Description
Familial colon polyposis. A rare hereditary disease in which multiple adenomatous polyps develop in the large intestine. It manifests itself as pain, frequent bowel movements, blood in the stool, anemia, pale skin and increased fatigue. There is a high probability of malignancy. Along with neoplasia of the large intestine, with familial polyposis of the colon, neoplasms of bones and soft tissues can be detected. When making a diagnosis, complaints, physical examination data, irrigoscopy, sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy with biopsy are used. Treatment is colectomy with the formation of an ileoproctostomy or ileostomy.
Treatment tactics
The main treatment is surgery. If the polyps do not bother you with intense symptoms, then doctors choose a wait-and-see approach with regular examinations of the body.
The following areas of treatment are identified::
- Method of operative electrocoagulation . Operative access is provided through an endoscope. Afterwards, the polyp is cut with a loop and removed. Next, the wound is cauterized using an electrode.
- Abdominal surgery . Suitable for large, serious polypous tumors, as well as for those at risk of cancer or existing malignancy.
- Bowel resection . It is used for cancerous transformation of cells and involves removing part of the affected intestine.
Surgeons often combine several surgical methods to target pathogenic lesions to achieve high therapeutic results.
Drug therapy is prescribed before and after surgery. In the first case, drug treatment is preparatory in nature, in the second it is intended to speed up the recovery period. Alternative treatment for intestinal polyps can be used only after consultation with your doctor.
The appearance of unpleasant symptoms associated with bowel function is a direct reason to seek advice from a proctologist. It is a face-to-face appointment that allows a specialist to identify the first symptoms of neoplasms in the intestines.
With a hereditary predisposition, the risk of polyposis intestinal disease persists throughout life. Even if the manipulation is successful, the risks of relapse remain. To prevent the development of colorectal cancer, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations, attend medical consultations, and maintain an active and healthy lifestyle.
Read what to do to avoid polyps in the intestines in our article.
You can make an appointment with a doctor directly on our website.
Version: MedElement Disease Directory
October 24-25, Kazakhstan, Nur-Sultan
New venue! Astana-EXPO territory, pavilion C3.5
Get a free ticket
International Healthcare Exhibition
October 24-25, Kazakhstan, Nur-Sultan
New venue! Astana-EXPO territory, pavilion C3.5
Get a free ticket
Additional facts
Familial colon polyposis is a genetically determined pathology characterized by the presence of multiple colon polyps. The number of polyps can range from hundreds to a thousand or more. In the absence of treatment, obligatory malignancy is observed. Familial polyposis affects one out of 6-12 thousand inhabitants of the Earth. There are several subtypes of the disease, all of them, regardless of the clinical manifestations and type of adenomatous polyps, end in the formation of adenocarcinoma. The first signs of familial colon polyposis usually appear in adolescence, malignancy is observed after 30-40 years. An aggressive course is possible with the appearance of the first symptoms in preschool age and malignancy before the age of 30, as well as an erased course with the formation of a clinical picture after 40 years and malignancy after 50 years. Treatment is carried out by specialists in the field of oncology, gastroenterology and abdominal surgery.
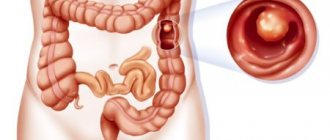
Familial colon polyposis
Clinic and diagnostics
The clinical picture of a sigmoid colon polyp is in most cases quite sparse and occurs with virtually no symptoms. Often, a neoplasm is discovered by chance during irrigoscopy or colonoscopy for some other disease. The first clinical picture may appear when the tumor reaches a fairly large size (3 cm or more) and is characterized by symptoms such as pain in the lower abdomen, especially intensifying during defecation, bloody and/or mucous discharge from the anus, various symptoms of intestinal dyspepsia (diarrhea, constipation, false urges). In the future, with a long course of the process, symptoms of chronic intestinal obstruction may appear, up to acute intestinal obstruction (most often in the later stages of tumor development).
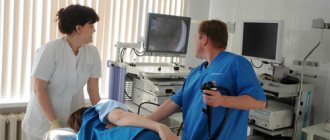
If a patient is suspected of having a polyp of the sigmoid colon, it is first necessary to conduct a sigmoidoscopy examination, as well as colonoscopy or irrigoscopy. The first method is quite simple and informative, as it makes it possible to examine the rectum and distal part of the sigmoid colon for the presence of polyps, and if detected, take a piece of tissue for a biopsy, which allows you to determine the degree of malignancy. A thorough examination of other parts of the intestine is required for scattered or diffuse polyposis. For these purposes, irrigation or colonoscopy is performed.
Irrigoscopy is an X-ray contrast method for examining the colon, performed by retrograde injection of a contrast agent. Allows you to detect polyps with a diameter of more than 1 cm. Small polyps are poorly distinguishable, which is a disadvantage of this technique, as a result of which it is now practically replaced by colonoscopy.
Colonoscopy is an endoscopic method for examining the mucous membrane and lumen of the colon. Allows you to detect polyps of almost any size, which is an advantage of this method over irrigoscopy. It is also possible to take a biopsy from a suspicious area of the mucous membrane.
Symptoms
In most cases, the first symptoms of familial polyposis appear at the age of 15-19 years. With an aggressive course, the disease manifests itself at the age of 5-6 years, with a weakened (attenuated) form - at the age of over 40 years. Patients complain of abdominal pain and increased bowel movements up to 5-6 times a day. The pain syndrome associated with familial colon polyposis is very diverse; pain can occur mainly in the upper or lower abdomen, be aching, twisting, or sharp. Gastric discomfort is possible, because of which experts sometimes focus on examining the upper gastrointestinal tract. Impurities of blood and mucus are detected in the stool. Heavy bleeding rarely occurs. A few years after the manifestation of familial colon polyposis, the number of polyps increases and they become larger. The presence of numerous tumors causes disorders of absorption and secretory processes. Trauma to more numerous and larger polyps than before causes increased blood loss. As a rule, this stage of familial colon polyposis occurs during a period of increased stress on the patient’s body: young men go into the army, girls become pregnant and give birth to children, which further aggravates the disorders listed above. Weakness and increased fatigue occur. Anemia develops.
Types of complications
If polyps in the sigmoid colon are not treated and the symptoms of the disease are ignored, then patients will develop further polyposis. This leads to unpleasant consequences for the patient’s entire body. In this case, degeneration into a malignant formation occurs. The presence of polyps in the sigmoid colon causes frequent bleeding and anemia. Due to the constant growth of growths, the lumen decreases, and all food enters through the resulting hole.
Photo of sigmoid colon polyp
The development of the disease into enterocolitis is dangerous because inflammation of the intestinal wall occurs. In addition, Crohn's disease or diverticulosis develop. After removal of the growth by polypectomy, a complication arises. The patient has perforation of the wall of the large intestine. After surgery to remove a polyp, the attending doctor takes measures to prevent the inflammatory process.
- polyps have the ability to degenerate into a cancerous tumor;
- if damaged, cause heavy bleeding, which is life-threatening;
- cause the formation of intestinal obstruction;
- cause severe inflammatory processes that lead to more dangerous complications;
- provoke the development of anemia and weakness.
Diagnostics
Due to the mild severity of the clinical symptoms of this disease in adolescence and young adulthood, timely diagnosis, followed by regular monitoring and the decision to perform one or another surgical intervention before the onset of malignancy of polyps, is of particular importance. When collecting anamnesis, attention is paid to characteristic symptoms (frequent bowel movements, anemia, blood and mucus in the stool), family history (presence of relatives with familial polyposis of the colon) and extraintestinal manifestations of the disease. In some cases, polyps can be identified already at the stage of rectal examination. To assess the condition of the lower intestines and determine the severity of familial colon polyposis, sigmoidoscopy is performed. Then a colonoscopy is performed. During endoscopic examinations, attention is paid to larger cherry or bright red nodes with a loose or lobulated surface (villous polyps), since such tumors are characterized by an increased likelihood of malignancy. Along with endoscopy, patients with familial polyposis of the colon are prescribed irrigoscopy, which acquires special diagnostic significance in the presence of circular neoplasias that impede the advancement of the endoscope. Patients are referred for fibrogastroduodenoscopy, since familial colon polyposis is often accompanied by gastritis or gastric polyposis. To detect extraintestinal manifestations of the disease, an external examination is performed. For bone neoplasia, patients undergo radiography and CT, for soft tissue neoplasia, MRI of the affected area is performed.
Clinical picture
Clinical diagnostic criteria
Symptoms, course
Clinic From 40 to 70% of polyps are asymptomatic. Clinical signs are rare and variable in severity and duration. The presence of any clinical sign listed below in a pronounced form should be alarming in terms of the presence of a more serious pathology (colorectal cancer Colorectal cancer is a malignant tumor of the mucous membrane of the colon or rectum, nonspecific colitis, etc.).
Main symptoms: 1. Rectal bleeding. It is clinically significant whether blood was noted in the stool during digital examination (polyps of the rectum, anal canal), during spontaneous passage of stool, or outside defecation. 2. Diarrhea or constipation. 3. Feeling of incomplete bowel movement. 4. Mucus in the stool (extremely rare). 5. Signs of anemia (weakness, pallor, fatigue, etc.) occur with chronic bleeding. 6. Abdominal pain: – in children associated with persistent intussusception; – in adults, as a rule, they do not occur; patients describe rather discomfort.
Allfield syndrome is a combination of familial adenomatosis of the colon with sebaceous cysts. The discovery of epidermoid cysts, often multiple, in young people should alert the doctor and force him to undertake an examination of the gastrointestinal tract.
Turco's syndrome is a familial adenomatosis of the colon in combination with malignant tumors of the central nervous system of neuroepithelial origin. Experts believe that with adenomatosis of the colon, all patients need to undergo a brain examination to diagnose a possible combination of adenomatosis and tumors of the central nervous system.
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome is a combination of familial adenomatosis of the colon with tumors of the endocrine glands (most often tumors of the thyroid gland).
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is a combination of polyposis of the gastrointestinal tract with characteristic melanin pigmentation of the mucous membranes of the lips and facial skin, most often around the mouth. The spots resemble freckles, but since freckles do not occur on the mucous membrane, the presence of age spots on the lips immediately catches the eye. When examining the oral cavity, melanin pigmentation is also detected on the buccal mucosa. It should be emphasized that the polyps in the described syndrome are hamartomas. A hamartoma is a nodular tumor-like formation that arises as a result of a violation of the embryonic development of organs and tissues, consisting of the same components as the organ where it is located, but differing in their incorrect location and degree of differentiation, and not adenomas (they have a different structure). The disease is often inherited and can occur in members of the same family.
Treatment
The only treatment for this disease is surgery. Since familial polyposis is an obligate precancer, the operation is aimed at completely removing parts of the large intestine affected by polyps. The most reliable way to prevent colon cancer in these conditions is complete removal of the large intestine and the formation of a permanent ileostomy before signs of malignancy appear. For obvious reasons, this approach usually does not suit young active patients with familial colon polyposis, so the question of the timing and extent of the operation remains debatable. Polyp-free areas are preserved. If there are single nodes in individual segments, endoscopic removal of neoplasia is performed. All affected parts of the intestine are then resected (in practice, this usually means removing most of the intestine). If possible, try to preserve the anal sphincter. The operation of choice for familial polyposis of the colon can be colectomy with ileorectal anastomosis, subtotal resection of the colon and rectum with relegation of the colon to the anal canal area, etc. In case of malignancy and complete damage to the intestine, colectomy is required in combination with extirpation or abdominal-anal resection of the rectum and ileostomy. .
Main types
Polypous lesions are classified not only by location, but also by structural features, structure, histology, and cancer risks.
The following types of intestinal polyp lesions are distinguished::
- Adenomatous . Large types of growths on a thick stalk are often combined with polyps in different parts of the stomach. The structure of the body of the growth is dense, the surface of the neoplasm is smoothed, of a uniform shade. The color does not differ from the mucous walls of the organ. The risks of malignancy are proportional to the volume of the polypous lesion. Find out what an adenomatous polyp in the stomach is here.
- Villous . The neoplasm resembles a lump, which has a wide base - stroma. The tumor is friable in structure, subject to trauma and bleeding. Both tumor tissue and villi can become malignant.
- Fibrous . The main location is the lower third of the rectum, almost near the anal sphincter. The growth is formed from a hemorrhoidal node, the structure corresponds to the connective tissue.
- Pseudopolyp . The neoplasm vaguely resembles a polyp. The nature of occurrence is an inflammatory process. Often pseudopolyps self-amputate after drug treatment.
- Combined . A combination of structural fragments characteristic of all existing types of pathological proliferation of intestinal mucous membranes.
Note ! All polyps have a clear structure: body, stalk and base-stroma. A polyp with a stalk (long or short) poses a danger not only in relation to cancerous transformations. Long polypous structures can be pinched by the sphincters of the intestines and twisted.
The stem of the growth consists of thick vessels, so any damage to them results in internal bleeding. When torsion occurs, intestinal tissue may become necrotic. Polyps without a stalk are more susceptible to malignancy when the base is a continuation of the body of the growth.
Can the growths come off on their own and disappear?
Sometimes, after the next examination, polyposis lesions are not detected in patients. During this time they simply disappear.
Polyps in the intestines can self-amputate if several basic factors are met:
- Single polyps on a stalk;
- Small growth;
- Localization of polyps in the rectum or colon.
Pathological growths can eliminate themselves if they are damaged, given the low strength of the polyp.
The traumatic factor may be:
- diagnostic procedures,
- constipation and difficulty in moving stool,
- pregnancy and childbirth,
- haemorrhoids.
It is important ! Self-amputation of a polyp is often accompanied by short-term bleeding from the anal canal. Self-amputation may be indicated by fecal occult blood tests; an example of the test result is here.
Forecast
Without treatment, the prognosis for familial colon polyposis is poor. Over time, one or more polyps transform into malignant neoplasms. Before the appearance of signs of malignancy, sphincter-preserving surgery can be performed in 85% of cases, after the appearance of symptoms of cancer - in 30% of cases. All patients who have undergone surgery for familial colon polyposis should be monitored at the dispensary. Patients undergo regular endoscopic examinations for the timely detection of malignant polyps in the preserved parts of the intestine. Tests are prescribed to assess the state of protein and salt metabolism.
What is a sigmoid colon polyp and its causes?
Sigmoid colon polyp is a growth of mucous epithelium in the sigmoid segment of the intestinal tract. In recent years, the disease has become increasingly common among the population, reaching almost 25% of all polypous formations.
Polyps are differentiated by:
- form,
- sizes,
- structural fullness,
- tendencies towards growth and malignancy.
Mucous neoplasms have a stalk or a wide base and can spread over the entire lining surface of the mucous membranes of an organ or be a localized growth.
The danger of the disease lies precisely in the difficulty of early diagnosis. Unfortunately, most cases are diagnosed at the stage of symptomatic manifestations, the malignancy of cells into a malignant tumor. Polyp of the sigmoid colon ICD 10 code - D12.5
Lack of treatment almost always leads to serious surgical complications. Depending on the shape and type of wall growth, the prognosis for intestinal cancer is formed.
Predisposing factors
The causes of intestinal polyps are multi-etiological in nature and arise under the influence of several negative factors at once.
The main causes of polypous degeneration of the mucous membranes of the sigma are:
- Pathologies and diseases of the intestinal tract of any origin;
- Features of the anatomy and functional development of the intestine, sigmoid colon;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Physical inactivity;
- Lack of food discipline;
- Deterioration of intestinal motility;
- Long-term drug treatment.
The disease can be aggravated by:
- addiction to alcohol, heavy food;
- surgical intervention on the lower parts of the digestive system.
Clinics for treatment with the best prices
Price
| Total: 125 in 11 cities |
| Selected clinics | Phones | City (metro) | Rating | Price of services |
| Clinical Hospital on Yauza | 7(495) 125..showRecord 7(495) 125-22-36 7(495) 125-04-15 | Moscow (metro station Ilyich Square) | 23500ք | |
| European MC in Spiridonievsky Lane | 7(495) 969..showRecord 7(495) 969-24-37 7(495) 933-66-55 7(495) 933-66-45 7(495) 510-54-14 | Moscow (m. Barrikadnaya) | 80362ք | |
| European MC in Orlovsky lane. | 7(495) 969..showRecord 7(495) 969-24-37 7(495) 933-66-55 7(495) 933-66-59 | Moscow (metro Prospekt Mira) | 80362ք | |
| European MC on the street. Shchepkina | 7(495) 969..showRecord 7(495) 969-24-37 7(495) 933-66-55 | Moscow (metro Prospekt Mira) | 80362ք | |
| Alpha – Health Center on Komsomolsky Prospekt | 7(495) 775..showRecord 7(495) 775-42-06 7(495) 266-98-92 | Moscow (metro station Frunzenskaya) | 18305ք(90%*) |
7(499) 969-25-74
7(495) 775-75-66
7(926) 800-07-19
Moscow (metro station Baumanskaya)28670ք(90%*)Family doctor on Miusskaya7(499) 969..showRecord7(499) 969-25-74
7(495) 775-75-66
Moscow (metro station Novoslobodskaya)28670ք(90%*)Family doctor on Usacheva7(499) 969..showRecord7(499) 969-25-74
7(495) 775-75-66
Moscow (Sportivnaya metro station)28670ք(90%*)Family doctor on Ozerkovskaya embankment 7(499) 969..showRecord7(499) 969-25-74
7(495) 775-75-66
Moscow (metro station Novokuznetskaya)28670ք(90%*)KB No. 85 on Moskvorechye7(499) 782..show 7(499) 782-85-857(926) 010-84-87
7(499) 324-70-15
7(499) 324-86-65
Moscow (m. Kantemirovskaya)—6810ք(80%*)* – the clinic does not provide 100% of the selected services. More details by clicking on the price.Nutritional recommendations
The usual diet after removal of polypous growths in sigma requires mandatory correction. The goal of the diet is to spare the digestive system and significantly reduce the load on the lower gastrointestinal tract. The therapeutic effect is aimed at preventing constipation, irritation of the intestinal walls, and reducing the traumatic factor.
The basic rules of the diet after removal of a polyp of the sigmoid colon are::
- Fractional meals in frequent small portions (up to 200 ml);
- Drink plenty of fluids, 30-40 minutes after each meal;
- Reducing the daily amount of salt;
- Elimination of fatty, fried foods;
- Maintain temperature conditions - all dishes should be warm and comfortable for the oral mucosa.
It is recommended to cook, steam, and stew dishes. It is important that all products undergo adequate heat treatment.
In the first days after surgery, it is recommended to eat grated or semi-liquid food.
Ideal products during the recovery period would be:
- weakly rich broths with vegetables and poultry;
- crackers, biscuits;
- boiled vegetables (for example, vinaigrette salad);
- thick jelly;
- porridge with milk;
- dairy products.
For drinks, it is better to choose a decoction of rose hips, dried fruit compotes, green tea, or a decoction based on medicinal herbs. During the late recovery period, you can gradually return to your usual diet.
If the removal was carried out due to a malignant tumor, then the therapeutic diet can be lifelong.
Sigma polyp removal process:
Polyps of the sigmoid colon carry potential risks to human health and life. Timely diagnosis and preventive medical examination reduce the risks of malignant tumor degeneration and improve the quality of life of patients for many years.
Read how to treat papilloma near the anus in our article.
Description
Familial colon polyposis. A rare hereditary disease in which multiple adenomatous polyps develop in the large intestine. It manifests itself as pain, frequent bowel movements, blood in the stool, anemia, pale skin and increased fatigue. There is a high probability of malignancy.
Along with neoplasia of the large intestine, with familial polyposis of the colon, neoplasms of bones and soft tissues can be detected. When making a diagnosis, complaints, physical examination data, irrigoscopy, sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy with biopsy are used. Treatment is colectomy with the formation of an ileoproctostomy or ileostomy.
Treatment of the disease
Surgical treatment is the main method in diagnosing this disease. Currently, several methods are used for radical removal of tumors:
- Sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopic polypectomy with electrocoagulation of the bed.
- Microsurgical retrograde tumor excision.
- Transanal tumor excision.
- Resection of the sigmoid colon with tumor.
- Radical removal of the sigmoid colon and regional lymph nodes with the formation of a colostomy.
The choice of a particular treatment method depends on the stage of tumor development, its anatomical location, the general condition of the patient, as well as available medical equipment.
After surgical intervention, the removed material is sent for histological examination, on the basis of which the question of the presence or absence of malignancy in the lesion is finally decided. If there are none, the patient is discharged from the hospital with recommendations for dispensary observation with periodic (once a year) colonoscopy to check for relapse of the disease. If malignant cells are found during the study, then the issue of a more radical method of surgical intervention is decided in order to prevent the spread and progression of the process.
Additional facts
Familial colon polyposis is a genetically determined pathology characterized by the presence of multiple colon polyps. The number of polyps can range from hundreds to a thousand or more. In the absence of treatment, obligatory malignancy is observed. Familial polyposis affects one out of 6-12 thousand inhabitants of the Earth.
There are several subtypes of the disease, all of them, regardless of the clinical manifestations and type of adenomatous polyps, end in the formation of adenocarcinoma. The first signs of familial colon polyposis usually appear in adolescence, malignancy is observed after 30-40 years. An aggressive course is possible with the appearance of the first symptoms in preschool age and malignancy before the age of 30, as well as an erased course with the formation of a clinical picture after 40 years and malignancy after 50 years. Treatment is carried out by specialists in the field of oncology, gastroenterology and abdominal surgery.
Diet after polyp removal
Compliance with a specialized nutrition system, adapted specifically for patients with mechanical intestinal injuries, will help avoid relapses of the disease. Basic nuances of patient nutrition:
A polyp of the sigmoid colon is formed due to abnormal proliferation of tissue in the mucous membrane of this part of the large intestine.
Growths are benign tumor-like neoplasms that are attached to the wall of the organ with a thin stalk or a wide base. They differ in composition, shape and size. The development of pathology is usually asymptomatic, but may be accompanied by defecation disorders, the appearance of pathological impurities in the stool and pain in the abdomen.
Large tumors can lead to intestinal obstruction and be accompanied by obstruction. It is important to take into account that in the absence of timely treatment, there is a risk of degeneration of benign polyps into malignant ones.
If there is a suspicion of diseases of the large intestine, the patient is referred for a consultation with a proctologist. The doctor makes a diagnosis based on digital examination, biopsy, rectosigmoidoscopy and irrigoscopy. Removal of the growth occurs through surgery.
Symptoms
In most cases, the first symptoms of familial polyposis appear at the age of 15-19 years. With an aggressive course, the disease manifests itself at the age of 5-6 years, with a weakened (attenuated) form - at the age of over 40 years. Patients complain of abdominal pain and increased bowel movements up to 5-6 times a day. The pain syndrome associated with familial colon polyposis is very diverse; pain can occur mainly in the upper or lower abdomen, be aching, twisting, or sharp. Gastric discomfort is possible, because of which experts sometimes focus on examining the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Impurities of blood and mucus are detected in the stool. Heavy bleeding rarely occurs. A few years after the manifestation of familial colon polyposis, the number of polyps increases and they become larger. The presence of numerous tumors causes disorders of absorption and secretory processes.
Trauma to more numerous and larger polyps than before causes increased blood loss. As a rule, this stage of familial colon polyposis occurs during a period of increased stress on the patient’s body: young men go into the army, girls become pregnant and give birth to children, which further aggravates the disorders listed above. Weakness and increased fatigue occur. Anemia develops.
Treatment with medications and folk remedies
After information about the number and size of formations is received, treatment begins, but polyps in the sigmoid colon cannot be eliminated with medication. You can try using alternative medicine. Before doing this, you should consult your doctor.
It must be remembered that only proven herbs and remedies are used to prepare medicines. Healing compositions may contain poisonous plants, so the dosage must be strictly observed. Otherwise, the body will get an additional health problem.
It is stored in the refrigerator and warmed up slightly before use.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EP6acOSHY1w
3 times a day before meals, take a composition of propolis (10 g) and animal fat (100 g). Brought to a homogeneous state in a water bath, it is stored in the refrigerator. Before use 1 tsp. The product is diluted in 1 glass of milk.
A decoction of hop cones and spruce needles has proven itself well. The crushed plants in a ratio of 1:4 are poured with 1 glass of water, brought to a boil in a water bath, left for half an hour, then drained. The resulting liquid is added to a volume of 200 ml and drunk in 3 doses.
Microclysters can relieve pain and reduce the size of polyps. An infusion of calendula, St. John's wort and chamomile is prepared for them. Herbs are taken in equal quantities and crushed. 2 tbsp. the mixture is poured with 1 glass of boiling water, left for 2 hours, filtered, and used warm.
Diagnostics
Due to the mild severity of the clinical symptoms of this disease in adolescence and young adulthood, timely diagnosis, followed by regular monitoring and the decision to perform one or another surgical intervention before the onset of malignancy of polyps, is of particular importance.
When collecting anamnesis, attention is paid to characteristic symptoms (frequent bowel movements, anemia, blood and mucus in the stool), family history (presence of relatives with familial polyposis of the colon) and extraintestinal manifestations of the disease. In some cases, polyps can be identified already at the stage of rectal examination. To assess the condition of the lower intestines and determine the severity of familial colon polyposis, sigmoidoscopy is performed.
Then a colonoscopy is performed. During endoscopic examinations, attention is paid to larger cherry or bright red nodes with a loose or lobulated surface (villous polyps), since such tumors are characterized by an increased likelihood of malignancy. Along with endoscopy, patients with familial polyposis of the colon are prescribed irrigoscopy, which acquires special diagnostic significance in the presence of circular neoplasias that impede the advancement of the endoscope.
Patients are referred for fibrogastroduodenoscopy, since familial colon polyposis is often accompanied by gastritis or gastric polyposis. To detect extraintestinal manifestations of the disease, an external examination is performed. For bone neoplasia, patients undergo radiography and CT, for soft tissue neoplasia, MRI of the affected area is performed.
Why are polyps dangerous?
The main danger of polypous lesions of the sigmoid intestine is the oncogenic transformation of the tissues of the formation, transformation into a malignant tumor.
In addition to the oncological process, there are other dangers:
- Development of iron deficiency anemia as a result of anorectal bleeding;
- Acute intestinal obstruction due to the impressive size of the polyp;
- Strangulation of the polyp and necrotization of the mucous membranes of the department.
Forecast
Without treatment, the prognosis for familial colon polyposis is poor. Over time, one or more polyps transform into malignant neoplasms. Before the appearance of signs of malignancy, sphincter-preserving surgery can be performed in 85% of cases, after the appearance of symptoms of cancer - in 30% of cases.
All patients who have undergone surgery for familial colon polyposis should be monitored at the dispensary. Patients undergo regular endoscopic examinations for the timely detection of malignant polyps in the preserved parts of the intestine. Tests are prescribed to assess the state of protein and salt metabolism.
Removal methods
Surgical removal of polyps in the sigmoid colon is the most optimal treatment method.
Proctology deals with the healing of growths; operations to eliminate the problem are effective methods; there are several types of surgical intervention:
- Polypectomy surgery is prescribed as a gentle technique. The mucosa is cleared of neoplasms by endoscopic removal. During the procedure, a loop of the electrode is tightened around the stalk or wide base of the polyp and a current is passed through it. Feeding of the growth stops. It is removed using endoscopic forceps.
- Polypectomy is intended to remove small growths. It needs to be carried out intermittently, and may require several stages (depending on the number of growths).
- Transanal removal. For resection of the sigmoid colon, the anus is stretched with a rectal speculum, and polyps or part of the affected intestine are removed with a scalpel. The removal site is sutured. The operation is performed under visual control.
- Radical removal is recommended if diagnostics showed the presence of not only polyps, but also a cancerous tumor. They are eliminated along with part of the sigmoid colon to avoid metastases.
Basic medical services according to treatment standards Select treatment using artificial intelligence
Doctor consultations | |
| Genetic consultation any doctor – 75 clinics doctor candidate of medical sciences – 30 clinics, MD, professor – 26 clinics | |
Surgery | |
| Any functional device Lip bumper – 112 clinics Trainer system – 347 clinics LM-activator – 261 clinics Kappa Schwartz – 10 clinics | |
Non-surgical treatment | |
| Radiology any X-ray of the sella turcica – 266 clinics Densitometry – 114 clinics | |
Treatment of polyps in the sigmoid colon
Since drug treatment for sigmoid colon polyposis does not produce any results, the only way to get rid of tumors in the intestine is by radically removing them.
Modern surgeons do this using the following methods:
- Colonoscopic or sigmoidoscopy polypectomy followed by electrocoagulation of the bed;
- Transanal excision;
- Endoscopic removal;
- Resection of a section of the sigmoid colon;
- Radical removal.
Polypectomy
The essence of this technique is as follows: a loop electrode is applied to the detected tumor, which is attached to the intestinal wall with a thin stalk, through a special channel of the operating endoscope.
By tightly grasping the leg of the polyp and tightening it with a loop, a complete cessation of blood flow is achieved, after which a high-frequency current is passed through the electrode.
A few seconds of exposure is usually enough to cut off the head of the polyp and char its stem. The body of the removed polyp is immediately removed from the patient’s body by suction to the endoscope or using grab forceps, and the bed of the removed tumor is additionally cauterized.
This is done in relation to small tumors with a thin stalk. If the stalk of the polyp turns out to be quite thick, the surgeon cuts off the polyp gradually, changing the cutting tactics and coagulation modes.
Polypectomy of large tumors with a wide base is carried out in several stages. The duration of breaks between surgical interventions can be from two to three weeks: during this time, the wounds remaining after surgery have time to heal.
The tissues of the removed tumors undergo mandatory histological examination for the presence of cancer cells.
Endoscopic polypectomy, well tolerated by patients, is a gentle procedure, after which a person does not need a rehabilitation period and can engage in normal work activities the very next day after surgery.
Transanal excision
Transanal excision of the polyp through the expanded lumen of the rectum. This type of surgery is performed under local anesthesia.
After injecting novocaine, the surgeon stretches the anal canal using a rectal speculum. The neoplasm intercepted by the clamp is cut off, and the resulting defect in the intestinal mucosa is sutured. Polyps with a wide base are removed using a scalpel within healthy tissue.
Considering the difficulty of completely removing a tumor, carried out in this way and therefore fraught with a high probability of relapse, this technique is not always appropriate.
Endoscopic method
Endoscopic excision of neoplasms of the sigmoid and rectum, carried out using an operating proctoscope equipped with two eyepieces (viewing and working) and microsurgical instruments.
During this endomicrosurgical intervention, hyperplastic and adenomatous polyps and villous tumors located no further than 20 cm from the anus are excised (within healthy tissues). The defect in the intestinal wall resulting from the operation is immediately restored.
Resection
Resection of a section of the sigmoid colon along with detected tumors, followed by anastomosis between the healthy edges of the intestine.
This treatment option, which requires abdominal surgery under general anesthesia, is used when polyps are multiple, severely ulcerated, or tend to merge.
Radical removal
If a histological examination of the tissues of the removed tumors reveals the presence of cancer cells, a radical removal of the affected sigmoid colon along with regional lymph nodes is performed, after which a colostomy is formed.
Diet after tumor removal
After removal of sigmoid colon polyps, the key to a quick and successful recovery of the patient, eliminating the possibility of relapses, is to follow a gentle diet. Its main purpose is to prevent constipation and conditions that provoke irritation of the intestinal walls.
How to organize nutrition for a patient who has undergone polypectomy surgery?
- His daily diet should contain at least six meals, eaten at regular intervals. The volume of one serving should be such that the product consumed fits into a handful.
- All dishes are prepared by boiling, stewing and steaming. Fried foods are strictly prohibited.
- The amount of table salt added to dishes is significantly limited.
- It is unacceptable to consume excessively hot or too cold food and drinks.
- The consumption of spicy, sour and salty foods is strictly prohibited.
- Solid food should be passed through a meat grinder or fine grater.
- Any porridge should be rubbed through a sieve or crushed in a blender.
A person suffering from polyposis is strictly prohibited from consuming:
- Fatty fish, poultry and meat.
- Any cabbage.
- Radishes and radishes.
- Canned food and marinades.
- Store-bought sauces (especially ketchup and mayonnaise).
- Strong coffee.
Strict adherence to the diet is recommended for the patient during the first month after surgery. A positive result of a control endoscopic examination is the basis for some mitigation of the nutritional requirements for the operated person.
Kinds
Depending on a number of features in medicine, there are different types of polyps that affect the mucous membrane of the sigmoid colon.
Some of them do not reach large sizes and manifest a number of symptoms in rare cases. But other types of formations can develop into cancer.
Hyperplastic
They are considered the most common, as they are found in most patients.
Hyperplastic type formations are usually no more than five millimeters and are light in color. In appearance they resemble flat plaques.
Against the background of the dark-colored mucosa, the formations are clearly visible. Over time, they manifest themselves with many symptoms, but despite this, in rare cases they degenerate into cancer. Pathology requires specialist supervision.
Adenomatous
They are the most dangerous type of sigmoid colon polyps, as they are prone to transformation into a malignant course.
They are considered a precancerous condition and require immediate treatment. Depending on the stage of development, formations can reach 1-5 cm.
This species is divided into several types, including villous, tubular and villous-tubular.
In the initial stages of formation they are asymptomatic. But over time, patients experience intestinal obstruction due to the large size of the formation.
In addition, villous polyps are often injured and accompanied by bleeding.
Diffuse
The main cause of occurrence is heredity. The formations are always multiple and are also observed in children and adults.
On this topic
- Digestive system
Differences between sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 9, 2020
A distinctive feature is rapid development and expansion. In certain cases, the presence of several hundred and even thousands of small neoplasms is observed.
Treatment depends on the type of polyps formed on the surface of the mucous membrane of the sigmoid colon.
What it is
A polyp is a benign neoplasm that affects the surface of the sigmoid colon, located on the left side of the abdominal cavity. It is in this department that the processes of digestion of food and the formation of feces take place.
A polyp of the sigmoid colon is considered a precancerous disease. The neoplasm is formed from fibers of glandular tissue and grows into the intestinal lumen.
In the initial stages of development, symptoms occur in rare cases and often resemble a common intestinal disorder. But over time, the polyp grows, reaches significant sizes and becomes the cause of pain.
If a number of signs of pathology occur, patients are forced to urgently seek medical help.