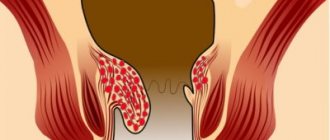
Treatment with dietary nutrition for fatty hepatosis
Nutritional treatment for fatty hepatosis (diet with a limitation of easily digestible carbohydrates and fats of animal origin) in combination with lifestyle modification (increased physical activity, normalization of body weight, giving up bad habits - drinking alcohol/smoking) against the background of hepatoprotective therapy - prescribing antioxidants and hepatoprotectors ( vitamin E , ursodeoxycholic acid , silibinin , betaine , a-lipoic acid ) allows you to achieve a positive result. As a rule, in uncomplicated cases with normal biochemical tests and a known etiology of the disease, regression of fatty liver is observed after 4-6 months.
Therapeutic nutrition for fatty liver hepatosis in patients with increased body weight/ obesity should, first of all, be aimed at its normalization. For this purpose, a hypocaloric diet is prescribed with individual selection of the energy value of the diet depending on age, body weight, level of physical activity, and gender.
For this purpose, special formulas are used to calculate the calories required to maintain basal metabolism, which are multiplied by the coefficient of physical activity, which is the calorie level of the daily diet. From this calculated value, 500-700 kcal are subtracted to reduce body weight.
However, at the same time, the minimum daily ration should not be less than 1500 kcal/for men and 1200 kcal for women. Patients should be cautioned against attempting rapid weight loss, since rapid weight loss can lead to the development of “acute” steatohepatitis with the formation of fibrosis against the background of an inflammatory process caused by an increase in the supply of free fatty acids to the liver against a background of relatively low peripheral lipolysis.
The guideline for safe/effective weight loss is: 1500 g/week for adults and 500 g for children. Patients with severe obesity (excess body weight by more than 20% of normal) are prescribed therapeutic Diet No. 8 according to Pevzner. The correlation of a decrease in body weight by 5-10% with regression of fatty liver hepatosis has been reliably confirmed. The diet for fatty hepatosis includes:
- Limit dietary fat to 30% of the total calorie intake.
- The ratio of polyunsaturated/saturated fatty acids in the diet should be more than 1, which is achieved by excluding solid animal fat, butter, fatty meat from the diet and increasing foods containing polyunsaturated fatty acids (seafood, unrefined vegetable oil, nuts, sea/river fish, dietary meat birds, olives);
- reducing the consumption of foods containing large amounts of cholesterol (no more than 300 mg/day). For this purpose, by-products (liver, kidneys), egg yolk, red caviar, fatty meats, dairy products, and smoked foods are excluded from the diet.
- Elimination of such methods of culinary food processing as frying and deep-frying.
- Enriching the diet with vitamins and prebiotic foods (vegetables/fruits, artichoke, Jerusalem artichoke, leeks).
- For patients with diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance, simple carbohydrates are excluded from the diet and complex carbohydrates are limited, which helps improve metabolism.
Answers to frequently asked questions
The diet for fatty liver is very varied, but requires strict adherence over a long period. When treating a disease, patients have many questions.
What diet is suitable for endogenous steatohepatosis?
Endogenous fatty liver hepatosis occurs against the background of metabolic diseases. To reduce the amount of fat in the parenchyma, adhere to a physiological diet. The principles of nutrition differ little from those observed within table No. 5.
How long does the diet last?
If the cause of liver dysfunction is poor nutrition, the diet is followed throughout life.
Is diet 8 according to Pevzner suitable for fatty hepatosis?
Diet No. 8 is recommended for obesity. It aims to reduce weight by reducing caloric intake. This nutritional system is suitable only for those patients with hepatosis whose body weight exceeds the norm by 20% or more.
Allowed diet products for fatty hepatosis
The diet for fatty liver hepatosis includes the inclusion of the following permitted products in the diet:
- Vegetable broths and soups based on them with the addition of cereals, noodles, and vegetables.
- Low-fat varieties of red meat (beef/veal), rabbit, chicken, turkey. The meat must be pre-boiled followed by cooking.
- Day-old/dried wheat bread up to 500 g per day. If well tolerated - rye bread, low-fat cookies, dry biscuit.
- Low-fat types of sea/river fish, baked with vegetables.
- Cereals in the form of casseroles, porridge.
- Low-fat fermented milk products: yogurt, kefir, bifidum-kefir, acidophilus and low-fat cottage cheese.
- Milk/sour cream only as an additive to prepared dishes.
- Chicken eggs in the form of a steam omelet/soft-boiled.
- Fresh, baked and stewed vegetables in the form of salads with the addition of vegetable oil, mashed potatoes and homemade squash caviar. Spices include garden herbs, cumin, bay leaf.
- Sour cream, milk and vegetable sauces.
- Non-acidic fruits/berries in fresh and processed form (jelly, compotes, mousses).
- Marmalade, honey, caramel, marshmallows, jams, toffee. Sugar is partially replaced with xylitol.
- Butter/vegetable oil is added only to ready-made dishes; heat treatment is excluded.
- Still table water, rosehip infusion, weak tea, vegetable juices, wheat bran decoction, coffee with milk (not strong).
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
| Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| Fruits | ||||
| apricots | 0,9 | 0,1 | 10,8 | 41 |
| quince | 0,6 | 0,5 | 9,8 | 40 |
| watermelon | 0,6 | 0,1 | 5,8 | 25 |
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| melon | 0,6 | 0,3 | 7,4 | 33 |
| kiwi | 1,0 | 0,6 | 10,3 | 48 |
| peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
| plums | 0,8 | 0,3 | 9,6 | 42 |
| persimmon | 0,5 | 0,3 | 15,3 | 66 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
| Berries | ||||
| strawberry | 0,8 | 0,4 | 7,5 | 41 |
| blueberry | 1,1 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 44 |
| Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
| dried figs | 3,1 | 0,8 | 57,9 | 257 |
| dried apricots | 5,2 | 0,3 | 51,0 | 215 |
| dried apricots | 5,0 | 0,4 | 50,6 | 213 |
| prunes | 2,3 | 0,7 | 57,5 | 231 |
| Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
| Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| buckwheat noodles | 14,7 | 0,9 | 70,5 | 348 |
| Bakery products | ||||
| wheat bread | 8,1 | 1,0 | 48,8 | 242 |
| Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| fruit and berry marmalade | 0,4 | 0,0 | 76,6 | 293 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
| Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
| Dairy | ||||
| kefir 1.5% | 3,3 | 1,5 | 3,6 | 41 |
| curdled milk 1% | 3,0 | 1,0 | 4,1 | 40 |
| acidophilus 1% | 3,0 | 1,0 | 4,0 | 40 |
| Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 1% | 16,3 | 1,0 | 1,3 | 79 |
| cottage cheese 1.8% (low-fat) | 18,0 | 1,8 | 3,3 | 101 |
| Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
| Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken breast | 29,8 | 1,8 | 0,5 | 137 |
| boiled chicken drumstick | 27,0 | 5,6 | 0,0 | 158 |
| boiled turkey fillet | 25,0 | 1,0 | — | 130 |
| Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
| Fish and seafood | ||||
| flounder | 16,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 83 |
| pollock | 15,9 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 72 |
| cod | 17,7 | 0,7 | — | 78 |
| hake | 16,6 | 2,2 | 0,0 | 86 |
| Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| peach juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,5 | 40 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
Treatment tactics for fatty hepatosis:
- elimination of all factors that negatively affect the liver;
- normalization of metabolism;
- restoration of liver cells;
- strengthening therapy;
- proper nutrition;
- lifestyle change.
Treatment of hepatosis is conservative, it is carried out on an outpatient basis or in the inpatient gastroenterology department.
First of all, medications are prescribed to help reduce the amount of fat in the body. They also have an additional effect: they prevent the formation of low-quality cells (“Atoris”, “Vasilip”). To normalize metabolism, improve the transport of oxygen through blood vessels and remove toxic substances and breakdown products from the body, vasodilators (“Vazontil”, “Curantil”) are used. To improve the activity of a slow metabolism, folic acid and vitamin B12 are used.
Sulfoamino acids help improve blood flow and, moreover, reduce the viscosity of bile. They perfectly remove excess lipids from the liver. These medications include: Heptral, Methionine, etc.
To restore hepatocytes (liver cells), when hepatosis is treated, the doctor prescribes essential phospholipids. "Phosphogliv", "Essentiale" and other active phospholipid drugs can increase the protective abilities of hepatocytes, preventing the harmful effects of toxins on them.
Treatment of fatty liver hepatosis may include taking medications with bile acid, if it is necessary to provide additional hepatoprotective and choleretic effects on the body. To relieve unpleasant symptoms such as belching, diarrhea and nausea, enzyme agents (Festal, etc.) are used; they improve the absorption of food.
Treatment of fatty hepatosis can be carried out at home with the help of medicinal herbs and plants. But this is only permissible in complex treatment with medications after consultation with the attending physician. With the right approach, medicinal plants will not harm, but will enhance and improve the effect of pharmaceutical products.
What plants can cure fatty hepatosis at home? Milk thistle, turmeric, curly sorrel and cinnamon are commonly used.
This herb is used to produce milk thistle oil, which can be purchased at pharmacies. It removes bile and toxins from the body, stimulates the regeneration of hepatocytes and protein synthesis.
The product “Gepabene” has the same properties, which is available in a more convenient form – capsules. They can even be taken to relieve pain.
Usually, 1 capsule is prescribed 3 times a day.
Reduces the accumulation of lipids in liver cells, the level of glucose and cholesterol in the blood. Cinnamon can be used to adjust your diet, as it reduces appetite.
Creates a balance between the excretion of bile and its production in the human body. It also reduces the amount of lipids near the liver tissue.
To treat liver hepatosis at home, it is enough to take 1 tbsp. decoction of curly sorrel roots 4 times a day.
It is easy to prepare such a decoction: the roots of the plant are crushed, poured with a glass of boiling water (1 tablespoon of herb), boiled on the stove for 10 minutes, and then infused for 4 hours.
It has a beneficial effect on the gallbladder and removes excess bile. Has an antioxidant effect (neutralizing oxidative processes). For convenience, it is available in the form of drops for oral administration (“Holagol”). The course of treatment lasts about a month. Take 5 drops half an hour before meals on a piece of sugar 3 times a day.
Completely or partially limited diet products for fatty hepatosis
The diet for liver hepatosis involves limiting the following foods:
- Broths based on meat/fish and mushrooms, as well as first courses based on them.
- Fatty meat and fatty varieties of sea/river fish, poultry meat (goose and duck), smoked meats, sausages, salted fish, canned food, seafood.
- Products containing flavoring additives, preservatives, confectionery products with a long shelf life, freeze-dried products.
- Offal (liver, kidneys, brains), cooking/animal fat.
- Legumes and vegetables containing coarse fiber (radish, radish, turnip, white cabbage).
- Products rich in oxalic acid/essential oils (sour sauerkraut, sorrel, garlic, onion, spinach).
- Fried/hard-boiled eggs.
- Hot spices/herbs (horseradish, pepper, mayonnaise, mustard, ketchup).
- Heavy cream/milk, full-fat cottage cheese, chocolate, cakes, cheese curds, puff pastry, coffee, cocoa, cakes, muffins.
- Sour berries/fruits (black currants, cranberries, green apples, red currants).
- Alcohol-containing and carbonated sweet drinks, and mineral waters.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
| Vegetables and greens | ||||
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| peas | 6,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 60 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| chickpeas | 19,0 | 6,0 | 61,0 | 364 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| parsley | 3,7 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 47 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| iceberg lettuce | 0,9 | 0,1 | 1,8 | 14 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
| Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
| Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
| marinated mushrooms | 2,2 | 0,4 | 0,0 | 20 |
| Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| peanut | 26,3 | 45,2 | 9,9 | 551 |
| seeds | 22,6 | 49,4 | 4,1 | 567 |
| Cereals and porridges | ||||
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| dumplings | 11,9 | 12,4 | 29,0 | 275 |
| Bakery products | ||||
| buns | 7,9 | 9,4 | 55,5 | 339 |
| Rye bread | 6,6 | 1,2 | 34,2 | 165 |
| Confectionery | ||||
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
| shortbread dough | 6,5 | 21,6 | 49,9 | 403 |
| Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
| Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
| Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
| Dairy | ||||
| milk 4.5% | 3,1 | 4,5 | 4,7 | 72 |
| cream 35% (fat) | 2,5 | 35,0 | 3,0 | 337 |
| whipped cream | 3,2 | 22,2 | 12,5 | 257 |
| sour cream 30% | 2,4 | 30,0 | 3,1 | 294 |
| Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| parmesan cheese | 33,0 | 28,0 | 0,0 | 392 |
| Meat products | ||||
| fatty pork | 11,4 | 49,3 | 0,0 | 489 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
| Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
| Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
| Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| salmon caviar granular | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| salmon | 19,8 | 6,3 | 0,0 | 142 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| salmon | 21,6 | 6,0 | — | 140 |
| trout | 19,2 | 2,1 | — | 97 |
| Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| dry red wine | 0,2 | 0,0 | 0,3 | 68 |
| vodka | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 235 |
| beer | 0,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 42 |
| Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| soda water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| cola | 0,0 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 42 |
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| sprite | 0,1 | 0,0 | 7,0 | 29 |
What can you eat?
The diet for fatty liver allows for breakfast, lunch and dinner dishes prepared exclusively by steaming or decoction. If you are a fan of fried meat or fish, then you should get into the habit of baking these products. Products high in lipotropic substances such as choline, methionine, inositol, betoin and lipoic acid are allowed and even recommended. Fat-dissolving substances help stimulate the synthesis of lecithin in the liver and remove fat from the organ.
What can you eat in small doses? The consumption of energizing drinks and sodas is provided. It is also possible to use low-fat sour cream in dishes.
For lunch you can enjoy dishes made from vegetables and cereals such as cabbage soup, borscht and milk soup. For the second course, if you have hepatosis, boiled vegetables are recommended as a side dish. In this case, cabbage, boiled onions and carrots have especially healing properties. Since the patient has to eat often, but not a lot, it is advisable to consume boiled fresh vegetables in salads.
For liver hepatosis, the diet includes the consumption of the following products:
If you have hepatosis, you can eat boiled pasta
- sunflower and pumpkin seeds without abuse;
- weak herbal teas with lemon, preferably without sugar, fruit and berry juices without sugar, compotes, mousses, jellies;
- boiled pasta;
- a limited list of seafood and fish, when purchasing which you need to be vigilant;
- oatmeal cookies, crackers, rye bread;
- kefir, curdled milk, milk. It is important that the fat content does not exceed two percent;
- boiled beets, pumpkin, zucchini, Chinese cabbage;
- baked apples, pomegranate;
- butter;
- sweet berries, dried fruits, jelly, not very sweet jam, honey, marshmallows.
An approximate menu for a week for this disease should consist of regular and satisfying portions. So, table No. 8 according to Povzner is the following diet:
- beginning of the day: first breakfast - oatmeal cooked in water, low-fat cottage cheese; for the second snack - a vegetable appetizer or a steamed omelette.
- lunch: vegetable broth soup, vegetables and fish balls, also steamed;
- dinner: vegetable casserole, vegetable salad, a small portion of boiled dietary meat;
- towards the end of the day: herbal tea or kefir.
The next day, low-fat yogurt and weak herbal tea are perfect for breakfast, and baked fish along with mashed potatoes will be a hearty and tasty lunch. By noon, a glass of diluted fruit juice and low-fat cottage cheese will be preferable.
For dinner on this day you can have a small portion of cauliflower soup, which must be accompanied by a teaspoon of low-fat sour cream. Before going to bed, you can eat bread or crackers.
Pros and cons of a diet for fatty hepatosis
The therapeutic diet for fatty hepatosis has several advantages and one disadvantage:
| pros | Minuses |
|
|
Healthy recipes
The diet for patients with fatty liver hepatosis is tied to table 5, the recipes are simple and accessible to everyone.
Steamed veal cutlets
Meat (500 g), freed from tendons and fat, grind in a meat grinder. Add a little salt and herbs, an egg, a spoonful of boiled rice. Form small cutlets, cook in a double boiler for 30 minutes.
Curd casserole with dried apricots
Add an egg, 2 tablespoons of flour, a handful of chopped dried apricots, and a spoonful of sugar to low-fat cottage cheese (500 g). Bake for 20 minutes.
Seafood salad with feta cheese
Boil seafood (300 g), add fresh cucumber, green salad, feta cheese. Stir and season with oil-based salad dressing.
These dishes are quite affordable and can be safely included in the menu and prepared for fatty hepatosis.
Reviews and results - diet for fatty hepatosis
Therapeutic nutrition diet for fatty hepatosis is the main component of the treatment of patients with fatty hepatosis, allowing to maintain the general condition and prevent the progression of the process, and in the initial stages of the disease - to achieve regression of fatty hepatosis and normalization of liver function.
- “...I was diagnosed with fatty liver hepatosis a year after suffering from viral hepatitis. They prescribed a diet and hepaprotectors. I followed a strict diet for almost 6 months, completely eliminated alcohol, and started working out at the gym. Now my health has improved significantly, my appetite has returned to normal and my blood tests are almost normal. But I don’t want to relax and I’ll go on a diet for another 2-3 months, and maybe I’ll even eat like this all the time, since eating like this doesn’t bother me”;
- “... Fatty liver hepatosis was discovered during an examination for cholelithiasis. After surgery to remove the stones, I decided to tackle the problem of fatty hepatosis. As I was told, there are no special medications for treatment. That's why they recommended a diet. To begin with, I was on a low-calorie diet for almost 6 months, limiting fats and carbohydrates, until my weight was more or less close to normal, since at a normal weight of 72 kg I weighed 98 kg. Then I switched to dietary Table No. 5 and now I’ve been on a diet for almost a year. It’s quite easy to tolerate, and since there are positive changes, it’s inspiring and I want to bring the liver back to normal completely.”
How to stop the disease
A diet for liver hepatosis, especially at the initial stage of the disease, can reverse the pathological process, restoring the health of the organ.
You can stop the process of liver destruction:
- providing drug treatment to effectively support organ function;
- reviewing your regime and diet;
- eating only healthy foods approved by your doctor;
- giving up bad habits;
- increasing your physical activity to stop excess weight gain;
- It is recommended to eat in small portions, increasing the frequency of meals to 5-6 times a day.
To prevent progression of the disease, it is recommended:
- reduce the load on the liver;
- restore normal lipid metabolism;
- ensure the removal of bile, clean the ducts;
- normalize the digestive process.
A person solves this problem with the help of nutrition, using dietary table No. 5, which regulates protein consumption, while simultaneously removing cholesterol-rich foods from the diet. The doctor determines which diet is most suitable for the patient, taking into account the general state of health.
Allowed dishes for hepatosis
Low-fat cheeses, yogurt and milk are very useful for hepatosis. However, the most valuable thing on the menu is the chicken egg, namely the protein, which is completely absorbed by the body without irritating it. So that the patient does not feel hungry, and his liver recovers as quickly as possible, a sample menu for the week should include the following dishes:
The best sources of protein are cottage cheese with minimal fat content, dishes made from lean chicken or turkey, rabbit, veal, and fish.
- First courses are the basis of the diet menu. Soups cooked exclusively with vegetables, fruits, and milk are allowed.
- You can use any side dishes, although they are especially useful: buckwheat, rice. You can include durum wheat pasta in your menu.
- For a snack: boiled, stewed, baked or raw vegetables with a small amount of greens.
- The menu for hepatosis allows lean meat or fish, boiled, steamed or in the oven.
- Omelet, 1 soft-boiled egg or whites of 2 eggs.
- Fresh, non-sour fruits, raw, boiled, baked and dried fruits.
- Dairy products: milk, kefir. Yogurt, sour cream, cottage cheese, low-fat cheeses.
- For sweets, the following are allowed: jelly, compote, mousse, marmalade, snowballs, marshmallows, jam, any candy without chocolate.
- Wheat bread, yesterday's rye bread, unleavened pies and kulebyaki stuffed with fish, meat, cottage cheese, apples. You can have biscuits, a little dry biscuit.
- Fats for hepatosis include butter and vegetable oil (refined).
- Drinks: weak black tea with milk, homemade juices, rosehip or wheat bran infusion, chamomile infusion.
Diet and basic principles
Modern domestic experts recommend that in case of fatty liver hepatosis, adhere to diet No. 5 - a scientifically based nutritional plan developed by the brilliant nutritionist Manuil Pevzner back in the last century. This option is optimal for all patients suffering from liver problems.
The basic principles of the diet are split meals 5-6 times a day in small portions, cooking dishes by boiling, steaming or baking, as well as a significant reduction in the consumption of polyunsaturated fats and simple carbohydrates.
The basic daily diet should include up to 120 grams of proteins, about 80 grams of fats (most of which are polyunsaturated), up to 300 grams of carbohydrates (the vast majority are complex, sugars no more than 50 grams), no more than 6 grams of salt and about 2 liters liquids excluding water in food.
Allowed foods
Below is a complete list of what you can eat with fatty liver hepatosis, which must be included in your daily diet.
- Meat - lean types . It is meat that contains a lot of protein, a kind of “building” material for the renewal of damaged liver cells. Both beef and pork are allowed to be used, but without tendons, fat, cartilage tissue, in lump or chopped form. Of meat by-products, it is possible to use only fresh boiled tongue;
- Bird . High-quality chicken or turkey meat without fat, skin, bones and films. Fatty species (for example, goose) should not be consumed;
- Fish . Fish contains a lot of useful substances and essential phosphorus, so you need to eat it regularly. Nutritionists recommend using cod, sea bass, pike perch, navaga and other subspecies of low-fat fish, as well as black caviar and herring soaked in a light salt solution;
- Eggs . Without special restrictions, you can use chicken egg white. Whole (with yolk) – no more than 1-2 pieces per day;
- Soup . Light, non-rich and low-fat vegetable soups with cereals, water or low-fat milk are allowed. It is not advisable to consume borscht and other types of fatty liquid dishes;
- Bakery products . It is recommended to eat rye or wheat bread in small quantities, preferably not fresh - this way it is less harmful to the stomach. Limited additional products include crackers, dry cookies and biscuits;
- Milk products . It is important and necessary for normalizing digestion and saturating the intestines with beneficial microflora, as well as as a relief for the liver. Almost all types of products are allowed, excluding those that are too fatty - from hard cheese, milk, cottage cheese to sour cream and cream (the last 2 positions are limited);
- Porridge . It is allowed to eat crumbly cereals, steamed or baked puddings;
- Pasta . Only from durum wheat in limited quantities. In case of severe obesity, they are completely excluded from the diet;
- Vegetables . Healthy and easily digestible type of product. All types except sour ones are allowed for use. In case of chronic diseases associated with malfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract, it is rational to exclude fresh or boiled white cabbage from the diet;
- Greenery . A useful source of vitamins and microelements must be included in the diet; only some of their types, listed in the list of undesirables, are used to a limited extent;
- Fruits and berries . It is advisable to consume them fresh, as well as add them to dishes with minimal heat treatment. Only sour varieties of these products are prohibited for use;
- Sweets . This type of food is mostly prohibited for consumption due to the large amount of simple carbohydrates. The exception is only marshmallows, marmalade, honey and sugar in limited quantities and on a natural basis;
- Spices . From the wide list of spices in diet No. 5, it is allowed to use dill, bay leaf, cloves, vanilla, parsley, coriander and cinnamon, naturally, observing the measure;
- Liquids . In addition to regular water, your daily diet can include vegetable and fruit juices, rosehip decoctions, and sweet berry jelly. Rarely – weak coffee and tea;
- Oil . Vegetable, naturally pressed (sunflower, corn, olive). Very limited – butter. Spreads and margarine are prohibited.
Prohibited Products
The list of main prohibited foods that cannot be eaten in case of liver hepatosis and must be completely excluded from the diet or at least significantly limited their use:
- Fatty meats, poultry and fish;
- Fresh baked goods, including pies, bread, puff pastries, etc., cocoa and dark chocolate;
- Rich broths with high fat content;
- Sausage in any form, smoked products;
- Meat or fish based by-products;
- Canned food, fatty sauces, marinades of all kinds;
- All sour varieties of fruit, including grapefruit, cranberries, not very ripe apples, tangerines and oranges;
- Green and onions, garlic, pickled and pickled tomatoes, sorrel;
- All types of mushrooms and broths based on them;
- Any legumes and lentils;
- Sour vegetables, including radishes, peppers and radishes;
- Dressings for dishes, both tomato and based on mayonnaise, horseradish, mustard;
- All spices, except for the narrow list of those listed above, are allowed for use in limited doses;
- Alcohol in any form and concentration, sweet soda, strong coffee and tea;
- Other groups and types of foods individually marked by your nutritionist as undesirable in each specific case.