some situations, tumor markers may be lowered. This indicates the absence of cancer, but the presence of possible damage to the kidneys or liver. Colon cancer shows a combination of markers CA 242, CA 19-9 and RAE.
Doctor's report
When examining indicators for the presence of intestinal cancer, experts compare test results with standard norms characteristic of healthy men and women. Deviations are calculated based on the concentration of tumor marker in the blood. If the difference in values is too serious, then cancer can be assumed.
In order to detect cancer of the intestine or other organ of the gastrointestinal tract on time, it is necessary to undergo a preventive examination every year to determine the content of tumor markers. The earlier cancer is diagnosed, the higher the patient's chances of recovery.
Cancer of the gastrointestinal tract today, alas, is very common. The reason for this is poor ecology, hereditary problems, addiction to bad habits, unhealthy lifestyle, chronic diseases, exposure to various radiations surrounding modern man, and other factors. Cancer tends to “grow younger”, affecting people even before the age of 30.
In the initial stages, the disease manifests itself in almost no way; patients do not experience negative symptoms. And when they appear, and people finally turn to a specialist, the disease has already seriously affected the body. A general blood test for intestinal cancer is not always able to detect the cancer process, and doctors have been looking for a way to detect cancer at its inception for many years. As a result of these searches, a new technique emerged - diagnosis using tumor markers.
A blood test for oncology usually detects two types of markers:
- highly specific - indicating a specific type of pathogenic cells;
- common, accompanying a variety of types of cancer.
Markers of intestinal cancer pathology allow specialists to solve a number of problems:
- Determine the location of the tumor.
- Monitor the patient's condition over time during treatment, monitor his condition after removal of the affected tissue.
- Prevent relapse of the disease.
- Identify people at risk for intestinal and gastrointestinal diseases in general.
The following main tumor markers for rectal cancer are used in diagnosis today:
- alpha-fetoprotein test. An increase in its concentration shows that there is a neoplasm in the sigmoid part of the intestine, and the concentration itself demonstrates the stage of the disease;
- CA 72-4 and often accompanying LASA-P are markers indicating problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- CA 242 - it is considered basic for the diagnosis of various intestinal tumors;
- test for carcinoembryonic antigen - more often called CEA. It is very sensitive to the occurrence of pathological formations in the colon;
- test for the marker CA 19-9 - another protein, the presence of which in the blood is characterized by colon cancer, as well as rectal cancer. As a rule, it complements CEA and the marker CA 242;
- protein CA 125 - this tumor marker for cancer warns of disease of the sigmoid intestine;
- The SCC antigen tells the doctor about a tumor near the anus;
- pathological intestinal neoplasms also lead to an increase in the level of CYFRA 21-1 protein.
Indications for analysis
Blood donation for tumor markers is carried out for two possible reasons: either there is a suspicion of cancer, or against the background of treatment, in order to track the dynamics of tumor decay.
Most often, patients receive the prescription due to complaints of poor health, lack of appetite or dyspeptic disorders. Reduced hemoglobin and the ineffectiveness of vitamin therapy and an iron-containing diet also signal the doctor about the need to look at the level of tumor markers.
After gastroscopy, this analysis is extremely rarely needed, since the clinical picture is usually clear. However, the level of these substances in the blood serves as a very reliable reflection of the advanced state of the disease. The higher the level of specific tumor markers, the more severe the patient’s condition and the more difficult his treatment. We can say that the level of tumor markers determines the expected outcome for a particular patient, indicating the likely outcome of treatment, the chances of survival of the patient or the need for surgery.
After surgery for gastric cancer, tumor markers must be reviewed a couple of times a year, since any oncological pathology tends to recur. After tumor removal, the kidneys eliminate all decay products, and the level of foreign tumor glycoproteins gradually decreases, reaching normal values the very next year.
Antigen ca 72-4
However, an increase in the CA 72-4 tumor marker will not always be a bad sign. High levels of this glycoprotein in the blood are a good prognostic sign after chemotherapy.
Venous blood is taken from the morning until 12 o'clock. For the study, blood is donated from a vein on an empty stomach; only 3-5 ml is enough. Before the analysis, it is better not to drink strong coffee or tea; it is better to limit yourself to plain or sparkling water. Immediately before taking blood, it is better not to smoke, as this provokes gastric secretion and can distort the result.
The attending physician who prescribed the test must be informed in advance about all medications that the patient takes constantly or periodically, and previous medical procedures performed. Laboratory testing is carried out using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), which means that, on average, the result of the examination can be found out the very next day.
When is an analysis for tumor markers of stomach cancer necessary?
It is necessary to do a study if any digestive problems often arise against the background of chronic fatigue and fever.
The analysis is also indicated for those who are over 40 years old or have a family history of cancer. In addition, regular screening during and after treatment is necessary. In the first case, the level of tumor markers informs about the effectiveness of treatment, and in the second, it signals an impending relapse long before its manifestation.
Organs of the gastrointestinal tract
The digestive system is the most massive in the human body. The length of the digestive canal in the body of an adult male reaches an average of 10 meters. The development of a malignant process in any part is accompanied by similar symptoms. Lack of bowel movements for 4 days, constipation, and bloating can be warning signs of many types of cancer. To determine the exact location, you need to understand the structure of the intestinal tract.
Small intestine
The first site of food absorption in the body is the small intestine. Conventionally, it is divided into duodenal, jejunal and sigmoid sections. The pathological process is localized in all areas equally, but tests for tumor markers give different results.
- CEA is the main marker of cancer of the small intestine, mainly the middle section. The values of this protein increase in cancer of the jejunum and, less commonly, of the ileum.
- CA 19-9 is an oncology antibody of the very first section of the intestine, the duodenum. It can also be detected by analyzing tumor markers of the stomach and esophagus.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Skin tumor markers, numbers of tumor markers for identifying skin melanoma
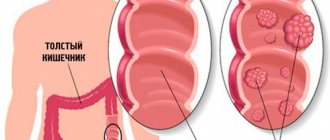
Colon
The large intestine is the last section of the digestive tract. Here feces are formed and abundant enzymatic reactions occur. The large intestine contains a variety of microflora, so cancer in these sections is easily detected by the results of protein tests in the blood and stool.
The main structures of the large intestine are the cecum, colon, sigmoid and rectum.
- CA 125 – protein 125 is assessed for suspected sigmoid colon cancer.
- CYRFA 21-1 is the name given to the conditional brother of rectal cancer. A critical increase in indicators occurs precisely with this type of cancer.
- SCC - like the previous marker, signals the development of cancer in the last section of the intestine.
Stages of bowel cancer
When is this analysis needed?
It is necessary to submit biological material for detection of cancer markers if the patient’s ultrasound, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging revealed formations of unknown origin.
An alternative to the laboratory method is only a needle biopsy. But this method is invasive and can cause cancer metastasis. The following clinical symptoms are also direct indications for diagnosis:
- Stool disorders. Constipation or, conversely, diarrhea may predominate. But more often, constipation (difficulty defecating) and diarrhea alternate.
- Unpleasant sensations in the stomach. Pain rarely accompanies neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract in the early stages. Therefore, the patient can only complain of bloating and a feeling of fullness in the epigastric or iliac regions.
- Dramatic weight loss. When a tumor reaches a certain size, it begins to take nutrients from the body for its own growth.
- Changes in the skin. They can manifest as rashes, pigmentation and other artifacts.
- The appearance of dense lymph nodes unpaired with the skin. They are often painless.
Decoding the results
If the values of pathological proteins are increased, a detailed examination of all body systems is required. An integrated approach increases the reliability of the diagnosis. Below is what tumor markers of the gastrointestinal tract are present in the blood and their relative norm.
- CA 242 – 0-30
- PEA – 0-5.5
- SA 72 – 3.8-4
- Tu M2 PK – 1.5
- AFP – 15
- SA 19-9 – 3.4
- CA 125 – 2.5
- CYRFA 21?1 – 3.3
- SCC – 1.5
Such substances appear in pathological quantities in the blood and during benign processes. Informational value means analyzing dynamics, how indicators change depending on a change in diet, stress, and medications used. If metastases are suspected, proteins are examined monthly to assess tumor growth.
Cancer is not a death sentence. The sooner a problem is diagnosed, the sooner a solution will be found for it. In the first stages without metastasis, organ-preserving operations are used. Such techniques are complemented by radiation and chemotherapy. Do not delay going to the doctor and self-medicate. With its dangerous development and large volumes, cancer is difficult to treat. In such cases, partial removal of the affected organ is recommended. They resort to palliative care - alleviation of symptoms.
The treatment option depends not only on the speed of medical prescriptions, but also on the person’s mood. You can’t give up and give up; cancer can be cured. However, if you consider yourself a loser, it is much more difficult to do this.
What are tumor markers for colon cancer: names, how to take them
Gastrointestinal tumor markers:
- REA. It is also characteristic of gastrinomas and rectal neoplasms.
- SCCA. It can increase in cancer of the esophageal gastrointestinal tract, anus, uterine cervix and lung tissue.
- CA 72-4. Very typical for tumors of gastric origin.
- CA 19-9. It increases sharply in all malignant neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract. But his numbers are used when determining the advisability of surgical intervention.
- CA 242. Also acts as a high-quality gastrointestinal marker.
- TU M2-RK. In addition to cancer of the gastrointestinal tract, it indicates a malignant process in the lung and kidney tissue.
- AFP. It is often found in females with tumors of the genitourinary system.
- CA 50. Its value is used when determining therapeutic tactics.
- CA 125. This biologically active substance is extremely specific and can be detected both in pancreatic carcinoma and in cancer of various organs of the gastrointestinal tract or female reproductive system.
Deciphering the results of the level of concentration of tumor markers helps to establish the presence of a pathological process in the organs of the digestive system.
The normal amount of proteins in the blood is:
- CA 242- 0-30 IU/ml;
- CEA – 0-5.5 ng/ml;
- CA 72, LASA – P – 3.8-4 IU/ml;
- Tu M2-PK – 1.5 IU/ml;
- AFP – 15 ng/ml;
- CA 19-9 – 3.4 IU/ml;
- CA 125 – 2.5 IU/ml;
- CYFRA 21−1 – 3.3 IU/ml;
- SCC – 1.5 ng/ml.
Exceeding the norm for the carbohydrate antigen CA 242 means the formation of cancer cells in the pancreas and large intestine. The stage of development of the disease is determined through a structural study of the okomarker. Early diagnosis of increased CA 242 levels guarantees positive dynamics in cancer treatment.
The presence of cancer is indicated by an excess of CEA concentration. A specific protein value greater than 5.5 units is a sign of a pathological change in the structure of the colon.
Accurate detection of cancer is possible with a comprehensive determination of intestinal tumor markers. Prescribing a combined analysis of specific and nonspecific proteins increases the likelihood of a correct diagnosis. The types of laboratory tests are determined by the doctor depending on the purpose of blood sampling: establishing the presence of a tumor, the location of the spread of cancer cells, monitoring the progression of pathology.
Among cancer diseases, intestinal cancer is of significant importance. Intestinal tumor markers are used to promptly identify symptoms characteristic of a given situation. Thus, the development of the pathogenic process is determined. You should understand the mechanism of operation of these substances and find out what laboratory tests are necessary.
Intestinal oncology
It is worth understanding the structural features of the intestines. Its main components are the small and large intestines. The small intestine includes the duodenum, ileum, and jejunum.
Considering the structure of the large intestine, it is worth noting the cecum, rectum and colon, which are its constituent components. The rectum area ends at the anus. Pathological processes of development of neoplasms are observed in different places.
A person feels constipated, which is natural if there is a tumor. It helps block the movement of bowel movements along its natural path.
There are several effective ways to determine the disease at the initial stage of development. This diagnosis includes a tumor marker for colon cancer.
They represent a special kind of chemical substances, in other words proteins, which can be identified using biomaterials.
The components can be produced both by malignant cells and neighboring organs. During diagnosis, the protein indicator, subject to the development of cancer, is at an exceeded level. Urine, blood, and in fairly rare cases, feces are used for analysis and evaluation of results.
Important! Tumor markers perform functional work, which is manifested in effective treatment monitoring. Their use helps determine the effectiveness of the course prescribed by a specialist.
So, the following tumor markers of the small intestine are distinguished:
- a type characterized by the development of a progressive type of cancer. This type is called highly specific;
- a type that helps confirm the presence of a malignant tumor. This is a non-specific type of marker.
Malignant neoplasms can reveal:
- CEA markers are particularly sensitive. The tumor marker of the large intestine is in the normal range – up to 5 units. Its absence is also possible;
- antigen CA72 – 4 is responsible for effective diagnosis in the field of colorectal oncology. A value of up to 6.3 is considered a normal level;
- indicates metabolic processes in the area of pathogenic Ti M2 cells - RK;
- If the CA19-9 value is exceeded, conclusions can be drawn about the presence of cancer. The norm fluctuates around 40 units;
- at the stage of initial development of cancer, CA 242 is detected. The optimal level is considered to be 0 – 30 units.
It is also worth noting that exceeding the normal level of the indicator is not a 100% guarantee that an oncological process is present. When observing this situation, it is necessary to conduct additional examination, in particular basic tests.
The procedure is carried out in different places. This is a government-type center or a private medical center. So, what tumor marker shows bowel cancer? These are SA 72 - 4, REA, SA 19 - 9, SA 242.
It is important to prepare properly for this process before donating blood for intestinal tumor markers. Experts recommend:
- minimize, completely avoid junk food. This category includes fried, smoked, fatty foods;
- The last meal before the procedure should take place 8 – 12 hours before;
- It is necessary for the patient to stop drinking alcohol or smoking.
It is important to take the test on an empty stomach, in the morning. You should rest before taking the test. By following all the above recommendations, you can achieve the most accurate result.
Important! The results of the analysis are received by the attending physician within 24 hours. To assess Ti M2 – RK, cal is used. Evaluation of this tumor marker is possible after a week.
You should learn about the characteristics of tumor markers.
CA 72-4 should not be found in the body of a healthy person. Its content is acceptable in cases where there is a tumor in the area of the large intestine. The recommendation in this case would be a screening procedure for colorectal cancer. Together, it determines this type with a CEA marker in the laboratory.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with What is the Roma premenopause index
A normal amount of CEA is produced during pregnancy by the body's digestive system. Based on the analysis data, it is possible to accurately determine the size of the tumor and evaluate this indicator for the further course of treatment. By assessing the marker, it is possible to predict possible relapses in the near future.
CA 19 – 9 is considered additional, which is assessed after the above markers. Among his main functional responsibilities is the ability to diagnose possible relapses. The marker is also able to detect the presence of a tumor in the ovarian area. With the help of its monitoring, qualified specialists monitor the effectiveness of treatment and its effect on the gastrointestinal tract.
The next, rather specific protein, CA 242, is generated in the rectum area, as well as in the large intestine. Thanks to its assessment, it is possible to determine the presence of a tumor of a certain period. This value is in the range from 3 months to 6.
There are also other types of tumor markers. In particular, this is CA 125, it is used to diagnose the sigmoid colon. This group includes SYFRA 21 - 1, which indicates the presence of a cancerous tumor in the rectal area. SCC determines the oncological process in the rectal canal area.
The advantages of this procedure are clear, but it is worth considering the negative side.
Advantages of use:
- the ability to diagnose a neoplasm at the initial stage of development of the disease;
- implementation by specialists of effective forecasting in order to minimize relapses after the course of therapy has been completed;
- monitoring the course of treatment.
Disadvantages of use:
- if the concentration of specific proteins is exceeded, the last stages of the disease can be determined;
- they are not fully specific; their ability to indicate the presence of neoplasms in other areas is known;
- Some indicators may change insignificantly, an increase is observed, for example. This situation is also typical for healthy people, so this method does not give 100% results.
conclusions
It is worth noting that diseases in the field of oncology are not a death sentence. It is only important to detect their appearance in a timely manner, preferably at the earliest stages of development. If treatment is delayed, the likelihood of recovery decreases.
In order to avoid an unpleasant, and in some cases a deplorable situation, it is necessary to protect yourself to some extent by taking tests and undergoing examinations to identify tumor markers. The specialist will interpret the results and diagnose your health condition.
Oncological services in Russia and abroad aim not only at curing patients, but also at early diagnosis. The meager initial symptoms of the disease dictate the need for high alertness among people who care about their health. Intestinal tumor markers are an accessible method of analysis and diagnosis of cancer.
A tumor marker of the gastrointestinal tract is a pathological protein. Intestinal markers indirectly indicate a tumor in the early stages of the disease, when there are no obvious symptoms. Pathological markers are tested in the early stages, when it is difficult to notice the neoplasm.
Clinical manifestations have disappeared, but the tumor is growing. The division of altered cells in the body occurs with rapid metabolism. As a cancer tumor grows, pathogenic substances enter the bloodstream.
Reliability and validity of indicators
In general, the analysis can be called a relatively reliable study, since it is usually performed with a diagnostic search for several markers of cancer in different organs. In this case, the main rule for making an accurate diagnosis is a repeated blood test for tumor markers. Observing the dynamics of the patient’s condition, the doctor makes a conclusion that based on a one-time increase in this indicator, one can only make an assumption about probable organ damage.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QqmMVciX7U4
Blood test for tumor markers: rules and some features
How is a tumor marker test performed? There are several important points that will improve the accuracy of the results:
- Blood is donated from a vein and strictly in the morning, and on an empty stomach (the last meal should be taken no later than eight hours before collection).
- During the analysis and before it, the person should not have any illness or undergo treatment. More or less reliable results can be obtained only in the case of a completely healthy and normal condition.
- One test will not give anything, so it is better to take several (which ones should be determined by the attending physician).
- Only a doctor can interpret the results, and certainly taking into account the patient’s existing diseases, as well as the characteristics of his body.
- If the results are positive, you should not take this as a sign of a tumor. You should retake the test in a few months. And it is important to do this in the same laboratory, since the sensitivity of the reagents used in different institutions can vary significantly, and this will affect the accuracy.