Goals of testing
Signs of a pathological condition are often blurred.
The present symptoms are only general in nature, so it is quite difficult to determine the disease by symptoms alone. In some cases, even differential diagnosis may be necessary to help exclude the development of other diseases of the epigastric region. Appendicitis is diagnosed by blood tests and palpation of the right hypochondrium. Since the disease often develops rapidly and requires immediate surgical intervention, laboratory tests are carried out on an emergency basis.
Surgery is rarely performed until test results are available. Only a qualified specialist can evaluate the clinical picture in accordance with the obtained diagnostic data.
In addition to tests, an examination by a doctor is required.
Symptoms of appendicitis
The first symptomatic signs of an inflamed appendix are:
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- prolonged severe pain in the right side of the abdomen;
- increased spasms during palpation of the area of the vermiform appendage of the cecum, physical exercise, changes in body position;
- stool irregularity;
- decreased appetite;
- weakness;
- increased body temperature;
- cardiopalmus;
- tearfulness in young children.
With inflammation of the appendix of the cecum, only some symptomatic signs may be observed for 6-8 hours. In older people, in accordance with age characteristics, appendicitis does not have pronounced manifestations. The main symptoms of the pathology in young children are diarrhea, vomiting, tearfulness, and lack of appetite.
Indications for prescribing a blood test
The blood sampling procedure is indicated if the following symptoms are present:
- persistently elevated temperature for more than 6–7 days;
- fever;
- loss of appetite;
- chronic constipation;
- diarrhea;
- increased fatigue;
- muscle cramps;
- periodic attacks of sharp and nagging pain on the right side of the abdominal cavity;
- nausea;
- bloating;
- painful urination;
- vomit.
In children, it is much more difficult to determine the signs of appendicitis than in adults, since children, due to their age, are not able to indicate the exact location of the source of physiological discomfort. If a child experiences acute pain that only subsides when the body is positioned on the right side, you should seek medical help as soon as possible.
Location of pain in appendicitis
Of course, many of the listed signs indicate a wide range of diseases, but the combination of a number of symptoms is a reason for an unconditional visit to a medical facility.
Blood test for appendicitis in childhood
The first signs of appendicitis
Is it possible to detect an attack of acute appendicitis in childhood using a blood test? Yes, the technique also gives a complete picture of the condition. But inflammation of the abdominal organs in children is much more dangerous, since appendicitis is much more difficult to confirm.
An inflamed appendix may occupy an unusual position, which makes diagnosis difficult. To confirm the disease, the white blood cell level must rise to a level of 11–15 units. It also helps determine the severity of inflammation.
Signs of appendicitis according to blood tests
Tests for appendicitis are usually not given for nothing. They are resorted to only in cases where it is necessary to accurately and clearly make a diagnosis. It should be understood that tests to confirm the diagnosis are taken only when there are additional symptoms that force the doctor to make this kind of diagnosis.
So, for example, among the following signs:
- severe abdominal pain that cannot be relieved by any measures;
- nausea and vomiting;
- weakness and loss of performance;
- increase in body temperature (and the numbers will not always be high).
If you have at least some of these symptoms, you should consult a doctor and conduct all the necessary research. This will save time, which is extremely important in case of appendicitis.
Therefore, it is worth immediately calling doctors who will take the patient to the hospital and conduct laboratory tests there to the maximum. And you shouldn’t refuse all the proposed research options. After all, this disease is extremely insidious. And the later it is detected, the more difficult it will be for a person to recover.
After laboratory tests, the doctor evaluates the changes in the indicators that the blood test gave for appendicitis.
Blood donation is carried out for several types of studies:
- general indicators;
- amount of C-reactive protein;
- leukocyte count;
- ESR;
- hCG indicator.
A general blood test shows the presence of an inflammatory process, so the level of leukocytes in appendicitis is exceeded. The acceptable indicator is 9, if inflammation progresses, then the analysis may show 14. With pathology of the appendix, the level of leukocytes increases - more than 18.
If some indicators in the general blood test are elevated, this may indicate the presence of inflammation
The number of white blood cells may increase under the influence of other diseases. Also, in older people this indicator may not change. For this reason, other tests are additionally carried out, the results of which together help to obtain an accurate clinical picture.
ESR is an indicator of the sedimentation rate of red blood cells (erythrocytes). ESR with appendicitis is also increased, but in pregnant women this indicator is natural, as is the level of hCG.
The diagnosis can be confirmed by testing the amount of C-reactive protein, which also increases under the influence of the inflammatory process.
You can talk about appendicitis if there is a large number of neutrophilic leukocytes in the blood
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor will need to correlate all the changes, and only when the level of each indicator increases above acceptable standards can a diagnosis be made.
It is difficult to determine inflammation of the appendix in children by the presence of symptoms. This is due not only to the characteristics of the child’s body, but also to the fact that the child, as a rule, cannot correctly describe his feelings.
Diagnosis of appendicitis in children is carried out using the same methods as in adults (examination, palpation and laboratory tests). The main difference is the result of the analysis. In accordance with the fact that the norms of the child’s blood parameters are lower, the leukocyte level, indicating pathology, will be different.
In a child, appendicitis is also confirmed with the help of tests; examination does not always provide accurate information
Leukocytes in children with appendicitis will be more than 11. If the figure approaches 15 - 16, then the probability of peritonitis is high. However, it should be taken into account that the normal number of leukocytes depends on the age of the child.
Standard leukocyte parameters according to age are shown in the table.
| Age | Leukocyte norm |
| from 0 to 3 years | 6-17 |
| from 3 to 6 years | 5-12 |
| from 11 years old | 9-12 |
The ESR level also changes. At the initial stage of the inflammatory process, no significant changes are observed. The rate at which red blood cells settle changes sharply during an acute attack of appendicitis.
The decision about the need for surgery is made by the doctor, taking into account the results of all tests
Only a qualified specialist who will take into account both the patient’s condition and the diagnostic results can recognize the pathology of the appendix and not make mistakes in assessing the research results.
Leukocytosis in complications of appendicitis
With the catarrhal form of appendicitis and initial destructive changes, leukocytosis is most often moderate, in the range of 12-14 x109 /l. If during this period there is no adequate treatment of the disease, that is, surgery, then in most cases complications develop. The most common of these is perforation of the organ and release of purulent mass into the abdominal cavity. Perforation with subsequent development of peritonitis can also be determined by the clinical picture of the disease and according to instrumental examinations.
- Peritonitis is characterized by pain throughout the abdomen, noticeable bloating, lack of stool, and general symptoms of intoxication. As this complication develops, the pulse becomes thread-like and frequent, and can reach up to 140 beats per minute. If you do a blood test at this time, it will reveal pronounced leukocytosis, increased compared to the norm of ESR. If leukopenia is detected, that is, a decrease in the number of leukocytes in the peripheral blood, then this indicates a severe pathology.
- Moderate leukocytosis can also occur in humans with the development of appendiceal infiltrate. This term refers to a condition in which inflammation from the appendix spreads to the intestinal organs and a welded conglomerate is formed. In addition to an increase in the number of leukocytes, this complication reveals a shift in neutrophils. A patient with appendiceal infiltrate is treated in the first weeks without surgery; he is prescribed antibacterial therapy, under the influence of which the inflammation is relieved and blood tests return to normal.
- Appendiceal abscesses develop 8-12 days from the onset of the disease. Ulcers can be located anywhere in the abdominal cavity. This complication can be suspected by a deterioration in the patient’s general well-being, an increase in temperature, chills, and an increase in pulse. Leukocytosis increases in the blood, and a shift to the left of the leukocyte formula is determined.
- Pylephlebitis is one of the most serious complications of appendicitis. This term refers to purulent thrombophlebitis of the portal vein of the liver. The general condition of the patient is very serious, the most constant symptom is stunning chills, rapid pulse and temperature up to 40 degrees. There is high leukocytosis and ESR in the blood.
When making a diagnosis of appendicitis and identifying its complications, all blood parameters are taken into account, they are carried out repeatedly throughout the day, identifying all changes. The decision to choose a treatment method is made taking into account the patient’s condition. In case of complications, the outcome of treatment largely depends on the patient’s age, time of admission to the hospital, and concomitant pathologies. With appendicitis, even now, deaths often occur, and they often occur due to the patient’s late presentation to a medical facility.
Features of urine testing for appendicitis
A complete blood count (CBC) is carried out, oddly enough, in two ways. The first, most common type of hematology screening, involves taking capillary blood from the ring finger. The laboratory technician treats the phalanx pad with medical alcohol, wearing new disposable gloves before doing this, and makes a shallow puncture using a lancet equipped with a sterile thin needle.
When a drop of blood appears on the surface, the medical worker will begin to take a sample of the biomaterial, periodically squeezing the top of the finger. At the end of the procedure, a cotton pad is applied to the wound in order to stop further blood loss. Since young children often experience severe stress at the sight of “scary” laboratory instruments, some clinics have introduced small automatic scarifiers in bright colors.
Is it possible to detect appendicitis by ultrasound?
The second method, based on taking blood from the ulnar vein, is used less frequently, but, unlike the previous one, it allows specialists to carry out, in parallel with the CBC, the determination of biochemical test parameters.
After applying a tourniquet to the shoulder, the nurse will clean the surface of the skin and ask you to actively clench and unclench your fist if necessary. Next, a needle is inserted into a clearly visible vessel, changing the angle of inclination.
When the syringe is filled with the required volume of blood, a sterile napkin is applied to the puncture site and the tourniquet is removed. If during the procedure a person experiences semi-fainting, numbness of the limbs, weakness or nausea, specialists should be notified immediately.
Appendicitis very often makes itself felt unexpectedly, therefore, during emergency delivery of a patient with obvious signs of inflammation, blood sampling is done immediately without appropriate preparation. The results of a routine test are usually provided the next day. An extract with marker indicators in intensive care will be ready within a few hours after the patient donates blood.
Leukocytes in appendicitis can also appear in urine tests, and not just blood. The analysis may well show appendicitis in the inflammation stage. But again, leukocytes in the urine do not in any way indicate appendicitis.
The number of leukocytes in this situation will not be too high. But still it may well be quite noticeable. The only thing worth considering is that you need to properly prepare for submitting the material for research, otherwise the tests will show a false result. For example, inflammation in the genitals. And here it is important not to confuse, because tests are needed to make a correct diagnosis.
A urine test for appendicitis is also necessary, as is a blood test. Urine contains components, the level of which may be an indicator of the pathological condition of the appendix.
In case of appendicitis, an assessment of the contents is necessary:
- protein cylinder;
- leukocytes;
- bacteria;
- red blood cells
With appendicitis, 40% of patients experience increased levels of red blood cells, bacteria and protein. If the intestinal process is located near the urinary tract and its ducts, then, most likely, bacteria will be present in the urinary organs. This also applies to leukocytes.
Urinalysis is also quite informative in diagnosing appendicitis
The presence of blood cells in the urine, on the contrary, reduces the likelihood of appendicitis, since red blood cells are most often present in the urine in diseases of the kidneys and genitourinary system.
For appendicitis, material is taken for analysis from a finger or, in some cases, from a vein. The procedure is painless. Leukocytes in appendicitis are above 18. This condition is quite understandable, because leukocytes in the human body are responsible for protection; if an infection or inflammation develops in the body, then these cells are the first to rush into battle, protecting the person from the consequences of the disease.
A study of the blood composition shows an increase in leukocytes in the catarrhal stage of inflammation to 9-12 thousand, and in the phlegmonous form to 17. If the figure is above 20 thousand, then an abscess or peritonitis is possible. When taking the test, take into account the individual characteristics of the human body, for example, during pregnancy, the level of leukocytes in the blood is normally always elevated, and this is not a deviation.
If you are wondering how to determine appendicitis yourself, pay attention to the characteristic signs; they are also a good reason to conduct a laboratory analysis. In case of inflamed appendicitis, a study in young children, men and women will show an increased content of leukocytes, and the patient himself will suffer from nausea, vomiting, severe abdominal pain, lethargy, and pale skin.
An increase in intoxication of the body leads to stool disorders, constipation or diarrhea. The insidiousness of appendicitis is that the pain syndrome is easily relieved with painkillers, although degenerative changes continue to develop, becoming more intense every hour. If surgical procedures to remove the caecum are not started in a timely manner, it will rupture and infection will occur.
When a drop of blood appears on the surface, the medical worker will begin to take a sample of the biomaterial, periodically squeezing the top of the finger. At the end of the procedure, a cotton pad is applied to the wound in order to stop further blood loss. Since young children often experience severe stress at the sight of “scary” laboratory instruments, some clinics have introduced small automatic scarifiers in bright colors.
Appendicitis very often makes itself felt unexpectedly, therefore, during emergency delivery of a patient with obvious signs of inflammation, blood sampling is done immediately without appropriate preparation. The results of a routine test are usually provided the next day. An extract with marker indicators in intensive care will be ready within a few hours after the patient donates blood.
What parameter included in the blood test is of interest to doctors?
A comprehensive examination and analysis of the results will allow you to make a diagnosis with great accuracy. What do these studies provide, and what parameters will be of interest to the doctor?
If the indicator reaches 18 units or more, then there is a high probability of developing appendicitis. If the value is above 20.0, the doctor may suspect intestinal perforation and the onset of peritonitis. This may be the basis for urgent surgical intervention.
The greater the number of leukocytes in the blood, the more extensive and intense the inflammation. And more dangerous. However, it must be remembered that in pregnant women the number of leukocytes is always increased, so OAC will not be a faithful assistant here.
Also, this analysis will be ineffective in diagnosing the disease in older people, since their leukocyte levels, as a rule, do not rise. Or shows a slight increase.
The presence of inflammation is indicated by an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate. However, this is not a specific indicator. And again, in pregnant women this parameter is always higher than normal due to physiological reasons.
In addition to the total number of leukocytes, it is necessary to establish which type of white blood cells predominates. The fact is that with appendicitis the content of neutrophilic leukocytes increases significantly.
C-reactive protein is another marker of the presence of an inflammatory process in the body. If this parameter is normal, then appendicitis is unlikely. However, an elevated level does not specifically indicate appendicitis, but only informs about the presence of some kind of inflammation.
HCG levels are checked in women. This will eliminate the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy and associated complications. In case of appendicitis, leukocytes will also appear in the urine, which will also suggest the presence of severe inflammation.
Timely and high-quality diagnostics will allow timely detection of the disease and initiation of treatment. Therefore, if a doctor prescribes any tests, there is no need to argue with him. It is better to go through them and find out for sure what is happening in the body. This will help avoid misdiagnosis. You should always remember that appendicitis is dangerous due to its complications and can lead to death if the inflamed appendage of the cecum is not removed in time.
Watch a video about how to treat gastritis, why it occurs, and what measures need to be taken.
First of all, whether with appendicitis or other diseases, doctors are interested in leukocytes in blood tests. After all, they make it possible to determine the presence of an inflammatory process in the body and the degree of its neglect.
Why exactly leukocytes - yes, simply because they belong to the category of substances of the human immune system. And white blood cells are the clearest marker that something is wrong. Therefore, a blood test is done first when appendicitis is suspected (in both adults and children) in order to determine the development of the disease as accurately as possible.
Sometimes doctors need additional confirmation and determination of the diagnosis. To do this, they may well take a urine test. Based on the color it will have, as well as the number of the same leukocytes, doctors determine the presence of a serious pathology.
It is recommended to take a urine test in any case; it will allow you to make a diagnosis faster and more accurately. Although urine analysis is not particularly related to the intestines, it also allows you to quickly track pathological changes in the body.
It is also worth doing an ultrasound to determine appendicitis. It will show as accurately as possible that there is such a problem as inflammation of the appendix. And, as a rule, this kind of research must be carried out in a complex manner.
Doctors advise never to refuse laboratory tests. Naturally, we are not talking about situations that have already become critical. Then consent is no longer required, and all tests are taken automatically, because emergency surgery is required.
In all other situations, it is advisable to follow the recommendations of doctors so as not to bring the situation to a critical limit. This will allow you to recognize the problem in time and avoid the development of serious complications. It is worth remembering that appendicitis is a deadly disease. And you can’t delay its treatment – both chronic and acute forms. After all, this can become the development of not only one pathology, but also a number of others. Very serious.
Preparing for diagnosis
A blood test only shows objective parameter values when the patient has taken care in advance to prepare his body for the upcoming diagnosis. So, 2-3 days before screening, it is necessary to review the diet, excluding marinades, pickles, smoked foods, semi-finished products, instant foods, and fried foods. The main emphasis should shift towards light soups, baked vegetables, slimy porridges, salads and steamed lean meats.
The quantity of confectionery products should be reduced to a minimum. It is better to give preference to dark chocolate and natural marshmallows. The last meal should be in the evening of the last day of preparation, since you must come to the clinic on an empty stomach. You can bring a small bottle of still water with you to quench your thirst.
Smoking immediately before entering the office is strictly prohibited. Cigarettes are allowed at least 4 hours before laboratory testing. If you are using previously prescribed chemical drugs, you should make an appointment with a doctor at least a week in advance to clarify further actions in terms of limiting or completely eliminating medications before diagnosis.
You should forget about the existence of coffee and energy drinks with alcohol. The use of weak tea without flavorings, freshly squeezed juices, compotes and water comes to the fore.
On the last day of preparation, you should stop any types of physical activity - they also contribute to changes in blood counts
Other diagnostic methods
In an acute process, a general urine test sometimes helps - in a quarter of all hospitalized patients, the bladder or ureter begins to react to inflammation in certain anatomical positions of the appendix.
A survey X-ray of the abdominal cavity in most patients reveals increased airiness of the large intestine and half of the colon on the right, and with perforation (breakthrough of contents from the appendix) an accumulation of gas in the abdominal cavity is detected.
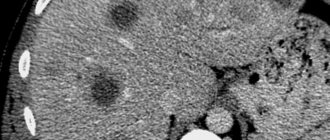
A research method such as ultrasound is very informative. It allows you to determine inflammation of the appendix in 90% of all patients. In this case, the appendix increases in diameter, its walls thicken, its shape changes, symptoms of mesenteric infiltration arise, and it is even possible to detect free fluid in the abdominal cavity. An experienced ultrasound doctor can determine acute appendicitis with an accuracy of up to 95% based on the visual picture alone.
Finally, the most informative method of direct visual diagnosis is diagnostic laparoscopy. If the doctor sees that the appendix and peritoneum are hyperemic, there are hemorrhages on the surface of the appendix, the mesentery is thickened, there is fibrin overlay on its surface and there is effusion in the abdominal cavity, then we are talking about indications for appendectomy.
If the patient has all of the above signs, and the picture is clear, then he will be taken for surgery and with a calm blood test, especially in the first few hours from the development of the disease. A blood test for appendicitis is an auxiliary diagnostic method; its role is to once again serve as a compelling argument for urgent surgery, or to postpone this operation for a while and leave the patient under dynamic observation.
In modern conditions, the importance of a general blood test for appendicitis, due to the introduction of ultrasound and diagnostic laparoscopy techniques, has decreased significantly. In the past, when the doctor was unable to visually evaluate the appendix by looking at it directly, he could only see it by opening the abdominal cavity. Of course, laparoscopy is much safer than laparotomy. But a general blood test, which is mandatory, and carried out cito (urgently), once again allows you to confirm the diagnosis of inflammation in the body, and gives additional confidence to the surgeon that it is necessary to perform an urgent operation.
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix of the cecum. One of the frequent complications of the disease is peritonitis, a serious condition that can cause death.
It is quite difficult to determine suppuration of the appendix only by external signs, since concomitant symptoms can accompany other conditions. Appendicitis can be determined by a blood test with maximum reliability. In deciphering the study, the doctor will be interested in the level of leukocytes.
A blood test for appendicitis is used to determine the total white blood cell count. An increase in the total number of white blood cells indicates suppuration of the appendix. The leukocyte formula for acute appendicitis shows how much a certain type of leukocyte exceeds the indicators of other varieties.
When interpreting the analysis obtained, the patient’s age, general health and temporary conditions, in particular the period of gestation, must be taken into account. When making a diagnosis, blood tests for leukocytosis are performed several times during the day, taking into account any, even the most minimal changes.
Differential diagnosis
The condition of the appendix, determined by blood, allows us to identify any changes in the leukocyte formula, as well as the number of neutrophils, reactive protein and the level of erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
The peculiarity of pathology is that the results of laboratory tests can be changed:
- during pregnancy (including ectopic);
In older people, tests do not always show a clear picture
- with the development of almost any inflammatory process in the body;
- in accordance with the characteristics of childhood.
Due to the fact that AK does not always provide accurate information, experts recommend additional examinations, which are necessary for the purpose of differential diagnosis of the disease.
To clarify the presumptive diagnosis of appendicitis, in addition to blood tests and ultrasound, it is necessary to conduct a urine test for the presence of an inflammatory process.
Ultrasound can help determine the presence of appendicitis.
Instrumental methods
In some cases, additional research is used. It is especially important to accurately verify the inevitability of surgery if the patient is in a “position” or there are medical contraindications to such an intervention. In this case, additional instrumental diagnostic methods are used.
What will help determine appendicitis:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. Ultrasound is considered one of the most informative. It will help you “see” the walls of the appendix and possible kinks and accumulations of fluid inside. The big advantage is the availability of the method (on average the price is from 500 rubles), as well as painlessness (can even be used to diagnose appendicitis in infants).
- Computed tomography or CT scan. An effective way to exclude other possible causes of illness and confirm the diagnosis. The only exception is that it cannot be used by pregnant women or young children.
- Magnetic resonance imaging or MRI. One of the most effective methods for diagnosing appendicitis. Can be used to examine pregnant women and young children.
- Medical thermography. Helps determine the localization of the inflammatory process by increasing the local temperature. If there are accompanying symptoms, it gives a complete picture and confirms the diagnosis.
- Laparoscopy will help to accurately determine the condition of appendicitis and possible pathologies of other organs. The examination is performed under general anesthesia through three small holes in the patient's abdomen. If the diagnosis has been confirmed, the appendix is removed laparoscopically. This method is effective if there are no complications and the threat of perforation of the appendix.
- X-ray is the oldest method of diagnosing appendicitis, but is still often used for this purpose. To determine a possible pathology, a contrast agent is used - barium derivatives, which shows the problem. The method is not 100% informative; it is most often used when there is a suspicion of intestinal pathology, because a contrast agent is introduced into the cavity through an enema.
Typically, the type of diagnosis is chosen by the attending physician depending on the severity of the patient’s condition and survey data and the presence of characteristic symptoms.
How to determine the presence of appendicitis by blood?
Inflammation of the appendix cannot be diagnosed by any one parameter. There are 5 main blood markers, which together provide comprehensive information about the state of the body:
- Red blood cells. Red blood cells transport carbon dioxide and oxygen.
- ESR. One of the most indicative values is the erythrocyte sedimentation rate in a test tube. It indicates the intensity of the disease.
- S-RB. Immediately after the manifestation of an inflammatory focus, the liver synthesizes C-reactive protein, which suppresses the development of latent infection.
- Leukocytes. Blood cells detect pathogenic cells and viruses, attack them from all sides, and then eliminate them.
- Band neutrophils. These compounds are a type of white blood cell. In addition to providing internal protection, neutrophils also restore the structure of damaged tissues.
| Age category | Possible values of blood parameters | ||||
| ESR (mm/h) | S-RB (mg/l) | Red blood cells (×10^12/l) | Leukocytes (U/l) | Band neutrophils (%) | |
| Up to 20–25 days | 0–2,8 | 0–5 | 3,9–6,6 | 7–32 | 4–12 |
| 1–2 months | 2–5 | 2,7–5,4 | |||
| 3–6 months | 4–6 | 3,1–4,5 | 3–8 | ||
| 6–12 months | 3–10 | 3,4–5,2 | 2–7 | ||
| 2–5 years | 5–11 | 3,7–5 | 5–c15.5 | 1–6 | |
| 6–14 years | 4–12 | 3,5–5,5 | 4,5–13,5 | 1–5 | |
| 15–17 years old | 2–15 (for girls), 1–10 (for boys) | 3–5.5 (for girls), 3.9–5.6 (for boys) | 4,5–11 | 1–6 (for women), 1–7 (for men) | |
| 18-–30 years old | 8–15 (for women), 2–10 (for men) | 3–5.5 (for women), 4.2–5.6 (for men) | 4.0–10.5 (for women), 4.2–9.0 (for men) | ||
| 30–60 years | 8–20 (for women), 2–10 (for men) | 3.5–5.1 (for women), 4.0–5.6 (for men) | |||
| 60 | 8–20 (for women), 2–15 (for men) | 3.4–5.2 (for women), 3.1–5.7 (for men) | 3.7–9.0 (for women), 3.9–8.5 (for men) | ||
If the number of red blood cells is minimal with an increased content of CRP, ESR, leukocytes and band neutrophils in the blood, then with a high degree of probability we can talk about the presence of progressive appendicitis in the patient. Since the indicators of pregnant women are often higher than normal, they are replaced by other diagnostic methods instead of OAC.
Often, a similar measure is used in relation to older people who have a weakened immune response. Many symptoms of an inflamed appendix resemble ectopic pregnancy, so female representatives sometimes have to donate blood for hCG levels. A result between 0 and 5.3 mIU/ml excludes gestation.
A small amount of feces will be enough for the study. It is not so easy to diagnose appendicitis. But still, stool tests will detect the presence of a problem in the intestines.
So, for example, it is enough to look at the color of the material collected for analysis. If the stool is black, foams and emits a too pungent and completely unbearable odor, you should think about it.
Why can feces act as an object for research? Because it is connected to the intestines, and the appendix is part of the digestive system. And if the appendix is overloaded and cannot cope with its duties, or even worse, it is overfilled and bursts, you will definitely see a reflection of this in the analyzes.
A shift of leukocytes to the left confirms appendicitis
[A complete blood count] shows a noticeable increase in leukocytes, and confirmation is the same shift to the left - on the scale of the percentage of certain types of cells, an increase in band neutrophils is clearly visible. It is their growth that indicates serious inflammation. The phase of the process can be clarified by the appearance of a shift to the right - the balance shifts towards segmented leukocytes with a clear increase in their number and an increase in ESR.
READ ICD 10 codes for phlegmonous acute form of appendicitis
A leukogram for inflammation of the appendix plays the role of not only confirmation, but also an indicator of the urgency of surgical intervention. When moving to a shift to the right, the decision is made taking into account the lack of time, since the process develops rapidly and towards the phlegmonous and perforative stages. And this is a direct threat of the occurrence of a periappendiceal abscess with transition to peritonitis.
When you need to see a doctor urgently
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=51n7O7Jpce8
Seeking medical help for diagnosis is necessary if you have symptoms:
- pain in the hypochondrium on the right;
- severe vomiting;
- dispersion (diarrhea/diarrhea);
- temperature increase.
The more intense the symptoms, the higher the risk of complications. In acute appendicitis, the patient may lose consciousness.
With any suspicion of developing appendicitis, there is a possibility of risk to human life, therefore all examinations, including blood and urine tests, are carried out as soon as possible. Based on the diagnostic results, a decision is made on surgical intervention to remove the appendix.
Additional tests
In addition to a general blood test, which determines the content of leukocytes, and urine tests, they can take blood for analysis, where they will determine the leukocyte formula, C-reactive protein and hCG. The leukocyte formula shows the percentage of leukocyte elements. If there is inflamed appendicitis, then an increase in neutrophils is observed.
C-reactive protein begins to be produced by the liver when internal organs become inflamed. If the test results show elevated white blood cells, but the level of C-reactive protein is normal, then appendicitis can be ruled out immediately. The elevated protein itself is evidence of many diseases, so diagnosing appendicitis with its help is necessary only in combination with the number of leukocytes and the patient’s symptoms. The C-reactive protein level does not exceed 10 mg/l. If symptoms persist for 12 hours and the protein level is greater than 12, the doctor may diagnose appendicitis.
Since the signs of appendicitis are very similar to the symptoms of ectopic pregnancy, a blood test for hCG is performed. If a woman does have an ectopic pregnancy, the level of human chorionic gonadotropin will be increased if the presence of hCG in the woman's blood is negative in the blood test. Sometimes, the doctor sends the patient for ultrasound diagnostics of the peritoneal organs. The study will be decisive in the diagnosis of appendicitis.
Based on the information obtained during the examination, the doctor makes a decision on surgical intervention. If you delay in cutting out appendicitis, the consequences will be very serious, including death.
A child, a woman or a man can experience inflammation of the appendage of the cecum, so it is much wiser to prevent the occurrence of inflammation by eating right and promptly eliminating urinary tract diseases. At the first symptoms, it is recommended to seek qualified help.
Urine analysis
Considering that all people are different and it can be difficult to determine the disease only by analysis, since even in the presence of inflammation, there are quite good indicators and the level of leukocytes is within the normal range. As an addition, the patient may be prescribed a urine test. The color of urine during illness will be very bright, the liquid takes on a dark orange and even brownish tint.
In half of the cases of inflamed appendicitis, the following is recorded:
- high level of leukocytes in urine;
- increase in red blood cells and bacteria.
A significant increase in the composition of red blood cells indicates diseases of the genitourinary system. A normal number of red blood cells, if present, an increased level of white blood cells makes it possible to exclude stones in the kidneys and ureters.
Diagnostic methods
For inflammation of the appendix, the main diagnostic methods are prescribed:
- primary examination - palpation;
- lab tests:
- blood;
- urine;
- instrumental research:
- computer, magnetic resonance imaging;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- medical thermography;
- laparoscopy;
- radiography.
Diagnostics allows you to detect the disease in a timely manner, prescribe effective treatment, and eliminate the pathology.
Initial examination
The first diagnostic method is an initial examination with palpation of the abdominal area. If the blood supply to the appendix is disrupted, strong, sharp pain is observed when pressing on the iliac region on the right side. In some clinical cases, the doctor may feel the inflamed appendix. The basic rule of palpation is to sharply release the hands after pressing on the abdomen. A description of associated symptomatic signs is an important part of the purpose of additional studies.
Lab tests
Submitting biological material for laboratory testing is important to determine further treatment for appendicitis. The exception is clinical cases when there is a serious complication that requires immediate surgical intervention to avoid the death of the patient. Based on the results of laboratory tests of blood and urine, it is possible to determine the cause of inflammation and eliminate possible problems with urination.
Biological material is collected to carry out the necessary tests:
- general blood and urine analysis if appendicitis is suspected;
- measuring the level of red blood cells, leukocytes;
- establishing the reactive protein indicator;
- determination of hCG level.
Establishing the number of leukocytes and erythrocytes contained in the blood allows us to identify the internal inflammatory process. Urine examination makes it possible to exclude diseases of the urinary system and determine the presence of pathogenic bacteria, infections, and viruses.
An increase in the number of leukocytes and red blood cells indicates the effect of an inflamed appendix on the urinary system. An indirect sign of damage to the vermiform appendage of the cecum is intense, dark color of urine.
Required parameters
The main indicator in laboratory analysis is the level of leukocytes in the blood. It indicates the presence of an internal inflammatory process and the nature of the pathology. Leukocytes in appendicitis have an indicator of 11-15 units in children, more than 18 in adults. High indices are grounds for emergency hospitalization and surgery. The predominance of the neutrophilic variety of leukocytes indicates that the inflammation becomes acute. Each person’s blood circulation is individual, therefore, to avoid inaccuracies, biological material is collected several times throughout the day.
Tests to determine inflammation of appendicitis involve determining the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. An increase in the indicator indicates an exacerbation of the pathology. Changes in hormonal balance during pregnancy in women are the cause of an unstable erythrocyte sedimentation rate index, as well as a possible slight increase in the level of white blood cells.
Signs of the inflammatory process are directly related to the level of reactive protein. Therefore, this indicator is not an infallible method for determining appendicitis, as it indicates a change in the functioning of any body system. For women, a blood test is required to determine the level of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) to distinguish appendicitis from signs of ectopic pregnancy. The accuracy of the result is ensured by the regularity and dynamism of the procedure.
Established standards
A blood test to determine appendicitis involves establishing the level of leukocytes in accordance with standardized indicators for age categories:
- infants and children under 3 years old – 6-17 units;
- 3-6 years – 5-12;
- 6-10 years – 6-11;
- more than 11 years – 4-9.
Each person’s body is individual, therefore, when obtaining the results of a blood test for appendicitis, it is necessary to take into account the peculiarities of physiology. A normal phenomenon is increased levels of leukocytes in pregnant women and the elderly, and a decrease in the index in male adolescents. After appendectomy surgery, your white blood cell levels will stabilize after a certain amount of time.
There are standards for erythrocyte sedimentation rate in accordance with gender characteristics: for women the rate should be 2-15 mm/h, for men – 8-15 mm/h, for children and adolescents – 3-12 mm/h. The standard C-reactive protein index is less than 10 mg/l.
Instrumental examination
Instrumental examination methods are auxiliary methods for determining inflammation of the appendage of the cecum, necessary for an accurate diagnosis during pregnancy and medical contraindications to surgical intervention.
Magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity allows you to visually examine areas of the cecum. Availability and absence of contraindications make it possible to conduct research on newborns and pregnant women. Measuring local temperature (medical thermography) is aimed at identifying the location of inflammation, where a significant excess of indicators is observed. The laparoscopic method allows you to determine the nature of appendicitis, as well as perform an appendectomy - emergency removal of the appendix.
Treatment methods for the disease depend on the form of the disease. Blood and urine tests for appendicitis can reveal the nature of the inflammatory process. Instrumental examination determines the influence of pathology on the functioning of the abdominal and pelvic organs. By submitting biological material for suspected appendicitis, you can establish the level of leukocytes and erythrocytes, indicating the degree of inflammation. Elimination of the affected process, as well as removal of the adenoids for adenoiditis, is the main method of treating the disease.
Almost 75% of all emergency operations in the department of pure surgery are appendectomies. How to make a diagnosis without error? Is a blood test important for appendicitis?
This diagnosis is made very often, in 10% of people throughout their lives. Most often, the risk of getting sick exists in people aged 20 to 25 years. The diagnosis of appendicitis is the most common after acute inflammation of the gallbladder, cholecystitis, which leads to sudden hospitalization. A quarter of all emergency hospitalizations are suspected of acute inflammation of the appendix, and at the same time appendicitis is the first diagnosis in terms of the number of surgical interventions performed for emergency indications.
Clinical picture of biochemical studies in inflammation of internal organs
The chemical composition of human blood is a constant value.
They donate blood for analysis in order to find out the quantitative relationships of its components. If the levels of white and red blood cells are increased, the composition of the plasma has changed, then you need to start treatment without delay. A mandatory laboratory test for the presence of leukocytes in the blood is prescribed if inflammation of the appendix is suspected. During acute inflammatory processes, the composition of human blood changes due to the ingress of bacterial metabolic products into it. Leukocytes with appendicitis increase in size and number.
Leukocytes in the body
They are the main tool of immunity, but at the first stage of inflammation this increase is imperceptible. The state of red blood cells also changes. Their number is not subject to strong fluctuations, but inflammation shortens the lifespan of the red blood cell.
Urine also changes its composition, which correlates with the type of disease. The amount of dead leukocytes and red blood cells in it increases, the alkaline reaction changes, and the most severe cases are accompanied by the appearance of protein. To determine appendicitis using a blood test, it must be taken early in the morning on an empty stomach.
The correct indicators for a mature person in relative values of leukocytes are from 4 to 8 units. In children they can reach 17. During pregnancy – 12-18. If leukocytes exceed 20, then there is a suspicion of peritonitis - a severe form of appendicitis that requires urgent surgical intervention.
Other signs of appendicitis:
- Physiological signs. An increase in temperature, painful lumps in the lower abdomen, vomiting, and loose stools are the first external signs. If the disease has progressed, bloody discharge may appear in the stool and urine. In particularly difficult cases, a fistula develops with access to the skin.
- Changes in the composition of urine. The vital activity of pathogenic microorganisms is reflected in all body secretions. The kidneys separate metabolic products, signaling the onset of the disease by the changed chemical composition of the filtrate. If proteins appear in the general urine analysis, the bacterial background is increased, and its color takes on an unhealthy, cloudy appearance, this is a sure sign of internal inflammation.
- ESR. An ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) analysis is designed to show what stage the disease is at. The activity of red blood cells varies depending on the state of the body. The inflammatory process provokes red blood cells to increase the consumption of their resources. ESR shows how long these cells live. Expressed in the height of the plasma layer and measured in millimeters per unit of time. In a healthy man it is 1-10 millimeters per hour, in a woman 3-15, in a child 12-17, in a newborn 0-2.
- However, only the results of a comprehensive examination, taking into account the total number of leukocytes and erythrocytes, will help to draw a conclusion about the nature of the disease.
Leukocyte formula shift
When assessing blood test results, the doctor examines not only the number of formed elements, but also estimates the proportion of each type of cell. The percentage of leukocytes is called the leukocyte formula, or leukogram.
A microscope is used to count the number of white blood cells. With its help, 100-200 blood cells are counted and their numbers are arranged in a special table. Then the percentage is calculated for each type. This is a leukogram. Under the influence of certain factors, it changes, moving left or right.
A shift in the leukocyte formula to the left is changes associated with an increase in the number of immature (young) neutrophils. This clinical picture indicates a severe degree of intoxication, as well as infectious processes.
A shift of the leukogram to the right occurs with an increase in the number of mature neutrophils, in other words, due to blood aging. Such a change indicates chronic pathologies of internal organs.
No surgery is performed until the results of the blood test are received. After receiving the necessary information, the doctor assesses the patient’s condition and, if the diagnosis is confirmed, prescribes surgery.
Be healthy!