Preliminary diagnosis of cirrhosis at home
In order for a person to seek help from a specialist, he must have grounds, that is, complaints about the manifestation of certain unpleasant signs. At home, you can assume the presence of such a disease yourself, based on the manifestation of symptoms such as:
- jaundice - not only the skin, but also the mucous membranes of the mouth and eyes acquire a yellow tint. This process is caused by the fact that the liver begins to function improperly and produce large amounts of bilirubin;
- a change in the shade of urine and feces, which develops against the background of the previous sign. Urine becomes dark brown and stool discolors to gray;
- an increase in the size of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity indicates that such a disorder has become a predisposing factor to the accumulation of fluid in the peritoneum. This process is caused by stagnation of bile in the liver ducts. In addition, discomfort and pain in the abdomen may appear when performing heavy physical activity, as well as swelling of the lower extremities;
- loss of appetite, which causes weight loss. At the same time, the person eats normally, but the weakened liver is not able to process and absorb beneficial substances coming from food;
- severe weakness - a large number of patients note a decrease in strength to such an extent that the person cannot perform even basic actions;
- a depressive state, which is accompanied by sleep disturbances and indifference to everything that happens;
- lack of sexual attraction to the opposite sex - often indicates the presence of cirrhosis of the liver, because the inflammatory process can affect nearby organs of the peritoneum and pelvis;
- a feeling of heaviness in the stomach and rapid satiety from food is explained by the fact that the enlarged liver puts pressure on the stomach;
- acquisition by male representatives of some signs of femininity, in particular an increase in the size of the mammary glands;
- constipation followed by diarrhea. In this case, the period of time for digesting food decreases. After eating, no more than an hour passes before defecation;
- loss of skin moisture and elasticity. In addition to a yellowish tint, the skin may be covered with dark brown spots;
- redness of the tongue and palms.
But the main symptom of liver cirrhosis with which people go to a medical facility is pain. In order to identify problems with the liver, you need to lightly press on the area of its projection, that is, in the area under the right ribs. With such a disease, a person will feel a strong nagging pain that persists for quite a long time. With a strong magnification of the affected organ, you can independently feel the contours of the liver through a thin layer of skin.
When to see a doctor
Early diagnosis of cirrhosis can significantly improve the quality and life expectancy of patients. You should consult a doctor if you systematically experience discomfort in the abdominal area, dyspepsia, flatulence, suffer from indigestion, are often bothered by pain in muscles and joints, and body temperature rises to subfebrile levels.
It is impossible to cure cirrhosis. But with early diagnosis, it is possible to significantly slow down the replacement of liver cells with connective tissue and significantly improve the quality of life. After all, pronounced symptoms of liver cirrhosis can appear only at the thermal stage of the disease, when the functional capacity of the liver is completely impaired, and it is no longer possible to help the patient.
Medical diagnosis
After the patient is admitted to the hospital, he is immediately sent for examination to a gastroenterologist. The first thing a specialist should do is to get acquainted with the person’s medical history and life history. This will make it possible to determine some of the causes of such a disorder, for example, long-term alcoholism or the presence of hepatitis.
Then the doctor must interview the patient. This will help identify the presence, initial time of appearance and intensity of expression of the clinical picture. After listening to the complaints, the specialist conducts a thorough physical examination to detect external signs of the disease.
Such an examination must necessarily include palpation of the entire area of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity. This measure will not only detect fluid accumulation and an increase in liver size, but also differentiate liver cirrhosis from other ailments that may have similar symptoms. For example, acute inflammatory processes in the peritoneum, gall bladder or pancreas. Such conditions require immediate surgery.
There are several ways to get cirrhosis pre-approved. They can be certain areas on the abdomen, which in response to palpation give increased sensitivity, pain points in the right hypochondrium, as well as various methods of applying pressure and studying the patient’s reaction. With such an ailment, in the projection of the liver, the doctor will feel the edge of this organ - it is dense, sharp and causes pain to the person. With significant magnification, when the liver extends beyond the hypochondrium, the doctor will feel hard, tuberous formations.
It is necessary to palpate the spleen in the area under the left ribs. This disease is characterized by a slight increase in its volume. Palpation and tapping of the lower peritoneum is carried out to detect accumulated fluid in this area.
Swelling of the lower extremities is determined by the remaining finger marks after pressure.
Self-examination as a diagnostic criterion
In most cases, the diagnosis of liver cirrhosis begins at the second stage of development of a dangerous pathology, when even the most inattentive person cannot ignore the warning signs of problems.
Cirrhosis is a general collective term for the process of degeneration of normal liver tissue into fibrous tissue. This is a polyetiological, multi-vector type of liver pathology accompanied by morphological changes, which can develop gradually or immediately manifest itself in an acute form. In the latter case, you do not need special knowledge to guess the presence of the disease.
Gradual progression also has general criteria that an attentive person immediately pays attention to. By analyzing subtle symptoms, you can come to certain conclusions.
The patient does not necessarily make a diagnosis right away, but one can guess the presence of pathological changes in the liver even from these subtle signs. Particular attention should be paid to the state of the body when:
- the presence of a disorder in the normal functioning of the digestive organs and biliary system (diseases of the gallbladder and ducts often lead to the development of biliary cirrhosis);
- constant contact with toxic substances in unfavorable environment or work in hazardous industries;
- permanent consumption of alcohol-containing drinks, regardless of their strength and quantity;
- diagnosed malfunctions of the immune system, especially in autoimmune pathologies;
- chronic form of viral hepatitis or infectious disease (syphilis, tuberculosis);
- permanent use of medications, especially steroids and anabolic steroids, antibiotics, NSAIDs;
- diseases of the cardiovascular or endocrine system, diagnosed hereditary pathologies of metabolism and absorption of certain components.
It is possible to make assumptions about the presence of a liver dysfunction without any special prerequisites, only on the basis of signs. Despite scientific research conducted by outstanding clinicians, the etiology of idiopathic cirrhosis, which develops without visible external prerequisites, has still not been determined. Thinking about how to diagnose liver cirrhosis is the prerogative of people with special education. All the patient needs to do is come for a consultation and tell them about the warning symptoms.
The main guidelines for the initial diagnosis of liver cirrhosis are pain in the right hypochondrium, manifested by weight loss, irritability, fatigue and general weakness. Alarming symptoms include changes in the skin (the appearance of uncharacteristic coloring, spider veins, hepatic palms and soles), aversion to food and ascites, and significant digestive disturbances.
But it is impossible to talk about cirrhosis without specific examinations, because in the early stages it can feel like any other liver pathology. The primary task is to contact a doctor to confirm or refute your own assumptions and begin timely treatment.
Laboratory diagnostic techniques
To find out the extent of liver damage and determine future treatment tactics, the patient is shown laboratory diagnostic methods to determine the presence of characteristic changes in the blood, urine and feces.
General and biochemical blood tests are necessary to identify changes in its composition. In liver cirrhosis, an increase in the number of leukocytes is found, as well as a decrease in red blood cells and hemoglobin. They check the ability of blood to clot and the presence of indicators that indicate liver damage.
Blood studies are also carried out for the differential diagnosis of liver cirrhosis with hepatitis and echinococcosis. In both cases, the presence of antibodies to viruses and parasites in the blood is checked.
The study of urine and feces is, first of all, aimed at identifying changes in their shade - the main indicator of disruption of the normal functioning of the affected organ. In addition, urine tests are necessary to determine the presence of a concomitant disorder, since with cirrhosis of the liver, immunity is reduced and a person is susceptible to frequent viral or colds.
After completing laboratory diagnostics, patients need to undergo a hardware examination.
Differential diagnosis
If there is any doubt, the attending physician will make a differential diagnosis. This will eliminate all possible diagnoses that are closely intertwined in symptoms, but at the same time are subject to doubt. As a result of such a diagnosis, the only correct diagnosis will be identified and made.
It is worth considering that chronic hepatitis, fatty hepatosis and cirrhosis lead to hardening of the liver and disruption of its structure. However, only with cirrhosis will portal hypertension (increased pressure in the portal vein) be clearly expressed.
In addition, there are a number of other pathological liver conditions whose symptoms are similar to cirrhosis. An experienced specialist will conduct a series of comparative studies that will lead to the only correct diagnosis and the prescription of productive treatment.
Instrumental methods for diagnosing cirrhosis
Instrumental diagnosis of liver cirrhosis includes:
- Endoscopy is a procedure for examining the surface of the abdominal organs, as well as examining the expanded venous network and the location of possible hidden bleeding that may accompany cirrhosis;
- Ultrasound - will show changes in the volume of the affected organ, the presence of stagnation of blood and bile;
- Laparoscopy is an endoscopic procedure to examine the liver, during which a biopsy is performed.
In addition, the radionuclide method is often used, in which isotopes are introduced into the blood and deposited in the liver cells. With cirrhosis, darkened spots will be visible on the ultrasound screen.
However, the most informative and common diagnostic method is ultrasound for liver cirrhosis. During such an examination, the size of the affected organ is studied, the correspondence of parameters between the lobes of the liver is traced, the characteristics of the blood supply are determined, as well as the structure of the bile ducts and gallbladder.
During such a procedure, it is very important to detect specific manifestations of the disease. Ultrasound signs of liver cirrhosis are:
- an increase in the size of the affected organ and pronounced uneven contours;
- change in the surface - it is uneven and lumpy, due to the formation of fibrous nodes;
- the presence of a large number of areas with increased echogenicity, i.e. sensitivity to ultraviolet rays;
- wrinkling of the right lobe of the liver - observed in the later stages of the disease;
- changes in the vascular pattern, reverse blood flow in the vessels is noted;
- decrease in gallbladder parameters;
- detection of a large amount of fluid in the peritoneum;
- splenomegaly.
It is by ultrasound examination that the diagnosis of “liver cirrhosis” is clarified and the most effective tactics for treating this disease are prescribed.
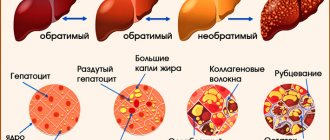
Cirrhosis is a pathological transformation of healthy functional hepatocytes (liver cells) into connective scar tissue that has no functional load. Cirrhotic changes in the exocrine gland (liver) are progressive and irreversible. The first signs of liver cirrhosis can only be determined by the results of laboratory tests and hardware diagnostics. At the initial stage of its development, the disease rarely manifests itself with pronounced external or painful symptoms.
People associate minor changes in well-being with fatigue or the manifestation of other chronic pathologies that were previously diagnosed. This is the main reason for late diagnosis. The disease cannot be eradicated (absolutely eliminated) through medications. Therefore, to the question that interests all patients, whether cirrhosis can be cured with tablets and injections, the answer will be negative.
How to detect cirrhosis of the liver?
At home, one may suspect a dysfunction of the organ. The problem can be determined by a medical examination, which takes place in several stages.
Inspection and palpation
First of all, a specialist in a medical institution collects an anamnesis. During the interview, he must identify information that influences the diagnosis:
- Frequency and duration of alcohol consumption.
- Past diseases - hepatitis, stones and inflammation in the biliary tract.
- Hereditary and autoimmune pathologies.
- Complaints: nature of pain, temperature, headaches, itching.
Then the doctor begins a general examination of the patient. The condition of the skin is assessed, weight and abdominal girth are measured. The condition of the muscles, the presence of spider veins, the growth of veins, and the condition of the navel are determined.
During the examination, palpation is performed - manual determination of the boundaries of the organ. Upon examination, there is a noticeable increase in the boundaries of the gland, tapping produces a dull sound, the shape is uneven and lumpy. The spleen is felt under the left ribs, which tends to increase in size during illness. The abdomen is examined to determine the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
Abdominal ultrasound
Diagnosis of liver cirrhosis using ultrasound allows one to determine the contours and exact dimensions of the organ, signs of ascites, and the presence of blood and bile stagnation. The diameter of the portal vein is measured. High echogenicity during examination is a sign of fibrosis.
For patients, ultrasound is painless and does not pose a risk to life. In preparation, you need to follow a diet for three days - exclude gas-forming foods, eat small portions every three hours, a light dinner is allowed the day before. Before the study, the doctor prescribes activated charcoal and a cleansing enema.
Blood and urine tests
General clinical tests can determine the presence of inflammatory processes, anemia, and clotting abilities. In a general blood test, this is evidenced by the following indicators.
- Hemoglobin. Normal is 120 g/l. Reduced in anemia.
- Red blood cells. In a healthy person, 4 × 1012, a smaller number allows one to suspect pathology.
- Leukocytes. If the value is exceeded 9x109, it indicates an inflammatory process.
- Platelets. A drop below 180x109 indicates a blood clotting disorder.
- ESR. Above 15 mm/h is a sign of inflammatory reactions.
This is interesting: What is the head of a jellyfish in liver cirrhosis?
A blood biochemistry test determines the condition of the affected organ more accurately. Excess levels of bilirubin, ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, and a decrease in total protein indicate pathological processes in the liver. Biochemistry is taken in the morning, before breakfast. Does not require a special diet.
A urine test determines the functional state of the kidneys to exclude ascites. The urine of a healthy person does not contain protein, casts or traces of bilirubin. An average portion of morning urine is provided for the study.
MRI and CT scan of the abdomen
Modern diagnostic devices make it possible to determine the condition of an organ in case of cirrhosis and to see the vessels layer by layer. Information data obtained from a person is processed by a computer and displayed on the screen in the form of photographs or three-dimensional images.
They differ in the principle of operation. A CT scan uses a narrow, low-intensity X-ray beam that creates a spiral around the body. Better distinguishes tissue density. Magnetic resonance imaging works on the principle of the body's response at the atomic level to electromagnetic radiation. Effective in examining soft tissues and areas of inflammation.
What happens in the liver
The liver is a fundamental organ in the hepatobiliary system of the body. The functional responsibilities of the gland are:
- detoxification (cleansing) of the body from decay products, poisons and toxins;
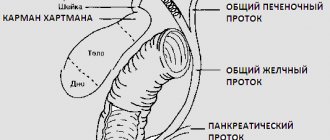
- production and secretion of bile (a biochemical fluid, without which the process of digesting incoming food is impossible);
- breakdown of proteins and the release of amino acids essential for the body;
- formation of glycogen and its processing into glucose reserves;
- maintaining stable hormonal balance;
- participation in the process of hematopoiesis.
In cirrhosis, the ability of hepatocytes to regenerate (recovery) is blocked. Under the influence of various unfavorable factors, thin partitions (septa) are formed in the liver tissue. The cells, fenced on all sides by septa, gradually die off, turning into scars; the gland loses its ability to perform vital functions. It is impossible to start the destructive process in the opposite direction, so liver pathology cannot be cured.
Reasons for development
Cirrhosis is classified into several types, depending on the cause:
- Viral. Progresses due to untimely or incorrect treatment of hepatitis of viral etiology (A, B, C).
- Pharmacological (medicinal). Develops against the background of an overdose or prolonged use of certain types of medications.
- Toxic (in most cases, alcoholic). Occurs due to regular uncontrolled drinking. In terms of gender, this type is more typical for men.
- Metabolic and nutritional. It develops as a complication of chronic endocrine diseases associated with metabolic and hormonal imbalances (obesity, diabetes).
- Congenital. It is formed in the fetus during intrauterine development under the influence of teratogenic factors or due to unfavorable genetics.
- Biliary. Has two forms. Primary biliary cirrhosis occurs due to the destructive effects of cells of the own immune system (autoimmune factor). The secondary form develops as a result of severe pathologies of adjacent organs, most often the gallbladder and its ducts (the presence of stones, cysts, tumors, inflammatory and infectious lesions of the bile ducts).
- Cryptogenic. Diagnosed when the nature of the origin is unclear, when the exact causes cannot be established.
Stage of the disease
The pathology has a chronic course with a gradual increase in symptoms and morphological transformations of the organ. Structural changes in the liver are classified according to the number and size of dead nodules formed in place of working hepatocytes. There are three degrees of damage: micronodular (the lesions do not exceed 0.3 cm in size), macronodular (the size of the lesions doubles), mixed (the presence of different-sized nodes).
The stage of pathology according to severity is determined according to the Child-Turcotte-Pugh rating scale:
- initial stage or compensated (class A);
- moderate or subcompensation (class B);
- decompensated or fatally severe (class C).
The patient undergoes a comprehensive examination according to five criteria, with a certain number of points assigned. The total indicator indicates the stage of the disease. The final stage is the terminal (fourth) stage of the disease, which is inevitably followed by the death of the patient.
Diagnostic measures
The cause of the disease and its stage can be determined through complex diagnostics, including microscopic blood tests, hardware methods, and biopsy of organ tissue. Biochemistry indicators:
- high digital indicator of liver enzymes: AST (aspartate aminotransferase), ALT (alanine aminotransferase), Alpha-Amylase;
- disruption of the interaction of nutrients and fat (lipid) metabolism.
Clinical analysis reveals leukocytosis and a high erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), as signs of an inflammatory process, as well as a low hemoglobin level. Ultrasound results show the following. Changes in the size of the gland and its ability to absorb ultrasound (echogenicity). The initial stage of the disease is characterized by proliferation of the gland and hyperechogenicity, that is, an increase in the density of the organ. In the process of degeneration of hepatocytes into nodes and scars, echogenicity decreases to complete absence in the decompensation stage, and the liver decreases in size.
Heterogeneous (heterogeneous) structure of the organ with nodular formations. An unevenly outlined outline (organ contours), with a characteristic round lower edge. An increase in the size of the spleen and splenic vein (in the initial stage of the disease – insignificant). In the subcompensated and decompensated stages, abdominal dropsy (ascites) is diagnosed. At the initial stage of the disease, this symptom is absent.
The results of the biopsy: destructive-dystrophic changes in tissue and hepatocytes, the presence of nodes and scars. Liver tissue is collected by laparoscopy (a tiny incision in the peritoneum) or by puncture (using a needle). The earlier diagnostic measures are carried out, the greater the patient’s chances of increasing life expectancy. With cirrhosis, which is detected at an early stage, life expectancy in 50% of cases remains for another 10–12 years. When diagnosed in the subcompensated stage – 5–8 years. The terms for severe patients are limited to three years.
How to recognize complications?
How to diagnose liver cirrhosis in the later stages of the disease in order to avoid complications of cirrhosis? In later stages, signs of the disease may appear:
- The abdomen increases in size, fluid accumulates in the abdomen in a volume of more than 15 liters. This complication of cirrhosis is called ascites. The anterior abdominal wall is tense, the navel turns outward, there may be ruptures of the navel;
- Difficulty breathing, it becomes rapid and superficial due to the restriction of the movement of the diaphragm and the occurrence of one of the complications - ascites in liver cirrhosis;
- Dilation of the veins on the skin of the abdomen in the form of a peculiar pattern of the head of a jellyfish, dilation of the veins in the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach, from where life-threatening bleeding can begin. This complication is called portal hypertension and appears in the later stages of liver cirrhosis.
And if liver cirrhosis is detected, you need to be aware of the signs of complications of the disease, which are very dangerous and can result in death if left untreated. These complications manifest themselves:
- Low pressure. Arterial systolic (upper) pressure is below 100 mmHg; when a person moves to a vertical position, it sharply decreases by 20 mmHg. The pulse is increased. Vomiting of blood, coffee grounds, and black stool may occur. These symptoms indicate the development of a formidable complication - bleeding from dilated veins of the gastric and esophageal mucosa;
- A decrease in the amount of daily urine can be determined as a sign of hepatorenal syndrome;
- Hepatic coma or confusion may present as a complication of cirrhosis such as hepatic encephalopathy;
- An increase in body temperature, abdominal pain of varying intensity, constipation, diarrhea, and vomiting are symptoms of bacterial peritonitis.
In order to detect cirrhosis in a timely manner, in addition to identifying clinical signs, it is necessary to use physical examination methods and a survey:
- body weight measurement. Patients with liver cirrhosis lose body weight;
- measuring the volume of the abdomen. A sharp increase in abdominal volume indicates the development of ascites (a complication of cirrhosis, the accumulation of a large amount of fluid in the abdomen);
Using a survey, the patient is identified:
- alcohol consumption: drinking alcohol for over 12 years, 40–80 ml of pure ethanol per day, allows one to suspect the development of liver cirrhosis;
- also, the fact of infection with viral hepatitis B, C, D should be alarming due to the likelihood of developing liver cirrhosis;
- diseases occurring with blockage of the biliary tract: obstruction of nearby organs by a tumor, gallstones or adhesions of the bile duct;
- history of autoimmune diseases;
- storage diseases: hemochromatosis and Wilson–Konovalov disease;
All these signs make it possible to identify patients with liver cirrhosis and then examine them in detail.
The next stage in recognizing this disease is diagnosis using research methods: laboratory and instrumental.
What laboratory tests and instrumental research methods are used to check the liver for cirrhosis? There is no single test for cirrhosis. In order to reliably identify the disease, it is necessary to be fully examined, that is, take a set of tests and undergo research.
First of all, this:
- General detailed blood test: determines hemoglobin, red and white blood cells, platelets and lymphocytes, erythrocyte sedimentation rate. In liver cirrhosis, changes are characterized by an acceleration of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, a decrease in the number of platelets, and the number of lymphocytes serves as an indicator of the degree of exhaustion of the patient’s body;
- biochemical analysis: increased activity of liver enzymes: alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, increased amount of bilirubin, both total and its fractions, decreased amount of total protein, increased concentration of gamma globulins;
They also determine glucose in the blood serum, the amount of sodium, potassium, creatinine and urea (increases with the development of a complication - hepatorenal syndrome).
In order to identify the cause of liver cirrhosis, the following studies are necessary:
- Determination of hepatitis viruses (RNA and DNA fragments in human blood) and antibodies to these viruses;
- If autoimmune liver damage is suspected, it is necessary to be tested for the detection of antinuclear, antimitochondrial, etc. antibodies;
- Study of cerulloplasmin (Wilson-Konovalov disease);
- Study of the amount of ferritin, transferrin for a presumptive diagnosis: hemochromatosis;
- Study of the hemostasis system: blood clotting time, prothrombin index, etc.;
- Analysis of urinary sediment and general urine analysis;
- Stool analysis.
Using instrumental research methods, you can learn about the extent of liver damage, the condition of the body and the stage of the disease.
These include:
- Ultrasound examination of the liver and nearby organs. Using this research method, the size of the liver, the echogenicity of the liver (high echogenicity indicates the detection of fibrosis), the size of the spleen (an increase indicates the development of a complication - portal hypertension), the state of the biliary system, the presence or absence of ascites are determined.
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy. With the help of this study, a complication of liver cirrhosis - varicose veins of the gastric and esophageal mucosa - can be determined. If this complication is not detected, then it is recommended to repeat fibrogastroduodenoscopy every three years for preventive purposes.
- A biopsy helps determine whether a patient actually has cirrhosis of the liver. This test allows you to check the liver for cirrhosis with almost 100% accuracy. The resulting material is examined under a microscope, the degree of fibrosis and the histological activity of the process are revealed. This study is carried out in the absence of hemorrhages and bleeding and under ultrasound control.
- Study of ascitic fluid. The cellular composition of this fluid is determined to exclude tumor ascites; biochemical analysis - determination of protein content, primarily albumin. If the concentration of blood albumin is more than 1.1 hl higher than the amount of albumin in ascitic fluid, then we can talk about portal hypertension and cirrhosis of the liver as the cause of ascites. They also determine the number of neutrophils (leukocytes - cells that are directly involved in inflammation): if the number of these cells exceeds 250 mm3, then peritonitis of a bacterial nature is diagnosed.
- To clarify the diagnosis, magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography of the kidneys, liver, spleen, biliary tract, and pancreas are used.
Symptoms of the initial stage
The initial period of the disease rarely proceeds in a forced mode. The patient may not be aware of the fatal disease until it passes from a latent stage to a more active one. Somatic signs of liver cirrhosis at an early stage are not pronounced. In some cases, there may be no symptoms at all. This picture is observed because a person still has a compensatory mechanism, that is, liver cells not affected by pathology, trying to resist, work with double the load.
At the initial stage, the following symptoms may be observed:
- weight loss not due to intense exercise or changes in eating behavior;
- dysania (sleep disorder) or chronic sleepiness;
- loss of strength, causeless lethargy and asthenia (neuro-psychological weakness);
- loss of appetite (sometimes aversion to food);
- heaviness in the epigastric (epigastric) region;
- intense gas formation;
- alternating constipation (constipation) and diarrhea (diarrhea).
Later, a bitter taste in the mouth appears (usually after waking up) and discomfort, but not pain, in the right area of the abdomen. Such meager symptoms do not cause serious concern in people and rarely bring them to the doctor’s office. Signs of early cirrhosis are usually determined in patients with other chronic pathologies during a routine examination. As the disease progresses, symptoms intensify. The skin and whites of the eyes turn yellow, pain appears in the right hypochondrium, and the legs swell. Hematomas appear on the body (without mechanical injuries).
Complications develop: accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites, otherwise dropsy), with possible peritonitis of bacterial etiology, varicose dilation of the portal veins through which blood is delivered to the liver, and an increase in pressure in them (development of portal hypertension), which subsequently damages the renal apparatus (hepatorenal syndrome), threatening renal decompensation.
The most common consequences of cirrhosis are liver failure and carcinoma (liver cancer).
General signs of cirrhosis
The symptoms of this disease are quite varied. The main signs that will help recognize cirrhosis of the liver are:
- attacks of nausea and vomiting. There may be blood in the vomit;
- pain in the right hypochondrium, pain can also be felt in the epigastric region. At the same time, it will become more intense after eating and physical activity;
- rapid weight loss;
- dry mouth and a feeling of bitterness;
- itching of the skin;
- increased fatigue;
- frequent stools, while they are liquid and discolored, urine darkens;
- decreased libido in men and disrupted menstrual cycle in women.
Painful sensations with cirrhosis appear due to the fact that the organ significantly enlarges and the parenchyma stretches. It is also important that at this stage there are already concomitant diseases, for example, gastritis and chronic pancreatitis, cholecystitis, and damage to the biliary tract. It is with dyskinesia that colic or mild nagging pain may occur in the right side.
The patient is also bothered by a feeling of heaviness in the liver area. Due to dysfunction of the gallbladder, a large amount of fatty acids is released and this provokes itching. Sometimes a person scratches the skin so much that an infection gets into the affected areas and pustules appear. This condition in cirrhosis requires treatment.
Yellowness of the skin is one of the main symptoms. It is due to the fact that the concentration of bilirubin (bile pigment) in the blood gradually increases. Since the blood clotting function is impaired when the liver is damaged, blood impurities are possible during vomiting. This blood appears due to dilation of the veins of the gastrointestinal tract.
Treatment tactics for initial changes
Since liver cirrhosis is an incurable disease, the goal of conservative therapy is to slow down the process of transformation of hepatocytes, prolong the regenerative ability of the organ, relieve pain, and delay the development of complications. For the treatment of all types of cirrhosis, the following are used:
- medicines of the hepatoprotector group (herbal, essential phospholipid, animal) that have a protective and restorative effect on hepatocytes;
- vitamin preparations;
- bile acids of synthetic origin;
- diet therapy (limited diet and complete exclusion of alcohol);
- herbal medicine using traditional medicine;
- physiotherapeutic procedures.
Depending on the etiology of the disease, the main therapy is supplemented with:
- lipotropics, to regulate metabolic processes and prevent fatty infiltration of the gland (with alcoholic liver damage);
- steroid hormones produced by the adrenal cortex (in toxic and biliary cirrhosis);
- immunostimulating drugs (for the primary biliary type);
- diuretics, otherwise diuretics, in the presence of dropsy.
Therapy is carried out under regular monitoring of blood counts and ultrasound results. The treatment of cirrhosis is carried out by a therapist (at initial treatment), a gastroenterologist, a hepatologist - a specialist in the field of diseases of the hepatobiliary system. If surgical intervention is necessary, a surgeon joins in.
Basic drugs for the treatment of cirrhosis
| Group | Name of medicine |
| Essential phospholipids | Essentiale Forte N, Essliver, Fosfontziale, Phosphogliv, Eslidin, Enerliv |
| Herbal hepatoprotectors | Karsil, Dipana, Silimar, Liv -52, Cynarix, Bonjigar |
| Hepatoprotectors of animal origin | Hepatosan, Sirepar, Progepar |
| Bile acids of synthetic origin | Ursosan and its analogues: Ursofalk, Urdoxa, Ursodez |
| Amino acids or lipotropic substances | Heptral, Hepa-Merz, Lipoic acid, Betargin |
| Hormone-containing medications | Cortisone, Hydrocortisone |
| Vitamin complexes | Thiogamma, Berlition 300, Thiolepta, Thiolipon |
Which specific medications will be prescribed depends on the stage of the disease, the presence of complications and concomitant chronic pathologies. All medications are prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication can be dangerous!
Physiotherapy
The main physiotherapeutic methods used in the complex treatment of liver pathology are:
- Plasmapheresis. Extracorporeal hardware method of cleansing. Blood is drawn in portions, purified in a hemocontainer and returned back into the systemic circulation.
- Diathermy. Deep heating of tissues with high-frequency effects using a special apparatus.
- Inductothermy. Electrotherapy method using a high-frequency (from 10 to 40 MHz) electromagnetic field.
Diet therapy
From the moment the diagnosis of liver cirrhosis is confirmed, until the end of life, the patient is prescribed dietary nutrition. Diet therapy helps reduce the load on the diseased liver, helps get rid of cholesterol deposits, prolongs the stage of compensation, and slows down the development of complications. General terms and Conditions:
- rational food intake (every 3–4 hours) with portions not exceeding 300–350 g at a time;
- strict limit on table salt;
- compliance with the daily caloric content of dishes (no more than 2500 kcal);
- elimination from the menu of dishes prepared by culinary frying (including over charcoal);
- compliance with the drinking regime (up to 2 liters daily);
- refusal of harmful foods and alcoholic drinks.
The menu is based on complex carbohydrates (vegetables, fruits, grains). In the initial stage, the consumption of protein products is allowed at the rate of 1 gram per kilogram of the patient’s weight. Subsequently, protein is excluded from the diet. The fat norm is 80 g/day. Dairy and fermented milk products (with a small percentage of fat content) are allowed. It is recommended to stew or bake vegetables.
| Category | Allowed | Forbidden |
| Vegetables | Cabbage of all varieties, pumpkin, zucchini | Eggplants, cucumbers, sweet peppers, tomatoes, spinach |
| Roots | Carrots, potatoes | Onions, rutabaga, radish, radish, horseradish |
| Fruits and berries | Apricots, apples, quince, melon, bananas, watermelon, peaches, plums, pears, kiwi, blueberries, strawberries | Grape |
| Cereals | Barley, oatmeal, semolina, rice, buckwheat | Millet |
| Flour products | Bread, durum pasta | Butter pastries made from shortbread and puff pastry |
| Sweets | Marshmallows, marshmallows, marmalade, jam | Milk chocolate, ice cream, butter cream |
| Fermented milk products | Low-fat cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt and acidophilus 1%, Ricotta cheese | Cream, sour cream, homemade cottage cheese |
| Meat | Chicken, turkey, rabbit | Pork, duck, bacon, goose |
| Fish | Cod, blue whiting, pollock, pike, hake | Salmon, halibut, beluga, mackerel, herring |
| Juices | Carrot, apricot, pumpkin | Tomato |
| Legumes | — | Peas, chickpeas, beans, lentils, beans |
In addition, the following are not allowed for use:
- fast food dishes;
- mushrooms,
- sausages and smoked products (lard, meat, fish)
- canned products: stewed meat, pates, canned fish (including caviar), pickled and canned vegetables, fruits in syrup.
Coffee and carbonated drinks are prohibited. Developing a daily menu on your own can be challenging. In this case, it is recommended to seek advice from a doctor. When diagnosing cirrhotic liver changes in the initial stage, the prognosis is relatively favorable.
The sooner a patient or doctor can recognize the signs of certain diseases, the easier and more effective the treatment will be and the likelihood of unwanted consequences will be minimized. How to diagnose liver cirrhosis, how many methods exist and what the examinations are - you will learn about all this from this article.
History of pathology
Liver cirrhosis - how can you determine the disease yourself? Symptoms of liver cirrhosis can be identified using the pathological history. Depending on the degree of damage to the liver tissue, signs may differ.
The compensated stage of cirrhosis is characterized by an asymptomatic course of the pathology, since most of the hepatocytes are not yet affected and they are fully functional. However, the following symptoms may appear:
- mild but periodic pain in the area of the right hypochondrium,
- slight decrease in body weight,
- attacks of nausea,
- general weakness,
- increase in body temperature.
You can recognize the subcompensatory form of cirrhosis by the following patient complaints:
- severe decrease in performance,
- increased fatigue,
- loss of appetite,
- prolonged and dull pain in the abdominal cavity on the right,
- vomiting and attacks of nausea,
- bowel disorders,
- increased gas formation,
- itching of the skin,
- yellowness in certain areas of the skin,
- temperature increase.
How can stage 3 cirrhosis be determined? The description of the anamnesis of the decompensated form consists of the following points:
- temperature more than 37.5 degrees,
- severe weight loss,
- complete lack of appetite,
- significant weakness
- the appearance of esophageal or gastric bleeding,
- increase in belly size,
- deterioration of consciousness and thinking.
Peritonitis
Spontaneous bactericidal peritonitis can occur in the decompensated stage of cirrhosis, the treatment of which is complicated and does not give positive results. It develops against the background of ascites. Characteristic symptoms:
- fever, chills;
- sharp abdominal pain;
- weakened bowel sounds;
- low blood pressure;
- tense anterior abdominal wall.
This complication develops in only 2-4% of patients, and with this disease the mortality rate is almost 90%.
- Odor from a person with cirrhosis of the liver
- How do people die from liver cirrhosis? Serious consequences of complications
- Signs of liver cirrhosis in men and women, treatment.
- Ascites in liver cirrhosis: how long do they live?
General inspection
Doctors periodically diagnose liver pathologies during a general examination, when the disease manifests itself in full. The symptomatic picture consists of the following factors:
- slight muscle atrophy,
- the appearance of spider veins and pronounced capillaries,
- expansion of the mammary glands in representatives of the stronger half of humanity,
- proliferation of veins in the abdomen,
- swelling of the limbs,
- development of hernias in the navel, groin and thigh areas,
- redness of the skin on the palms,
- expansion of the phalanges of the fingers,
- rash,
- change in the boundaries of the liver tissue and spleen, as well as the appearance of a dull sound when tapping,
- increased blood pressure and increased heart rate.
Palpation
It is also possible to check the liver for cirrhosis by palpation. At the initial stage, the liver tissue retains its consistency and increases slightly. But the size of the liver at the decompensated stage increases significantly . In this situation, the affected organ is located beyond the edge of the rib arch and can protrude several centimeters. In this case, the doctor notes a lumpy and uneven shape of the liver tissue, and the patient experiences pain.
Laboratory research
For a comprehensive diagnosis of cirrhosis, laboratory tests such as urine and blood tests, as well as biochemistry, are performed.
Blood analysis
A blood test is a mandatory procedure if cirrhosis is suspected and is characterized by the quantitative determination of indicators such as hemoglobin, leukocytes, red blood cells, and ESR.
- Hemoglobin. The normal hemoglobin level is 110 g/l and above. In a person suffering from cirrhosis of the liver, these values may be significantly lower.
- Leukocytes. If the concentration of leukocytes exceeds 9 billion/l, we can confidently speak about the progression of the inflammatory reaction in the patient’s body.
- If the number of red blood cells is less than 4 million/1 mm3 of blood, there is a high probability that pathological changes occur in the tissue.
- For healthy men, normal ESR values should not exceed 10 ml/hour, and for the opposite sex - 15 ml/hour. Otherwise, necrotic and inflammatory reactions in the body are diagnosed.
Analysis of urine
Urine examinations make it possible to determine the degree of kidney function , because according to medical statistics, in 8 out of 10 cases the patient is found to have ascites or renal failure. Cylinders and traces of bilirubin should be completely absent, and the permissible values of protein, red blood cells and leukocytes should be no more than 0.03 g, 1-2 and 2-3 units, respectively.
Biochemistry
A biochemical blood test is one of the most informative research methods and is always prescribed if liver pathology is suspected. Doctors study indicators such as:
- Alanine aminotransferase, which is an enzyme of the digestive gland. In a healthy person, the ALT level is in the range of 0.5-2 µmol, and an increase in this level indicates the presence of inflammation in the liver tissue.
- Aspartate aminotransferase is another significant liver enzyme, the excess of which over 41 U/L confirms the fact of liver necrosis.
- Alkaline phosphatase is another marker of liver problems. The normal value of this indicator should not exceed 140 IU/l.
- Bilirubin is a bile pigment, and when it increases beyond 16.5 mmol/l, the degree of progression of liver pathology can be determined.
Diagnosis of cirrhosis
It is impossible to diagnose the disease on your own, since this requires not only a visual examination of the patient and collection of complaints, but also a number of other examinations. The patient is prescribed a blood test, a urine test, a test for hepatitis, an ultrasound examination, magnetic resonance imaging, and a liver biopsy.
However, this does not mean that the patient should not monitor his health. When the first signs of liver pathology appear, you should consult a doctor.
Additional examination methods
To make the diagnosis of liver cirrhosis more reliable, doctors conduct various additional studies. For the most part, the presence of this disease can be determined using ultrasound, scintigraphy, MRI, CT, fibrogastroduodenoscopy and biopsy.
- Ultrasound is prescribed to determine the general contour and size of the liver, as well as to measure the diameter of the portal vein, recognize the structure of the tissue and determine the presence or absence of fluid. In addition, ultrasound can detect foci of malignant neoplasms, if any.
- Scintigraphy refers to radionuclide studies and is characterized by the introduction of radiopharmaceutical substances into the patient’s body and monitoring their fixation. This examination allows you to determine the functionality of the liver tissue. The affected tissue is unable to completely retain radiopharmaceutical substances, which is actually visible in the image with cirrhosis. And also with liver pathology, the spleen enlarges, since it is its tissue that takes up radiopharmaceutical substances that the liver cannot retain.
- CT and MRI are performed to identify foci of cancer in the liver tissue. To determine the nature of cancerous tumors and obtain more accurate data, the patient is injected with a special contrast agent. It is also worth noting that these examination methods are mandatory before transplantation of affected tissues.
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is one of the most informative methods for diagnosing internal hemorrhage in cirrhosis.
- A biopsy allows you to determine an accurate diagnosis and consists of sampling and further morphological examination of liver tissue.
Laboratory diagnosis of liver cirrhosis
After the initial examination, the gastroenterologist may send the patient for blood and urine tests if cirrhosis is suspected. A basic laboratory test does not have high reliability, but in combination with a physical examination it already helps to get a rough picture. Blood biochemistry in liver cirrhosis is more significant and more informative than general tests. The doctor does the decoding, but some points are clear to the patient:
Name of diagnostic method
General blood analysis
the fraction of albumin and total protein is reduced, but the following are increased:
- alkaline phosphatase;
- bilirubin concentration;
- globulin fraction;
- activity of liver transaminases (AST, AlT);
- urea, creatinine
the presence of protein and a large number of red blood cells in the urine
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of liver cirrhosis with a complete picture of the disease does not encounter any particular difficulties. In order to distinguish one liver pathology from another, doctors prescribe the patient an immunogram, coagulogram and hemogram, which allow them to identify specific signs. Differential diagnosis of liver cirrhosis is a very important stage of examination, the quality of which determines the patient’s life expectancy.
Liver cancer
Cancer and cirrhosis of liver tissue have similar clinical manifestations, especially if it is cirrhosis-cancer. The latter pathology is characterized by such manifestations as:
- sharp progression of pathology,
- significant depletion of the patient's body,
- the appearance of fever,
- abdominal pain,
- increase in the number of leukocytes,
- low hemoglobin content,
- increase in ESR indicators.
To make a definitive diagnosis, doctors often perform an alpha-fetoprotein test, laparoscopy with targeted biopsy, and angiography.
Liver fibrosis
Fibrosis of the liver tissue is characterized by excessive formation of collagen tissue , which is not observed in cirrhosis. In addition, in the case of fibrosis in humans, there is a lobular architecture in the liver tissue.
Benign subleukemic myelosis
In most cases, this disease is accompanied by an increase in fibrous tissue, as well as expansion of the liver and spleen tissue. Fibrosis almost always causes portal hypertension, and doctors mistake subleukemic myelosis for cirrhosis. To accurately establish the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed a trephine biopsy , and if the results of the examination reveal the fact of proliferation of connective tissues, the presence of a large number of megakaryocytes, and cellular hyperplasia is determined, then this is clearly not cirrhosis.
Cardiac cirrhosis of the liver
This disease is characterized by the appearance of fairly high blood pressure, swelling of the veins in the neck, shortness of breath and cyanosis. For reliable recognition, echocardiography or x-ray kymography is also performed.
Constructive pericarditis
This pathology manifests itself as a feeling of heaviness in the hypochondrium on the right, an enlarged and compacted hepatic lobe on the left side, painless palpation, severe shortness of breath and increased blood pressure during normal functioning of the cardiovascular system. Differential diagnosis consists of X-ray kymography or echocardiography.
Alveolar echinococcosis
Doctors identify the presence of specific antibodies, an increase in the size of the organ and limited mobility of the diaphragm as the main reliable factors for alveolar echinococcosis. To establish an accurate analysis, the patient is sent to scan the liver tissue and undergo an x-ray.
Liver cirrhosis is a rather serious disease, which is characterized by various complications. Unfortunately, at the moment only 2-3 people out of 10 suffering from cirrhosis at the stage of decompensation live more than 3 years. For this reason, it is very important to diagnose this pathology in a timely manner. If you experience any of the listed signs, you should seek professional advice as soon as possible.
Analyzes and research methods
To check your liver, first of all, your doctor will order tests. Pay attention to the following indicators:
- ALT and AST. These are enzymes that are present in the liver in very large quantities. When organ cells are destroyed, the level of these enzymes increases. The higher their test score, the more global the damage to the organ. Typically, ALT and AST increase simultaneously. As a rule, this indicates oncology or hepatitis.
- Bilirubin. This is a component that is included in human bile. Its formation and elimination occurs regularly. If problems occur in the liver, bilirubin begins to accumulate in the blood, and this leads to jaundice. This result can have a variety of reasons - from low-risk conditions to serious diseases.
- Prothrombin index. This index is an indicator of blood clotting, but it is often prescribed for liver tests. It shows the functioning of blood vessels and veins, which plays an important role in the functioning of the organ we are discussing.
- Albumen. This is a protein that is produced by the liver and is found in large quantities in the blood. Decreased albumin levels indicate organ damage.
- Alkaline phosphatase. It is an enzyme involved in the release of phosphoric acid. If the phosphatase level increases, this may indicate tumors in the organ.
- Test for antibodies to viral hepatitis antigens. The analysis is quite expensive, but effective because In most cases, hepatitis occurs latently, which is a threat not only to the patient, but also to those around him.
- In addition to the analyses, a number of additional studies are also carried out. They conduct genetic studies, ultrasound of the liver and biliary tract, biopsy, magnetic resonance therapy, computed tomography, etc. Analyzes and survey indicators are evaluated together, because Only an integrated approach to studying the problem will give the most informative results.