Minus 24 kg without leaving home! A Muscovite who lost weight in quarantine “blew up” Russia with her recipe
Flatulence and bloating - what could be more unpleasant than these sensations? Especially if you are at an important event at this time. Often, the above-mentioned unpleasant sensations in the body arise due to poor nutrition.
Therefore, in order to get rid of these most unpleasant processes in the abdominal area as soon as possible, we strongly recommend that you follow a special diet, the essence of which will be described in the following material. So, we present to your attention a diet to get rid of flatulence and bloating.
Diet goals
When faced with the problem of increased gas formation, you should first find out its cause: identify chronic gastrointestinal diseases and rule out gluten and lactase deficiency. People have been suffering from flatulence for years, not realizing that simply giving up a few foods can bring them significant relief.
Note! Lactase deficiency is not such a rare phenomenon; almost a quarter of the adult population of our planet is unable to digest milk sugar.
Specific dietary recommendations depend on the “set” of existing chronic diseases, the symptom of which is flatulence, the type of acidity, the nature of the stool and other physiological characteristics of the person.
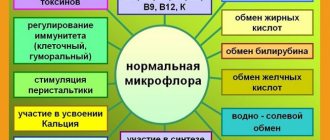
The main purpose of any diet as a nutritional system is to minimize the irritating effect of foods and the load on the gastrointestinal tract, restoring a favorable “microbiological” climate in the intestinal cavity.
The tool of the diet is dishes prepared in a special way that have received new consumer qualities. In case of flatulence, dishes and products that do not provoke fermentation and putrefactive processes in the intestines are of particular relevance, are easily digestible and ensure timely evacuation of food without causing either diarrhea or constipation.
Dietary approaches
Although healthy nutrition is necessary not only for patients, we can say that diet is a way of life, a forced selective, systematic approach to nutrition.
Three pillars on which any diet is based:
- temperature restrictions (both excessively hot and cold dishes provoke increased secretion of gastric and pancreatic juice);
- requirements for the compatibility of products (their incompatibility causes a “conflict of interest” and complications in the form of stimulated release of intestinal gases);
- special consistency of food products as a factor for sparing the gastrointestinal tract.
Basic principles of building a dietary nutrition system for problems of the digestive system:
- mandatory mechanical (and) or thermal processing of food, giving it a uniform consistency;
- mandatory presence in the diet of at least one liquid dish per day;
- consumption of nutritious viscous porridges such as oatmeal;
- preference for low-fat fermented milk products;
- separate consumption of fresh and boiled foods;
- fractional meals;
- limiting the consumption of sweets, as well as separating sweet foods (desserts, fruits) into a separate meal;
- significant limitation of consumption of starchy vegetables, flour products, yeast baked goods and fats (especially in fried foods);
- complete exclusion of carbonated drinks, kvass and beer from the diet.
Taking these conditions into account makes it possible for each person to form an individual dietary diet independently.
Nutritional Features
For constipation
If constipation is associated with excessive gas formation, you need to revise your diet in favor of products that have a laxative effect. These are foods high in fiber. If you have problems with excessive gas formation, it is recommended to exclude such foods. Experts insist on soft fiber and advise eating prunes, carrot and beet juices, and plant foods that do not cause fermentation processes in the body.
A mandatory condition of the diet is the inclusion of unrefined vegetable oil in the diet. This causes additional lubrication of the intestines and helps with bowel movements. Increased consumption of purified water. In other key aspects of the diet for excessive gas formation and constipation, it is based on the same provisions.
The essence of the problem
A tendency to flatulence can be a symptom of serious diseases that have become chronic, or it can be an annoying individual feature of the digestive process of a particular person, unique as the composition of his bacterial intestinal flora, the pattern of the iris or fingerprints.
The appearance of signs of flatulence is a kind of alarm bell that should not be ignored. In addition to everyday inconvenience and awkward situations, neglected intestinal problems will certainly make themselves felt by a decrease in the overall tone of the body and immunity.
Note! Increased gas production may be due to the body's individual reaction to certain foods.
The special role of glucose
Without glucose, metabolism in our body and the existence of a nutrient medium for intestinal bacteria is impossible. Figuratively speaking, it is the fuel that, burning in the “furnace” of metabolism, ensures the occurrence of complex biochemical reactions. Glucose is an effective antitoxic agent, without which infusion therapy (intravenous infusions) and the return of a person to life in emergency situations is impossible.
Its breakdown occurs with the release of gases. Under conditions of pathological digestion in a closed intestinal volume, excess glucose is guaranteed to cause bloating.
Important! If you are prone to flatulence, the consumption of fresh vegetables and fruits containing a lot of sugar, especially grapes, should be dosed, no more than 0.5 kg per day, and separated from the main meal.
Prohibited
In order not to provoke the accumulation of gases, you should sharply limit or completely eliminate (depending on the scale of the problem) the consumption of fresh bread, especially bran and rye. An alternative can be its yeast-free varieties, crackers, biscuits.
Foods that cause bloating even in healthy people are strictly prohibited, namely: raw vegetables and fruits rich in fiber (cabbage, asparagus, radishes, raw onions and whole milk).
Protein foods, especially those containing coarse fiber, require additional “digestive” efforts of the body (and adequate “enzyme” supply), therefore, against the background of a deficiency of bile, pancreatic juice or hydrochloric acid, food is retained in the stomach and (or) intestines, provoking the processes of putrefaction and increased gas formation with a noticeable predominance of hydrogen sulfide. Mechanical grinding of meat fibers facilitates their processing in the gastrointestinal tract and reduces the load on it, and at the same time the risks of excess gas formation. All legumes, being a source of vegetable protein, fall into this category of products.
The digestion of coarse plant fiber, which under normal physiological conditions acts as a product that cleanses the intestines, has the same consequences. Heat treatment softens and breaks down its fibers, facilitating absorption processes and accelerating evacuation from the intestines. In this sense, a striking example of antagonists is fresh cabbage (strictly prohibited) and stewed cabbage (allowed).
Prohibited Products
Products that cause flatulence include:
- yeast baked goods;
- sweets;
- pasta;
- fermented milk foods;
- rye and wheat bread;
- carbonated drinks;
- ice cream;
- whole milk;
- semi-finished products;
- caviar;
- corn;
- meat and fish of fatty varieties;
- sausage;
- salted fish;
- marinades;
- mushrooms;
- smoked meats;
- pickles;
- seasonings and spices;
- canned food;
- sauces;
- nuts;
- salo;
- cream;
- fried or hard-boiled eggs;
- millet, pearl barley and barley cereals;
- sugar substitute;
- jam;
- beer;
- kvass.
It is not allowed to eat foods that contain large amounts of proteins and carbohydrates. It is not recommended to eat a lot of salty and sweet foods.
Bloating and increased gas production are caused by vegetables such as:
- radish;
- cabbage;
- turnip;
- radish;
- spinach;
- soy;
- swede;
- garlic;
- legumes (peas, chickpeas, beans, beans);
- bell pepper;
- onion.
Fruits that are not recommended to eat if you are sick include:
Dried fruits such as prunes or raisins can also cause flatulence. If you have intestinal flatulence, you should not eat fatty foods. Exotic foods and foods containing a lot of spices and seasonings are prohibited.
It is forbidden to eat food containing poorly indigestible fiber and simple carbohydrates, which provoke putrefactive processes. If a person has an individual intolerance to a certain product, then such food should not be consumed either.
Admission rules
Rushing while eating not only leads to insufficient chewing of food. It “turns on” a whole chain of digestive disorders. Insufficiently chopped food is not properly saturated with gastric juice, is not adequately “acidified” and, without being prepared, enters the duodenum, causing it to become overloaded and lethargic.
In addition, the air that gets into the stomach during lively conversations during dinner is only partially released through belching. Once in the small intestine, bubbles of swallowed air in some areas of the mucosa create gaps between the food mass and the intestinal walls, making adequate absorption of metabolic products and normal peristalsis impossible. They complement intestinal gases accumulated in the lower gastrointestinal tract and cause a feeling of fullness, severe discomfort, and sometimes intense cramping pain.
Diet for flatulence (bloating)
The term “intestinal flatulence” means an increased content of gases in the intestines and the resulting symptom complex in the form of rumbling, a feeling of heaviness and distension in the abdomen, an increase in its volume, frequent and often involuntary passage of gases, causing the patient significant discomfort. Increased gas content promotes intestinal distension and stimulates peristalsis , causing pain.
Severe flatulence can affect the patient’s mental state, disrupt normal lifestyle, and cause restlessness, anxiety and depression .
The gastrointestinal tract of an adult normally contains about 200 ml of various types of gases (nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide, methane, oxygen, ammonia), which are enclosed in bubbles of various sizes and evenly distributed throughout the mass of chyme.
The main ways gas enters the body and the reasons for its increased formation in the intestines are:
- aerophagia (increased swallowing of air) when eating with an incorrect diet (talking at the table, fast food, chewing gum, drinking carbonated drinks);
- high metabolic activity of microflora, mainly in the large intestine, caused by excessive consumption of foods that cause increased gas formation and enhance fermentation processes, as well as disruption of the processes of digestion/absorption in the small intestine and the entry of undigested proteins, fiber, and complex carbohydrates into the large intestine;
- development of dysbacteriosis ;
- disruption of nutrient absorption;
- decreased intestinal motility, enzymatic deficiency (usually lactose), the presence of mechanical obstacles in the intestines - feces due to constipation , tumors;
- stagnation of blood in the intestinal area.
Thus, the causes of flatulence , in addition to poor nutrition, can be chronic liver diseases, intestinal dysbiosis , pancreatitis with enzyme deficiency, intestinal diseases ( enteritis , colitis ), irritable bowel syndrome. It is extremely important to understand the cause of flatulence in each specific case, for which the patient should undergo examination.
Sample daily menu
If you are prone to bloating and flatulence, the following approximate daily menu is recommended.
Breakfast. Steam omelette with pieces of lean ham or cubes of boiled meat, a glass of weak tea, cheesecakes with a spoon of sour cream.
Lunch. Fresh vegetable salad with dill, seasoned with fragrant sunflower oil, a glass of green tea with biscuits.
Dinner. Pumpkin puree soup with herbs, chicken tenders with buckwheat porridge, boiled beet salad with nuts, dried fruit compote.
Afternoon snack. Pancakes with meat, fruit jelly, crackers with caraway seeds.
Dinner. Fish cutlets with mashed potatoes on water or porridge, rosehip broth with wheat crackers.
At night - a glass of kefir or a banana, a dry biscuit.
The daily content of basic nutrients for flatulence is as follows:
- fats - no more than 50 g;
- carbohydrates in the form of complex sugars - up to 200 g;
- proteins -100-120 g.
The energy “capacity” of the diet for flatulence is no more than 1600 kcal, and the salt consumption rate is 6 g per day.
Diet for flatulence - how to quickly get rid of symptoms, menu and reviews
Diet for flatulence is the same therapeutic procedure as taking medications or abdominal massage. Light and nutritious meals prepared in compliance with all the rules help the patient get rid of discomfort in the intestines, normalize digestion, eliminate problems with stool and improve the quality of life in general.
Proper diet for flatulence and bloating in adults
The purpose of therapeutic nutrition is to combat increased gas formation and its causes, which are fermentative and putrefactive diarrhea.
Properly organized dietary nutrition:
- Normalizes the motor function of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Reduces inflammatory processes;
- Fights rotting and fermentation in the lower digestive tract;
- Provides the patient with complete, perfectly balanced nutrition;
- Restores normal intestinal microflora.
The diet prescribed in cases of flatulence corresponds to treatment table N5, however, taking into account the physiological characteristics of the patient and the presence of other gastrointestinal problems, a sample menu is compiled individually.
Therapeutic nutrition for flatulence and bloating has a lower energy value compared to the norm - up to 1600 kcal, of which:
- Protein – up to 120 grams;
- Fat – up to 50 grams;
- Carbohydrates – about 200 grams.
In addition, the consumption of monosaccharides is limited.
What can you eat
The list of products allowed for consumption by people suffering from flatulence includes mainly those that:
- They have a carminative effect;
- Restrains the formation of gases.
The main difference between dishes prepared from these products is that they do not linger in the intestines. Their slow, gentle movement throughout the digestive tract promotes easy and painless passage of gases and normalization of the bowel movement process.
Since fermentative and putrefactive bacteria actively multiply during flatulence, the intestinal microflora undergoes significant changes. In order to inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria and create conditions under which normal microorganisms will actively develop, the patient needs to eat the right foods:
- Dried (“yesterday’s”) bread;
- Wheat crackers;
- Weak chicken or fish broth;
- Steamed and baked dishes from lean poultry meat (turkey or chicken) - cutlets, meatballs, meatballs, meatballs, galantine, soufflé and others;
- Boiled sea fish (cooked whole or cutlets from it, fish croquettes are also allowed);
- Low-fat fermented milk products and dishes using them - pureed cottage cheese and a variety of cottage cheese casseroles, sour cream, curdled milk, fermented baked milk, biokefir;
- Eggs - mainly in the form of an omelet, steamed or soft-boiled;
- Boiled or baked vegetables - dishes from pumpkin, zucchini, potatoes, carrots, beets;
- Slimy porridges - semolina, rice (mashed), oatmeal and buckwheat (cooked in water and also pureed, since whole grains can cause bloating, flatulence and diarrhea).
In order to enrich your diet with vitamins and give food a pleasant taste and aroma, you need to include garden herbs - parsley and dill - in your daily menu, add spices to your dishes - bay leaf, cumin seeds.
As for drinks, there are no significant restrictions: the consumption of green tea, rosehip decoction, apple compote, strawberries, raspberries, blueberries and other seasonal fruits is allowed. Once a day you can drink a small cup of cocoa with skim milk.
What is strictly prohibited
Products, the use of which during flatulence is strictly prohibited, contribute to increased gas formation. They can be divided into several subgroups.
- The first subgroup contains everything that the patient’s body cannot normally absorb - as usual, these are dairy products (if the body does not produce enough lactase).
- The second includes coarse plant fiber - a food substrate for intestinal microflora, which enhances the growth and activation of the vital activity of pathogenic microorganisms that cause fermentation and gas formation.
- In the third group are simple carbohydrates, which are easily broken down in the digestive tract and cause the process of rotting of the food mass.
To inhibit the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria and prevent increased formation of gases in the intestines, it is necessary:
Temporarily remove from consumption dishes that contain large quantities of carbon dioxide and organic acids, which means they contribute to increased intestinal motility;
Reduce the consumption of meat products due to the presence of connective tissue in them (protein foods tend to linger in the digestive tract for a long time, resulting in increased fermentation);
Do not consume foods containing food additives, preservatives, organic acids, large amounts of salt and spices - all of this has an irritating effect on the digestive system.
During treatment you should avoid:
- Fresh (“today’s”) bread – both rye and wheat;
- Fresh baked goods - it is advisable to abstain from them altogether, but if it is very difficult to resist buying a bun or sweet pie, at least eat yesterday’s ones;
- Pasta, dumplings and dumplings;
- Fatty and stringy meat - pork, beef;
- “heavy” poultry meat – duck, goose, game;
- Sausages - the flavor enhancers, stabilizers and soy they contain cause very strong gas formation;
- Strong broths with a high content of extractives;
- Canned vegetables containing vinegar and spices – pickles and marinades;
- Any mushrooms – including oyster mushrooms and champignons;
- Animal fats - lard, butter, homemade village sour cream and cream;
- Various kinds of appetizers like caviar or salted fish;
- Certain types of cereals - pearl barley, millet, barley;
- Hard-boiled eggs and scrambled eggs - the favorite fried egg made in lard by many causes turmoil in the intestines and pain in the stomach;
- Some vegetables - beans, peas, lentils, beans, radishes, radishes, daikon, all types of cabbage, raw onions and dishes using it;
- Fruits with a sweet taste - pears, melons, peaches, some varieties of apples, grapes;
- Dried fruits – dried apples and pears, dried apricots, prunes, raisins;
- Any spices;
- Hot sauces - both industrially produced and homemade;
- Honey;
- Jam;
- Chocolate – sometimes you can eat one or two cubes, just choose bitter;
- Cocoa and coffee with whole milk;
- Fermented milk products with high fat content and distinct sourness.
All carbonated drinks, including mineral waters, are strictly prohibited. A glass of soda, drunk too hastily or on an empty stomach, can cause stomach turmoil, severe belching and flatulence, even in a person with a completely healthy intestine. It is also worth refraining from such drinks, in the preparation process of which yeast is used: beer, kvass, kumiss.
Menu (Power Mode)
If you are prone to flatulence, you need to eat food correctly: calmly, slowly, chew the food until it becomes pureed, opening your mouth only to put a new portion into it.
Refrain from talking while eating (or at least don't drop words between two spoons) and give up the habit of washing down each bite with water or tea.
This will help avoid accidental swallowing of air (a phenomenon called aerophagia), and the load on the digestive system will become noticeably less.
Eat meals strictly by the hour. It's quite easy to adapt to this.
In addition, by getting used to receiving “fuel” at certain hours, your digestive tract will work in accordance with a given regime: gastric juice, bile acids and pancreatic enzymes will be intensively produced only when you start eating. This will significantly reduce the likelihood of other, more dangerous, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Are you used to chewing gum to freshen your breath and clean your teeth after eating? Alas, you will also have to give up this habit: while chewing, you can involuntarily swallow air, which will serve as a provoking factor for an attack of flatulence, and your stomach, deceived by the process of imaginary chewing, intensively produces juice in anticipation of the arrival of food, preparing the ground for the development of gastritis.
Follow your diet. It’s better to eat more often, literally every one and a half to two hours. Small portions of dietary dishes are digested and absorbed faster, and everything that the body could not process leaves the intestines in a timely manner without causing any pathological process.
Eat only warm food. By eating foods that are too hot—literally steaming—or too cold, you risk irritating your digestive tract. Hot tea, a spoonful of “fiery” borscht, as well as a hastily swallowed portion of ice cream, help increase the secretion of gastric juice and pancreatic enzymes, which irritate the intestines.
Follow cooking rules. Large pieces of fried meat are too harsh a test for the digestive tract. If you suffer from flatulence, prepare food differently: boil, bake in foil, simmer in a small amount of water or broth. The main thing is to avoid an abundance of fat and golden brown crust.
Follow the rules of product compatibility. For example, if you don’t want to suffer from bursting abdominal pain after breakfast, don’t drink a cucumber or an apple with milk, and don’t eat sweets and salty ones. Such combinations of products overload the digestive system, increase peristalsis and promote the fermentation process in the intestines.
Limit your salt intake. A level teaspoon per day is quite enough, and it is advisable to add some salt to an already prepared dish.
Drink plenty of fluids. One and a half to two liters of ordinary filtered water contribute to the timely evacuation of feces, due to which the fermentation process, inevitable in case of stagnation, cannot occur.
An approximate menu for a day with flatulence looks like this:
- First breakfast - pureed rice porridge, a glass of green tea with crackers.
- Second breakfast – mashed cottage cheese with a spoonful of sour cream (unsweetened).
- Lunch - a portion of vegetable soup, a piece of baked chicken breast with a side dish of mashed potatoes, vegetable salad, a slice of toasted bread, a compote of dried sour apples.
- Afternoon snack – strawberry jelly and two biscuits.
- Dinner – pureed buckwheat porridge, steamed chicken cutlet, boiled beetroot and carrot salad, a glass of rosehip decoction.
- At night (an hour before going to bed) – a glass of low-fat kefir with rye crackers.
Folk remedies for flatulence
To free the intestines from gases and relieve abdominal pain, it is recommended to take decoctions of medicinal plants along with the diet, such as:
- Peppermint - pour one tablespoon of dry leaf into an enamel mug with a lid, pour 250 ml of boiling water, let it brew for half an hour, then strain and take a third of a glass 15 minutes before meals three times a day;
- Dill seed - pour a tablespoon of seeds with a glass of boiling water, cover tightly with a lid and leave in a warm place for at least three hours, then strain and take three spoons an hour before meals;
- Chamomile - brew a spoonful of dried flowers with a glass of boiling water, let it brew (at least two hours), strain and take one or two spoons twenty minutes before meals.
Currently reading: The main causes and elimination of flatulence after eating
What happens if you don't follow a diet
When starting treatment for flatulence, you will have to be patient. Dietary foods do not look as appetizing as fried ones, with an abundance of fat and a beautiful golden crust, tickling the nostrils with the aroma of overseas spices. But they are very useful. By neglecting your diet, you risk facing a number of unpleasant and even dangerous consequences:
- Death of normal intestinal microflora;
- Activation of putrefactive and fermentative bacteria;
- The release of toxins is the result of bacterial activity;
- Intoxication of the whole body;
- Hypovitaminosis - the synthesis of some vitamins (for example, group B) is possible only when the intestines are inhabited by normal microflora.
By following a therapeutic diet, you will forever forget about flatulence and the discomfort associated with it - abdominal pain, loud rumbling and a distinct feeling of where the accumulated gases are moving through the intestines at that moment. Eat right - and you will be healthy!
Reviews
Source: https://ogkt.ru/meteorizm/dieta-pri-meteorizme-kishechnika-i-vzdutii-zhivota-u-vzroslyh.html
Business hours
The requirement for fractional meals during flatulence is due to the fact that only small portions of food entering the gastrointestinal tract are adequately impregnated with digestive juices. A small volume of food mass does not have time to undergo fermentation, is digested in a timely and adequate manner and is evacuated by the large intestine without delay.
The activity of the gastrointestinal tract is conditioned-reflex in nature, and, therefore, it independently adjusts to a rhythm determined, among other things, by a number of external conditions. The tools for such adjustment are bowel movements, the regularity of which is the most important indicator of normal digestion, and eating at certain hours when the production of digestive juices and necessary enzymes is maximum.
How to deal with the problem at home
You can get rid of flatulence and bloating on your own. To do this, you need not only to follow a diet, but also to use special folk remedies that will help improve the digestion process.
- Dill salad. Dill is a real cure for bloating and constipation, so it can be added to salads. To do this, just finely chop the greens and add to any dish to taste. Eating dill 2-4 times a day quickly improves the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Tea with mint and lemon. Lemon helps not only normalize the functioning of the intestines, but also restore metabolism. To do this, you need to brew weak tea, adding a few slices of citrus to it. If desired, you can add 1-2 mint leaves. You need to drink the medicinal drink 1-3 times every day.
- Juice from carrots, parsley and lemon. To prepare the product, you need to mix 100 g of parsley and one medium carrot in a blender. Then add 1-2 teaspoons of sugar and a slice of lemon. The drink should be drunk fresh, as it loses its beneficial properties 20 minutes after preparation. If you regularly consume this juice, bloating and problems with digesting food will disappear.
- Chamomile and fennel infusion or tea. Chamomile is the best remedy for bloating and problems with the digestive tract. To prepare the herbal remedy, you need to brew chamomile and fennel (a tablespoon of mixed dry ingredients per glass of boiling water), let it brew for 15 minutes and drink, preferably without sugar. This infusion can be taken by both adults and children, because it is believed that these herbs are not capable of irritating the gastric mucosa.
- Tea with rosehip. Rosehip is the best natural diuretic. It cleanses the kidneys, stomach and intestines well. To prepare tea, it is recommended to brew 20 g of rose hips in 300 ml of boiling water, let it brew for 10-15 minutes and then drink, preferably without sugar and on an empty stomach. It should be noted that you need to drink the drink 3-5 times a day, because this not only cleanses the intestines, but also removes toxins from the entire body.
- Calendula infusion. The plant is used in medicine to treat diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, including the intestines. To do this, you need to pour boiling water over calendula flowers in the ratio of 10 g of dry raw material per 200 ml of water and let it brew for 20-25 minutes, then drink on an empty stomach without honey and sugar. If you drink the decoction 3-4 times a day, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract will improve, bloating and pain will disappear.
If you regularly use such recipes, you will be able to remove bloating and other unpleasant symptoms quickly and painlessly. Folk remedies can be used by adults and children, as they are considered safe, with the exception of possible individual allergic reactions to some ingredients.