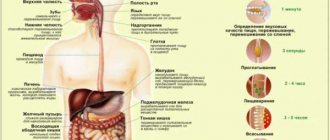
Types and forms of the disease
This disorder is conventionally divided into organic and functional. Organic indicates disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, functional indicates pathological changes in the stomach and intestines.
Ailments are divided according to types and causes. If dyspepsia is caused by a lack of digestive enzymes, it is divided into gastrogenic, enterogenic and pancreatogenic. If caused by an intestinal infection, it is divided into dysentery, intoxication dyspepsia and salmonellosis. If we are talking about the non-digestion of a specific product, a fermentative form is isolated, putrefactive or yeast, fatty or soapy.
Fermentation form
This form of the disorder is caused by excessive consumption of foods, which include legumes, cabbage with fruit, and honey with kvass. Subsequently, acidophilic flora is formed in the intestines, which causes discomfort.
The main features of this form are:
- bloating;
- frequent release of gases;
- frequent urge to defecate;
- the stool is foamy, with a characteristic sour odor.
In this case, abdominal pain is absent or mildly expressed. If we examine feces in laboratory conditions, it contains many starch grains, iodophilic microbes with organic acids and fiber.
The patient does not suffer much from his condition. The solution to the problem in this case is to follow a diet. Ignoring the problem leads to the emergence of a chronic form, which can develop into chronic enteritis, enterocolitis.
Putrid form
The yeast form of dyspepsia is characterized by a disturbance in the breakdown of elements. A decrease in the level of secretion of enzymes such as pepsin and trypsin leads to incomplete protein breakdown. This process is accompanied by the release of methane, hydrogen sulfide, skatole and indole, which irritate the intestines.
This form manifests itself through:
- weaknesses;
- decreased appetite;
- bloating;
- dizziness;
- dark-colored stool with a putrid odor.
Long-term course of the disorder can lead to chronic hepatitis with colitis, enterocolitis.
Fat form
Soap or fatty forms of dyspepsia are less common. Occurs when consuming large amounts of fatty foods. This disorder is associated with impaired fat breakdown - the lipolytic function of the pancreas cannot cope with its work. This may also be caused by a disruption in the flow of bile into the intestines, and the rapid passage of food through the small intestine.
Classification of dyspepsia
Depending on which part of the digestive system malfunctioned, indigestion is divided into:
- intestinal;
- gastric;
- hepatic
Dyspepsia happens:
- Nutritional. The cause of the pathology is disturbances in the functioning of the small intestine, which can occur as a result of improperly organized nutrition or physical impact. For example, dyspepsia can occur in pregnant women due to the fact that the growing uterus puts pressure on the intestines.
- Functional. It is characterized by disturbances in the absorption process in the small intestine (due to a genetic predisposition to malfunctions of this organ), which is manifested by a whole range of symptoms. Very often this type of dyspepsia is observed in children.
In turn, nutritional disorders are divided into:
- Fat. At risk are those people who are not averse to “pampering” themselves with fatty foods. And to be more precise, such difficult-to-digest fats as lamb or pork. Fatty dyspepsia is characterized by copious, light-colored stools that have a greasy sheen and a neutral or slightly alkaline reaction.
On a note! This type of dyspepsia may be accompanied by pancreatitis and gastritis.
- Fermentation. Occurs as a result of eating carbohydrate-containing foods (for example, fruits, sugar, legumes, kvass, cabbage and baked goods). As a result of their intake into the intestines, microflora of a fermentative nature develops. A person’s stomach swells, “rumbling” is heard, and gas formation increases. As a rule, stools are loose, frequent and acidic.
- Putrid. The cause of the pathology is protein products, the process of digestion of which in the intestines occurs rather slowly. The main symptoms of this disease are: dark-colored diarrhea (has an alkaline reaction), weakness, loss of appetite and decreased performance.
On a note! Putrefactive dyspepsia can be caused by stale meat products
Why does the stomach not digest food?
Common reasons for problems with digestion of food are:
- slow metabolism;
- insufficient amount of enzymes involved in the breakdown of substances;
- the presence of diseases associated with the gastrointestinal tract;
- harmful bacteria are present on the mucous membranes of the stomach and intestines;
- pregnancy;
- alcohol abuse;
- improper and unbalanced diet;
- non-compliance with daily routine and meals.
Causes of pathologies
Possible causes of indigestion (we have already discussed the signs above):
- Insufficient amount of gastric juice secretion, which can occur against the background of B vitamin deficiency, disorders associated with the evacuation of contents, or serious changes in the morphological nature of the gastric mucosa.
- Irregular eating.
- Incorrectly adjusted and balanced diet, for example, too often including in your diet foods that irritate the gastric mucosa; caffeinated drinks and sparkling water.
- A lifestyle that can hardly be called active, that is, a minimum of movements and a maximum of “sitting and lying down.”
- Drinking “hot” drinks.
- Consequences of surgery.
- Smoking.
- Depression and stressful situations.
- Lactose or gluten intolerance.
- Taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Increase in outside air temperature.
- Loss of central nervous system control over gastric acid secretion.
- Exercise immediately after a large meal.
- Functional digestive disorders can occur due to poorly chewed food. As a result, an insufficient amount of gastric juice is formed so that it can be absorbed by the body under the action of enzymes.
- Eating foods that cause increased gas formation.
Digestive disorders can occur due to the presence of the following serious pathologies:
- Inflammation of the pancreas, that is, pancreatitis.
- Stomach ulcers.
- Pathologies of the endocrine, nervous, excretory or respiratory systems.
- Esophageal dyskinesia.
- Cholecystitis.
- Gallbladder pathologies.
- Inflammatory processes in the small intestine.
- Giardiasis.
- Intestinal obstruction (ie, cystic fibrosis). The pathology is caused by the absence of a certain enzyme involved in the digestion process.
- Oncology of any digestive organ.
Important! All the reasons listed above are quite serious so as not to take them into account and self-medicate. The best way out in this situation would be to consult a specialist who will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Signs of poor digestion
When food is not digested by the stomach, this event is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- painful sensations in the abdomen;
- feeling of heaviness in the abdomen;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- defecation disorders in the form of diarrhea;
- lack of appetite.
Lack of appetite
When the stomach functions abnormally, a whole range of unpleasant symptoms arise, including lack of appetite. There is no appetite because the body is busy processing previous food. Since for some reason this process is difficult, the feeling of fullness may be present throughout the day, and if pathology is present, appetite may be absent for a long time.
Heaviness in the stomach
The feeling of heaviness is associated with stopping the process of breaking down food. The symptom of a stone in the stomach, which is uncharacteristic for a healthy person, can last up to several hours. In the absence of serious pathology, this phenomenon goes away without a trace.
Pain inside the abdomen
Pain is felt in the epigastric area, which worsens the already poor state of health. They can be short-term or last up to several hours. It depends on what problem or disease provoked the pain syndrome.
Nausea and vomiting
If you feel sick after eating, there can be many reasons for this. Depending on the accompanying symptoms and factors, this phenomenon can be assessed differently. Nausea and vomiting are protective reactions to eating stale food. This also happens if you have eaten a lot of fatty or meaty foods and overeating has occurred. Overheating, intoxication with tobacco smoke and other unpleasant odors increase nausea.
Diarrhea
Depending on what caused the disruption to the normal functioning of the digestive system, diarrhea can last up to several days. The most common reasons that provoke diarrhea are overeating, the presence of fatty foods in the diet, failures in the production of enzymes for digesting food, accelerated peristalsis, stress and dysbiosis.
Temperature increase
Due to the fact that the stomach cannot cope with the processing of food, it stagnates, ferments or rots. If this process is started, the body begins to fight harmful bacteria that could provoke this process or arise during the process of decay. This may be accompanied by an increase in body temperature.
External factors that can impair digestion
Incorrect nutrient balance
Nutrients are not only proteins, fats and carbohydrates, the balance of which, in principle, can be controlled. The diet may contain too much salty or smoked foods, fiber, or foods that cause excess bile secretion, which require additional enzymes to process. This creates additional stress on the digestive organs, which can result in poor digestion1,2.
Unhealthy Lifestyle
Lack or excess of sleep, poor physical activity, staying in one position for a long time, smoking, alcohol, fast food and ready-made snacks - all this has a bad effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract1,2.
Self-medication
As well as incorrect medication regimen or addiction to traditional medicine. Many of them can have side effects, some of which include indigestion1.
Shattered nerves
Sometimes poor digestion is associated with the state of the human nervous system - there is even a special term “psychological constipation.” The fact is that we often “eat up” stress or bad mood, which also has a bad effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract1.
How to help your stomach digest food
In order for the stomach to begin to function normally, it is worth finding out the cause of the failure. If this happened once and did not happen again, there is no need to worry. If gastric constipation occurs periodically, you need to consult a doctor who will prescribe treatment and diet.
Nutritional Features
To restore stomach function, you should follow some nutritional recommendations:
- eat food in small portions;
- chew food thoroughly;
- do not drink a lot of liquid before meals;
- practice separate nutrition (take protein and carbohydrate foods separately from each other);
- Do not eat near the TV or on the go.
In addition, dishes should look appetizing, as this helps the secretion of gastric juice. This is especially true if the cause of gastric stoppage was insufficient enzyme levels. If we are talking about fermentative dyspepsia, it is worth excluding carbohydrates from the diet for several days. After two days, increase the consumption of proteins in the form of cottage cheese, chicken breast, turkey and boiled fish. You can include meat broth and some white bread. Afterwards, you can eat porridge cooked in water, drink fruit jelly and eat fruit puree.
If putrefactive dyspepsia is diagnosed, they fast for the first day and then eat carbohydrates for the next day. You can also eat crackers for 2-3 days, drink fruit juices and eat apples in quantities of up to one and a half kilograms. Next, add rice and semolina porridge, also boiled in water. You can start adding meat and fish to your diet only after 5-7 days of the diet.
Fatty dyspepsia requires restrictions in the form of fatty foods and carbohydrates. Include cottage cheese (low-fat), boiled fish and lean meat. Transition to your previous diet gradually, eliminating frequent consumption of fatty foods.
Drug therapy
Depending on the cause of the disorder, the list of prescribed medications may vary. The main unpleasant symptoms are relieved with the help of antispasmodics, enzyme preparations, histamine blockers and proton pump blockers.
The former eliminate pain, making you feel better; enzyme preparations stimulate the digestive process in the stomach and duodenum. Histamine blockers work to reduce acidity, and the latter are taken to eliminate sour belching and heartburn.
Features of treatment
Stomach dyspepsia is not considered a very dangerous pathology, especially if it is not associated with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. But its manifestations cause a person a lot of trouble. Therefore, it is advisable to get rid of them immediately. Effective treatment of indigestion is only possible when the cause of the disorder is eliminated. Therefore, first of all, it is recommended to undergo an examination. You should not take medications without a doctor's prescription. And in many cases, it is impossible to eliminate dyspeptic syndrome only with the help of drug therapy. Complex treatment is required, the specifics of which depend on the cause of the pathology.
If signs of indigestion appear frequently, you should consult a doctor, or perhaps a therapist. He will prescribe the necessary diagnostic procedures and advise what to do to get rid of the discomfort. And if necessary, the therapist will give a referral to a gastroenterologist.
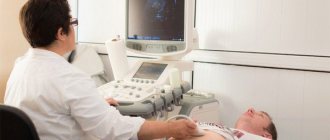
A timely examination will help to diagnose serious diseases in time and begin their treatment. It is especially important to exclude the presence of any tumors in the gastrointestinal tract. For this purpose, fibrogastroduodenoscopy and tissue biopsy are required. An ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs is also often performed. It helps identify abnormalities in the liver, gallbladder and pancreas. Sometimes other diagnostic procedures are necessary: blood tests, stool tests, intragastric pH-metry, colonoscopy. They are prescribed by a doctor individually.
If the examination did not reveal any diseases, treatment for indigestion consists of changing the patient’s lifestyle and diet. Usually, in this case, such measures are sufficient, but sometimes the doctor may prescribe medications to relieve symptoms.
Features of diagnosis for indigestion of food
At the first stage of diagnosis, the specialist collects data on the intensity of pain, location of discomfort and accompanying symptoms. Examines the patient and palpates the abdomen.
Next comes a series of instrumental diagnostic methods such as ultrasound or computed tomography and electrogastroenterography. The latter method allows you to monitor intestinal motility and detect disorders. X-rays are performed if a tumor is suspected. Diagnostics of the surface of the organ is carried out using an endoscope. In addition, blood and urine tests are taken.
Folk remedies
- Baths. To relieve intestinal spasms and intestinal colic, baths with linden blossom are recommended: 8-9 handfuls of linden blossom, brew 1 liter of hot water, boil, let it brew and pour into a hot bath. Linden blossom also has an antibacterial effect. The duration of the bath is no more than 15 minutes.
- Elecampane. To normalize the activity of the gastrointestinal tract, drink an infusion of elecampane. Grind the rhizome and roots of this plant and pour 1 teaspoon with a glass of boiled, cooled water. Leave to infuse for 8 hours, covered. Strain and drink 1/4 cup 3-4 times a day 20 minutes before meals for at least 2 weeks.
- Blackberry (root). 10 g of blackberry root are boiled in 1/2 liter of water until half the volume of liquid has evaporated. The broth is filtered and mixed with the same amount of aged red wine. Take 1 tablespoon every 3 hours for sluggish digestion.
- Blackberry and calendula. A mixture of blue blackberry leaves (2 tablespoons) and calendula officinalis flowers (1 tablespoon) is steamed in 1 liter of boiling water, drink 2/3 cup 3 times a day.
- Enema. In old age, it is necessary to give an enema at least once a week, even if the stomach is working normally, because a short-term retention of feces in the intestines can, without showing any pain, poison the body. It is also very good to drink infusions of herbs on an empty stomach - mint, chamomile or wormwood. This is very useful and helps improve digestion.
- Wormwood or Chernobyl. For intestinal colic, take an infusion of wormwood or Chernobyl. Pour a teaspoon of herbs into a glass of boiling water and leave for 20 minutes, then strain. Take a tablespoon before meals 3-4 times a day.
- Collection based on buckthorn bark. Brew two tablespoons of the mixture (calamus rhizome - 1 part, buckthorn bark - 3 parts, mint leaves - 2 parts, nettle leaves - 2 parts, dandelion root - 1 part, valerian root - 1 part) with 2 cups of boiling water, boil for 10 minutes and strain. Drink 1/2 glass in the morning and evening.
- Collection based on plantain. Brew two tablespoons of a mixture of knotweed herb - 1 part, cinquefoil herb - 1 part, plantain leaves - 2 parts with 2 cups of boiling water, leave for 30-40 minutes, strain. Drink half a glass 4 times a day 30 minutes before meals.
- Collection based on chamomile. The following collection will help regulate intestinal activity and get rid of pain. Mix 15 g of fennel fruits and calamus rhizomes, 20 g of valerian roots and mint leaves and 30 g of chamomile. Pour 10 g of the mixture into a glass of boiling water and keep in a closed enamel container in a water bath for 15 minutes. Bring the resulting volume to the original volume and start taking it after 45 minutes. Drink 3/4 glass 3 times a day after meals. The decoction relieves inflammation and normalizes digestion. The pain will stop after 2 weeks.
- Collection based on licorice. Brew two teaspoons of a mixture of buckthorn bark - 2 parts, anise fruit - 2 parts, yarrow herb - 1 part, mustard seeds - 2 parts, licorice root - 3 parts with 1 glass of boiling water, boil for 10 minutes and strain. Drink half a glass in the morning and evening as a tea to regulate intestinal activity.
- Collection of herbs No. 2. Rhizome with roots of valerian officinalis, peppermint herb, flowers and herb of chamomile, flowers of calendula officinalis mixed equally. Pour a tablespoon of the mixture into a thermos with a glass of boiling water overnight and strain. Take 1/3 cup half an hour after meals 3 times a day for bloating (flatulence).
- Herbal collection No. 1. For intestinal colic, increased gas formation and colitis, a decoction of yarrow, sage, mint and chamomile in equal proportions is recommended. A teaspoon of the mixture is brewed with boiling water, like tea, left for half an hour covered and drunk 1/2 cup 2-3 times a day.
- Celery. 3–4 g of chopped celery root are poured into 1 liter of water, left for 8 hours, filtered. Take 1 teaspoon 3 times a day. You can use other recipes: a) 1 tablespoon of seeds is poured into 2 glasses of cold boiled water, left for 2 hours and filtered. Take 1 tablespoon 3 times a day; b) drink fresh juice from the roots 1-2 teaspoons 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals.
- A mixture to normalize digestion. The following mixture normalizes all metabolic processes well: honey – 625 g, aloe – 375 g, red wine – 675 g. Grind the aloe in a meat grinder (do not water it for 5 days before cutting). Mix everything. Take 1 teaspoon for the first 5 days, and then 1 tablespoon 3 times a day 1 hour before meals. Duration of treatment – from 2 weeks to 1.5 months.
- Cumin and marjoram. To improve digestion, especially after heavy meals with fatty foods, take cumin with marjoram. To prepare a medicinal decoction, pour a glass of boiling water into 1 tablespoon of ground cumin and marjoram seeds, let it brew for 15 minutes and drink 1/2 cup 2 times a day.
- Black poplar. 2 teaspoons of dry crushed sedge buds (black poplar) are poured into 1–1.5 cups of boiling water, left for 15 minutes and filtered. Drink 1/3 glass 3 times a day. You can also use a tincture: 1–2 teaspoons of raw material are poured into 1/2 cup of 40% alcohol, infused for 7 days and filtered. Take 20 drops of tincture 3 times a day.
- Dill for hiccups. For persistent hiccups, Russian doctors prescribed a decoction of dill fruits (seeds). In addition, it improves digestion, soothes coughs, and is used for flatulence. Pour a tablespoon of seeds into a glass of boiling water and leave for half an hour, then strain. Take a tablespoon 4-5 times a day 15 minutes before meals. The decoction also has a slight diuretic and lactogenic effect.
- Fennel. 10 g of fennel fruits are poured into a glass of boiling water, heated in a water bath for 15 minutes, cooled to room temperature, filtered and the volume of the resulting infusion is adjusted to 200 ml. This amount is drunk in equal portions throughout the day for indigestion.
- Barley. 100 g of barley with 4-5 pears are boiled in 1 liter of water over low heat for 20 minutes, cooled, filtered and used as a remedy for belching.
Preventing poor stomach digestion
If your stomach cannot cope with digesting food, you should follow preventive measures, which include:
- limiting the consumption of fatty and spicy foods;
- reduce salt intake;
- exclude adherence to strict diets;
- give up fast food;
- reduce sweets in your diet;
- eliminate bad habits;
- avoid stress;
- undergo regular examinations.
Digestive problems can be resolved on your own or by consulting a doctor. In most cases, they occur one-time, but frequent occurrence of ailments requires consultation with a specialist.
What is important to know about your stomach:
Adjusting your diet
By fasting for 1-1.5 days (that is, refusing to eat solid food) and adjusting your diet, you can cope with indigestion in the stomach. Then follow these recommendations and everything will be back to normal:
- Eat more raw and fresh plant foods (especially in summer and spring). They help improve metabolism.
- Remember: nutrition should be balanced and varied.
- Don't overeat. This will have a bad effect on your performance. As a rule, those who like to eat a lot and often get tired quickly, and they are also more susceptible to various ailments than anyone else.
- Try to cook just enough to eat everything at once and not store leftover food. During long-term storage, the processes of rotting and fermentation begin, which can cause upset of the digestive system.
- Chew your food thoroughly.
- Don't forget about product compatibility. Otherwise, “antagonist” foods will cause fermentation in the intestines.
On a note! Milk should be drunk separately from other foods and do not combine fatty and protein foods together.
- In order for the gastrointestinal tract to start working well, you need to exclude smoked meats, canned food, all kinds of marinades, carbonated drinks, seasonings and dishes that are high in fat from your diet.
- A child who suffers from indigestion should not be given any sweets.
- To normalize the functioning of the digestive organs, you should eat porridge, rye bread, a variety of juices, and weak tea; vegetable soups cooked in water; as well as boiled fish and meat.
Important! For putrefactive dyspepsia, carbohydrates should predominate in the diet; during fermentation - proteins (the amount of fast carbohydrates should be kept to a minimum).
Symptoms
The main symptom of dyspepsia is a feeling of fullness in the stomach after eating small portions of food. This symptom occurs because the previous food is not digested and remains in the stomach.
And the disease can also be recognized by the following characteristic signs:
- bloating and feeling of fullness in the abdomen;
- frequent belching;
- nausea;
- vomiting, after which there is a strong feeling of hunger;
- heartburn;
- constipation;
- periodic abdominal pain that occurs regardless of food intake;
- discomfort in the upper spine;
- lack of appetite and rapid satiety.
If you frequently experience these symptoms, seek medical help immediately. An advanced disease leads to pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, dyspepsia is often a sign of a serious illness. Therefore, you should not postpone your visit to the doctor, because the sooner adequate treatment is prescribed, the easier the therapy itself will be.
Basic recommendations
Patients with digestive problems must adhere to the following rules:
- Eat meals at the same time every day. The stomach will get used to producing hydrochloric acid at a certain period, which will improve digestion.
- Plan your daily diet so that it includes all the necessary nutrients and elements.
- Eat 5-6 times a day in small portions.
- Don't eat 3 hours before bedtime.
- All food should be boiled or steamed.
- Drink at least 2 liters of water per day.
- Food should be warm, not hot or cold.
- Do not drink water, tea, coffee or other liquids with food. This will dilute the concentration of hydrochloric acid, which will worsen the digestion process. Drink water 30 minutes before meals and an hour after it.
- One or two days a week, eat only lean dishes to relieve your stomach.
To improve digestion, take a 30-minute walk after eating. But during therapy, avoid sports such as abdominal exercises.